Upper Limb Muscle AOIs
1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
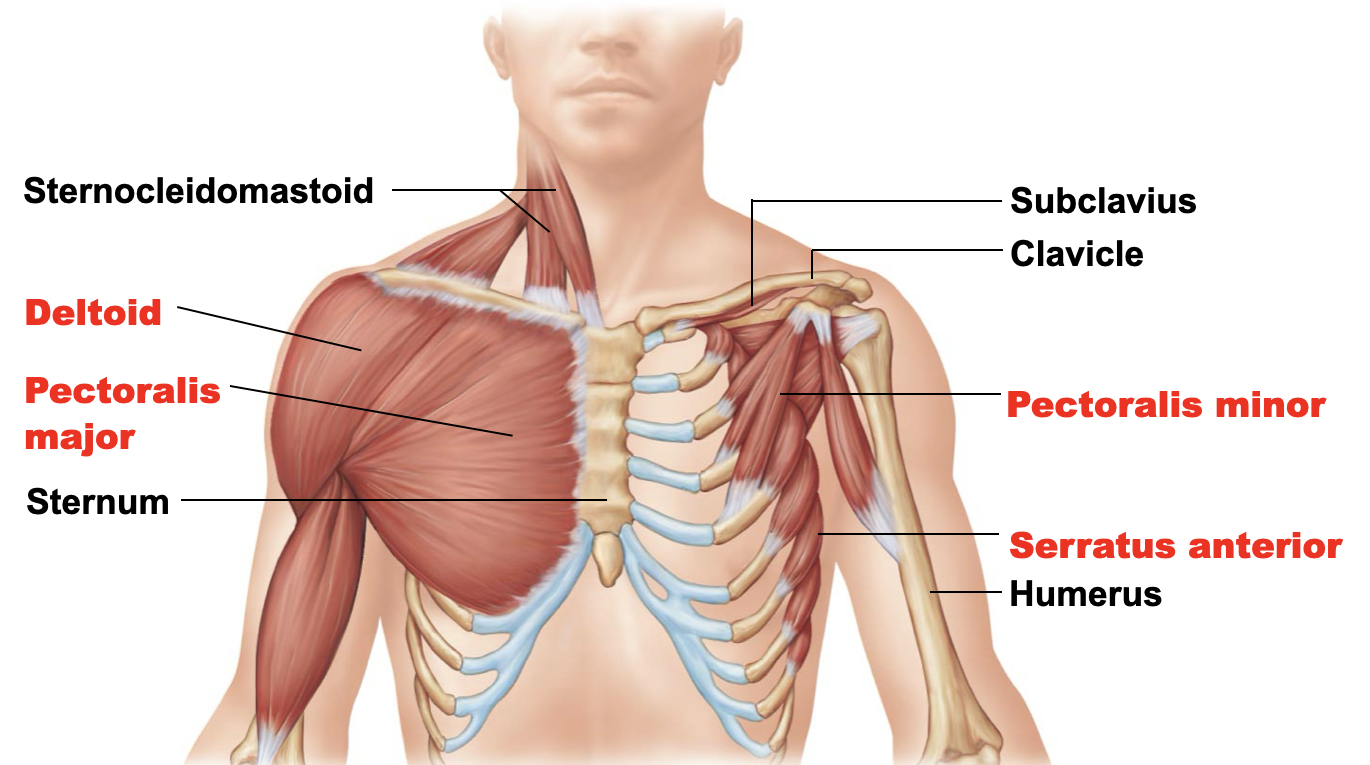
pectoralis major
A: prime mover of arm flexion, adduction, and rotating of the arm
O: portion of the clavicle, sternum, and into costocartilage - possibly down to rib 7
I: intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
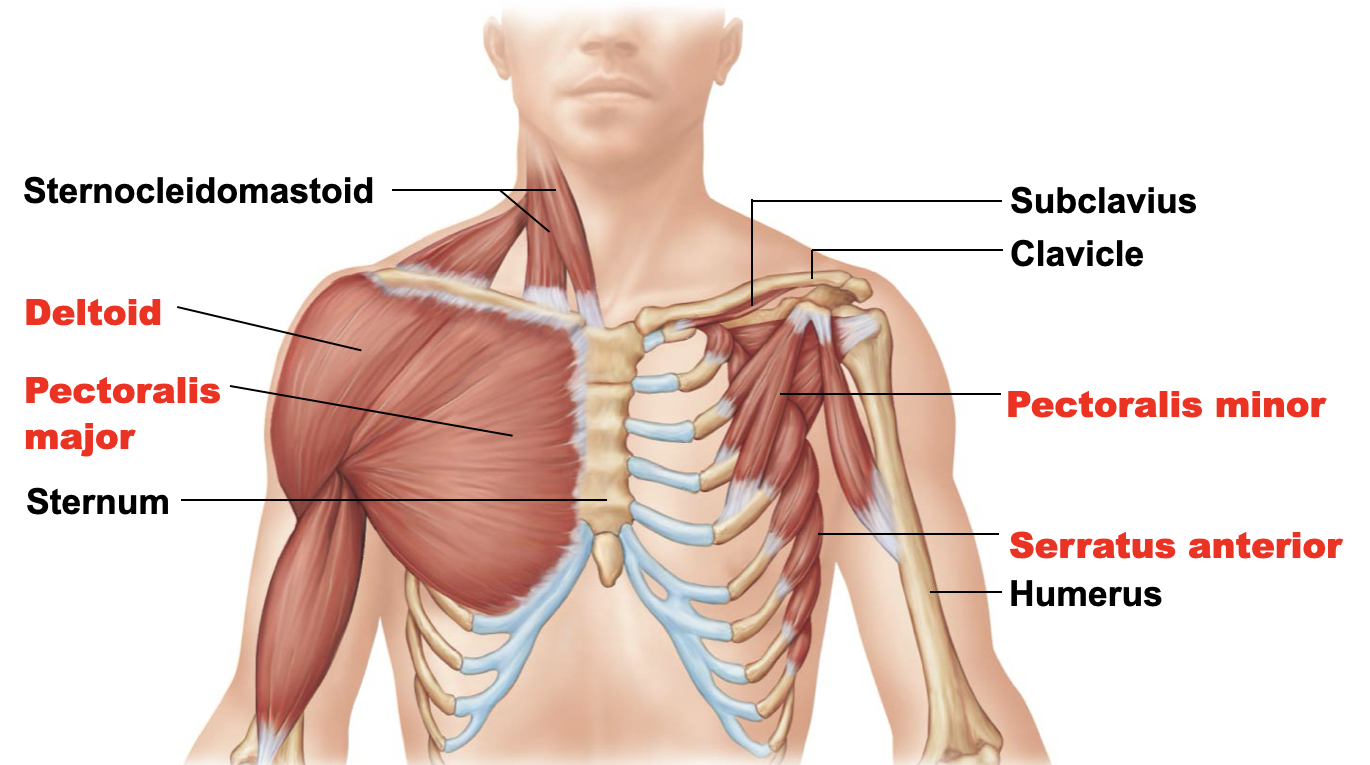
pectoralis minor
A: draw the scapula forward and inferiorly
O: anterior surface of the ribs (3-5)
I: coracoid process of the scapula
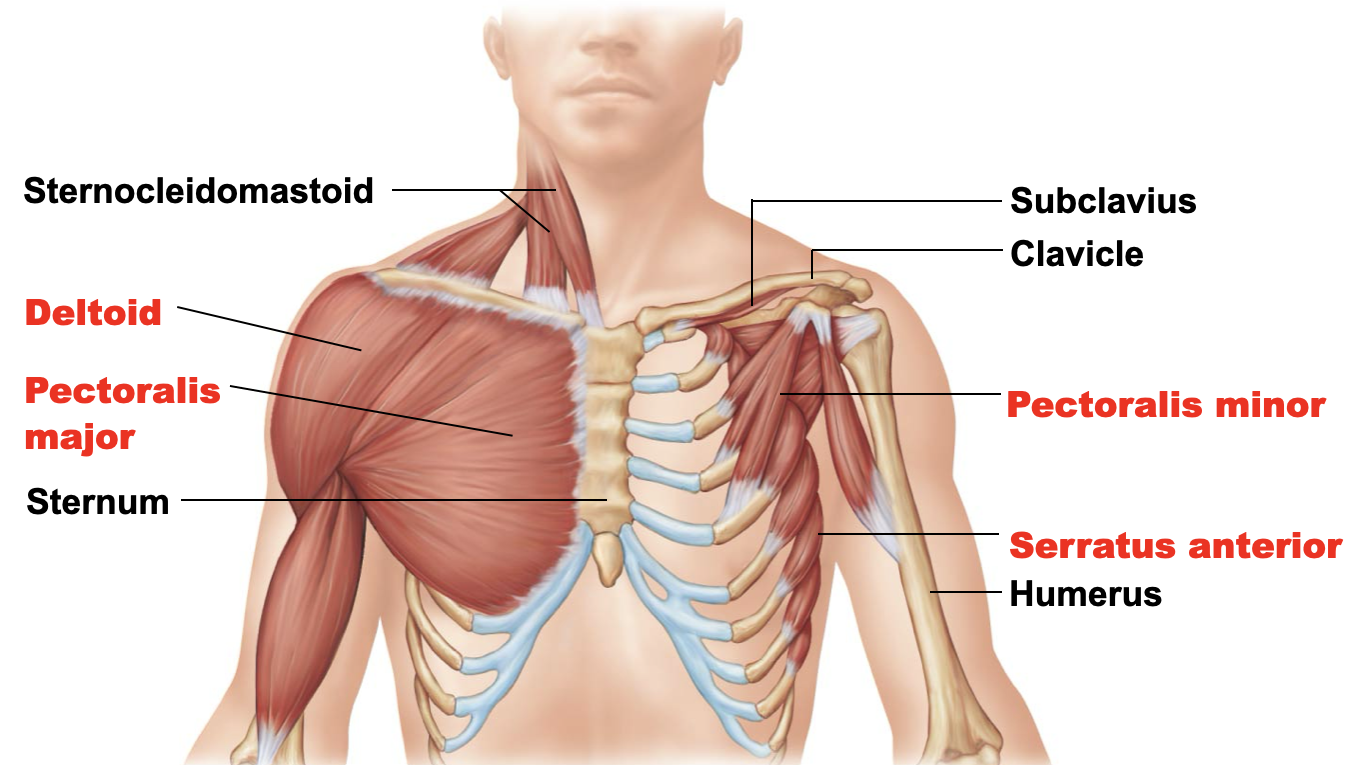
serratus anterior
A: protracts, rotates, and holds the scapula against the wall
O: lateral aspect of the ribs almost to rib 9
I: inferior portion of the medial border of the scapula
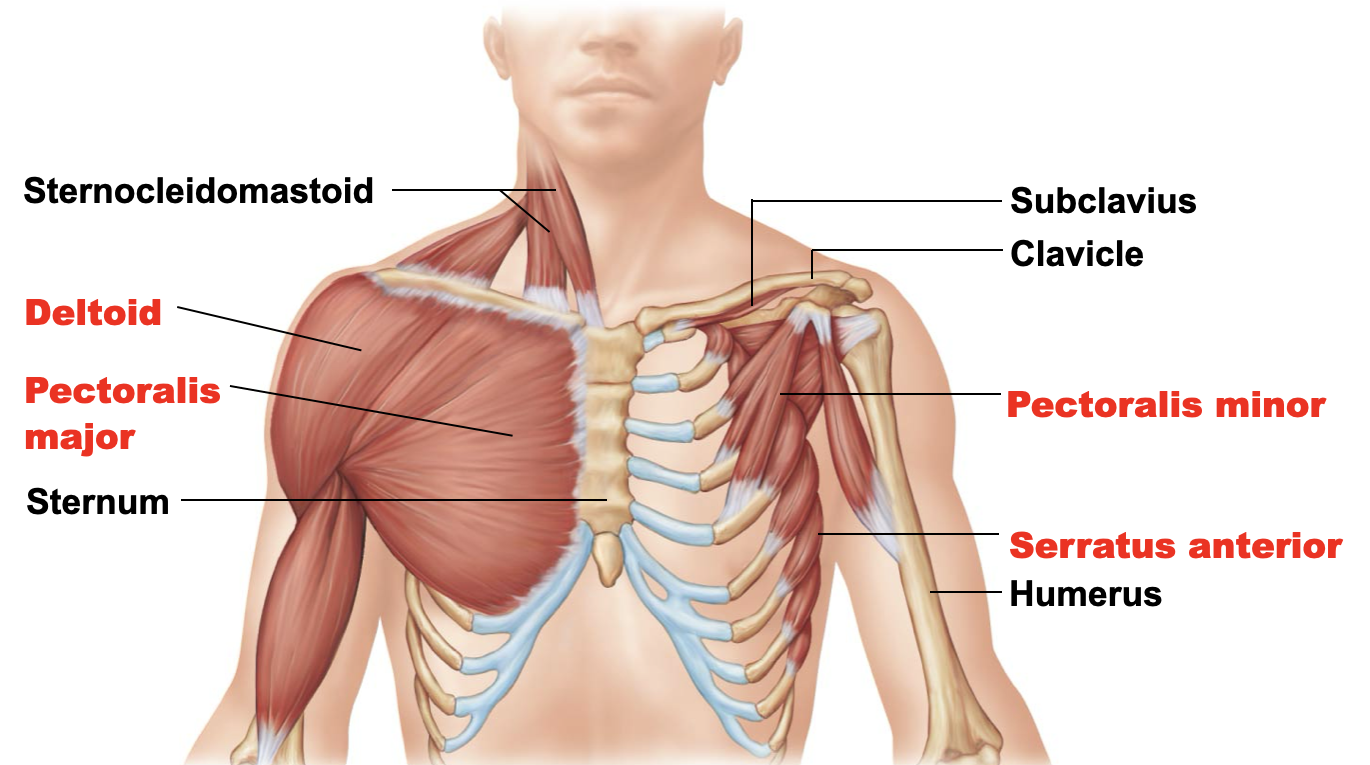
deltoid
A: prime mover of arm abduction
O: lateral ¼ of the clavicle
I: into the posterior side: acromion process and spine of the scapula
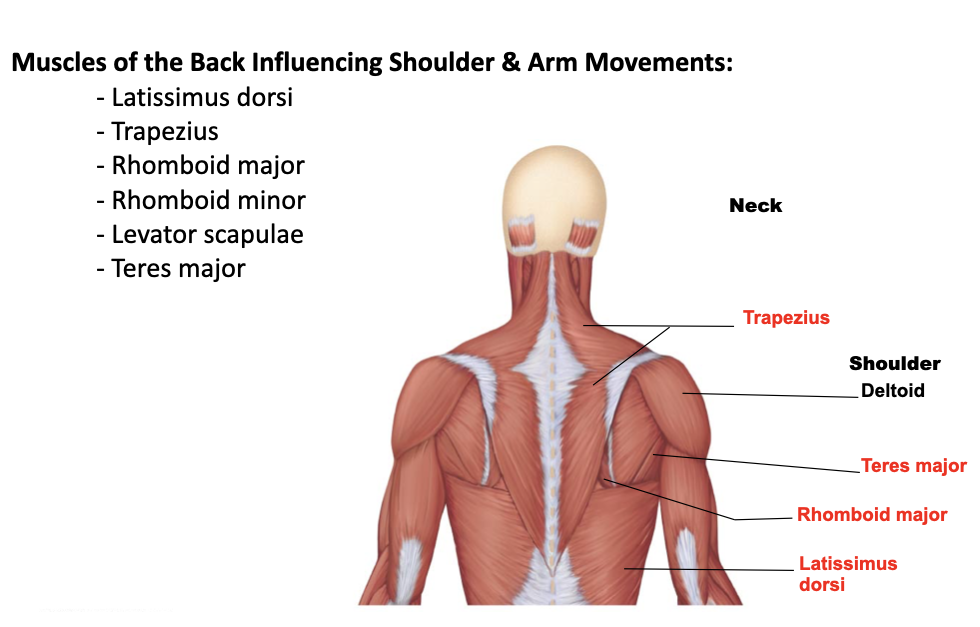
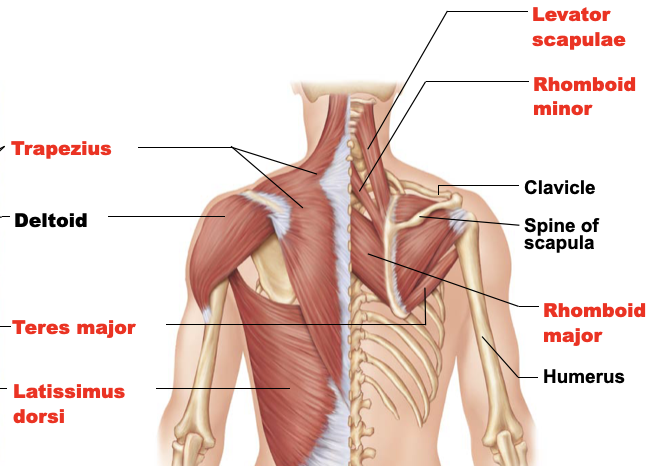
latissimus dorsi
A: adducts the arm, medially rotates, “rowing” and “swimming”
O: indirect attachment to lower 6th thoracic vertebrae and lumbar vertebrae by aponeurosis
I: intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
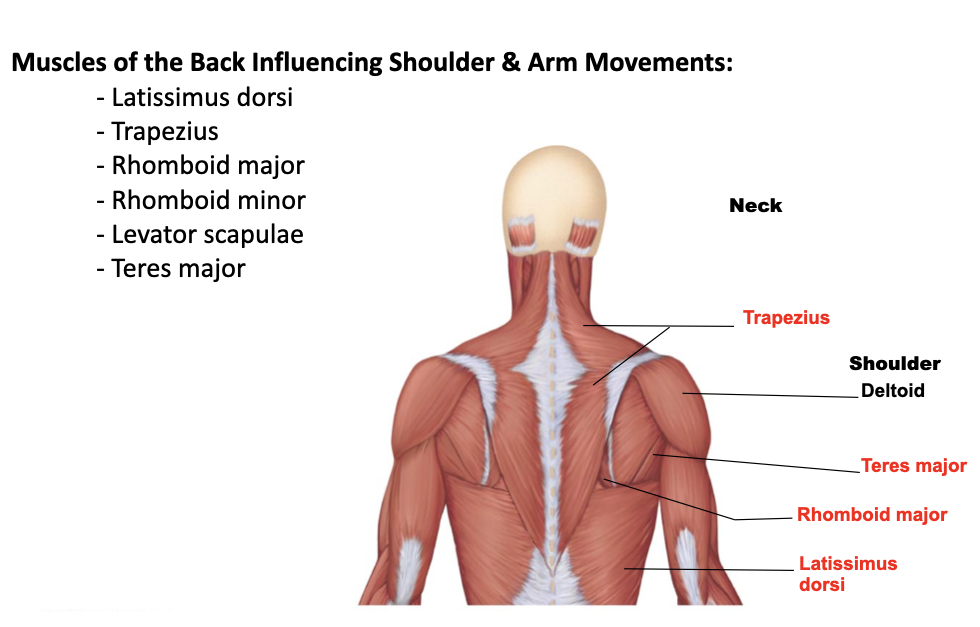
trapezius
A: extends the head, raises, rotates, retracts, and stabilizes the scapula
O: occipital bone, ligament of nuchal (nuchal line down to the vertebral column - C7 to thoracic vertebrae)
I: acromion and spinous process of the scapula and lateral 2/3 of the clavicle
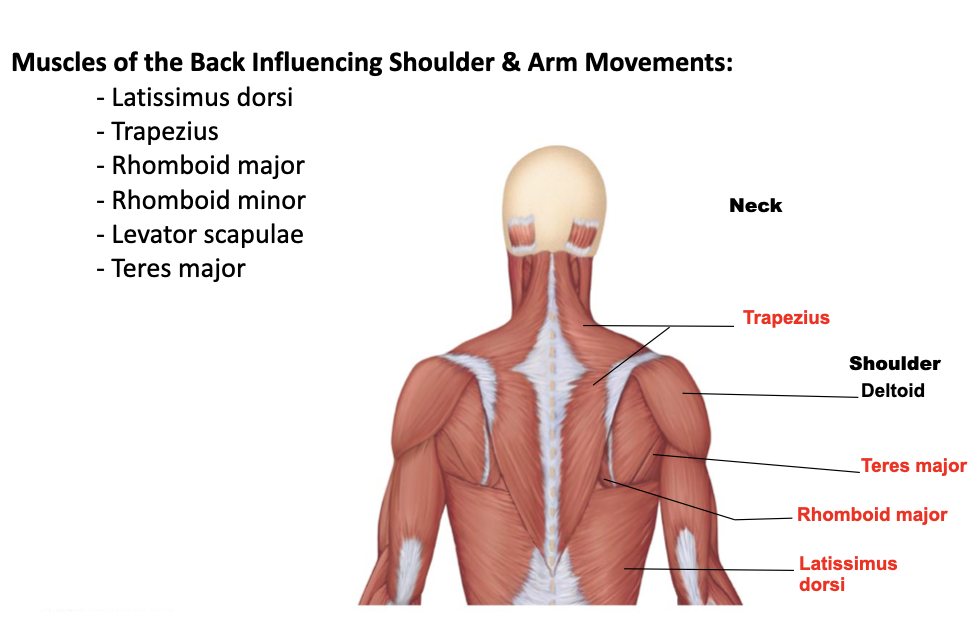
teres major
A: extend, medially rotate, and adduct the humerus
O: posterior surface of the inferior angle of the scapula
I: intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
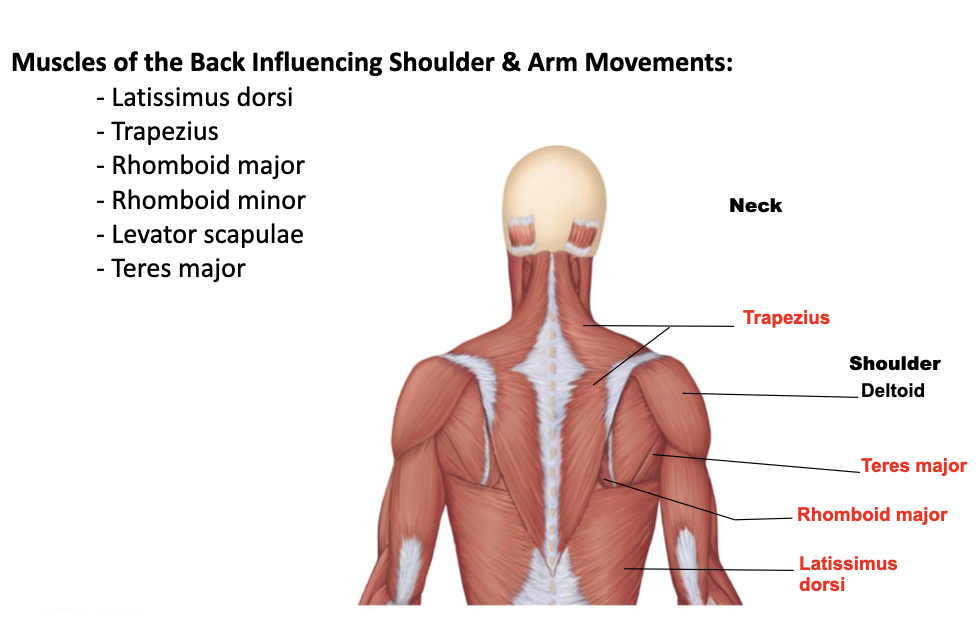
rhomboid major
A: pull the scapula medially and retraction
O: spinous processes of the C7 to T3
I: medial border of the scapula
rhomboid minor
A: pull the scapula medially and retraction
O: spinous processes of C7 to T3
I: medial border of the scapula
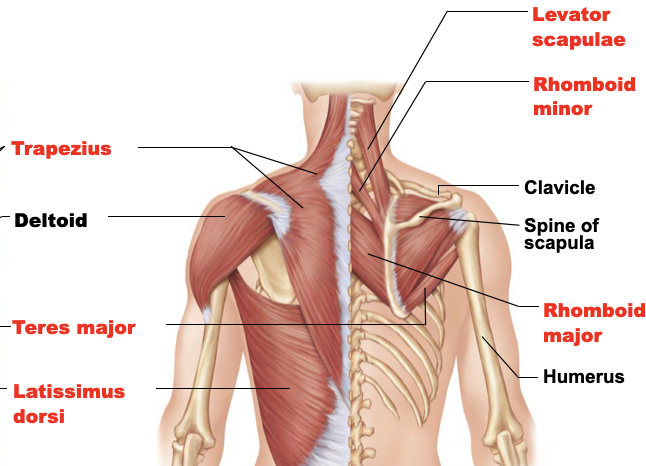
levator scapulae
A: elevate scapula
O: transverse processes of C1 and C4
I: superior portion of the medial border of the scapula
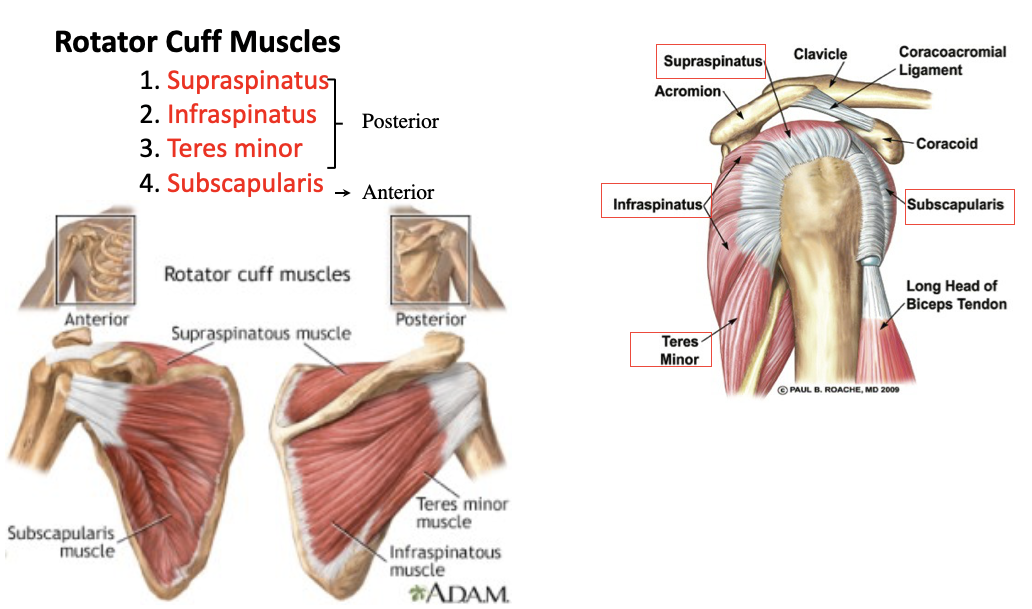
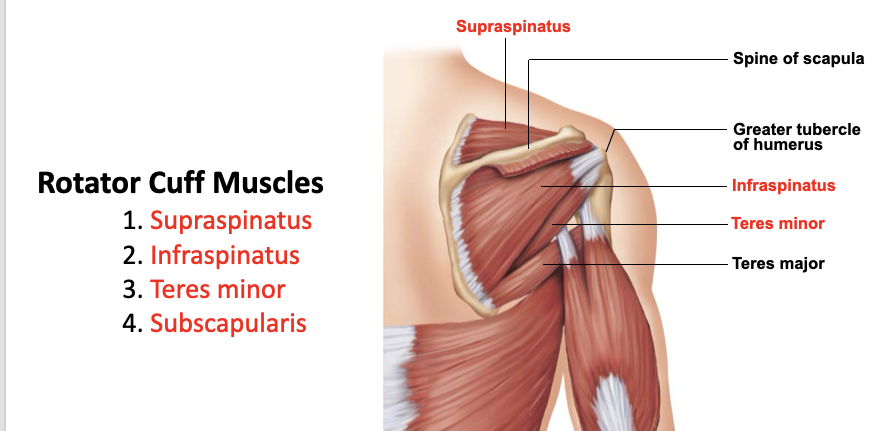
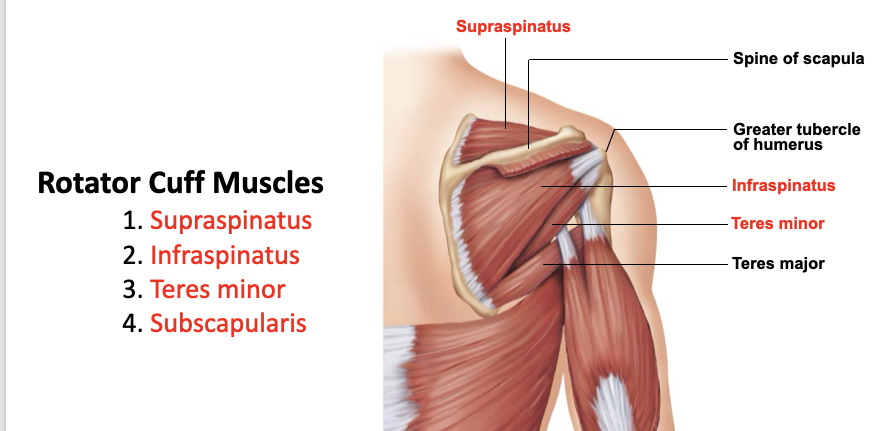
supraspinatus
A: rotation of the humerus and aids in stability
O: supraspinous fossa of the scapula
I: greater tubercle of the humerus
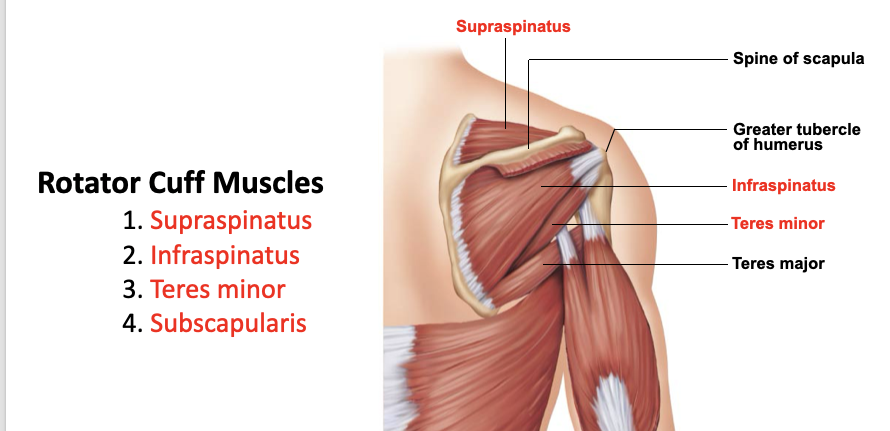
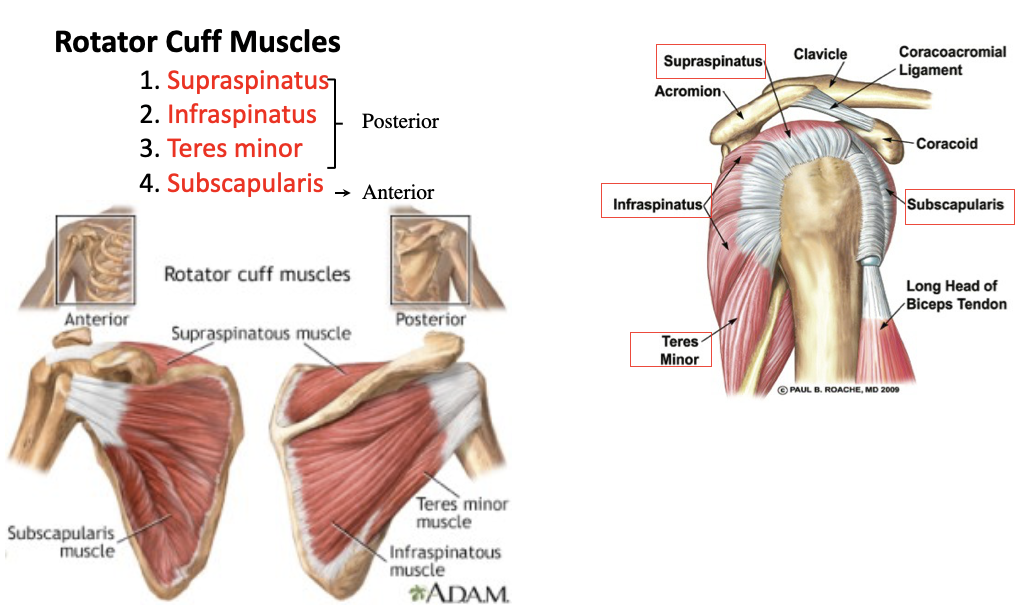
infraspinatus
A: rotation of the humerus and aids in stability
O: infraspinous fossa of the scapula
I: greater tubercle of the humerus
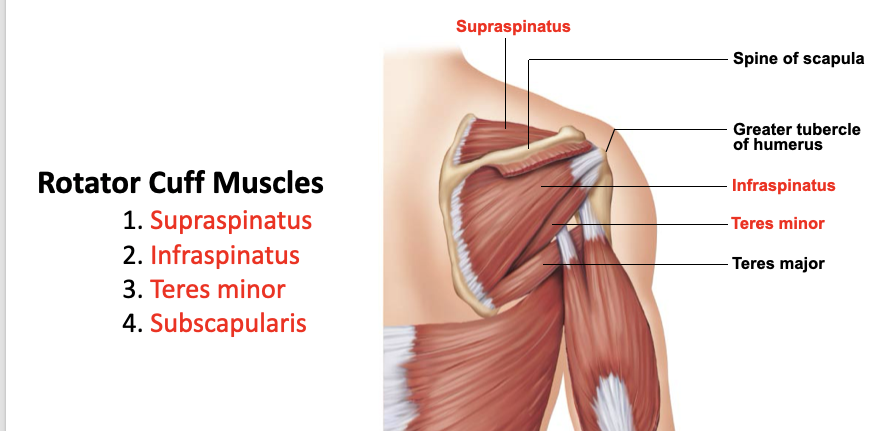
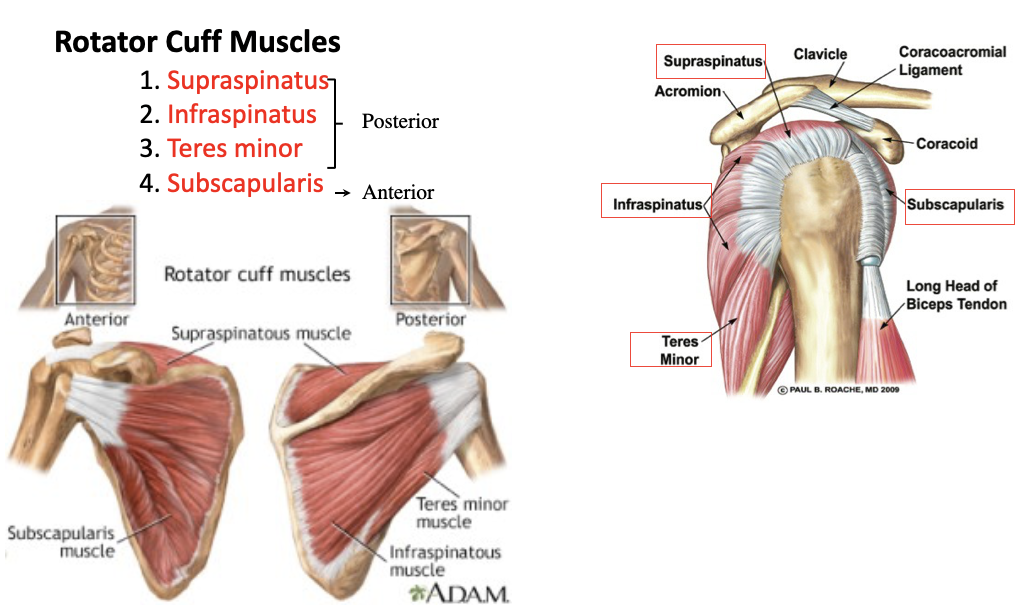
teres minor
A: rotation of the humerus and aids in stability
O: lateral margin of the scapula
I: greater tubercle of the humerus
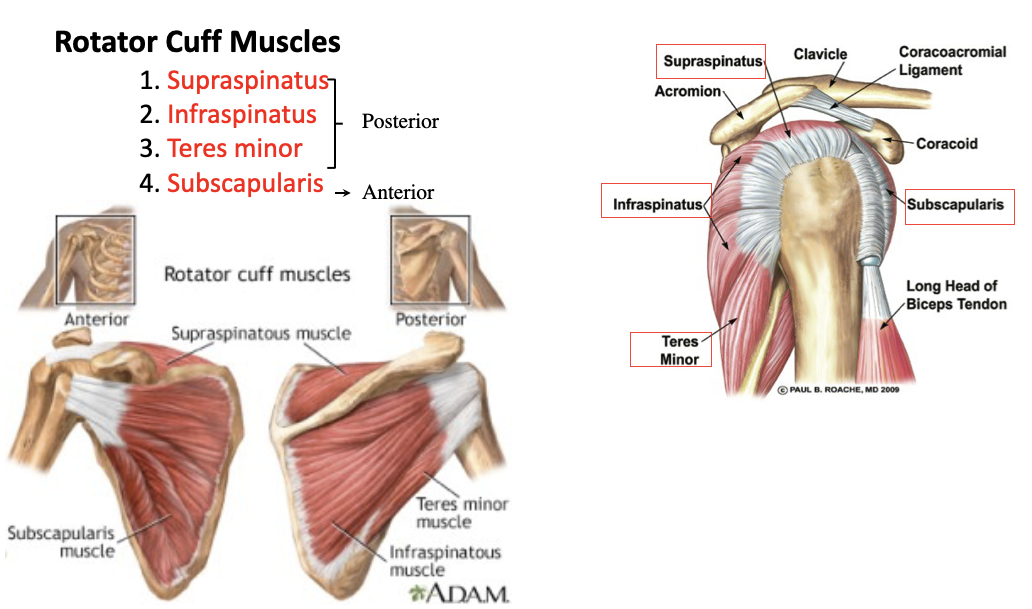
subscapularis
A: rotation of the humerus and aids in stability
O: subscapular fossa
I: lesser tubercle of the humerus
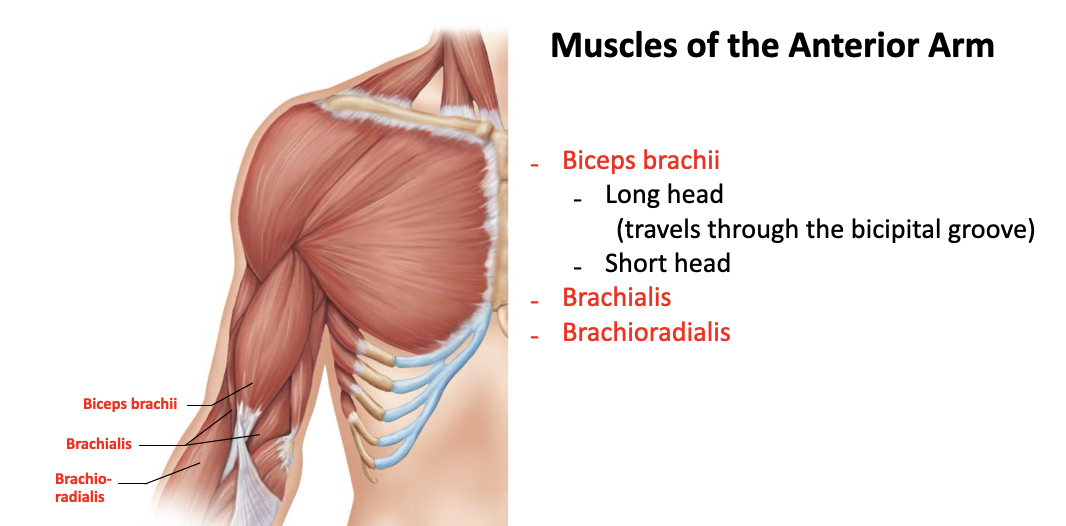
biceps brachii (short/long head)
long head runs through the intertubercular sulcus and is more lateral
short head runs near the coracoid process of the scapula and is more medial
A: flexor of the elbow, supination
O: Short Head - coracoid process
O: Long Head - supraglenoid tubercle and lip of glenoid cavity
I: radial tuberosity
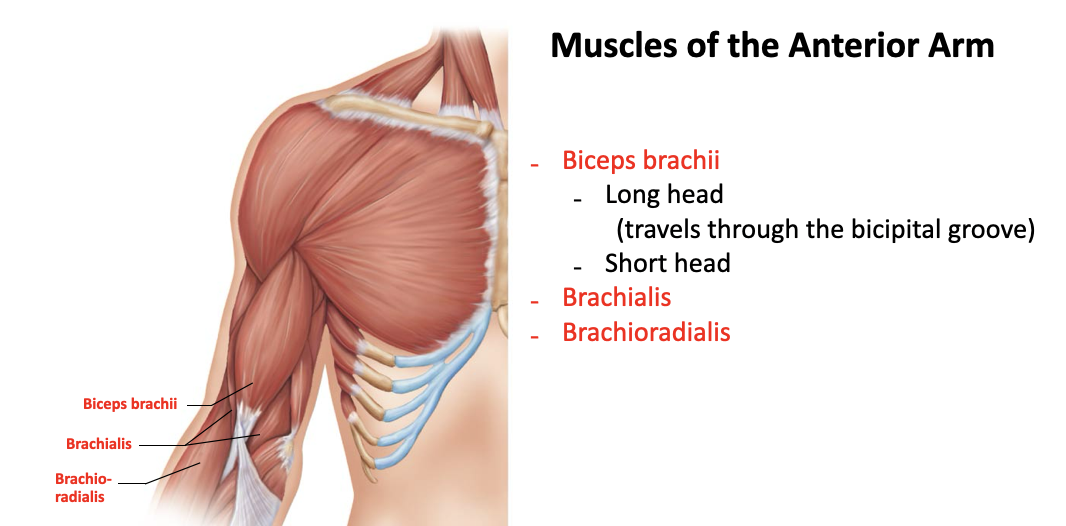
brachialis
A: flexor of the forearm
O: distal portion of the anterior humerus
I: coracoid process of the ulna
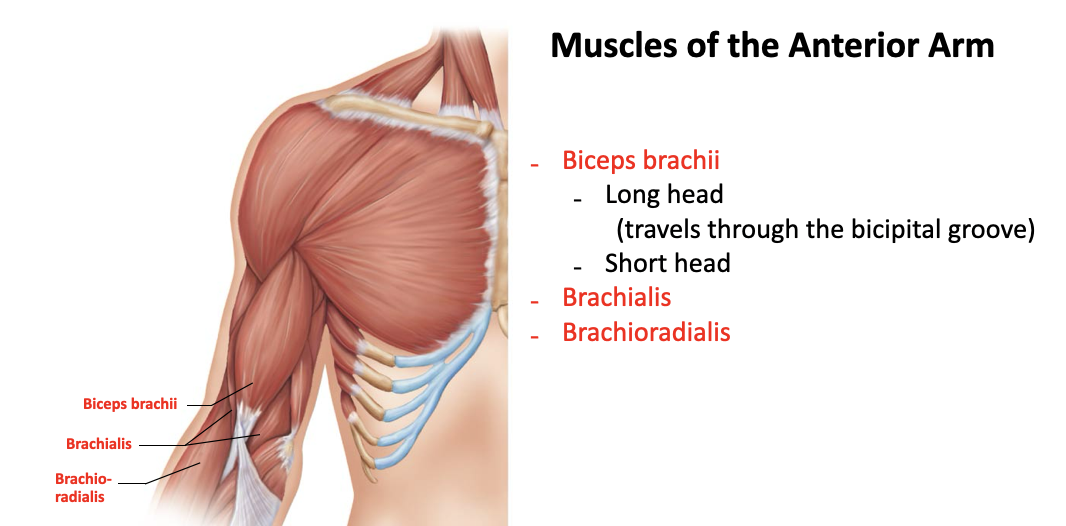
brachioradialis
A: synergist in forearm flexion
O: lateral ridge at the distal end of the humerus
I: base of radial styloid process
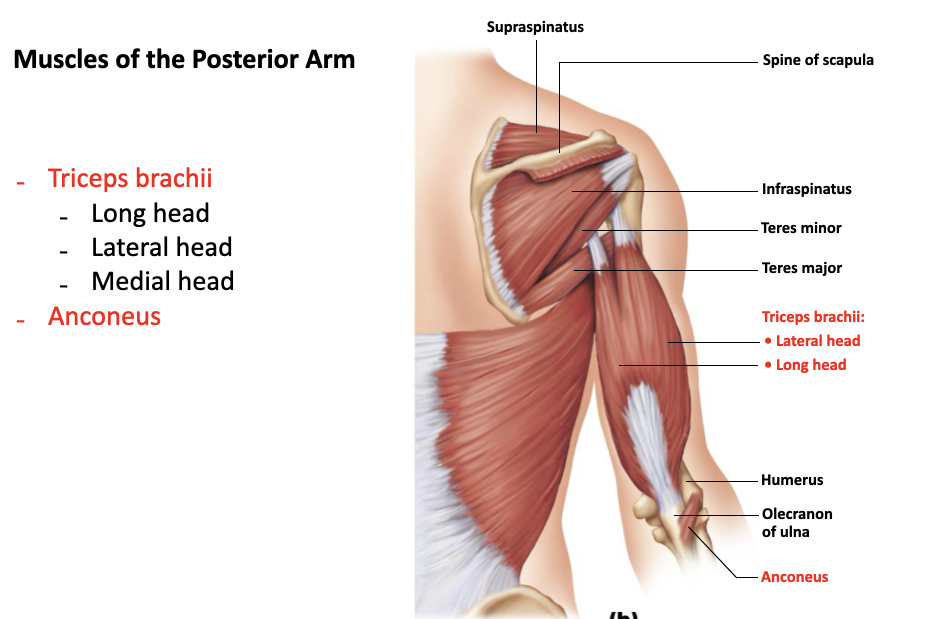
triceps brachii
A: powerful forearm extension, antagonist of forearm flexion
O: long head - inferior margin of glenoid cavity
O: lateral head - posterior humerus
O: medial head - distal radial groove on posterior humerus
I: olecranon of ulna
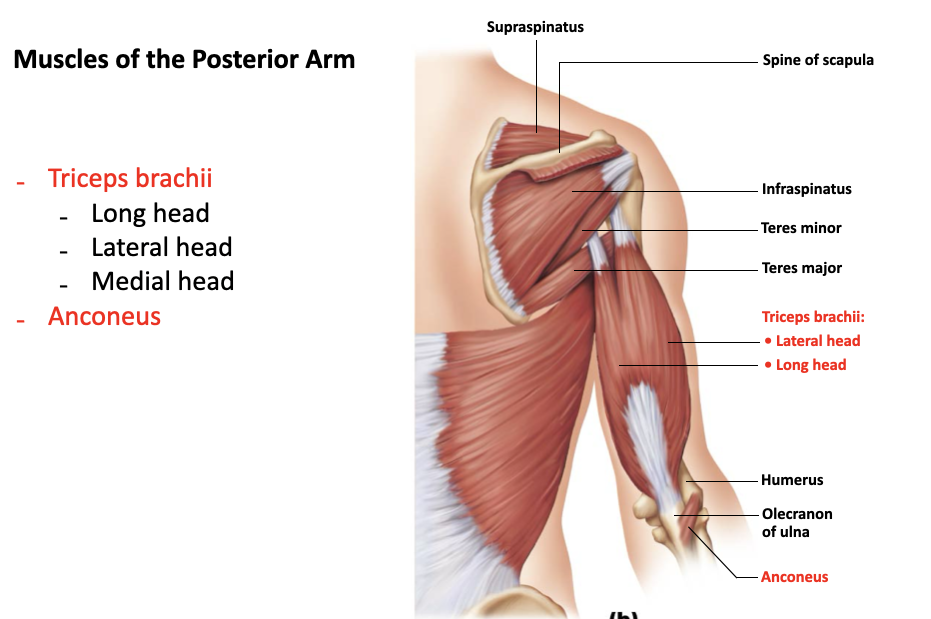
anconeus
A: abducts ulna during forearm pronation
O: lateral epicondyle of humerus
I: lateral aspect of olecranon of ulna
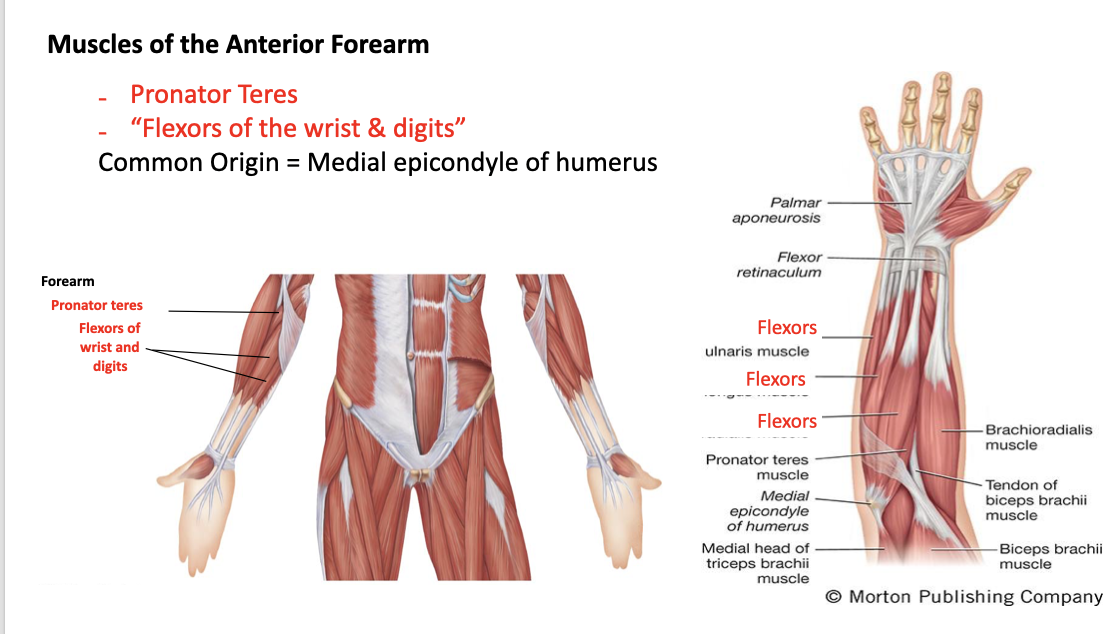
pronator teres
A: synergist with pronator quadratus to pronate the forearm
O: medial epicondyle of the humerus and coronoid process of the ulna
I: midshaft of the radius
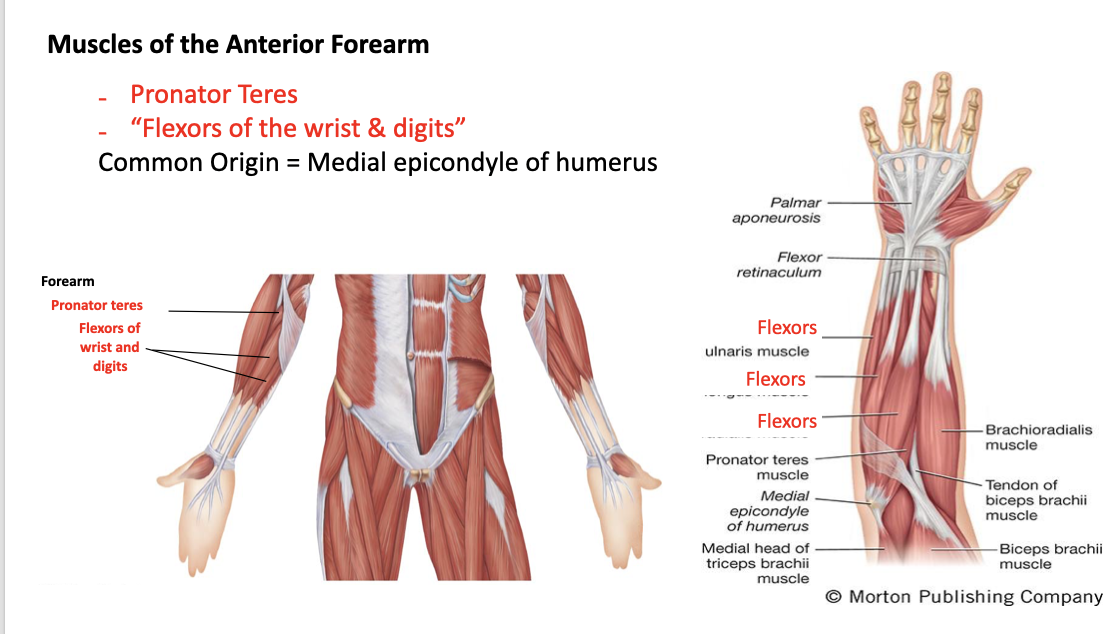
flexors of the wrist and digits
A: flex the wrist and fingers
O: medial epicondyle of humerus
I: many different insertions due to flexion of different fingers and carpals
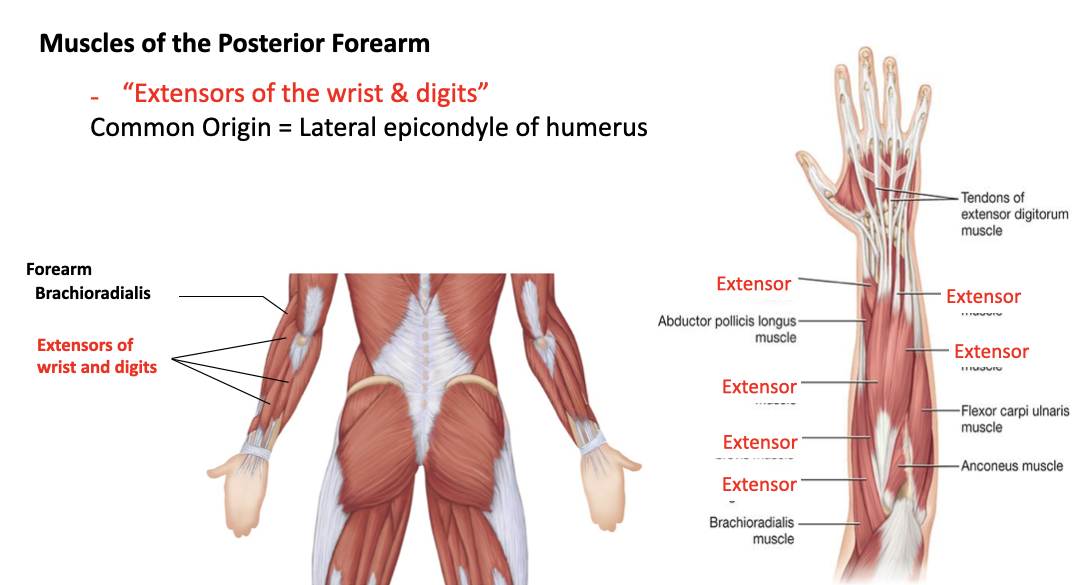
extensors of the wrist and digits
A: extending the wrist and digits
O: lateral epicondyle of humerus
I: many different insertions
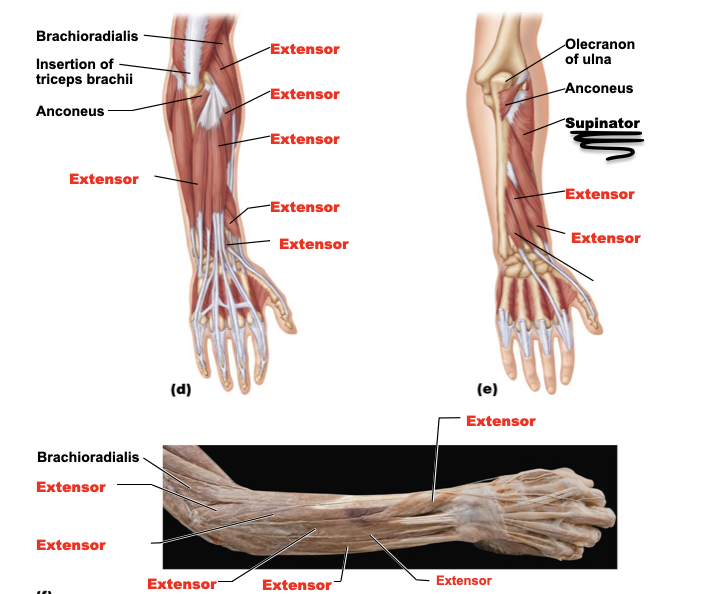
supinator
A: acts with biceps brachii to supinate the forearm
O: lateral epicondyle of the humerus
I: proximal end of the radius