Tissue Engineering and ECM
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Tissue
group of cells, usually with common embryonic origin, function together to carry out specialized activities (similar cells form a tissue)
Types of Tissues
Epithelial
covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands
Muscle
enables movement
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
Connective
supports, binds, protects other tissues
bone, cartilage, tendons, fat
Nervous
sends/receives signals
Epithelial Tissue
Protection, support, regulation, secretion, separation, etc
All substances that enter body must cross epithelium
Form linings and secretion glands
Tightly packed
Avascular
Apical and basolateral surfaces (apical top faces outside or external cavity, basal connected to bottom surface)
self-renewal
Connective Tissue
ECM gives tissue structural integrity
fibroblasts, chondrocytes, osteoblasts
Transport
Energy storage
Immune protection
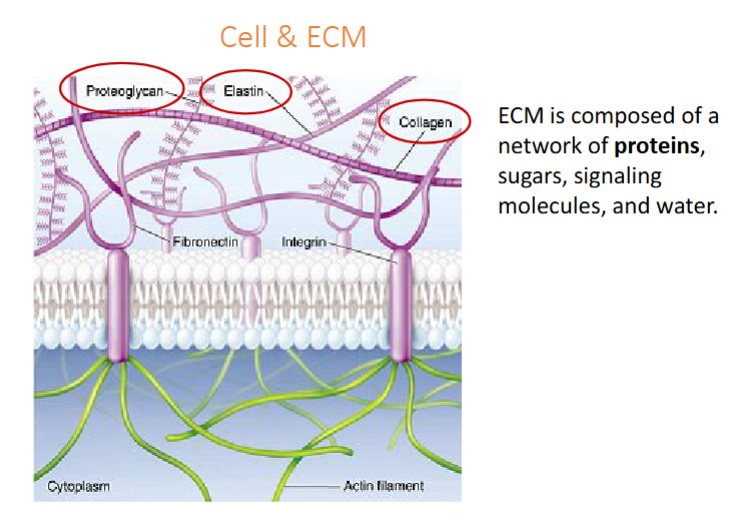
ECM
composed of network of proteins, sugars, signaling molecules, water
Proteoglycans, elastin, collagen
regulates cell functions like growth, movement, differentiation, communication
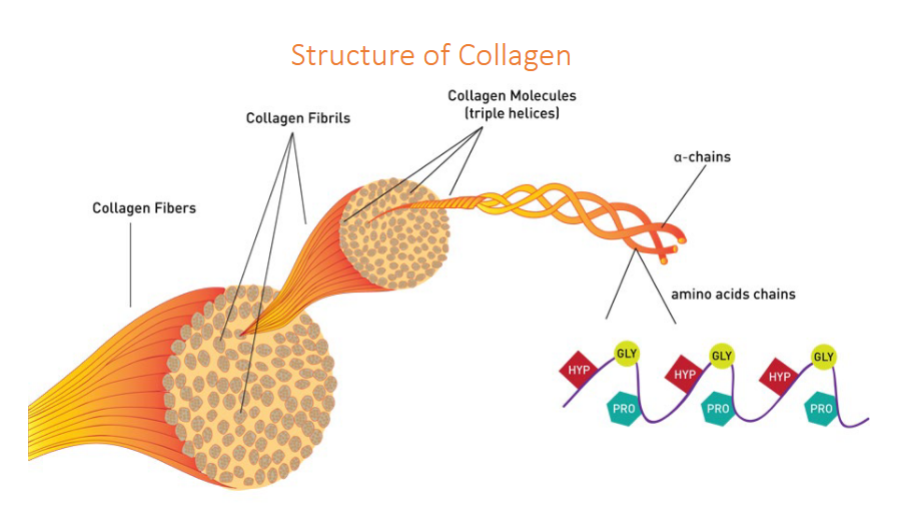
Collagen
Distribution in Human Body
85% tendons
75% skin
90% bones
70% joint cartilage
70% ligaments
6% tendinous muscles
Function: enables flexible deformation while providing high mechanical strength to collagenous tissues such as tendons
Forms long, triple helical fibers, collagen fibers composed of collagen fibrils, collagen molecules are triple helices of a-chains with amino acids
Pathological States:
Osteogenesis Imperfecta: brittle bone disease
Elastin
Mainly found in:
Aorta
Mouse carotid artery
skin
lung alveoli
Function:
Gives tissues elasticity, allowing them to stretch and return to original shape
Disorders:
marfan syndrome: reduced cross linking of elastin, fibers too weak or too few
long limbs, lens dislocation, abnormal spine curvature, protruding backbones
Loss of elastin in arteries results in stiffness (Atherosclerosis)
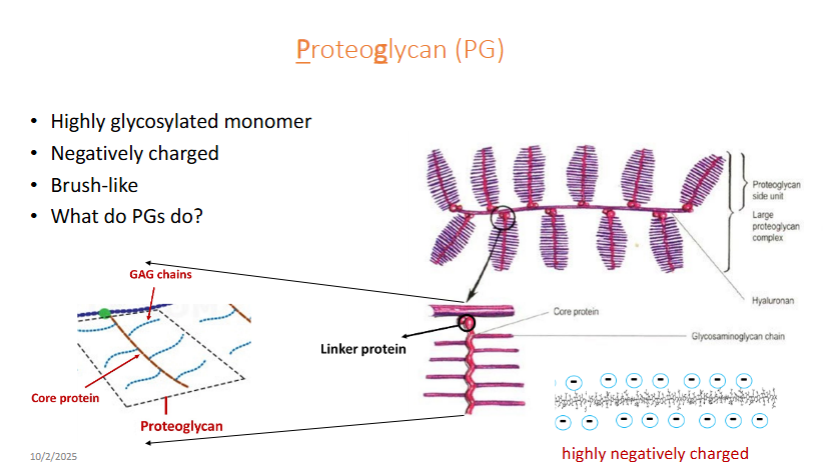
Proteoglycan
Highly glycosylated monomer
Negatively charged
brush-like
Function:
lubricants, shock absorbers space fillers
PG highly negatively charged GAG chains attract and trop water (like gel), hydrating, lubricating, and resisting/absorbing mechanical load in tissues.
Pathological states:
Osteoarthritis: reduced joint cushioning
Decellularization
Leaves behind a scaffold that can be used for potential clinical applications
implants, tissue repair, cardiac repair
Can be used to understand drug testing and disease modeling