Lecture 15 Understanding Aggression and Violence in Psychology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Aggression
Any physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt someone or something.
Violence
Aggression intended to cause extreme harm (e.g., injury, death).
Hostile aggression
Behavior intended to harm that is motivated by feelings of anger and hostility.
Instrumental aggression
Behavior intended to harm that has other motives than hostility.
Predictors of Aggression
Personality, Age.
Aggressiveness in young children
25% of 1-3 year olds' interactions are aggressive!
Stability of Aggressiveness
Aggressiveness is almost as stable as intelligence over time.
Lower inhibition
A predictor of aggression.
Less ability to express wants/needs
A predictor of aggression.
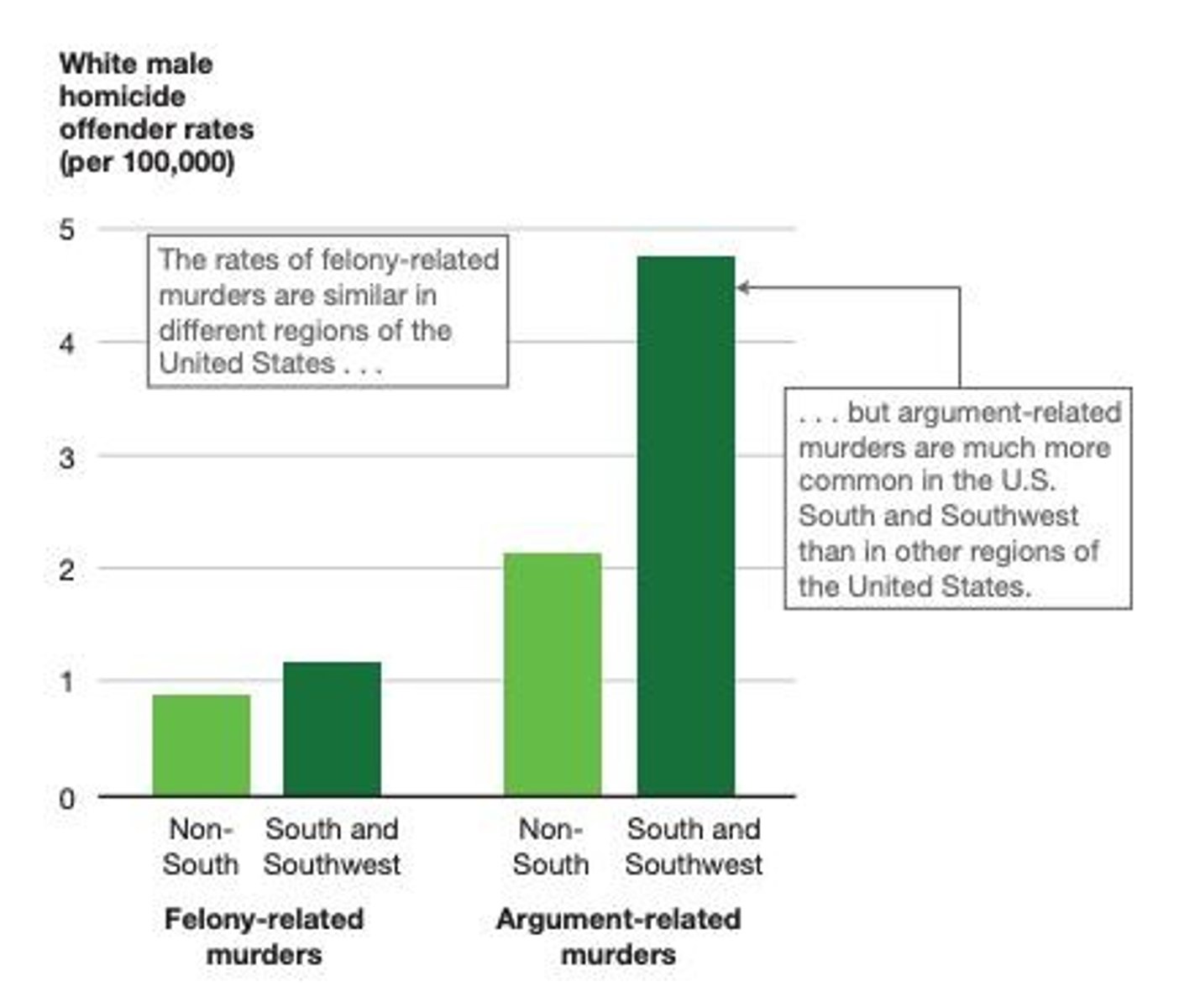
Age and murder rates
Most murders are committed by people ages 18-24!
Dark Triad of personality
Narcissism, Psychopathy, Machiavellianism.
Hostile Attribution Bias
Tendency to perceive ambiguous actions as hostile.
Hostile Perception Bias
Tendency to perceive social interactions as being aggressive.
Hostile Expectation Bias
Tendency to expect others to react aggressively.
Gender and Aggression - Men
More physically aggressive.
Gender and Aggression - Women
More likely to engage in relational or emotional aggression.
Role of testosterone
In women, Estradiol acts similarly and converts to testosterone in the body.
Testosterone spikes
For those who care about dominance and status, testosterone/estradiol can spike after competition.
Culture of honor
A culture defined by its members' strong concerns about their own and others' reputations, leading to sensitivity to insults and a willingness to use violence to avenge any perceived wrong.
Unpleasant stimuli
Can lead to fight-or-flight response.
Frustration-aggression hypothesis
Frustration always leads to aggression, and aggression is always the result of frustration.
Frustration
Response to having a goal blocked.
Aggression without Frustration
Aggression can occur without frustration.
Berkowitz (1989) Theory Update
Includes learned helplessness, arousal, interpretation, anger, and aggression.
Learned Helplessness
Repeated uncontrollable negative outcomes leads people to give up trying to avoid them.
Situational Cues
Situational cues can increase the likelihood of anger.
Weapons Effect
The presence of weapons can increase aggression.
Temperature and Aggression
Increased temperature leads to increased violence.
Evolutionary Rejection
Rejection is equated to death, highlighting the evolutionary advantages of being in a group.
Rejection and Physical Pain
Rejection can lead to physical pain and physical ailments.
Alcohol and Aggression
Cognitive impairment and decreased inhibitions from alcohol can lead to aggression.
Alcohol and Brakelines Analogy
Alcohol cuts the brakelines, metaphorically representing its effect on inhibitions.
Expectancy Theories
Social attitudes and expectations about alcohol can influence aggression.
Alcohol-Related Words
Exposing people to alcohol-related words can make them act more aggressively.
Media Violence and Aggression
The violence portrayed in the media may influence aggression.
Correlational Research
Kids who engage with more violent media tend to be more violent.
Longitudinal Study Findings
Watching violent TV as a child is associated with committing violent or criminal acts as a teen.
Anderson and Bushman (2001) Meta-Analysis
Playing violent video games is associated with increased aggression (r = 0.19) and decreased helping (r = -0.16).
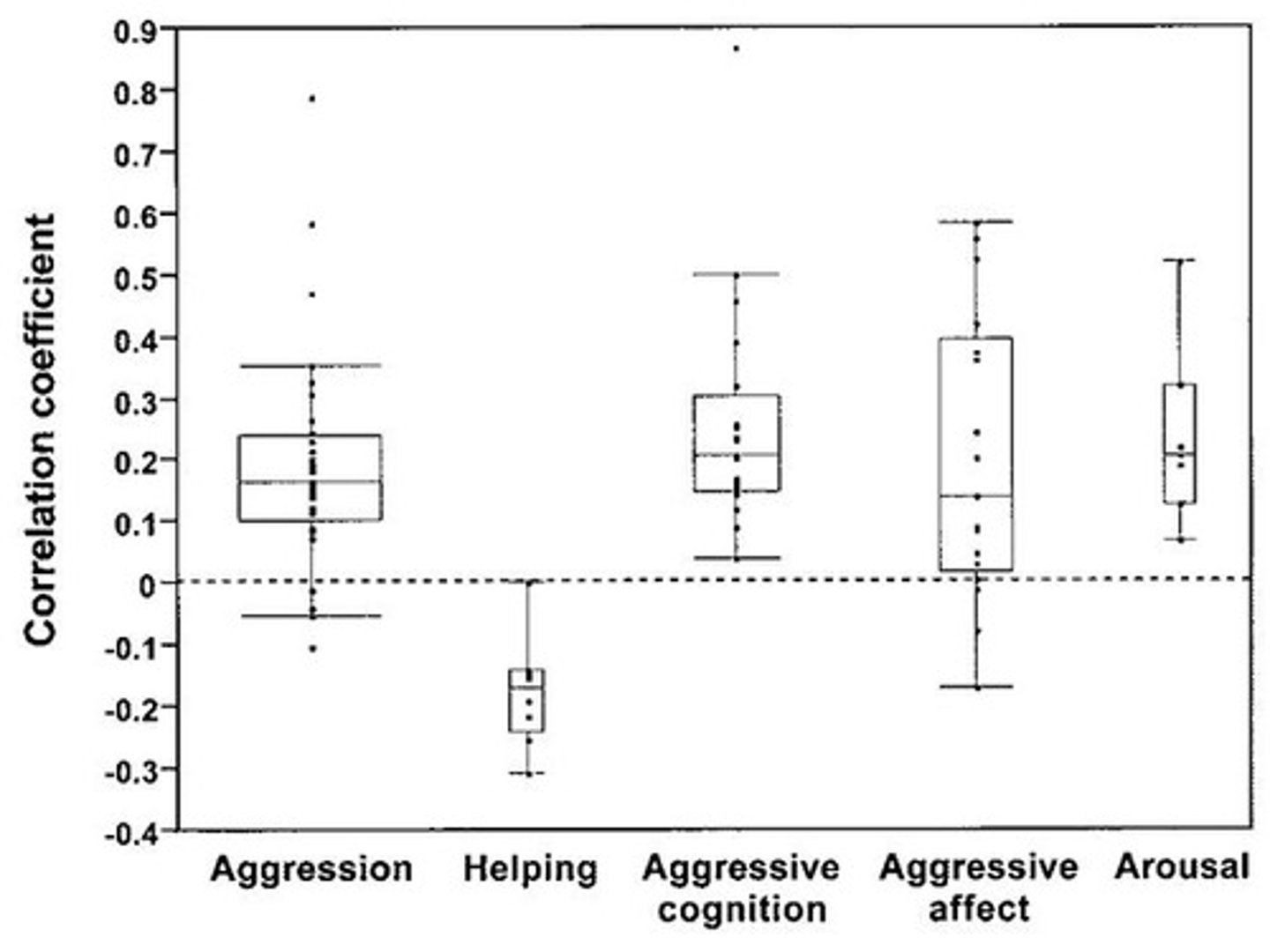
Experimental Evidence of Media Violence
Studies show a small, short-lived effect of media violence on aggression.
Reasons for Media Influence on Aggression
Increased arousal, perceived norms, identifying with the perpetrator, situational cues, media that justifies violence, imitation, desensitization, and social learning theory.
Reducing Aggression
Strategies include early intervention, punishment, promoting non-aggressive values, non-aggressive models, developing empathy, and mindfulness practice.