Chapter 18 Study Guide
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Sixth Mass Extinction
The current global decline in species diversity, with approximately 50,000 species extinctions per year.
Genetic Diversity of Wild Species
High genetic diversity ensures a wider range of genotypes, improving survival chances and reproduction.
Inbreeding Depression
A condition in populations with low genetic diversity, leading to poor survival and reproduction chances.
Genetic Diversity of Domesticated Species
Concerns about declining genetic variation in crops and livestock that humans depend on.
Extinct Livestock Breeds in Europe
Half of the livestock breeds that existed in 1900 are now extinct.
At Risk Livestock Breeds
43 percent of the remaining livestock breeds in Europe are currently at serious risk of extinction.
Declining Animal Breeds in North America
80 percent of evaluated domesticated animal breeds are either declining or facing extinction.
Seed Diversity Preservation
Nations are storing seed varieties in specially designed warehouses to preserve genetic diversity.
Threatened Species
Species with a high risk of extinction in the future, according to the IUCN.
Near-threatened Species
Species that are very likely to become threatened in the future.
Least Concern Species
Species that are widespread and abundant.
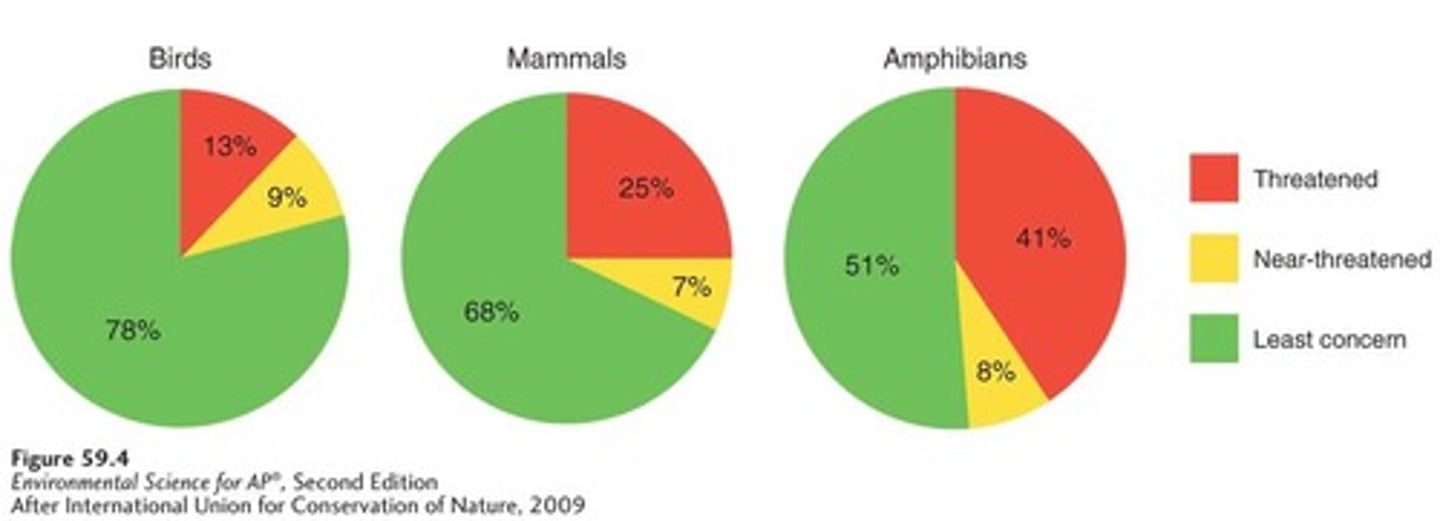
Threatened Birds, Mammals, and Amphibians
21 percent of birds, 32 percent of mammals, and 49 percent of amphibians are currently classified as threatened or near-threatened.
Intrinsic Value
Value independent of any benefit to humans.
Instrumental Value
Worth as a tool that can be used to accomplish a goal.
Ecosystem Services
Five categories: Provisions, Regulating services, Support systems, Resilience, Cultural services.
Provisions
Goods that humans can use directly, such as lumber, food crops, and medicinal plants.
Natural Sources of Prescription Drugs
About 70 percent of the top 150 prescription drugs sold in the United States come from natural sources.
Regulating Services
Natural ecosystems regulate environmental conditions, including carbon removal from the atmosphere.
Nutrient and Hydrologic Cycles
Ecosystems play a crucial role in regulating these cycles.
Support Services
Natural ecosystems provide services like pollination and natural pest control.
Resilience
Depends greatly on species diversity.
Cultural Services
The aesthetic benefit provided by nature that people are willing to pay for.
Decline of Ecosystem Services
15 out of 24 different ecosystem functions are declining or used at an unsustainable rate.
Habitat Loss
The major cause of declining species diversity, primarily due to human development.
Exotic Species
A species living outside its historical range, also known as alien species.
Invasive Species
A species that spreads rapidly across large areas and poses a threat to biodiversity.
Overharvesting
The removal of individuals from a population at a rate faster than it can replace them.
Lacey Act
A U.S. act that prohibits interstate shipping of all illegally harvested plants and animals.
CITES
A 1973 treaty formed to control the international trade of threatened plants and animals.
Red List
A list of worldwide threatened species.
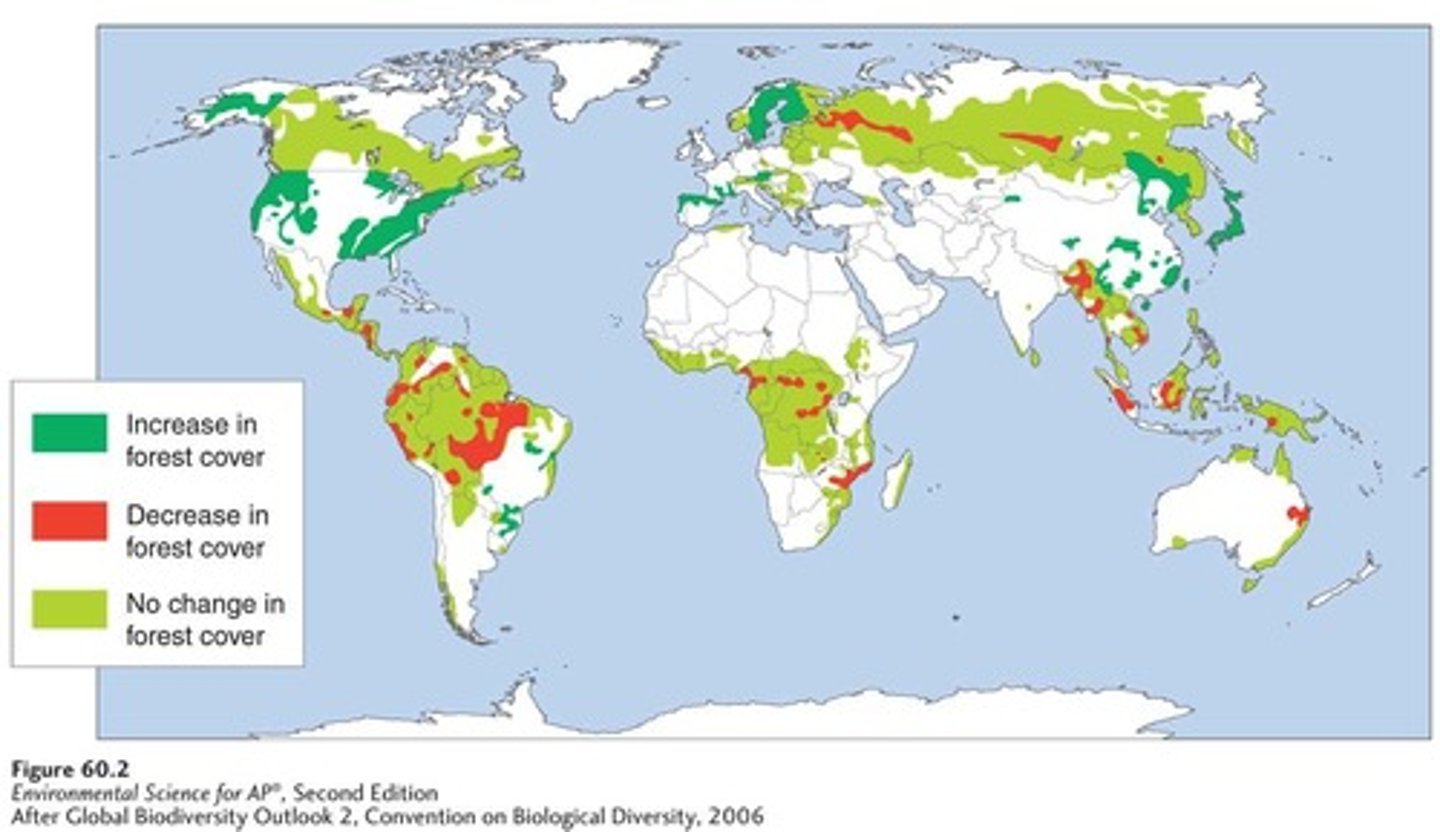
Habitat Loss - Changing Forests
Some regions experienced large declines in forested land from 1980 to 2000.
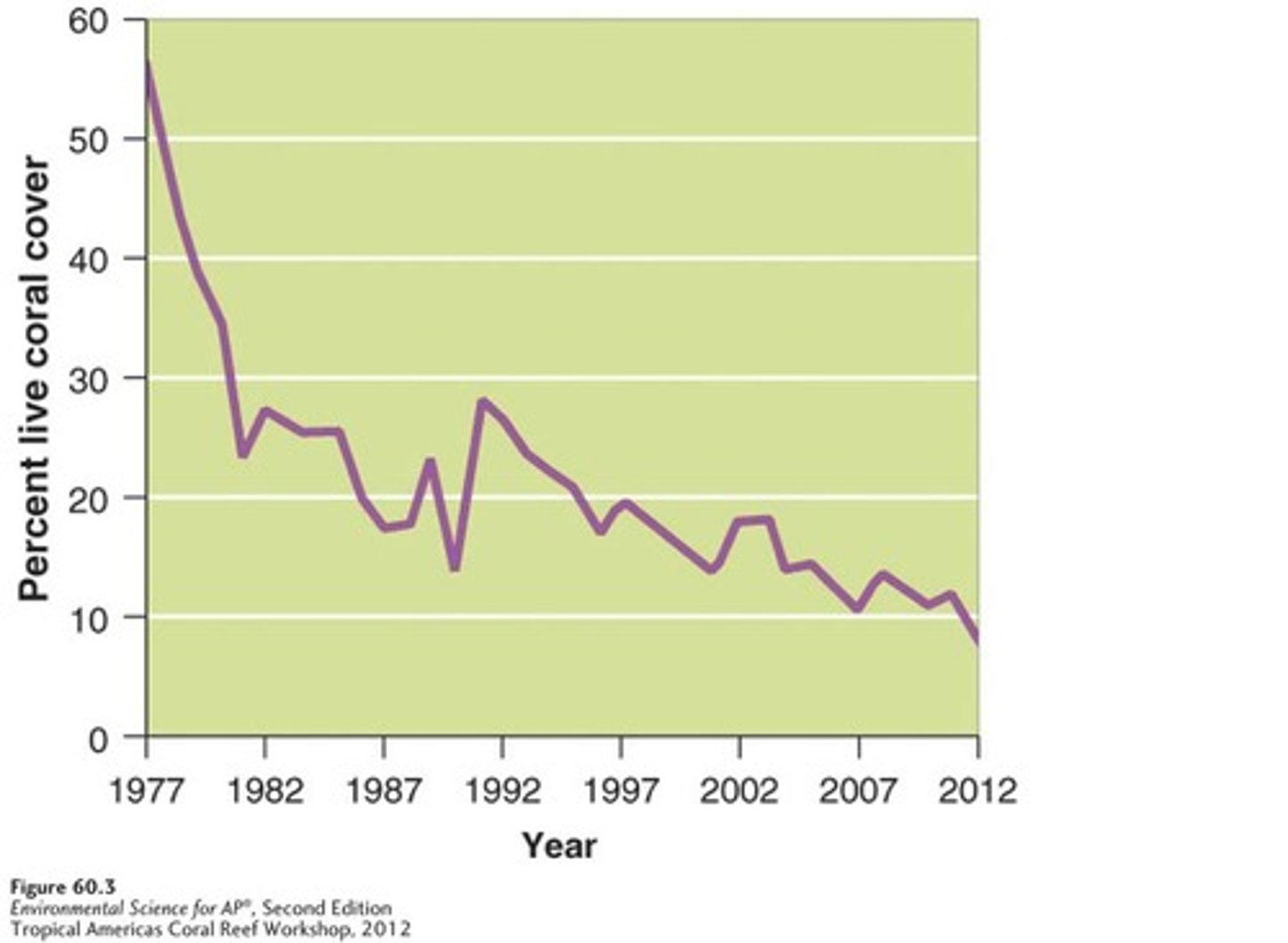
Habitat Loss - Coral Reefs
The percentage of alive coral in Caribbean reefs has declined sharply from 1977 to 2012.
Native Species
Species that live in their historical range, typically where they have lived for thousands or millions of years.
Pollution
A factor that reduces populations and biodiversity.
Climate Change
A factor that affects species diversity.
Overharvesting - Extinction
Extreme overharvesting can lead to the extinction of a species.
Human Development
The primary cause of habitat loss affecting species diversity.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Pollutant Impact
If a pollutant kills one plant species with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, the ecosystem can still fix nitrogen if other species survive.
Species requiring specialized habitats
These species are particularly prone to population declines due to habitat loss.
Movement of Exotic Species
Humans have frequently moved animals, plants, and pathogens around the world over the past several centuries.
Scientific Funding
Grants awarded to scientists for biodiversity research without promise of economic gain.
Pollution
Can have harmful effects on species.
Biodiversity Threats
Come from toxic contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, acids, and oil spills.
Endocrine Disrupters
Can have nonlethal effects that prevent or inhibit reproduction.
Nutrient Release
Causes algal blooms and dead zones.
Thermal Pollution
Can make water bodies too warm for species to survive.
Climate Change
Has the potential to affect species diversity.
Species Migration
A species may respond to warming temperatures by migrating to a suitable climate.
Marine Mammal Protection Act
A 1972 U.S. act to protect declining populations of marine mammals.
Endangered Species
A species that is in danger of extinction within the foreseeable future throughout all or a significant portion of its range.
Threatened Species
Any species that is likely to become an endangered species within the foreseeable future throughout all or a significant portion of its range.
Endangered Species Act
First passed in 1973, it authorizes the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to determine which species can be listed as threatened or endangered.
Convention on Biological Diversity
An international treaty to help protect biodiversity with three objectives: conserve biodiversity, use biodiversity sustainably, and share benefits from commercial use of genetic resources.
Protecting Entire Ecosystems
Has been a major motivating factor in setting aside national parks and marine reserves.
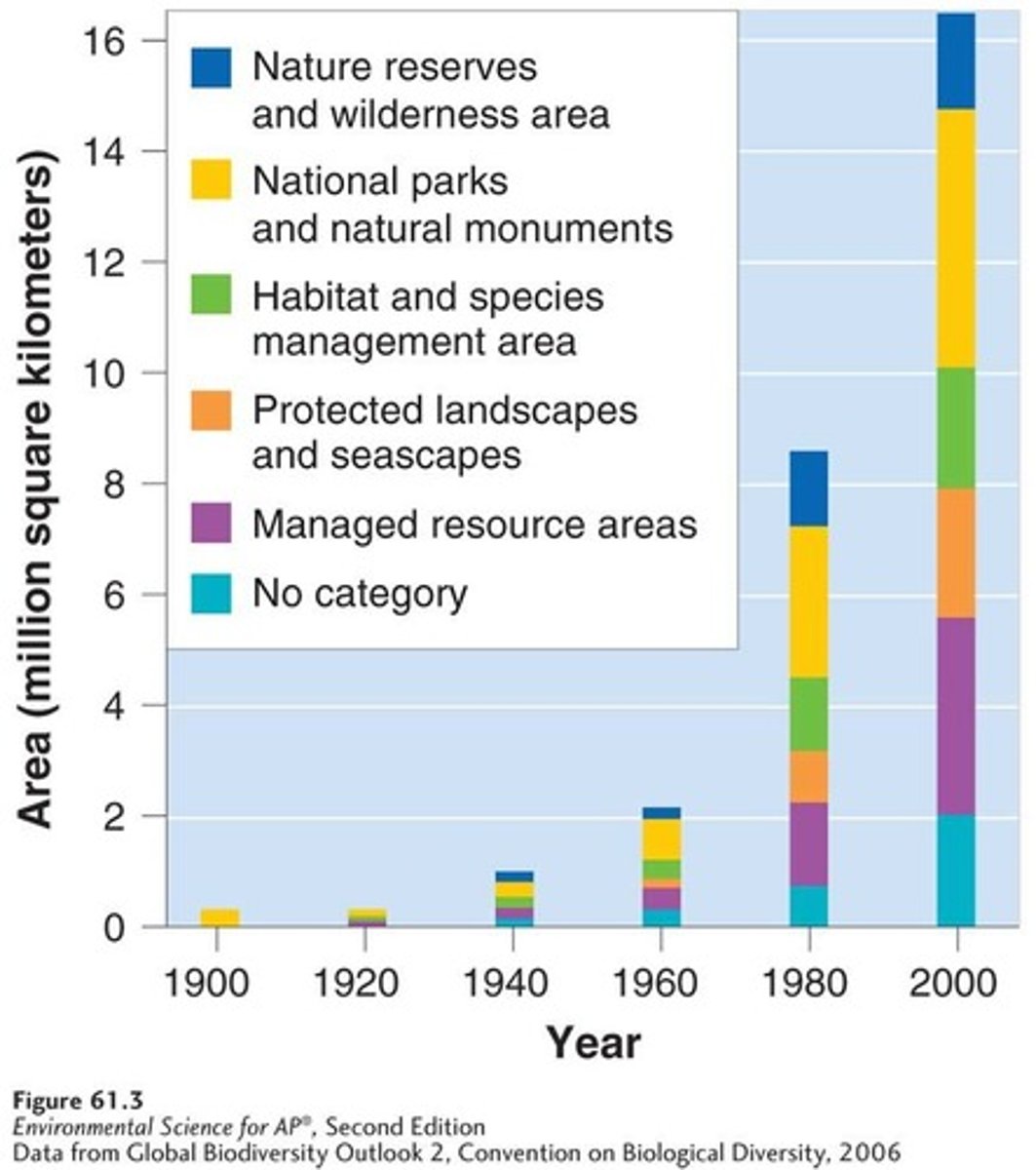
Protected Land Changes
Since the 1960s, there has been a large increase in the amount of land under protection worldwide.
Island Biogeography
Theory applied to islands of protected areas in less hospitable environments.
Metapopulations
A species is more likely to be protected from extinction if it can be rescued by dispersers from a neighboring population.
Edge Habitat
Habitat that occurs where two different communities come together, forming an abrupt transition.
Biosphere Reserve
Protected area consisting of zones that vary in the amount of permissible human impact.
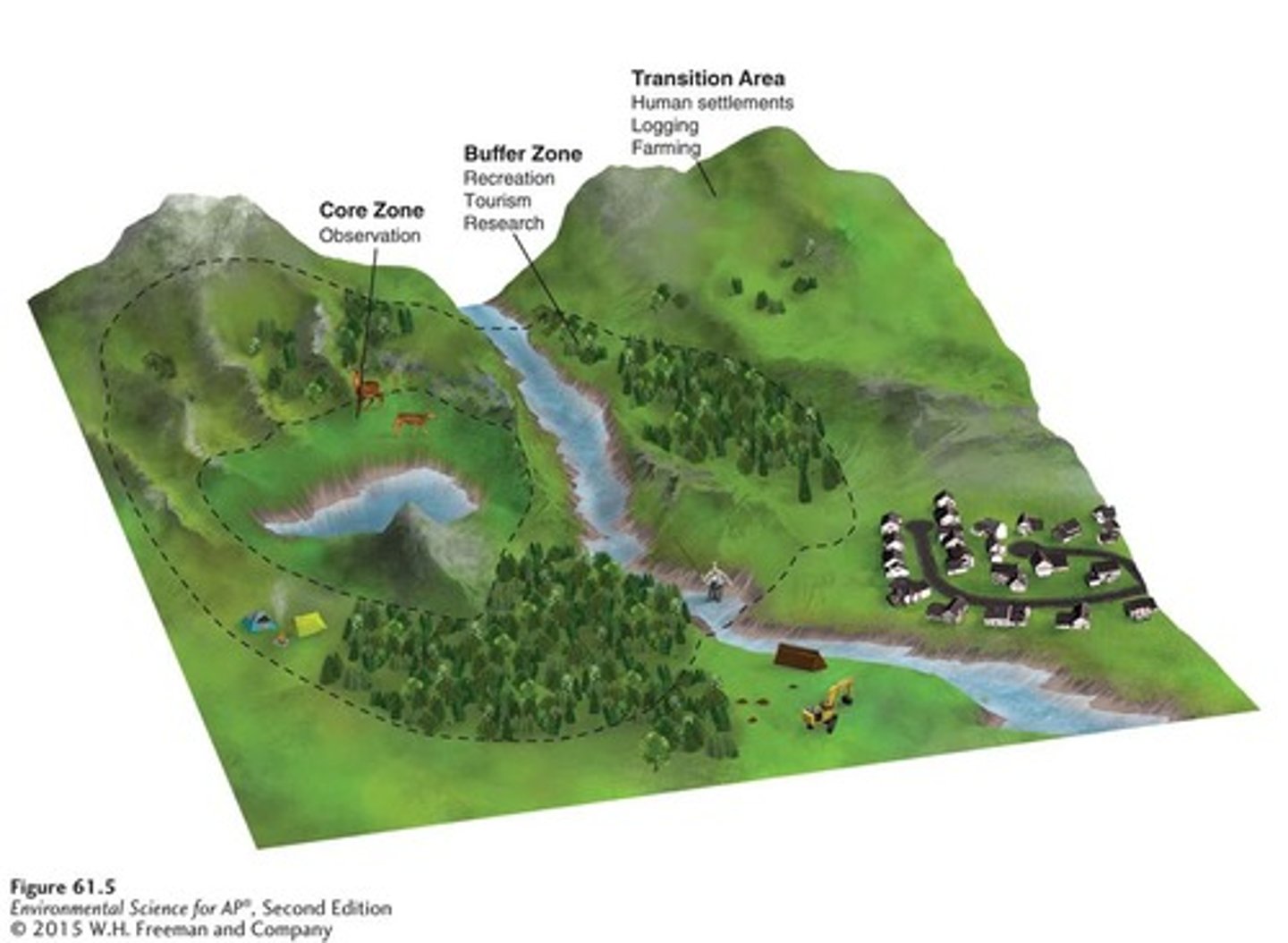
Biosphere Reserve Design
Ideally consists of core areas with minimal human impact and outer zones with increasing levels of human impacts.