BCM.16 - LIPIDS
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
2 bonds in a lipid
1) Water-headgroup = hydrogen bonds / electrostatic forces
2) Tail-tail = Van der waals ( stronger if molecules are long, branched, saturated ) Th
The most common membrane lipid
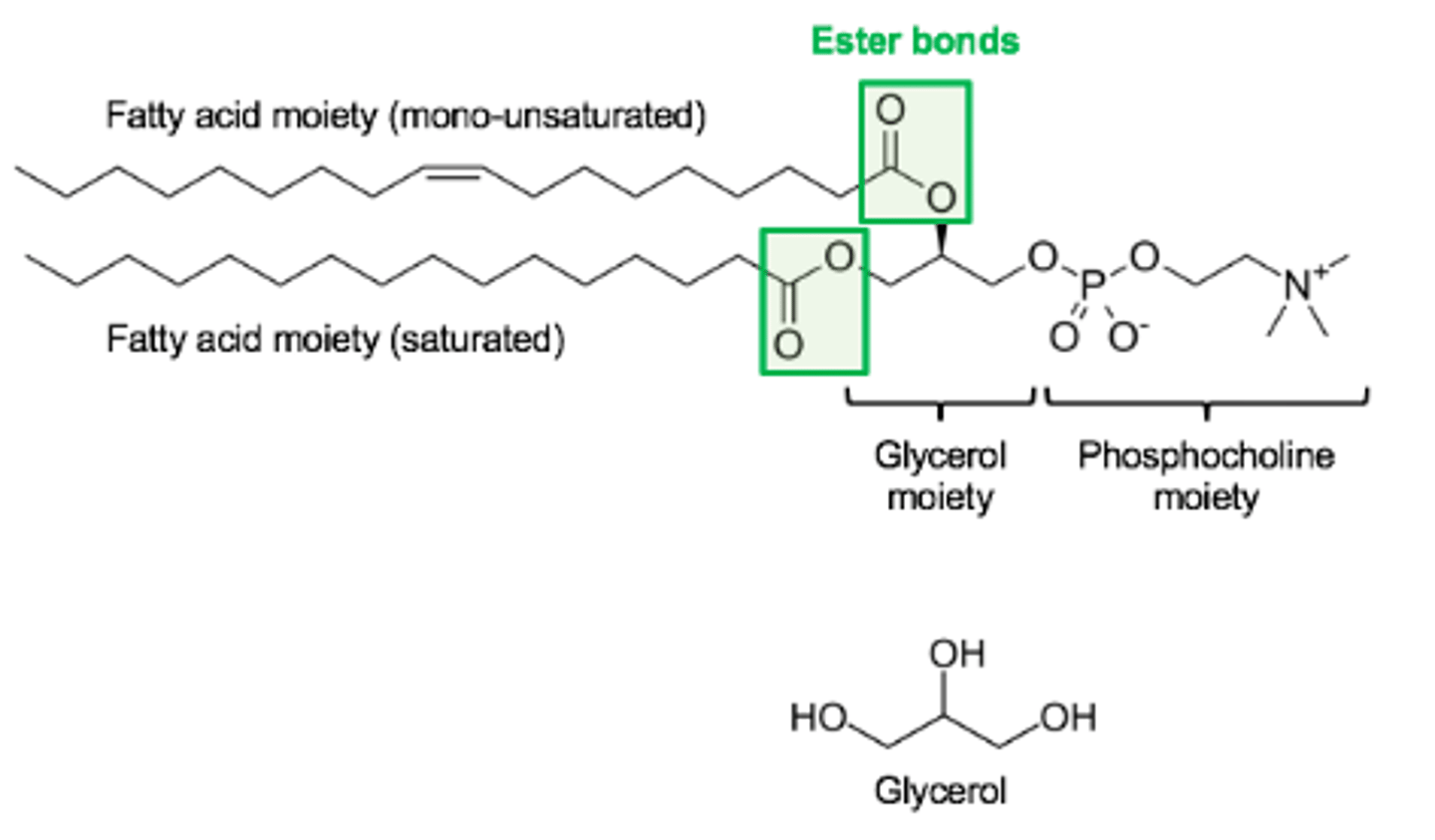
Glycerophospholipids
( Phospholipid with glycerol )
- Contain fatty acids ( saturated or unsaturated )
- The two fatty acids are covalently linked to glycerol via ester bonds.
- The third OH group of glycerol is bound to another moiety (phosphocholine in the example shown here) which is called the "head group" of the lipid.
Longer fatty acids have ...
Melting point increases...
.Because fatty acids are synthesised from C2 units (acetyl-CoA) they have an ...
higher melting points than shorter fatty acids.
~10°C per C2 unit
even number of carbon atoms.
Saturated fatty acids have ...
The biggest drop in melting point is caused by the ...
Because the double bonds are in the ... the tails become kinked and do not pack as well as straight saturated tails. This makes the solid state less stable.
higher melting points than unsaturated fatty acids.
first double bond.
cis configuration,
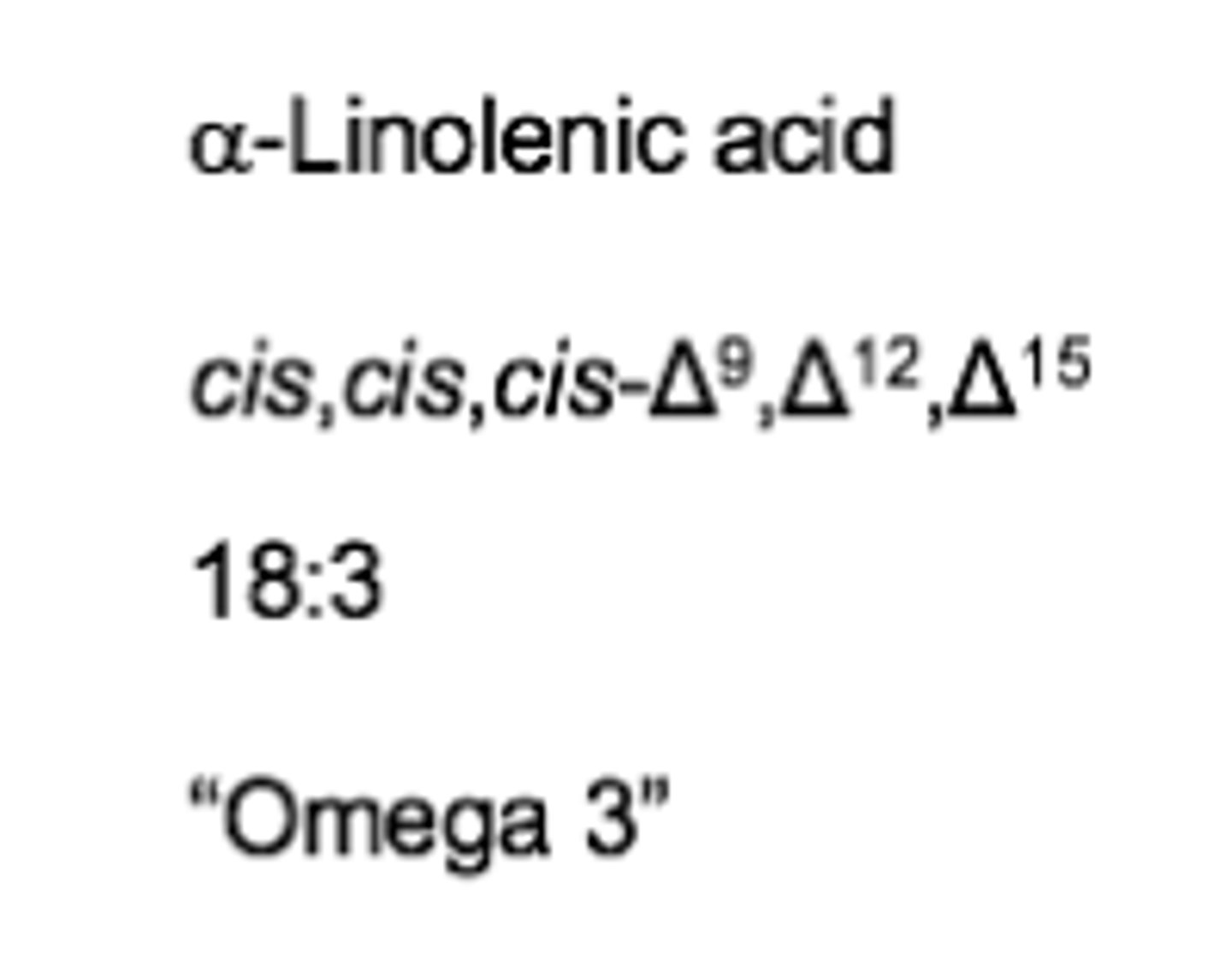
4 ways for fatty acid nomeclature
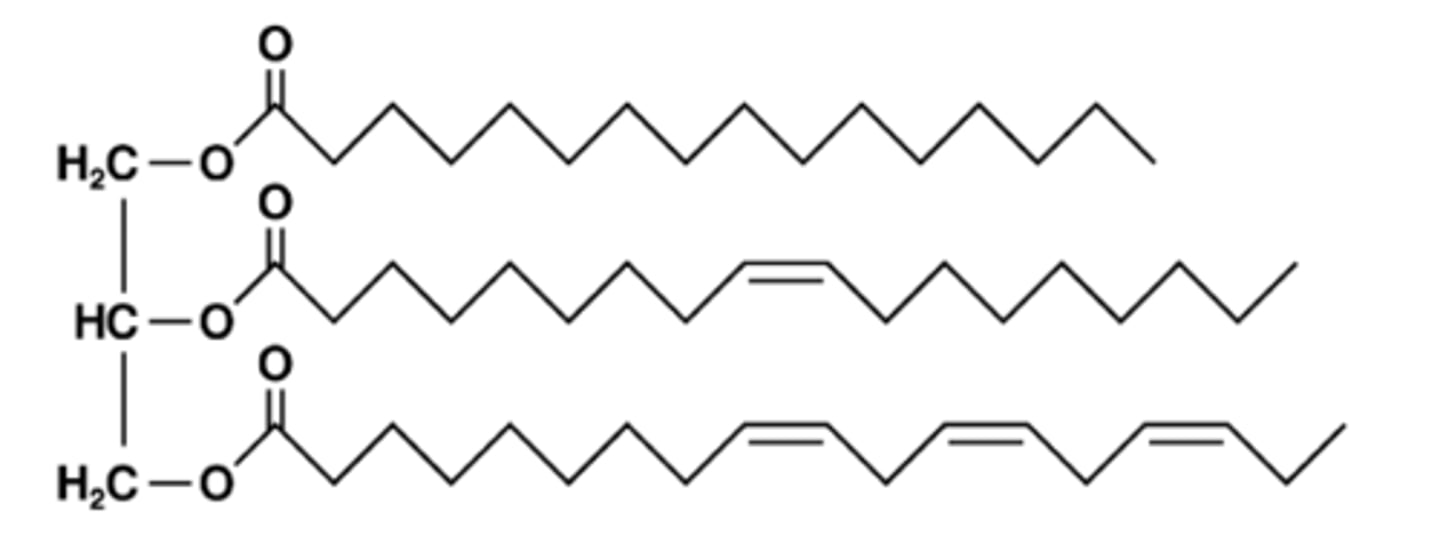
Most dietary fats are
triacylglycerols
Unsaturated fats found in many poikilotherms
- Cold-water fish
- Plants (variable, hardening off of seedlings*)
- modified to maintain membrane fluidity as temperatures changes, prevents membranes freezing / melting.
Saturated fats found in homeotherms
- Birds
- Mammals (including milk)
- modified to maintain membrane fluidity as temperatures changes, Prevents membranes freezing / melting.
What is hardening off
(*Plants raised indoors or in a greenhouse need to be acclimatised to cooler temperatures, lower humidity and increased air movement for about two to three weeks before they are planted outdoors. This 'toughening up' process is known as hardening off)
Fat provides...
energy and insulation ( Fat has a higher calorific content than carbohydrates).
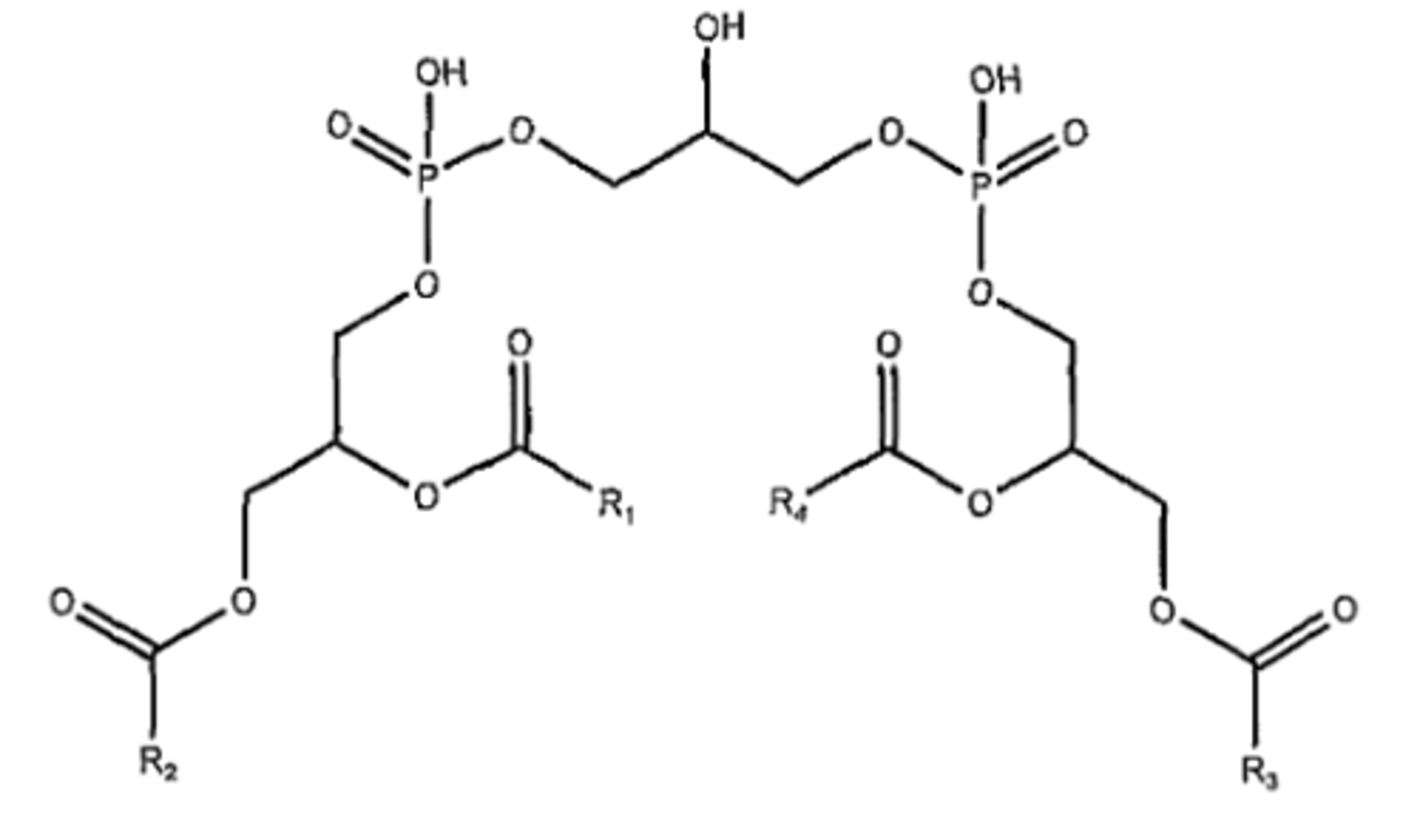
Glycerophospholipids : Cardiolipin
- Make up ~20% of the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- Essential for the function of enzymes involved in oxidative phosphorylation.
- They consist of two covalently linked phospholipid groups with 4 fatty acid chains instead of 2.
- It is ONLY produced in the mitochondrial inner membrane where it interacts closely with membrane proteins involved in oxidative phosphorylation and ATP transport.
- In Cristae, its two juxtaposed phosphate groups may act as a local proton trap on the membrane surface.
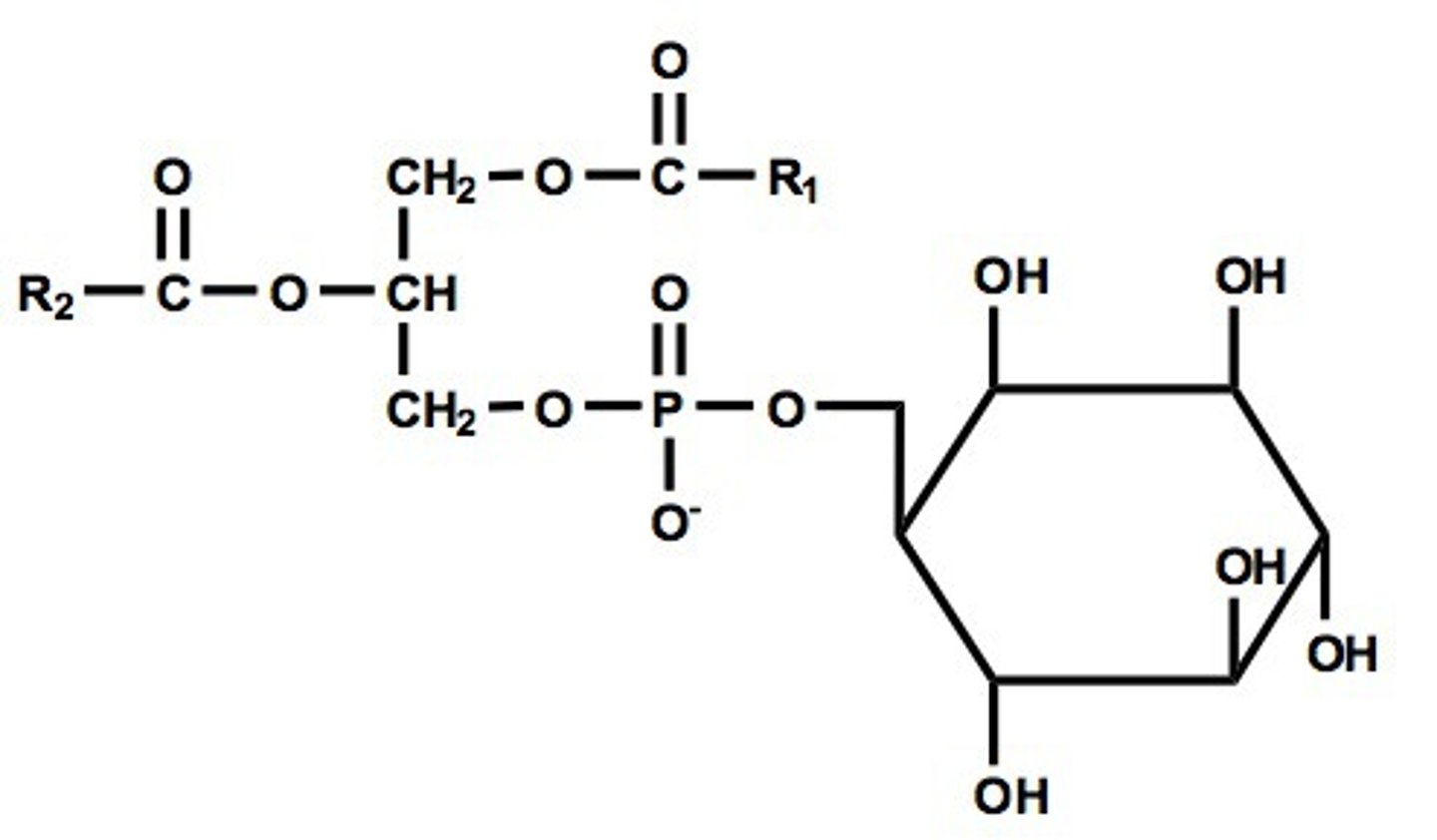
Glycerophospholipids : phosphatidylinositol
- Reversibly phosphorylated on C 1,4,5
- Concentrated in the cytosolic monolayer of the membranes
- Modified to create protein binding sites via phosphorylation.
- Various lipid kinases can add phosphate groups at distinct positions on the inositol ring, creating a binding site that recruits specific proteins from the cytosol to the membrane.
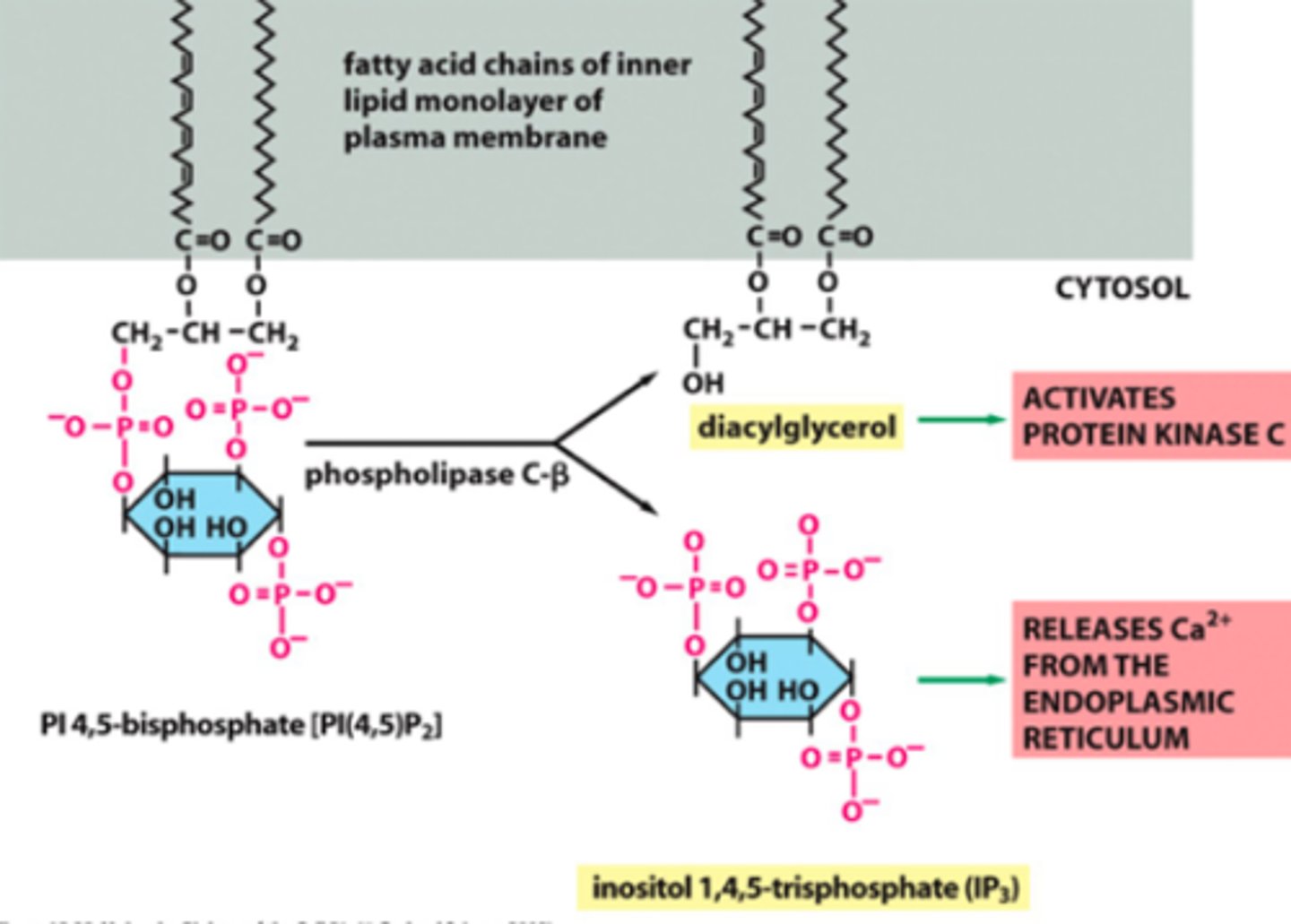
Cleavage of phosphoinositide's generates
Second messengers for cell signalling
- Diaacylglycerol activates protein kinase C
- IP3 Releases Ca2+ from the ER
Two major classes of lipids:
Glycerophospholipids
Sphignolipids
Isoprenoid lipids
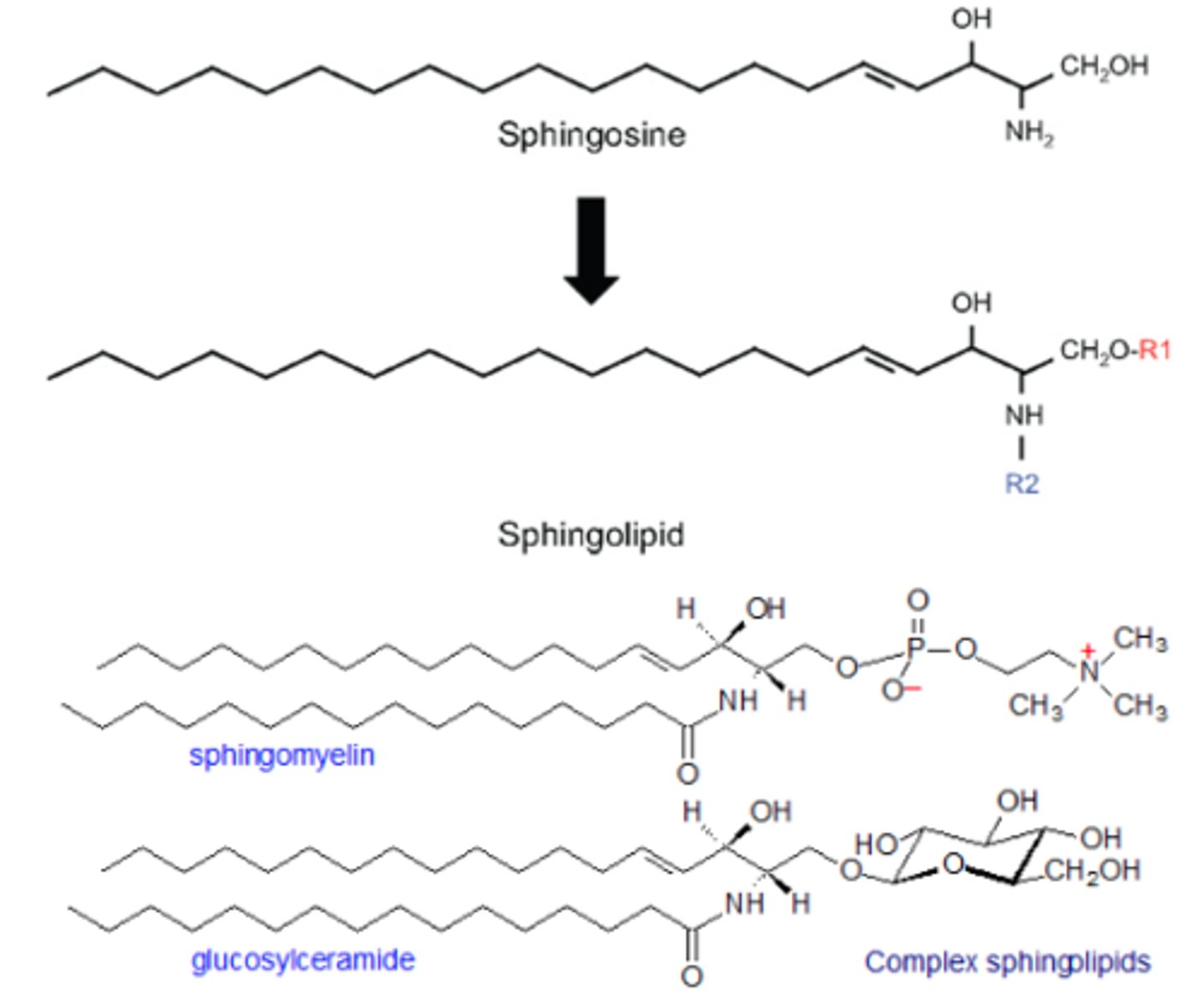
Sphignolipid structure
Sphingosine backbone replaces glycerol and one fatty acid
Sphingosine + fatty acid = ceramide (amide, not ester)
Sphingosine + fatty acid + phosphocholine = sphingomyelin
Ceramides
1) support structural elements,
2) participates in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells.
Sphignomyelin
1) surrounds and electrically insulates many nerve cell axons.
2) synthesis of sphingomyelin at the plasma membrane by sphingomyelin synthase 2 produces diacylglycerol, which is a lipid-soluble second messenger that can pass along a signal cascade.
3) In addition, the degradation of sphingomyelin can produce ceramide which is involved in the apoptotic signalling pathway.
Glycolipids
1) important functions in the nervous system.
- In animal cells they are made from sphingosine.
- Charged glycolipids ( eg gangliosides) presence alters the electrical field across the membranes and the concentrations of ions eg Ca2+ at the membrane surface which in turns effects the transmission of electrical impulses.
2) Act as binding sites for lectins in the process of cell-cell adhesion.
3) Mutant mice deficient of gangliosides show abnormal nervous systems eg axonal degradation and reduced myelination.
Gangliosides
Glycolipids with a head group composed of oligosaccharides with a terminal (NANA) molecule.
Asymmetric distribution of lipids in the plasma membrane (example: human erythrocytes) -
Phosphatidylserine (PS) is excluded from the outer leaflet by an active process (flippase). Exposure of PS on the cell surface is a pro-apoptotic "eat me" signal.
isoprenoid lipids
Contain isoprenyl units
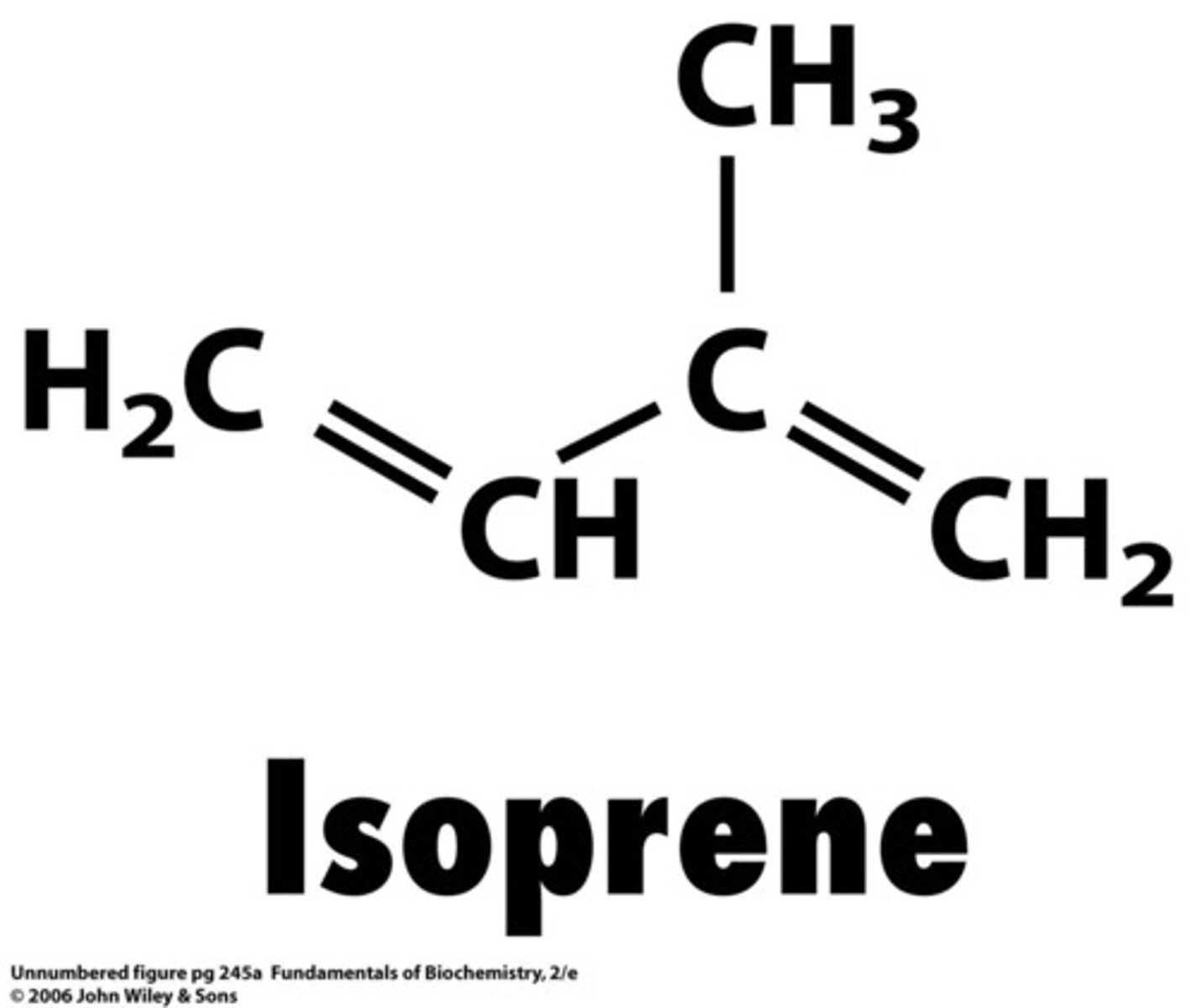
Terpenes are ...
Terpenoids (or isoprenoids) are..
- carbohydrates derived from the condensation of isoprene units
- modified terpenes containing oxygen atoms, but the distinction is often not made and all three terms are used interchangeably.
Example of a terpene
Cholesterol
Tetraterpene carotenoid pigments are the source of ... , which is essential for ... Other vitamins that are wholly or partly isoprenoid include ... The ... which are involved in the derivation of energy by the oxidation of food, are also formed from isoprenoids.
vitamin A
vision and is involved in growth, reproductive function, and neural development in animals.
vitamin E, important in reproduction, and vitamin K, necessary for the blood-clotting process.
ubiquinones (coenzyme Q),
Because of their limited solubility in water, lipids are transported by the circulation...
LDL = Low-density lipoprotein ("bad" cholesterol)
HDL = High-density lipoprotein ("good" cholesterol)
As micelle-like particles that consist of a core of triacylgycerols (triglycerides) and cholesteryl esters surrounded by a coating of protein, phospholipid and cholesterol.
.... of proteins anchors them to the membrane.
This usually happens when..
Isoprenylation
The protein is N substituted
Other types of lipid modifications include:
myristoyl and palmitoyl anchors (GPI) anchors.
Explain the effect of cholesterol on lipid bilayers
Cholesterol has conflicting effects on membrane fluidity. Rigid steroid rings stiffen membrane (less fluid above transition temperature...but they also interfere with the crystallisation of fatty acid chains (prevent sharp freezing below transition temperature).
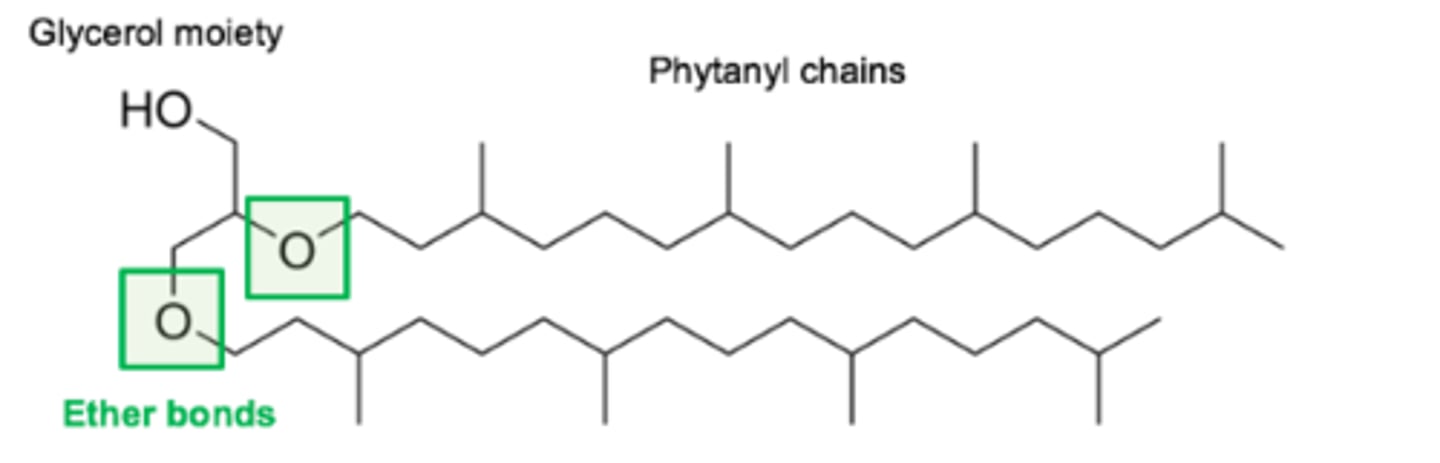
Describe the specialised lipids found in extremophiles.
The lipid shown is archaeol.
The ether linkages make archaeal lipids resistant to hydrolysis in extreme conditions.
Methanopyrus kandleri grows at temperatures up to 122°C in hydrothermal vents (“black smokers”).