B5 Death to Anatomy PQs
1/172
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BRS Anat, BRS Embryo, 27', 28'
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
173 Terms
TruLearn: A researcher identified a group of modified neuroendocrine cells within the adrenal gland that are derived from neural crest cells. These cells most likely produce…?
Aldosterone
Androstenedione
Cortisol
Epinephrine
Estrogen
Epinephrine
TruLearn: A researcher identified a group of modified neuroendocrine cells within the adrenal gland that are derived from neural crest cells. These cells most likely produce…?
Epinephrine
Regarding the previous question, from which of the following does the chromaffin cells receive input from?
Pelvic splanchnic n.
L vagal trunk
Greater splanchnic n. and Lesser splanchnic n.
Post-synaptic sympathetic fibers
Phrenic n.
Greater splanchnic n. and Lesser splanchnic n.
A surgeon is performing an adrenalectomy and is looking to clamp the origin to the superior suprarenal a. Which artery was clamped?
Abdominal aorta
Inferior phrenic a.
Renal a.
L renal v.
Inferior esophageal a.
Inferior phrenic a.
TruLearn: A 32 y/o male presents w/ flank pain. Urinalysis reveals RBCs. PE reveals tenderness to the R lumbar paraspinal musculature and flexion posturing of the R hip. Which of the following muscles is most useful for localizing the source of the current symptoms?
Iliacus
Psoas major
Psoas minor
Quadratus lumborum
Rectus abdominis
Psoas major
A 42 y/o female presents w/ flank pain, blood in urine, nausea, and vomiting. She claims she recently started a strict diet and lost 50 lbs in the past 3 months. Abdominal CT revealed a descended L kidney by 2 spinal levels with coiling of the ureter at the renal hilum. Which of the following is a contributing factor to this patients presentation?
Renal fascia rupture
Inferior opening of the perirenal space
Inferior opening of the pararenal space
Paranephric fat swelling/edema
Interstitial fluid accumulation within the renal sinus
Inferior opening of the perirenal space
TruLearn: A 16 y/o female presents to the ED w/ 1-week hx of burning w/ urination and increased urinary frequency and urgency. PE reveals tender costovertebral angles. Abdominal CT reveals a horseshoe kidney. Which of the following structure limited the embryologic migration of the kidney in this patient?
Common iliac a.
Inferior mesenteric a.
Splenic v.
Superior mesenteric a.
L renal v.
Inferior mesenteric a.
A 12 year old male presents to the ED w/ acute onset abdominal pain w/ associated blood in urine, nausea, and vomiting. He also complains of testicular pain. CTA revealed a varicocele. Given the most probable diagnosis, which of the following is true?
Abdominal aortic stenosis results in hypoperfusion of the L testicular a.
Entrapment of the R renal v. results in kidney ischemia
Traction of the SMA induces torsional forces on the kidneys
L renal v compression by SMA reduces drainage of the kidney
Varicocele is caused by emboli, most likely from undiagnosed Afib
L renal v compression by SMA reduces drainage of the kidney
A 47 y/o male presents to the ED w/ flank pain for 2 days w/ blood in his urine and new onset nausea and vomiting. PE revealed positive CVA tenderness with no abdominal guarding. An abdominal xray was taken as shown. Where is this man’s kidney stone located?
Ureteropelvic junction
Crossing of the iliac vessels
Uterovesical junction
Renal pelvis
Ureterosplanchnic line
Ureteropelvic junction
A 58 year old women w/ PMHx of ovarian cancer w/ subsequent bilateral oophorectomy 4 days ago presents to the ED w/ symptoms of abdominal pain, fever, and hematuria. Differential diagnosis includes iatrogenic injury of the ureter during her operation. Which structure was most likely being operated on when her injury occurred?
Ovarian a.
Uterine a.
Ductus deferens
Round ligament of the uterus
Fallopian tubes
Ovarian a.
A 34 year old male presents after an MVC where he received a full workup. Incidentally, it was noted on abdominal CT that he has a duplicated ureter. Which of the following is a potential complication of the inferior ureter?
Obstruction
Infection
Cystic dilation
Rupture
Reflux
Reflux
A developing fetus w/ reduced levels of retinoic acid may have agenesis of which of the following structures?
Urogenital ridge
Nephrogenic cord
Pronephros
Mesonephros
Metanephros
Metanephros
TruLearn: 41 y/o females undergoes a uncomplicated hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. The sx was complicated by adhesions from prior appendectomy. She complains of post operative flank pain and, lateral, abdominal distention. Abdominal US reveals free fluid in the pelvis. The structure most likely injured during sx directly originates from which of the following systems?
First brachial arch
Mesonephros
Metanephros
Pronephros
Third brachial pound
Metanephros
Which of the following is the origin of the nephrogenic vesicles?
Ureteric bud
Mesonephros
Aorta
Metanephric blastema
Collecting ducts
Metanephric blastema
TruLearn: A researcher find that early exposure of mice embryos to Compound A results in bilateral renal agenesis, and that those w/ agenesis show normal structures that develop from the ureteric bud but lack the other renal structures. These embryos most likely have absent…?
Collecting ducts
Distal convoluted tubules
Minor calyces
Renal pelvis
Ureters
Distal convoluted tubules
Embryologic origin of Distal convoluted tubules?
Metanephric blastema
Which of the following structures of the bladder is continuous w/ with the allantois
Prostatic urethra
Vesical part
Phallic part
Vestibule
Pelvic part
Vesical part
In females, this structure will develop into labia minora while in males, it fuses together.
What is, pelvic portion of the bladder
What is, urachus
What is, allantois
What is, genital tubercle
What is, urethral folds
What is, urethral folds
In the development of male vs female genitourinary tract, which of the following is true?
The phallic portion of the bladder become the vestibule in both males and females
In males, the urachus obliterates while in females it becomes the tunica vaginalis
The pelvic portion of the bladder become only the prostatic urethra in males but the entire urethra in females
Males and females have a spongy component of the urethra, but are histologically unique between males and females
The pelvic portion of the bladder become only the prostatic urethra in males but the entire urethra in females
Around what time does androgen production begin?
Week 8
Week 30
Month 2
Month 12
Year 3
Year 3
A 22 year old male was found dead in his home. Autopsy reports drug overdose with incidental discovery of multiple fluid filled sacs within both kidneys, resulting in a granular surface that is not architecturally abnormal. Which of the following statements is true?
His disease was inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion
His diseases is not progressive
His condition is a result of nephrogenic developmental failure
His disease is a result of PKHD1 mutation
Abnormal protein folding of polycystin-1 resulted in his pathology
His disease is a result of PKHD1 mutation
A 26 year old male presents to UC w/ complaints of lower back pain. He states it started after lifting weights at the gym but now the pain is keeping him awake at night. PE showed diffuse tenderness along the paraspinal muscles. He states inhaling deeply exacerbates the pain, as well as worsens along his right flank when he hikes up his right hip. Given the most probable muscle strained, which of the follow structures lies directly anterior?
Endoabdominal fascia
Anterior layer of thoracolumbar fascia
Psoas Fascia
Erector spinae m.
Medial arcuate ligament
Anterior layer of thoracolumbar fascia
A 46 year old female w/ PMHx of GERD is following up with her PCP regarding a hiatal hernia. Which of the following structures contains this patients hernia?
Left crus of the diaphragm
Central tendon of the diaphragm
Inguinal canal
Right crus of the diaphragm
Median arcuate ligament of the diaphragm
Right crus of the diaphragm
What is housed in Right crus of the diaphragm?
esophageal hiatus
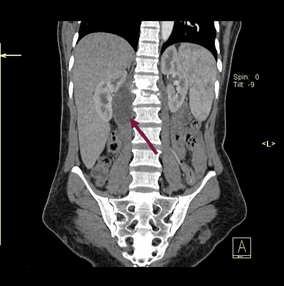
A 49 year old male w/ PMHx of Crohn’s presents to UC w/ complaints of flank pain for the past 4 days. He was noted to have a limp when walking towards the patient room. PE was positive for pain during passive R high flexion and he prefers to sit with his knees pulled towards his chest. Abdomen was benign, no g/r/t. He was noted to have a low grade fever. Abdominal CT is as shown. Given the most probable diagnosis, which of the following is true?
Ipsilateral flexion would relax the affected structure
Phrenic n. carries afferent fibers to the structure
L1 to L3 ventral rami are carrying pain stimulus from the affected structure
The affected structure is superiorly attached to rib 12
The affected structure is inferiorly attached to the greater trochanter
L1 to L3 ventral rami are carrying pain stimulus from the affected structure
During anatomy lab, a structure is observed exiting the lateral border of psoas major before providing innervation to the medial upper thigh and some parts of the genital region. Which of the following is the root level of this structure?
T12
L1
L2-L3
L2-L4
L4-L5
L1
L1 contributes to _____ and ________
iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal
A 27 year old female 30 weeks gravida presents to her OBGYN w/ complaints to new onset numbness to the anterolateral aspect of her upper right thigh. He OB suspect meralgia paresthetica. Which of the following is true regarding this patient?
The affected nerve emerges from the belly of psoas major m.
The affected nerve carries GSA, GSE, and post-symp fiber types
The suspected diagnosis only occurs in pregnant women
The affected nerve runs deep to the inguinal ligament
The affected nerves runs lateral to the ASIS
The affected nerve runs deep to the inguinal ligament
What fiber types goes genitofemoral n. carry in males? (more than 1 answer)
GSA, GSE, & Post-ganglionic sympathetic
A runner presents after a muscle strain in her left pelvic area. She states the pain worsens w/ she rotates her thigh externally. The muscle is question runs deep to the sacrotuberous ligament. Which of the following provides innervation to this muscle?
Ventral rami S1-S2
Sciatic n.
N. to obturator internus
Superior gluteal n.
Pudendal n.
N. to obturator internus
A female presents to the ED after an MVA and US confirmed intraperitoneal hemorrhage in the space superior to subperitonal organs. Within which of the following spaces is the blood most likely pooling?
Rectouterine pouch
Rectovesical pouch
Lesser pelvis
Pelvic inlet
Pelvic diaphragm
Rectouterine pouch
During a hysterectomy, the surgeon notes the cardinal ligament and recalls ‘24 VCOM anatomy lecture and knows it is a condensation of which structure?
Membranous pelvic fascia
Transversalis fascia
Parietal pelvic fascia
Endopelvic fascia
Visceral pelvic fascia
Endopelvic fascia
A female presents after an MVA with fracture of the R sacral ala. Which of the following structures is disrupted?
Pelvic diaphragm
Pelvic outlet
Pelvic inlet
Perineum
Pelvic midplane
Pelvic inlet
Dr. Dittmar walks into lab and realizes 2 pelvises were not labeled. Luckily, she remembers that one belongs to a male and the other a female. Which of the following traits would typically identify the pelvis as female?
Heart shaped inlet
Narrow pubic arch
Rounded obturator foramen
Small pelvic outlet
Wider sciatic notch
Wider sciatic notch
Which of the following structure is seen in both superior and inferior view of the pelvic floor?
Puborectalis m.
Sacrococcygeal ligament
Deep transverse perineal m.
Perineum
External anal sphincter
Puborectalis m.
Which of the following describes the action of the 3 muscles that make up much of the pelvic diaphragm?
Coccyx flexion
Contraction during micturition
Contraction during sneezing
Relaxation at baseline
Flexion of the pelvic
Contraction during sneezing
A patient w/ PMHx of Crohn disease presents w/ pain and fullness around the anal region w/ associated fever. Pertinent hx include anal fissures. He is scheduled for an I&D the next morning. Which of the following structures may be compressed by the patient’s abscess?
Superior rectal n.
N. to obturator internus
Lateral cutaneous femoral n.
Perineal n.
Sciatic n.
Perineal n.
Which of the following structures is formed by labia minora folds and is highly susceptible to injury during delivery?
Labia majora
Prepuce of clitoris
Frenulum of the clitoris
Copra cavernosa
Fourchette
Fourchette
A 31 year old female presents to her PCP w/ complaints of vaginal swelling and painful sexual intercourse for the past week. PE reveals a tender swelling lateral to the right labia majora. The structure affected is within which of the following spaces?
Deep perineal pouch
Superficial perineal pouch
False pelvis
Ischioanal recess
Pelvic diaphragm
Superficial perineal pouch


A 48 year old male presents to the ED after an MVA. FAST exam was positive for fluid surrounding the prostate deep to the pelvic peritoneum. Damage in which of the following structures is the probable etiology of this fluid?
ASIS
Membranous urethra
Spongy urethra
Pelviuretic junction of the ureter
Bulb of the penis
Membranous urethra
A 67 year old female presents to her PCP w/ genital itching for 3 month. Exam reveals a dark lesion lateral of the labia majora. Biopsy under local anesthetic is planned. Which of the following is the origin of the nerve providing sensory input to this area?
Posterior femoral cutaneous n.
Perineal n.
Pudendal n.
Ilioinguinal n.
Genitofemoral n.
Posterior femoral cutaneous n.
Which of the following is the origin of the blood supply to the mons pubis?
Internal pudendal a.
Dorsal a. of the clitoris
External pudendal a.
Perineal a.
External iliac a.
Internal pudendal a.
A 36 year old male presents to his PCP w/ increasing breast size. Which of the following is the most probable etiology?
Puberty
Age
Mastitis
Weight gain
Breast cancer
Weight gain
A 45 year old female presents with complaints of swelling and pain of her left breast for the past week. Exam reveals mastitis on the lower inner quadrant of the left breast. Which of the following structures are likely involved?
Subclavian nodes
Axillary nodes
Supraclavicular nerves
Terminal branches of internal thoracic aa.
Lateral mammary n. branches
Terminal branches of internal thoracic aa.
Of the 5 perineal muscles in the male perineum, which one is innervated by the dorsal nerve of the penis and is matched with the correct symptom when it is dysfunctional?
External urethral sphincter, urinary incontinence
Superficial transverse perineal m., fecal incontinence
Bulbospongious m., impotence
Ischiocavernosus m., impotence
Deep transverse perineal m., hernia
External urethral sphincter, urinary incontinence
A 37 year old man is having his testicle removed due to testicular cancer. Once removed, the surgeon remarks that the testice has two distinct coverings. You being a knowledgeable medical student point out that those coverings are in order from superficial to deep:
External and Internal Spermatic Fascia
Tunica Vaginalis and Tunica Albuginea
Cremasteric Fascia and Internal Spermatic Fascia
Dartos Fascia and Cremasteric Fascia
Dartos Fascia and Tunica Albuginea
Tunica Vaginalis and Tunica Albuginea
A high school boy needs to urinate for a drug test to play football. You are assisting the doctor in collecting the sample. You, being a well educated OMS II Block 5 competent medical student, know that the correct flow of urine from the bladder to the glans via the urethra is:
Prostatic urethra, membranous urethra, intramural urethra, spongy urethra
Intramural urethra, membranous urethra, prostatic urethra, spongy urethra
Intramural urethra, spongy urethra, prostatic urethra, membranous urethra
Membranous urethra, prostatic urethra, spongy urethra, intramural urethra
Intramural urethra, prostatic urethra, membranous urethra, spongy urethra
Intramural urethra, prostatic urethra, membranous urethra, spongy urethra
An unfortunate man presents to your office with a right testicular torsion. His twisting of the spermatic cord has compromised his right testicle. What specific structure within the cord will be responsible for the necrosis of the testicle that will ensue if the torsion is not fixed?
Testicular a.
Cremaster m.
Ductus Deferens
Cremasteric a.
Genital branch of Genitofemoral n.
Testicular a.
A 65 year old man arrives in the ER having just been in a car wreck. Emergent surgery is performed in order to fix the pelvic fracture he suffered. During surgery it is noted that damage has been sustained to the pudendal canal. Which of the following structures is not at risk due to damage to the canal?
Inferior rectal a,
Dorsal nerve of the penis
Pudenal n.
External pudendal a.
Perineal n.
External pudendal a.
A 35 year old man presents post catheterization with a complaint of lower abdominal pain and a fullness in his pelvic region. Imaging shows fluid around the bladder and the rectum filling the retropubic space. Paracentesis reveals the fluid to be blood. Which part of the urethra was damaged during the catheterization resulting in the patient presentation?
Spongy urethra
Intramural urethra
Membranous urethra
Prostatic urethra
Left and Right ureter
Membranous urethra
A 27 year old woman is diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy. Due to the advanced nature of the embryo, extensive damage has been done to the fallopian tubes. The recommendation is to take out the tube entirely. What part of the broad ligament of the uterus must be taken out along with the tube?
Mesometrium
Round ligament of the uterus
Mesovarium
Ovarian ligament
Mesosalpinx
Mesosalpinx
A 27 year old woman is diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy. Due to the advanced nature of the embryo, extensive damage has been done to the fallopian tubes. The recommendation is to take out the tube entirely. What part of the broad ligament of the uterus must be taken out along with the tube? = Mesosalpinx
Referring to the woman in the previous question, where are ectopic pregnancies most likely to lodge themselves?
Infundibulum
Isthmus
Uterine
Ampulla
Uterine Ostia
Ampulla
While performing an oophorectomy (removal of ovary), the surgeon accidentally cuts on of the ligaments of the ovary. Unfortunately, massive bleeding ensues. The surgeon scrambles to control the bleed. Which ligament did the surgeon cut and what vessel in most likely contributing to the profuse bleeding?
Ovarian ligament containing the Uterine a.
Ovarian suspensory ligament containing the Uterine a.
Mesovarium containing the Ovarian a.
Ovarian ligament containing the Ovarian a.
Ovarian suspensory ligament containing the Ovarian a.
Ovarian suspensory ligament containing the Ovarian a.
A 75 year old woman with cirrhosis and hypoalbuminemia presents with ascites. Her abdomen is distended, and she has gained a considerable amount of water weight. In which part of the woman’s abdominal cavity did fluid first collect?
Vesicouterine pouch
Rectovesical pouch
Rectouterine pouch
Anterior fornix
Posterior fornix
Rectouterine pouch
During a speculum exam, what part of the cervix is made visible using the speculum?
Vaginal Cervix
Anterior Fornix
Supravaginal Cervix
Posterior Fornix
Internal Os
Vaginal Cervix
A 50 year old woman sustain damage to her paracolpium resulting a vaginal wall prolapse. Physical exam reveals the prolapse to be in the anterior wall. What is the correct name and contents of the prolapse?
Enterocele containing bladder
Cystocele containing bladder
Rectocele containing rectum
Cystocele containing small bowel
Enterocele containing small bowel
Cystocele containing bladder
A 29 year old man presents to your clinic with fertility issues. After a battery of tests, it is determined that his infertility is due to a lack of seminal fluid production. The drastic reduction in his seminal fluid is most likely due to dysfunction of what structure(s)?
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate Gland
Bulbourethral Glands
Seminiferous Tubules
Vas Deferens
Seminal Vesicles
A 65 year old man with known atherosclerotic disease presents lower abdominal pain and issues urinating. CT scan shows marked ischemia and necrosis of the bladder. Thrombosis of which vessel most likely let to this outcome?
Renal a.
Aorta
Common Iliac a.
Internal Iliac a.
External Iliac a.
Internal Iliac a.
What structure of the prostate does the ejaculatgory duct use to deposit semen into the prostatic urethra?
Urethral Crest
Vas Deferens
Seminal Colliculus
Prostatic Sinus
Seminal Vesicle
Seminal Colliculus
A 45 year old man was in a minor car wreck but suffered no major injuries. He presents several weeks later with a copulatory issue. After diagnostic tests and a physical exam, you determine the patient has suffered damage to the part of the pelvic splanchnic nerves that supply the cavernous nerves. What was the man's presenting symptom?
Trouble ejaculating
Trouble with erection
Trouble producing semen
Urinating while copulating
Numbness of the penis
Trouble with erection
A man with benign prostatic hypertrophy is undergoing TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate). Which clinical zone of the prostate is most likely responsible for the enlargement and will most likely be resected?
Peripheral Zone
Central Zone
Transitional Zone
Anterior Zone
Transitional Zone
Which of the following correctly shows the path of sperm from the testes to the urethra?
Ductus Deferens, Ampulla of the Ductus Deferens, Epididymis, Ejactulatory Duct, Prostatic Urethra
Epididymis, Ampulla of the Ductus Deferens, Ductus Deferens, Prostatic Urethra, Ejactulatory Duct
Ejactulatory Duct, Prostatic Urethra, Ductus Deferens, Ampulla of the Ductus Deferens, Epididymis
Epididymis, Ductus Deferens, Ampulla of the Ductus Deferens, Ejaculatory Duct, Prostatic Urethra
Epididymis, Ampulla of the Ductus Deferens, Ductus Deferens, Ejaculatory Duct, Prostatic Urethra
Epididymis, Ductus Deferens, Ampulla of the Ductus Deferens, Ejaculatory Duct, Prostatic Urethra
A 27 year old women who is at 6 weeks gestation comes in for an ultrasound. The doctor claims that after inspecting the fetus, it is a girl. How can the doctor make this conclusion?
The lack of elongation of the genital tubercle
The failure of the appearance of a scrotum
The development of embryological breast tissue
The doctor cannot as the embryo is sexually indifferent
The orientation of the developing pelvis
The doctor cannot as the embryo is sexually indifferent
At week 7, the XX embryo begins to feminize with the development of the would be ovaries. How would such an embryo change if it was androgen resistant?
The embryo would masculinize and develop testes
The embryo would become hermaphroditic possessing both male and female genitals
The embryo would develop internal male genitalia and external female genitalia
The embryo would develop internal female genitalia and external male genitalia
The embryo would still develop ovaries as such development is genetically controlled by the X chromosome
The embryo would still develop ovaries as such development is genetically controlled by the X chromosome
In the presence of estrogen, the paramesonephric develops in the female embryo. Which of the following structures is not a derivative of this duct?
Fallopian Tubes
Epoophoron
Uterus
Cervix
Superior ⅓ of the vagina
Epoophoron
A new born girl is discovered to have an ectopic ovary that is stuck in her abdomen. A failure of what embryological structure would allow the ovary to wander out of its anatomically normal position?
Cortical Cords
Germ Cells
Gubernaculum
Mesonephric Duct
Paramesonephric Duct
Gubernaculum
In the development of an embryo, folding will migrate germ cells to the gonadal ridge. If an error in folding prevents this migration, what happens in the development of the embryo?
The total agenesis of the urogenital tract
The agenesis of the gonads
A urogenital fistula
A persistent cloaca containing urethra, anus, and/or vagina
An imperforate anus
The agenesis of the gonads
A newborn screening of a neonatal girl reveals she posses a uterine abnormality characterized by the persistence of the uterine septum. The diagnosis of the child is:
Unicornuate uterus
Didelphys
Bicornuate uterus
Septate uterus
Atretic uterus
Septate uterus
Which of the following triplets correctly matches the cell type with its product and the product’s function?
Sertoli cells produce testosterone which promotes degeneration of the paramesonephric ducts
Leydig cells produce testosterone which promotes the degeneration of the paramesonephric ducts
Sertoli cells produce anti-mullerian hormone which is required for genital duct development
Leydig cells produce anti-mullerian hormone which promotes the degeneration of the paramesonephric ducts
Sertoli cells produce anti-mullerian hormone which promotes the degeneration of the paramesonephric ducts
Sertoli cells produce anti-mullerian hormone which promotes the degeneration of the paramesonephric ducts
A Male infant is born without a scrotum, possessing only exposed testicles. What precursor to the scrotal swellings failed to develop?
Urethral Folds
Anal Folds
Cloacal Folds
Genital Swellings
Urethral Groove
Genital Swellings
During development, a male fetus experiences a disruption to the mesonephric ducts. Which of the following structures will not be affects by this aberration?
Epididymis
Ductus Deferens
Bulbourethral Glands
Ampulla of the Ductus Deferens
Seminal Vesicle
Bulbourethral Glands
A one year old boy presents with cryptorchidism. The parents are hesitant to resolve the issue for fear of having surgery on their young child. If the parents forgo surgery what is a major complication the baby boy may face?
Inguinal Hernia
Dysuria
Nephritis
Urinary Incontinence
Testicular Cancer
Testicular Cancer
Under the hormonal influence of TDF, the gonads begin to differentiate into testes. Which one of these processes is not directed by the influence of TDF?
Degeneration of the Mesonephric Duct
Degeneration of the Paramesonephric Duct
The Development of Leydig Cells
The Development of Sertoli Cells
The Development of Spermatogonia
Degeneration of the Mesonephric Duct
A neonate is born to a 30 year old mother. The delivery doctor is having trouble identifying the sex of the child. Testing reveals masculinized external genitalia and female appearing internal genitalia. The mother admits to being treated with androgens while pregnant. What is the diagnosis of the child?
46,XY Gonadal Dysgenesis
45,XO Gonadal Dysgenesis
46,XY Disorder of Sexual Development
46,XX Disorder of Sexual Development
46,XY Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
46,XX Disorder of Sexual Development
A 63-year-old man comes to the emergency
department with back pain, weakness, and short-
ness of breath. On examination, he has an aneu-
rysm of the abdominal aorta at the aortic hiatus
of the diaphragm. Which of the following pairs of
structures would most likely be compressed?
(A) Vagus nerve and azygos vein
(B) Esophagus and vagus nerve
(C) Azygos vein and thoracic duct
(D) Thoracic duct and vagus nerve
(E) Inferior vena cava (IVC) and phrenic nerve
(C) Azygos vein and thoracic duct
3. A 2-year-old boy presents with pain in
his groin that has been increasing in nature
over the past few weeks. He is found to have a
degenerative malformation of the transversalis
fascia during development. Which of the fol-
lowing structures on the anterior abdominal
wall is likely defective?
(A) Superficial inguinal ring
(B) Deep inguinal ring
(C) Inguinal ligament
(D) Sac of a direct inguinal hernia
(E) Anterior wall of the inguinal canal
(B) Deep inguinal ring
7. During an annual health examination of a
46-year-old woman, a physician finds hyperse-
cretion of norepinephrine from her suprarenal
medulla. Which of the following types of nerve
fibers are most likely overstimulated?
(A) Preganglionic sympathetic fibers
(B) Postganglionic sympathetic fibers
(C) Somatic motor fibers
(D) Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers
(E) Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers
(A) Preganglionic sympathetic fibers
11. A 43-year-old man complains of abdominal
pain just above his umbilicus. On examination,
a tumor is found anterior to the IVC. Which of
the following structures would most likely be
compressed by this tumor?
(A) Right sympathetic trunk
(B) Left third lumbar artery
(C) Third part of the duodenum
(D) Left renal artery
(E) Cisterna chyli
(C) Third part of the duodenum
13. A young boy is brought to the hospital after
a bicycle accident and possible pelvic fracture.
While awaiting a computed tomography (CT)
scan of his pelvis, a physician proceeds with
a focal neurologic examination. In testing the
child’s reflexes, which of the following nerves
would carry afferent impulses of the cremas-
teric reflex?
(A) Subcostal nerve
(B) Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
(C) Genitofemoral nerve
(D) Iliohypogastric nerve
(E) Femoral nerve
(C) Genitofemoral nerve
16. A 78-year-old man is suffering from
ischemia of the suprarenal glands. This
condition results from rapid occlusion of direct
branches of which of the following arteries?
(A) (B) Aorta, splenic, and inferior phrenic arteries
Renal, splenic, and inferior mesenteric
arteries
(C) Aorta, inferior phrenic, and renal arteries
(D) Superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric,
and renal arteries
(E) Aorta and hepatic and renal arteries
(C) Aorta, inferior phrenic, and renal arteries
25. A pediatric surgeon has resected a structure
that is a fibrous remnant of an embryonic or
fetal artery in a 5-year-old child. Which of the
following structures is most likely to be divided?
(A) Lateral umbilical fold
(B) Medial umbilical fold
(C) Median umbilical fold
(D) Ligamentum teres hepatis
(E) Ligamentum venosum
(B) Medial umbilical fold
27. An elderly man with prostatic hypertrophy
returns to his urologist with another case of
epididymitis. An acute infection involving the
dartos muscle layer of the scrotum most likely
leads to an enlargement of which of the follow-
ing lymph nodes?
(A) Preaortic nodes
(B) Lumbar nodes
(C) External iliac nodes
(D) Superficial inguinal nodes
(E) Common iliac nodes
(E) Common iliac nodes
42. A 58-year-old man is presented with
edema of the lower limb and enlarged
superficial veins of the abdominal wall.
Examination of radiographs and angiograms
reveals obstruction of the IVC just proximal
to the entrance of the renal vein. This venous
blockage may result in dilation of which of the
following veins?
(A) Left suprarenal vein
(B) Right inferior phrenic vein
(C) Right hepatic vein
(D) Left gastric vein
(E) Portal vein
(A) Left suprarenal vein
50. A 53-year-old woman with known kidney
disease presents to a hospital because her pain
has become increasingly more severe. A physi-
cian performing kidney surgery must remem-
ber that:
(A) The left kidney lies a bit lower than the
right one
(B) The perirenal fat lies external to the renal
fascia
(C) The renal fascia does not surround the su-
prarenal gland
(D) The left renal vein runs anterior to both the
aorta and the left renal artery
(E) The right renal artery is shorter than the
left renal artery
(D) The left renal vein runs anterior to both the
aorta and the left renal artery
53. A 3-year-old boy is admitted to the
children’s hospital with complaints of rest-
lessness, abdominal pain, and fever. An MRI
examination reveals that he has a double ureter.
Which of the following embryonic structures is
most likely failed to develop normally?
(A) Mesonephric (Wolffian) duct
(B) Paramesonephric (Müllerian) duct
(C) Ureteric bud
(D) Metanephros
(E) Pronephros
(C) Ureteric bud
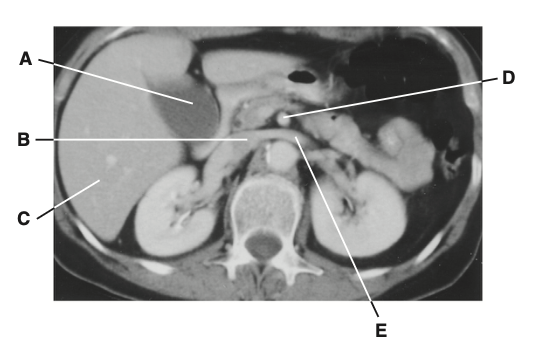
63. Which structure receives blood from the left
gonad and suprarenal gland?
E = left renal vein = runs anterior to the aorta but posterior to the superior mesenteric artery and receives blood from the gonad and suprarenal gland.
1. A 68-year-old woman with uterine carci-
noma undergoes surgical resection. This can-
cer can spread directly to the labia majora in
lymphatics that follow which of the following
structures?
(A) Pubic arcuate ligament
(B) Suspensory ligament of the ovary
(C) Cardinal (transverse cervical) ligament
(D) Suspensory ligament of the clitoris
(E) Round ligament of the uterus
(E) Round ligament of the uterus
2. A 17-year-old boy suffers a traumatic groin
injury during a soccer match. The urologist
notices tenderness and swelling of the boy’s left
testicle that may be produced by thrombosis in
which of the following veins?
(A) Left internal pudendal vein
(B) Left renal vein
(C) Inferior vena cava
(D) Left inferior epigastric vein
(E) Left external pudendal vein
(B) Left renal vein
3. On a busy Saturday night in Chicago, a
16-year-old boy presents to the emergency de-
partment with a stab wound from a knife that
entered the pelvis above the piriformis muscle.
Which of the following structures is most likely
to be damaged?
(A) Sciatic nerve
(B) Internal pudendal artery
(C) Superior gluteal nerve
(D) Inferior gluteal artery
(E) Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
(C) Superior gluteal nerve
4. A 22-year-old woman receives a deep cut
in the inguinal canal 1 in. lateral to the pubic
tubercle. Which of the following ligaments is
lacerated within the inguinal canal?
(A) Suspensory ligament of the ovary
(B) Ovarian ligament
(C) Mesosalpinx
(D) Round ligament of the uterus
(E) Rectouterine ligament
(D) Round ligament of the uterus
5. A 29-year-old carpenter sustains severe
injuries of the pelvic splanchnic nerve by a deep
puncture wound, which has become contami-
nated. The injured parasympathetic pregangli-
onic fibers in the splanchnic nerve are most likely
to synapse in which of the following ganglia?
(A) Ganglia in or near the viscera or pelvic
plexus
(B) Sympathetic chain ganglia
(C) Collateral ganglia
(D) Dorsal root ganglia
(E) Ganglion impar
(A) Ganglia in or near the viscera or pelvic
plexus
6. A 59-year-old woman comes to a local hos-
pital for uterine cancer surgery. As the uterine
artery passes from the internal iliac artery to the
uterus, it crosses superior to which of the fol-
lowing structures that is sometimes mistakenly
ligated during such surgery?
(A) Ovarian artery
(B) Ovarian ligament
(C) Uterine tube
(D) Ureter
(E) Round ligament of the uterus
(D) Ureter
7. A 29-year-old woman is admitted to a hospi-
tal because the birth of her child is several days
overdue. Tearing of the pelvic diaphragm dur-
ing childbirth leads to paralysis of which of the
following muscles?
(A) Piriformis
(B) Sphincter urethrae
(C) Obturator internus
(D) Levator ani
(E) Sphincter ani externus
(D) Levator ani
8. A 37-year-old small business manager re-
ceives a gunshot wound in the pelvic cavity,
resulting in a lesion of the sacral splanchnic
nerves. Which of the following nerve fibers
would primarily be damaged?
(A) Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers
(B) Postganglionic sympathetic fibers
(C) Preganglionic sympathetic fibers
(D) Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers
(E) Postganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers
(C) Preganglionic sympathetic fibers
9. A young couple is having difficulty
conceiving a child. Their physician at a
reproduction and fertility clinic explains to
them that
(A) The ovary lies within the broad ligament
(B) The glans clitoris is formed from the cor-
pus spongiosum
(C) Erection of the penis is a sympathetic
response
(D) Ejaculation follows parasympathetic
stimulation
(E) Fertilization occurs in the infundibulum or
ampulla of the uterine tube
(E) Fertilization occurs in the infundibulum or
ampulla of the uterine tube
10. A 46-year-old woman has a history of
infection in her perineal region. A comprehen-
sive examination reveals a tear of the superior
boundary of the superficial perineal space.
Which of the following structures would most
likely be injured?
(A) Pelvic diaphragm
(B) Colles fascia
(C) Superficial perineal fascia
(D) Deep perineal fascia
(E) Perineal membrane
(E) Perineal membrane
11. A 58-year-old man is diagnosed as having
a slowly growing tumor in the deep perineal
space. Which of the following structures would
most likely be injured?
(A) Bulbourethral glands
(B) Crus of penis
(C) Bulb of vestibule
(D) Spongy urethra
(E) Great vestibular gland
(A) Bulbourethral glands
12. An elderly man with a benign enlarge-
ment of his prostate experiences difficulty in
urination, urinary frequency, and urgency.
Which of the following lobes of the prostate
gland is commonly involved in benign hyper-
trophy that obstructs the prostatic urethra?
(A) Anterior lobe
(B) Middle lobe
(C) Right lateral lobe
(D) Left lateral lobe
(E) Posterior lobe
(B) Middle lobe
13. A 59-year-old man is diagnosed with pros-
tate cancer following a digital rectal examina-
tion. For the resection of prostate cancer, it is
important to know that the prostatic ducts open
into or on which of the following structures:
(A) Membranous part of the urethra
(B) Seminal colliculus
(C) Spongy urethra
(D) Prostatic sinus
(E) Prostatic utricle
(D) Prostatic sinus
14. A 29-year-old woman with a ruptured ec-
topic pregnancy is admitted to a hospital for
culdocentesis. A long needle on the syringe is
most efficiently inserted through which of the
following structures?
(A) Anterior fornix of the vagina
(B) Posterior fornix of the vagina
(C) Anterior wall of the rectum
(D) Posterior wall of the uterine body
(E) Posterior wall of the bladder
(B) Posterior fornix of the vagina