Nervous tissue
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal chord (+optic nerve)
Peripheral nervous system
All nervous tissue outside CNS
Sensory/afferent division
Information to the CNS
Motor/efferent system
Information from CNS to the organs (muscles and glands)
Nervous system helps to
Maintain homeostasis
Initiate voluntary movement
Responsible for perception, memory, behaviour
Three major functions
Sensory — external + internal stimulus transferred CNS
Integrative — analysis + storing of info
Motor — stimulus of effectors through PNS
Neurons
Nerve cells that can be large
Conscious + unconscious control
Do not divide
High metabolic rate — will quickly die without O2
Has cell body where
short + branched dendrites convey nerve impulses
a longer single axon conducts nerve impulses to another neuron or tissue
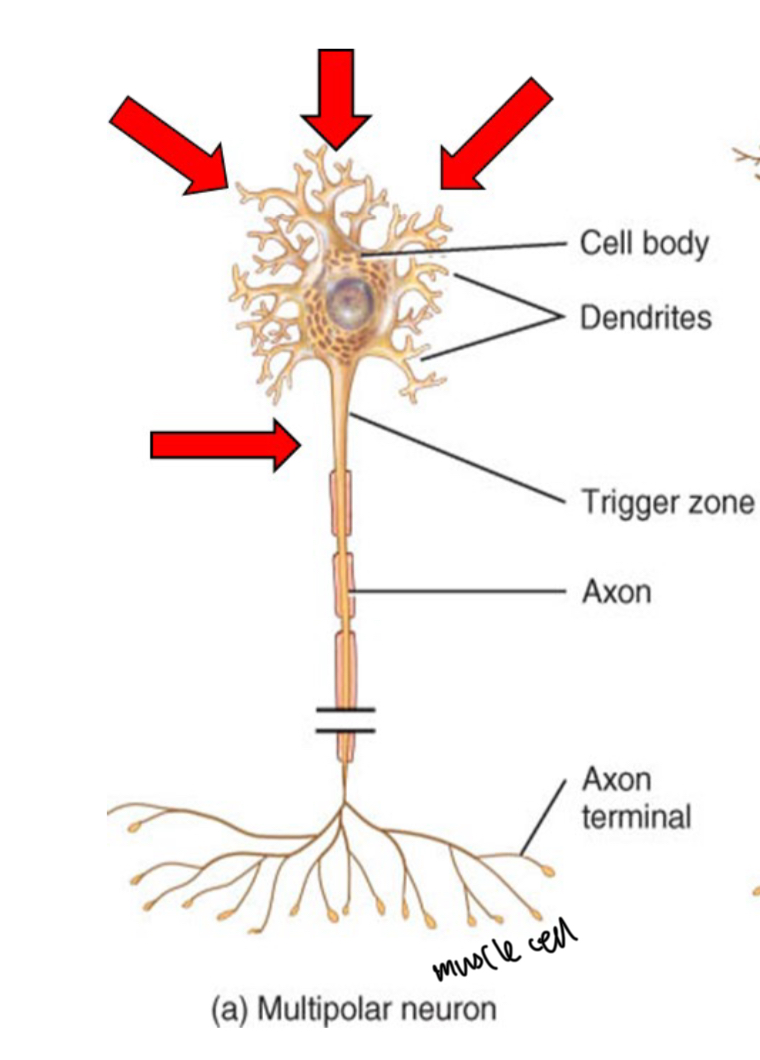
Dendrite
Receiving/input part of neuron
Axon
Carries out the nerve impulse away from neuron
Output portion of neuron
Multipolar neurons
Have 2 or more dendrites and a single axon
Most common neurons in CNS
All motor neurons (controlling skeletal muscle) are in this class
Longest neuron type, from the spinal cord to the toes.
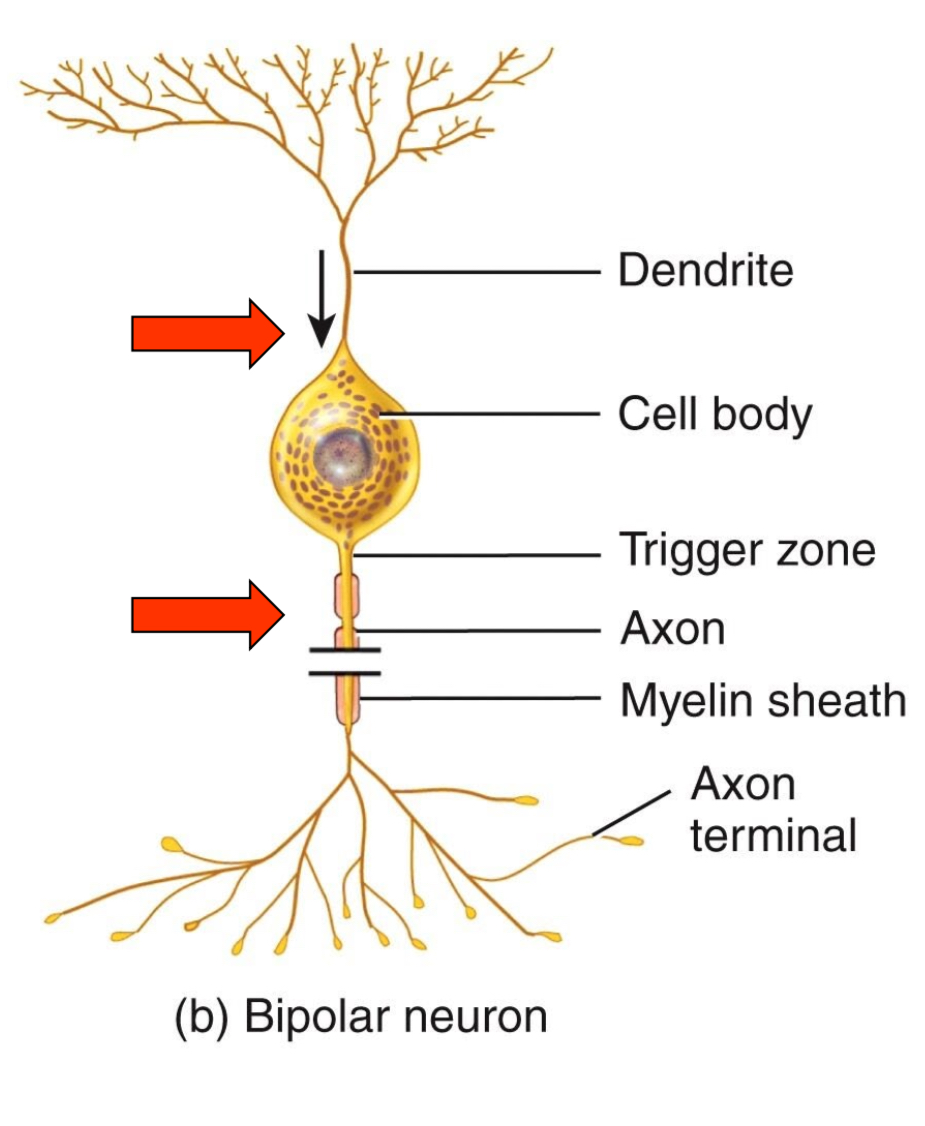
Bipolar neurons
Two distinct processes
1 dendritic process (can branch at tip but not at cell body)
1 axon
Has cell body between axon and dendrite
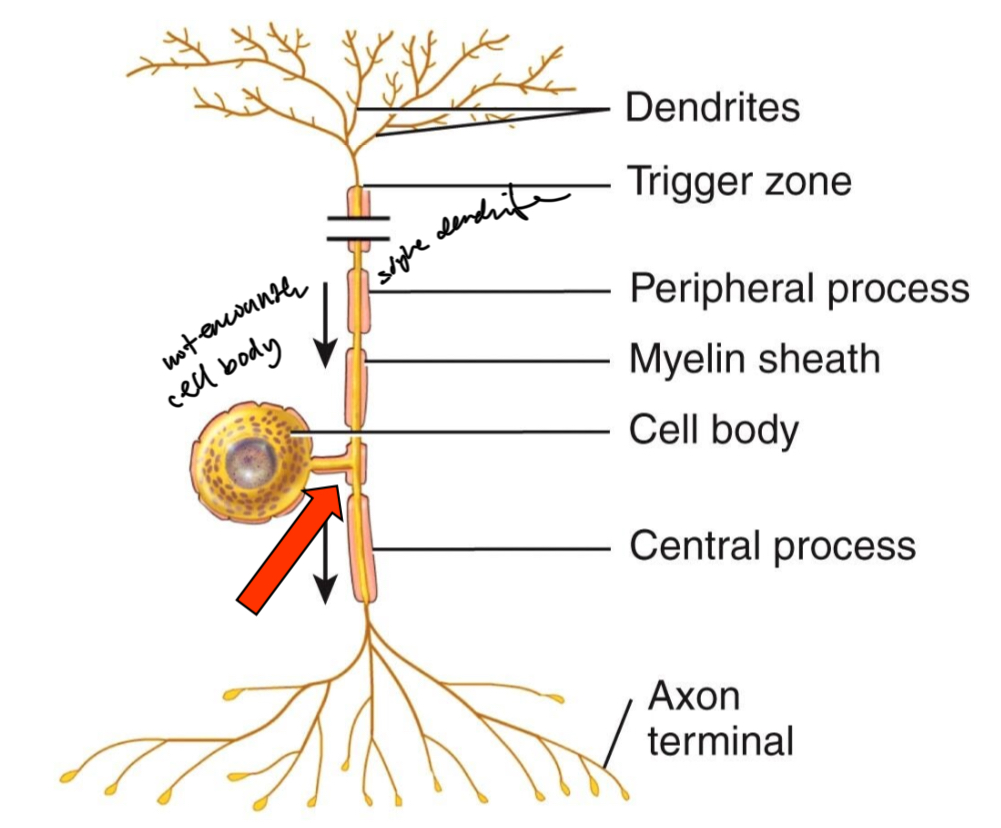
Unipolar neuron
Dendrites and axon are continuous
Cell body is off to one side
whole thing to where dendrites converge called axons
Most sensory nerves
Very long, spine to toe
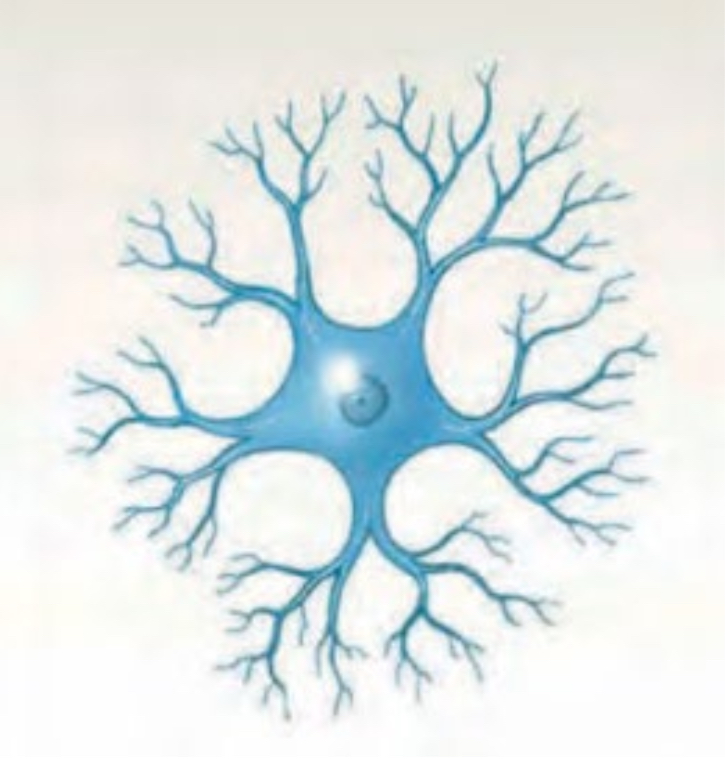
Anaxonic neurons
Rare, function misunderstood
cannot distinguish dendrites from axons
Found in brain + special sense organs

Neurologlia
Found in CNS and PNS
makes up ~50% the volume of the CNS (“glue”)
smaller than neurons but more numerous (5-50x)
do NOT propagate action potentials, but can communicate
can divide within the mature nervous system
Neuroglia functions
Physical structure of nervous tissue
Repairs framework of nervous tissue
Undertake phagocytosis
Supply nutrients to neurons
Regulate interstitial fluid in neural tissue
Neuroglia in CNS
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal cells
Neuroglia in PNS
Schwann cells
Satellite cells
Astrocytes
Star shaped , largest, most numerous, syncytium network
Support (have microfilament) and repair (scar)
Communicate with neurons through gliotransmitters such as such as glutamate
Maintain environment around neuron such as by regulating ions
Maintain blood brain barrier through endothelium, wraps around vessels and influence permeability
Ogliodendrocytes
Forms insulating multilayered myelin sheath (protein lipid layer) around CNS axons
Can myelinated more than one axon, accelerates action potential
Microglia
Phagocytes (resident macrophages) — protection
Ependymal cells
Produces cerebral spinal fluid
Lines CSF filled ventricles in the brain and the central canal in spinal cord
Single layer of predominantly cuboidal cells have cilia (flow) and microvilli (sampling)
Located in ventricles and other locations where CSF is found
ACNS mechanical buffer, moves nutrients and waste
Shwann cells
PNS version of ogliodendrocytes
forms insulating myelin sheath around axons, or just support and surround several non myelinated axons
Just one axon at a time for myelination, but many if for structure and support
Satellite cells
Surround neuron cell bodies
Support fluid and exchange, like astrocytes in CNS