Geography Revision :(
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Mantle
The thick layer of hot, solid rock between Earth's crust and core.
Convection Currents
Circular movements of heated fluid (like magma) that rise when warm and sink when cool, helping move Earth's tectonic plates.
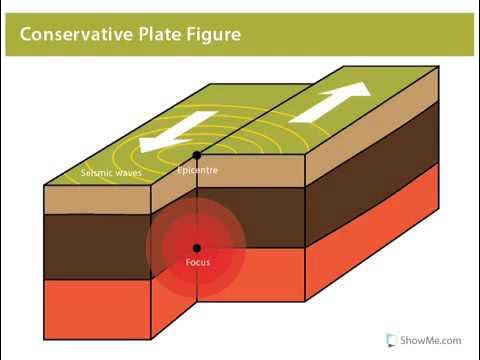
Conservative Plate Boundary
A place where two tectonic plates slide past each other without creating or destroying crust, often causing earthquakes.
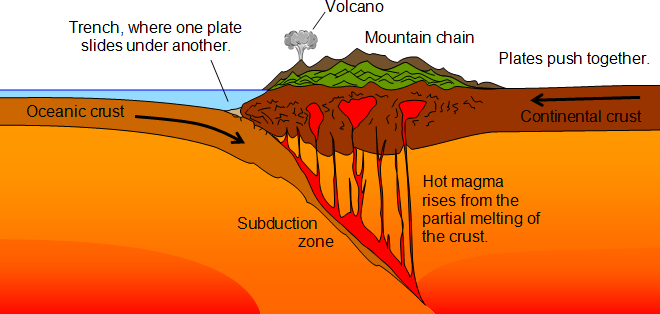
Destructive Plate Boundary
A boundary where an oceanic plate sinks beneath a continental plate, causing earthquakes, volcanoes, and the destruction of crust.
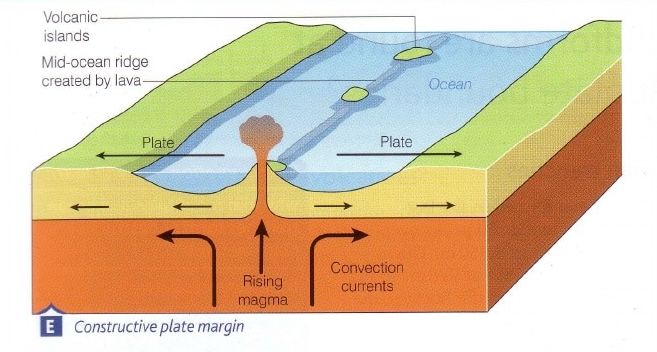
Constructive Plate Boundary
A boundary where two tectonic plates move apart, allowing magma to rise and form new crust, often creating volcanoes and mid-ocean ridges.
Subduction
The process where one tectonic plate sinks beneath another into the mantle, usually at a destructive plate boundary.
Earthquakes
Sudden shaking of the ground caused by the movement of tectonic plates, usually along faults or plate boundaries.
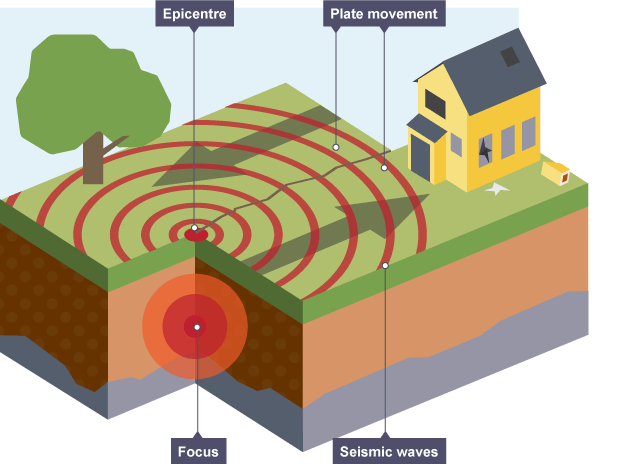
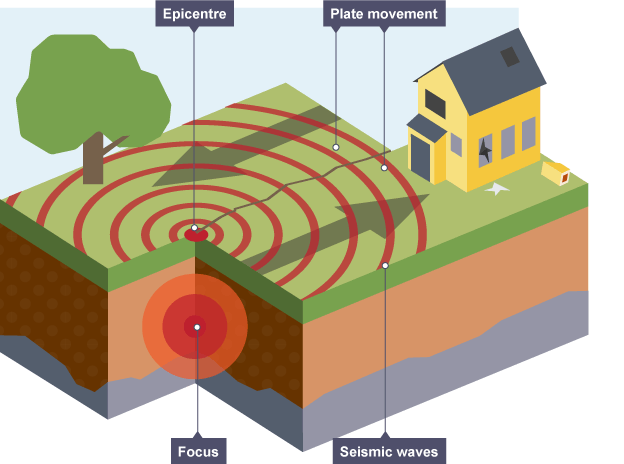
Focus
The point inside the Earth where an earthquake starts.
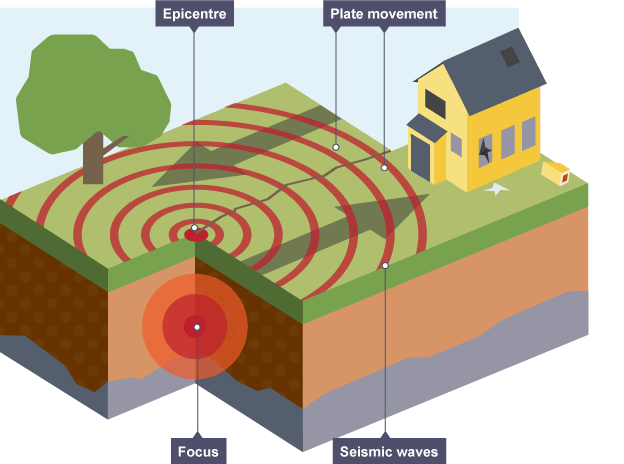
Epicentre
The point on the Earth's surface directly above the earthquake's focus, where shaking is usually strongest.
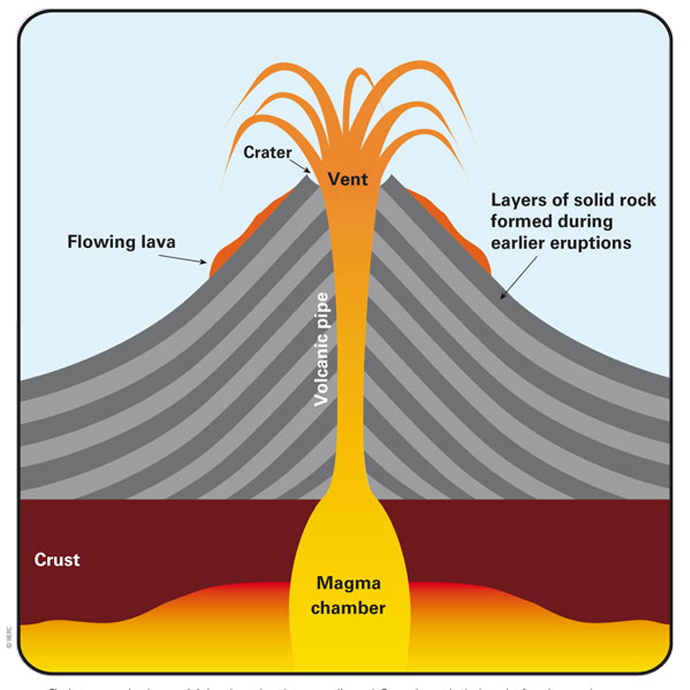
Magma
Hot, melted rock found beneath the Earth's surface.
Seismograph
An instrument that detects and records the strength and duration of earthquakes.
Shield Volcano
A wide, gently sloping volcano made from runny lava that spreads over a large area.
Composite Volcano
A tall, steep volcano made from layers of lava and ash, known for explosive eruptions.
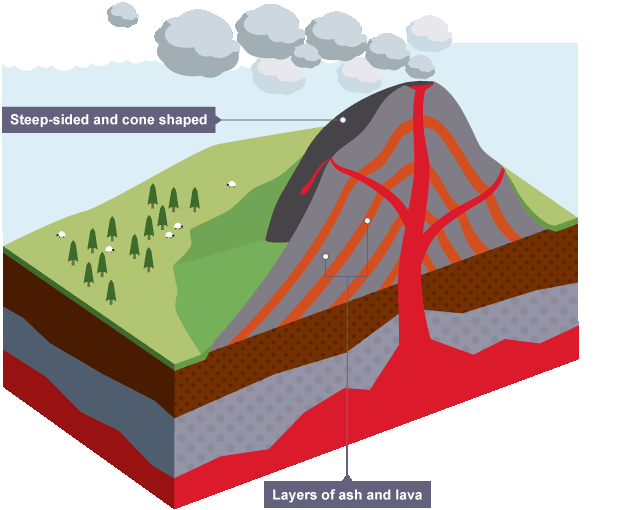
Viscous
Thick and sticky; describes lava that flows slowly.
Benioff Zone
A sloping area of earthquake activity along a subducting plate, where the oceanic crust sinks into the mantle.
Development
The process of a country or region improving its economy, health, education, and quality of life.
Quality Of Life
A measure of people's well-being, including health, comfort, happiness, and access to basic needs.
Standard Of Living
The level of wealth, comfort, and access to goods and services a person or group has.
Birth Rate
The number of live births per 1,000 people in a year.
Death Rate
The number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population each year.
HDI
A measure of development using life expectancy, education, and income to show overall quality of life in a country.
GDP
(Gross Domestic Product) The total value of all goods and services produced in a country in one year. It shows the size of a country's economy.
GDP Per Capita
The total value of all goods and services a country produces in a year. It shows the size of a country's economy.
Literacy Rate
The percentage of people in a country who can read and write.
Life Expectancy
The average number of years a person is expected to live in a specific country or region.
Infant Mortality Rate
The number of babies who die before their first birthday per 1,000 live births in a year.
LDC
A country with low income, poor healthcare and education, and limited access to basic services.
HIC
A country with a high level of income, good healthcare, education, and access to services.
Bottom-up Development
Small-scale projects led by local people to meet community needs, often using local knowledge and resources.
Top-down Development
Large projects planned and controlled by governments or big organizations, often with less input from local people.
Appropriate Technology
Simple, low-cost, and easy-to-use tools or techniques that suit the local people’s needs, skills, and environment.
Weather
The day-to-day conditions of the atmosphere, like temperature, rain, wind, and sunshine.
Climate
The average weather conditions in a place over a long period, usually 30 years or more.
Temperature
A measure of how hot or cold the atmosphere is, usually shown in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit.
Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from the sky, like rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
High Pressure
A weather system where air is sinking, usually bringing clear skies and dry, calm weather.
Low Pressure
A weather system where air is rising, often causing clouds, wind, and wet or stormy weather.
Wind Speed/Direction
Wind speed is how fast the air is moving; wind direction shows where the wind is coming from.
Anticyclone
A high-pressure system with sinking air that brings dry, clear, and calm weather.
Depression
A low-pressure system with rising air that brings clouds, rain, and windy weather.
Relief Rainfall
Rainfall that happens when moist air is forced to rise over mountains, cools down, and releases rain.
Convectional Rainfall
Rainfall caused when the sun heats the ground, making warm air rise, cool, and form rain clouds.
Frontal Rainfall
Rainfall that happens when warm and cold air masses meet, causing the warm air to rise over the cold air, cool, and form rain clouds.
Air Mass
A large body of air with the same temperature and moisture levels throughout.