Physiology | Lesson 40: Renal Sodium and Potassium Balance
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Under normal conditions, salt and water losses from the body exactly ________ salt and water gains to the body
Under normal conditions, salt and water losses from the body exactly equal salt and water gains to the body
NaCl intake = NaCl loss from the body
Na+ is reabsorbed by ____________________________ across the basolateral membrane throughout the tubule
Na+ is reabsorbed by primary active transport across the basolateral membrane throughout the tubule
Primary active transport creates the ____________________________
Primary active transport creates the ion gradient that powers secondary active transport
Primary active transport (Na+/K+-ATPase) uses _________________, which pumps ____________ out and _______________ into the cell.
Primary active transport (Na+/K+-ATPase) uses ATP directly to pump ions against their concentration gradient, which pumps Na+ out and K+ into the cell.
What is meant by “downhill” entry of Na+ into tubular cells?
Sodium moves passively from the tubular lumen into the cell, following its electrochemical gradient created by the Na+/K+ ATPase pump on the basolateral membrane.
Describe sodium (Na⁺) transport in the proximal tubule
Na⁺ entry is coupled with glucose and amino acids, and H⁺ (via co-transport or counter-transport).
Describe sodium (Na+) transport in the loop of Henle
Na⁺ enters with K⁺ and Cl⁻ through the Na⁺–K⁺–2Cl⁻ cotransporter.
Describe sodium (Na+) transport in the distal tubule
Na⁺ entry occurs with Cl⁻ via the Na⁺–Cl⁻ cotransporter.
Describe sodium (Na+) transport in the collecting duct
Na⁺ enters through epithelial Na⁺ channels (ENaC), regulated by aldosterone.
What are the two most important hormones for regulating Na+?
Aldosterone
Atrial natriuretic peptide
Aldosterone
released from the _________________ when _______ is low or __________ is high
___________ salt and water reabsorption to __________________ ECFV
___________ salt and water excretion to _______________ ECFV
Causes systemic and renal arteriole ____________ to increase MABP
Aldosterone
released from the adrenal cortex when Na+ is low or K+ is high
increases salt and water reabsorption to increase ECFV
decreases salt and water excretion to increase ECFV
Causes systemic and renal arteriole constriction to increase MABP
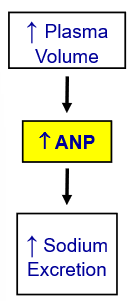
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide
released from the ____________ when blood volume or pressure is _________
_____________ salt and water reabsorption to ___________ ECFV
_____________ salt and water excretion to ______________ ECFV
causes systemic and renal arteriole ____________ to decrease MABP
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide
released from the atria of the heart when blood volume or pressure is high
decreases salt and water reabsorption to decrease ECFV
increases salt and water excretion to decrease ECFV
causes systemic and renal arteriole dialation to decrease MABP
Aldosterone _____________ and ANP _____________ renal Na+ reabsorption
Aldosterone increases and ANP decreases renal Na+ reabsorption
Steps of Regulation of Aldosterone secretion by the renin-angiotensin system (RAS)
(1) When blood pressure, blood volume, or Na⁺ levels drop, the kidney’s juxtaglomerular (JG) cells release renin.
(2) Renin converts angiotensinogen (from the liver) into angiotensin I.
(3) Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) (mainly in the lungs) converts angiotensin I into angiotensin II.
(4) Angiotensin II stimulates the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone.
(5) Aldosterone increases Na⁺ reabsorption (and K⁺ secretion) in the distal tubule and collecting duct, which raises blood volume and pressure.
What are the stimuli for renin secretion?
o ↑ atrial distention & ↑ plasma volume
o ↓ Blood pressure (detected by renal baroreceptors)
o ↓ Na⁺ or Cl⁻ concentration at the macula densa
o ↑ Sympathetic nervous activity (β₁-adrenergic stimulation of JG cells)
When MABP decreases, what reflexes are initiated that lead to changes in Na+ reabsorption and ultimately blood volume?
Baroreceptors (in carotid sinus and aortic arch) sense the drop.
This activates the sympathetic nervous system, causing:
Constriction of afferent arterioles, lowering GFR and reducing Na⁺ and water loss.
Increased renin release, activating the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS).
Aldosterone then increases Na⁺ reabsorption in the distal nephron.
Result: Na⁺ and water are retained, raising blood volume and pressure.
When MABP increases, what reflexes are initiated that lead to changes in Na+ reabsorption and ultimately blood volume?
Baroreceptors reduce sympathetic output.
Afferent arterioles dilate, GFR rises, and Na⁺ excretion increases.
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is released, which inhibits Na⁺ reabsorption and suppresses renin and aldosterone.
Result: Na⁺ and water excretion increase, lowering blood volume and pressure.
Describe the mechanism of potassium (K⁺) secretion in the nephron
K⁺ secretion occurs in the distal tubule and collecting duct, driven by the Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase and K⁺ channels, and is increased by aldosterone, high plasma K⁺, and rapid tubular flow
High plasma K+ causes ___________ aldosterone and ____________ K+ secretion into urine
High plasma K+ causes increased aldosterone and increased K+ secretion into urine
Low plasma K+ causes ___________ aldosterone and ____________ K+ secretion into urine
Low plasma K+ causes decreased aldosterone and decreased K+ secretion into urine
Kidneys maintain ECFV by regulating the amount of ________ in urine
Kidneys maintain ECFV by regulating the amount of Na+ in urine
______________ → rate of urinary Na+ excretion by kidneys is above usual levels
______________ → rate of urinary Na+ excretion by kidney is below usual levels
Natriuresis → rate of urinary Na+ excretion by kidneys is above usual levels
Antinatiuresis → rate of urinary Na+ excretion by kidney is below usual levels
The Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is activated when _______________
The Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is activated when BP or blood volume is low
The Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) causes ______________________________________
The Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) causes vasoconstriction and aldosterone release, which increases sodium and water reabsorption → raises blood volume → raises BP
T/F: Kidneys have parasympathetic nervous system innervation
False; kidneys only have sympathetic nervous system innervation
Where does secondary active transport get its energy from?
Secondary active transport uses stored energy from the Na+ gradient created by the Na+/K+ ATPase pump
Ion channels allow _______ diffusion of ions down their concentration gradient
Na⁺ channels, K⁺ channels, Cl⁻ channels, Ca²⁺ channels
Ion channels allow passive diffusion of ions down their concentration gradient
Na⁺ channels, K⁺ channels, Cl⁻ channels, Ca²⁺ channels
Facilitated diffusion uses _____________, but no _____________
(i.e. glucose)
Facilitated diffusion uses carrier proteins, but no energy (ATP)
(i.e. glucose)
In the proximal tubule, Na+ moves into the cell ________________ amino acids (secondary active transport)
In the proximal tubule, Na+ moves into the cell together with amino acids (secondary active transport)
In the proximal tubule, Na+ enters the cell and H+ is ______________ into the tubular fluid
In the proximal tubule, Na+ enters the cell and H+ is secreted into the tubular fluid (antiport)
The ATPase pump uses ATP and maintains _______ Na+ inside the cell to allow sodium to keep entering from the luminal side
The ATPase pump uses ATP and maintains low Na+ inside the cell to allow sodium to keep entering from the luminal side
T/F: Sodium is never secreted by the nephron epithelial cells
True, sodium only undergoes reabsorption
In the proximal tubule:
______________ is reabsorbed
______________ is reabsorbed
______________ is secreted
In the proximal tubule:
sodium is reabsorbed
glucose is reabsorbed
hydrogen ion is secreted
_________ membrane → side of the cell facing the tubular fluid
_________ membrane → side of the cell facing the blood
luminal membrane → side of the cell facing the tubular fluid
basolateral membrane → side of the cell facing the blood
__________ and __________ are co-transported with sodium, while __________ is exchanged with sodium
glucose and amino-acids are co-transported with sodium, while hydrogen is exchanged with sodium
Counter-Transport of Sodium and Hydrogen (Na⁺/H⁺ Exchanger)
H+ is secreted into the lumen __________ its concentration gradient
Counter-Transport of Sodium and Hydrogen (Na⁺/H⁺ Exchanger)
H+ is secreted into the lumen against its concentration gradient
__________ and __________ channels are on the luminal membrane of the collecting duct, whereas there are no ______________ channels on the luminal membrane of the proximal tubule
sodium and potassium channels are on the luminal membrane of the collecting duct, whereas there are no sodium channels on the luminal membrane of the proximal tubule
Na+ reabsorption is an __________ process occuring in all tubular segments except __________________ (b/c they don’t have any proteins in the luminal membrane that will transport sodium)
Na+ reabsorption is an active process occuring in all tubular segments except descending limb of loop of Henle (b/c they don’t have any proteins in the luminal membrane that will transport sodium)
Water reabsorption happens via ___________, but is dependant upon __________________
Water reabsorption happens via osmosis, but is dependant upon Na+ reabsorption
Water moves through ______________
highly expressed in ____________________
absent in luminal membrane of collecting ducts unless __________ is present
Water moves through aquaporins
highly expressed in proximal tubule
absent in luminal membrane of collecting ducts unless ADH is present
AQP1 → only found in _________________
AQP2, AQP3, AQP4 → only found in ______________
AQP1 → only found in proximal tubule
AQP2, AQP3, AQP4 → only found in collecting duct
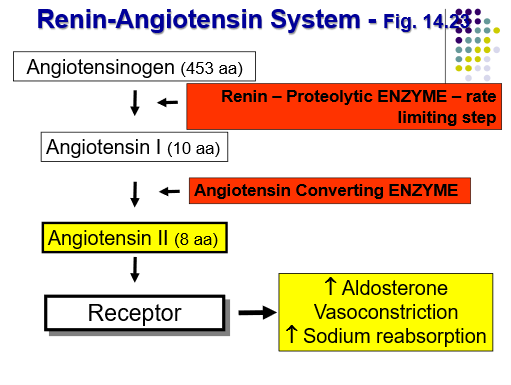
Angiotensinogen circulates in the blood and does nothing untul it comes in contact with the protein hormone _____________
Angiotensinogen circulates in the blood and does nothing untul it comes in contact with the protein hormone renin
Steps of the Renin-Angiotensin Hormone System
Angiotensinogen → does nothing until it comes in contact with renin
Renin clips off a 10 amino acid segment called Angiotensin I
Angiotensin I does nothing until it comes in contact with the angiotensin converting enzyme
Angiotensin converting enzyme will clip off 2 amino acids off of Angiotensin I, creating Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II binds to it receptor and increases aldosterone secretion and vasoconstriction, which then causes increased rate of sodium reabsorption
Aldosterone increases _______________ and ______________ in the collecting duct
Aldosterone increases Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion and excretion in the collecting duct
____________ secrete renin
Juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin
What does an decrease in plasma volume result in?

What does an increase in plasma volume result in?