Robots
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 8, 9, and 11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
forced worker
word “robot” is based on a Czech word (“robotoa”) which means ____________
Isaac Asimov’s
who created “three laws of robotics”
three laws of robotics
a robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being come to harm
a robot must obey orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the first law
a robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the first or second laws
load of crap
the three laws of robotics are a _____________ created in a book
industrial robot
an automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose, manipulator programmable in three or more axes, which may be either fixed in place or mobile for use in industrial automation applications
automated positioning device
most industrial robots
speed, accuracy, and repeatability
industrial robots are used in tasks that require ___________________________
For these types of tasks, robots typically outperform humans
automotive industry, electronics, and cargo transport
common applications of industrial robots
three D’s
dull
dirty
dangerous
typical robot uses
die casting
forging
painting
welding
material handling (pick & place; palletizing)
components of a robot system
sensors/controls that provide a robot with information about its external environment
mechanical part or manipulator
end-effectors that processes an object
controller that processes information provided by the sensors and drives end-effectors
power supply
robot manipulator (body)
composed of chains of rigid bodies called links, and connected together by joints
body primary function
to enable and move the end-effectors end of the arm to do the required work
ex. a robotic gripper
arm and body motions and wrist motions
a robotic movement can be divided into two general categories
robot joints
prismatic joints
revolute joints
prismatic joint
provides a linear/translational sliding motion to a link along an axis
linear joint
orthogonal joint
revolute joints
provides rotating movement to a link around an axis
permit only angular motion
rotational
twisting
revolving
L O R T V
joint symbols
linear (L)
linear sliding movement

orthogonal (O)
transitional sliding movement

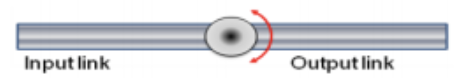
rotational (R)
provides rotating motion with the axis of rotation perpendicular to the axes of the input and output links
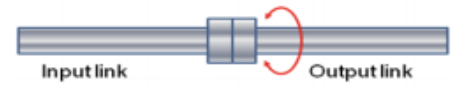
twisting (T)
joint rotates but rotation is parallel to the axes of the two links
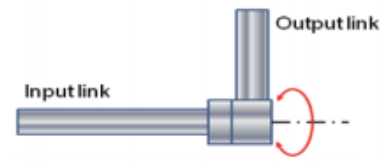
revolving (V)
joint rotates but the output link axis is perpendicular to the rotational axis
work envelope
created when a robot moves its end-effector forward, backward, up and down
distances are determined by the length of a robot’s arm and the design of its axes
each axis contributes its own range of motion
robot can only perform within the confines of its ____________
maximum space
the three-dimensional volume encompassing the movements of all robot parts through their axis
determined by the length of robot’s arm and design of its axis
restricted space
the portion of the maximum space to which a robot is restricted by limiting devices
maximum distance that the robot, end-effector, and work piece can travel after the limiting device is actuated
safeguarded space
defined by the perimeter safeguarding devices
operating space
that portion of the restricted space that is actually used by the robot while performing its task program
encoder
in each robot joint
home position
a fixed position location for a robot where the joint encoders for each axis read zero
unique for each model of robot
typically robots return to this to confirm its encoder are operating correctly at the beginning of every cycle
industrial robot system
a system that includes industrial robots, the end-effectors, and the devices and sensors required for the robots to be taught or programmed, or for the robots to perform the intended automatic operations, as well as the communication interfaces required for interlocking, sequencing, or monitoring the robots
end effector
the device at the end of a robotic arm, designed to interact with the environment
EOAT
end of arm tooling
gripper
magnets, vacuum cups
tools
MIG gun, spot welder, spray gun, nut runner
robot teaching
to program a manipulator arm by manually guiding it through a series of motions and recording the position in the robot controller memory for playback
teach mode
a robot controller mode in which a robot manipulator is programmed by manually guiding it through a series of
teaching
to program a manipulator arm by manually guiding it through a series of motions and recording the position in the robot controller memory for playback
teach pendant
a handheld control box, which is used by an operator to remotely guide a robot through the motions of its tasks. the motions are recorded by the robot control system for future playback
250 mm/sec
robot movement speed in teaching mode is automatically limited to ______
Jacobian matrix
matrix algebra is integral in robotics for computing the position of a robot’s end effector by representing transformations between coordinates frames; the _______ is employed to analyze the relationship between joint velocities and end effector velocities, aiding in motion planning and control.
accuracy
the precision with which a computed or calculated robot position can be attained; normally worse than the arm’s repeatability; is not constant over the workspace, due to the effect of link kinematics
repeatability
a measure of how closely a robot can repeatedly obtain a taught position. for instance, once a manipulator is manually placed in a particular location and this location is resolved by the robot, the ____ specifies how accurately the manipulator can return to that exact location
robot singularity
for a standard six joint manipulator, a kinematic singularity is a point in the workspace where the robot loses its ability to move the end effector in some direction no matter how it moves its joints. it typically occurs when two of the robot’s joints line up, making them redundant
often causes sudden rapid movements
pounce position
an arbitrary point used before (and sometimes after also) a series of points defining a path; it is used to safely park the arm+tool in a convenient location ready to move to the beginning point of the path
pounce position
a specific point in a robot’s workspace where it is positioned to be ready for a quick, precise movement
key characteristics of pounce position
proximity - usually close to the area where the robot will perform its primary task
safety - it’s a position where the robot is unlikely to collide with other objects or people
efficiency - it’s a position that allows the robot to move quickly and efficiently to its target when provided an input
robot fixturing
a custom designed device used to locate or support the work piece during the operation
welding, machining
consistent hold
clamping
nesting
close set
space
robot work
load/unload
general duty clause
OSHA does not have a specific “robot” standard, instead it falls under the ____
general duty clause
each employer shall furnish to each of his employees employment and a place of employment which are free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to his employees
OSHA rules that apply to robots
OSHA 1910.212 general requirements for all machines
OSHA 1910.219 mechanical power transmission apparatus
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 control of hazardous energy (lock-out/tagout)
NFPA 79 2015 electrical standard for industrial machinery guidelines
consensus standards
OSHA Technical Manual: Section IV: Chapter 4 - Industrial robot system safety
OSHA STD 01-12-002: Guidelines for robotics safety
Robotic Industries Association (RIA)
American National Standard for Industrial Robots and Robot Systems - Safety Requirements
Technical Report for Industrial robots and robot systems - Safety Requirements
OSHA robotic safety standards
robot accidents do not occur under normal operating conditions but, instead during programming, program tough-up, or refinement, maintenance, repair, testing, setup or adjustment
robot safe guarding - effective robotic safeguarding system should be based upon a hazard analysis
a combination of safeguarding methods may be used
envelope (space), maximum
the volume of space encompassing the maximum designed movements of all robot parts including the end-effector, workpiece, and attachments
restricted envelope
that portion of the maximum envelope to which a robot is restricted by limiting devices
operating envelope
that portion of the restricted envelope that is actually used by the robot while performing its programmed motions
fixed barriers
should cover the operating space and restricted space
interlocked barrier guard
a safety device used in industrial settings that prevents a machine from operating unless the guard is securely closed
safeguarding methods
fixed barrier guard
interlocked barrier guard
audible and visible warning systems
awareness barrier device
presence sensing devices
emergency robot braking
layout
wherever practicable, the ___ should allow tasks to be performed from outside the safeguarded space
if it is necessary to perform tasks within the safeguarded space there shall be safe and adequate access to the task locations
access paths should not expose operators to hazards, including slipping, tripping and falling hazards
designers should take into account the frequency and ergonomic aspects of the task
AUTO
around
under
through
over
AUTO
a fixed barrier needs to be sized such that a person cannot reach ___
fixed barrier
securely installed; requires tools to install/remove; not easily removable
safeguarding devices
personnel should be safeguarded from hazards associated with the restricted envelope through the use of one or more safeguarding devices
sensitive protective equipment (SPE)
safety mat systems
safety light curtains
safety beams
safety laser scanners
safety vision systems
minimum safe distance formula
S = (K * T) + C
K - speed constant
T - overall stopping time in sec
C - depth penetration factor in mm
muting
temporary automatic suspension of a safety function during the non-hazardous portion of the process/machine cycle
ex. muting light curtain during entry/exit of pallets on a palletizing machine
blanking
bypassing a portion of the sensing field of a presence-sensing safeguarding device
ex. small gap in light curtain to allow feeding of material through it to punch press while still protecting the operator
safety mats
pressure-sensitive safeguarding products that are designed to detect the presence of people in the sensing surfaces
anchor to the floor
risk assessment
involves identifying hazards, estimating risks, and implementing mitigation measures like engineering controls, administrative protocols, and safety equipment to ensure compliance with safety standards
it is required to ensure the safety of workers, bystanders, and equipment, as mandated by international standards
collaborative robots
designed to work in collaboration with humans through physical interaction in a shared workspace
four types of collaborative systems
power and force limiting
hand guiding
speed and separation monitoring
safety monitored stop
(these are not mutually exclusive)
power and force limiting (PFL)
where incidental contact initiated by robot is limited in energy to not cause operator harm
forces robot can exert are limited
robot system design eliminates pinch points, sharp edges, etc.
robot complies and reacts when contact is made
conditions requiring frequent operator presence
hand-guiding operation
operator uses hand-operated device to transmit motion commands or leads robot movement through direct interface
robot motion responds to operator commands
may run in non-collaborative operation resumes when operator leaves collaborative workspace
speed and separation monitoring
where the robot speed reduces when an obstruction is detected
separation distances are monitors
robot speed directly correlates to separation distance - zones dictate allowable speed
stop condition given if direct contact proximity is attained
safety-rated monitored stop
the robot/collaborative robot stops before the operator enters the collaborative workspace
with a traditional robot this may be achieved with a ______ control system that complies with requirements in ANSI/RIA 15.06-2012
stop-motion condition ensured
drive power remains on
motion resumes after obstruction clears
robot motion resumes without additional action