mass spectrometry
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
To measure the mass of an atom, we use a…
mass spectrometer
Which of these are stages in time of flight mass spectrometry? (4)
Ionisation
Ion drift
Acceleration
Detection
After ions are detected by the mass spectrometer, the computer produces a…
mass spectrum
The x axis label of a mass spectrum is…
mass to charge ratio
Use the mass spectrum below to calculate the relative atomic mass of mercury.
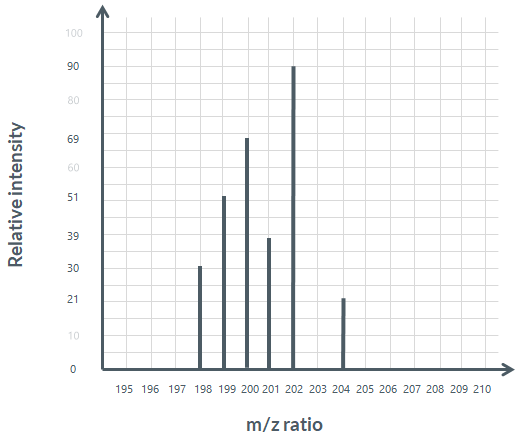
Total ions: 30+51+69+39+90+21=300
Hg198:30/300 ×100=10 percent
Hg199:51/300 ×100=17 percent
Hg200:69/300 ×100=23 percent
Hg201:39/300 ×100=13 percent
Hg202:90/300 ×100=30 percent
Hg204:21/300 ×100=7 percent
Ar=200.6
A sample of ruthenium is analysed by time of flight mass spectrometry and the data is shown in the table below.
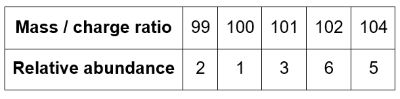
Identify the ion that reaches the detector first.
Give the correct representation of ion with charge.
99Ru+
The ion with the smallest mass / charge ratio travels the fastest. So, 99Ru+ reaches the detector first
A sample of ruthenium is analysed by time of flight mass spectrometry and the data is shown in the table below.

Identify the ion that produces the largest electrical current at the detector.
Give the correct representation of ion with charge.
102Ru+
The most abundant ion generates the largest electrical current at the detector. This is 102Ru+.
A sample of ruthenium is analysed by time of flight mass spectrometry and the data is shown in the table below.

Suggest the identity of the ion that produces a low-abundance signal at m/z=51
Give the correct representation of ion with charge.
102Ru2+
Double ionisation of 102Ru generates a rare 102Ru2+ ion with a mass/charge ratio of 102/2=51.