Chapter 1 Discovering the Night Sky. Discovering the Universe 11th edition
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Is the North Star—Polaris—the brightest star in the night sky?
No. Polaris is a star of medium brightness compared with other stars visible to the naked eye.
What do astronomers define as constellations?
Astronomers sometimes use the common definition of a constellation as a pattern of stars. Formally, however, a constellation is an entire area of the celestial sphere and all the stars and other objects in it. The boundaries of constellations are lines of constant right ascension and lines of constant declination that meet at right angles. Viewed from Earth, the entire sky is covered by 88 different-sized constellations. If there is any room for confusion, astronomers refer to the patterns as asterisms.
When is Earth closest to the Sun?
On or around January 3 of each year. Perihelion
What causes the seasons?
The tilt of Earth's rotation axis with respect to the ecliptic causes the seasons. They are not caused by the changing distance from Earth to the Sun that results from the shape of Earth's orbit.
How many zodiac constellations are there?
here are 13 zodiac constellations, the least-known one being Ophiuchus.
Does the Moon have a dark side that we never see from Earth?
Half of the Moon is always dark. Whenever we see less than a full Moon, we are seeing part of the Moon's dark side. So, the dark side of the Moon is not the same as the far side of the Moon, which we never see from Earth.
Is the Moon ever visible during the daytime?
The Moon is visible at some time during daylight hours almost every day of the year. Different phases are visible
What causes lunar and solar eclipses?
When the Moon is crossing the ecliptic in the full or new phase, the shadows of Earth or the Moon, respectively, then fall on the Moon or Earth. These shadows on the respective surfaces are eclipses.
Patterns of Stars
The surface of the celestial sphere is divided into 88 unequal areas called constellations.
The boundaries of the constellations run along lines of constant right ascension or declination.
The patterns of bright stars seen in many constellations are called asterisms.
Earthly Cycles
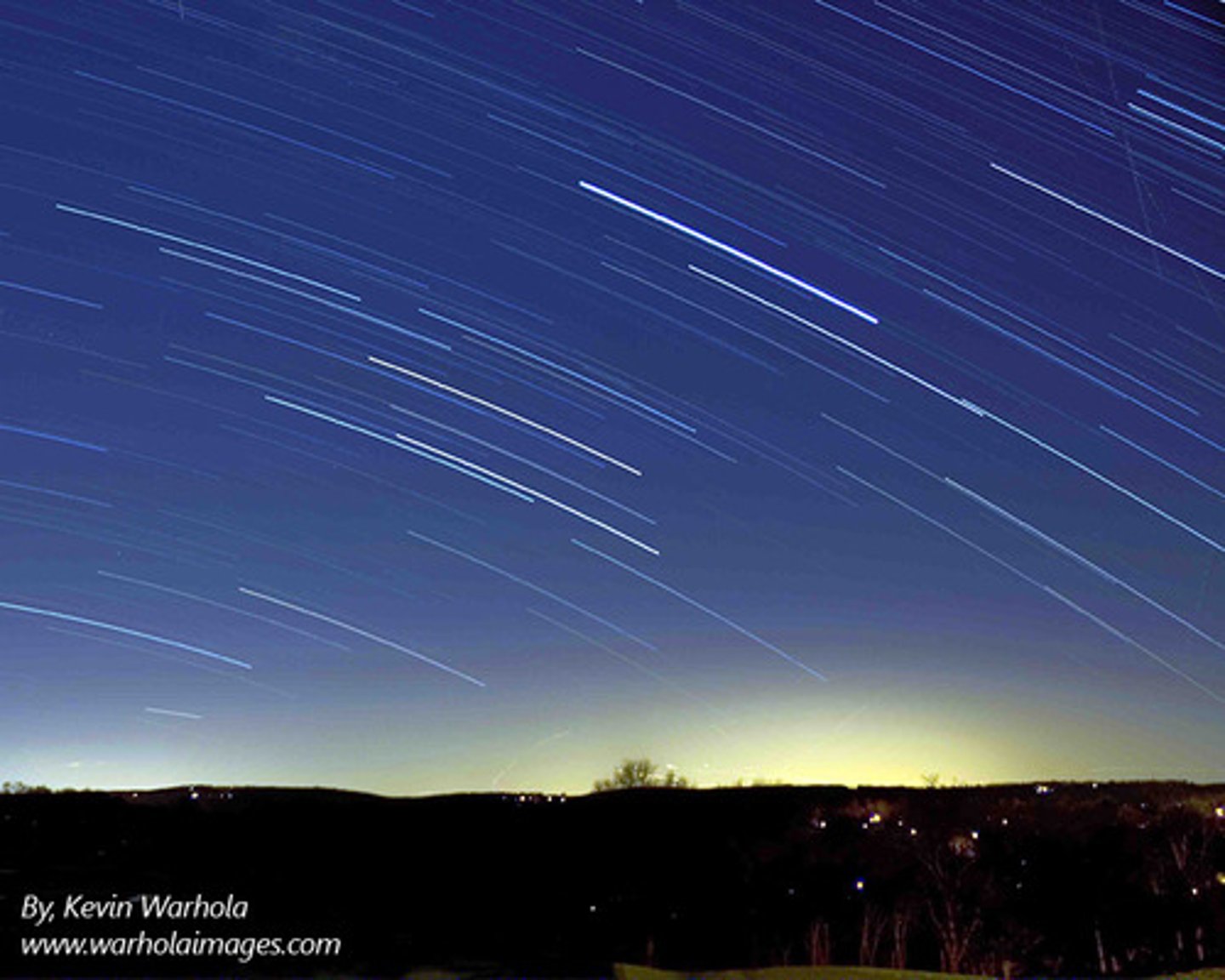
The celestial sphere appears to revolve around Earth once in each day-night cycle. It is actually Earth's rotation that causes this apparent motion.
The poles and equator of the celestial sphere are determined by extending the axis of rotation and the equatorial plane of Earth out onto the celestial sphere.
Earth's axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23½° from a line perpendicular to the plane of Earth's orbit (the plane of the ecliptic). This tilt causes the seasons.
Equinoxes and solstices are significant points along Earth's orbit that are determined by the relationship between the Sun's path on the celestial sphere (the ecliptic) and the celestial equator.
Earth's axis of rotation slowly changes direction relative to the stars over thousands of years, a phenomenon called precession. Precession is caused by the gravitational pull of the Sun and the Moon on Earth's equatorial bulge.
The length of the day is based on Earth's rotation rate and the average motion of Earth around the Sun. These effects combine to produce the 24-hour day on which our clocks are based.
The phases of the Moon are caused by the relative positions of Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. The Moon completes one cycle of phases in a synodic month, which averages 29½ days.
The Moon completes one orbit around Earth with respect to the stars in a sidereal month, which averages 27.3 days.
Eclipses
The shadow of an object has two parts: the umbra, where direct light from the source is completely blocked; and the penumbra, where the light source is only partially obscured.
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves through Earth's shadow. During a lunar eclipse, the Sun, Earth, and the Moon are in alignment, with Earth between the Sun and the Moon, and the Moon is in the plane of the ecliptic.
A solar eclipse occurs when a strip of Earth passes through the Moon's umbra. During a solar eclipse, the Sun, Earth, and the Moon are in alignment, with the Moon between Earth and the Sun, and the Moon is in the plane of the ecliptic.
Depending on the relative positions of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth, lunar eclipses may be penumbral, partial, or total, and solar eclipses may be annular, partial, or total.
Explain why Figure 1-15 must have been taken facing west. Hint: Examine Figure 1-18 (Suns daily path and energy it deposits here)
In the northern hemisphere, stars move southward (to the right) as they rise and northward (to the right) as they set. If this figure were taken in the morning, the stars would be moving in the wrong direction.

Why are some of the paths in Figure 1-31 wider than others?
The angle that the shadow strikes Earth determines how wide the eclipse path is. This angle varies with latitude, time from noon, and distance of the Moon from Earth. For example, near the equator, near noon, and with the Moon relatively far from Earth, the shadow is thinnest, while near the poles, especially far from noon, and when the Moon is closest to Earth, the shadow is particularly wide.
Describe the Orion constellation.
The region of the celestial sphere, with connected boundaries running at right angles to each other, containing the Orion asterism and everything else in that region.
In what season in the southern hemisphere is Earth closest to the Sun? In what season in the northern hemisphere is Earth closest to the Sun? If the changing distance from Earth to the Sun caused the seasons, what should be true about the answers to the first two parts of this question
Summer. Winter. They should both be the same, since the whole Earth would then be affected equally by the changing amount of heat with distance from the Sun.
What observational evidence do we have that the Moon does not make its own light?
If the Moon made its own light, then we should see all parts of it glowing equally, or at least all of it glowing all the time.
What is the difference between the "far" side of the Moon and the "dark" side of the Moon?
The far side of the Moon is the side always facing away from Earth, while the dark side is the side of the Moon facing away from the Sun at any time.
Through how many constellations does the Sun pass each year? What are these constellations called?
13, Zodiac constellations.
Which of the following statements is correct for someone standing at one of Earth's poles?
a) The Sun rises and sets every day.
b)The Sun is directly overhead on the summer solstice in that hemisphere.
c)The Sun is in the sky continuously for 6 months.
d)The Moon is never visible.
e)The stars rise vertically and set vertically.
c)The Sun is in the sky continuously for 6 months.
Azimuth
Angle from due north eastward along the horizon to the point on the horizon where the altitude line to an object starts. (It is sometimes measured from due south.)
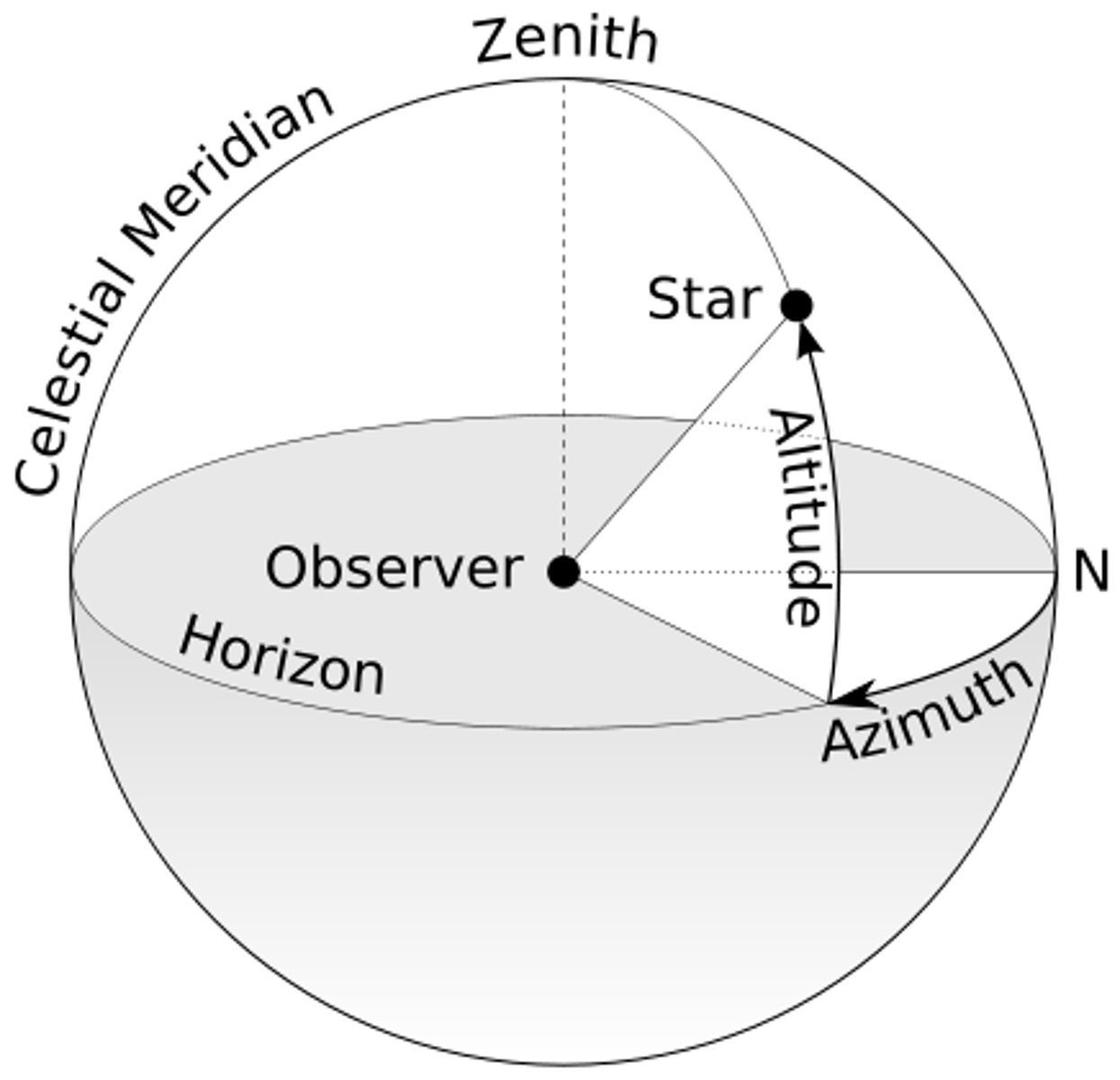
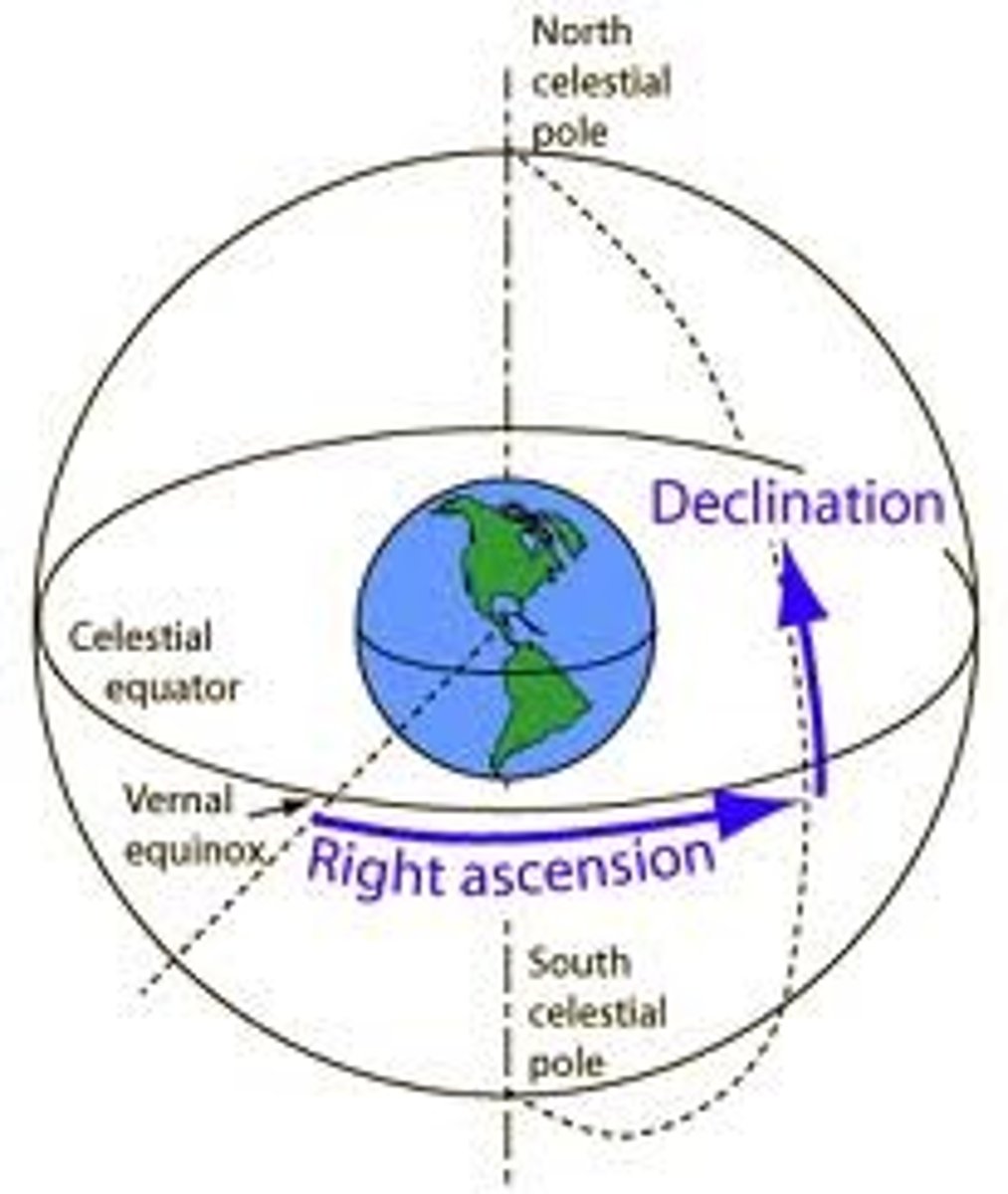
Declination
The coordinate on the celestial sphere exactly analogous to latitude on Earth; measured north and south of the celestial equator.
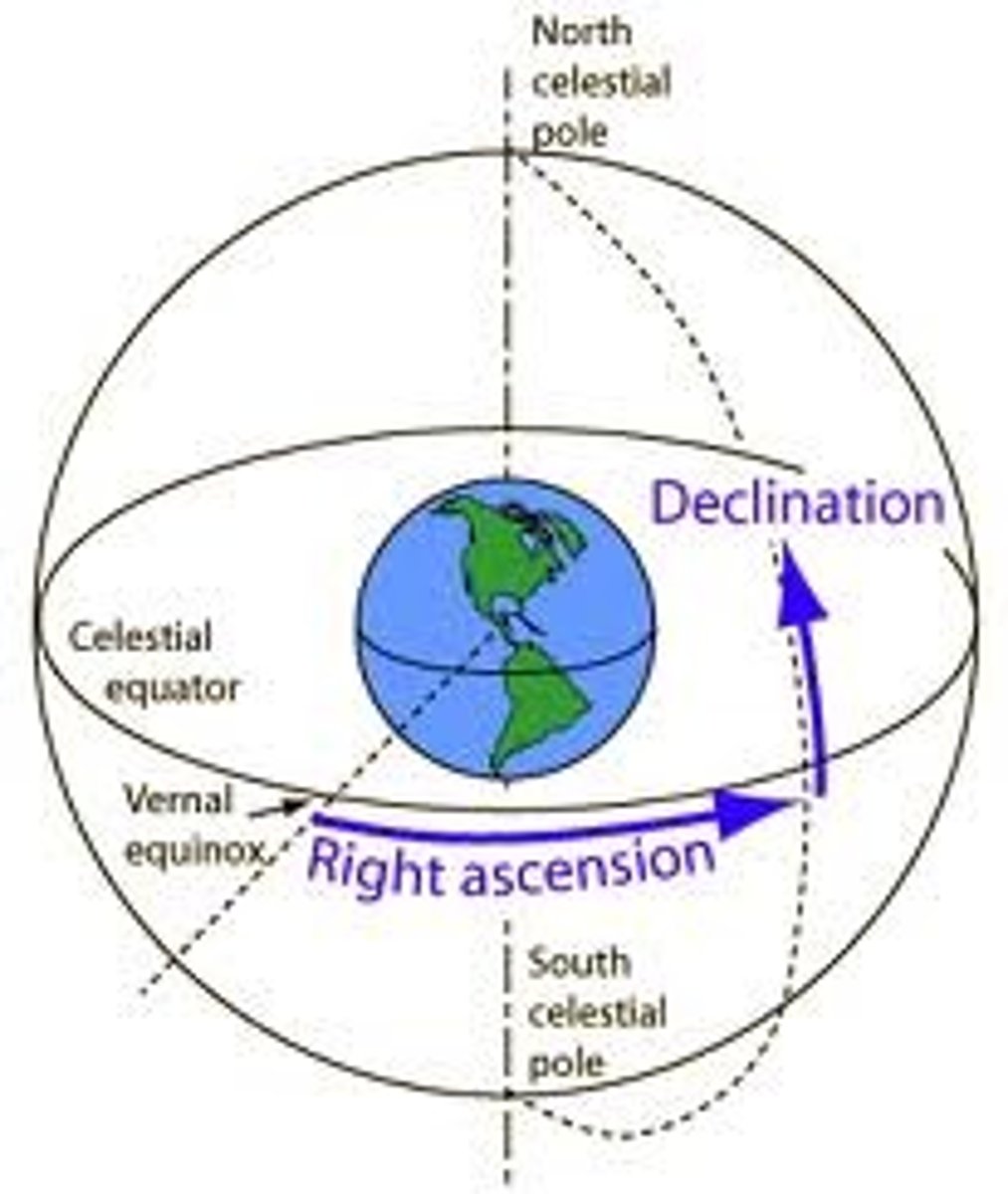
Right Ascension
The celestial coordinate analogous to longitude on Earth and measured around the celestial equator from the vernal equinox.
Diurnal Motion
apparent daily motion of the stars caused by earth's rotation
Sideral Period
The orbital period of one object about another measured with respect to the stars. So, Earth's sidereal year is 365¼ days long
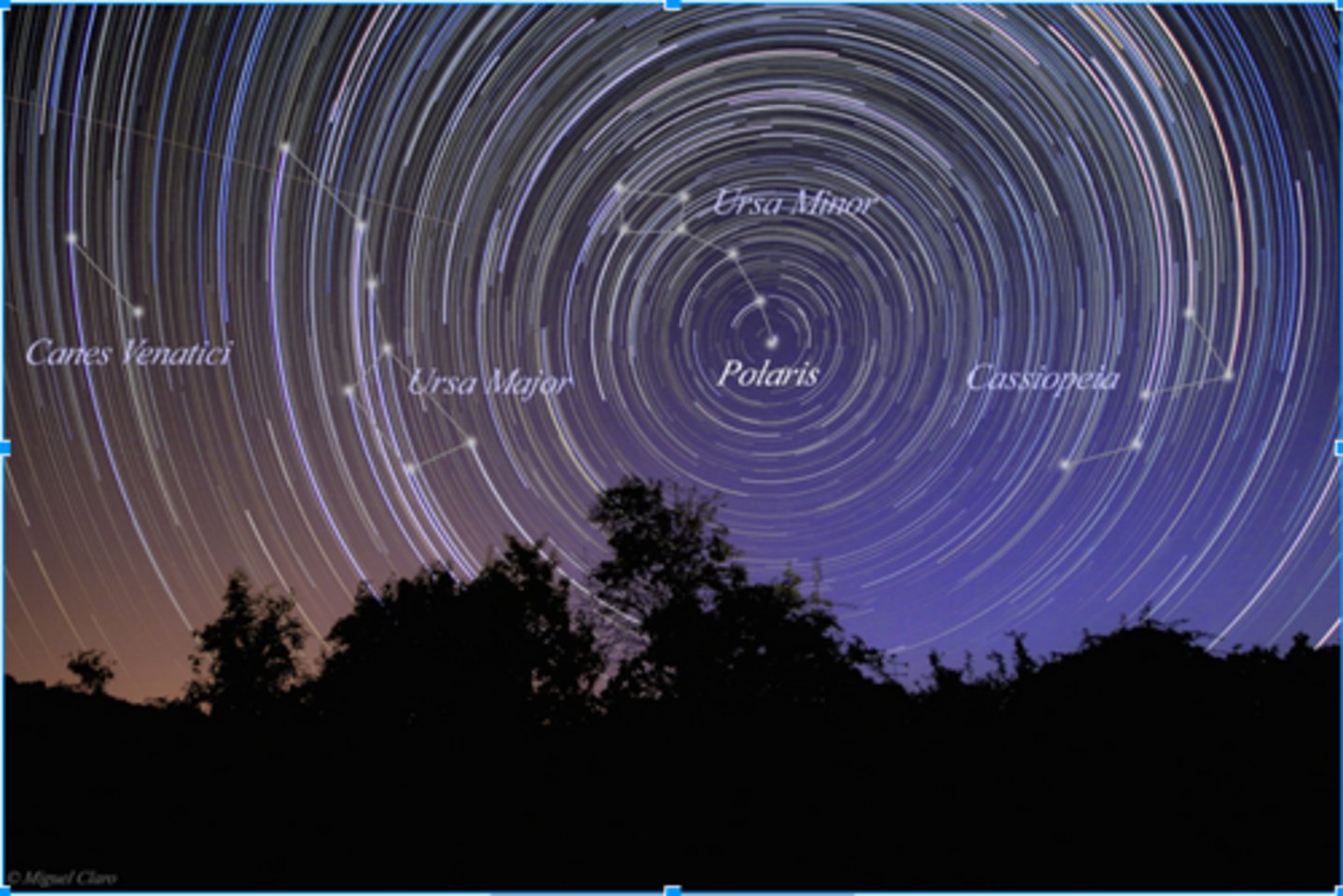
Circumpolar
A term describing a star that neither rises nor sets but appears to rotate around one of the celestial poles.

penumbra eclipse
a lunar eclipse in which the Moon passes only through Earth's penumbra
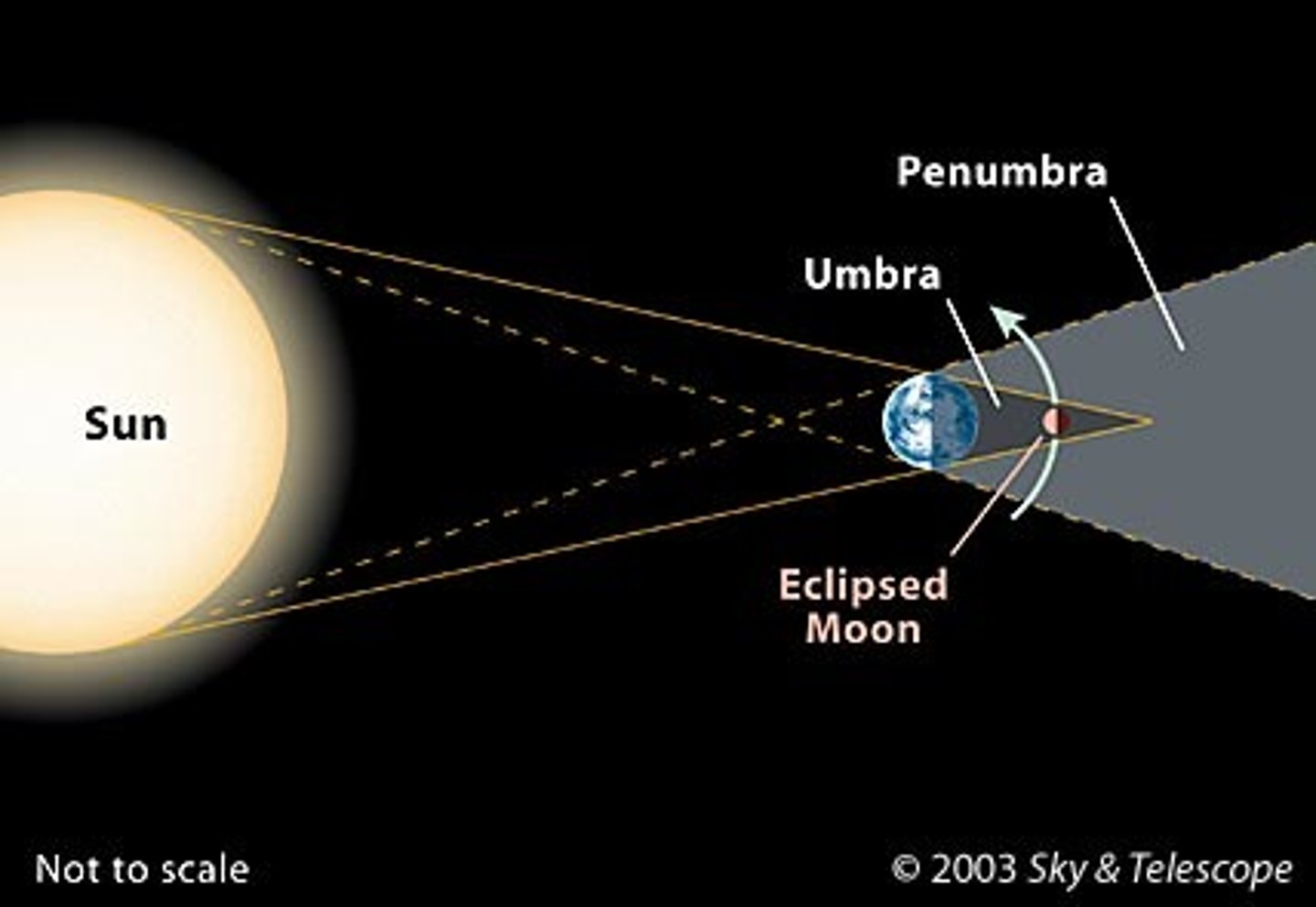
partial eclipse
A lunar or solar eclipse in which the eclipsed object does not appear completely covered.
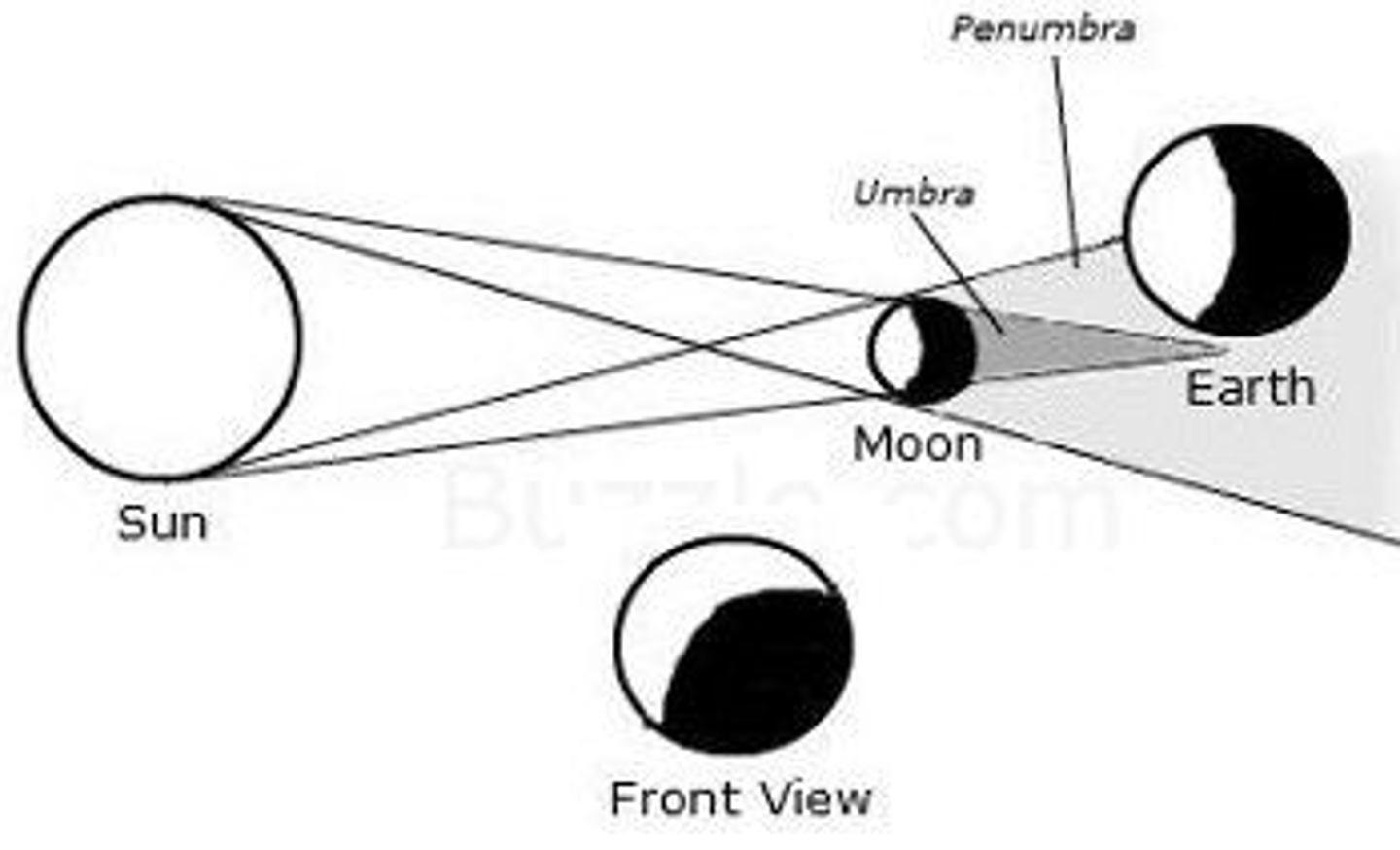
total eclipse
A solar eclipse during which the Sun is completely hidden by the Moon, or a lunar eclipse during which the Moon is completely immersed in Earth's umbra.

terminator
The line dividing day and night on the surface of any body orbiting the Sun; the line of sunset or sunrise.

Siderial Month
The period of revolution of the Moon with respect to the Sun; the length of one cycle of lunar phases; 29½ Earth days.