Genetics Final Exam Quick Review
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
How many chromosomes do we have?
46 with 23 pairs
What is our diploid number?
46
What is our haploid number?
23
Meiosis
Reduces amount of genetic material by half
Produces haploid gametes or spores, each containing one member of a homologous pair of chromosomes
Crossing Over/Recombination
Meiotic event
Genetic exchange between members of homologous pairs of chromosomes
Meiosis: When does DNA Replication take place?
S phase
Meiosis: How many times is DNA replicated in a typical cell?
Once
What does Meiosis look like? (what order?)
Stages of Meiosis 1: prophase 1, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, telophase 1
Stages of Meiosis 2: prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase 2
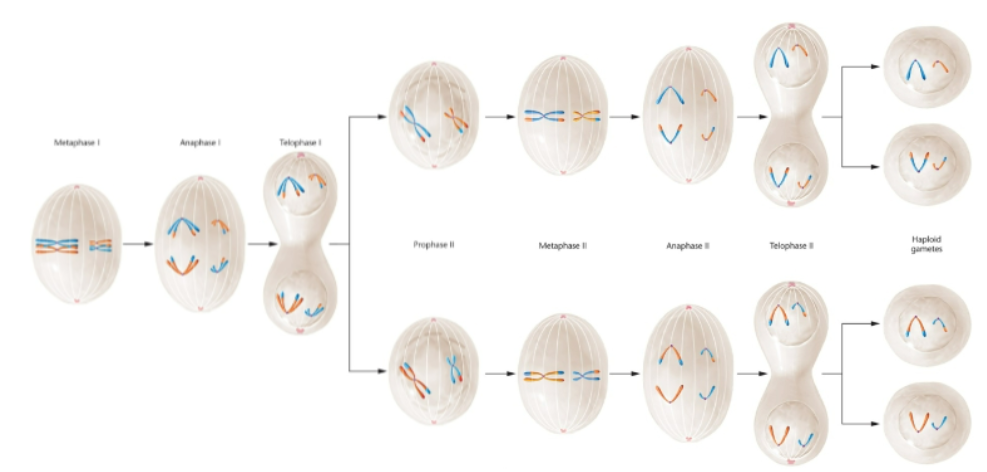
Meiosis: prophase 1
homologous chromosomes pair up (tetrads) and crossing over occurs
Meiosis: metaphase 1
tetrads line up and spindle fibers attach to the centromeres
Meiosis: anaphase 1
chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell
Meiosis: telophase 1
cell divides into 2 haploid daughter cells that each contain one set of chromosomes
Meiosis: prophase 2
chromosomes condense again, spindle fibers form and attach to centromeres
Meiosis: metaphase 2
chromosomes line up along metaphase plate
Meiosis: anaphase 2
sister chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell
Meiosis: telophase 2
cells divide and result in 4 non-identical haploid daughter cells
What is a bivalent?
a pair of homologous chromosomes
When does crossing over occur?
Prophase 1
Does crossing over occur between sister chromatids or non-sister chromatids?
non-sister chromatids
What is a chiasma?
point where two non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes cross and physically link during meiosis
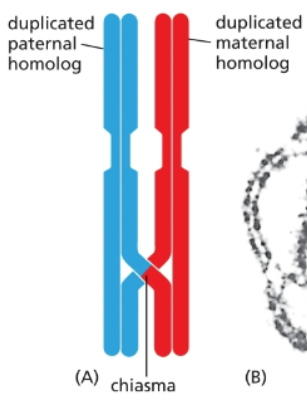
Are genes that are close together more or less likely to have a recombination event occur between them?
Less likely
At the end of mitosis, you end up with _________ daughter cells
two genetically identical
At the end of meiosis, you end up with ___________ cells (gametes).
four genetically unique haploid
What is non-disjunction?
the failure of chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division (meiosis or mitosis), resulting in daughter cells with an abnormal number of chromosomes (aneuploidy)
Exs. Down Syndrome, Turner Syndrome, and Klinefelter Syndrome
What does Mitosis look like? (order?)
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
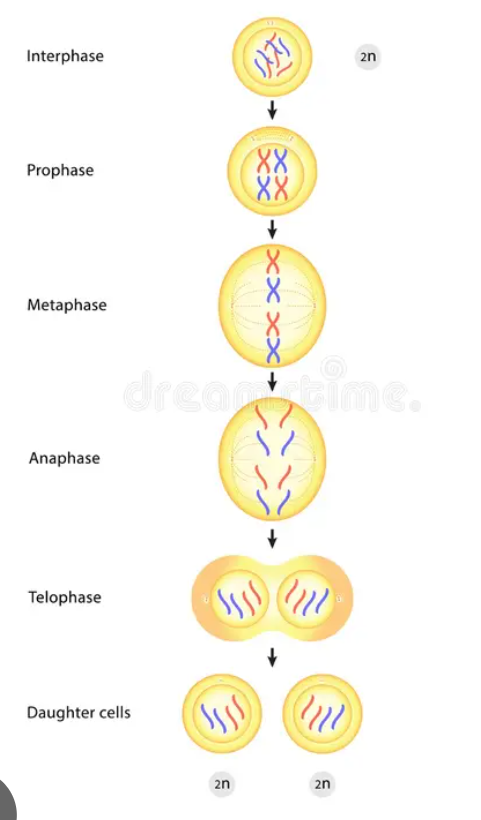
Mitosis: interphase G1 phase
cells grow and synthesize necessary proteins for DNA replication
Mitosis: interphase S phase
DNA is replicated and results in 2 sister chromatids
Mitosis: interphase G2 phase
cells continue to grow and prepare for mitosis
Mitosis: prophase
DNA coils into chromosomes, spindle fibers form
Mitosis: metaphase
chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Mitosis: anaphase
chromosomes are pulled apart
Mitosis: telophase
two new nuclear membranes form around the separated DNA
Mitosis: cytokinesis
cell divides into 2 identical daughter cells
Chromosomes, in diploid organisms, provide…
basis for biparental inheritance
Alleles
different versions of genes
Particulate unit factors (genes)
Basics of heredity
Passed unchanged from generation to generation
Determine various traits expressed by each individual plant (Mendel)
Mendel’s Postulates
Unit factors exist in pairs
Dominance/Recessiveness
Segregation
2 copies of each gene, one from mom, one from dad
genes exist as alleles- one can be dom and another recessive
alleles segregate independently (bc chromosomes segregate independently)
What is a genotype?
an organism's complete set of inherited genetic instructions (DNA), often described as the specific combination of alleles (gene versions) for a particular trait
What is a phenotype?
the observable physical or functional trait that results from the genotype interacting with the environment
What does homozygous mean?
having two identical alleles (gene versions) for a specific trait, one inherited from each parent (DD, dd)
What does heterozygous mean?
having two different alleles of a particular gene or genes. (Dd)
What is the typical F2 phenotypic ration for a monohybrid cross?
3:1
How is a dihybrid cross different from a monohybrid cross?
A monohybrid cross studies inheritance of a single trait, while a dihybrid cross studies two traits simultaneously
What kind of bonds form the sugar phosphate backbone of DNA?
Phosphodiester bonds (covalent)
What kind of bonds form between bases on opposite strands?
Hydrogen Bonds
What are the 4 bases of DNA and RNA?
ATGC
AUGC
What bases complement and bond?
A - T(or U) and G - C
What base pair forms the stronger bond?
G - C (three hydrogen bonds)
DNA has polarity, runs in 5’ to 3’ direction. Do you remember what
gives it that polarity?
Because DNA is negative it runs towards the positive
Do the two strands run parallel or antiparallel?
antiparallel
Are the two DNA strands complementary or identical?
complementary
What is a nucleosome?
the fundamental building block of chromatin, consisting of a segment of DNA tightly wrapped around a core of eight histone proteins (an octamer), resembling "beads on a string" and allowing DNA to be efficiently packaged within the cell's nucleus
What are histones?
any of a group of basic proteins found in chromatin
When in the cell’s life is DNA highly compacted and when is it relaxed?
Compacted: Cell Division
Relaxed: Interphase
What modifications make DNA more compact? Relaxed?
Compact: involves histone methylation (H3K9me, H3K27me) and DNA methylation, creating dense heterochromatin
Relaxed: occurs via histone acetylation, phosphorylation (like KAP-1), and removal of methyl marks, loosening chromatin (euchromatin) for gene access
Are chromosomes completely uniform?
No, they vary in size
What makes up the bulk of our chromosomes?
long strand of DNA tightly wrapped around spool-like proteins called histones, forming structures called nucleosomes that coil further into chromatin, and finally condense into visible chromosomes during cell division
What is PCR?
Polymerase Chain Reaction
uses heat instead of helicase to separate DNA to find genetic sequences
What is the enzyme used in PCR?
Taq DNA Polymerase
How is PCR different from replication in the cell?
(in vitro) selectively amplifies specific DNA segments using temperature cycles and Taq polymerase
What are primers and how do they work?
short, synthetic DNA sequences that act as starting points for DNA copying, binding to opposite ends of a target DNA segment, while the DNA polymerase enzyme extends from their 3' ends to create new, complementary strands, exponentially amplifying the desired DNA sequence
What is epistasis?
masking the expression of one or more genes (non-mendelian inheritance)
Ex. Auguti
What is codominance?
when both alleles in a heterozygote are fully and separately expressed (like AB blood type)
What is incomplete dominance?
when the heterozygous phenotype is a blend or intermediate of the two homozygous parents (like red and white flowers making pink flowers)
Multiple alleles
occur when a gene has more than two versions (alleles) in a population (ABO blood group system)
Lethal alleles
mutated gene versions that cause an organism's death, usually early in development, by disrupting essential functions
Ex. Huntington’s Disease
Gene Linkage
the tendency for genes located close together on the same chromosome to be inherited together (less likely separated by crossing over)
Sex linkage
genes located on the sex chromosomes (X or Y) that are inherited along with them, causing a trait to be expressed differently in males and females
What is the enzyme that copies the DNA?
DNA Polymerase
What are primers in DNA Replication?
short, single-stranded DNA or RNA pieces that provide a crucial starting point for DNA polymerase to synthesize new DNA, acting like "platforms" that bind to a specific template sequence to kick off replication
DNA Replication: What is the enzyme that makes primers?
DNA Primase
How is the double helix unzipped?
Helicase
What are Okazaki fragments?
short, newly synthesized DNA segments that form on the lagging strand during DNA replication
What enzyme joins the Okazaki fragments?
DNA Ligase
What is the central dogma?
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
Does the double helix need to be unzipped for transcription?
Yes
What enzyme makes mRNA?
RNA Polymerase
Does transcription require primers?
No because RNA polymerase can initiate RNA synthesis directly from a DNA promoter sequence.
What is the job of the general transcription factors? (GTFs)
are crucial proteins that help start gene transcription by assembling a complex at a gene's promoter, guiding RNA polymerase II (Pol II) to the correct starting point on the DNA, unwinding the DNA, and stabilizing the entire initiation machinery, ensuring genes are accurately and efficiently turned "on" to make RNA
What is a promotor?
a specific DNA sequence, usually upstream of a gene, that acts as the "on switch" and binding site for RNA polymerase and transcription factors, telling them where to start making an RNA copy (transcription) of the gene, thus controlling its expression
Where is the TATA box?
Promoter region, 25-35 bp
What are the 3 major mRNA modifications that occur before an mRNA leaves the nucleus and can be translated?
5' capping, 3' polyadenylation, and RNA splicing
What are exons and introns?
intron - non-coding, does not get translated
exon - coding, gets translated
What is a codon?
a sequence of three consecutive nucleotides (bases like A, U, G, C) in a DNA or RNA strand that acts as a code unit, either specifying a particular amino acid (the building block of proteins) or signaling the start or end of protein synthesis
What’s the start codon?
AUG
What are the stop codons?
UAA, UAG, and UGA
Some can some can’t (crucial modifications on 5’ cap)
What is the organelle that does translation?
Ribosome
What makes up this organelle? (ribosome)
rRNA and various proteins
What kind of bond connects amino acids in the growing polypeptide
chain?
Strong Peptide Bonds
What adaptor molecule brings the amino acid to the mRNA?
tRNA
Aminoacyl synthetases attach amino acids to these adaptor
molecules. How many synthetases are there?
20
What is a frame shift?
a genetic mutation caused by adding or removing nucleotides (bases) in a DNA sequence that are not in multiples of three, shifting the entire "reading frame" for the ribosome, leading to completely different, often non-functional, proteins downstream from the mutation
What is a transcription factor?
proteins that control gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences and regulating when and how genes are turned on or off
Describe enhancers vs activators
Enhancers - DNA sequences that boost gene expression
Activators - the proteins that bind to enhancers (or promoters) to make this happen
Describe silencers vs repressors (regulatory proteins)
Repressors - proteins that bind to DNA (operators/silencers) to block RNA polymerase, turning genes off, like in the lac operon.
Silencers - specific DNA sequences, often distant from the gene, that act as binding sites for these repressor proteins, causing long-range looping to inhibit transcription, effectively reducing or stopping gene activity in eukaryotes
Are enhancers and silencers always close to the promoter in eukaryotes?
No
Do eukaryotes have operons?
No, usually in prokaryotes
What is an operon?
“genetic switch”
a functional unit of DNA in prokaryotes (like bacteria) containing a cluster of related genes, a single promoter, and an operator, all controlled by one regulatory mechanism, allowing the cell to turn these genes on or off together for efficient resource management, like when processing a specific food source
What histone modification is likely to increase gene expression?
acetylation