2 - Facies and Facies Associations
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is the definition of facies?
Facies: a body of sediment or rock characterised by a particular combination of lithological, physical and biological characteristics that distinguishes it from units above, below or adjacent to it.
What descriptors are used for facies
Grain type and composition
Texture (grain size, sorting, roundness)
Sedimentary structures
Colour
Biological structures and content (traces fossils, body fossils)
Describe this facies:
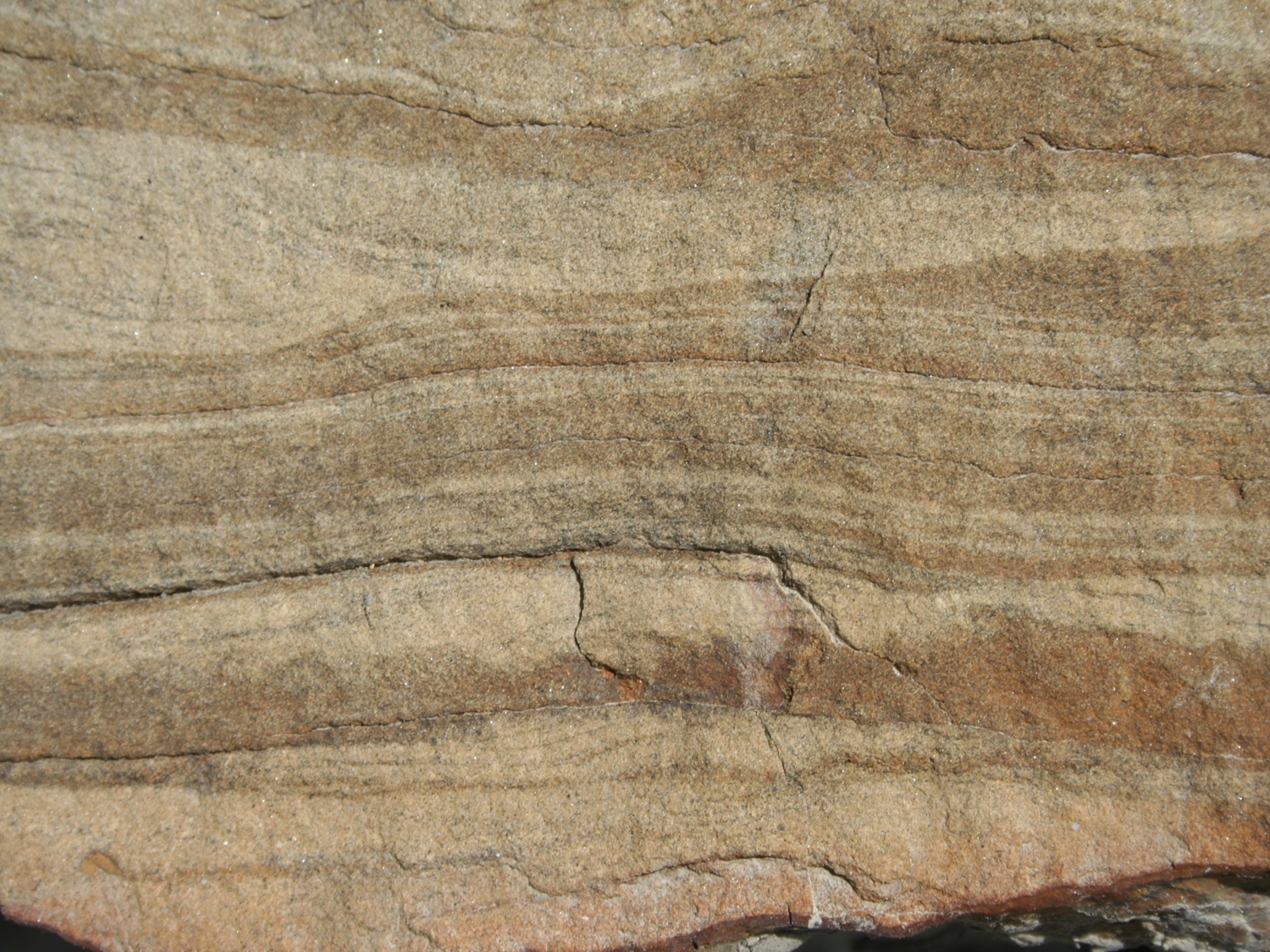

Grain type and composition
Quartz, feldspar, mica (sandstone)
Texture
Fine sand <125Mu, well sorted, well rounded
Sedimentary structures
Plane-parallel lamination
Ripple cross lamination
Colour
Beige-brown layers
Biological structures and content (traces fossils, body fossils)
Nothing obvious in this photo
Facies: Fine-grained, laminated and cross laminated sandstone
How is the scale of facies described?
The scale is arbitrary and driven by pragmatism (time, effort, money, and the ultimate purpose of the work)
Entire exposure = clastic facies
Can be split into 2: Carbonate mudstone and Siliciclastic sandstone facies
Siliciclastics can be split into 2: Thinly-bedded sandstone facies and thickly bedded sandstone facies
Thinly bedded facies can be split into many varieties, for example: Fine-grained, laminated and cross laminated sandstone
What is the process to go from facies to environment?
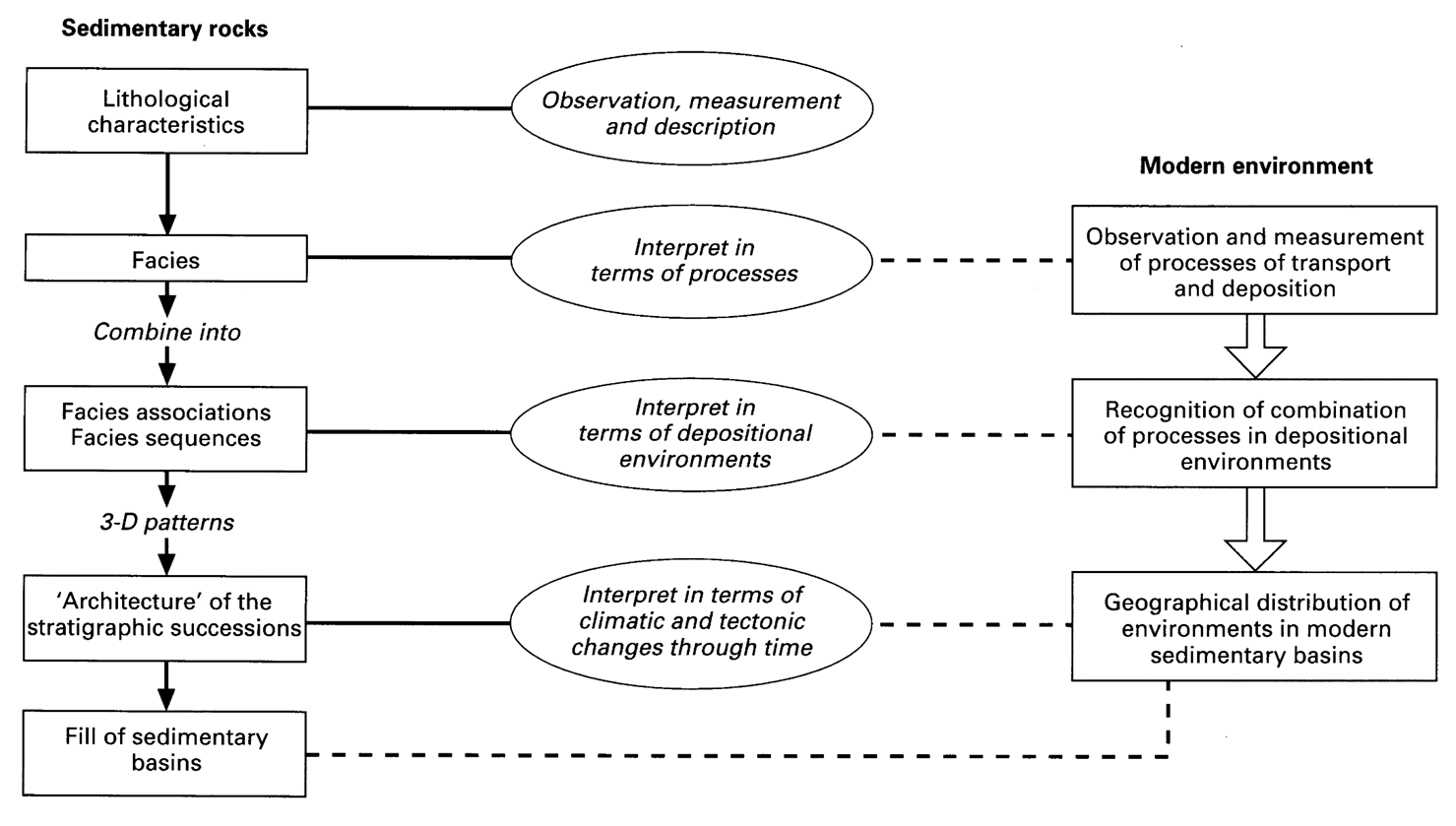
Define facies association
Facies Association: a collection of multiple, genetically-related facies formed within a single depositional system
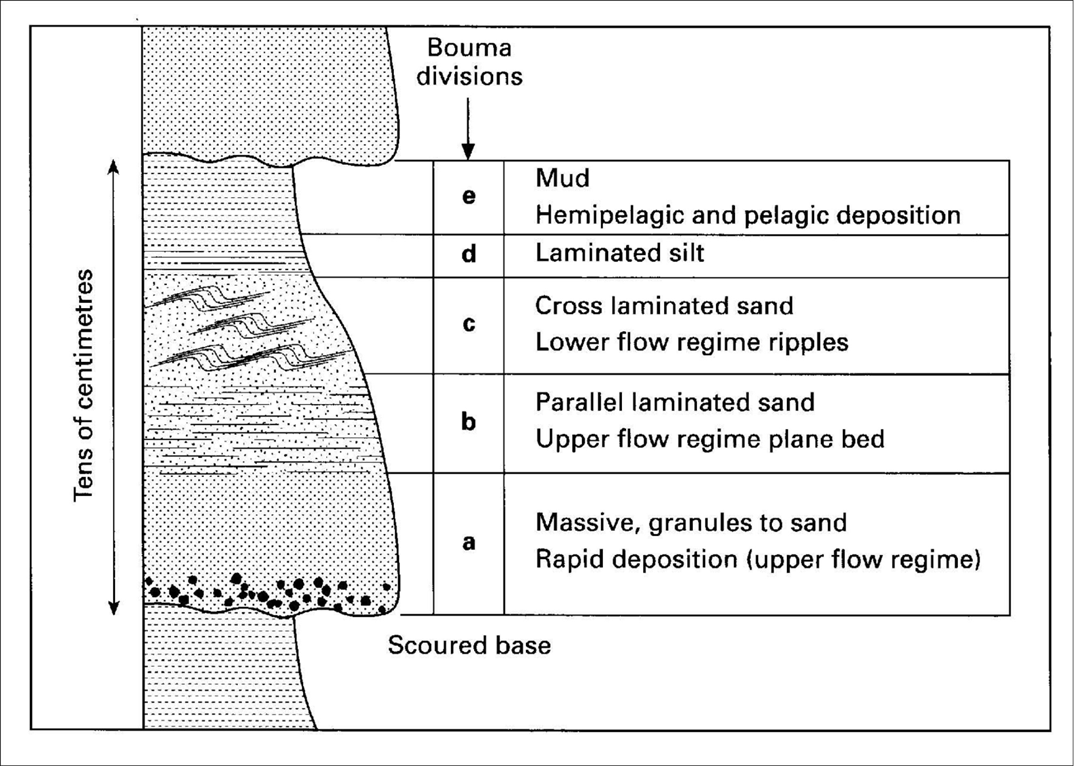
What are some bed scale facies associations?
Some facies associations are found repetitively in the stratigraphic record and, therefore, have informally been given names, such as the Bouma sequence.
Often thought of as synonymous with ‘turbidite’ but it’s just one collection an organisation of these facies
What is Walther’s Law?
‘The various deposits of the same (environmental) area and, similarly, the sum of the rocks of different environmental areas were formed beside each other in time and space, but in crustal (i.e. vertical) profile we can see them lying on top of each other….it is a basic statement of far-reaching significance that only those environmental areas can be superimposed that are observed side-by-side at the present time’