BIOL1020 Quiz 2
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Larger biological molecules quiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
The label on a container of margarine lists "hydrogenated vegetable oil" as the major ingredient. What is the result of adding hydrogens to vegetable oil?
|
Which of the following is true of cellulose?
It is a major structural component of plant cell walls. Cellulose is made up of glucose units linked by beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds.
The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires
the removal of a water molecule, a process known as dehydration synthesis.
What type of covalent bond between amino acid side chains (R groups) functions in maintaining a polypeptide's specific three-dimensional shape?
Disulphide bond
What is the structural feature that allows DNA to replicate?
The complementary base pairing between nucleotides, where adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine, allows DNA to replicate accurately.
The amino acids of the protein keratin are arranged predominantly in an α helix. This secondary structure is stabilized by
hydrogen bonds between the backbone atoms of the polypeptide chain.
Dehydration reactions are used in forming which of the following compounds?
triacylglycerides, polysaccharides, and proteins. These compounds are formed by linking monomers through the removal of water.
Polysaccharides, triacylglycerides, and proteins are similar in that they
are synthesized from subunits by dehydration reactions.
A molecule with the chemical formula C6H12O6 is probably a
Carbohydrate and monosaccharide only.
Which of the following polymers contain nitrogen?
chitin
Molecules with which functional groups may form polymers via dehydration reactions?
either hydroxyl or carboxyl groups
Which type of interaction stabilizes the α helix and the β pleated sheet structures of proteins?
The hydrogen bonds between the backbone atoms of the polypeptide chain.
Which of the following statements concerning saturated fats is not true?
They have multiple double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids.
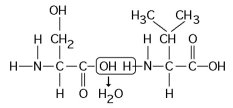
Which of the following statements is/are true regarding the chemical reaction illustrated in the figure above?
It results in a peptide bond.
There are 20 different amino acids. What makes one amino acid different from another?
Different side chains (R groups) attached to an α carbon
What maintains the secondary structure of a protein?
Hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one peptide bond and the carboxyl group of another peptide bond.
What aspects of protein structure are stabilized or assisted by hydrogen bonds?
Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures, but not primary structure.
Why are human sex hormones considered to be lipids?
They are not soluble in water.
At which level of protein structure are interactions between the side chains (R groups) most important?
Tertiary structure
If cells are grown in a medium containing radioactive 35S, which of these molecules will be labelled?
Only proteins, as sulfur is present in some amino acids.