Honors Biology - Cells
1/37
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Eukaryotic Cell
A cell with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (know all). Found in multicellular organisms and unicellular protists. 10-100 micrometers
Prokaryotic Cell
A cell without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, typically found in bacteria and archaea. 1-10 micrometers

Prokaryotic Cell Diagram
Fimbriae → finger-like projections on bacteria that stick onto surfaces
Ribosomes → in bacteria, same function as in eukaryotes (protein synthesis)
Nucleoid → region where the circular DNA chromosome is
Capsule → The sticky outermost layer of a bacterium that has fimbriae on it.
Flagella → see cilia and flagella → aid in movement
Cell wall
Light Microscope (Magnification, Resolution, Advantages and Disadvantages)
beam of light passes through or reflects off the cells and passes through the glass lens
Magnification → apparent increase in size compared the original size of the object
max is 1000x
Resolution → ability to distinguish between two proximal (nearby) objects
max is 0.2 micrometers
Advantages → can see living cells + objects in appropriate color
Disadvantages → less magnification and resolution
cell appears in og color
Electron Microscope
beam of electrons passes through or reflects off the cells and passes through the electromagnets
Magnification → can achieve up to 10 million times
Resolution → provides extremely high detail, resolving power up to 0.1 nanometers
Advantages → high magnification and detail
Disadvantages → cannot view living cells and black and white images
two different types
Scanning vs. Transmission Microscope
Two types of electron microscopes are used for imaging.
Scanning microscopes provide 3D images of surfaces and the external structure, while transmission microscopes allow for viewing of internal structure through cell sections (slices of cells).
Cell Theory
all living things are composed of cells, and all cells come from other cells.
Plasma Membrane
Structure: made of two layers of phopholipids → phospholipid bilayer
Function: controls the transport of substances into and out of the cell
ex. non polar molecules and gases can diffuse pn own, hydrophillic molecules require channel proteins to pass.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
as cell size increases, surface area-to-volume ratio decreases
organelles
“little organ”
“each have a unique funtion
surronded by membranes
Endomembrane System
a network of internal membranes in eukaryotic cells that are either directly or indirectly connected in which organelles work together to sythesize, modify, and transport macromolecules (proteins + lipids)
Materials can easily move between them, allowing for:
efficient transport of molecules within the cell → membrane of nuclear envelope continuous with lumen of RER
compartmentalization of reactions → protects RXNS specific to each organelle (occur simultaneously)
consistent membrane composition and enzyme environments → phospholipid bilayer (organelles, vesicles), environment is ideal for each organelle’s enzymes
Nucleus
Structure
surrounded by a double-layer membrane called the nuclear envelope (each layer is a phospholipid bilayer)
holes in the nucleus called nuclear pores → allow material in and out of the nucleus
Nucleolus → region of rRNA (ribosomal) and proteins that produce it, its function is to synthesize ribosomes
Connected directly to the RER
Function: to store and protect DNA
DNA/Genes/Chromosomes
DNA is a nucleic acid = a polymer of nucleotides
A gene is a specific nucleotide sequence.
Function: gene is compiled into RNA which then delivers the instructions to a protein.
Chromosomes (a structure composed of DNA and attached proteins) - long strand of genes
Eukaryotic cells have one or more linear chromosomes while Prokaryotic cells have only one circular chromosome.
Condensed Chromosome → DNA is "threaded" around a "spool" of proteins (good for transportation)
Uncondensed Chromosome (Chromatin) → good for copying (for RNA
The proteins bound to DNA allow for the Chromosome to change its structure
Features that all Cells Share
Cell/plasma membrane
Cytosol - liquid part of cytoplasm (cytosol+organelles)
DNA → Prokaryotic (1 circular chromosome), Eukaryotic (many linear chromosomes)
Ribosome → cell structures that make proteins
Smooth ER (SER)
Structure
interconnected network of tubules
smooth in appearance because the SER membrane lacks ribosomes
SER is directly connected to the RER (lumens connected)
Functions
detoxification of harmful chemicals (liver)
store calcium ion (Ca+2) (required for muscle contractions)
In all cells → produce lipids (phospholipids → used for membranes)
Rough ER (RER)
Structure
network of flattened sacs (cisternae)
rough in appearance due to the presence of ribosomes on its surface (bound)
RER is directly connected to the SER, directly connected to the nuclear envelope, and indirectly connected to the Golgi
Functions
makes proteins destined for secretion (outside of the cell) or insertion into membranes
make membranes for vesicles, cell membrane, organelle membranes
know the production of proteins (attached)

Production of a Protein in the RER
A ribosome (4 degree enzyme) uses mRNA to make a polypeptide (1 degree)
Polypeptide, once inside the RER, is folded and attached with sugars, making it a glycoprotein
A transport vesicle buds off the RER with the glycoprotein inside
A transport vesicle takes a glycoprotein to the Golgi apparatus
Ribosome (NOT AN ORGANELLE)
Structure
rRNA + proteins
large and small subunits (burger) → 4o enzyme
Functions → differ depending on the location of the ribosome
creates polypeptides from amino acids
translates mRNA into polypeptide chains
Bound ribosomes→ synthesize proteins for secretion or interact with a membrane (cross or embed), ex., in RER
free-floating ribosomes → found in cytosol (liquid part of cytoplasm), synthesize proteins with a function in the cytosol
SER and RER connection
SER → makes phospholipids → delivered to RER to make membranes
RER and Nuclear Envelope Connection
instructions (mRNA) → building ribosomes
fast for reading RNA
RER makes membranes NE needs
The nucleolus produces ribosomes, which need to be embedded in the RER
Golgi Apparatus
Structure
flattened sacks (made of membrane) in a network (vesicles allow for movement between)
sacks not connected, unlike RER
Has directionality: Cis face (“Receiving”) (close to RER) and trans face (“Shipping”) (close to plasma membrane; other side)
Function
modifies proteins (by adding parts, removing parts, or changing parts through chemical reactions)
Tags proteins for destination
After Golgi (3 Fates)
Plasma Membrane - functions as membrane proteins (glycoprotein, channel protein, enzyme)
Jobs outside the cell - ex. gastrin
Lysosome - recycled/hydrolysis
Lysosome
Structure → A ball of membrane that contains hydrolytic (hydrolysis) enzymes
Function → digests macromolecules and worn-out organelles and helps recycle cellular components.
Directly connect themselves with a food (storage) vacuole
Contracticle Vacuole
Organism: unicellular, freshwater eukaryote (protists)
Structure: a ball of membrane with channels that extend from the center
Function: to pump out excess water, preventing the cell from bursting
Central Vacuole
Organism: plants
Structure: a ball of membrane that contains H2O, ions, enzymes, nutrients (food)
Function: Store water to maintain the pressure of the cell
Food (Storage) Vacuole
Organism: plants and animals
Structure: ball of membrane
Function: holds food for temporary storage
Peroxisomes
Structure: ball of membrane that contains enzymes
Function
break down fatty acids → releases energy
detoxification of harmful substances (produced by some chem RXNS) into less harmful byproducts like H2O2 → (catalase) H2O + O2
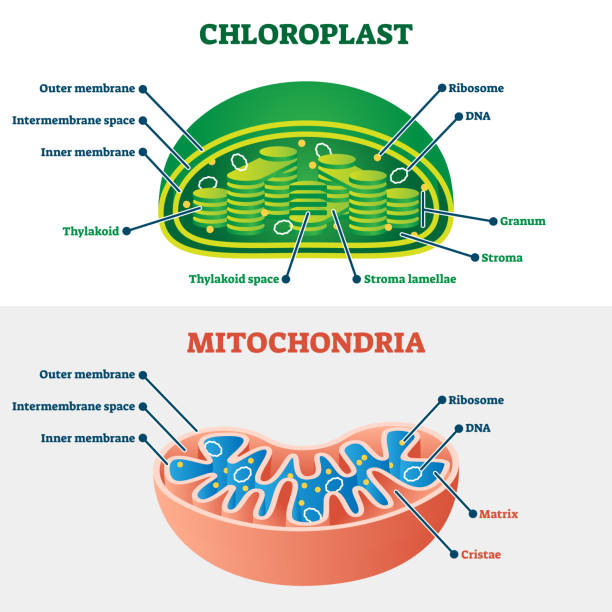
Mitochondria/Mitochondrion
Structure
outer membrane
inner membrane (highly folded, increases SA as enzymes that make ATP line the inner membrane)
intermembrane space
cristae (folds)
matrix (inside fluid)
Function → perform cellular respiration
purpose to convert the chemical energy of glucose to chemical energy of ATP
Equation + be able to explain in words: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP; In the presence of oxygen, glucose is broken down into CO2, H2O and ATP
Organisms: all eukaryotes (plants, animal, unicellular)
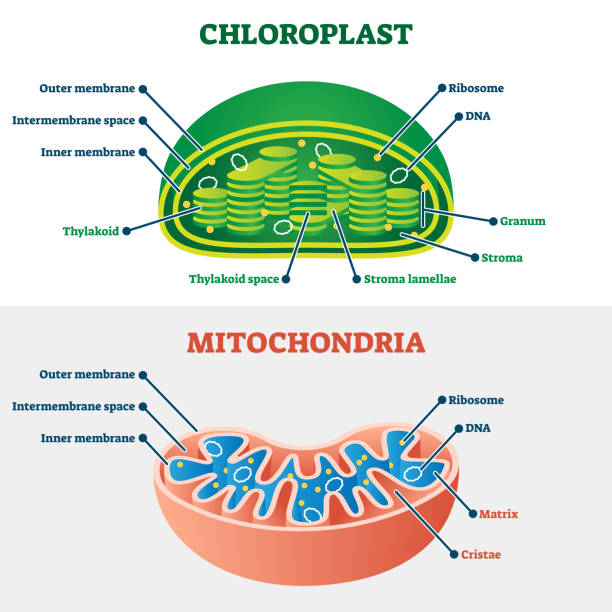
Chloroplast
Structure
Outer membrane
Inner membrane
Intermembrane space
Stroma (fluid)
Thylakoids (disks)
Granum (stack of disks, increases SA as chlorophyll lines membranes of disks)
Chlorophyll (pigment, light absorption
Function → photosynthesis
Convert solar energy into chemical energy of glucose know chemical formula (sunlight + H2O + CO2 = Glucose + O2)
Plants must make their own glucose since they don't consume it
Organisms: plants, unicellular organisms (algae)
Endosymbiosis
Reason why mitochondria and chloroplasts aren't apart of endomembrane system
Eukaryotic cell engulfed prokaryotic cell for symbiotic relationship
Evidence of endosymbiosis:
double layer membrane (outer is plasma membrane added when engulfed)
Have own DNA (circular not linear chromosomes) and ribosomes sim to prokaryotic ribosomes
Divide by binary fission (bacterial cell division)
Cytoskeleton
a dynamic network of protein fiber that give a cell its shape, provide internal organization, and enables movement → scaffolding system inside the cytoplasm
made of 3 types of proteins that each contribute to cell structure and shape, and also have specialized functions, including microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments
Microtubles
provide shape and support for the cell
provide tracks along which organelles and chromosomes move
main component of cilia and flagella
constantly break and rebuild (can do this for cell division)
Intermediate filaments
cell shape
anchor some organelles
permanent → don’t break and rebuild
microfilaments
cell shape
cell movement (muscle contractions and amoeboid movement)
attach to the extracellular matrix to keep cells of the same type together in an organ
Cilia and Flagella
Structure
both made of microtubules
cilia → short projections, often numerous
flagella → long projections, most often singular
Function
cilia → movement of materials or movement of a cell
flagella → whips around to move cells
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
complex network of molecules outside the cell that provide structural and biochemical support to the cells within a tissue → scaffolding that holds cells together and helps them communicate with their environment.
Structure
The main components are glycoproteins and collagen fiber
Proteins in the ECM connect to the intergin protein in the cell membrane, which tethers the cytoskeleton (microtubules) to the ECM.
Function
to communicate information from the outside of the cell to the inside
Cell Junctions (Types and Functions)
Specialized connections where the plasma membranes of neighboring cells (animal) come into close contact
Function → allow cells to...
Adhere to one another for tissue stability
Communicate through signals or materials
Seal off spaces between cells to control the movement of substances
Structure
Tight junction → Holds cells close together, keeps liquids in
Anchoring junction → Flexible connection
Gap junction → Channels that allow the movement of materials
Cell Wall
Structure → Rigid outer layer that surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells, fungi, bacteria, and some protists
Made of cellulose
Function:
Provides shape and structural support for plant cells
Protects from mechanical stress or bursting when water enters
plasmodesmata → pores/passageways that allow for the movement of materials through the cell wall