Genetics: Inheritance
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12 Biology Final Review
Last updated 8:41 PM on 5/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
Gregor Mendel
\-determined that parents pass discrete heritable factors on their offspring, which retain individuality generation after generation.
\-each parent passes down a factor, one may be dominant over the alternative form.
\-each parent passes down a factor, one may be dominant over the alternative form.
2
New cards
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
\-Each individual has 2 factors (genes) for each trait that separate during the formation of gametes.
\-Each gamete contains only one factor from each pair of factors
\-Each gamete contains only one factor from each pair of factors

3
New cards
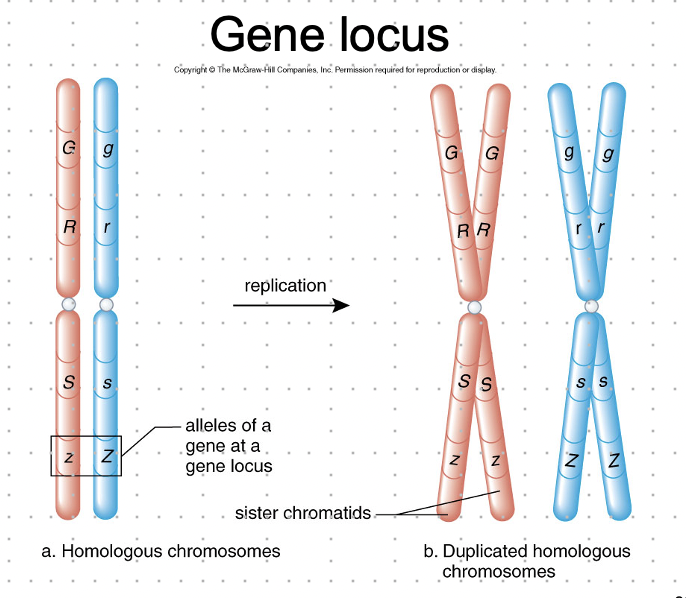
chromosomes
\-come in homologous pairs which have genes controlling the same traits. genes are located at the same point/locus on each member of the pair
\-genes are sections of chromosomes
\-genes are sections of chromosomes
4
New cards
alleles
alternative forms of a gene for a trait
5
New cards
Dominant Alleles
\-represented by the capital letter
\-a certain traits will result if the individual has at least 1 dominant allele
\-a certain traits will result if the individual has at least 1 dominant allele
6
New cards
Recessive Alleles
\-represented by the lowercase letter
\-for a recessive trait to result the individual must have 2 copies of the recessive allele
\-for a recessive trait to result the individual must have 2 copies of the recessive allele
7
New cards
Genotype
\-genetic composition of an individual with regard to a specific trait
\-may either be homozygous dominant, heterozygous, homozygous recessive Ho
\-may either be homozygous dominant, heterozygous, homozygous recessive Ho
8
New cards
Homozygous Dominant
2 copies of the dominant allele
9
New cards
Heterozygous
1 copy go the dominant allele and 1 of the recessive
10
New cards
Homozygous Recessive
\-2 copies of the recessive allele
11
New cards
Phenotype
\-physical appearance of the individual with regard to a trait
\-homozygous dominant and heterozygous individuals will have the same phenotype, whereas the homozygous recessive individual will have a different phenotype
\-homozygous dominant and heterozygous individuals will have the same phenotype, whereas the homozygous recessive individual will have a different phenotype
12
New cards
Gamete Formation
\-during meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate so there is only 1 member of each pair in a gamete
\-there is only 1 allele for each trait in each gamete
\-no 2 letters in a gamete can be the same letter of the alphabet:
o if the genotype is Ww, then gametes from this individual will contain either W or w
o whereas if the genotype is WwLl (2 traits) gametes can be the following: WL, Wl, wL, wl
\-there is only 1 allele for each trait in each gamete
\-no 2 letters in a gamete can be the same letter of the alphabet:
o if the genotype is Ww, then gametes from this individual will contain either W or w
o whereas if the genotype is WwLl (2 traits) gametes can be the following: WL, Wl, wL, wl
13
New cards
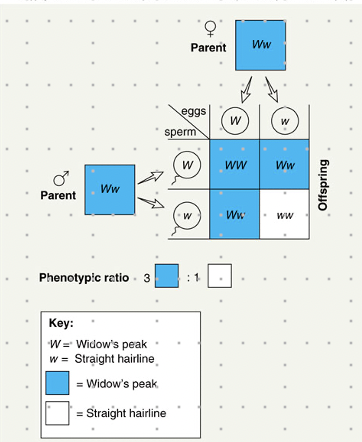
Punnet Squares
easy way to figure out all possible combinations of eggs and sperm
14
New cards
Genetic Ratios
\-In a punnet square we had the following offspring: WW, Ww, Ww, ww
* the genotypic ratio is 1 WW: 2 Ww: 1 ww
* the genotypic ratio is 1 WW: 2 Ww: 1 ww
15
New cards
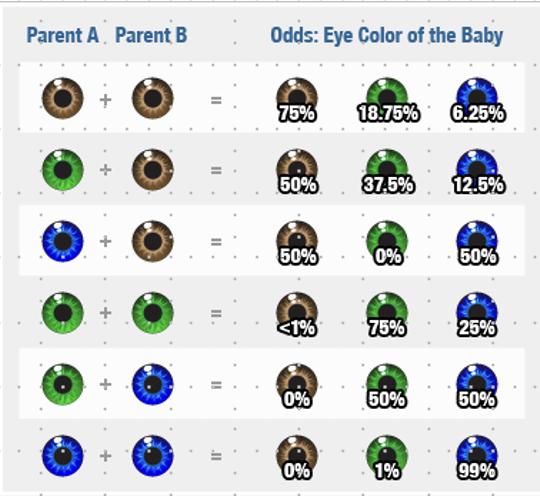
Genetic Probability (product rule)
\-another way to phrase the phenotypic ratio is in terms of probability
\- the chance of 2 or more independent events occurring together is the product of their chance of occurring separately
\- the chance of 2 or more independent events occurring together is the product of their chance of occurring separately
16
New cards
Genetic Probability (sum rule)
the chance of an event that occurs in more than one way is the sum of the individual chances
17
New cards
test cross
\-since homozygous dominant individuals are phenotypically the same as heterozygous individuals (both appear the same) test crosses are utilised to determine the likely genotype of an individual :
18
New cards
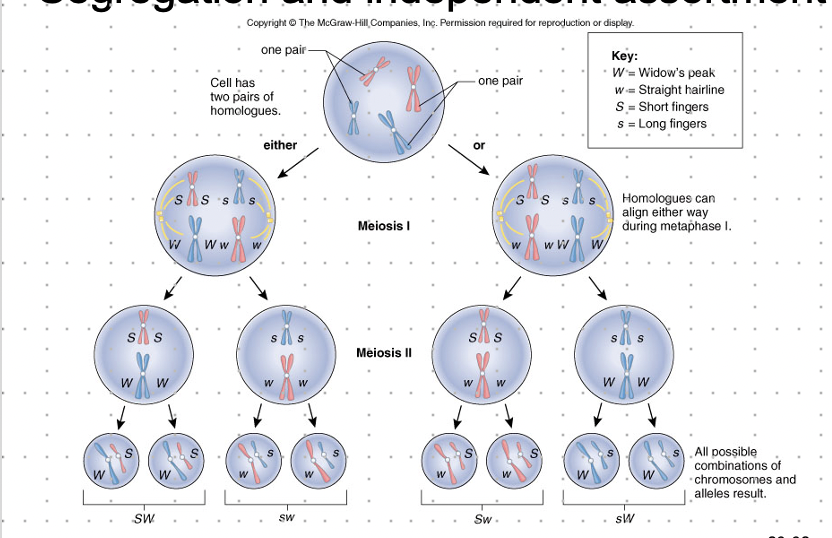
Law of Independent Assortment
\-alleles of 2+ different genes are sorted independently of other genes.
\-whichever allele is received by a gamete for 1 gene doesn’t affect which allele for a different trait is received
\-gamete can receive any possible combo of alleles
\-whichever allele is received by a gamete for 1 gene doesn’t affect which allele for a different trait is received
\-gamete can receive any possible combo of alleles
19
New cards
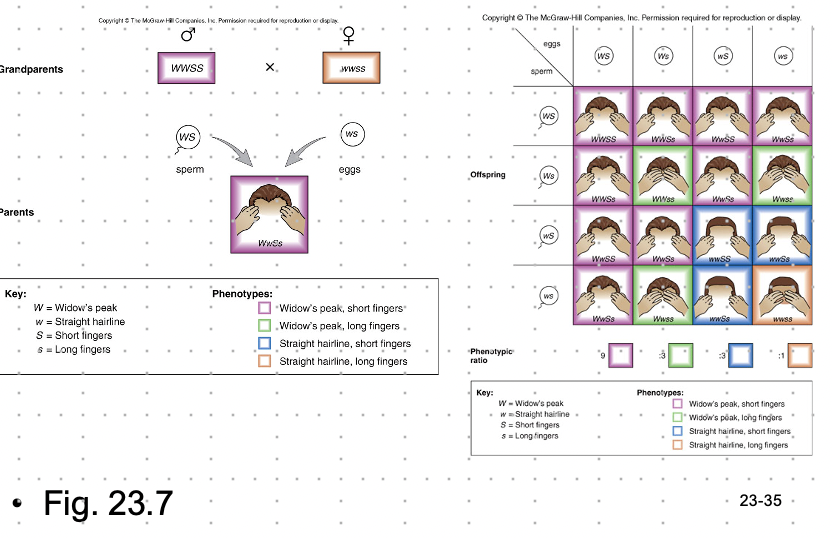
Dihybrid Cross
20
New cards
Two-trait Test Cross
\-cross an individual with the dominant phenotype for each trait with an individual with the recessive phenotype of both traits
21
New cards
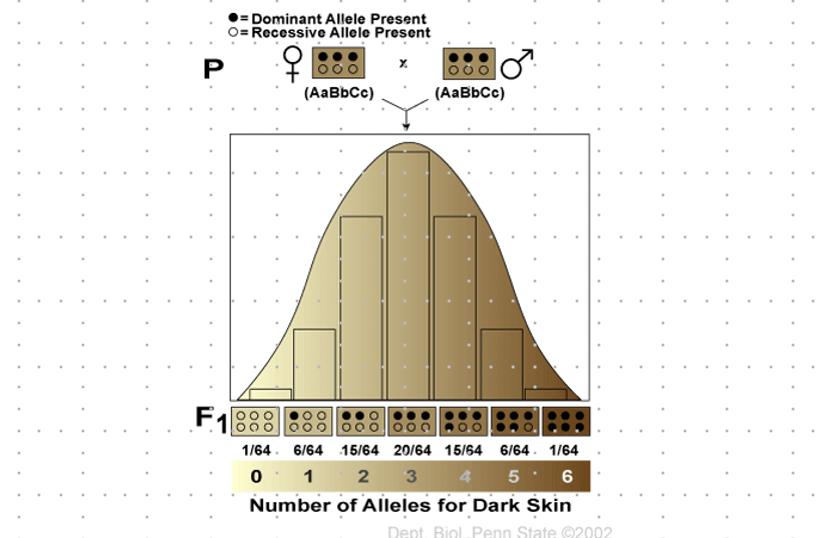
Polygenic Inheritance (Bell Curve)
\- controlled by 2 or more sets of alleles, each dominant allele codes for a product and effects are additive
\-result is a continuous range of phenotypes, where the distribution resembles a bell curve
\-result is a continuous range of phenotypes, where the distribution resembles a bell curve
22
New cards
Polygenic Inheritance (combo)
\-parakeet feathers are controlled by 2 genes, B (blue) and Y (yellow)
\-green parakeets have at least 1 dominant allele for each gene, and white parakeets have only the recessive alleles
\-green parakeets have at least 1 dominant allele for each gene, and white parakeets have only the recessive alleles
23
New cards
Environmental Influences
\-enviornment can influence gene expression, and therefore phenotype.
\-human twin studies show that polygenic traits are most influenced. if they share a common trait despite being raised in different households, it is likely genetic
\
\-human twin studies show that polygenic traits are most influenced. if they share a common trait despite being raised in different households, it is likely genetic
\
24
New cards
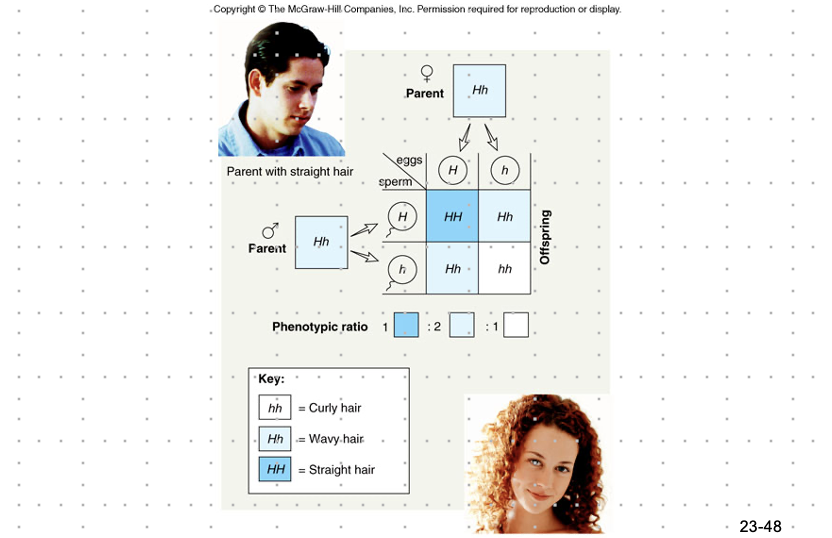
Incomplete Dominance
\-heterozygous individuals have a phenotype intermediate to the 2 homozygous individuals.
* ex. curly hair woman and straight hair man produce wavy hair kids
* snapdragons are either R/red or r/white, so a Rr flower is pink
* ex. curly hair woman and straight hair man produce wavy hair kids
* snapdragons are either R/red or r/white, so a Rr flower is pink
25
New cards
co-dominance
\-occurs when both alleles are equally expressed
* ex. blood type AB represents A and B equally
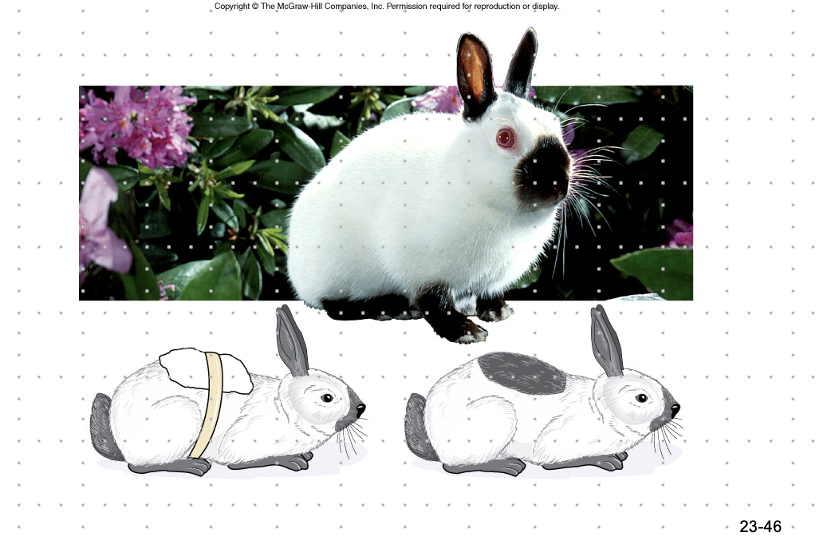
* rhododendrons exhibit both white and pink petals
* ex. blood type AB represents A and B equally
* rhododendrons exhibit both white and pink petals
26
New cards
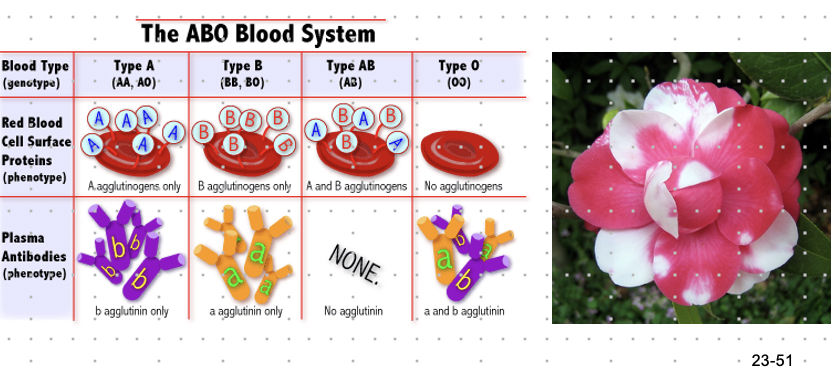
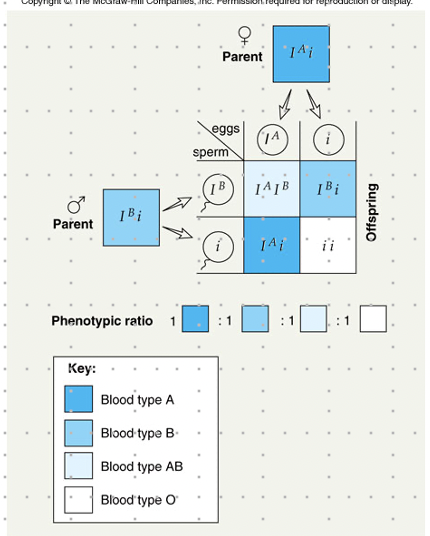
multiple allele inheritance
\-gene exists in several allelic forms, but each person still has only 2 of the possible alleles
* ex. ABO blood types:
* Ia= A antigens on red blood cells
* Ib= B antigens on red blood cells
* I= neither A or B antigens
* phenotype: A → genotype: IaIa or lal
* phenotype: B → genotype: lblb or lbl
* phenotype: AB → genotype: lalb
* phenotype: O → genotype: II
* ex. ABO blood types:
* Ia= A antigens on red blood cells
* Ib= B antigens on red blood cells
* I= neither A or B antigens
* phenotype: A → genotype: IaIa or lal
* phenotype: B → genotype: lblb or lbl
* phenotype: AB → genotype: lalb
* phenotype: O → genotype: II
27
New cards
Paternity Testing
\- ABO blood groups often used
* can disprove paternity, but not prove it
\-Rh factor:
* another antigen on the RBC, where Rh + has the antigen and Rh - does not
* multiple alleles for Rh - but all are recessive to Rh positive
* can disprove paternity, but not prove it
\-Rh factor:
* another antigen on the RBC, where Rh + has the antigen and Rh - does not
* multiple alleles for Rh - but all are recessive to Rh positive
28
New cards
sex chromosomes
\-22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex chromosomes (therefore 23 total)
\- XX: female sex chromosomes, XY: male sex chromosomes
\- XX: female sex chromosomes, XY: male sex chromosomes
29
New cards
sex linked traits
\-traits controlled by genes in the sex chromosomes
\- X chrom. has many genes, whereas the Y does not
\- X chrom. has many genes, whereas the Y does not
30
New cards
Carriers
\-when a female is heterozygous for a sex linked trait, therefore able to pass onto her children
31
New cards
X linked traits
\-as males only have one X chromosome, recessive traits are more common in men
\- ex. colourblindness is x-linked
* the X chromosome has genes for normal colour vision, so XB= normal vision and Xb= colourblindness
\- ex. colourblindness is x-linked
* the X chromosome has genes for normal colour vision, so XB= normal vision and Xb= colourblindness

32
New cards
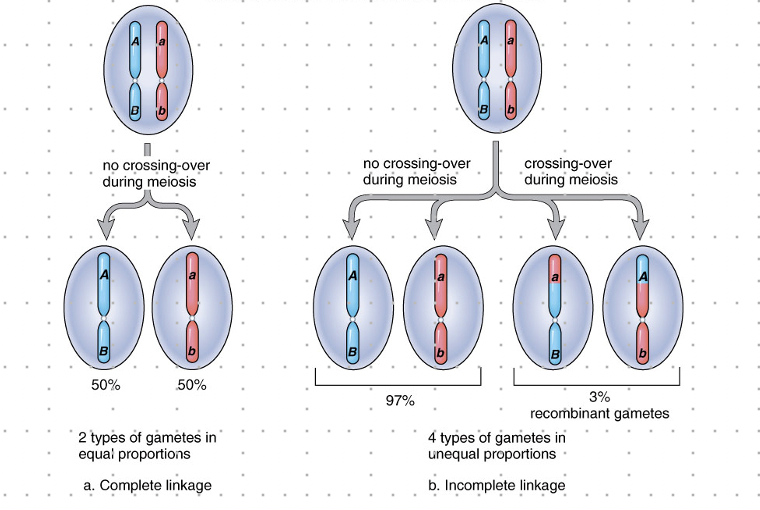
Linked Genes
\-a chromosome has several genes, and the sequence of those genes is fixed bc each allele has a specific locus.
\-all genes on a single chromosome form a linkage group. when linkage is complete, a dihybrid produces only 2 types of gametes
\-any time traits are inherited together, a linkage group is suspected. or, if very few recombined phenotypes appear in offspring, linkage is also suspected
\-all genes on a single chromosome form a linkage group. when linkage is complete, a dihybrid produces only 2 types of gametes
\-any time traits are inherited together, a linkage group is suspected. or, if very few recombined phenotypes appear in offspring, linkage is also suspected