anaerobic respiration/fermentation
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
when does fermentation occur
oxygen is unavailable
fermentation — what does it begin and end with
begin → glycolysis, end → when NAD+ generated
where does fermentation and aerobic respiration mainly differ
ETC because no oxygen available → can’t pass down to final electron receptor and causes NADH buildup → NAD+ shortage
2 main types of fermentation
alcohol & lactic acid
alcohol fermentation steps
conversion of pyruvate → 2-carbon acetaldehyde molecules → converted to ethanol, regeneration 2 NAD+ molecules in the process
3 things produce ethanol
yeast, fungi, bacteria
lactic acid steps
pyruvate directly reduced to lactate by NADH to regen NAD+ needed for resumption of glycolysis
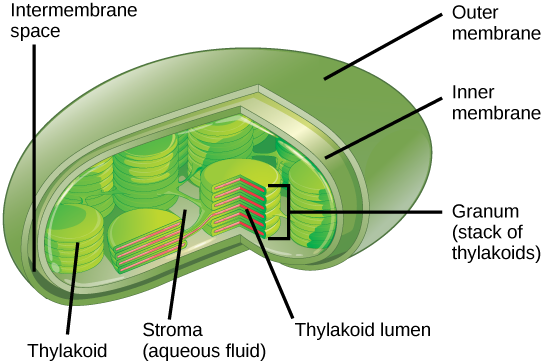
where does the 1st stage of photosynthesis occur
stroma → thylakoid membrane system
bundle sheath cells
cells that are tightly wrapped around the veins of a leaf. Site for Calvin cycle in C4 plants
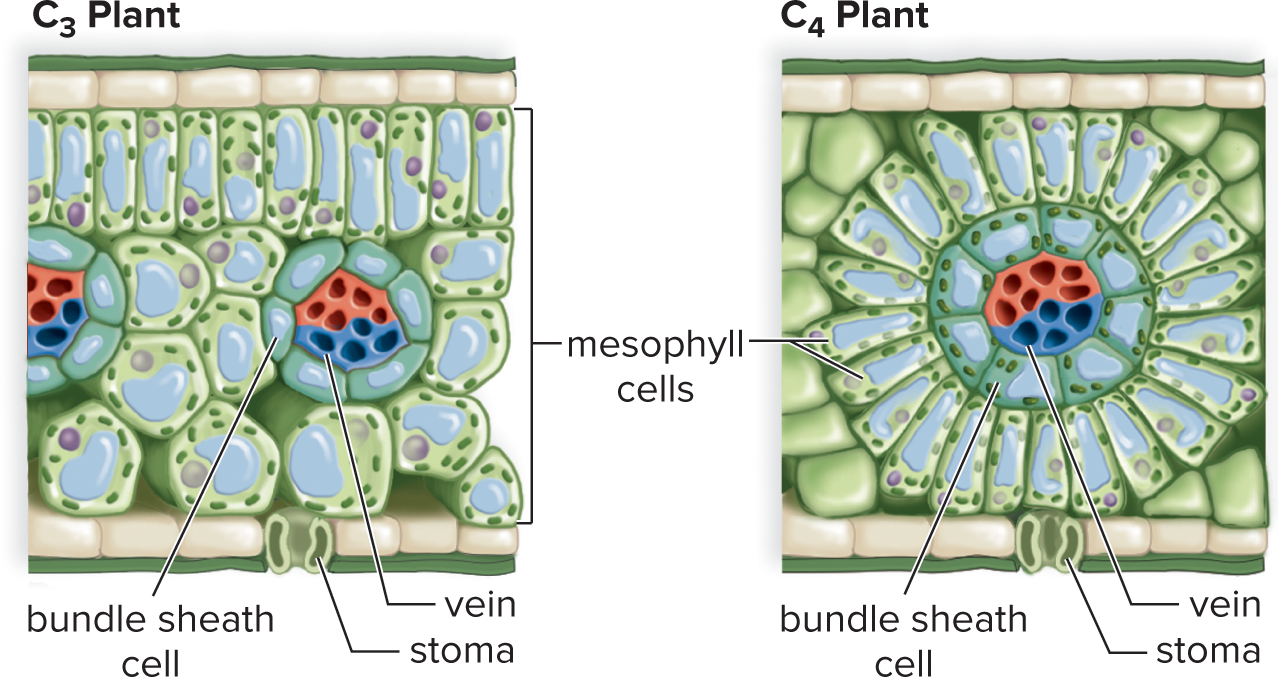
C4 plant
plant has adapted its photosynthetic process to more efficiently handle hot & dry condition
mesophyll
interior tissue of a leaf
photolysis
water is broken up by an enzyme into hydrogen ions and oxygen atoms → occurs during light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
photophosphorylation
ATP is produced during the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis. Chloroplast equivalent of oxidative phosphorylation
photorespiration
oxygen competes with CO2 and attached to RuBP
photosystem
cluster of light-trapped pigment involved in the process of photosynthesis. Photosystems vary tremendously in their organization and can possess hundreds of pigments. 2 most important systems = I & II of light reactions
pigment
a molecule that absorbs light of a particular wavelength. Pigments are vital to the process of photosynthesis and include chlorophyll, carotenoids, phycobilins
rubisco
enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the Calvin cycle in C3 plants
stomata
structure through which CO2 enters a plant and water vapor and O2 leave
transpiration
natural process by which plants lose water via evaporation through their leaves
photosynthesis 2 sets of reactions
light-dependent & light-INDEPENDENT reaction
light-dependent reactions (noncyclic)
starts in thylakoid system
pigments of thylakoid sys. organize themselves into photosystems (varying combos of chlorophyll a&b, phycobilins, carotenoids)
light excites photosystem, absorbing the photon and transmits energy (losing E with each step) eventually reaching chloro a → 1st step of photosynthesis
TL;DR passing electron to primary electron receptor aka chloro a
As light strikes photosystem 2, energy is absorbed and passed along until it reaches P680 chlorophyll. When it’s excited it passes electrons to primary electron acceptor
2 chlorophylls
chlorophyll a - major pigment of photosynthesis
chlorophyll b - accessory pigment → help pick up light when chloro a can’t do it effectively
light-dependent reactions pt 2. (noncyclic)
photolysis in thylakoid space takes electrons from H2O and passes them to P680 to replace the electrons given to the primary acceptor
this reaction causes lone oxygen atom and pair of hydrogen ions. Lone oxygen atom quickly finds another oxygen buddy & pairs with it, creating O2 → FIRST PRODUCT OF THE LIGHT REACTIONS
light-dependent reactions pt 3 (noncyclic)
as electrons are passed from P680 to P700, lost energy is used to create ATP (chemiosmosis) → 2nd product of light reactions via photophosphorylation
after P700 electrons are excited, it passes the energy to its own primary electron acceptor, which are sent down to another chain to ferridoxin, donating the electrons to NADP+ to make NADPH → 3rd and final product of light reaction
inputs to light reactions
water and light
light reactions produce 3 products
ATP, NADPH, O2
oxygen produced in light reactions comes from…
WATER NOT CO2
the 2 reaction centers
photosystem I & II (P700, P680 respectively)
cyclic pathway only uses photosystem I or II
photosystem I
why is cyclic pathway cyclic
electrons pass down the electron chain and eventually back to P700. Energy given off is used to make ATP. O2 and NADPH is not produced
important for Calvin cycle
how is ATP formed in this process
as electrons are passing form the primary electron acceptor to the next photosystem, H ions are picked up from outside the membrane and brought back to the thylakoid
creates H+ gradient similar to ox-phos
when H ions are taken from water during photolysis, the proton gradient grows larger, causing some protons to leave → forms ATP
inputs into Calvin cycle
NADPH (provides hydrogen and electrons)
ATP (provide energy)
CO2
where calvin cycle occurs
stroma of chloroplast (fluid around thylakoid aka poker chips)
beginnng of calvin cycle
carbon fixation — binding of carbon from CO2 to a molecule that can enter the Calvin cycle (usually RuBP)
reaction is assisted by the rubisco enzyme
6-carbon molecule breaks into 2 3-carbon molecules, 3PG
ATP & NADPH donate phosphate group & hydrogen electrons to 3PG, making G3P
most G3P converted into RuBP
remaining G3P is used to make carbs for plant
in calvin cycle, which is used more, ATP or NADPH
ATP → creates need for cyclic photophosphorylation
the carbon of the sugar produced in photosynthesis comes from the [__] of the calvin cycle
the carbon of the sugar produced in photosynthesis comes from the CO2 of the calvin cycle
transpiration
natural process by which plants lose water by evaporation from their leaves → close stomata to conserve water during high temps
photorespiration
excess oxygen competes with CO2 & attached to RuBP → formation of 1 molecule of PGA & 1 phosphoglycolate
what happens to plants that experience photorespiration?
lowered capacity for growth → sugar formed in photosynthesis comes from PGA, not phosphoglycolate
C4 photosynthesis
converts CO2 into 4-carbon molecule (oxaloacetate) in the mesophyll cells
converts that product to malate
takes the malate into the bundle sheath cells
malate releases CO2, which reacts w/ rubisco to make carbohydrate
CAM photosynthesis
plants close their stomata during the day, collect CO2 at night, and store CO2 in the form of acids until needed during the day for photosynthesis