ch 11,6, 7, 8 broad overview
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:06 AM on 4/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
IUCN Red List
updated list of species facing high risks of extinction. amphibian species at high risk
2
New cards
single greatest cause of biodiversity loss
habitat loss
3
New cards
4 primary causes of extinction + pop decline
habitat loss, invasive species, pollution, overharvesting
4
New cards
biome experiencing greatest habitat loss
tropical rainforest
5
New cards
The Endangered Species Act
1973, prime peice of legislation protecting US biodiversity. forbids actions that destroy endangered species or their habitats
6
New cards
The Convention on Biological Diversity
1992, 193 nations promoting the conservation of species, using biodiversity in a sustainable manner, and fairly distrubuting biodiversity’s benefits
7
New cards
umbrella species
large species that roam great distances
8
New cards
parks and protected areas
meant to conserve species and habitats
13% of earth’s land is protected
13% of earth’s land is protected
9
New cards
anthropocentric
human-centered, nonhuman entities have no intrinsic value, evaluates costs and benefits solely on human impact
10
New cards
biocentric
intrinsic value to all living things, tree hugger, values nature above industry
11
New cards
ecocentric
assesses actions in terms of their costs and benefits to all ecological systems, living and nonliving, middle ground
12
New cards
preservation ethic
JOHN MUIR, preserving natural systems for their own intrinsic value
13
New cards
conservation ethic
GIFFORD PINCHOT, wise use of natural resources-- utilitarian standard
14
New cards
land ethic
ALDO LEOPOLD, include environemtn in ethical framework pls
15
New cards
classical economics
adam smith, self-interested economic behavior will benefit society as a whole if monitored by laws and private property rights, and operating within competitive marketplace
16
New cards
neoclassical economics
includes psychcological factors underlying consumer choices and considers supply, demand, costs, benefits. largely describes today’s market systems
17
New cards
cost-benefit analysis
neoclassical approach, assesses the costs paid to gain benefits, used to evaluate public projects, do not proceed if costs exceed benefits
18
New cards
external costs
costs borne by members of soceity uninvolved in the economical exchange
19
New cards
steady-state economy
does not grow or shrink, mirrors natural ecological systems
20
New cards
GDP (gross domestic product)
all economic activity, good or bad, does not account for nonmarket values, increased by pollution
21
New cards
GPI (geniune progress indicator)
differentiates between good and bad economic activity, has been flat in recent years, more accurate depiction of society’s well-being
22
New cards
ecolabeling
provides buisnesses with incentive to move towards more sustainable processes
23
New cards
Millennium Development Goals for 2015
eight broad goals for sustainable development
1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
2. Achieve universal primary education
3. Promote gender equality and empower women
4. Reduce child mortality
5. Improve maternal health
6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases
7. Ensure environmental sustainability
8. Global partnership for development
1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
2. Achieve universal primary education
3. Promote gender equality and empower women
4. Reduce child mortality
5. Improve maternal health
6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases
7. Ensure environmental sustainability
8. Global partnership for development
24
New cards
tragedy of the commons
everyone takes freely, nothing left
25
New cards
National Environmental Policy Act
established EPA and required that an environmental impact statement (EIS) be prepared for federal action like logging, or building a highway or dam
26
New cards
Clean Water Act
1972, established goal of creating fishable, swimmable waterways by setting a maximum amount of pollution that can be discharged into waterways and requiring permits to do so. recent amendments focused on stormwater drainage and municipal sewage discharge facilities
27
New cards
Clean Air Act
1970, established air quality standards for primary and secondary pollutants and required states to develop specific plans for cleaner air like emissions testing of cars
28
New cards
Endangered Species Act
1973, identifies threatened and endangered species in the US, puts their protection ahead of economic consideration, protects their habitats, and helps the FIsh & Wildlife Service prepare recovery plans
29
New cards
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA)
1980, established the Superfund for emergency response and remediation of toxic and hazardous waste sites
30
New cards
Resources Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
1976, the primary law pertaining to the disposal of solid and hazardous wastes, setting standards and requiring permits for “cradle to grave” management
31
New cards
Safe Drinking Water Act
1974, authorizes the EPA to set quality standards for tap water provided by public water systems and to protect drinking water from sources of contamination
32
New cards
Green taxes
polluter-pays-principle, taxes buisnesses that are environmentally harmful, provides a market-based incentive to invest in “cleaner” processes
33
New cards
cap-and-trade system
acceptable level of pollution is determined by the govt, which then issues permits. companies can trade and benefit off of selling their permits
34
New cards
Montreal Protocal
1989, treaty aimed at reducing the emission of airborne chemicals that deplete stratospheric ozone. is considered the **most successful effort to date** in addressing the global environmental problem
35
New cards
Kyoto Protocol
2005, an agreement drafted in 1997 that calls for reducing emissions of 6 greenhouse gases to levels lower than their 1990 levels by 2012. US refuses to ratify this b/c economics
36
New cards
current world population
7\.8b (as of 2021)
37
New cards
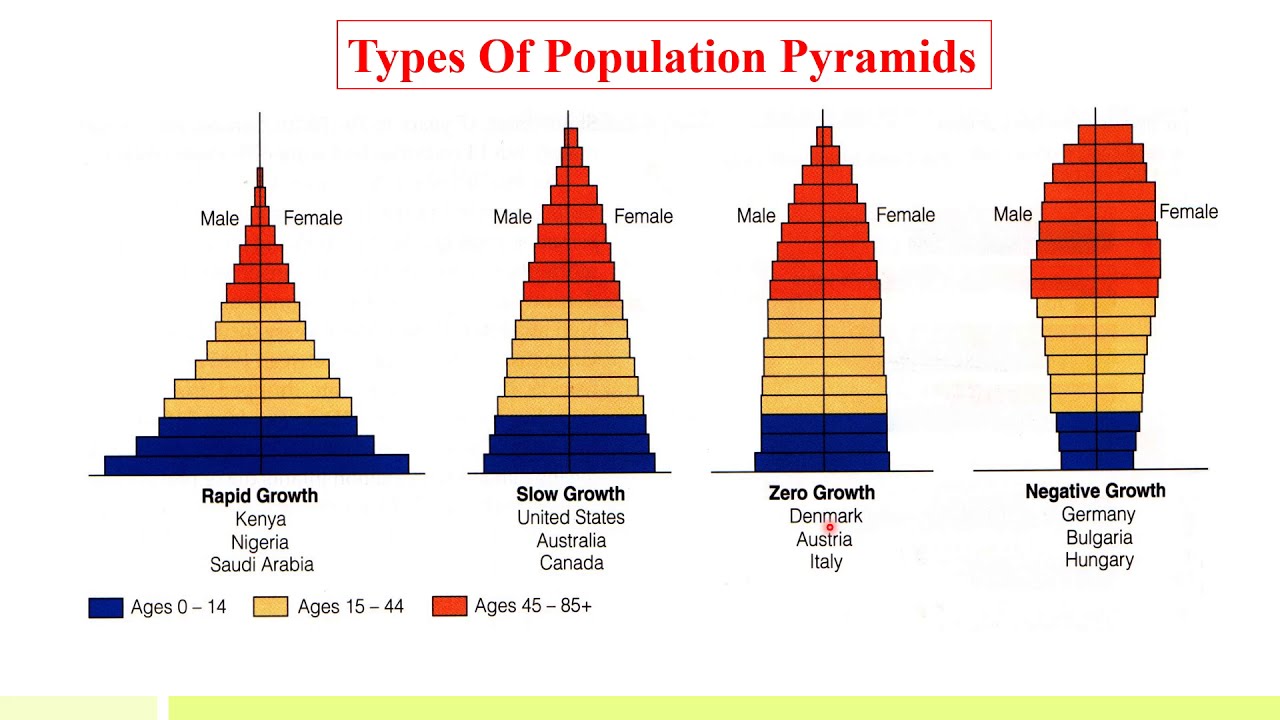
age structure diagrams, left to right
increasing rapidly, increasing slowly, stable, decreasing
38
New cards
total fertility rate
average number of children born per woman during her lifetime
39
New cards
improved medical care results in ____
a lower TFR
40
New cards
replacement fertility
the TFR that keeps the size of a population stable (2.1)
41
New cards
demographic transition stages (pg 90 prep book)
pre-industrial, death and birth rates high
transitional, declining death rates
industrial, birth rates decline
post-industrial, low birth and death rates, stable pop
transitional, declining death rates
industrial, birth rates decline
post-industrial, low birth and death rates, stable pop
42
New cards