Edexcel IGCSE Physics : 7 Radioactivity and Particles
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Describe the structure of an atom
consists of a central positive nucleus containing neutrons and protons
orbited by negatively charged electrons
Describe the structure of an atom using notation
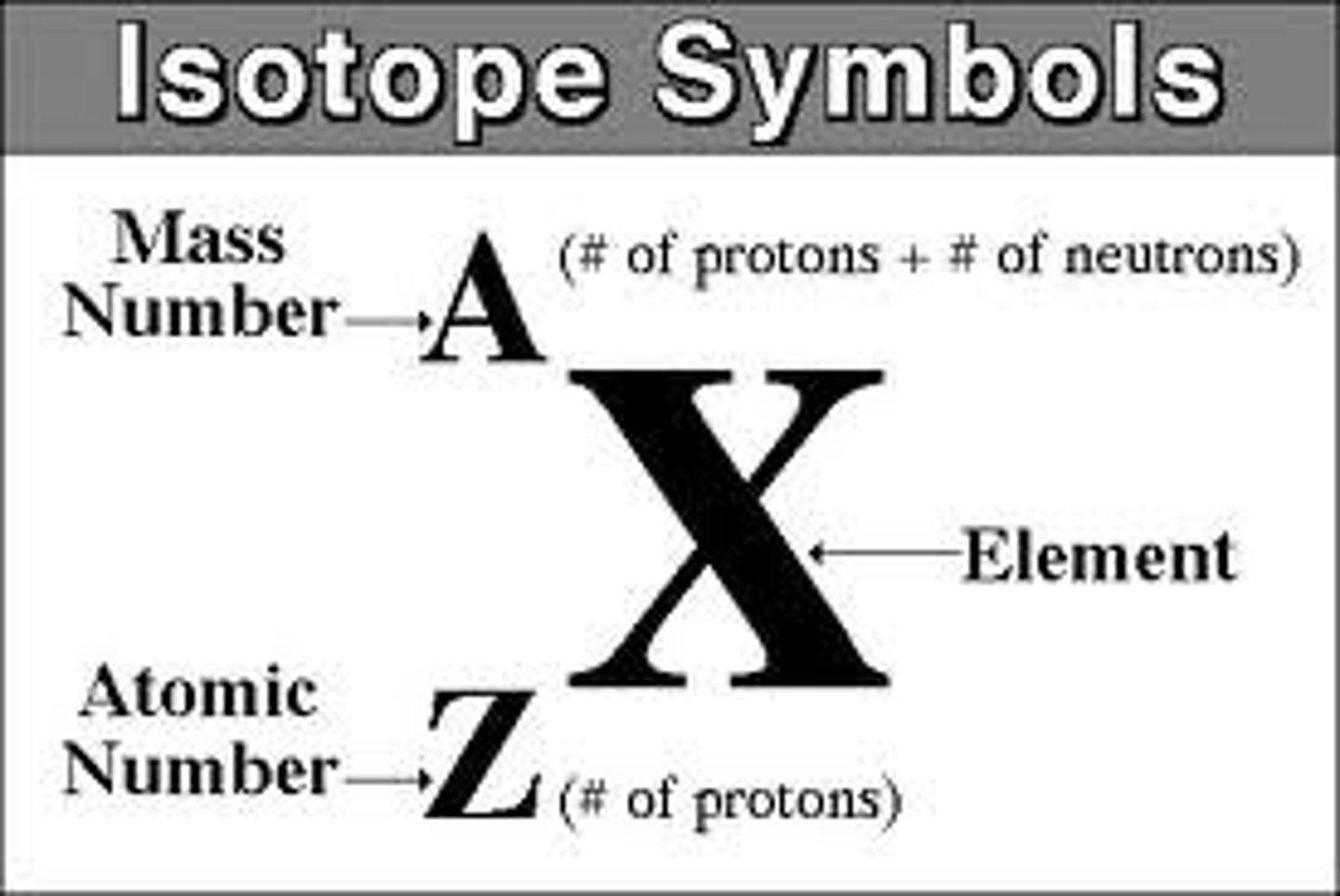
Define the term atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
also called proton number
Define the term mass number
the number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
also called nucleon number
Define the term isotope
an atom with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
What are the types of ionising radiation and how are they produced ?
ionising radiation is emitted from unstable nuclei in a random process
the types are :
alpha
beta
gamma
neutron
Describe the properties of alpha particles
highly ionising
weakly penetrating
stopped by a sheet of paper
heavy and big
Describe the properties of beta particles
moderately ionising
moderately penetrating
stopped by a thin sheet of aluminium
(is an electron )
small and fast
Describe the properties of gamma particles
pure energy , emitted alongside alpha or beta decay
lowly ionising
highly penetrating
stopped by thick layer of lead
no mass
moves very fast
practical: investigate the penetration powers of different types of radiation using either radioactive sources or simulations

What is the effect of alpha radiation on atomic and mass numbers ?
reduces mass number by 4
reduces atomic number by 2
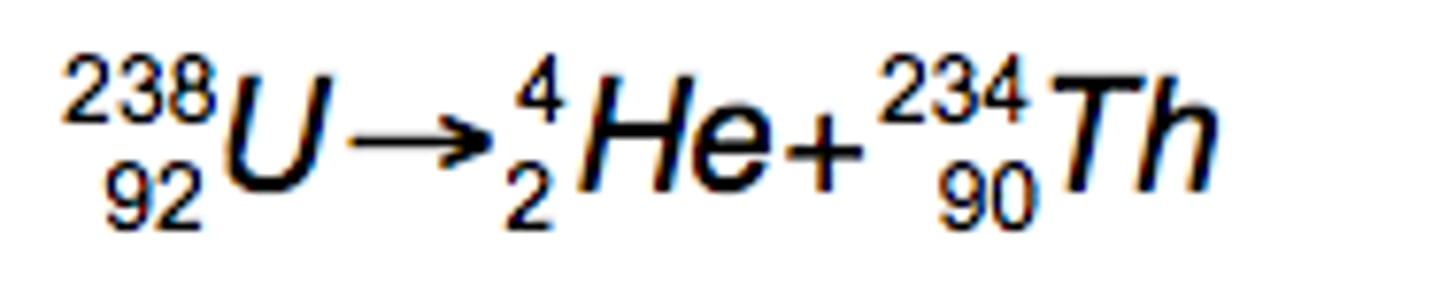
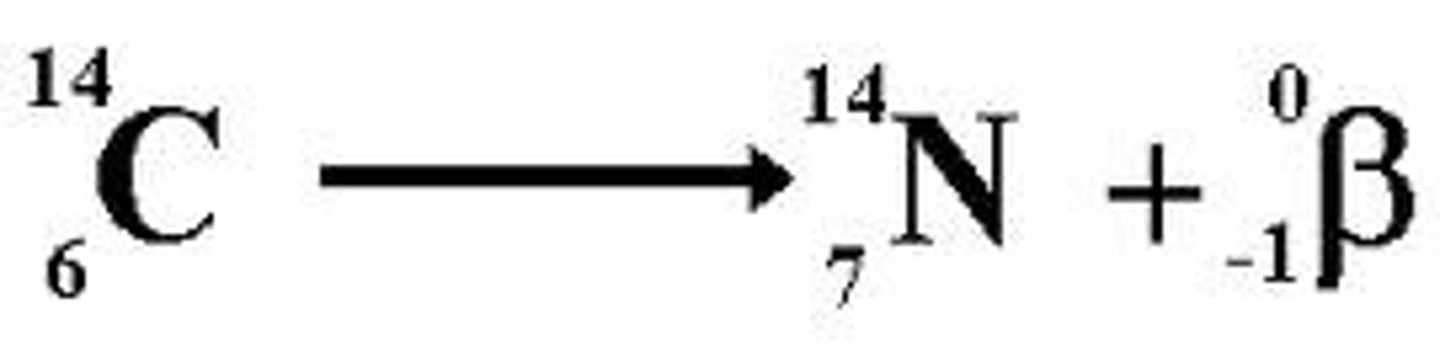
What is the effect of beta radiation on atomic and mass numbers ?
mass number stays the same
the atomic number increases by 1
What is the effect of gamma radiation on atomic and mass numbers ?
mass number stays same
atomic number stays the same
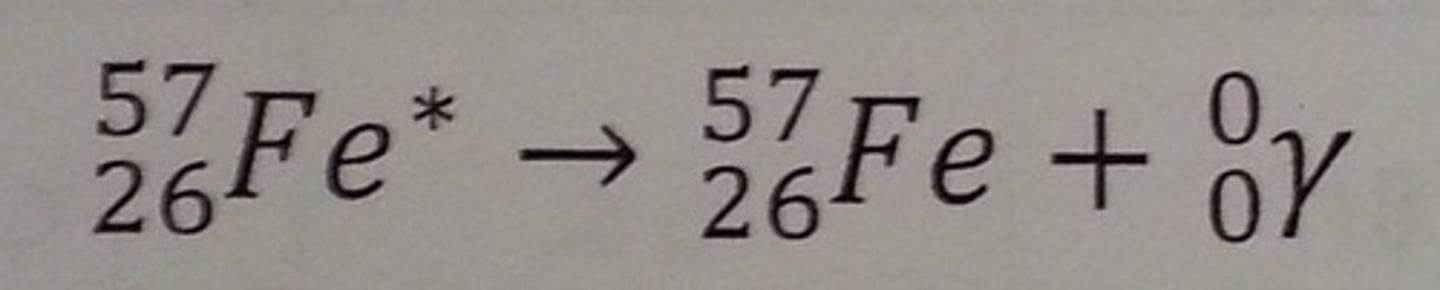
What is the effect of neutron radiation on atomic and mass numbers ?
mass number decreases by 1
atomic number stays the same
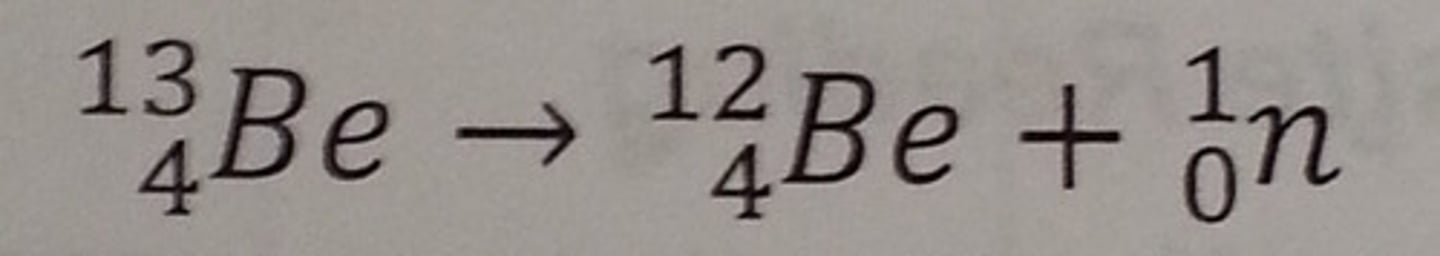
How do you balance a nuclear equation
Balance the mass numbers and atomic numbers on each side of the equation
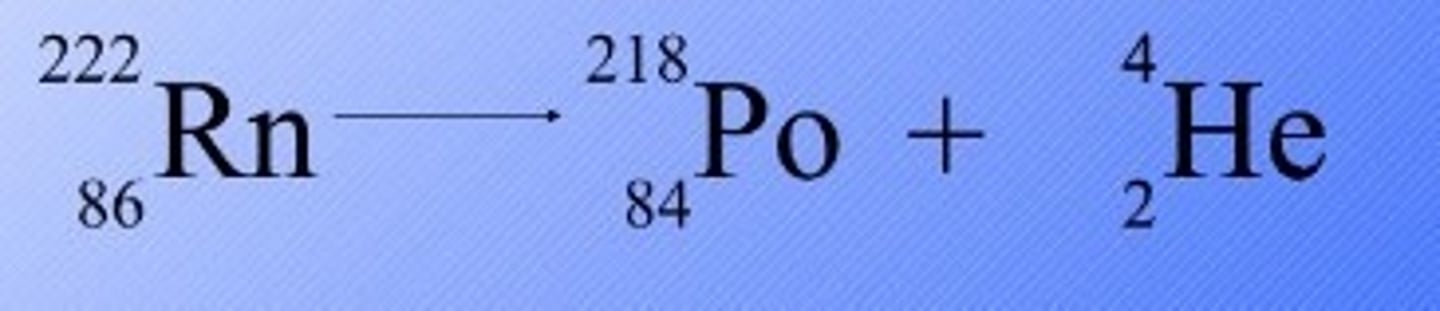
What are the background sources of ionising radiation ?
Two sources are :
The Earth
when the earth was formed it contained many radioactive isotopes , most decayed but some are still producing radiation
Space
nuclear reactions such as supernovas produce cosmic rays which hit the earth , these cosmic rays contain ionising radiation
How can we detect ionising radiation?
Photographic Film:
when developed it gets darker the more radiation it absorbs (from white to black)
Geiger-Muller tube:
Counts the number of times it absorbs nuclear radiation
What happens to the radioactivity of a source?
the activity(number of decays per second) of a radioactive source decreases over time
What is radioactivity measured in ?
Becquerels (Bq)
the number of decays per second
Define the term half-life
the half-life of an isotope is the time taken for half the nuclei to decay or the time taken for the activity to half , it is different for different isotopes
How do you carry out half-life calculations from information and from a graph
if given the initial activity , you find the level it must be at to half and you must then find the corresponding time value on the graph
Describe the uses of radioactivity in industry?
Thickness detector :
a gamma source is placed above the metal and a detector is placed directly below the metal
if the count rate on the detector is too low it means the metal is too thick and then a computer will tell the roller to thin the metal
Cracks detection in jet engines:
a gamma ray source is placed inside the jet engine and photographic film is attached to the outside
when the film is developed, if there is a crack in the engine it will show up on the film as a darker area
Describe the uses of radioactivity in medicine?
Medical Imaging:
a radioactive (gamma) isotope is attached to a drug called a tracer
this is injected into the patient
we can then monitor the tracer outside the patients body to find out if organs are absorbing too much or too little of the tracer
Sterilisation:
gamma ray emitters are used to kill bacteria or parasites on equipment so it is safe for operations
Radiotherapy:
gamma emitters emit a high does of radiation at cancer cells in order to kill them
What is contamination and irradiation and what is the difference between them ?
contamination- when a radioactive source is introduced into or onto an object, the contaminated object becomes radioactive for as long as it is in contact with the source
irradiation - when an object is exposed to a radioactive source which is outside the object, the irradiated object does not become radioactive
Describe the dangers of ionising radiations ?
ionising radiation can kill cells by ionising them
or can cause cell mutations in living organisms , some mutations can lead to cancer
they are difficult to dispose off and if stored incorrectly can pollute land and pollute rivers and kill animals
Which nuclear reactions can be a source of energy?
nuclear reactions , including fission, fusion and radioactive decay can be a source of energy
Describe how a U-235 nucleus is split by fission ?
1. a U-235 nucleus absorbs a slow moving nucleus
2. The nucleus becomes unstable and splits apart, producing its products
What are the products of fission of a U-235 nucleus ?
1. two daughter nuclei:
barium-144 and krypton-89
2. produces gamma radiation and three more neutrons
3. produces a huge amount of energy which is carried away as the kinetic energy of two atoms produced and some emitted as gamma radiation
Describe how a chain reaction is produced during the fission of U-235 nuclei
1. when a U-235 nucleus undergoes fission it releases neutrons
2. these neutrons may go on to strike other U-235 nuclei and be absorbed, carrying on a chain of fission reactions
What do the control rods do in the fission process in a nuclear reactor ?
absorbs neutrons to keep the number of neutrons such that only one fission neutron goes on to induce a further fission
usually made of boron or cadmium
What does the moderator do in the fission process in a nuclear reactor?
slows down neutrons to make it easier to induce further fission
the moderator gets hot as it absorbs kinetic energy from neutrons
made of graphite
What does shielding do around a nuclear reactor?
absorbs any ionising radiation or neutrons produced in the reactor and contain the reactor in the event of an explosion
made of a thick lead layer
What is the difference between nuclear fusion and nuclear fission ?
1. fusion is the combining of nuclei
fission is the splitting of nuclei
2. fission produces more energy than fusion
3.fission produces more radioactive particles and more waste
4. fission is more risky as it can cause nuclear chain reactions and meltdowns
What is nuclear fusion?
the creation of larger nuclei resulting in a loss of mass from smaller nuclei, accompanied by a release of energy
What is the role of fusion with regards to starts ?
fusion is the energy source for stars
Why can't nuclear fusion take place at low temperatures and pressures ?
1. nuclear fusion requires a lot of kinetic energy to occur and so it requires a high temperature and pressure
2. this is because nuclei are positively charged
3. so they repel each other
4. to overcome these strong electrostatic forces of repulsion a lot of kinetic energy is required to allow this process to occur