Nervous System Flashcards
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Path of Light Through the Eye
Cornea → Aqueous humor → Pupil → Lens → Vitreous humor → Retina (photoreceptors) → Optic nerve → Brain
Path of Sound Through the Ear
Pinna → Auditory canal → Tympanic membrane → Ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) → Oval window → Cochlea → Auditory nerve → Brain
Sense of Olfaction (Smell)
Olfactory receptor cells in nasal cavity → Olfactory bulb → Olfactory tract → Brain
Sense of Gustation (Taste)
Taste buds on papillae detect chemicals in food → Signals sent via facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves → Brain
Receptor Cells
Photoreceptor, Mechanoreceptors, Chemosreceptors
• Photoreceptors (eye – light)
rods and cones
Mechanoreceptors
(ear – sound & touch)
• Chemoreceptors
(nose & tongue – smell & taste)
• Rods
low light, black/white
• Cones
color vision, bright light
Cornea
Clear, avascular, and first refractive surface – helps focus light
Blind Spot
No photoreceptors where the optic nerve exits the eye
Refractory Media
Cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor – all help bend light
Eye Disorders
Presbyopia, Cataract, Astigmatism, Glaucoma
• Presbyopia
age-related difficulty focusing on close objects
• Cataract
clouding of the lens
• Astigmatism
irregular curvature of cornea/lens
• Glaucoma
increased intraocular pressure, damaging optic nerve
Hearing
Human Hearing Range: 20Hz-20,000Hz
Ceruminous Glands
Produce earwax (cerumen) for protection
Presbycusis
Age-related hearing loss
Papillae/Taste Buds
Structures on tongue containing taste receptors
Dysgeusia
Distorted sense of taste
Anosmia
Loss of smell
Why Mucus & Saliva Matter
Mucus traps particles & helps olfaction
Saliva dissolves food chemicals for taste
Cerebral Hemispheres
thought, memory, movement
Diencephalon
relays info, regulates homeostasis
Brain Stem
vital functions (breathing, heartbeat)
Cerebellum
balance and coordination
4 Lobes of Cerebrum
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital
• Frontal
reasoning, speech (Broca’s), motor skills
• Parietal
touch, spatial awareness
• Temporal
hearing, memory, language (Wernicke’s)
• Occipital
vision
Diencephalon Parts
Thalamus, hypothalamus, and Epithalamus
Thalamus
sensory relay
Hypothalamus
Homeostasis, Hormones
Epithalamus
Includes pineal Gland
Brain Stem Parts
Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Oblongata
Limbic System
Emotions, memory
Includes Amygdala and Hippocampus
Amygdala
fear/emotion
Hippocampus
memory
Master Gland
Pituitary
Pineal Body
Produces melatonin (sleep cycle)
Gyri
ridges
Sulci
grooves
Corpus Callosum
Connects left and right hemisphere
CNS
brain & spinal cord
PNS
all other nerves
Synapse
Space between neurons
Neurons
transmit signals
Neuroglia
support neurons
Neuron Types
Unipolar, Bipolar, and Multipolar
• Unipolar
sensory (PNS)
• Bipolar
special senses (eye, nose)
• Multipolar
motor neurons (CNS)
Afferent/Sensory Neurons
Unipolar
Efferent/Motor Neurons
Multipolar
Neuron Anatomy
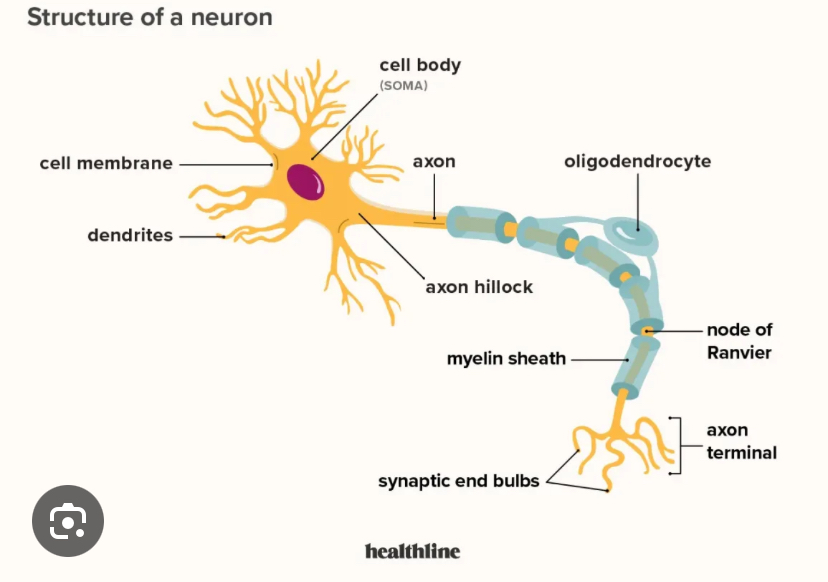
• Dendrites
receive signals
• Axon
sends signal away
• Soma (Cell Body)
contains nucleus
• Myelin
insulation (made by Schwann cells)
• Neurilemma
outer layer of Schwann cell
• Nodes of Ranvier
gaps for faster conduction
• Axon Terminals
transmit to next neuron
Nerve Transmission Steps
Polarization (resting potential)
Depolarization (signal sent)
Repolarization (returns to rest)
Protection of Brain & Spinal Cord
Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid
• Meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
• Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
cushions, delivers nutrients
Nerves
12 Cranial Nerves, 31 Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerve I – Olfactory (smell)
Cranial Nerve II – Optic (vision)
Cranial Nerve VIII – Vestibulocochlear (hearing/balance)
Longest Nerve
Vagus nerve
Spinal Cord Ends
L1-L2 (conus medullaris)
Cauda Equina
bundle of spinal nerves at lower end
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Protects brain; allows O₂, CO₂, glucose; blocks toxins, bacteria
Alcohol
affects cerebellum, frontal lobe, hippocampus
Nicotine
stimulates dopamine → addiction
Marijuana
affects memory (hippocampus), coordination
Aphasia
speech/language disorder
Broca’s Area
speech production (damage = expressive aphasia)
Wernicke’s Area
language comprehension (damage = receptive aphasia)