Tectonic Hazards Revision
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Layers of the Earth
Inner core, outer core, mantle, crust, lithosphere
Lithosphere
The rigid crust and upper mantle, broken into tectonic plates
Asthenosphere
The semi-molten mantle below the lithosphere where convection occurs
Density of oceanic crust
~3.0 g/cm³
Density of continental crust
~2.7 g/cm³
Main tectonic plates
Pacific, North American, South American, African, Eurasian, Antarctic, Indo-Australian
Plate boundary
The edge of tectonic plates where most earthquakes and volcanoes occur
Movement of tectonic plates
Via convection currents in the mantle, causing divergence, convergence, or lateral movement
Types of plate boundary
Divergent/constructive, convergent/destructive/collision, conservative/transform
Constructive/divergent boundary example
Eurasian Plate and North American Plate at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Destructive/convergent boundary example
Nazca Plate and South American Plate at the Andes subduction zone
Collision boundary example
Indian Plate and Eurasian Plate at the Himalayas
Conservative/transform boundary example
North American Plate and Pacific Plate at the San Andreas Fault
Location of most earthquakes
At plate boundaries, along fault lines
Earthquake
A sudden shaking of the Earth caused by stress release at a fault
Focus
The point underground where the earthquake starts
Epicentre
The point on the surface above the focus
Seismic waves
Energy waves that travel through the Earth after an earthquake
Types of seismic waves
P-waves (fast, compressional), S-waves (slower, shear), Love-Waves, Rayleigh-Waves
Love waves
Seismic surface waves causing horizontal ground movement; very destructive
Rayleigh waves
Seismic surface waves causing rolling, elliptical motion, damaging to buildings
How do earthquakes happen?
Plates stick, pressure builds, sudden slip, seismic waves radiate
Scale measuring earthquake magnitude
Moment Magnitude Scale (or Richter Scale)
Scale measuring earthquake intensity
Mercalli Scale
Secondary effect of an earthquake
Tsunamis, landslides, building collapse
Tsunami
A giant sea wave triggered by underwater earthquakes
Magma
Molten rock beneath the Earth's surface
Lava
Molten rock on the surface
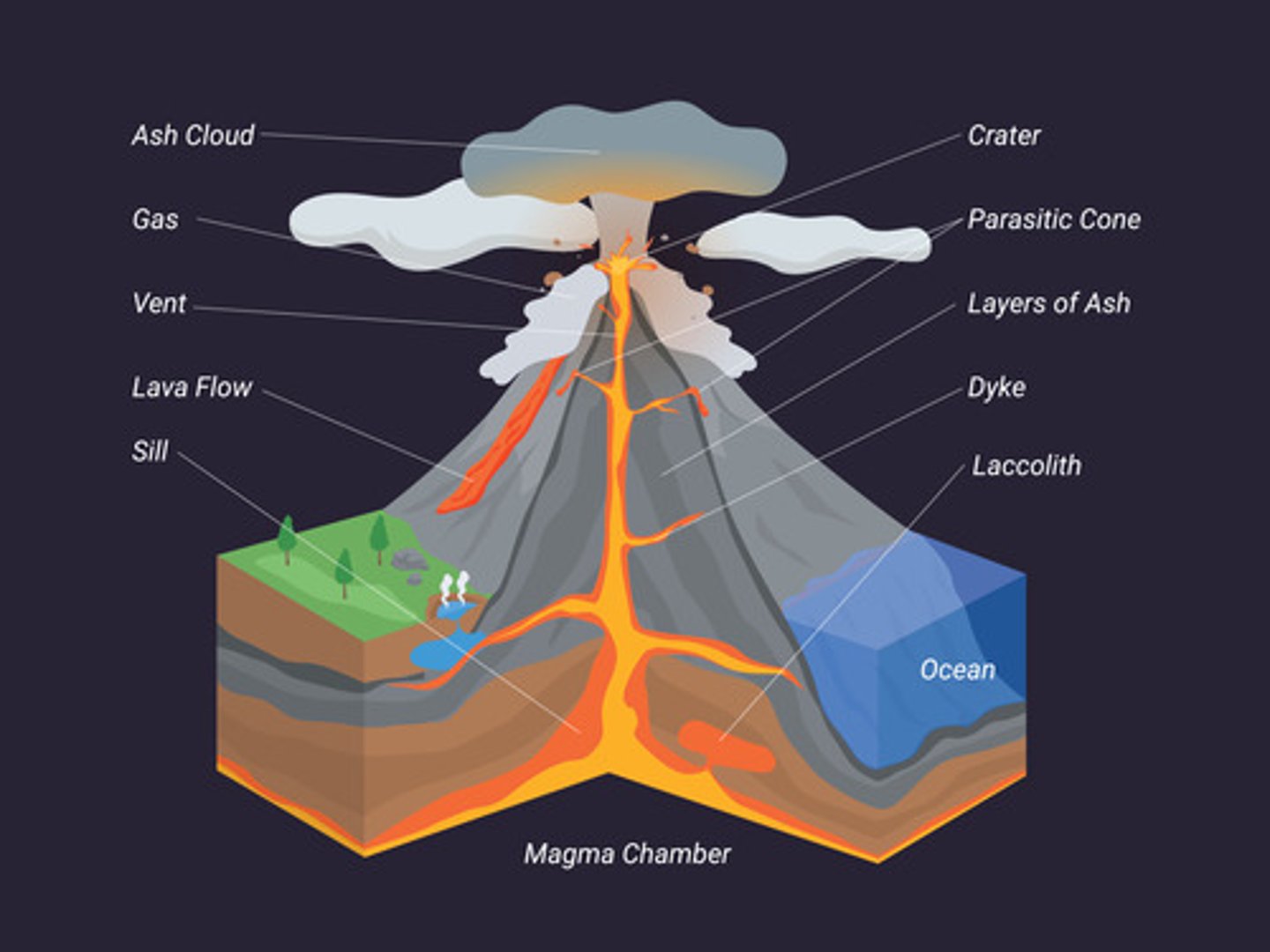
Main features of a volcano
Crater, vent, magma chamber, secondary cone (parasitic cone)
Shield volcano
A wide, gently sloping volcano with basaltic lava flows
Example of a shield volcano
Mauna Loa, Hawaii
Composite/strato volcano
Tall, steep-sided volcano made of layers of ash and lava
Example of a composite volcano
Mount Fuji, Japan
Cinder cone volcano
Small, steep volcano built from cinders and tephra
Example of a cinder cone
Paricutin, Mexico
Classification of volcanoes by activity
Active, dormant, extinct
Volcanic hazards
Lava flows, pyroclastic flows, ash falls
Lahar
A mudflow of volcanic ash and water
Tephra
Material ejected from a volcano during an eruption
Volcanic hazard speed impact
Faster hazards cause more destruction and less time to evacuate
Importance of eruption size/frequency
Larger/frequent eruptions increase risk and damage
Example of toxic gas from volcanoes
Sulphur dioxide (SO₂)
Pyroclastic flow
A fast-moving, hot gas and ash cloud
Difference between lahars and pyroclastic flows
Lahars are mud/ash, slower; pyroclastic flows are hot, fast, gas
Positive effect of volcanic eruptions
Fertile soils or tourism/research opportunities
Secondary cone
A smaller vent/cone forming on the side of the main volcano
Tohoku earthquake date
11th March 2011
Tohoku earthquake magnitude
9.0 (Moment Magnitude Scale)
Plates causing Tohoku earthquake
Pacific Plate subducting under North American Plate
Depth of Tohoku earthquake focus
30 km
Main primary hazard of Tohoku earthquake
Tsunami
Height of tsunami waves
Up to 40 metres
Secondary effect of Tohoku earthquake
Fukushima nuclear meltdown
Number of deaths in Tohoku earthquake
Around 20,000
Economic cost of Tohoku earthquake
$235 billion
Long-term response to Tohoku earthquake
Higher sea walls, tsunami warning systems
Location of Montserrat
Caribbean island
Start date of Montserrat eruption
18th July 1995
Type of Montserrat volcano
Composite/Stratovolcano
Plates causing Montserrat eruption
Atlantic Plate subducting beneath Caribbean Plate
Main hazard of Montserrat eruption
Pyroclastic flows
Number of deaths in Montserrat eruption
19 people
Capital affected by Montserrat eruption
Plymouth buried
Percentage of Montserrat uninhabitable
Two-thirds
Population migration from Montserrat
Many to the UK
Monitoring installed for Montserrat
Montserrat Volcano Observatory (MVO)
Rift valley
Lowland formed at divergent boundaries
Mid-ocean ridge
Underwater mountain range at constructive margins
Ocean trench
Deep depression where a plate is subducted
Fold mountains
Mountains formed at continental collision zones
Accretionary wedge
Sediments scraped off subducting plate at destructive boundary
Benioff zone
Zone of earthquake focus down a subducting plate
Difference between continental & oceanic crust
Oceanic: dense, basalt; Continental: less dense, granite
Orogeny
Mountain-building process
Slab pull
Force from dense sinking plate pulling rest of plate
Ridge push
Force from elevated mid-ocean ridge pushing plates apart
Conservative boundary
Plates slide past each other (e.g., San Andreas)
Collision boundary
Plates crash, forming mountains (e.g., Himalayas)
Destructive boundary
Oceanic subducts under continental (e.g., Andes)
Constructive boundary
Plates move apart, magma rises (e.g., Mid-Atlantic Ridge)
Primary response
Immediate actions: rescue, medical aid, food, shelter
Secondary response
Longer-term: rebuilding, planning, infrastructure repair
Technology for earthquakes
Seismometers, GPS
Technology for volcanoes
Gas sensors, satellite imagery
Why do volcanoes erupt at destructive boundaries?
Subduction melts mantle, magma rises
Why do earthquakes occur at conservative boundaries?
Plates stuck, pressure builds, sudden slip
Pyroclastic flow speed
Up to 600 km/h
Positive human reason for living near a volcano
Fertile soil, geothermal energy, tourism
Importance of magnitude in disaster planning
Determines scale of damage, response required