AP Bio Units 1-4 Review Diagram | Quizlet
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
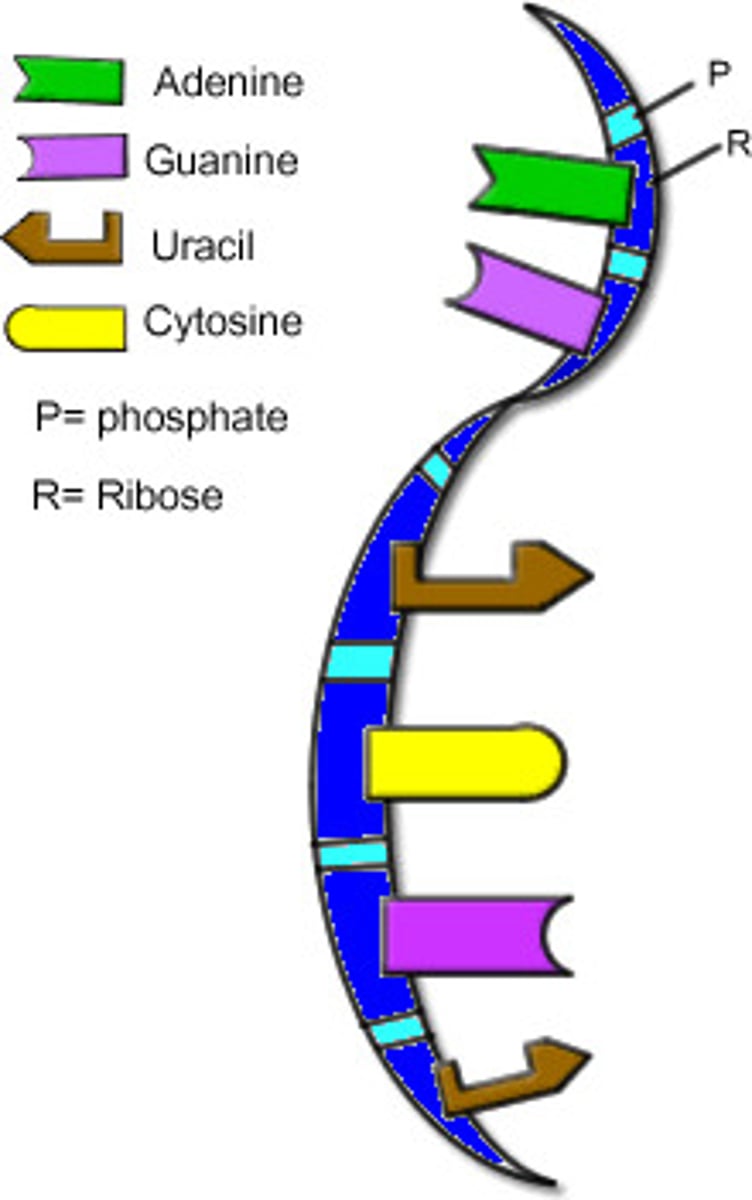
RNA
ribonucleic acid; single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
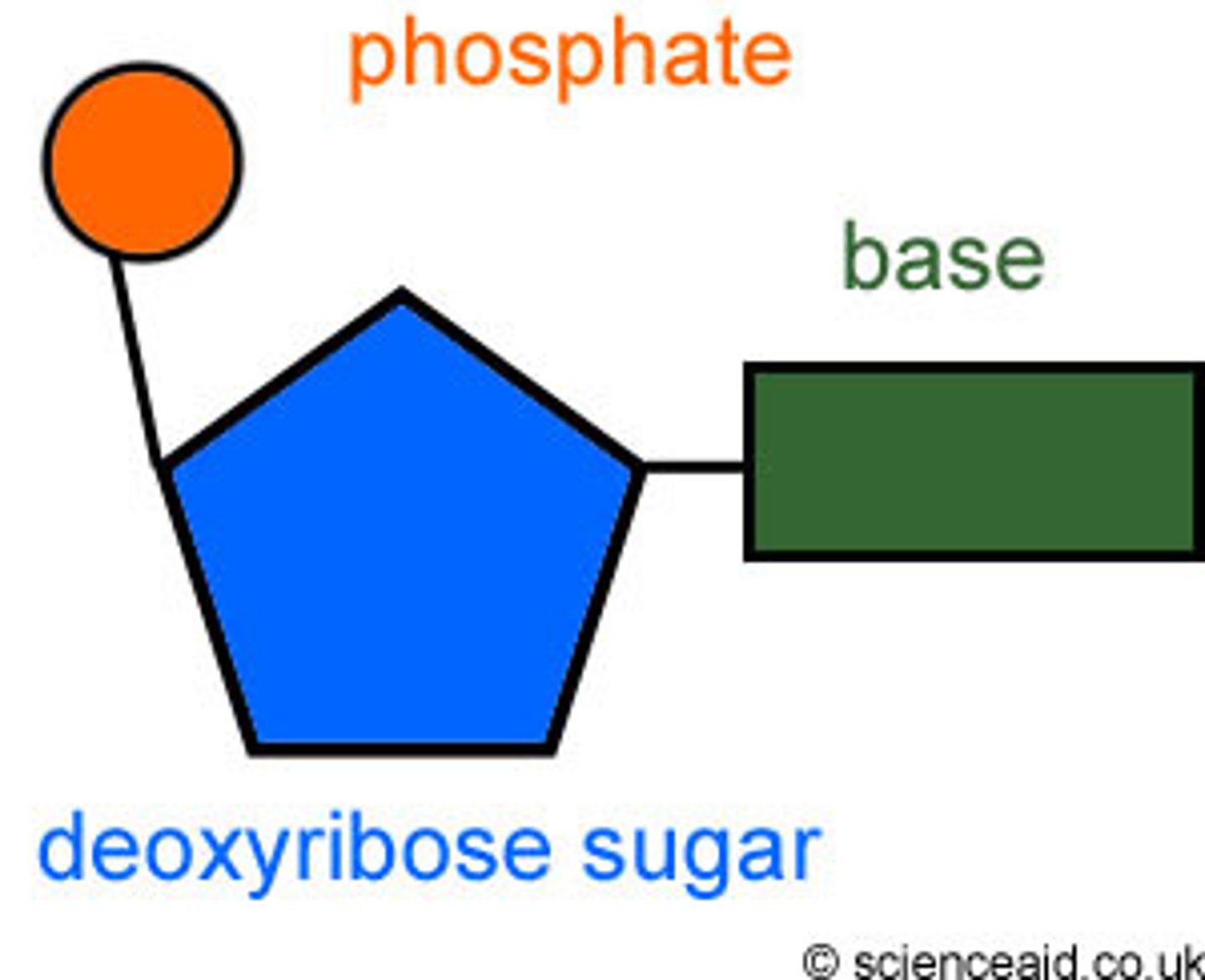
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
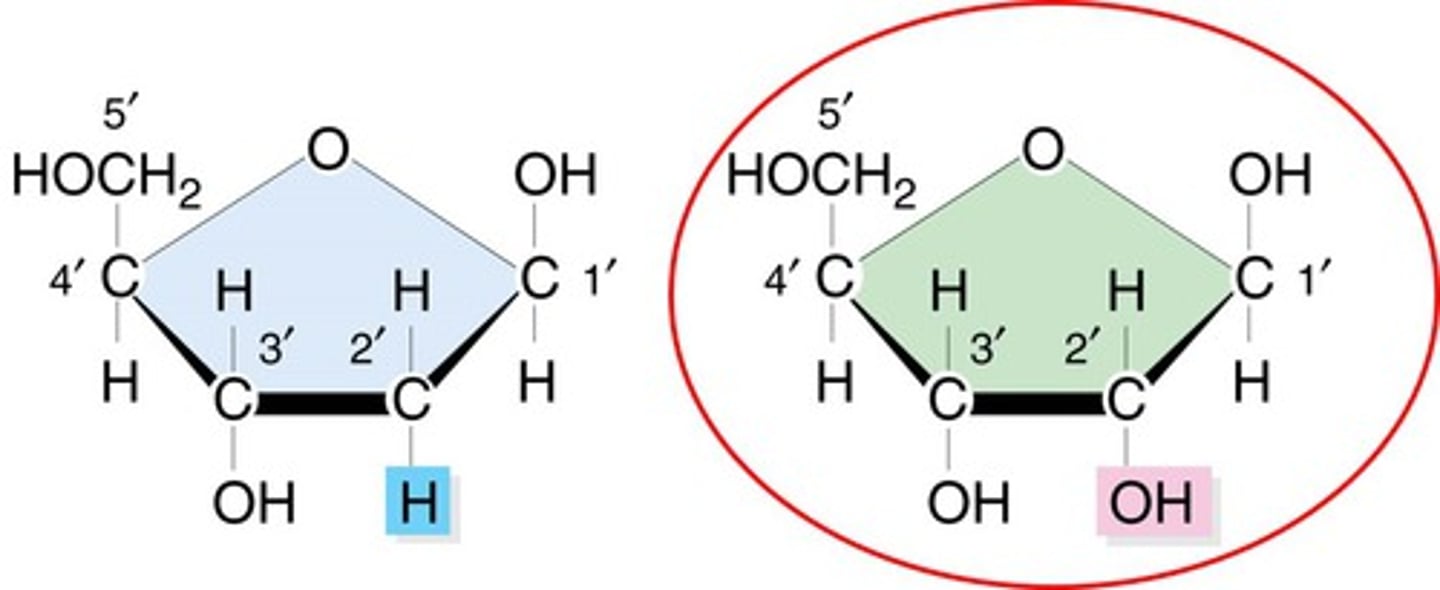
deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides; contains one less oxygen that the five-carbon sugar in RNA nucleotides
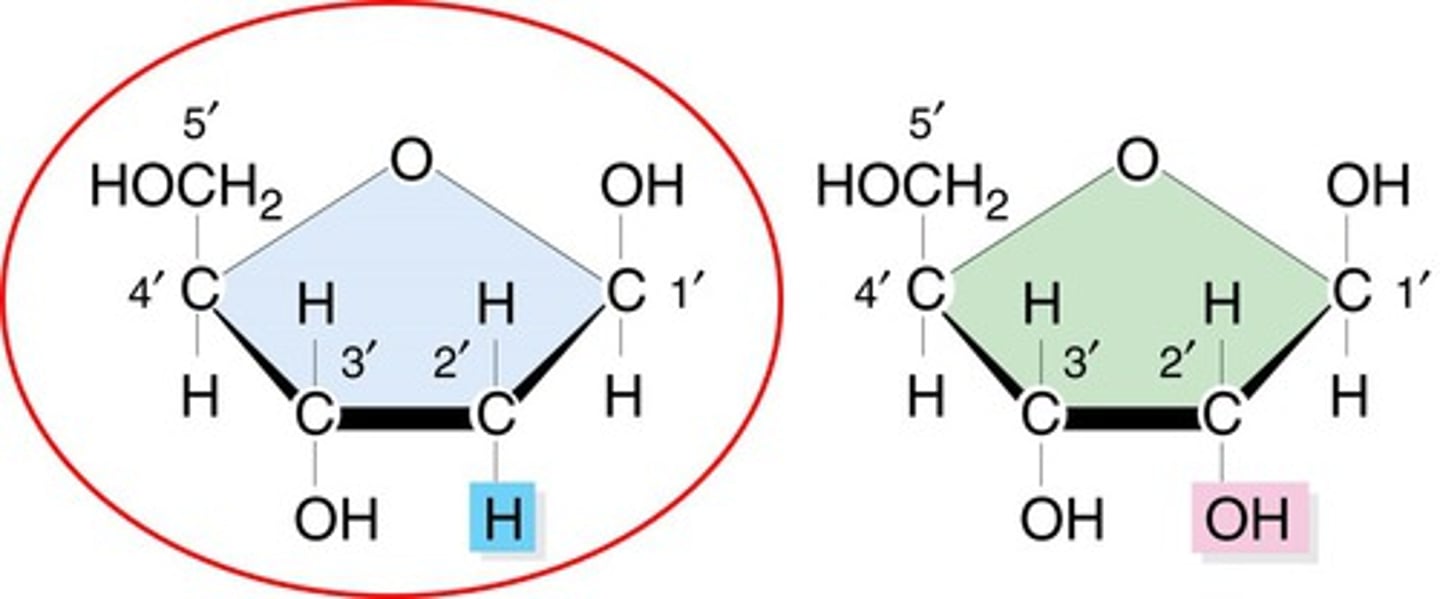
ribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of RNA nucleotides
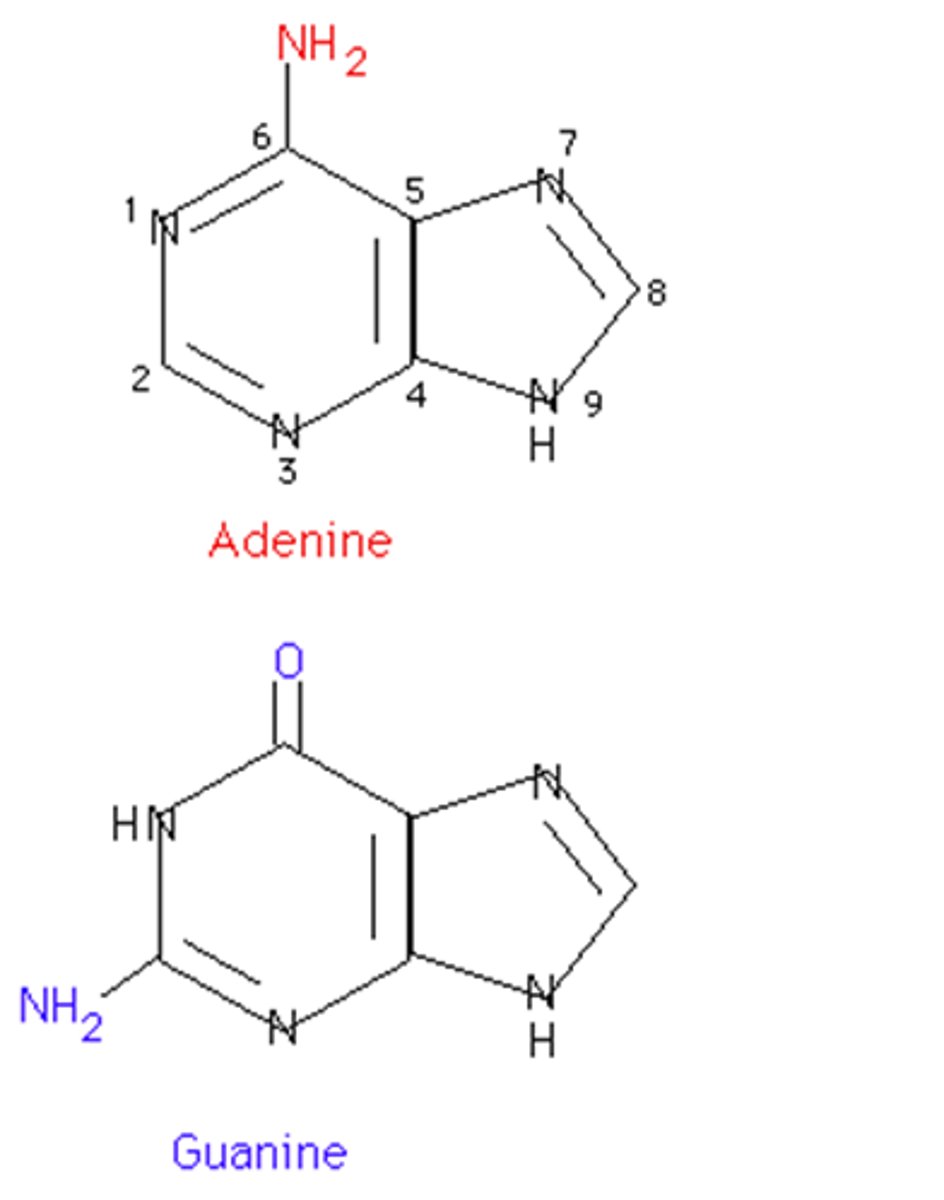
purine
double-ring nitrogenous base; adenine and guanine
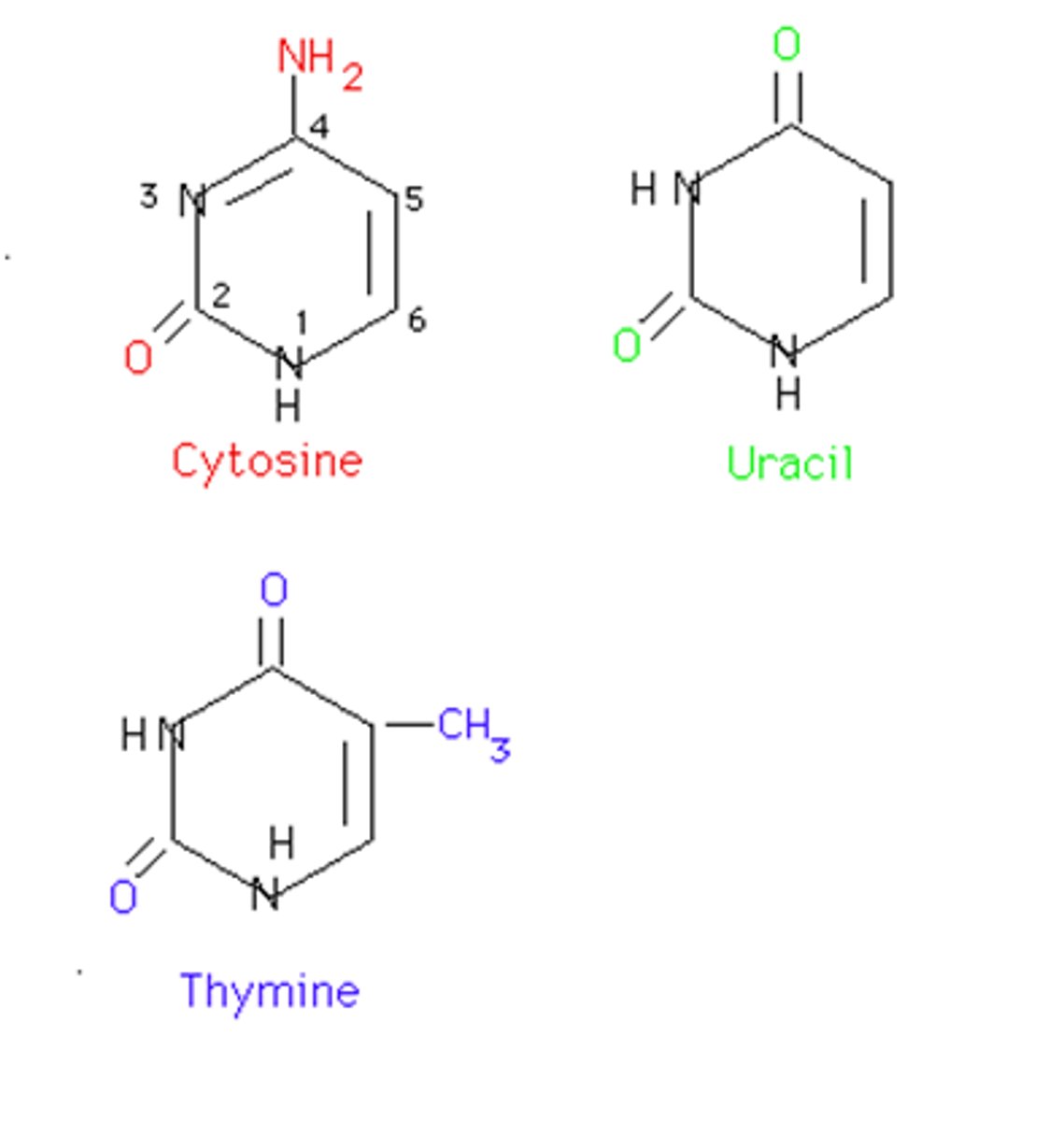
pyrimidine
single-ring nitrogenous base; thymine, cytosine, or uracil (CUT)
adenine
The base that pairs with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA
thymine
the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with adenine in DNA.
guanine
The base that pairs with cytosine in DNA and RNA
uracil
The base found in RNA (but not in DNA) that base pairs with adenine
cell signaling
The process of cell-to-cell communication mediated by signaling molecules and membrane receptors. Composed of three steps:
1) reception
2) transduciton
3) response
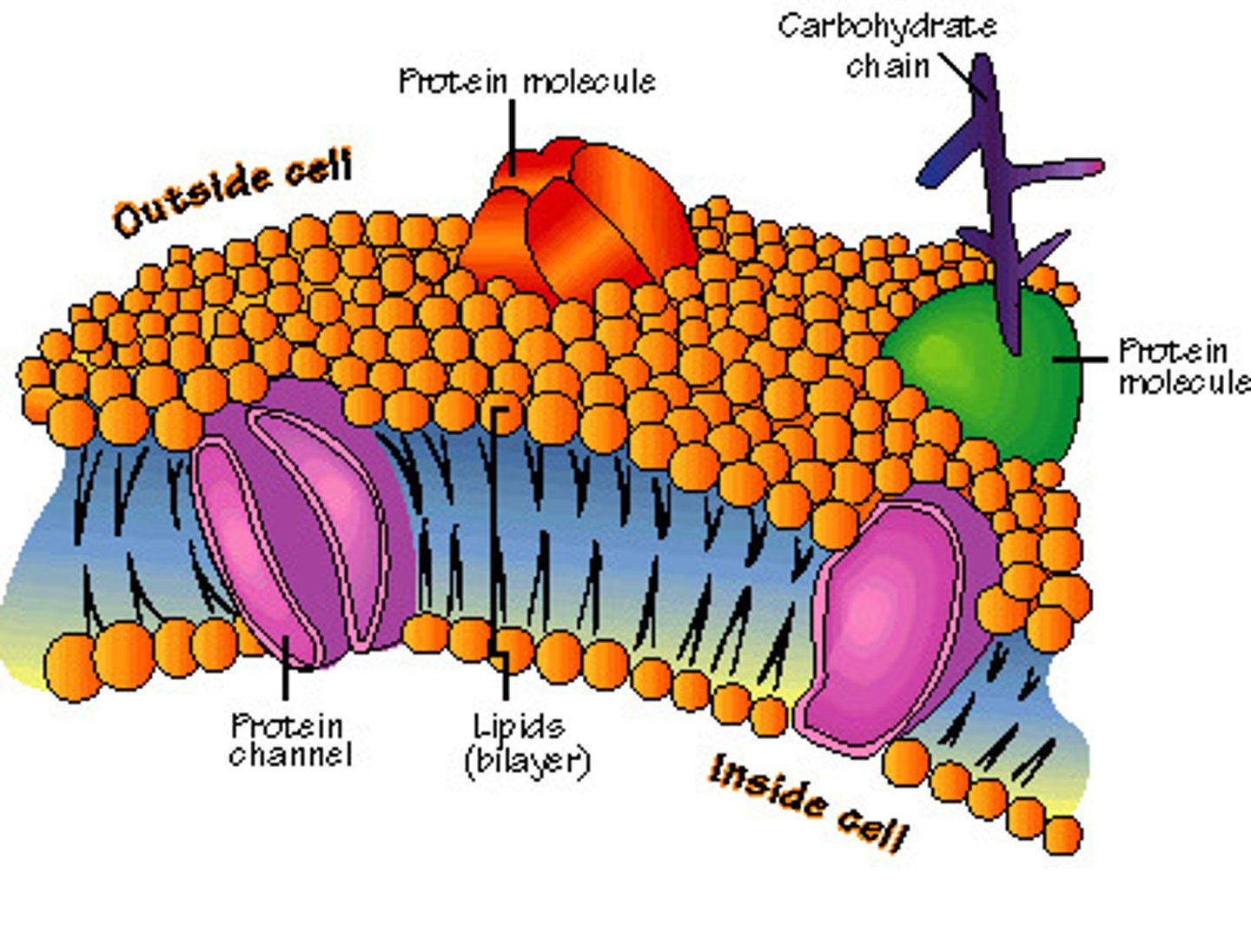
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells; another term for cell membrane
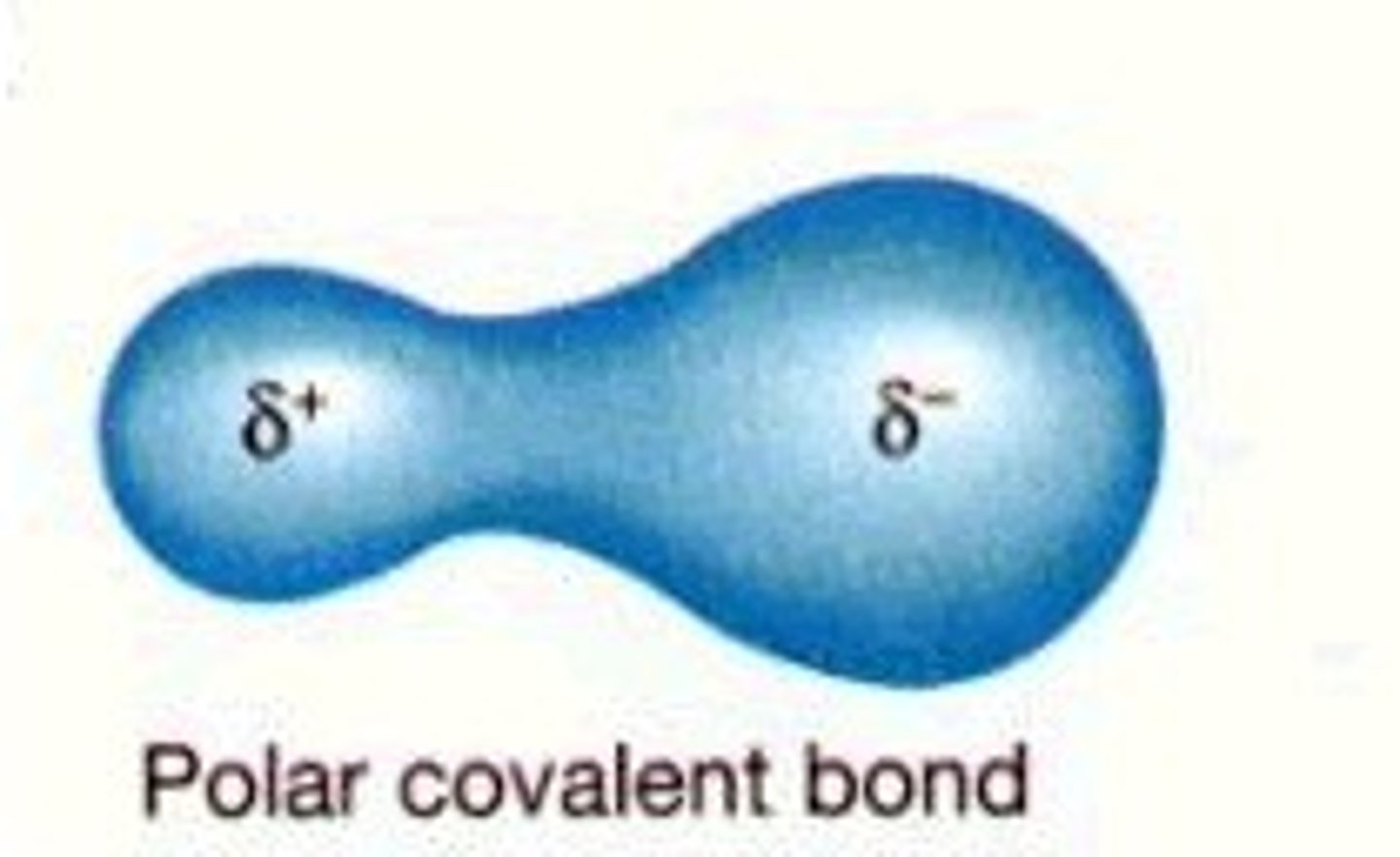
polar
Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water.
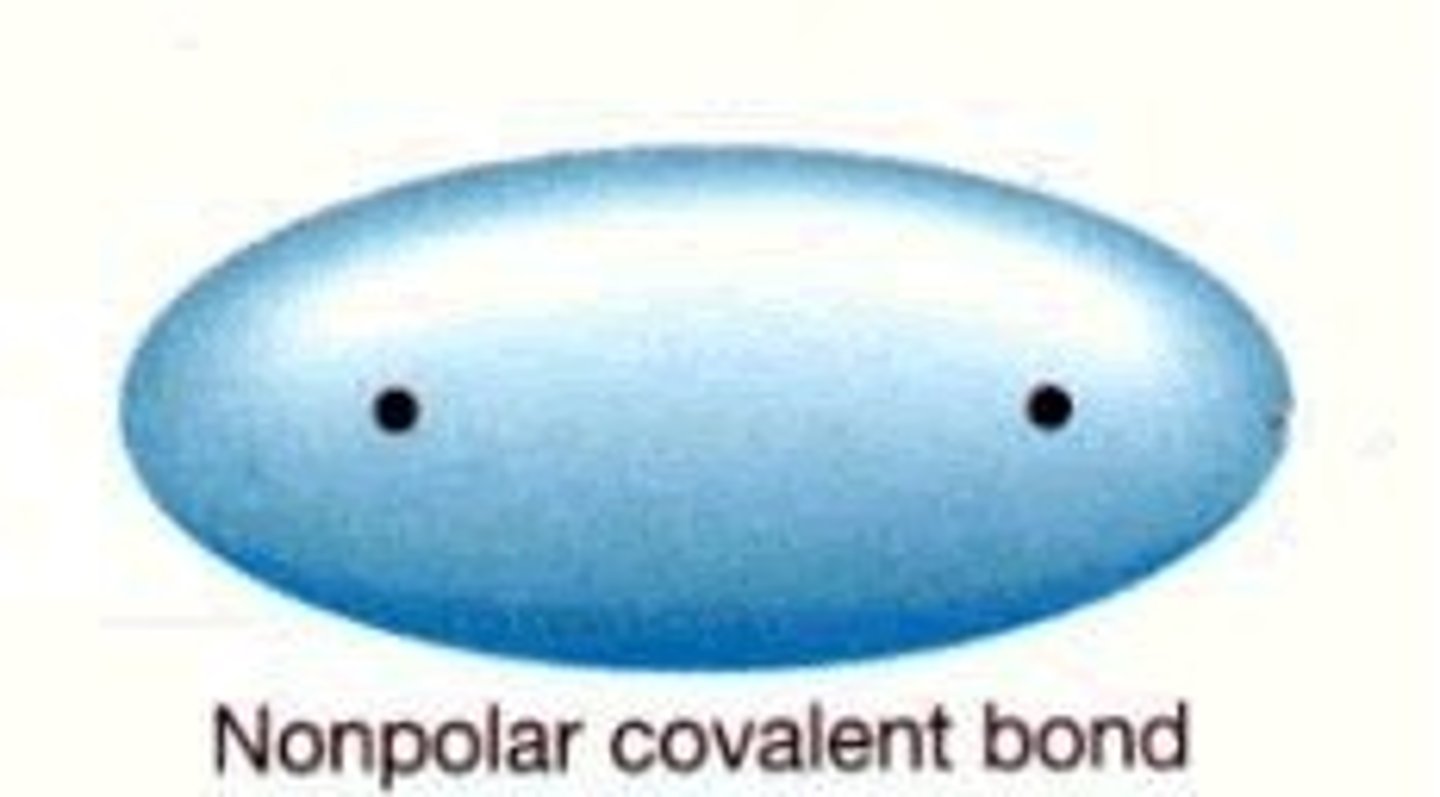
nonpolar
No partial charges. Do not mix with water.
intracellular receptor
receptors located inside the cell rather than on its cell membrane; activated by membrane-permeable ligands such as steroid hormones
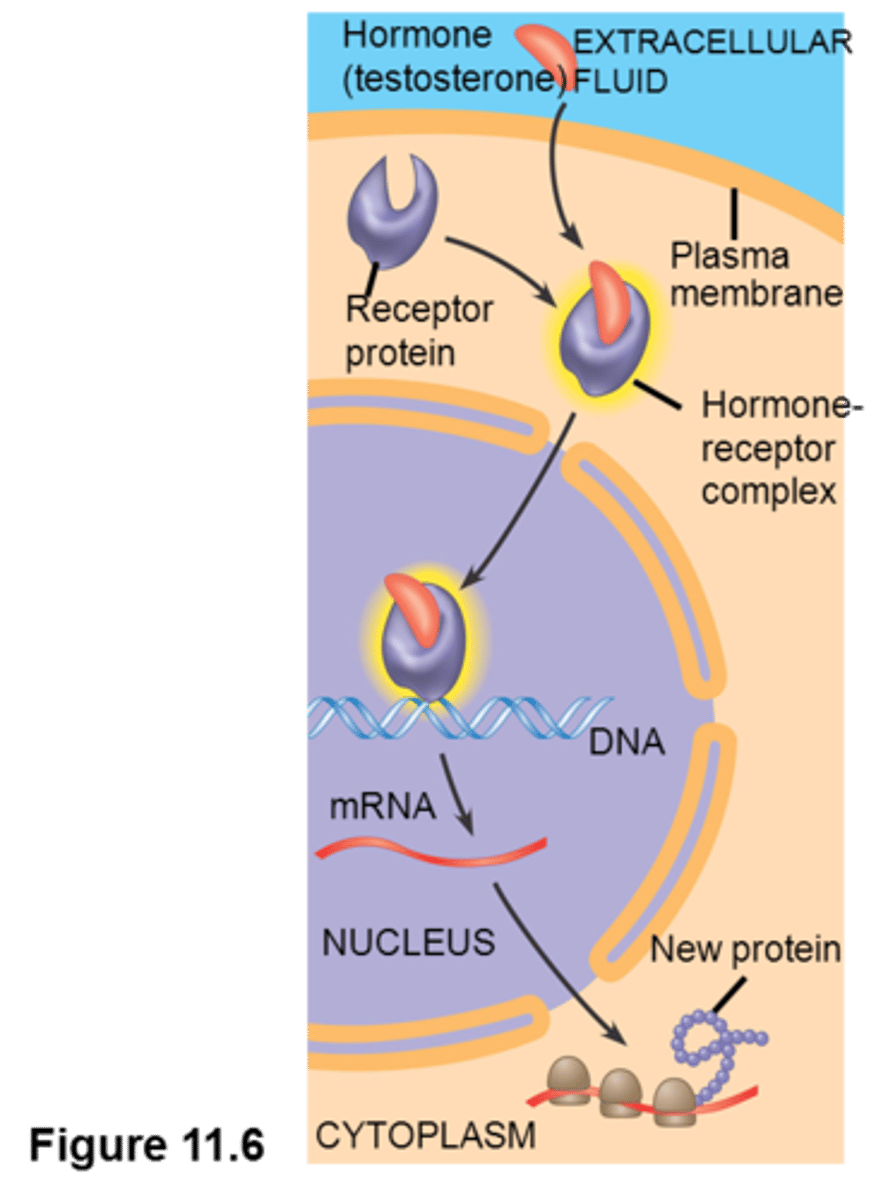
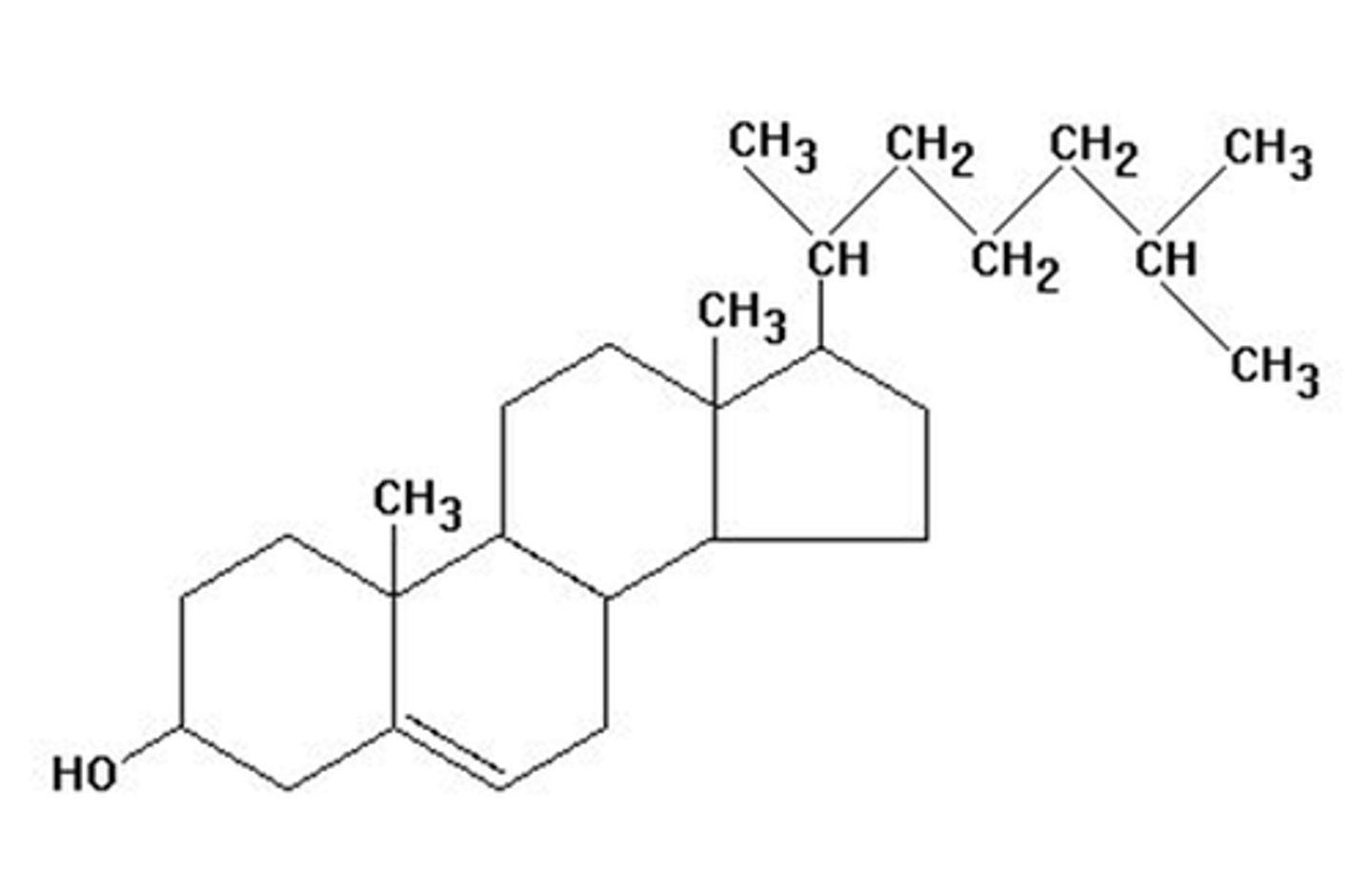
steroid hormone
Nonpolar, lipid hormones that activate intracellular receptors; testosterone and estrogen are examples
receptor
protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response

ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
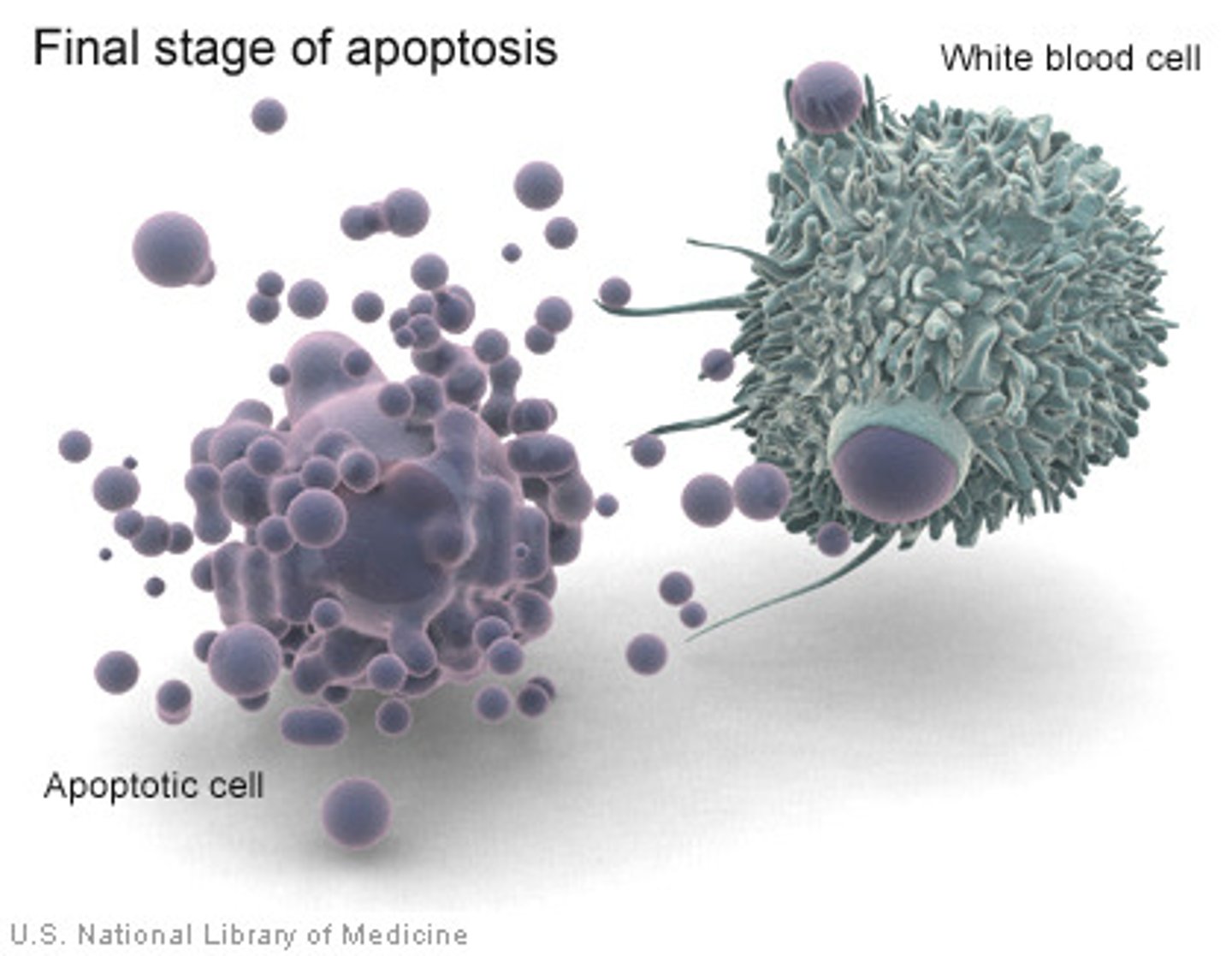
apoptosis
programmed cell death involving a cascade of specific cellular events leading to death and destruction of the cell
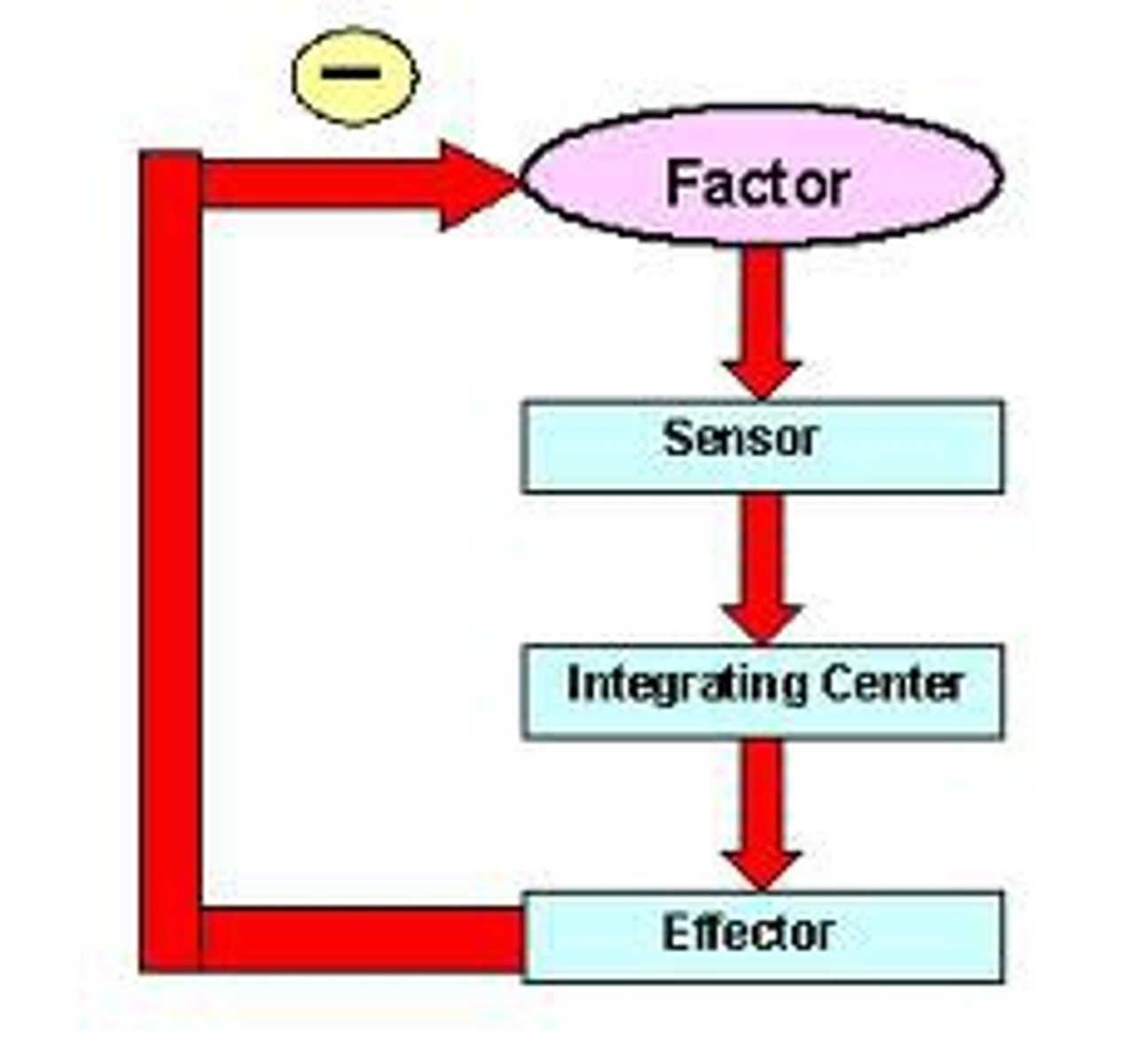
negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
positive feedback
A physiological control mechanism in which a change in some variable triggers mechanisms that amplify the change.
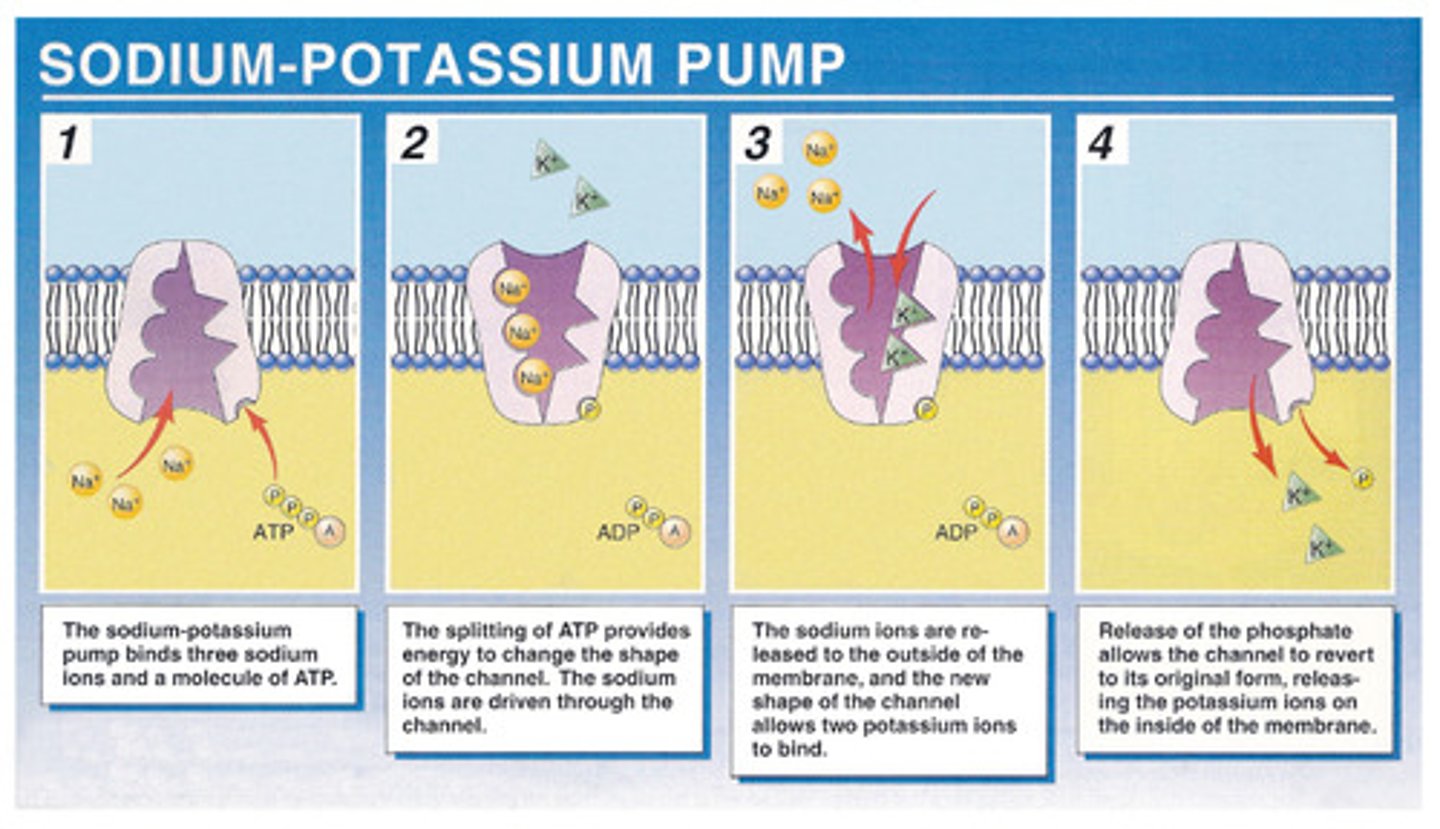
sodium-potassium pump
A transport protein in the plasma membrane of animal cells that actively transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. Important for establishing the resting potential of neurons. Also called Na+/K+-ATPase
membrane potential
the voltage (charge) difference across a membrane
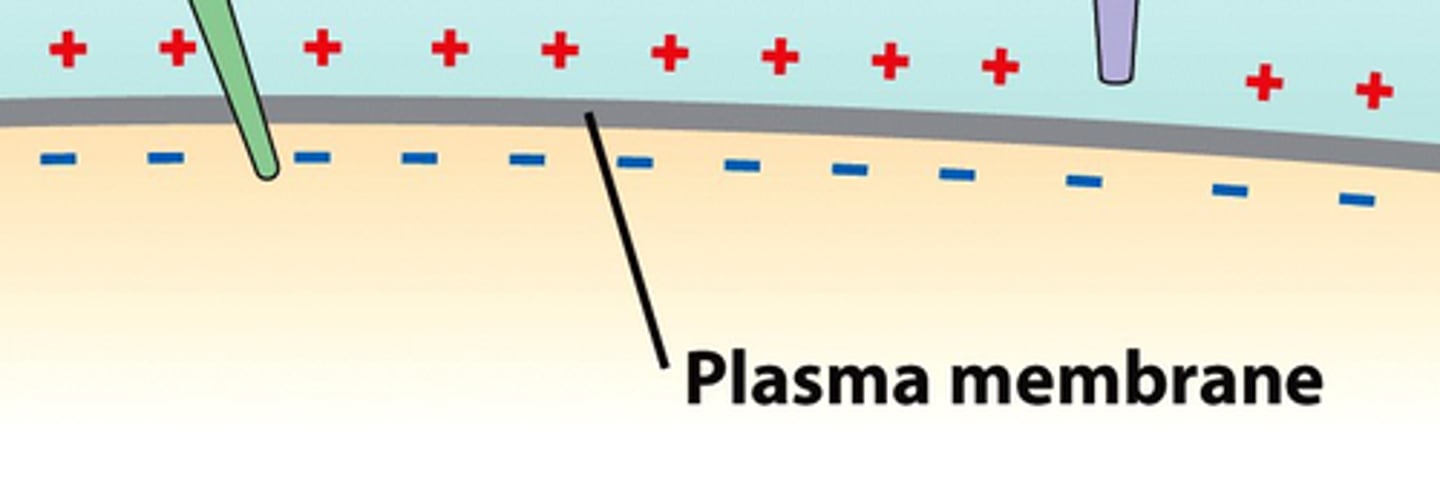
electrochemical gradient
The diffusion gradient of an ion, which is affected by both the concentration difference of an ion across a membrane (a chemical force) and the ion's tendency to move relative to the membrane potential (an electrical force).
null hypothesis
the hypothesis that there is no significant difference between specified populations, any observed difference being due to sampling or experimental error.

tertiary protein structure
three-dimensional folding pattern of a protein due to interactions between amino acid R-groups
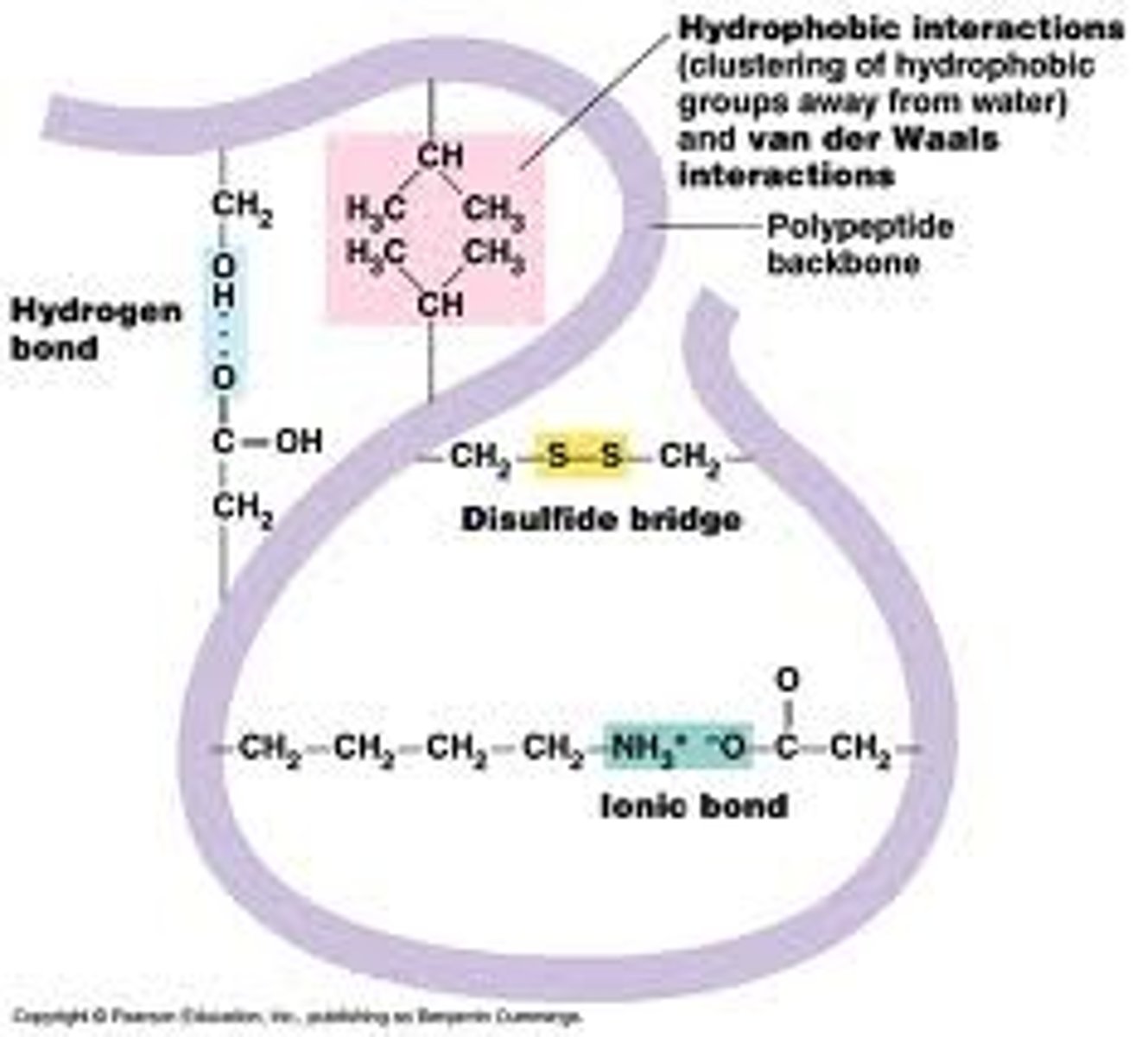
ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
reception
The target cell's detection of a signal molecule coming from outside the cell.

transduction
the signaling molecules binds to the receptor and changes it shape, causing the receptor to change its function
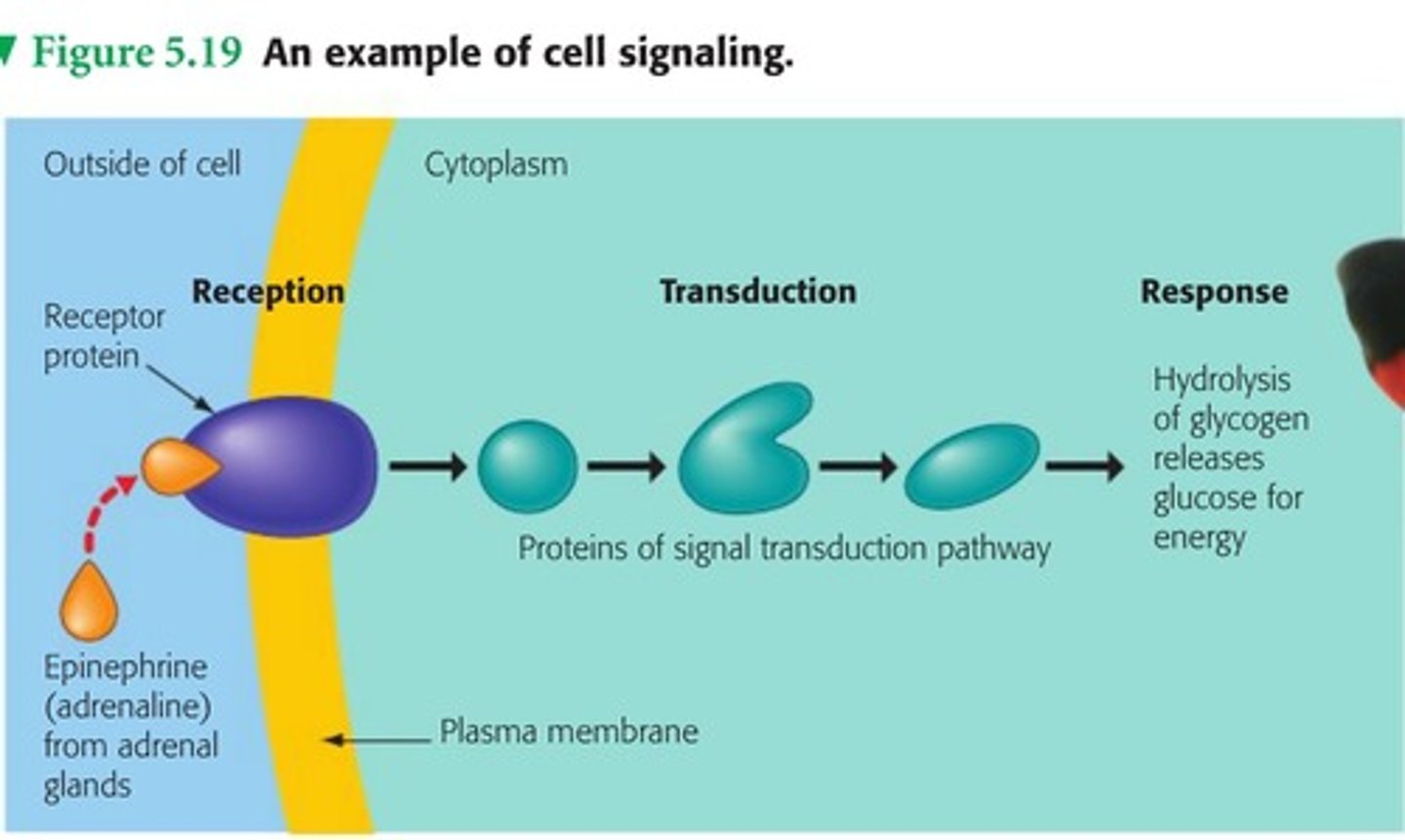
response
In cellular communication, the change in a specific cellular activity brought about by a transduced signal from outside the cell.
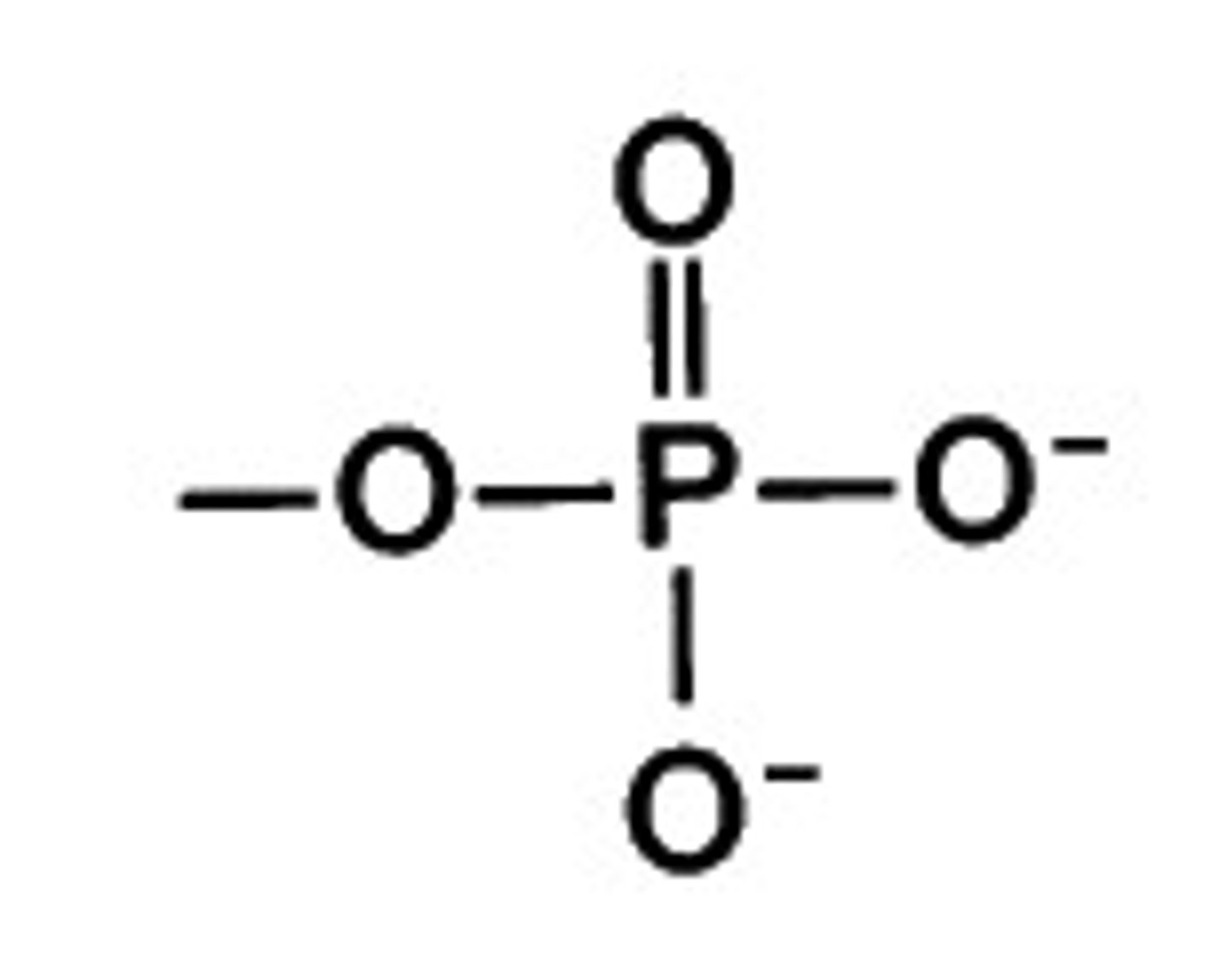
phosphate group
A chemical group consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms; has a negative charge
phosphorylation
The transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a molecule.
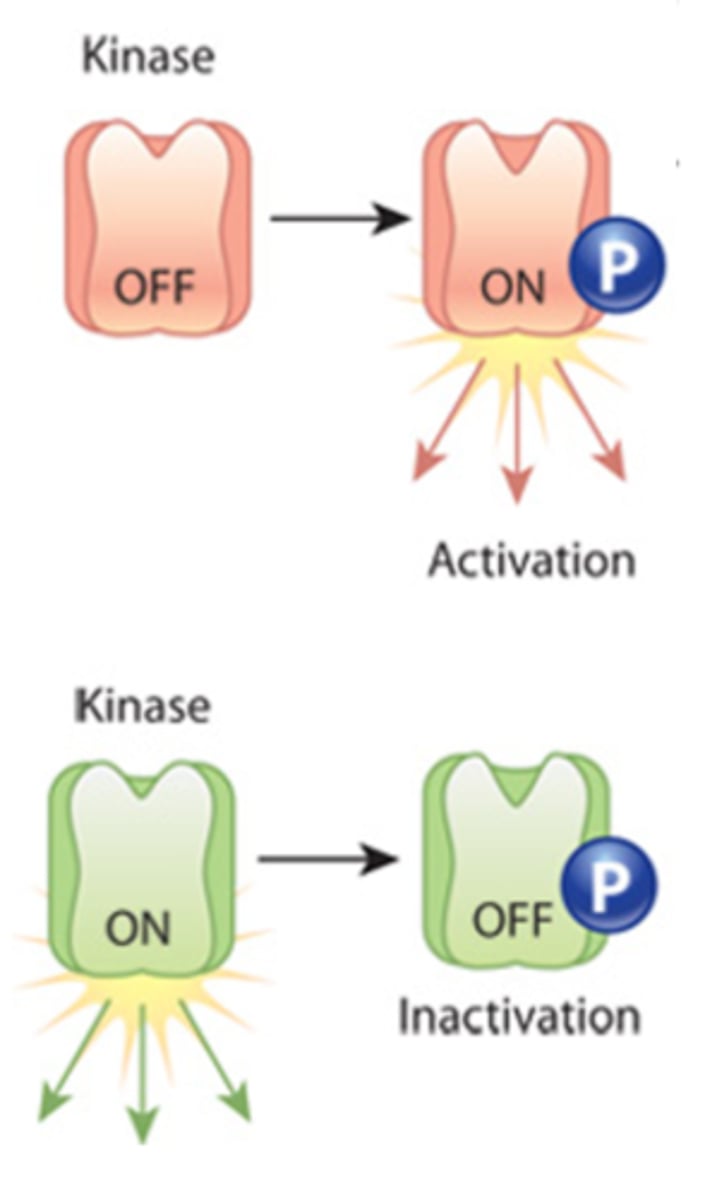
kinase
An enzyme that adds a phosphate group to a molecule
phosphatase
An enzyme that removes a phosphate group from another molecule.
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
a large family of proteins that function as receptors; they provide a mechanism for molecules outside a cell to influence the inner workings of the cell.
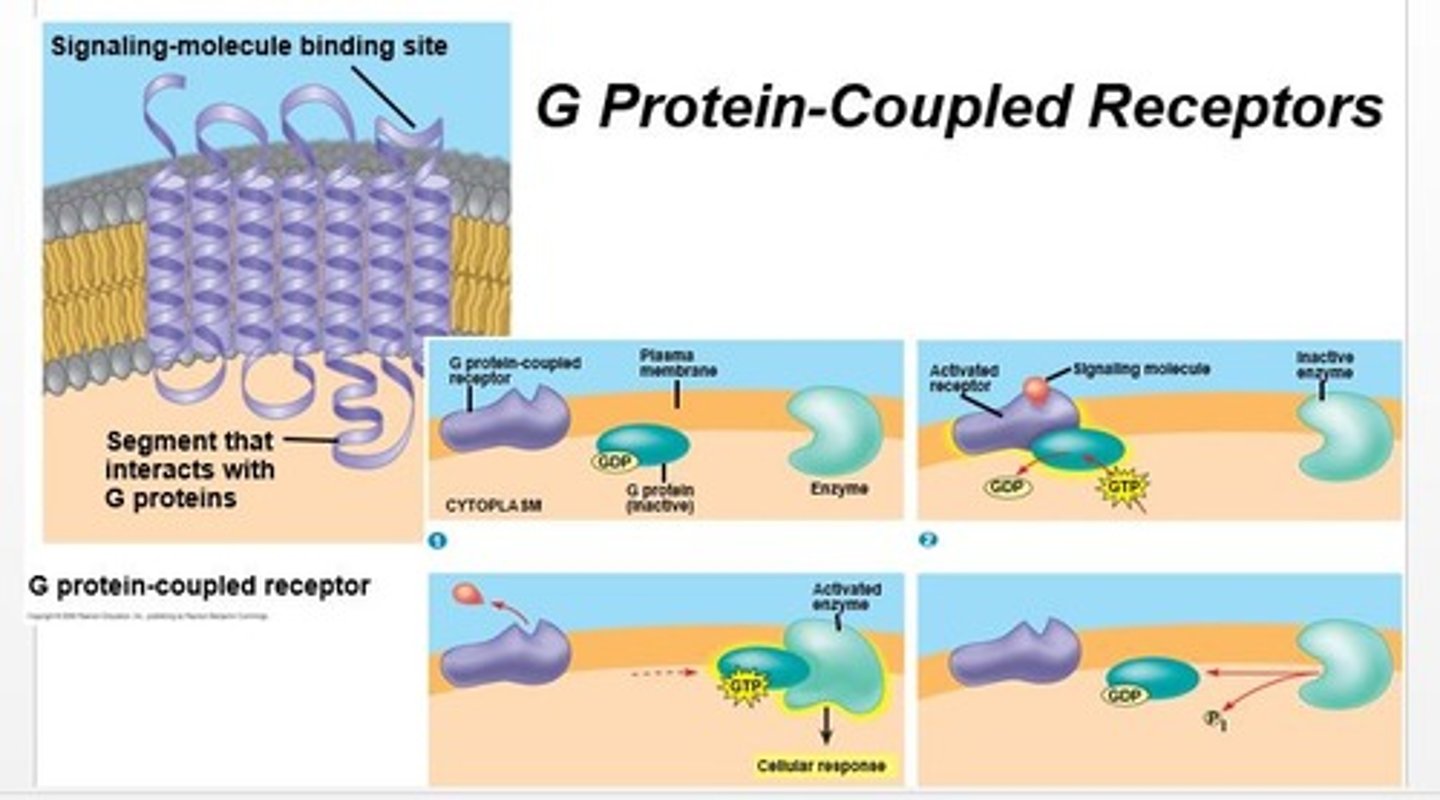
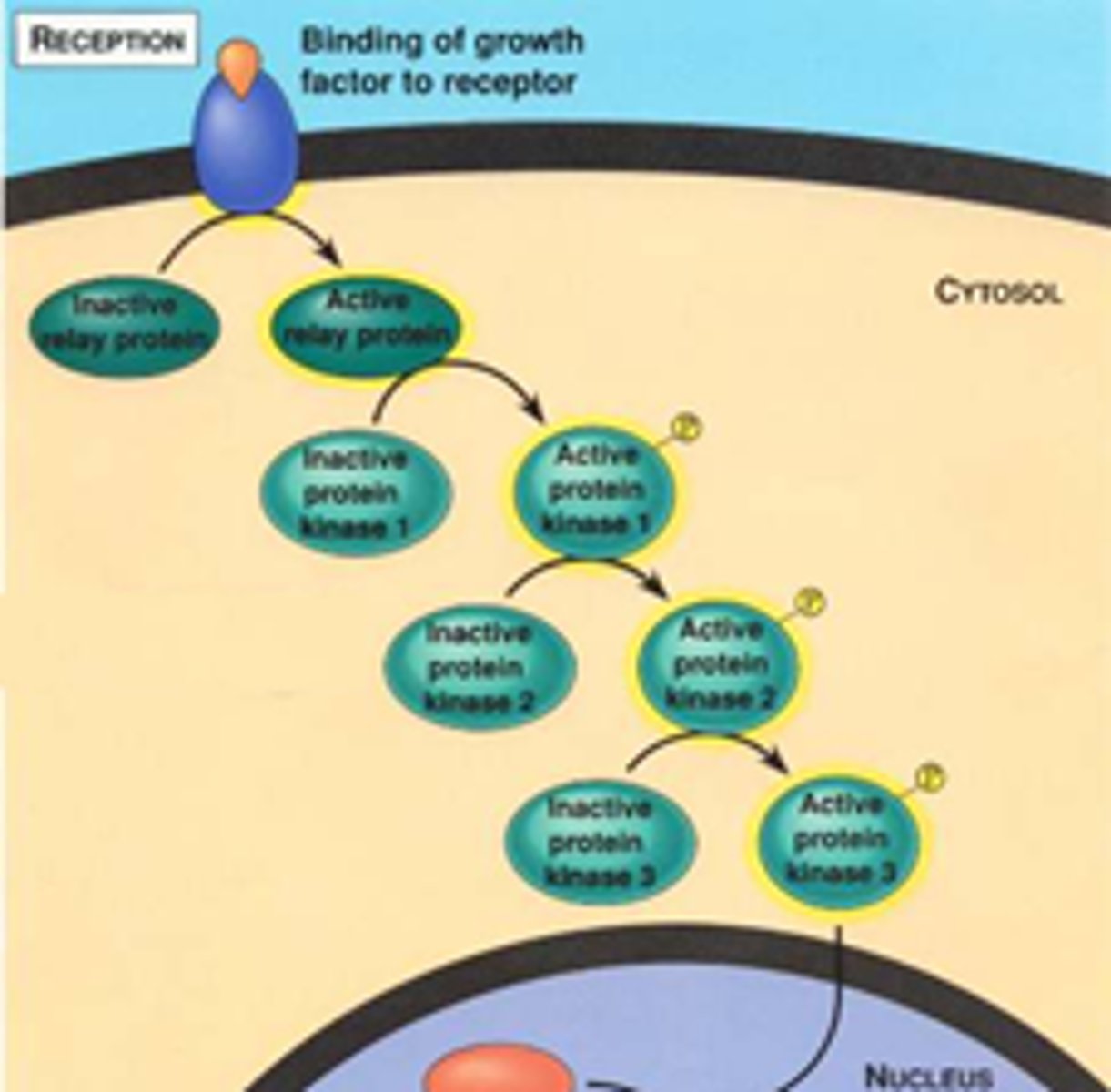
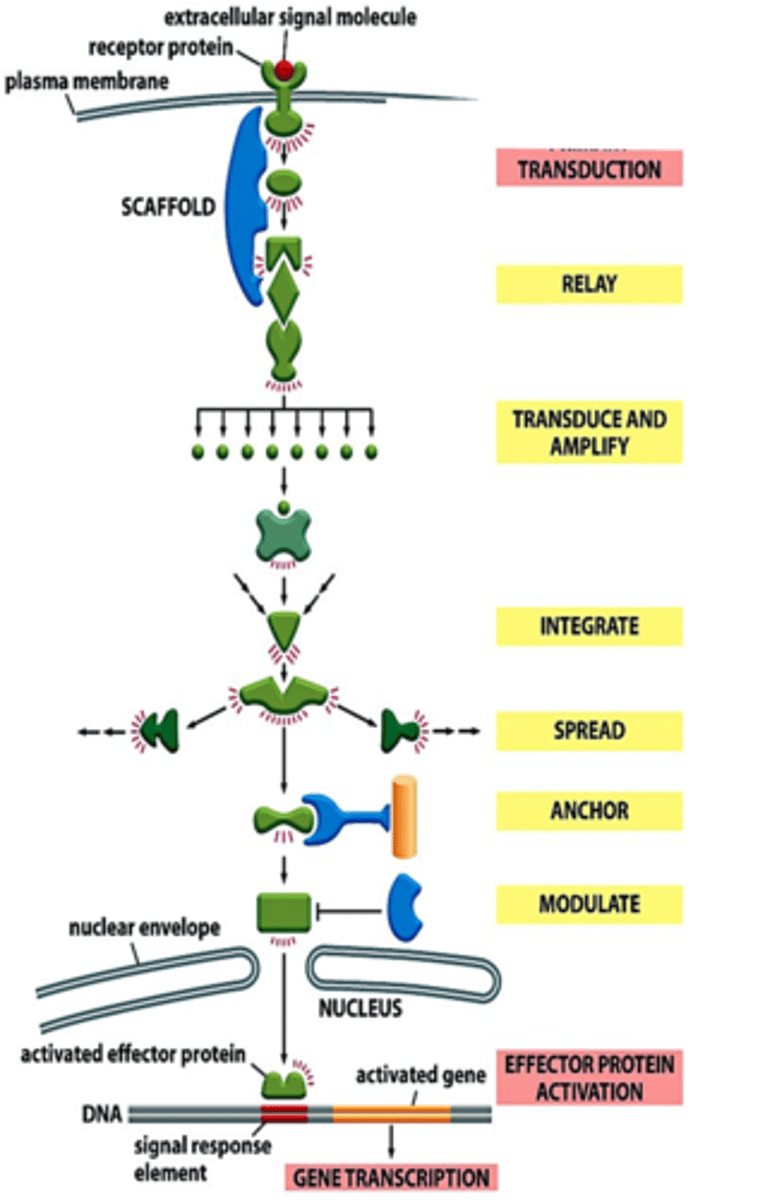
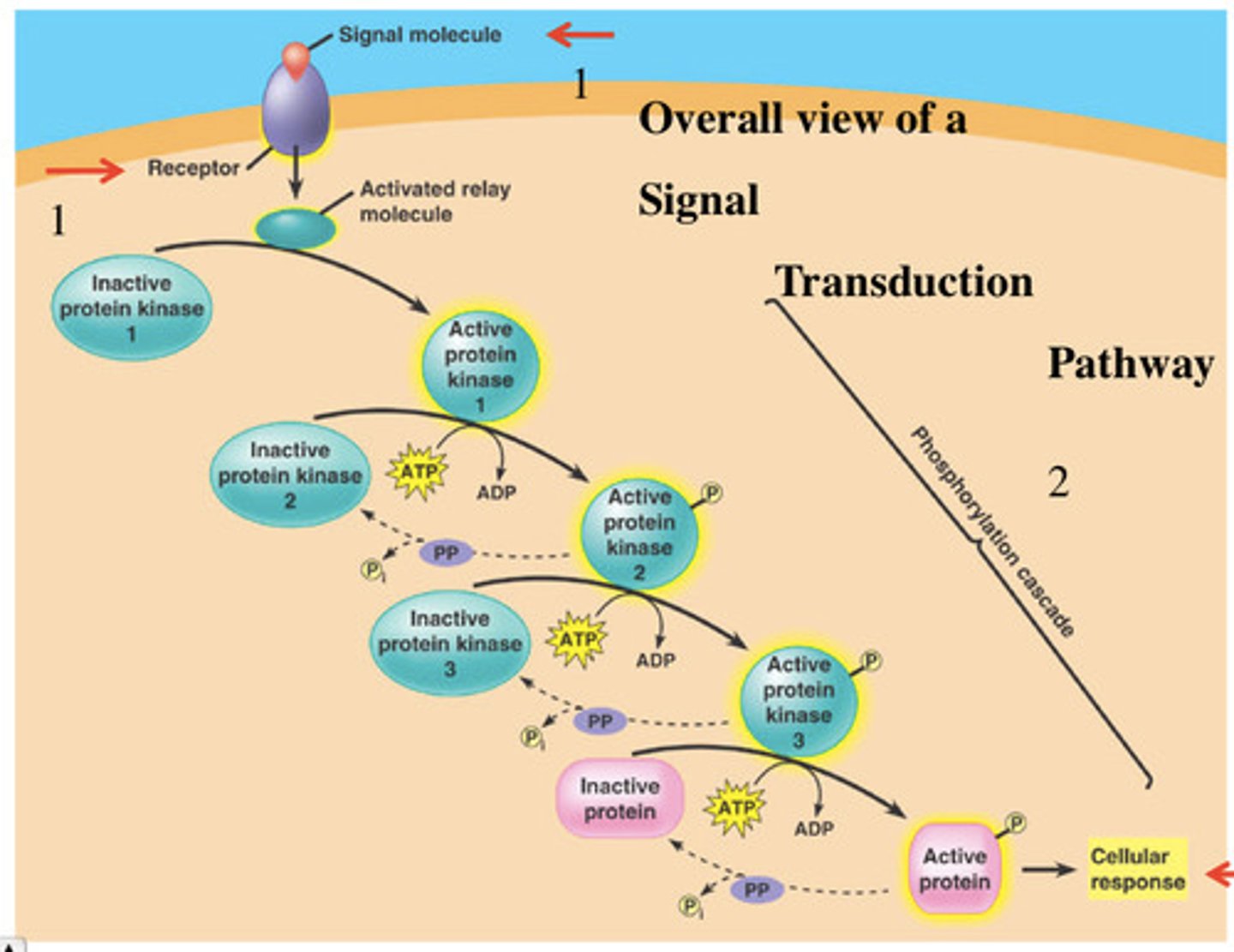
Signaling cascade
Series of events, starting with the binding of a ligand to a receptor. This sequence of events ultimately results in a change in cellular behavior
second messenger
a molecule that is generated when a specific substance attaches to a receptor on the outside of a cell membrane, which produces a change in cellular function
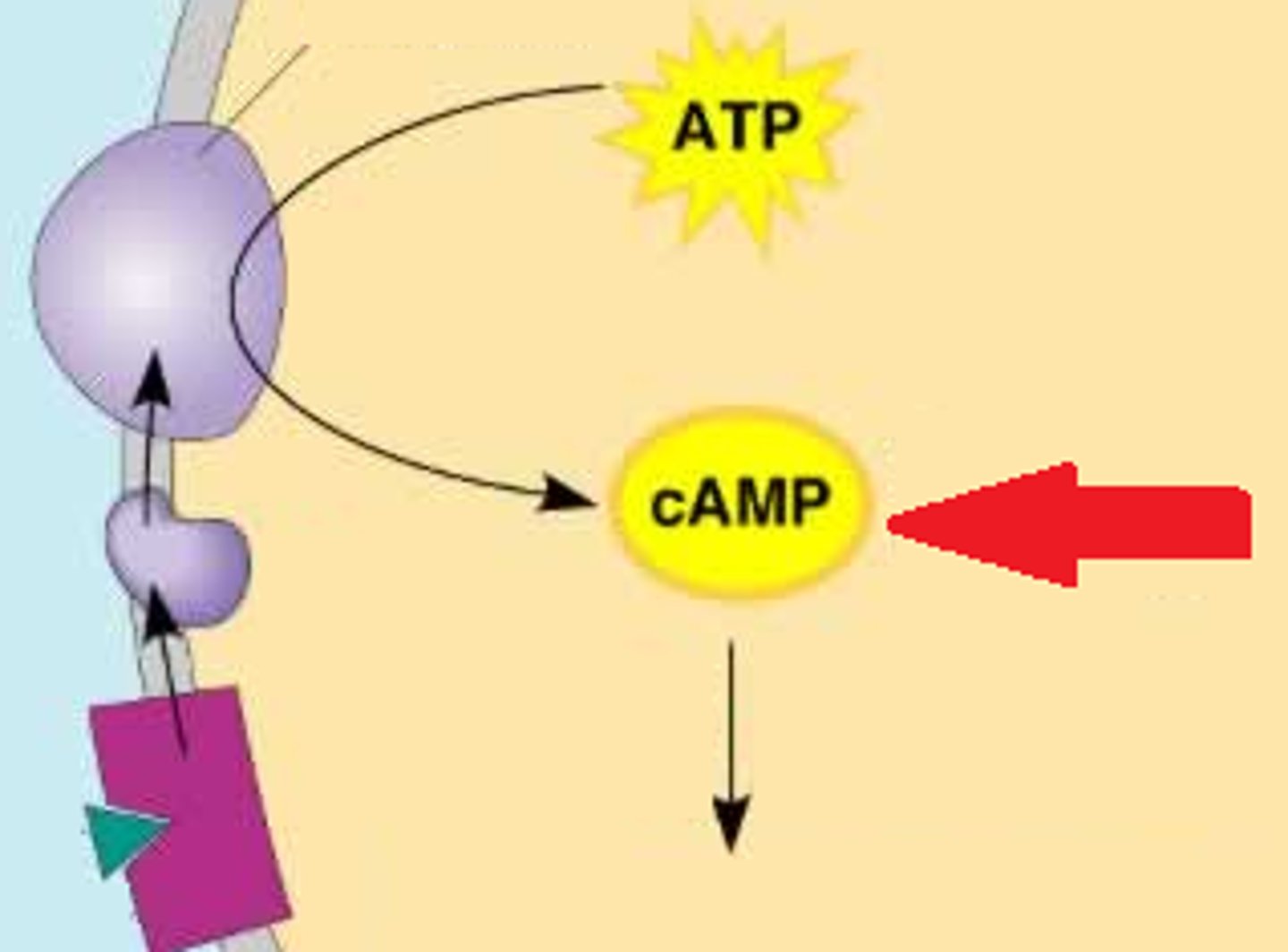
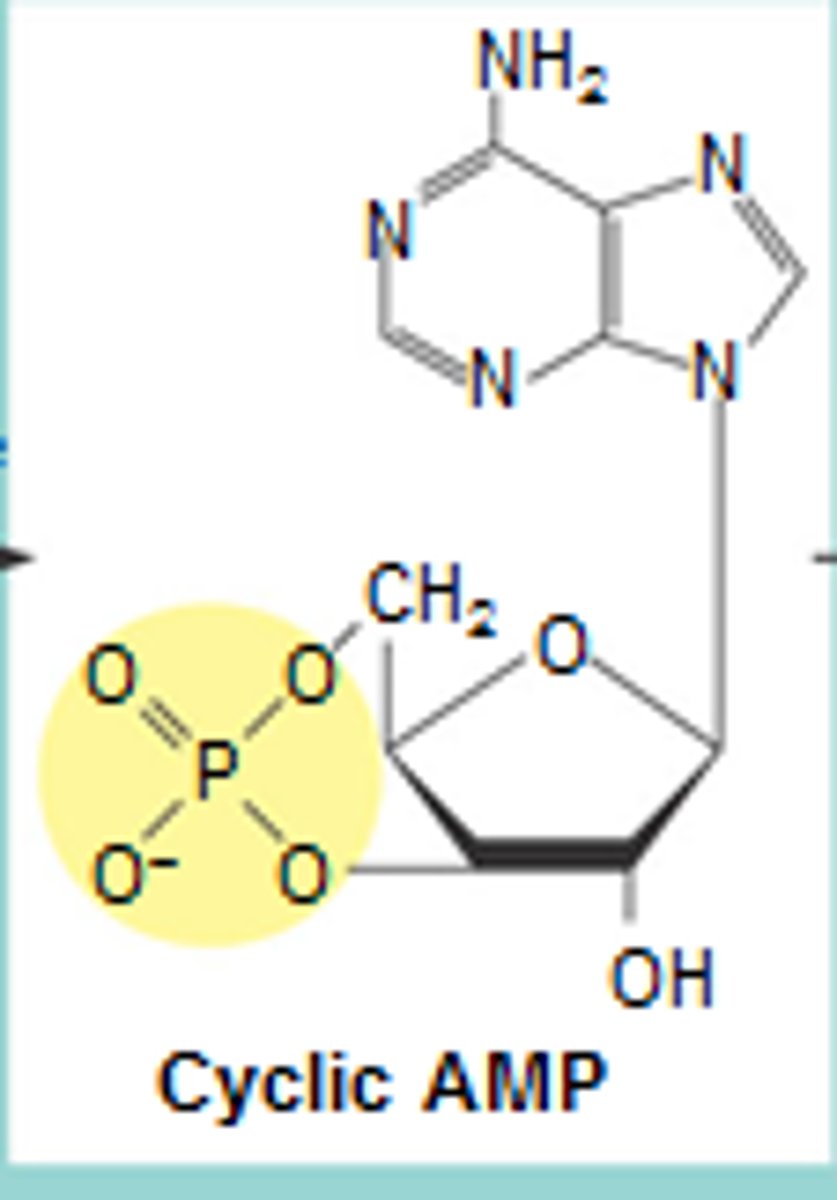
cAMP
a second messenger produced in GPCR signaling
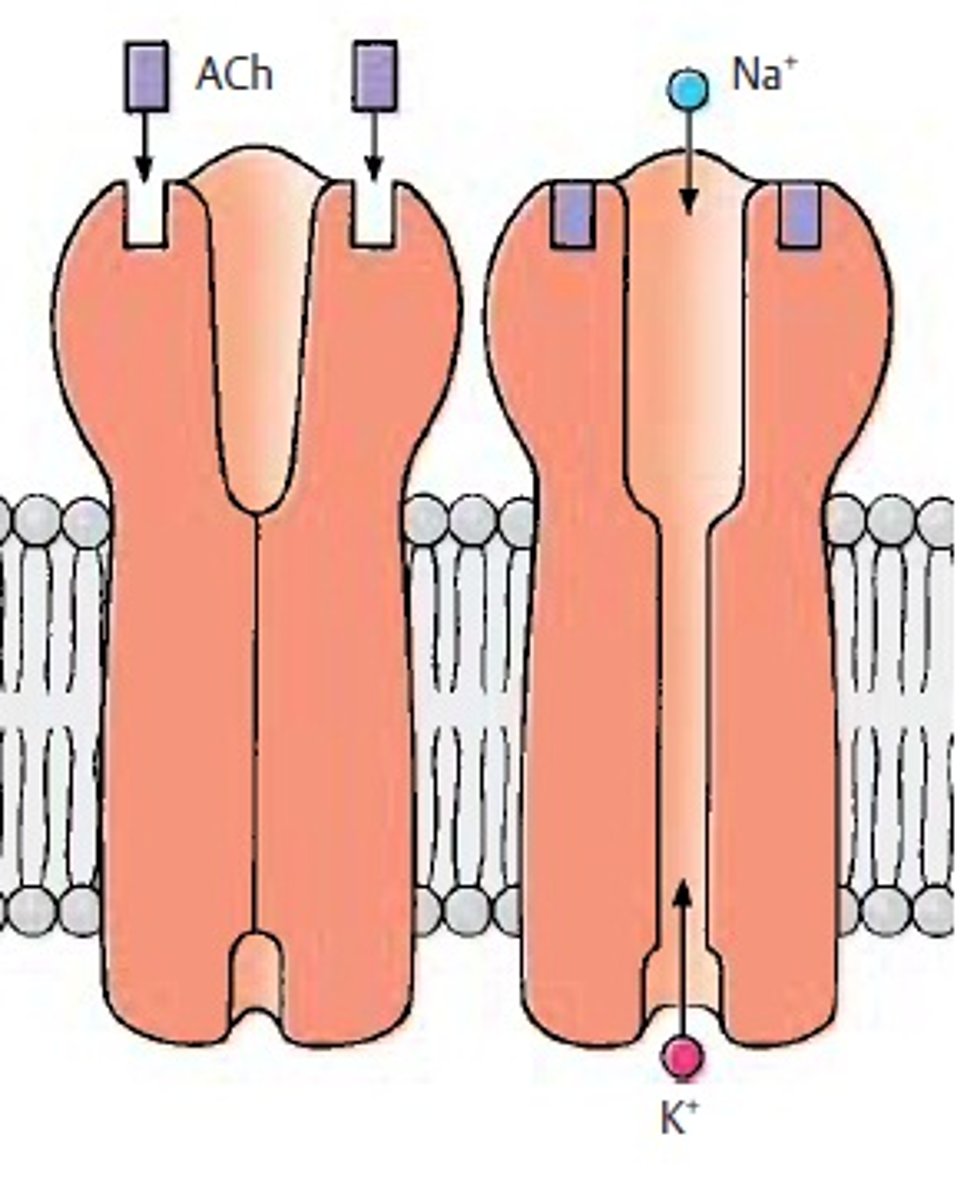
ligand-gated ion channel
Type of membrane receptor that has a region that can act as a "gate" when the receptor changes shape. When the receptors are activated they open and allow ions to cross the cell membrane.
receptor tyrosine kinase
A cell surface receptor that also has kinase activity; when these receptors are activated they stimulate phosphorylation cascades
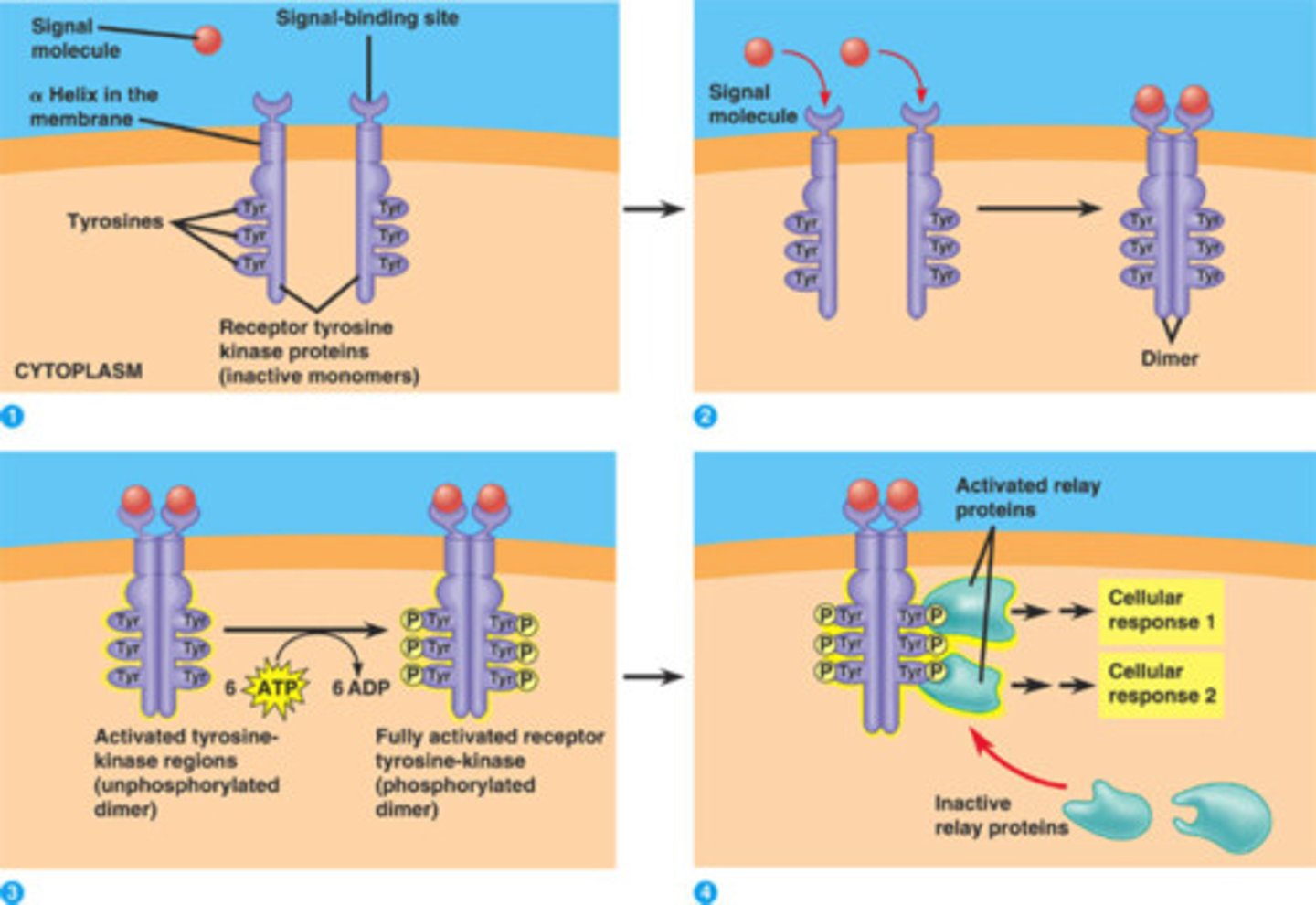
phosphorylation cascade
a sequence of events where one enzyme phosphorylates another, causing a chain reaction leading to the phosphorylation of many proteins
photosynthesis
Process by which autotrophs produce glucose using energy from the sun and CO2
chemical reaction for photosynthesis
6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) +energy -->
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (oxygen)
cellular respiration
The process by which cells break down simple food molecules to release the energy they contain.
chemical reaction for respiration
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (oxygen) -->
6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) + ATP (energy)
Steps of photosynthesis
1. Light-dependent reactions
2. Calvin cycle
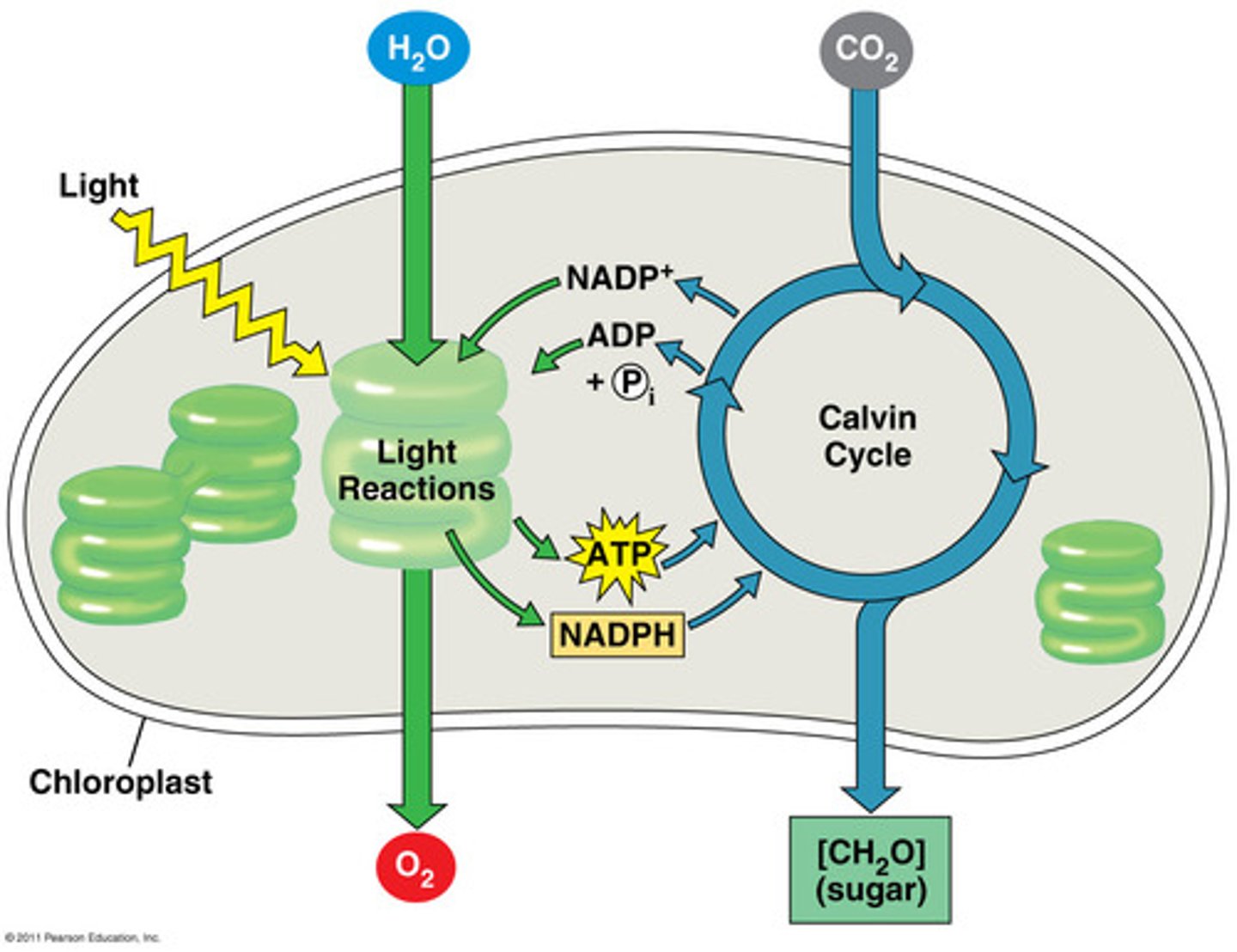
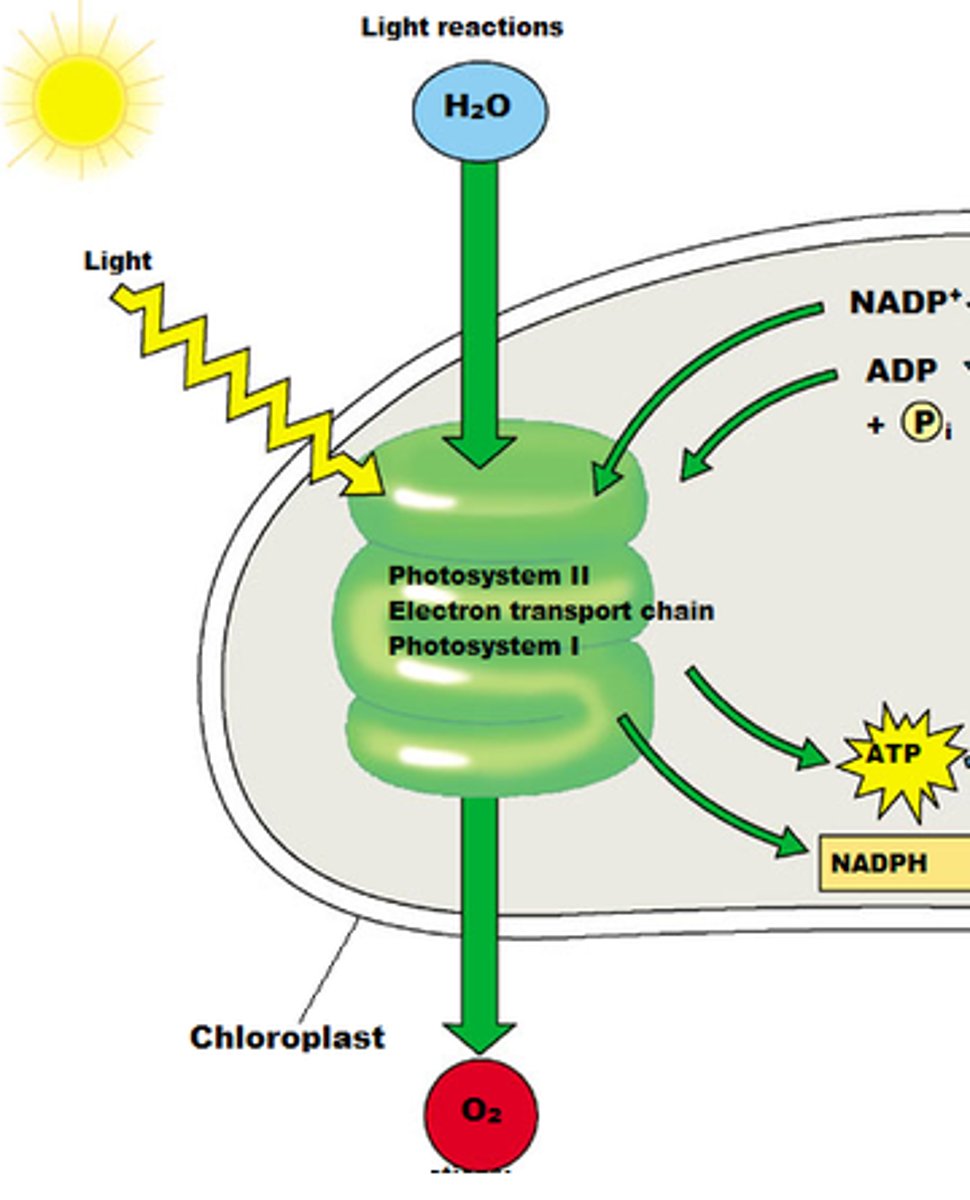
light-dependent reactions
First step of photosynthesis; uses energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
Calvin Cycle
Second step in photosynthesis; uses ATP and NADPH (from light reactions) and CO2 to build organic molecules such as glucose

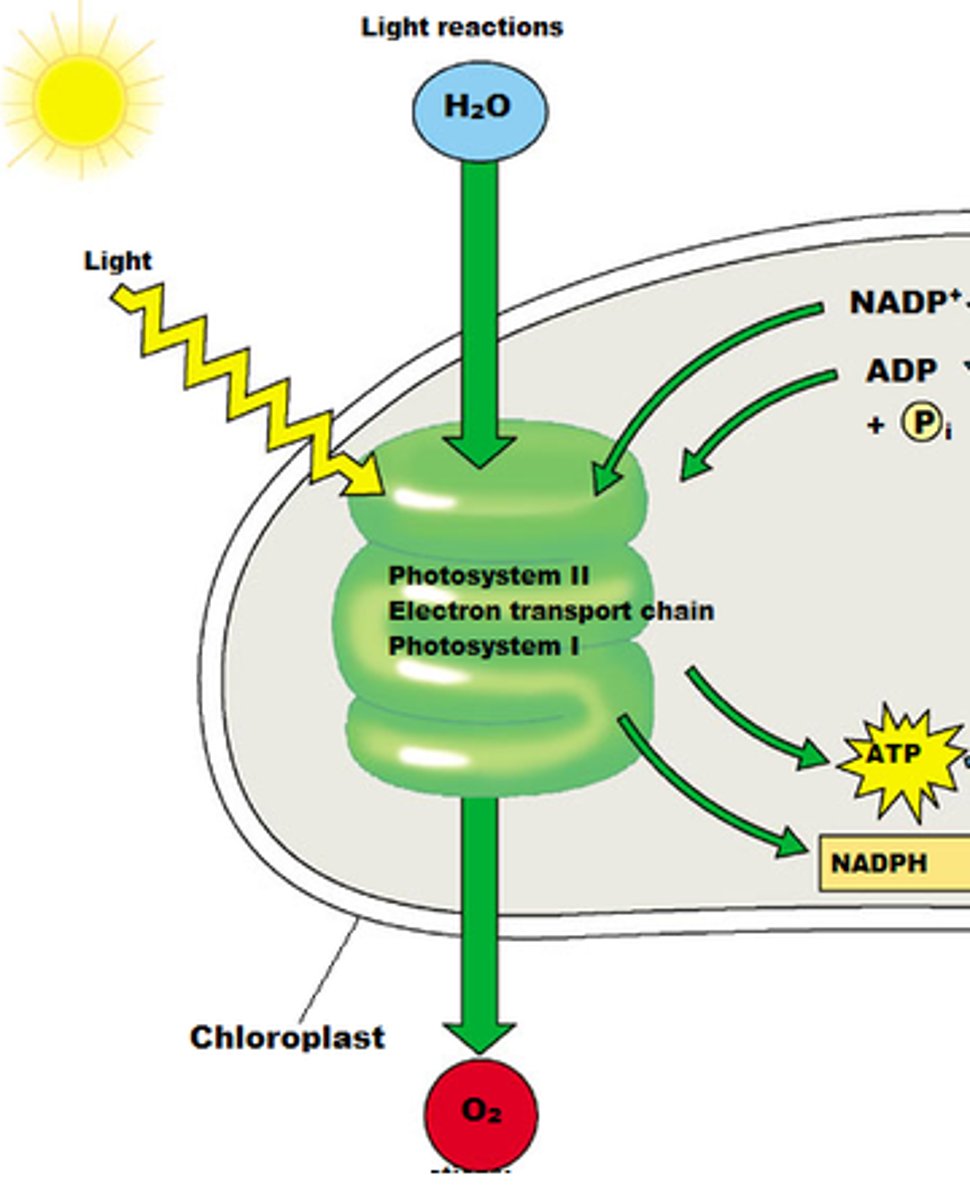
outputs of light-dependent reaction
O2, ATP, and NADPH
inputs of light-dependent reaction
Light (photons), water, NADP+, and ADP+Pi
inputs of Calvin cycle
ATP, NADPH, and CO2
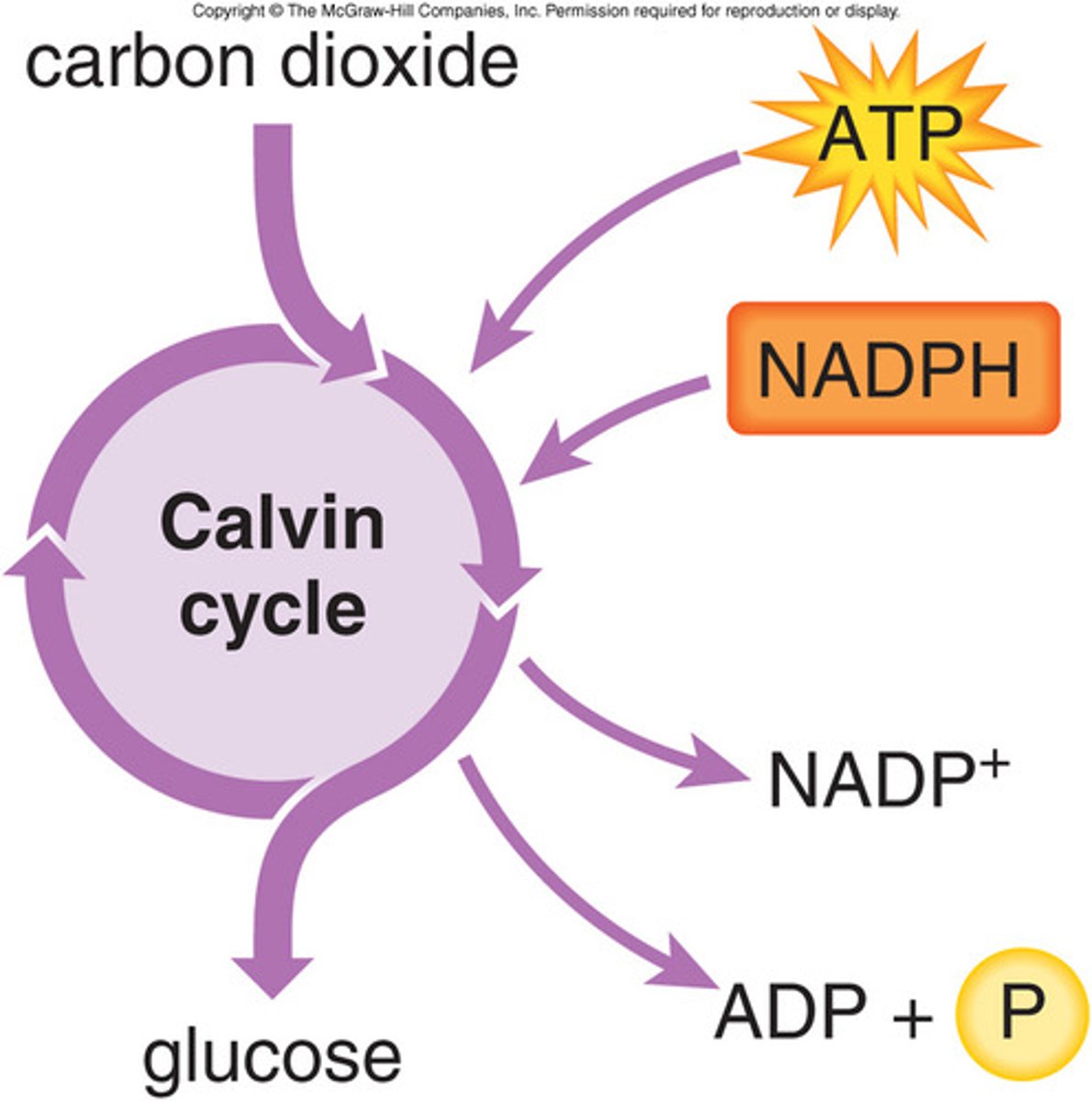
outputs of Calvin cycle
Glucose, ADP, and NADP+

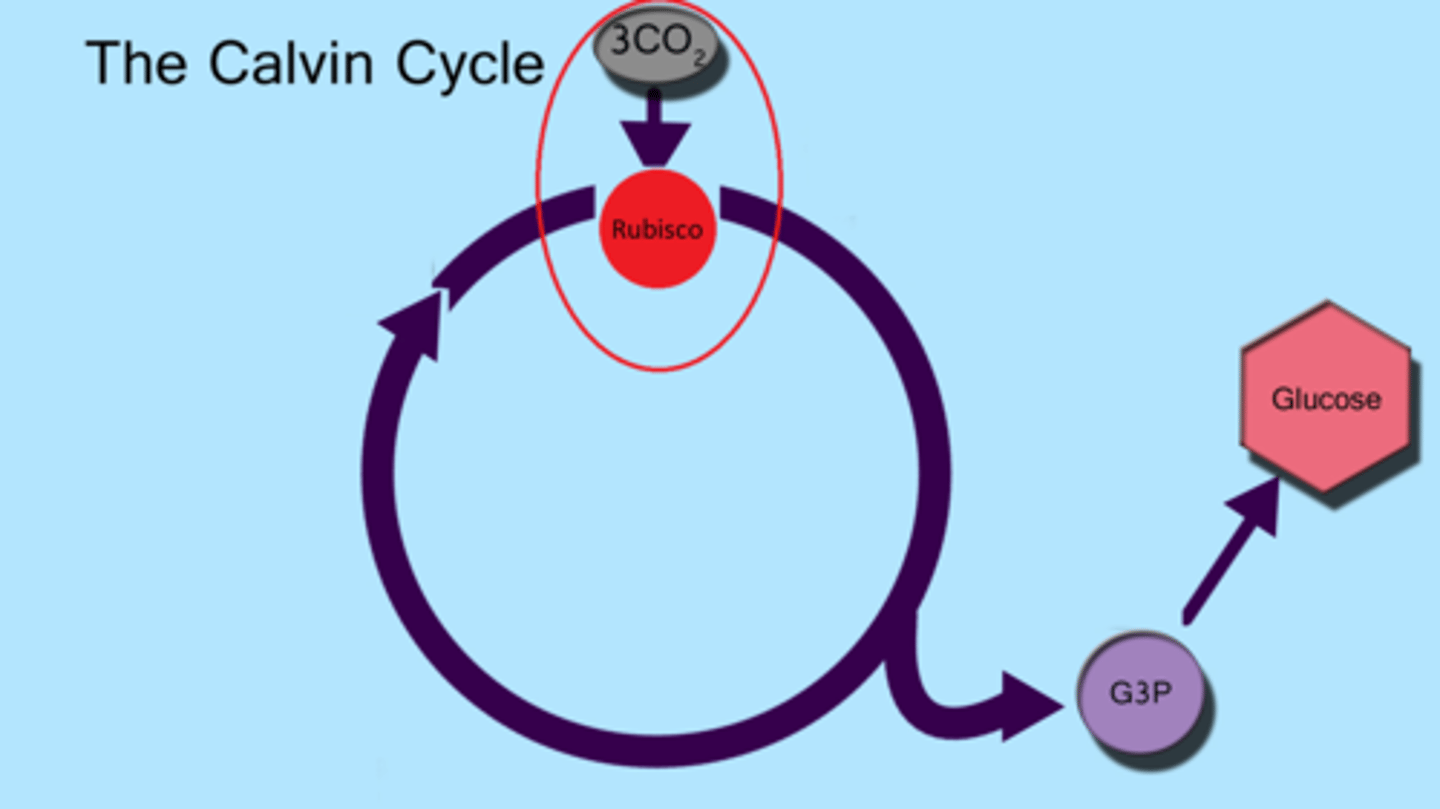
rubisco
The most abundant protein on earth. Performs carbon fixation in the Calvin Cycle.
carbon fixation
The initial incorporation of carbon into organic compounds.
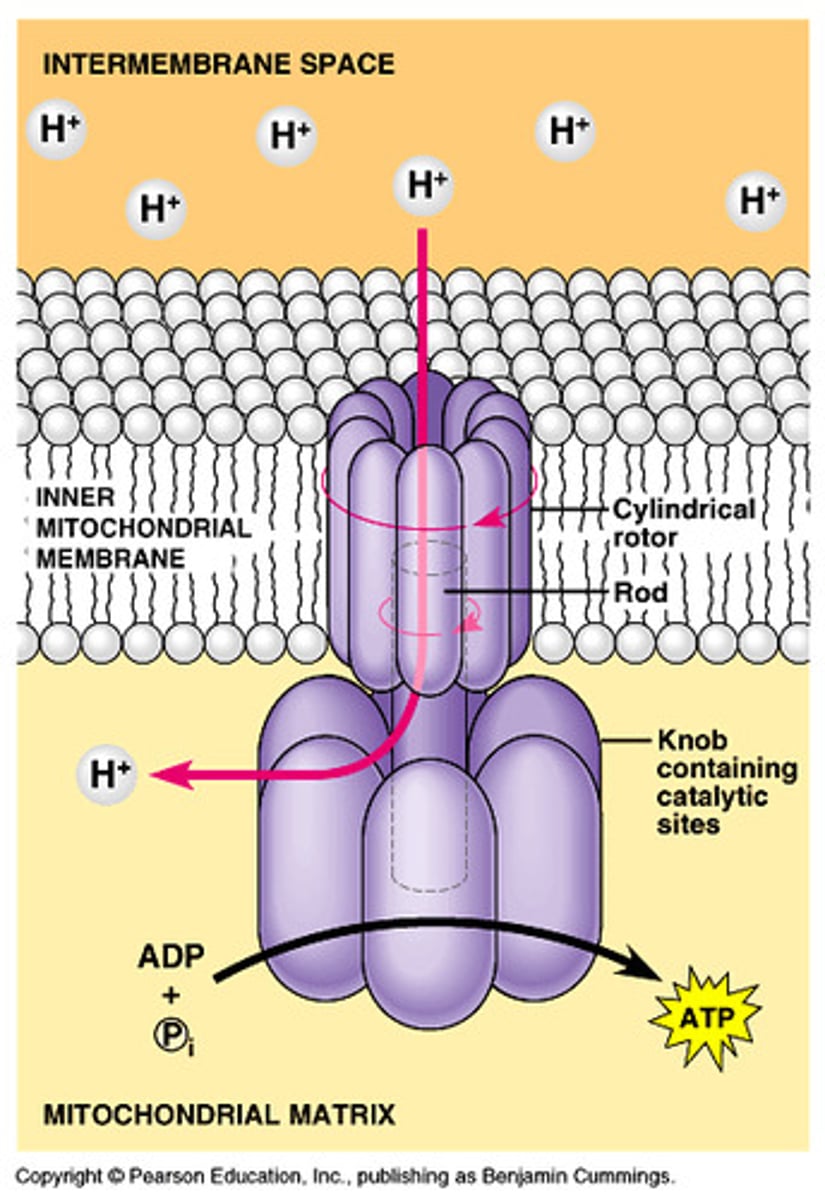
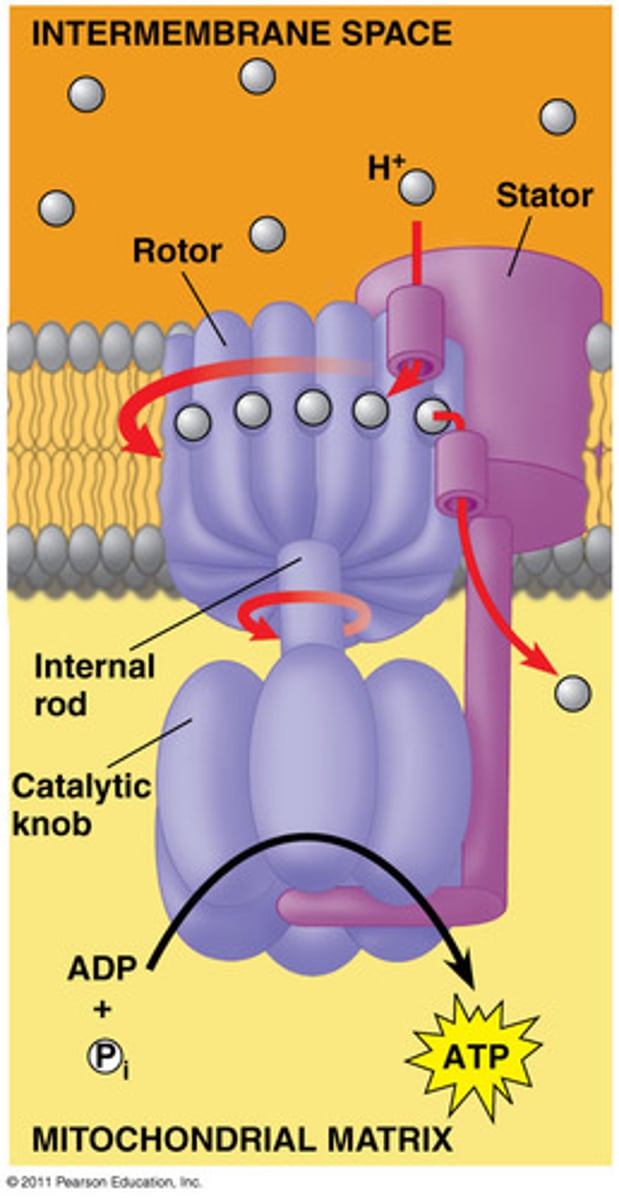
ATP synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions diffusing down their concentration gradient to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
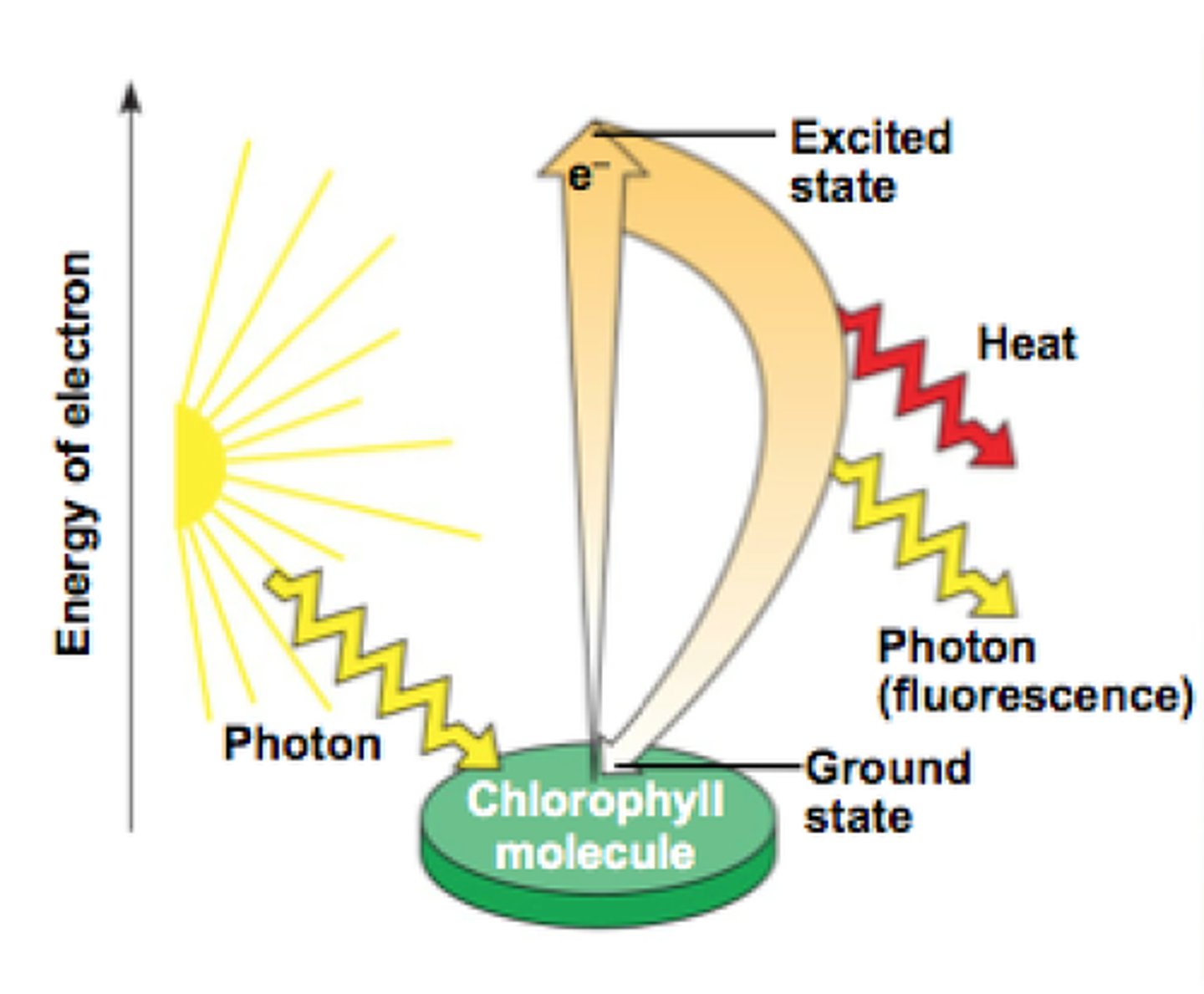
chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
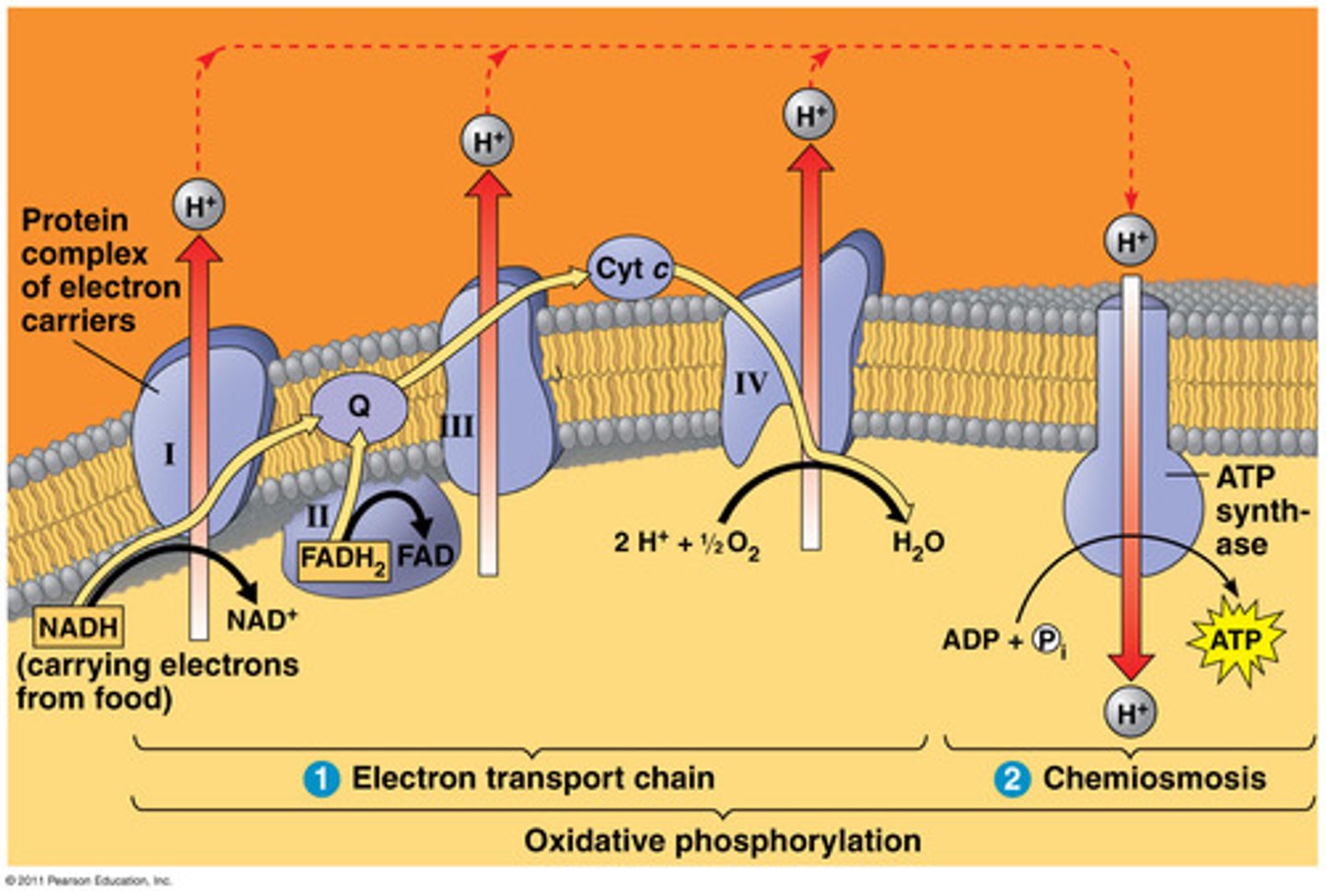
electron transport chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP.
NADPH
An electron carrier involved in photosynthesis. Light drives electrons from chlorophyll to NADP+, forming NADPH, which provides the high-energy electrons for the reduction of carbon dioxide to sugar in the Calvin cycle.
photon
a particle of light
H+
hydrogen ion (proton)
TERM
thylakoid
DEFINITION
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
TERM
granum
DEFINITION
A stack of thylakoids in a chloroplast
TERM
stroma
DEFINITION
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
TERM
intermembrane space
DEFINITION
narrow region between the inner and outer membranes
proton pump
An electrogenic pump that moves H+ ions into the thylakoid lumen; powered the electron transport chain.
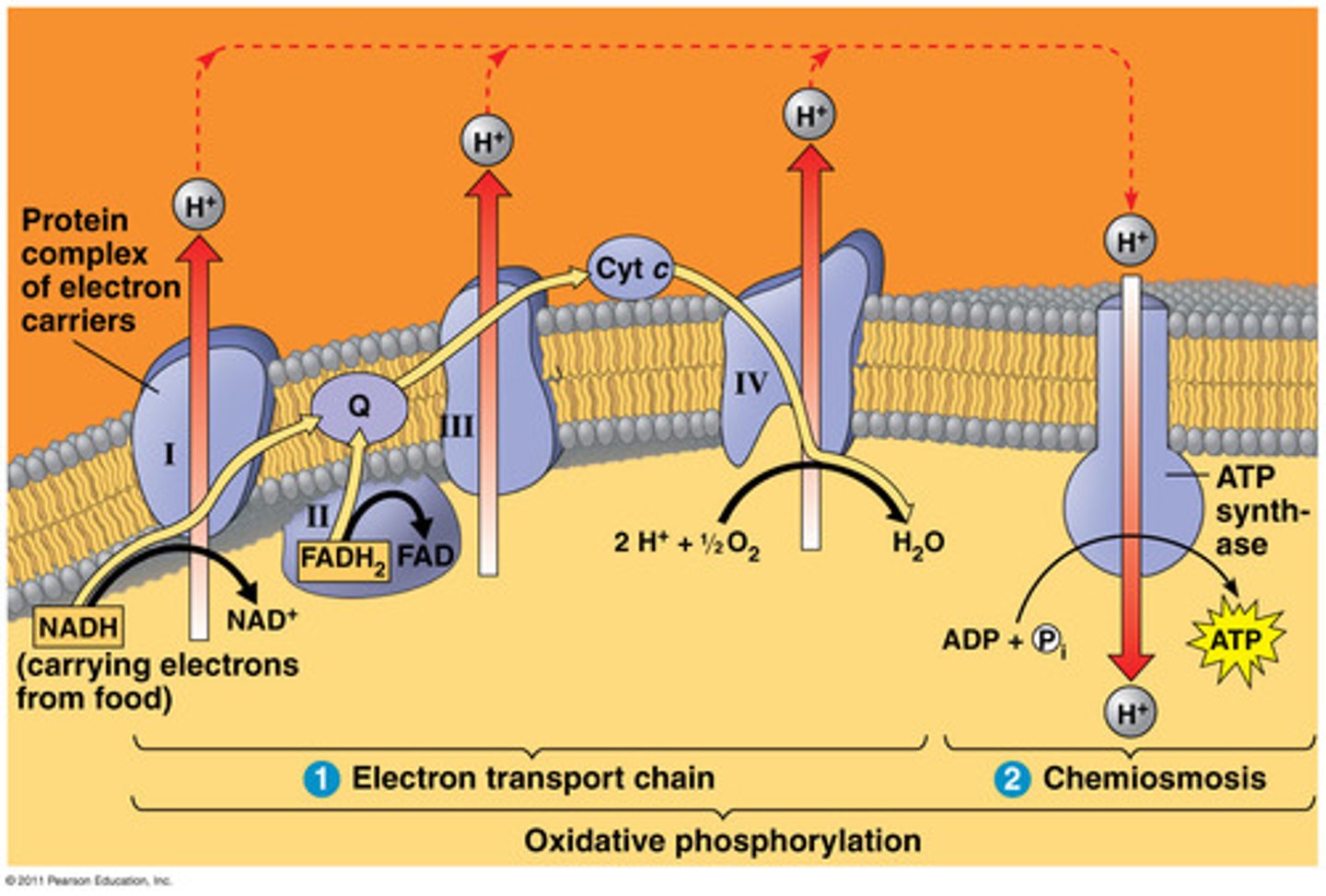
TERM
inner membrane
DEFINITION
The membrane of the mitochondria that is the site of electron transport and chemiosmosis.
matrix
Innermost compartment of the mitochondrion
glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvate
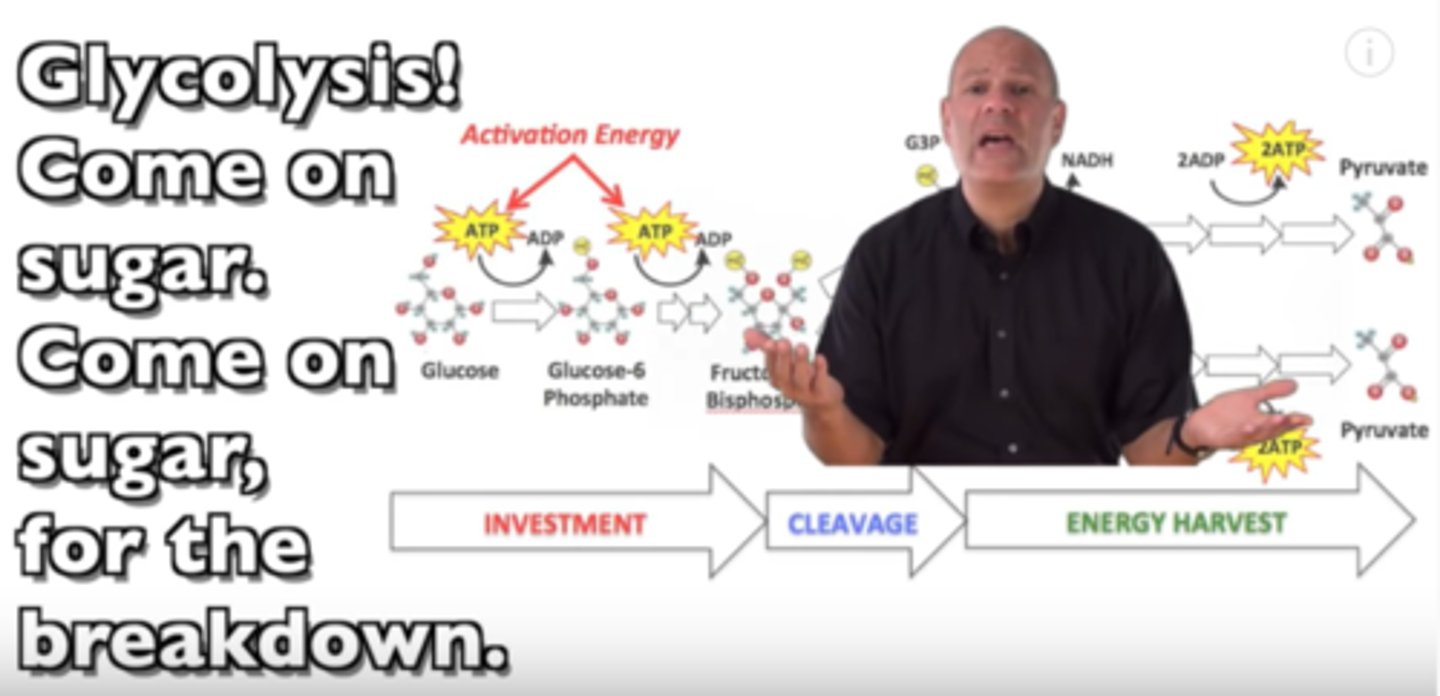
aerobic respiration
requires oxygen; occurs in the cytosol and mitochondria
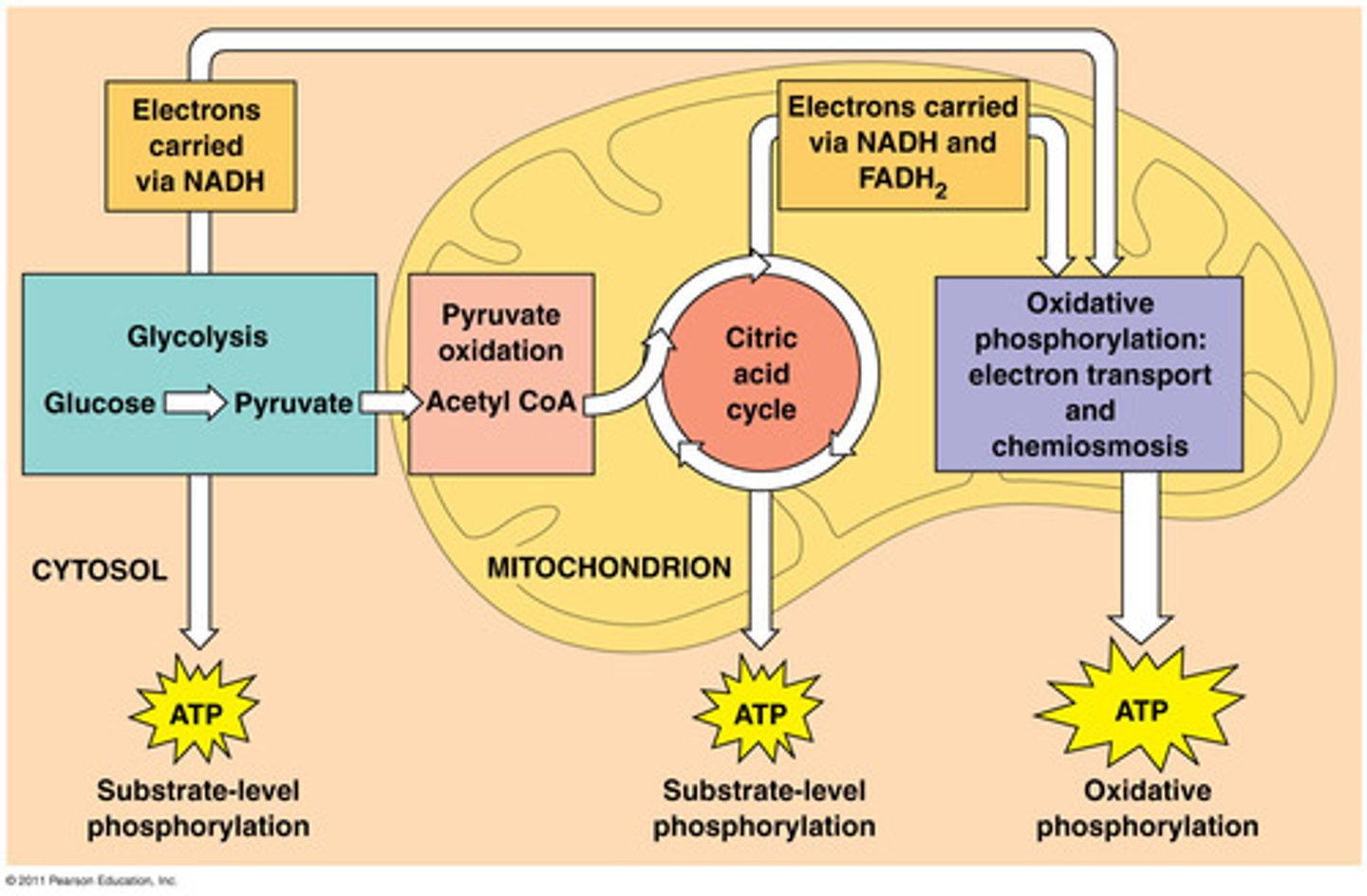
anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen; occurs in the cytosol
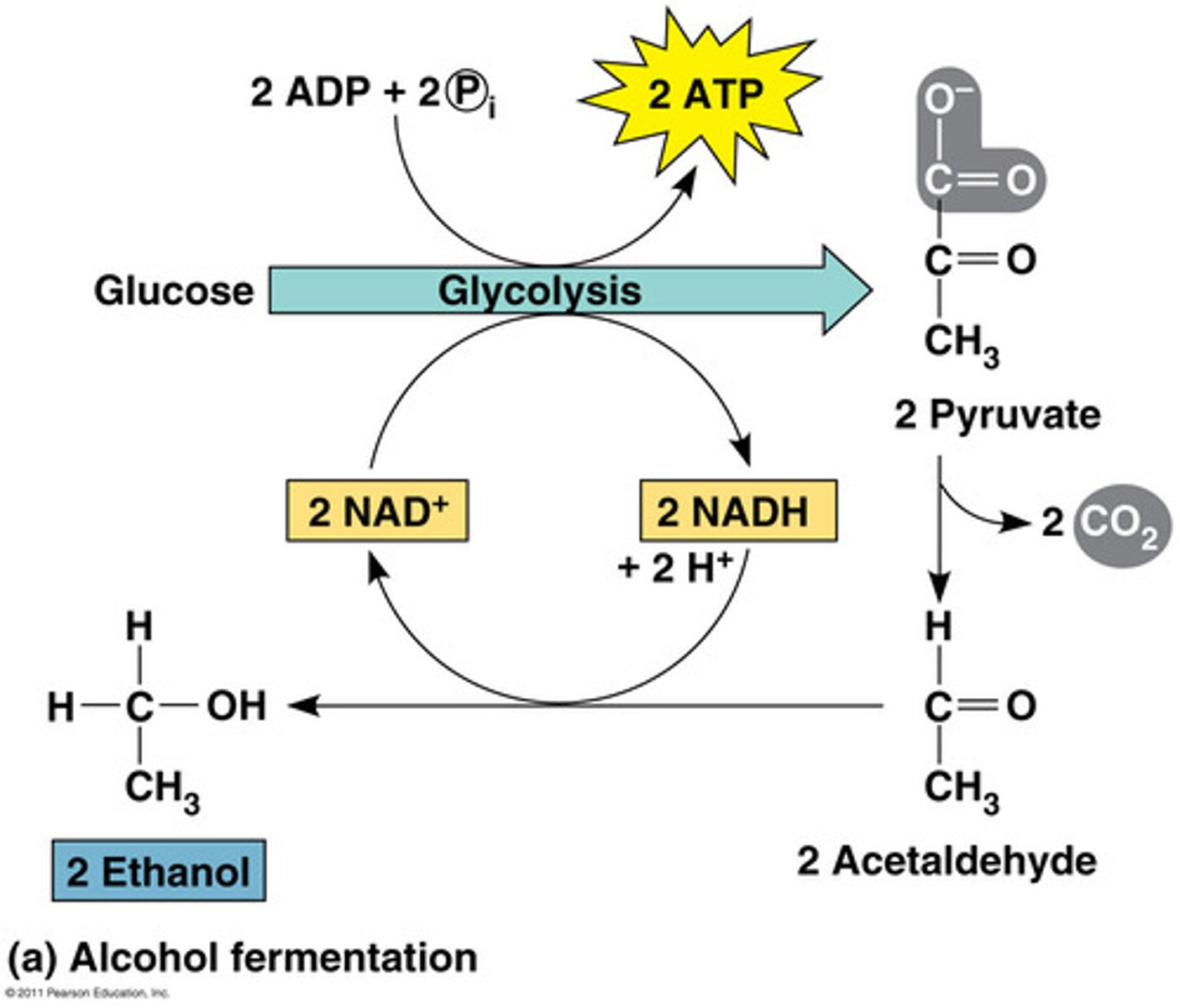
fermentation
A process that replenishes NAD+ to be used in glycolysis, so that ATP can be made via anaerobic respiration; produces a characteristic end product, such as ethanol (alcohol) or lactic acid.
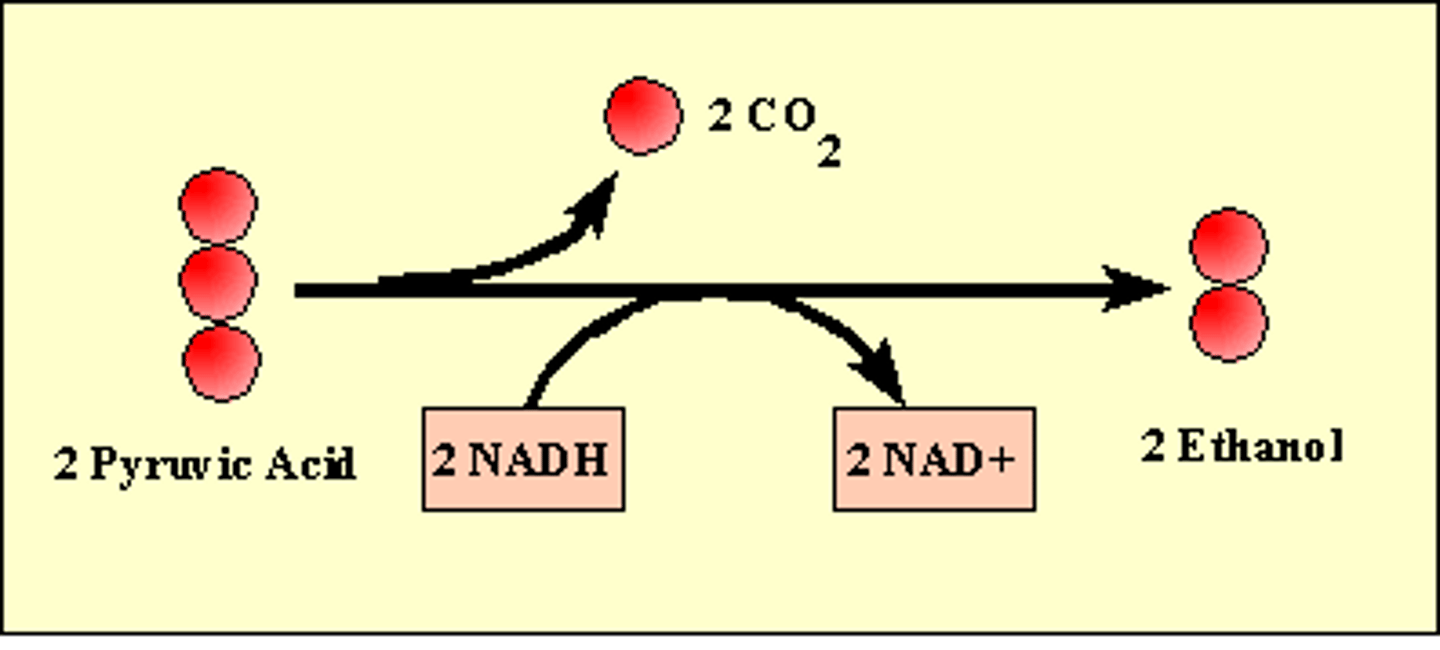
NADH
An energy-carrying coenzyme produced by glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. NADH carries energy to the electron transport chain, where it is stored in ATP.
electron carrier
a compound that can accept a pair of high-energy electrons and transfer them, along with most of their energy, to another molecule
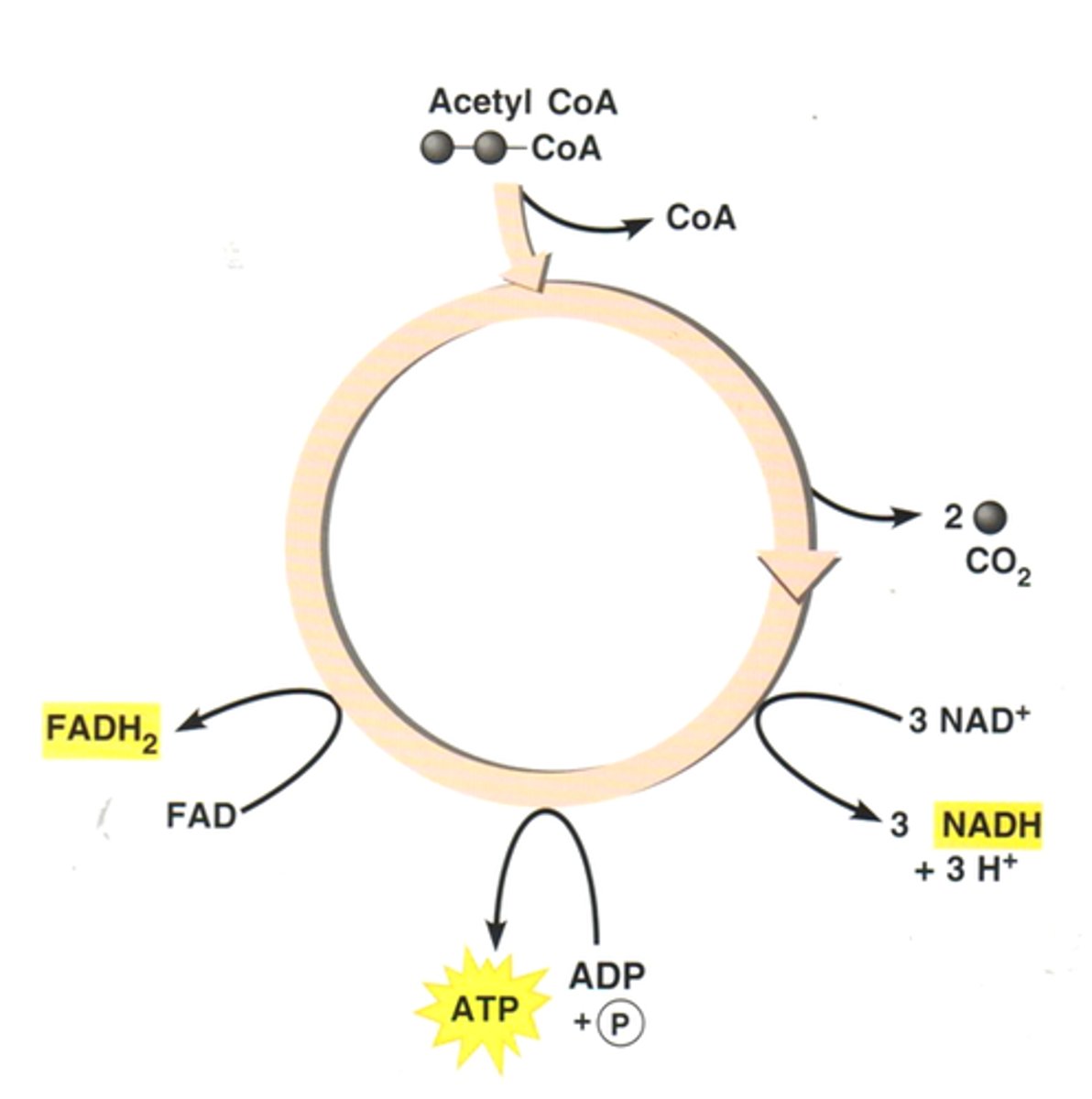
FADH2
electron carrier produced during the Krebs cycle
Krebs Cycle
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid (pyruvate) is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions; also known as The Citric Acid (TCA) Cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain; the final stage of aerobic cellular respiration.
endergonic
A chemical reaction that requires the input of energy in order to proceed.

exergonic
a chemical reaction that releases energy
cristae
Infoldings of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electon transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP.
H+ gradient
proton motive force that drives the ATP synthase to make ATP
electron acceptor
A reactant that gains an electron and is reduced in a reduction-oxidation reaction. Oxygen in respiration and NADP+ is photosynthesis.
metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
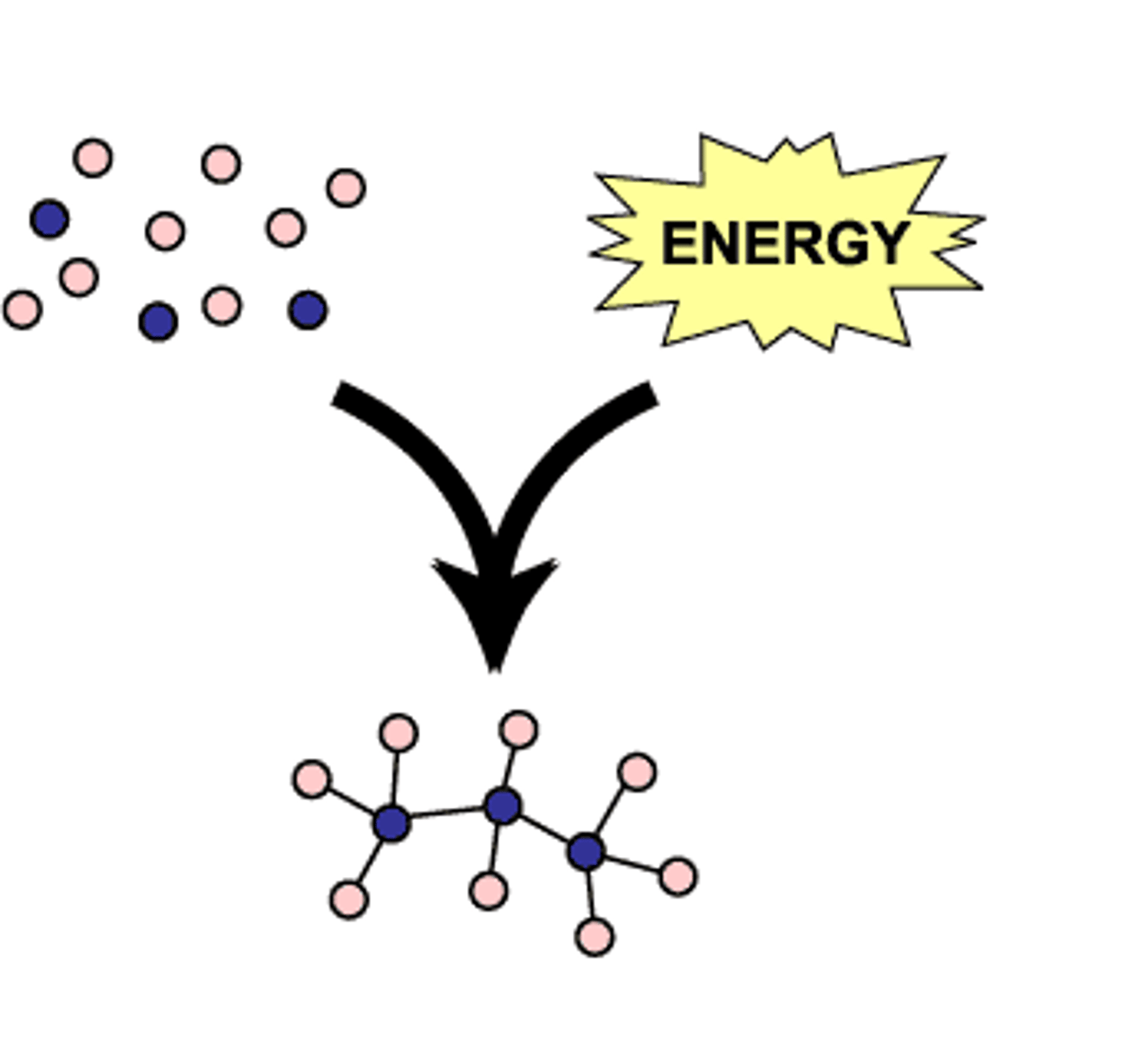
anabolism
Metabolic pathways that build larger molecules
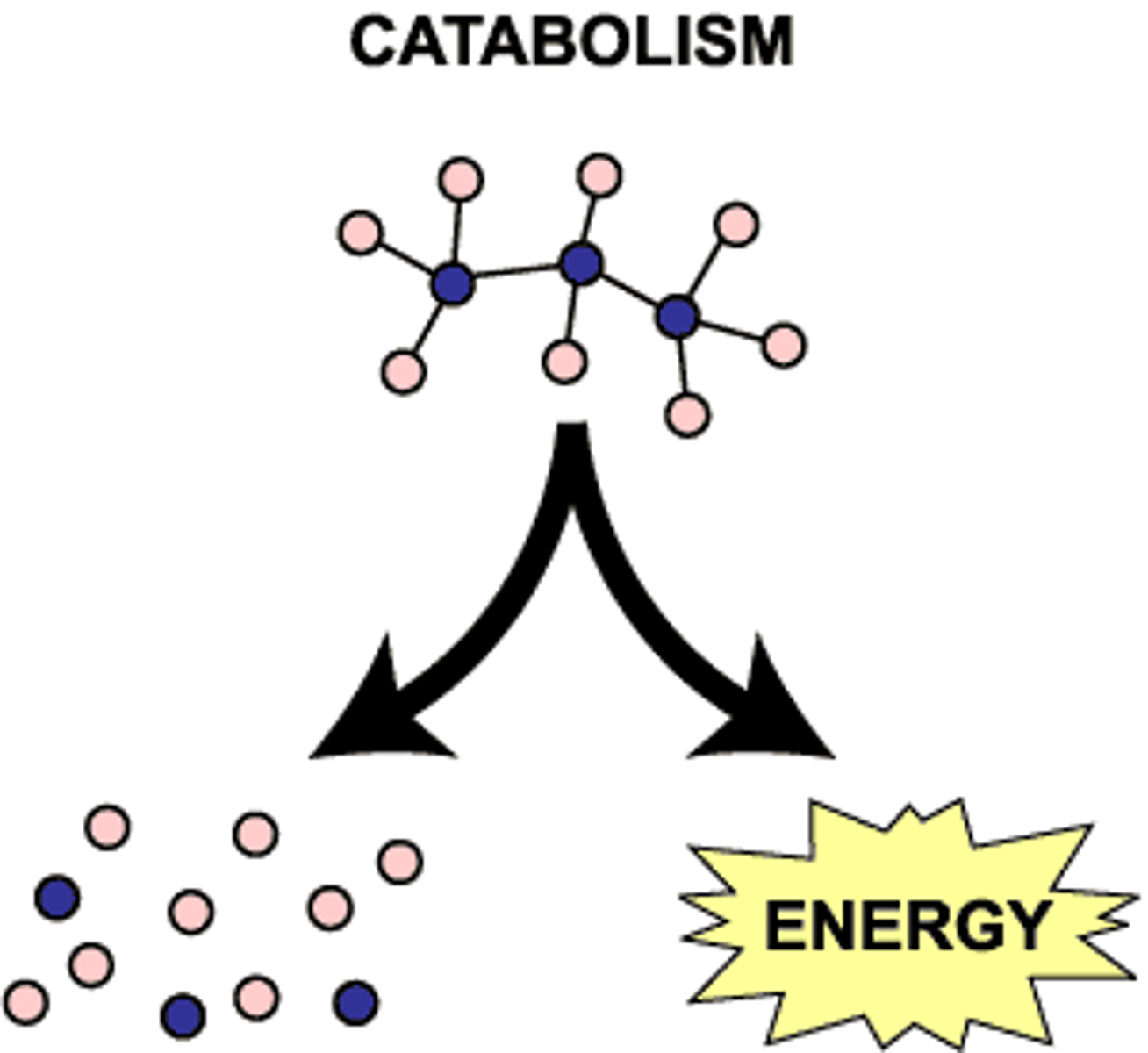
catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules
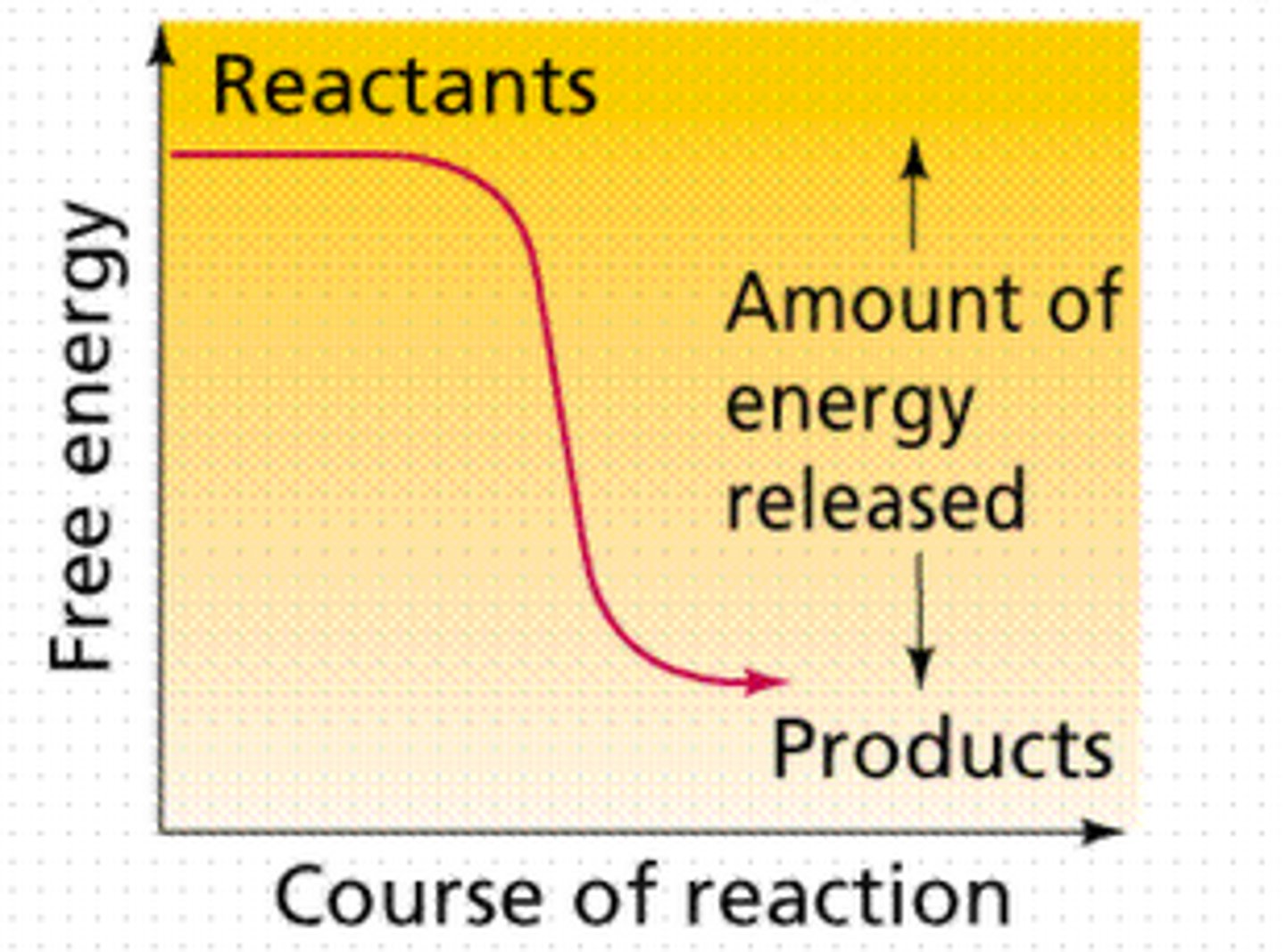
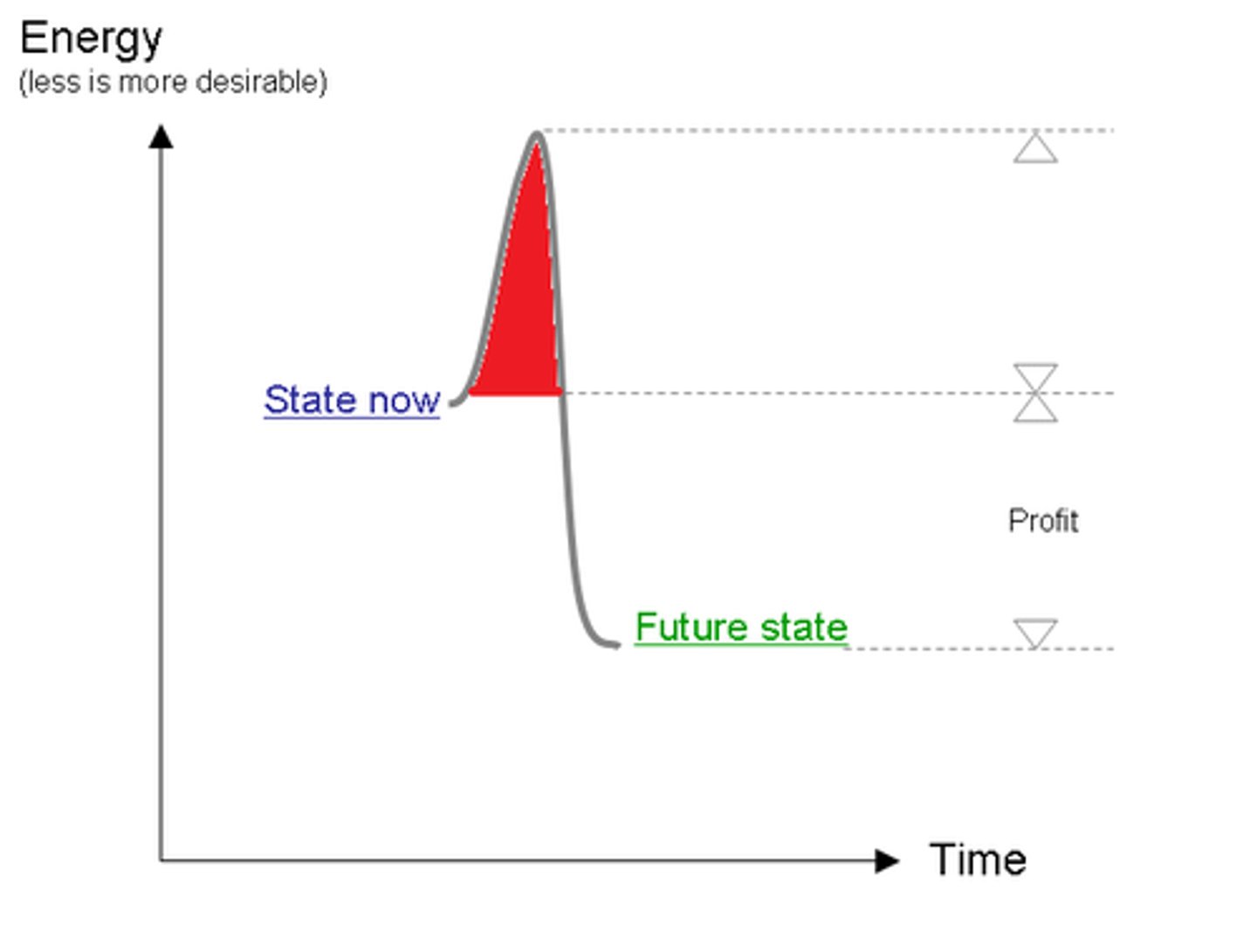
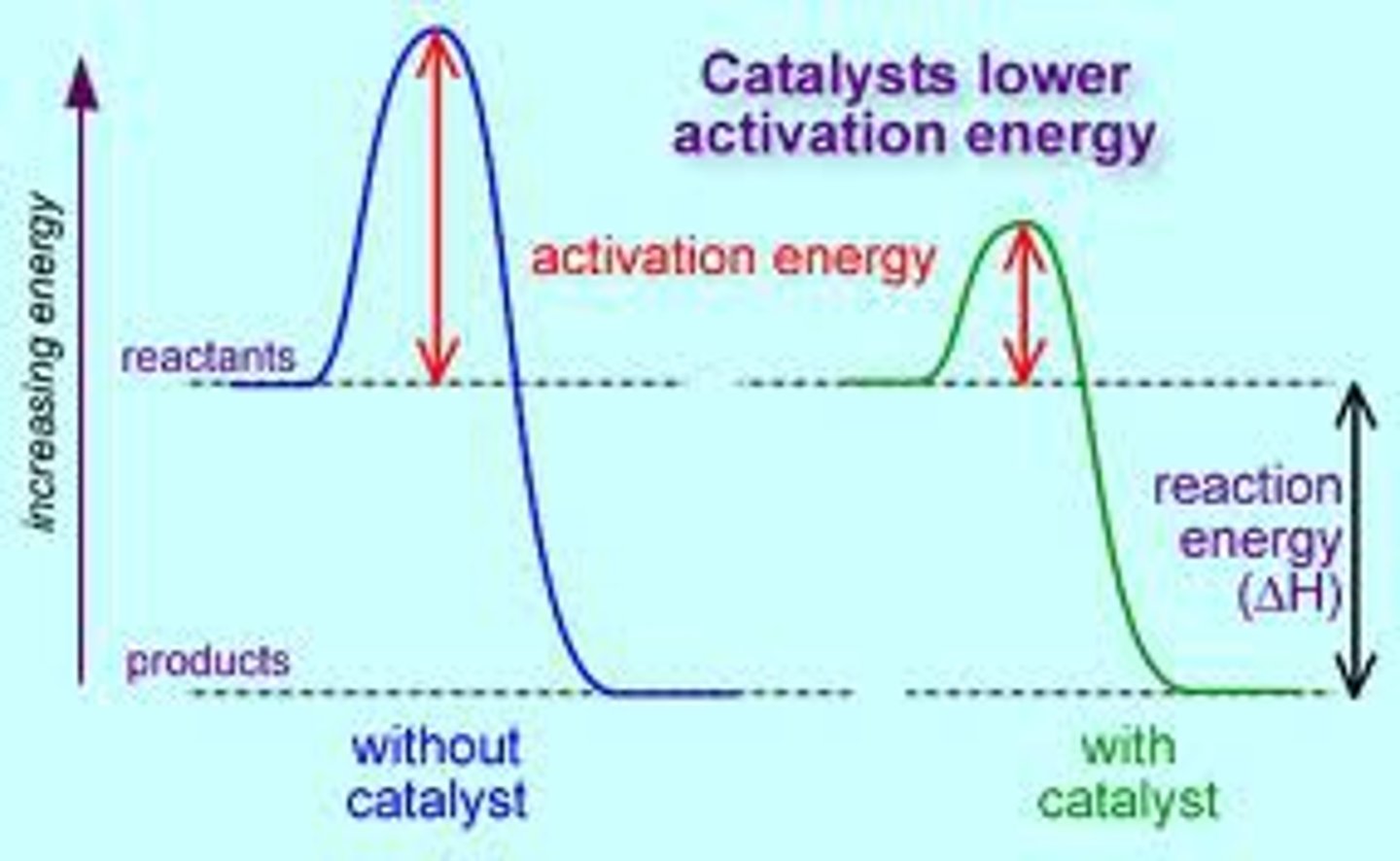
activation energy
Energy needed to start a chemical reaction
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
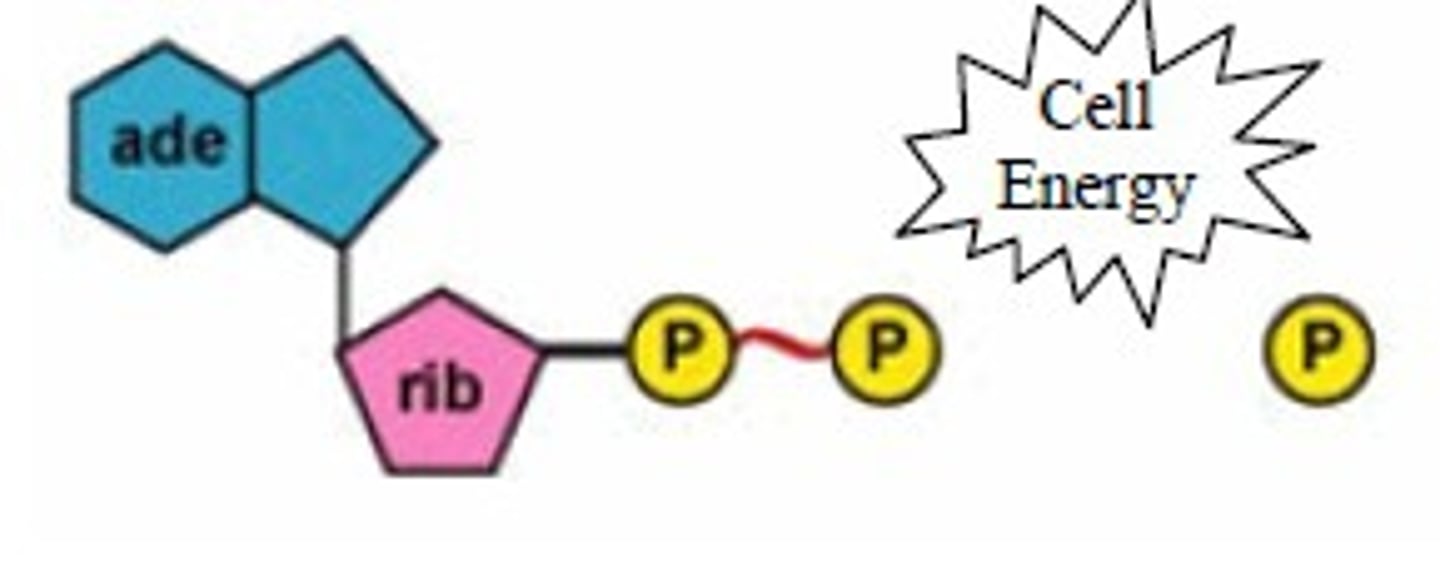
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
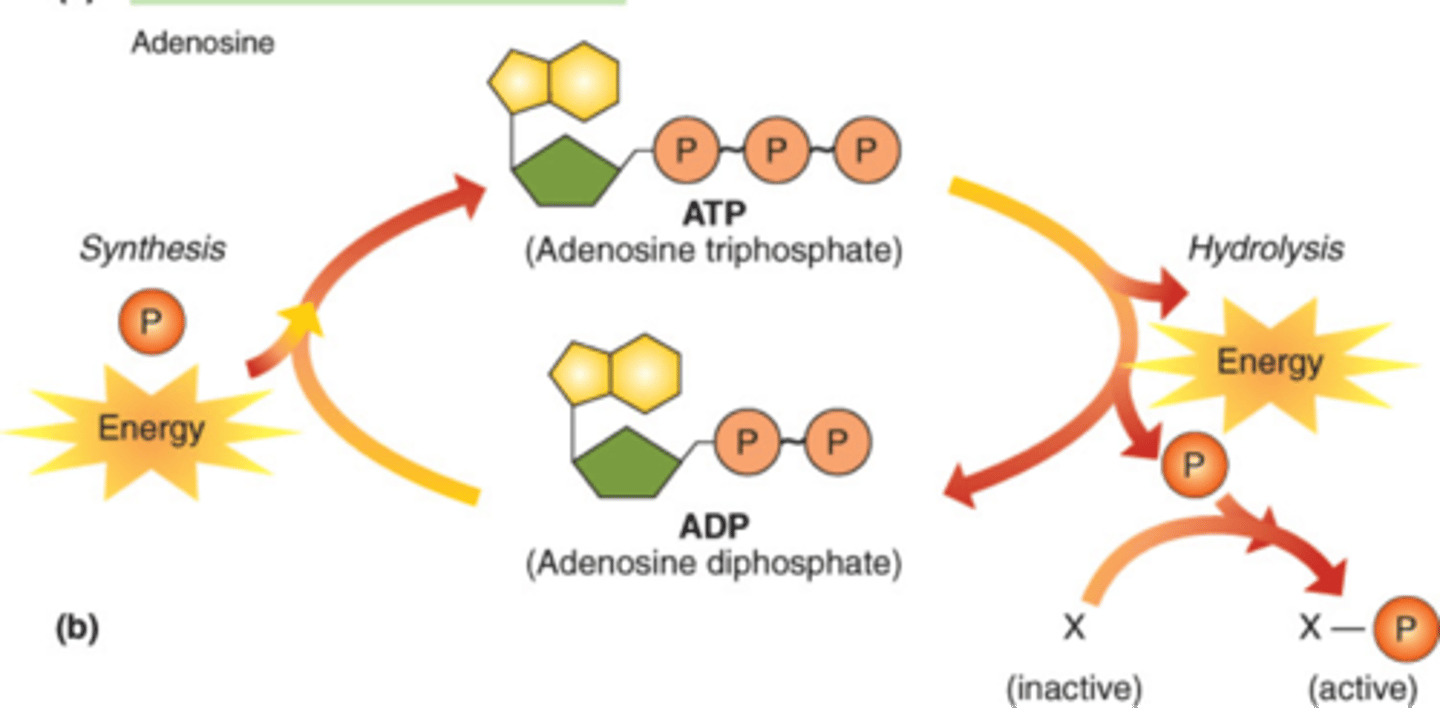
ADP
(Adenosine Diphosphate) The compound that remains after a phosphate group is removed from ATP, releasing energy
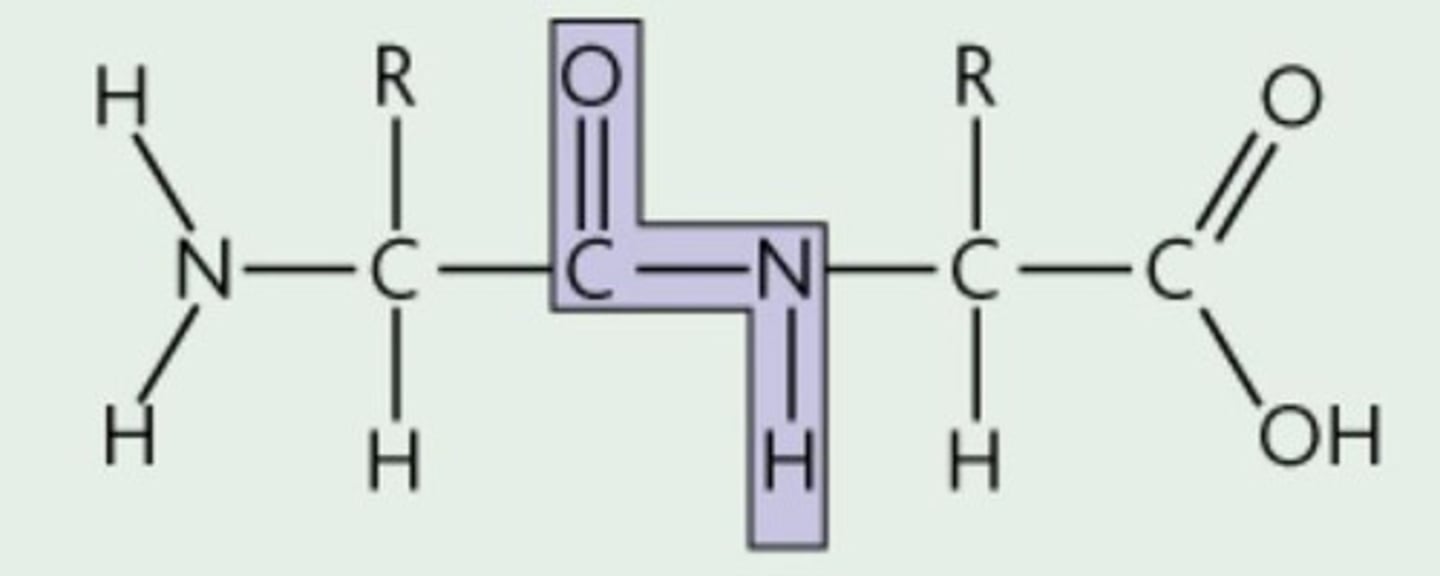
peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids
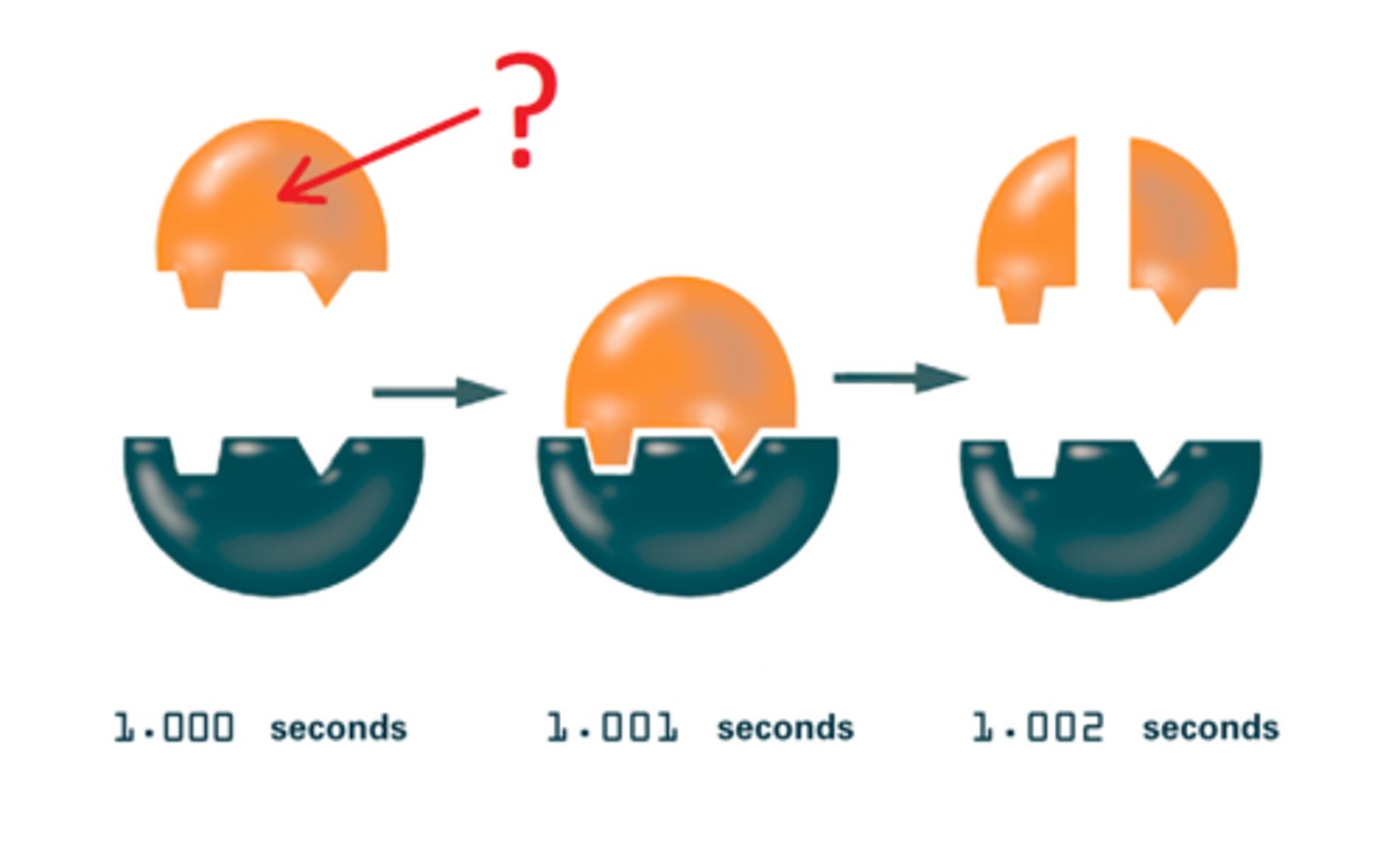
enzyme
protein that speeds up a chemical reaction (catalyst)
active site
a region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction.
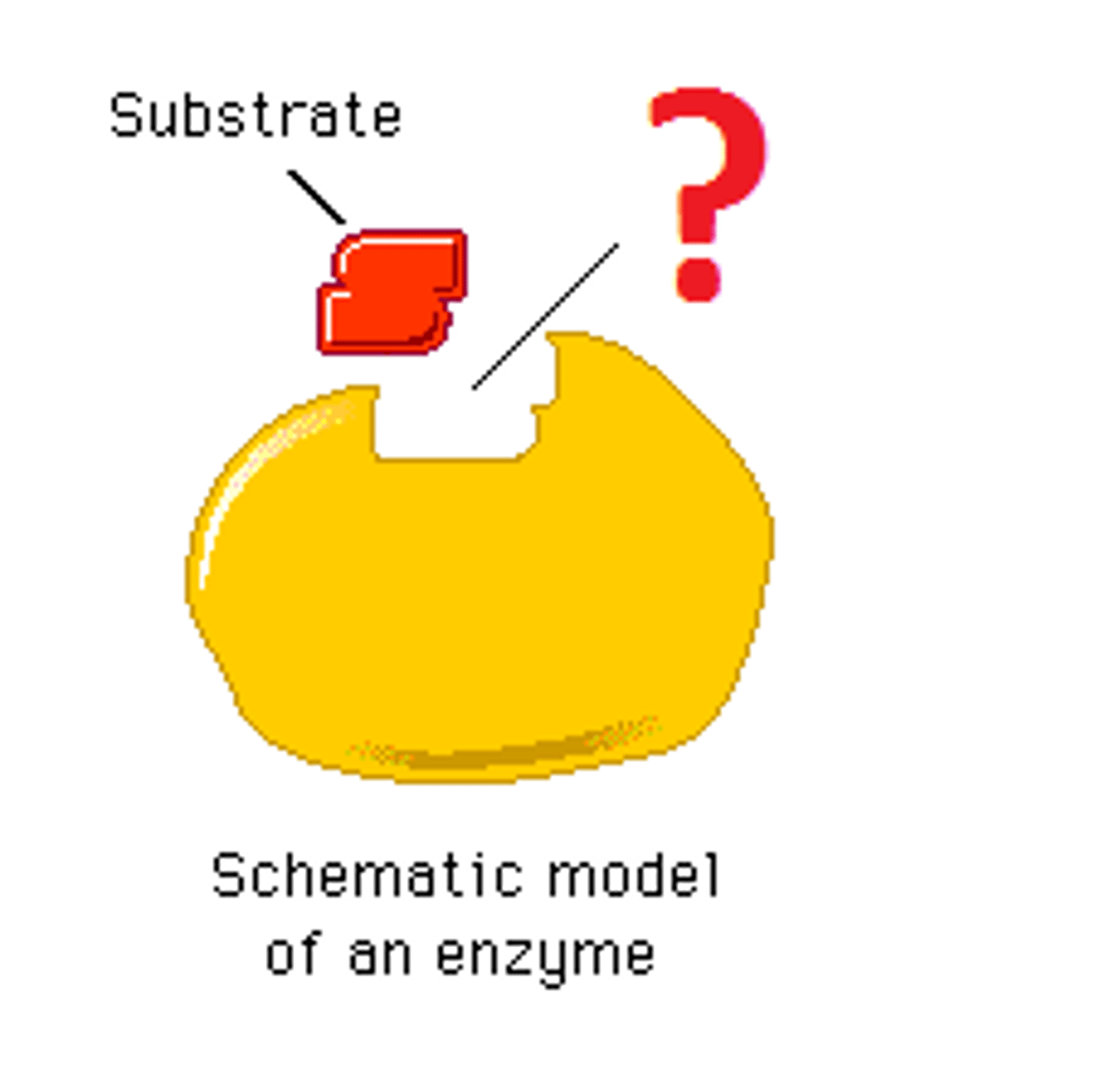
substrate
reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
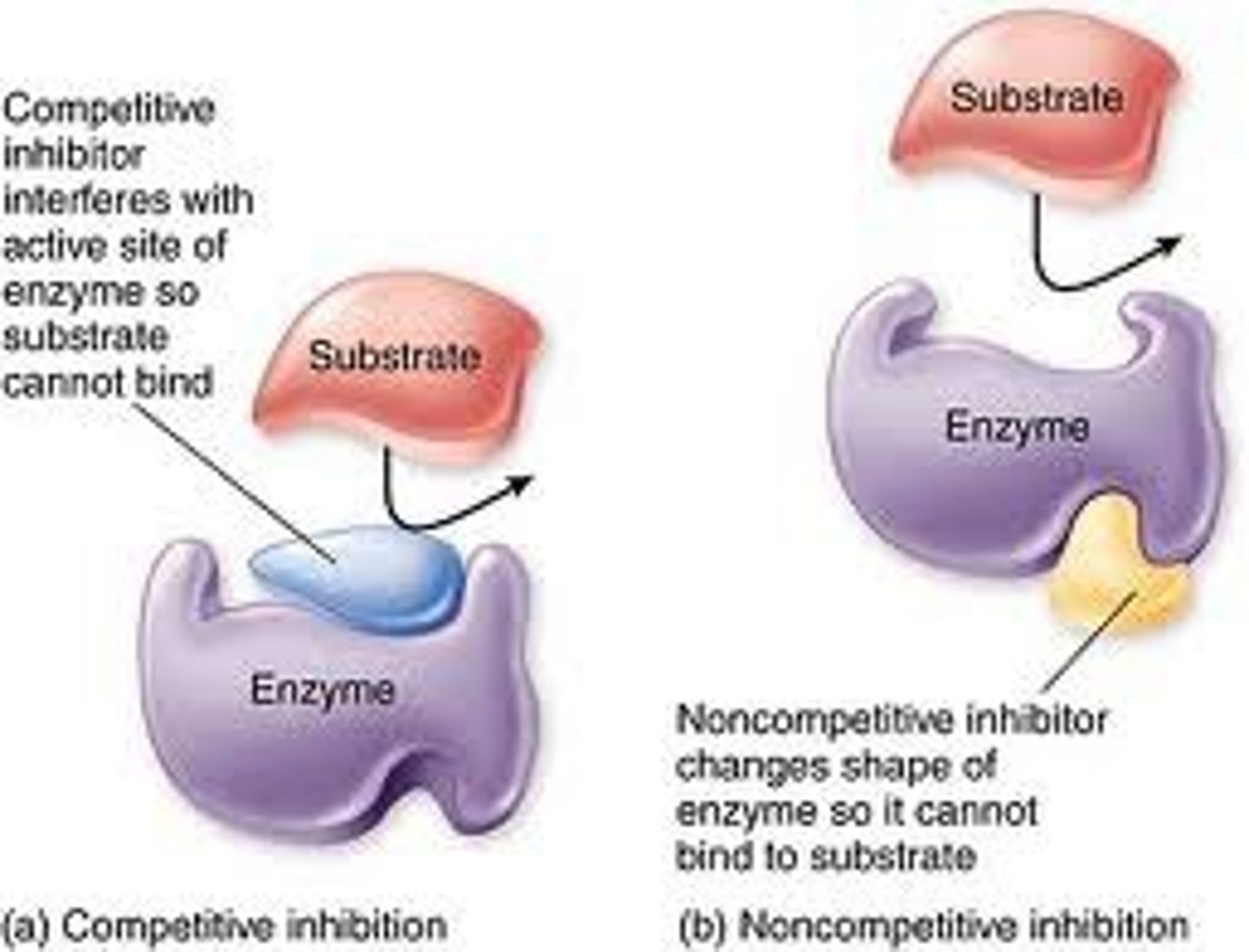
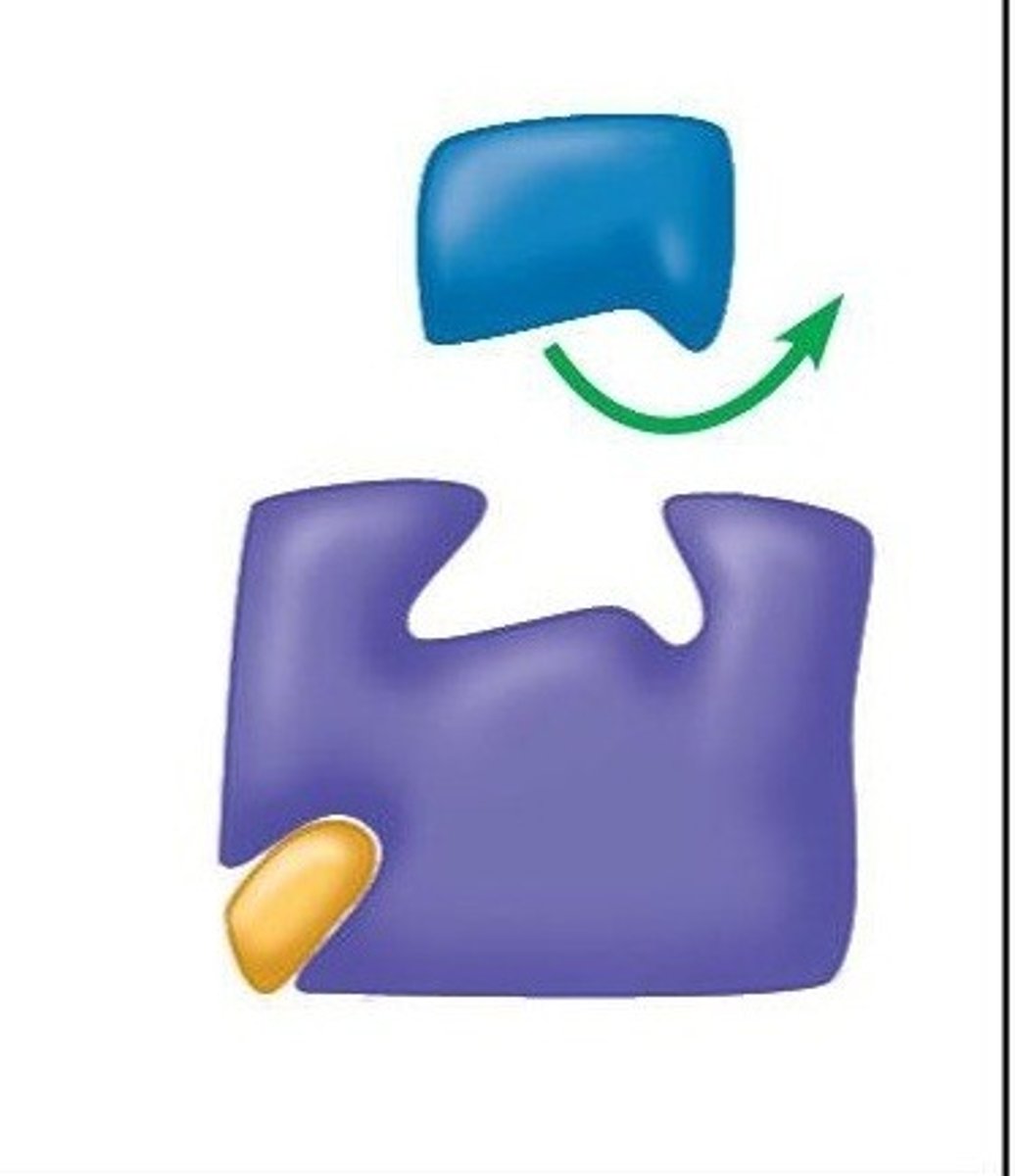
noncompetitive inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing the enzymes shape so that it can no longer catalyze a chemical reaction

endosymbiosis
The theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent prokaryotes that were engulfed (phagocytosis) by another much larger cell.
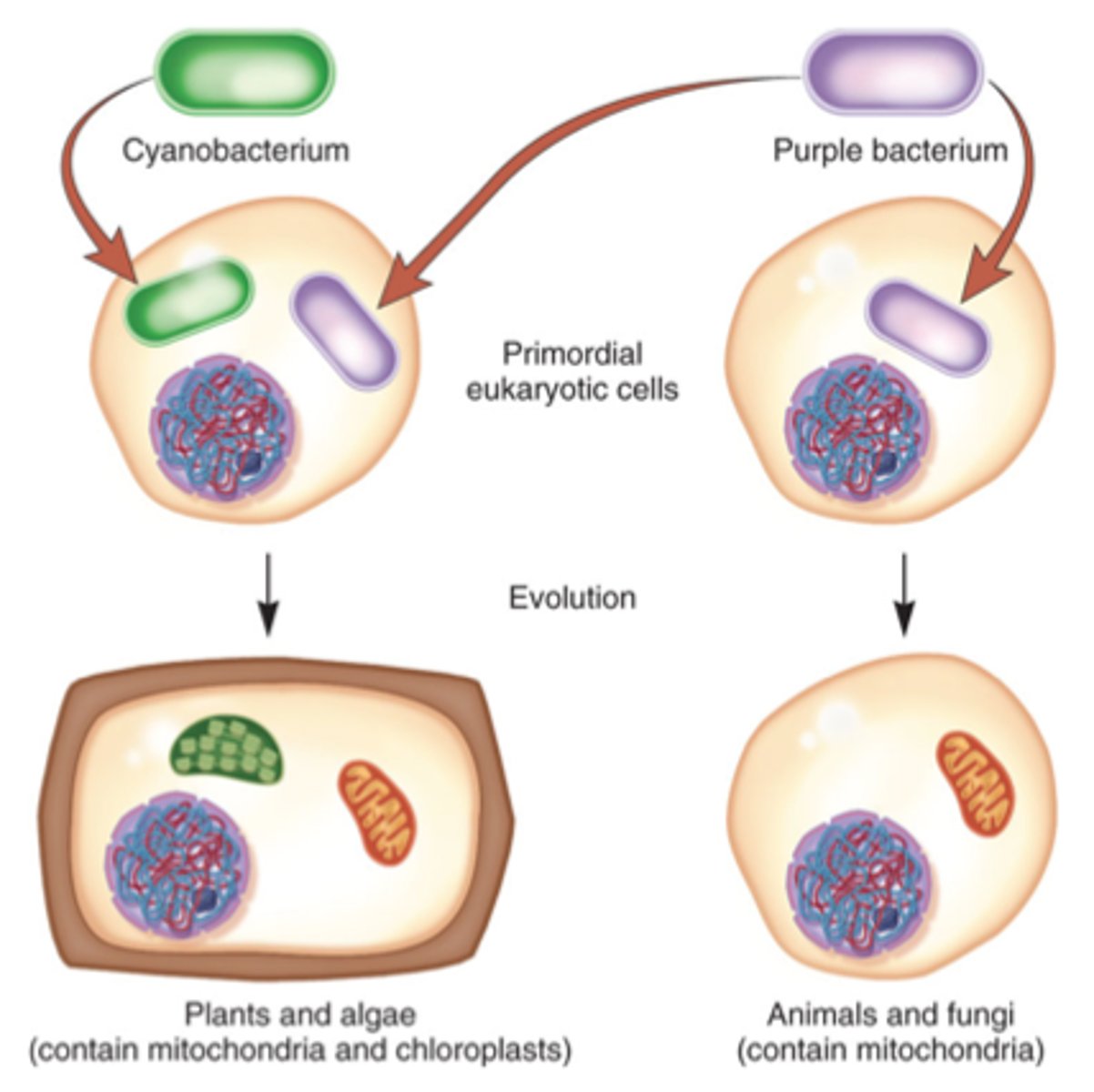
endosybiosis: evidence in support
Chloroplasts and mitochondria have:
1- double membranes
2- their own DNA
3- their own ribosomes
eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
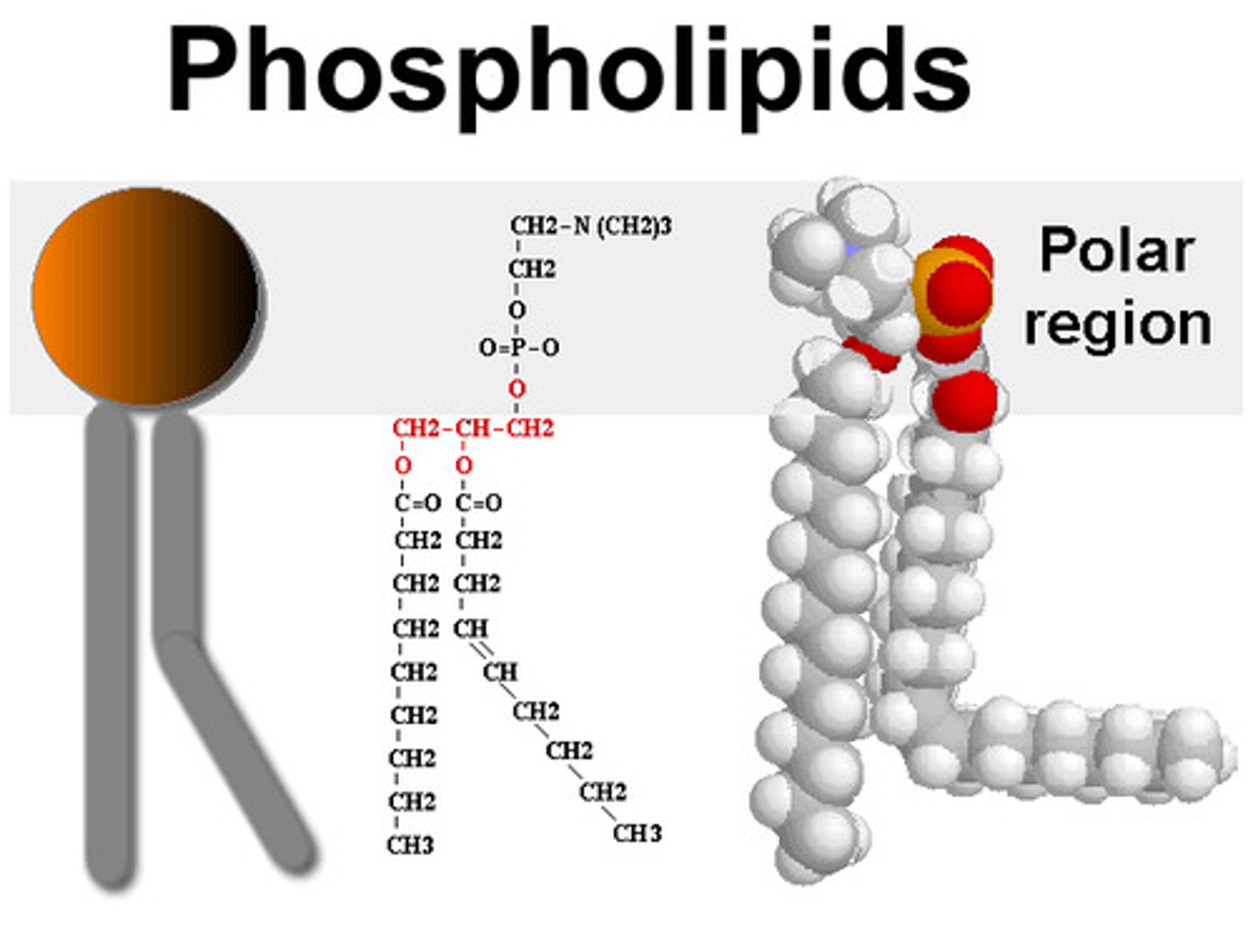
phospholipid
A lipid containing a polar phosphate head and nonpolar fatty acid tails
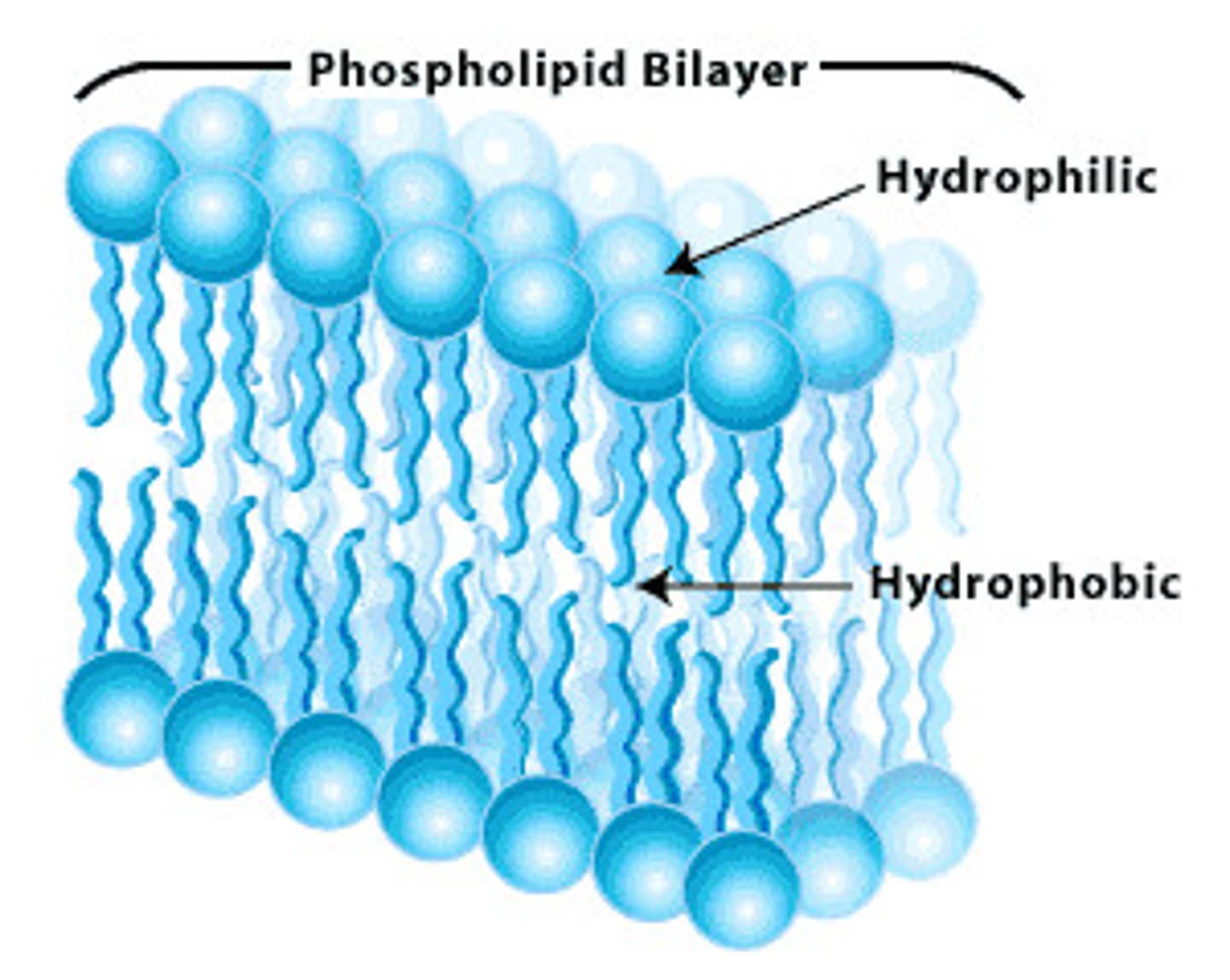
phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up cell and organelle membranes.
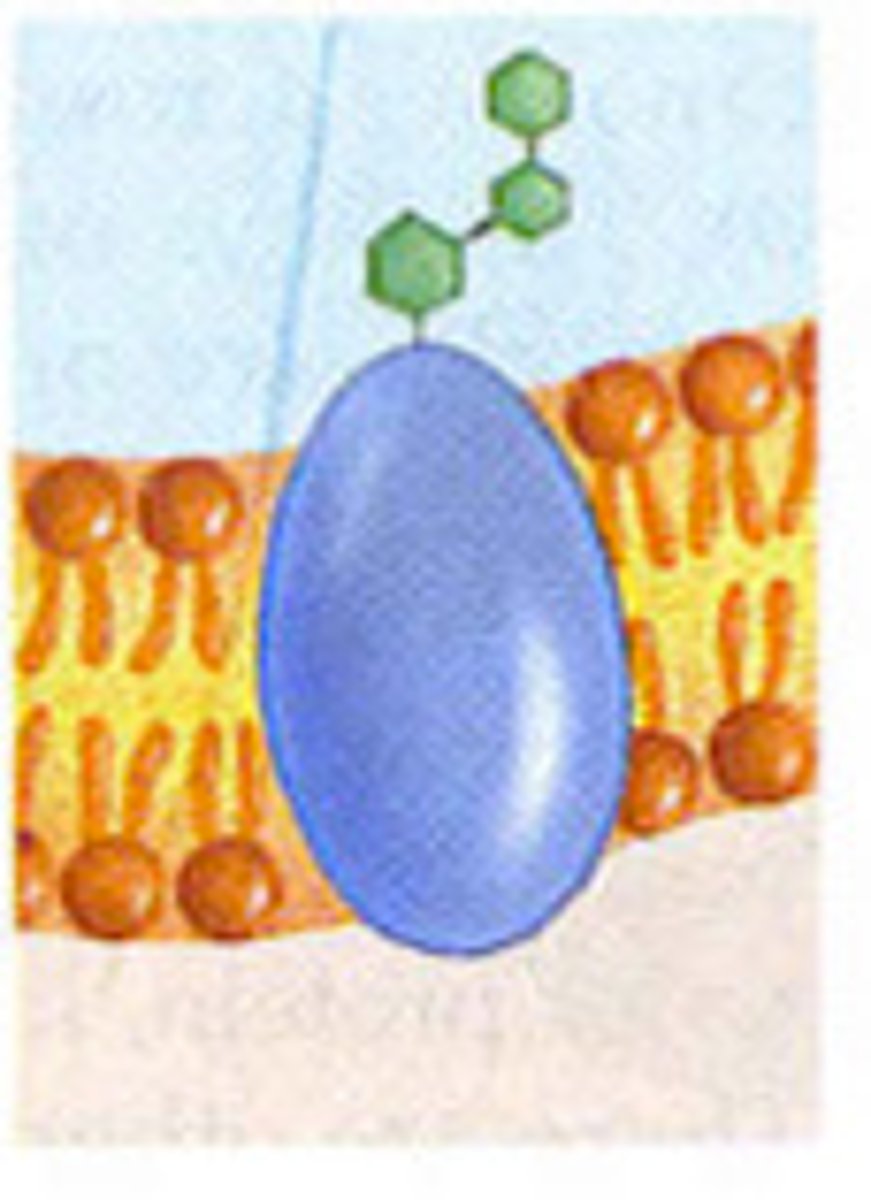
glycoprotein
A protein with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates. Important in cell-to-cell communication.