Oils and Fats:
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the two main Types of rancidity in the deterioration of fats and oils?
Hydrolysis and oxidative (enzymic/non enzymic) rancidity
outline hydrolysis rancidity
hydrolysis of triacylglycerols into Fatty acids and glycerol, which can occur by lipase action. The problem is caused by FFAs, specifically SCFAs, especially in butter.
Name one food where Hydrolysis rancidity is acceptable
Blue cheese
Name the kind of reaction in Oxidative rancidity
FA Autoxidation, a free radical chain reaction
What is a free radical
a highly reactive molecule with unpaired electrons
Outline the steps of FA Autoxidation
1; initiation
2; propagation
3; decomposition
4; termination
Outline step 1 of FA Autoxidation
Initiation: Heat, Light or a metal ion causes a Hydrogen to be removed from an unsaturated FA, creating a Lipid Free-radical (R). This process involves singlet oxygen.
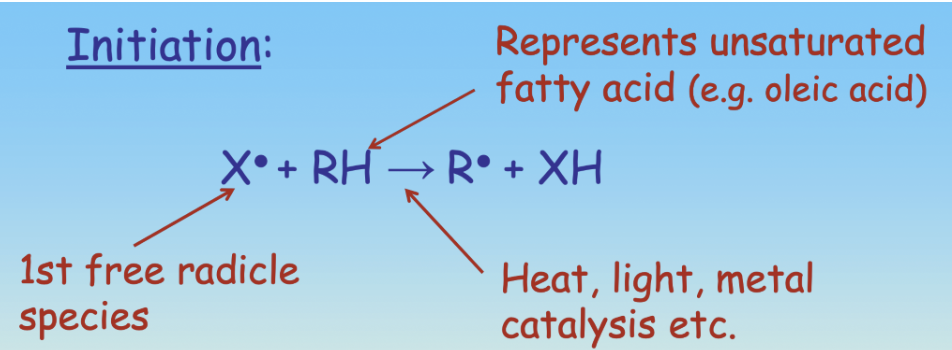
Is FA Autoxidation an enzymic or non enzymic form of oxidative rancidity?
non-enzymic
Outline step 2 of autoxidation of FA
Propagation:
1: Formation; The lipid free radical (R) reacts with atmospheric triplet oxygen to create a lipid-peroxyl Radical (ROO)
The lipid-peroxyl radical is a strong oxidifierand it attracts a H atom from a nearby FA, forming hydroperoxide: (ROOH) and a new lipid free-radical (R, from the FA)
2: Decomposition; the hydroperoxide can decompose spontaneously into alkoxy and peroxy. These 2 are responsible for the formation of aldehydes and ketones that cause the change in flavours during rancidity.
How many steps does propagation have in autoxidative rancidity
2: Formation of hydroperoxides and decomposition of hydroperoxides
Outline the termination stage
When 2 free radicals interact with each other, they form stable products, and the chain reaction ends, typically during a period with a high cincentation of free radicals