Cultural Variations in Spatial and Numerical Cognition
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
What frame of reference do some cultures use exclusively when discussing spatial layouts?
The intrinsic (or object-centered) frame of reference.
Which frame of reference do some cultures prefer for small-scale spatial discussions?
The absolute frame of reference.
What is the primary factor influencing the frame of reference people use for remembering spatial layouts?
Language, reflecting a Whorfian effect.
How do people across cultures tend to remember small-scale spatial arrays?
Using the same frame of reference they use to talk about them.
What advantage do Jahai hunter-gatherers have over English speakers according to recent studies?
They are better at discriminating both colors and odors.
How do English speakers typically describe odors?
By referring to a possible 'source' of the smell, such as Big Red gum.
What similarity exists between Jahai speakers' smell terms and English speakers' color terms?
Jahai speakers use a set of 'basic smell terms' similar to the 'basic color terms' of English speakers.
Why might the Jahai be better at naming smells than a study suggests?
Because the stimuli used in the study (e.g., turpentine) were culturally unfamiliar to them.
What research study is referenced regarding factors affecting overall codability across the senses?
Majid et al., 2018.
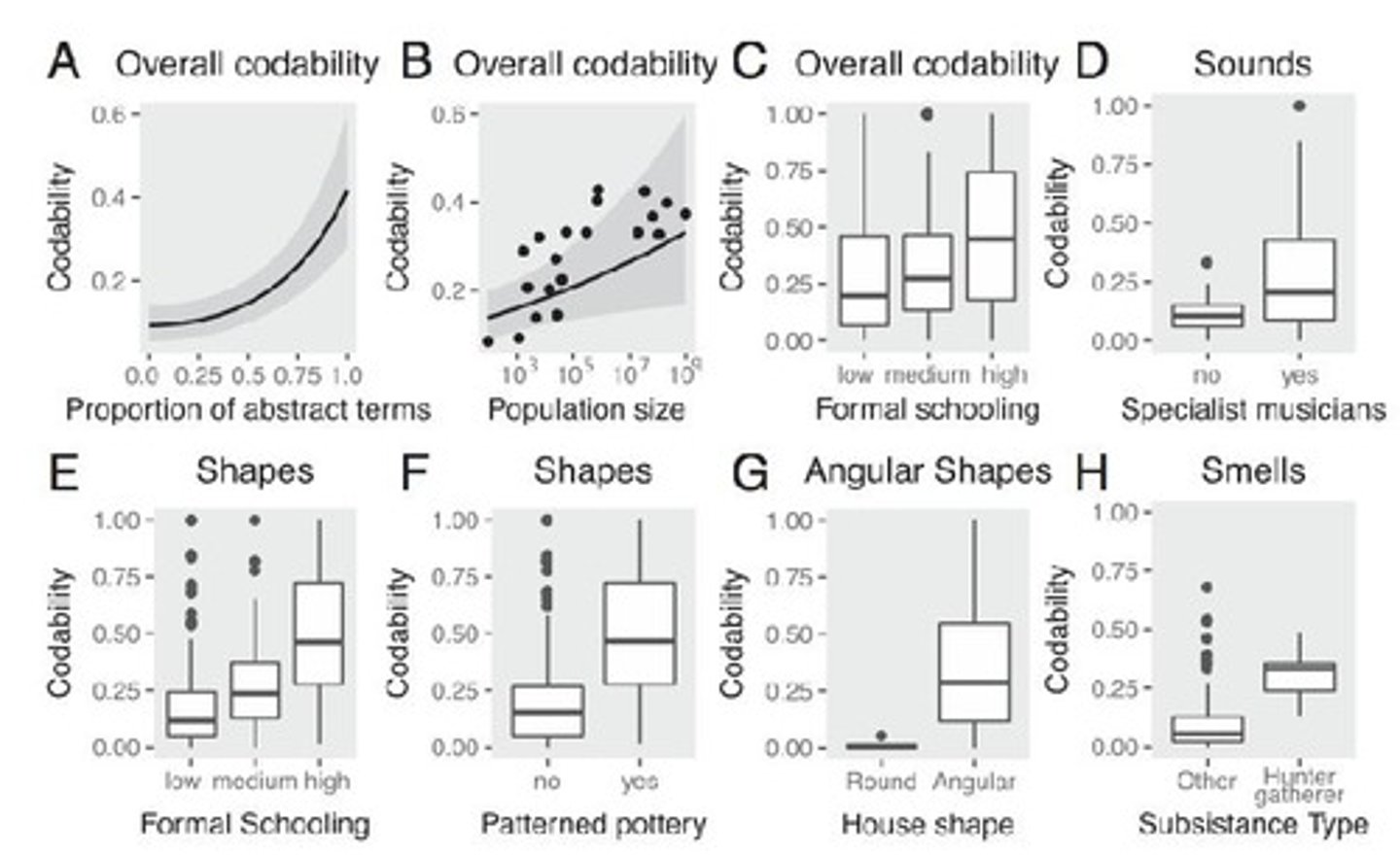
What is the main finding regarding the codability of senses across languages according to Majid et al., 2018?
There is no single hierarchy that emerges; there is a lot of variability.
Which sense is generally considered the least codable across languages?
Smell is the least codable of the senses, with some exceptions.
What cultural factors may influence the codability of senses?
Population size and formal education are correlated with codability across domains.
How do hunter-gatherer societies view odors in terms of codability?
Hunter-gatherers are more likely to treat odors as codable.
What has been traditionally noted about the description of experiences in different cultures?
Some aspects of experience are easier to describe (more 'codable') than others.
What are the six key ways in which numeral systems vary across languages?
Base, object-specificity, counting practices, transparency, limits, and bulkiness.
What is meant by 'anumeric' languages?
Some languages may be fully 'anumeric,' meaning they do not have numeral systems.
What cognitive consequences arise from not having numerals in a language?
Not having numerals appears to have cognitive consequences, as does the transparency and bulkiness of one's numeral system.
How do numerals function as cognitive tools?
Numerals allow us to exceed our evolved abilities for subitizing and approximate quantity estimation.
What are examples of grammatical quantifiers mentioned in the notes?
Some, none, few.
What are cardinal numbers?
Cardinal numbers are used for counting (e.g., one, two, three...).
What are ordinal numbers?
Ordinal numbers indicate position or order (e.g., first, second, third...).
What is the significance of the 'bulkiness' of a numeral system?
The bulkiness of a numeral system can affect cognitive processing and understanding of numbers.
What does 'object-specificity' refer to in numeral systems?
Object-specificity refers to how numeral systems may vary in their application to specific objects.
What does 'transparency' mean in the context of numeral systems?
Transparency refers to how easily the structure of a numeral system can be understood.
What is the relationship between counting practices and numeral systems?
Counting practices can vary significantly across different languages and cultures.
What does the term 'limits' refer to in numeral systems?
Limits refer to the maximum number that can be expressed or counted in a numeral system.
How do cultural factors shape the hierarchy of senses?
The hierarchy of senses (vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell) is significantly shaped by culture.
What does the term 'variability' imply in the context of codability of senses?
Variability implies that different languages and cultures may have different ways of expressing sensory experiences.
What is the implication of the findings on codability for understanding human experience?
The findings suggest that cultural context plays a crucial role in how sensory experiences are articulated.
How do the findings of Majid et al., 2018 contribute to the understanding of language and cognition?
They highlight the interplay between language, culture, and cognitive processes in expressing sensory experiences.
What is the significance of the lecture on 'Senses' in relation to the codability of odors?
It emphasizes that while odors have been considered uncodable, this varies across languages and cultures.
What is the base of the English numeral system?
Base 10
What are the first ten numbers in the English base 10 system?
One, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten.
What percentage of languages use base 10 systems?
64%.
What is the percentage of languages that use base 20 systems?
10%.
What are some examples of other numeral bases mentioned in the notes?
Base 4, Base 5, Base 6, Base 8, Base 60.
What is a notable feature of numeral systems in some languages compared to English?
Some languages have numeral systems specialized for counting particular things.
What is an example of a specialized counting system in English?
Counting bagels in dozens.
What is the highest attested number word in hunter-gatherer languages from South America?
It varies, but often not very high.
What is the counting limit in most major global number systems?
Infinitely high.
What is the counting limit in small-scale groups in certain regions?
Not very high.
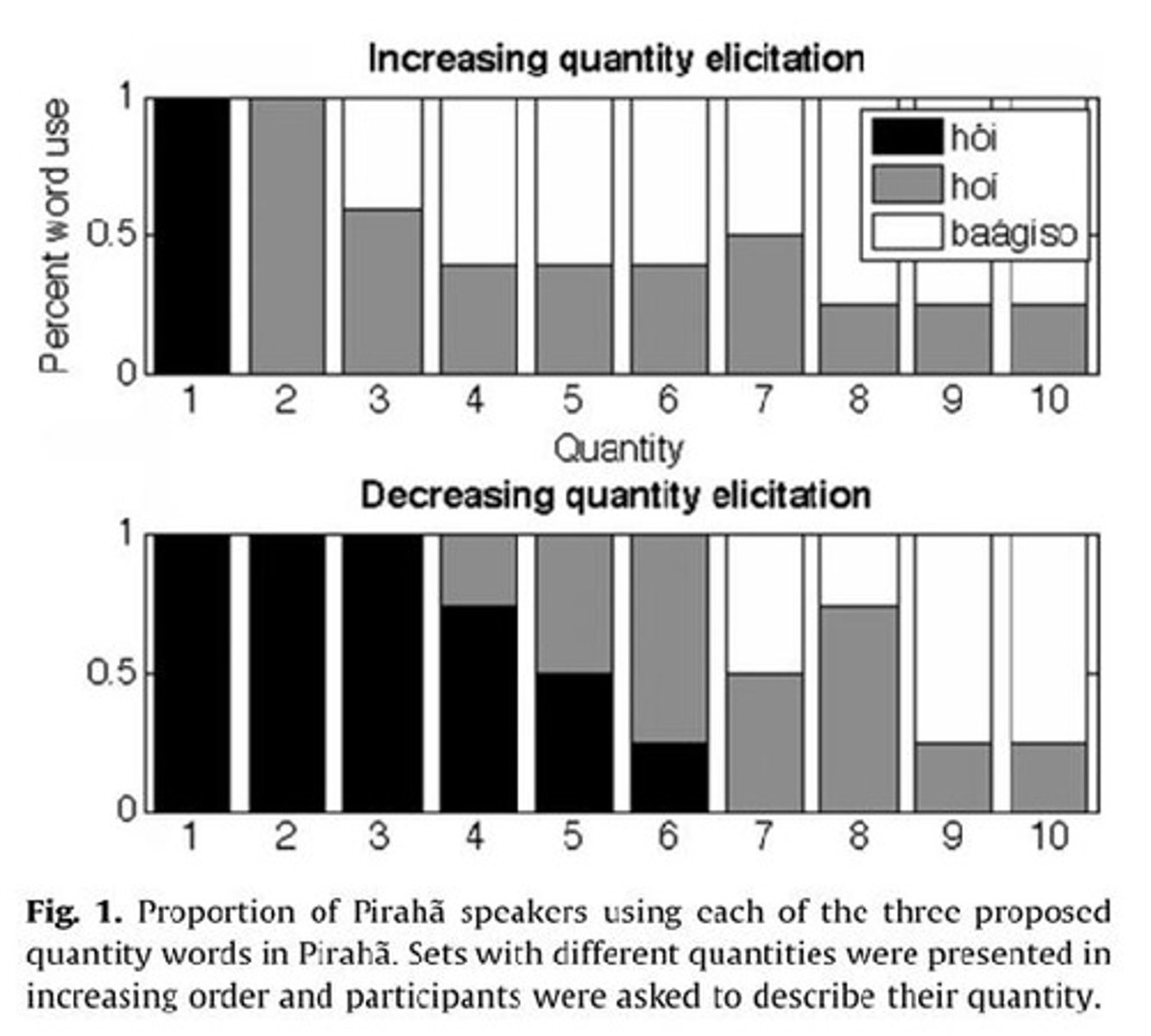
What type of numeral system does the Pirahã language use?
Originally considered a 'one-two-many' system.
What are the terms used in the Pirahã counting system?
'One' (hói), 'two' (hoí), 'many' (baagiso).
What conclusion was drawn about the counting terms in the Pirahã language?
They are quantifiers, not exact number words.
What is the significance of the base structure of English numerals compared to Mandarin?
It is not as transparent.
What is the source of the information regarding numeral systems in Papua New Guinea?
Evans, 2009.
What is the source of the information regarding limits in number systems?
Epps et al., 2012.
What is the percentage of languages that use other bases aside from base 10 and 20?
15%.
What is the term used for languages that have a limited number of number words?
Low limit languages.
What is the relevance of the Sumerian numeral system?
It formed the basis of our system of minutes and seconds.
What is an example of a language with a low limit on counting?
Pirahã.

What is a characteristic of number words in English?
They can be used to count anything and everything.
What is the significance of the survey of 189 languages in Aboriginal Australia?
It shows the number system limits in those languages.
What are quantifiers in the context of number words?
Terms like some, none, and few that indicate quantity but are not exact numbers.
What is the significance of the Pirahã language regarding numerals?
Pirahã is fully anumeric, meaning it does not have a system for counting.
What are the six aspects of variation in number words ('numerals')?
1. Base of numeral system 2. Object-specificity 3. Limits 4. Transparency 5. Counting practices 6. Bulkiness
What does 'transparency' refer to in numeral systems?
It refers to how clear the base structure of the numeral system is.
How does English demonstrate a base 10 numeral system?
English uses a clear progression: one, two, three... up to ten, then eleven, twelve, etc.
What is an example of a numeral system that is clear in its structure?
Mandarin, which uses a systematic approach to counting.
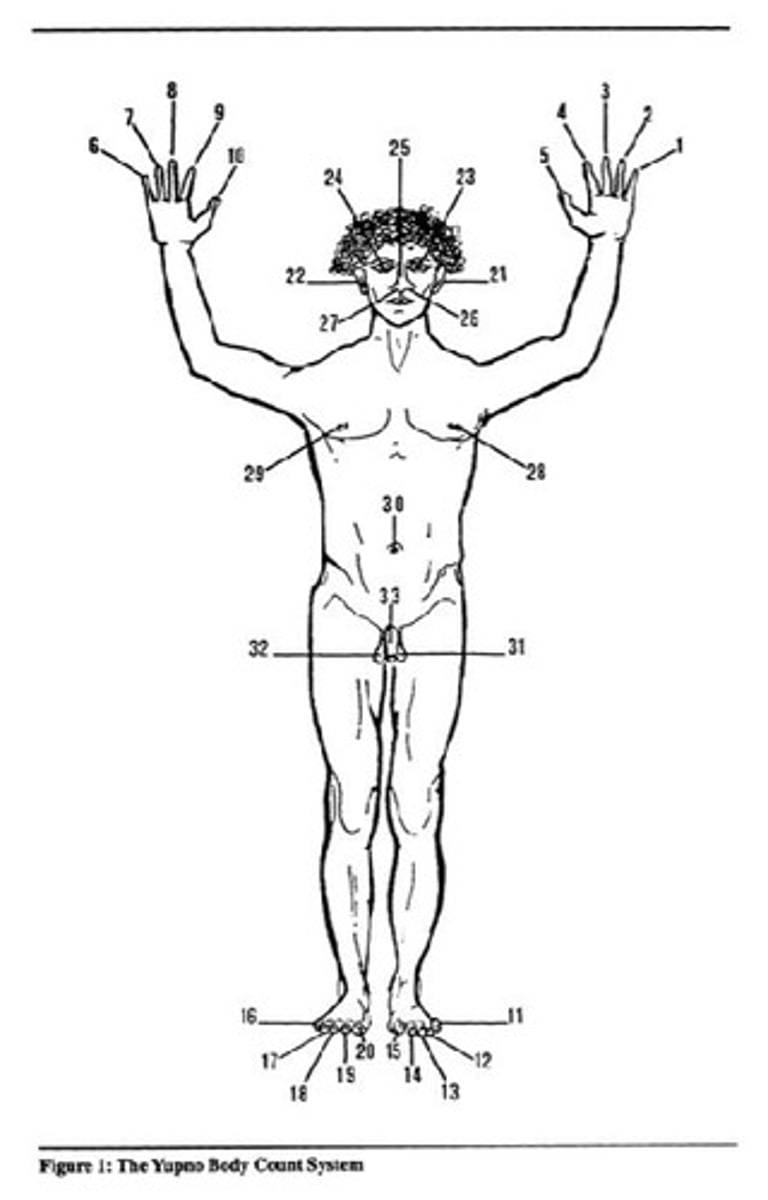
What are some counting practices observed in Papua New Guinea?
Body count systems are pervasive, with 900 systems attested.
What is Bede's counting system known for?
It was widely used in medieval Europe.
How do numeral systems differ in terms of bulkiness?
Some systems, like English and Mandarin, are compact, while others, like Hup numerals, are bulky.
What is the role of object-specificity in numeral systems?
It refers to how numerals may vary based on the specific objects being counted.
What is the cognitive consequence of the aspects of variation in number words?
These aspects may influence how individuals perceive and process numerical information.
What are cardinal numbers?
Numbers that indicate quantity, such as one, two, three.
What are ordinal numbers?
Numbers that indicate position or order, such as first, second, third.
What does 'limits' refer to in the context of number words?
It refers to the constraints on how numbers are expressed or understood within a language.
What is an example of a numeral system that incorporates non-numerical words?
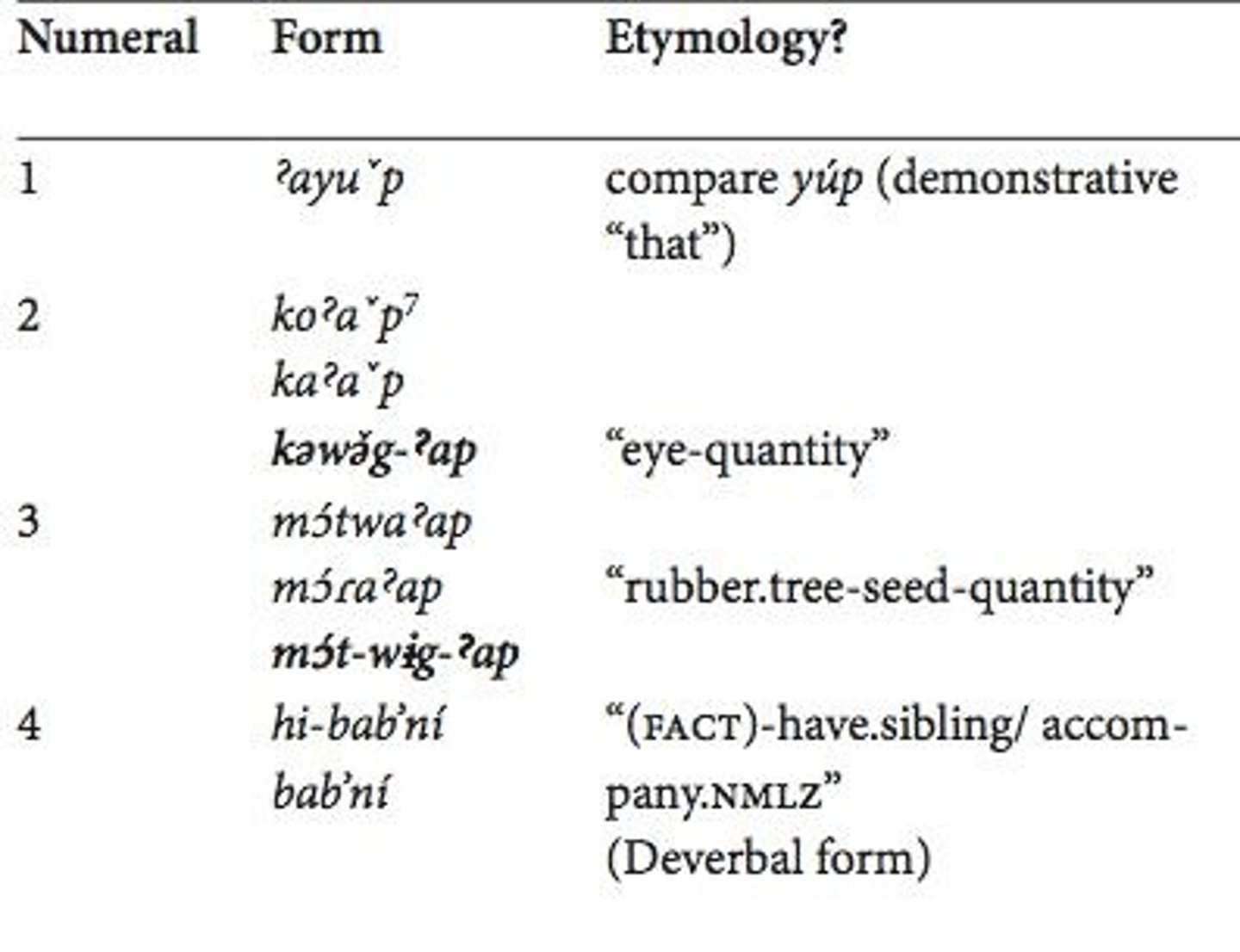
Numeral systems in the Vaupes region of Amazonia, which use body part terms.

What is the significance of the study by Frank et al., 2008?
It discusses the aspects of variation in number words and their implications.
What is the relationship between counting practices and numeral systems?
Counting practices can vary widely and influence how numerals are structured and understood.
How does the concept of 'bulkiness' affect numeral systems?
Bulkiness can make a numeral system less efficient or harder to use.
What is the difference between exact number words and quantifiers?
Exact number words specify a precise quantity, while quantifiers indicate a range or an approximate amount.
What is the significance of the term 'wug' in linguistic studies?
It is often used in experiments to demonstrate grammatical rules in language acquisition.
What is the importance of studying numeral systems across different cultures?
It helps to understand cognitive processes and cultural differences in quantification.
What is an example of a counting system learned in some Indian school systems?
Finger counting systems that vary by region.
How do numeral systems reflect cultural practices?
They can incorporate local objects and practices, influencing how numbers are conceptualized.
What are the six aspects of variation in number words?
1. Base of numeral system 2. Object-specificity 3. Limits 4. Transparency 5. Counting practices 6. Bulkiness
What conclusion did Frank et al. (2008) reach regarding Pirahã speakers and exact numbers?
Pirahã has no terms for exact number.
What was the main focus of the experiments conducted by Gordon (2004) on Pirahã speakers?
To determine if Pirahã speakers can reproduce and remember exact quantities.
What was the method used in experiments A-D by Gordon (2004)?
Participants were shown a quantity of batteries or ground nuts and had to reproduce the quantity.
What was the method used in experiment E by Gordon (2004)?
Participants were shown a set of drawn lines and had to draw a matching set.
What was the duration of the array shown to participants in experiment F by Gordon (2004)?
Participants were shown the array for only 1 second.
What was the method used in experiment G by Gordon (2004)?
Participants were shown a group of nuts in a can; the experimenter then removed nuts one at a time and asked whether there were still nuts left.
What was the method used in experiment H by Gordon (2004)?
Participants were shown a box with a particular number of fish on the lid and later given a choice between the same box and one with one more or fewer fish.
What does the mean estimate of Pirahã speakers suggest about their guessing?
They are not guessing randomly; the mean estimate increases in a linear fashion.
What does the variation around the mean (SD) indicate in Gordon's experiments?
The amount of variation around the mean increases in a linear fashion, suggesting approximate quantity estimation.
What is the main conclusion about Pirahã speakers' ability to reproduce and remember quantities?
Pirahã speakers have serious difficulty reproducing and remembering exact quantities and seem to use approximate quantity estimation beyond ~3.
What do several further studies with the Pirahã support regarding their cognitive abilities?
They support the conclusion that Pirahã speakers have difficulty with exact quantities.
How is the base of the English numeral system characterized?
English is base 10, with a specific structure for numbers one to ten and beyond.
How does the numeral system in Mandarin compare to English?
Mandarin is also base 10, with a structured progression similar to English.
What makes the English numeral system opaque in the teens?
The terms eleven, twelve, thirteen, fourteen, etc., do not follow the base 10 structure clearly.
What is the significance of the term 'bulkiness' in the context of number words?
Bulkiness refers to the complexity and structure of numeral systems and their cognitive implications.
What cognitive consequences arise from the limits of numeral systems?
Limits can affect the ability to think numerically and reproduce exact quantities.
What is the relationship between counting practices and cognitive consequences?
Different counting practices can influence how individuals conceptualize and estimate quantities.
What does transparency in a numeral system refer to?
Transparency refers to how clearly the structure of the numeral system conveys numerical relationships.
How does the concept of object-specificity relate to number words?
Object-specificity pertains to how number words can vary based on the types of objects being counted.
What role does cognitive variation play in numeral systems?
Cognitive variation can lead to differences in how people understand and use numbers based on their language and culture.
What is the Mandarin word for 'one'?
yi
What is the Mandarin word for 'two'?
er
What is the Mandarin word for 'three'?
san