Lab Module 8: Quantitative Micobiology
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Microbial Growth
Population growth rather than growth of individual cells
Binary Fission
The parent cell enlarges and duplicates it chromosome. A septum forms in the middle, creating two new cells.
Generation Time
The time its takes for a bacteria to go through binary fission
Lag Phase
Period of time it takes for the bacteria to reach a physiological state capable of rapid cell growth and division
Log (Exponential) Phase
the stage of fastest cell growth and division during which DNA replication, RNA transcription, and protein production all occur at a constant, rapid rate.
Stationary Phase
characterized by the slowing down and plateauing of bacterial growth due to nutrient limitation and/or toxic intermediate accumulation. Bacterial cells continue to survive in this stage, although the rate of replication and cell division is drastically reduced.
Death phase
severe nutrient depletion leads to the lysing of cells.
Nt = N0 X 2n
Equation used to calculate exponential growth.
where:
Nt is the number of cells in population at time T
N0 is the number of cells in population at time 0
n is the number of divisions
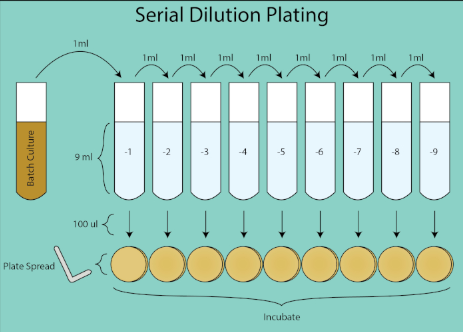
Colony Forming Units and Serial Dilutions
provides a direct measurement of bacterial cell counts.The standard unit of measure for CFU is the number of culturable bacteria present per 1 mL of culture (CFU/mL) determined by serial dilution and spread plating techniques. For each timepoint, a 1:10 dilution series of the batch culture is performed and 100 µl of each dilution is spread plated using a cell spreader. The plates are then incubated overnight and clonal colonies enumerated. The dilution plate which grew 30-300 colonies is used to calculate the CFU/mL for the given timepoint. Stochastic variation in colony counts under 30 are subject to greater error in the calculation of CFU/ml and counting colonies greater than 300 can be underestimated due to colony crowding and overlapping. Using the dilution factor for the given plate, the CFU of the batch culture can be calculated for each timepoint.
Standard Plate Count
means of determining the cell density in a liquid sample using colony counts from dilutions of the broth transferred to agar plates
Turbid (cloudy)
Bacterial growth in a broth determined by this visual change
Optical density
absorption of light measured by a spectrophotometer
Direct Microscope Count
uses a microscope and special slide to facilitate the counting.
Neubauer or Petroff-Hauser chamber
Special slide that has been ruled into squares and can hold a specific amount of volume of liquid. (AKA Hemacytometer)
Trypan blue
a dye that can be added to the sample to differentiate living and dead cells.
Cells/ml = ( # of cells) x (104) x (Dilution Factor)
# Squares Counted
Equation used to determine the concentration of cells in a sample using the hemacytometer