Social Studies - Grade 8 Exploration to Reconstruction
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of flashcards covering key concepts and terms from the lecture notes on U.S. history from exploration to reconstruction.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Reasons for Exploration
Wealth, religion, expansion of empires, claiming territory, finding new trade routes to Asia.
Spain's Claims
Florida, Texas, California; established missions.
France's Exploration
Claimed land in the New World primarily for profit through fur trading.
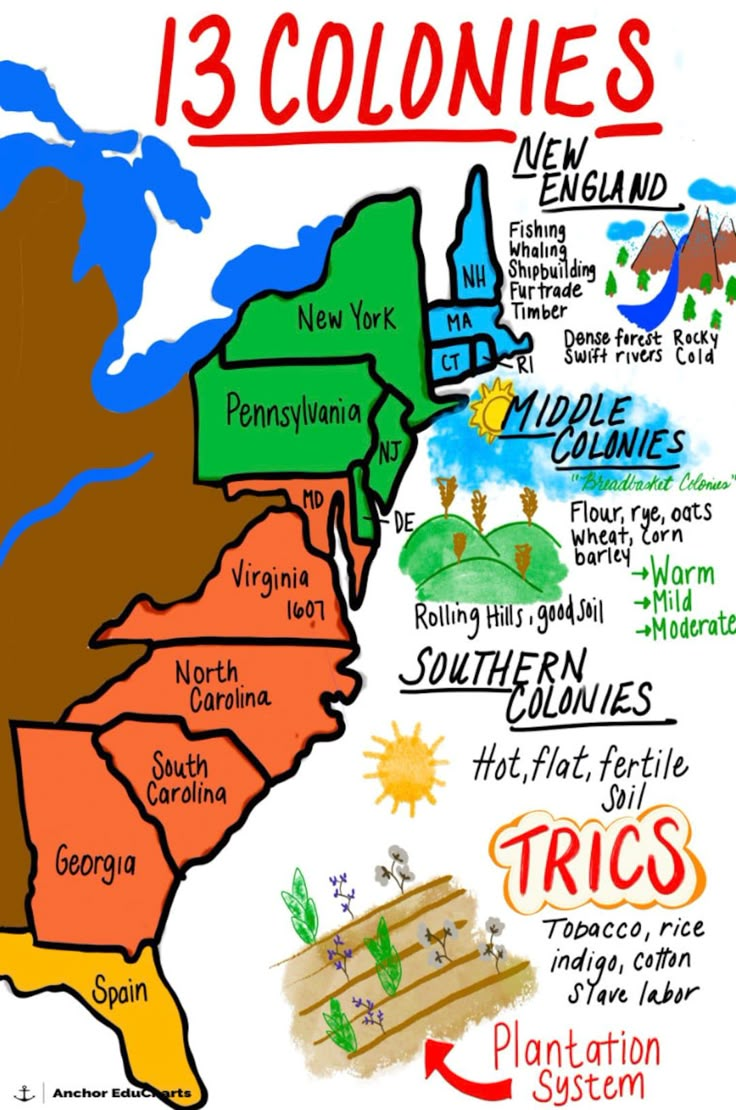
New England Colonies
Characterized by rocky soil and cold climate; focused on fishing, lumber, and shipbuilding.
Religious Toleration
The acceptance of different religious beliefs; exemplified by Roger Williams founding Rhode Island.
Massachusetts Colony
New England colony founded by Puritans/Pilgrims seeking religious freedom; Boston as major port.
Middle Colonies
Rich farmland, moderate climate; cultivated oats, wheat, and raised livestock.
Quakers
First anti-slavery group, known for their role in Pennsylvania.
Southern Colonies
Fertile soil and warm climate; economies based on cash crops; utilized slave labor.
Maryland Colony
Founded for Catholics seeking religious freedom.
Representative Government Growth
Caused by distance from Britain and frameworks like Mayflower Compact.
Mercantilism
Economic policy where British controlled colonial trade, causing discontent among colonists.
Proclamation of 1763
Law preventing colonists from moving west of Appalachian Mountains which they ignored.
Consent of the Governed
The principle that government requires the permission of the people to govern.
Intolerable Acts
British response to the Boston Tea Party; led to the First Continental Congress formation.
Declaration of Independence
Written by Thomas Jefferson; outlined grievances against King George III.
Unalienable Rights
Fundamental rights such as life, liberty, and pursuit of happiness.
Saratoga
Turning point of the American Revolution; secured French support for Americans.
Yorktown
Site of the last major battle of the American Revolution where British were defeated.
Articles of Confederation
First government of the U.S.; weak due to fear of power abuse, lacking executive branch.
Northwest Ordinance
Process for admitting new states; requires 60,000 settlers for application.
Great Compromise
Resolved representation issues in Congress; led to a bicameral legislature.
Three-Fifths Compromise
Agreement on how slaves would be counted for representation and taxation.
Federalists
Supporters of the Constitution favoring a strong central government.
Anti-Federalists
Opponents of the Constitution advocating for state powers and a bill of rights.
Checks and Balances
System ensuring that no one branch of government becomes too powerful.
Citizen Responsibilities
Duties include serving on juries, voting, staying informed, and obeying laws.
1st Amendment
Guarantees freedoms of religion, speech, press, assembly, and petition.
4th Amendment
Protects against unreasonable searches and seizures.
6th Amendment
Guarantees the right to a fair trial.
8th Amendment
Prohibits cruel or unusual punishment and excessive fines.
10th Amendment
Reserves powers not given to the federal government to the states.
Hamilton’s Financial Plan
Steps to stabilize the economy including the establishment of the National Bank.
Farewell Address
George Washington's warning against political parties and permanent alliances.
Federalist Party
Led by Hamilton; advocated for a strong federal government and industrial economy.
Democratic-Republican Party
Led by Jefferson; favored agricultural economy and limiting federal power.
Marbury v. Madison
Established judicial review; Supreme Court can declare laws unconstitutional.
Gibbons v. Ogden
Affirmed federal authority over interstate commerce.
Louisiana Purchase
Acquisition that doubled the size of the U.S. in 1803.
Causes of the War of 1812
Included British impressment of U.S. sailors.
Monroe Doctrine
Policy preventing European colonization in the Western Hemisphere.
Jacksonian Democracy
Expansion of voting rights and increased political participation.
Nullification Crisis
Conflict over whether states could invalidate federal laws.
Worcester v. Georgia
Supreme Court ruling favoring Native Americans land rights, ignored by Jackson.
Hudson River School
Group of artists known for painting American landscapes.
Effects of the War of 1812
Boosted U.S. manufacturing due to British goods boycott.
Industrial Revolution
Period marked by advancements in inventions impacting manufacturing.
Cotton Gin
Invention that increased cotton production and demand for slave labor.
Interchangeable Parts
Manufacturing process that led to mass production of goods.
Free Enterprise
Economic system with minimal government regulation based on supply and demand.
Women in the Workforce
Early involvement in textile mills and employment outside the home.
Canals
Man-made waterways that facilitated trade and transportation.
Steamboat and Railroads
Technological advancements that increased transportation efficiency.
Telegraph
Communication device invented by Samuel Morse for rapid long-distance messaging.
Urbanization
The growth of cities as people moved for factory jobs.
Immigrants in the 19th Century
Irish and others moved to the U.S. for opportunity, faced nativist backlash.
Missouri Compromise
Effort to maintain a balance between free and slave states.
Manifest Destiny
Belief that U.S. was destined to expand across the continent.
Oregon Territory
Land gained from treaty with Britain fulfilling Manifest Destiny.
U.S.-Mexican War
Conflict arising from Texas's annexation and ensuing border disputes.
Mexican Cession
Territory acquired after the U.S.-Mexican War, fueling slavery debates.
California Gold Rush
Mass migration to California post-gold discovery; significant immigration influx.
Second Great Awakening
Religious revival movement leading to social reform efforts.
Dorothea Dix
Advocate for prison reform and mental health facilities.
Temperance Movement
Campaign led by women to reduce alcohol consumption.
Abolitionist Movement
Efforts to end slavery, featuring notable figures like Frederick Douglass.
Transcendentalism
Philosophical movement emphasizing individualism and social reform.
Women’s Rights Movement
Advocated for suffrage and equal rights for women.
Sectionalism
Economic interests divided between North (industrial), South (agricultural), and West (mining).
Fugitive Slave Act
Legislation that required the return of runaway slaves.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
Allowed territories to decide on slavery, leading to violent conflicts.
Debate Over Slavery
Central issue leading to the Civil War, particularly opposing Republican policies.
Abraham Lincoln
President during the Civil War, committed to preserving the Union.
Union Advantages
Greater industrial resources and manpower during the Civil War.
Vicksburg
Strategic victory for the Union; gained control of Mississippi River.
Appomattox Court House
Site of the Confederate surrender, marking the end of the Civil War.
Reconstruction
Post-Civil War era focusing on rebuilding the South and integrating freed slaves.
Radical Republicans
Political faction that sought to punish Confederate leaders and enhance rights for freedmen.
13th Amendment
Constitutional amendment abolishing slavery.
14th Amendment
Granted citizenship to all persons born in the U.S. and equal protection under the law.
15th Amendment
Protected voting rights for African American males, countered by poll taxes.
Hiram Rhodes Revels
First African American elected to the U.S. Senate.
Black Codes
Restrictions imposed on freed slaves aimed at limiting their newfound liberties.
Freedmen’s Bureau
Agency designed to assist freed slaves with education and employment.
Sharecropping
Agricultural system that trapped former slaves in debt and poverty.
Transcontinental Railroad
Major infrastructure project that accelerated westward settlement and trade.
Northern Economy
Characterized by factories, trade, and wage labor.
Southern Economy
Relied heavily on agriculture and slave labor.
Western Economy
Focused on mining and agriculture.
Compromise of 1850
Agreement balancing free and slave states while enacting a stricter fugitive slave law.
What contributed to the growth of representative government in the 13 colonies?
The distance from the 13 colonies to Great Britain led to the growth of representative government, as it made direct control from the British Parliament difficult.
What are the different regions of the 13 colonies?
The 13 colonies are divided into three regions: New England Colonies, Middle Colonies, and Southern Colonies.
List the New England Colonies.
Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Hampshire, and Connecticut.
List the Middle Colonies.
New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware.
List the Southern Colonies.
Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.
What were the 13 colonies?
The 13 colonies were British settlements established along the east coast of North America from the early 17th century to the 18th century, which eventually declared independence from Great Britain.
How did the cotton gin impact the demand for slavery?
The invention of the cotton gin by Eli Whitney in 1793 significantly increased the demand for slave labor in the Southern United States, as it made cotton processing more efficient and profitable, leading to a greater reliance on enslaved workers to cultivate and harvest cotton.
What were the requirements for admitting new states under the Northwest Ordinance?
The requirements for admitting new states under the NORTHWEST ORDINANCE:
A territory must have a population of at least 60,000 residents.
It had to have a written constitution.
The new state must ensure that the rights of its inhabitants were protected, including the prohibition of slavery in the Northwest Territory.
What is the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights is the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution, which guarantee fundamental rights and freedoms to individuals.
What is the First Amendment?
The First Amendment grants freedom of speech, press, religion, assembly, and petition. Example: A person can express their opinion about the government without fear of retaliation.