MMSC230 Forensic Pathology
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
11/6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Ancient Times:
humans have used substances for various purposes, including medicinal, religious, and recreational, for thousands of years. Evidence suggests that opium was used as early as 5000 BCE, and alcohol production dates back to at least 7000 BCE
The Middle Ages:
while some substances were used in moderation, excessive use and drunkenness were condemned by religious authorities
Renaissance and Enlightenment:
increased trade and exploration led to the introduction of new substances, such as tobacco and coffee, to Europe. The use of opium and alcohol became more widespread
19th Century:
the development of new technologies, such as the hypodermic needle, led to increased use of injectable drugs like morphine and heroin. These substances were often used for medicinal purpose,s but also had a high potential for abuse and addiction
20th Century:
The 20th century saw the rise of recreational use
Late 20th and 21st Century:
drug abuse remains a significant global problem, with the opioid crisis being a major public health concern. The use of prescription drugs for non-medical purposes has also become a growing issue
Throughout history, drug abuse has been viewed in different ways
from a moral failing to a medical condition. Today, it is widely recognized as a complex disease that affects both the brain and behavior
Drug Overdose
Drug overdose is the leading cause of accidental death in the US
52,404 lethal drug overdoses in 2015
20,101 overdose deaths related to prescription painkillers
12,990 overdose deaths related to heroin in 2015
Fivefold increase from 2002-2014
Ways of Administration:
Smoking (pot)
Huffing (inhaling volatile) gasoline, toluene
Snorting
Ingesting
Injecting: veins, under skin
Tolerance:
Always repeated use of a drug, no longer acts the same way it initially did
Takes higher amounts to produce same effect
Dependence
Neurons only function normally when drug is present physiological withdrawal will occur
Not sunonymous with addiction, however, usually accompanies it
Ex: patient with cancer taking morphine
Cocaine
White powder (hydrochloride salt)
Originates from coca leaves
Peru, Bolivia, Columbia
Crack: salt processed with baking soda and heated to remove salt
Not water soluble, comes in rock crystales
Cheaper
Heated, then vapor is inhaled
Tears made from coca leaves can combat altitude sickness
Snorted: high lasts 15-30 min
Smoking: rapid intense effect, high lasts 5-10 min
Causes euphoria, reduced fatigue, mental alertness, loss of appetite or need to sleep
Acts through reward center in midbrain
Main metabolites BZE can be found in urine up to a week, up to 3 weeks with high doses
Varies with concomitant use of other drugs
Different state, different rules. Not all drug deaths can be viewed as accidental or natural.
Toxidrome causes elevated blood pressure, heart attack, hyperthermia, increased heart rate, dilated pupils, chest pain, stroke, seizures, headaches, abdominal pain
One of the few drugs with cardiotoxicity
Vasospasm and myocardial infarction
Can cause delirium, jump from height, aggressive, associated with sudden death when taken to custody
Often used with alcohol: cocaethylene is found in blood, increased risk of sudden cardiac death
“Cut” with adulterants leading to acute and chronic pulmonary toxicity - “crack lung”
Baking soda
Talcum powder
Lactose sugar
Levamisole
Increased weight and more profits
Abusers can develop tolerance
National survey on drug use and health reports 1.5 million cocaine users
Decline in recent years due to increased price
Pregnancy: prematurity and growth retardation, decreased IQ, ADHD
No FDA-approved medication to treat addiction
PCP
Angel dust
Developed in the 1950s and used as a dissociative anesthetic
Discontinued in the 60s due to dysphoria and hallucinations
In 1979, all legal manufacturing was terminated
Crystalline powder, tablets, capsules
Creates a feeling of detachment, hallucinations, slurred speech, acute anxiety, hostility, paranoia
Very dangerous and addictive
Cannabis
Comes from the hemp plant Cannabis sativa
Smoked dried leaves, flowers, stems, seeds
10% of users become dependent
Can cause shallow breathing, dizziness, dry mouth, dilated pupils, depression, and anxiety
Causes relaxation, detachment from reality
Most commonly abused drug
Affects short-term memory, ability to focus and learn, and coordination
HR increased 2x times
Active component delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
1 in 3 people in the US have tried at least once
Big changes have recently occurred in the legislature of several states
Allowed for sale in stores or for medicinal use
Medicinal synthetic cannabinoids:
Marinol for nausea associated with chemotherapy, increased appetite in AIDS pt
Medical marijuana is currently approved for a myriad of conditions
Cancer, glaucoma, HIV, chronic pain, nausea, cachexia, muscle spasm
November 2016: 28 states and the District of Columbia legalized cannabis for personal use
Rules vary by state
2012: Colorado and Washington states legalized to use older than 21
2014: Oregon, Alaska, Washington, DC
2016: California, Maine, Nevada, Massachusetts
In stark contrast to the legalization happening at the state level, it is still a Schedule I drug and federally illegal.
Cultivation and distribution are felonies
Possession misdemeanor
K-2
“Spice”
Herbal mixtures have, similar effect to marijuana
Synthetic or designer cannabinoid compounds
Common use in teenagers
Agitation, hallucinations, elevated BP, vomiting
Extreme addictive potential
Illegal to sell, buy, or possess the main chemicals in these drugs
Benzodiazepines
Anti-anxiety agents attach to the GABA receptor
Withdrawal can be fatal
Seizures
Often abused with opiates, potentiate their effect
Valium-diazepam
Often prescribed as muscle relaxer
Xanax - alprazolam
Ativan - lorazepam
Serax - oxazepam
Opium
Extracted from poppy plant (growth cycle 120 days)
Needs warm climate with lower humidity
Central Asia, South America
Produced when poppy flower dies in 10-12 day period
Extremely labor intensive
Chemical structure can be altered to produce many opiates
Sleep inducing, was used in medicine for centuries
16th century laudanum use as painkiller
1806- German biologist isolated active ingredient morphine named after “god of dreams”
1953 - used as painkiller after introduction of hypodermic syringe
Heroin
Derived from morphine alkaloid found in opium, 2-3x times more potent
Highly addictive, creates rush
Schedule 1
White powder with bitter taste
Mostly sold as white or brown powder
Cut with other drugs or adulterants
Sugar, starch, quinine, strychnine
First produced in 1874 as diacetylmorphine
1897 Bayer Pharmaceuticals created drug combining aspirin and heroin; used as effective treatment for asthma, tuberculosis and morphine addiction
Heroin was restricted to prescription-only use in the U.S. in 1914 and banned in 1924
Chemical addiction can develop with one dose
High risk of OD
Actual strength never known
Can be smoked, snorted, ingested, injected, suppository
Inhalation: smoking cigarette which is dipped in liquid heroin: “chasing the dragon”
IV use produces quick rush: flushing of skin, dry mouth, wakeful and drowsy state, respiratory depression, decreased BP, pinpoint pupils, nausea, convulsion, coma
Quickly metabolizes to morphine, which binds to opioid receptors in brain
6-MEM metabolite detected in urine and vitreous fluid
IV users inject into veins in their neck, arms, hands/feet
Often use shared, contaminated needles
Risk of HIV, HCV, bacterial and fungal infections
Skin poppers, inject the drug under the skin, not into a vein
Risk of abscesses, endocarditis
Heroin Resurgence
Painkillers became more regulated, more stricter regulations on prescribing
People who were legally prescribed opioids (Vicodin, oxycodone) for pain got addicted but have no more access to drugs, and turned to heroin as a substitute
Methadone
Can be prescribed for chronic pain patients or for former heroin addicts
Methadone clinics
High street abuse potential
A longer half-life does not create a quick high
Fentanyl/Heroin Epidemic
In 2014 increased amount of OD
Testing did not detect 6-MEM or morphine, or traces
Fentanyl was detected in the majority of cases
National alert about fentanyl:
OD is at an alarming rate, representing a significant threat to public health and safety
100 times more potent than morphine and 50 times more potent than heroin
The danger is that the drug users do not know what they are buying:
Heroin, heroin laced with fentanyl, cocaine, and fentanyl or fentanyl alone
Fentanyl
Looks like heroin
Powerful synthetic painkiller, used frequently in the ICU settings (IV), anesthesia (IV), chronic pain (lollipop, patch)
Very fast acting
Schedule II drug
Illegal sale from Mexico and China
Bath salts
Designer drugs of abuse
The name has nothing to do with a hygiene product
CNS stimulators, the main component MDPV
Similar to cathinone
Alcaloid found in the khat plant and methamphetamine
2011 DEA emergency scheduling to control MDPV and all other chemicals in BS
President Obama in 2012 signed law ban on all chemicals found in BS, placed in Schedule I
Ban the production of any chemicals mimicking BS
Before these rulings, they were easily accessible in convenience stores, gas stations, internet
Packaged in plastic or foil 200-500 grams
$20 a package
Inhalants
Volatile substances that are inhaled to produce mind-altering effects
Solvents: paint thinners and removers, gasoline, glue
Aerosols: spray paints
Gases: ether, nitrous oxide
Nitrites: isobutyl nitrite
Methamphetamine
Stimulant, used during WWII
Increases dopamine in brain
Clinically similar to amphetamine
Comes in clear crystal chunks or shiny blue white rocks “ice”
Smoked through small glass pipe but can be snorted and injected
Crystal meth
Can be made from over counter medications
Psuedoephedrine
Meth mouth, intense itching, weight loss, hallucination, paranoia
Prescribed Stimulants
Chemically similar to methamphetamine
Adderall
Ritalin
Concerta
Enhance ability to concentrate, memorize, and increase attention and motivation
Alcohol Abuse
More than 85,000 deaths a year in the US are directly attributed to alcohol use
Annual economic cost of alcohol use is estimated to be over $250 billion
Roughly 1 in 10 deaths among working age adults results from excessive drinking
In year 2000, 40% of all traffic fatalities were due to alcohol
One of the drugs that can be fatal if you go cold turkey
Leads to liver cirrhosis
Causes hypertension, dilated cardiomyopathy
Increases risk of malignancies
Esophageal, throat, mouth
Withdrawal cna be fatal
Seizures
Chronic use leads to cognitive impairment
Wernicke’s encephalopathy
A neurological disorder caused by a severe deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1)
Often coexists with other substance abuse, depression, mental health
Lifetime rate of suicide attempts among frequent alcohol users in the US was 7%
US general adult population rate of 1%
Drug Scene Investigation
Check for pills, crack pipes, glassine bags, powdery substances, pill bottles, syringes, cooker spoons, razor blades
A lot of times the scene is “sterile”
If prescription bottles are found document amount prescribed, used and remained
Name of doctor, dates
If missing: used, stolen, sold
Drug Mules
Be aware about practice of smuggling drugs: body packers of mules (massive overdose and death if drugs rupture in body)
External Exam
Look for injection sites: fresh or scarred track marks
Check unusual places between toenails or fingernails
Foam in the nares or the mouth
Pill fragments in stomach contents
Lung and brain swelling
Microscopic finding
In lungs can see crystalline material
Suicide
Is the third leading cause of death for ages 15-24
⅔ of people who commit suicide are depressed at the time of death
Adolescent female 16-19 years old are 6x more likely to experience depression if they abuse ethanol
Drug abuse is strongly associated with prevalence of depression
Depression among physicians
Rates of depression is higher in medical students and residents 15-30% than general population
The lifetime prevalence of depression among physicians is 13% in men and 20% in women
CDC statistics
2012 suicide 10th leading cause of death in USA roughly 40,000 death reported
From 2000 to 2012 ther ehas been a 21% increase
Mortality and Morbidity weekly report, 2016
Study analyzed 12,312 suicides
77% males, 22.8% females
84% aged 16-64
Highest rate age 45-54, 22.7%
Lowest age 16-24, 11.6%
By occupation:
Protective services (law enforcement, firefighters)
Legal
Healthcare
Conditions associated with suicide
Mental illness
Depression
Alcohol and drug abuse
30-50% of alcoholics suffer from clinical depression
Terminal illness
Postpartum depression
Mental illness and suicide
Bipolar disorder
Major depression
Schizophrenia
PTSD
90% of all individuals who completed suicide meet criteria for 1 or more psychiatric conditions
Archive International
Study of medical conditions and risk of suicide in elderly in Ontario 1992-2000
Rates are hgih among elderly
Increases with male sex, advanced age, alcohol and substance abuse, mood disorders
Specific med conditions:
CPOD, CHF, depression, severe pain
Firearm, hanging, self-poisoning
Suicide Rates:
Second leading cause of death for teens and young adults, ages 10-34
13.6% of adults 18-25 had serious thoughts of suicide in the past year (2023)
Stressors in the Elderly
chronic health problems, the death of loved ones, social isolation and loneliness, and financial worries. Other significant stressors involve major life changes like retirement or moving, the loss of independence, and caregiving responsibilities for a spouse or family member.
Retirement
Loss of loved ones
Social isolation
Disability
Negative Impacts of Social Media:
Cyberbullying: online harassment, threats, and humiltion can have a devastating impact on a teen’s mental health. Cyberbullying can be relenltess and inescapable, leading to feelings of isolation and despair
Social comparison and insecurity: social media often presents idealized versions of people’s lives, leading to feelings of inadequacy
Social isolation and reduced face to face interaction
Sleep disruption
Key Considerations
Vulnerability
Context matters
Positive aspects
Suicide in Veterans
US veterans with substance abuse have higher risk of suicide
Study look at 4 million veterans
Substance abuse affect 8% of males and 3% of females
Every day 20 US veterans die by suicide
Self-Inflicted Injuries
Manifest in different ways
Stabbing and cutting
Firearms and explosives
Jumping from height
Jumping into water
Burning
Suffocation
Hanging
Electrocution
Railroad injuries
Poisoning
Hanging
Self-suspension by rope, scarf, shoelaces, bedsheets, etc.
Often not full suspension
Ligature mark is present
Usually does not completely encircle the neck
Mark is abraded, dried
Upward direction
Petechiae in eyes are rare
Knife Wounds
In suicide, favor certain locations
Throat, wrists, chest
Multiple
Superficial trial cuts
Usually incised
Gunshot wound
Men > women
Weapon found at the scene
Soot around the wound
Location: temple, neck, mouth, chest
Suicide by Submersion
Common with both genders
Depend on availability of water: river, lake, even bathtub
May be associated with drug OD and occasionally accidental
Jumping from heights
Very important to know circumstances to determine motivation
Aortic rupture
Splenic laceration
Pelvic fractures
Spinal injuries
Asphyxiation
Lack of oxygen
Plastic bag suffocation
Can be homicide, accident (little kids) and suicidal
Rapid
Leaves no physical signs
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Odorless, tasteless, colorless gas formed by hydrocarbon combustion
Binds to hemoglobin causing impaired oxygen transportation
Organ ischemia
Metabolic derangements
Fire smoke inhalation is most common
Color of skin, muscle and blood is cherry pink
Blood levels > 20%, often reaching 80%
The elderly and pregnant are more sensitive to lower levels
Putting head in gas oven was a common way to commit suicide in the past
Replacement of coal gas to natural gas
Motor vehicle exhaust gases
In small spaces lethal level of CO can build up fast
History and scene investigation is important
Ethylene Glycol
Common household agent, antifreeze
Lethal in excess of 100 ml (soda can 345 ml)
Coma and death within first day
Causes kidney injury and metabolic derangement
Refractory crystals of calcium oxalate form in kidney’s tubules
Cyanide Poisoning
Blocks ATP use in the cell during aerobic metabolism
Most common reason is industrial societies is victims of domestic fire
Is liberated in combustion of carbon and nitrogen
Plastics, household items, rubber, polyurethane
Reported that significant levels of cyanide are present in up to 35% of all fire victims
Acute poisoning usually suicidal
Fatal dose is small
Almond smell can be detected
Tissue can be bright pink
Diagnosis is made via blood CN concentrations
Which of the following drugs was originally used in the 1950s and 60s as a dissociative anesthetic but was discontinued due to addiction and severe side effects?
PCP
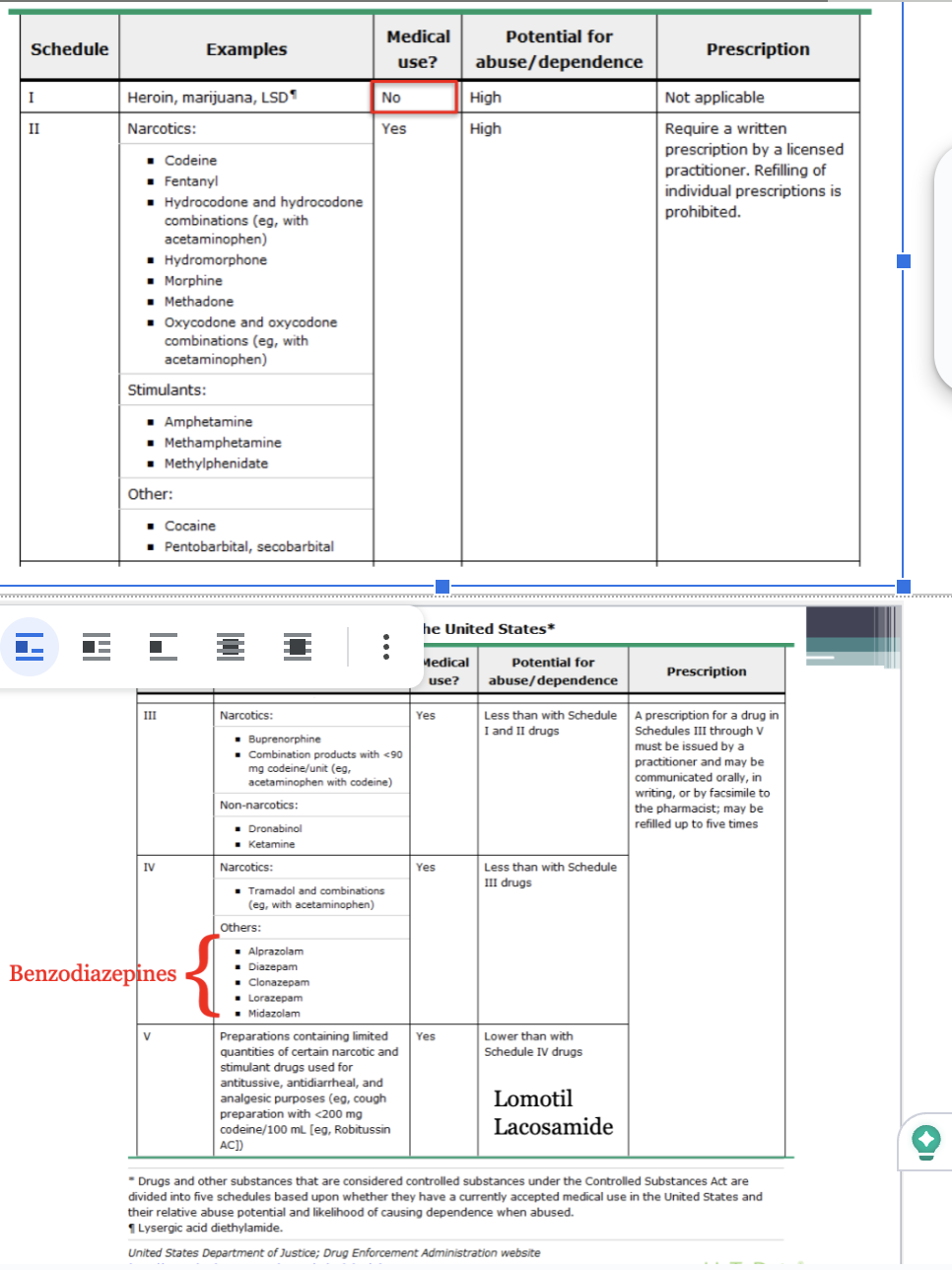
The five drug schedules: The Controlled Substances Act outlines five schedules for drugs:
Schedule I: High abuse potential and no accepted medical use, such as heroin.
Schedule II: High abuse potential with severe dependence risk, but have accepted medical uses under restrictions. Examples include fentanyl and oxycodone.
Schedule III: Moderate to low dependence potential and accepted medical use, like ketamine.
Schedule IV: Low abuse potential and dependence risk, with accepted medical use, including drugs like Valium.
Schedule V: Lower abuse potential than Schedule IV, accepted medical use, and limited narcotic content, such as certain cough preparations.
Asphyxia
Greek origin, meaning breathlessness
Lack of O2 in the blood → failure of cells to utilize O2 → failure of the body of eliminate CO2
Terminal asphyxia is the end point of life for virtually all causes of death
Ex: GSW, MI, ruptured aneurysm
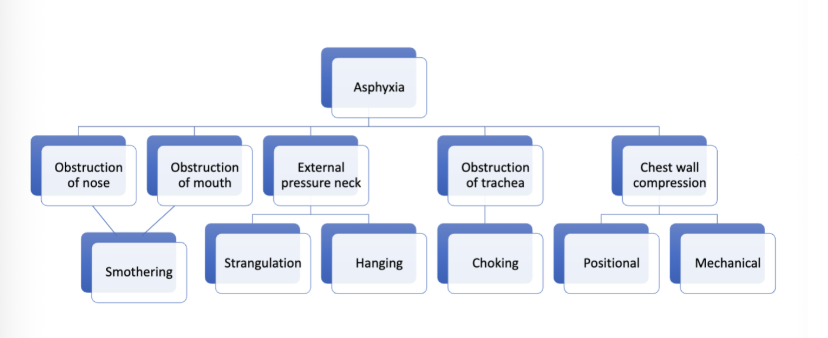
Smothering
Mechanical obstruction or occlusion of external airways (nose and mouth)
Homicide - pillow over face, gag over nose or mouth
Smothering agents - fabric, sheet, pillow, hand
Strangulation
Mechanical pressure on the neck
Airway occlusion
Occlusion of neck veins
Compression of carotid arteries
Baroreceptor (pressure receptor) and vagal (parasympathetic) reflexes
Hands, ligature, arm-locks, garrote
Frequently accompanies sexual assaults
Women > Men
Few physical findings:
Petechial hemorrhages
Sclera, conjunctivae, eyelids
Blood in nares and ears
Visceral congestion
Injury to deep structures of the neck
Occulsion of neck veins
Congestion, cyanosis and petechiae above the line of constriction
External jugular vein needs 2kg pressure to block blood return from head
Petechial hemorrhages
Rupture of small venules due to a rise in venous pressure
Less pressure for jugular veins (superficial)
More pressure for carotid arteries (deeper)
Neither specific or sensitive
Can be seen in CPR, different body positions, and severe retching
Neck dissection
Specialized examination in strangulation cases
All organs are removed, including the brain
Layer by layer dissection of strap muscles
Thyroid gland examination
Hyoid bone
Fractured or contused soft tissue around it
Thyroid cartilage
Suffocation
Reduction of oxygen in inhaled air
Most common replacement of oxygen by other gases (CO2 in grain silo, nitrogen in ship tanks, industrial metal chambers, refineries)
Plastic bag over head common suicide method
Traumatic asphyxia
Restriction of respiratory movements and preventing inspiration:
Burial in the earth after the collapse of the excavation
Pinned under overturned vehicle
Crushing in crowd
Autopsy findings
Marked congestion and cyanosis in chest wall
Bleeding from ears and nose
Positional asphyxia
Person’s position leads to mechanical obstruction of respiration
Common in infants, patients with cerebral palsy or under influence of drugs or alcohol
Usually accidental
Co-sleeping
Baby bjorns
Crib bumpers
Stuck in between mattress and wall/bed frame
Hanging
This was covered in previous suicide lecture
Judicial hanging, unlike suicide, the mechanism of death is fracture/dislocation of cervical vertebrae C1/C2 or C2/C3
Death is immediate due to compression of the brain stem and respiratory collapse
Choking
Blockage of trachea (windpipe) due to foreign bodies or acute inflammations
Foreign bodies
Marbles/toys
Dentures
Food
Common offenders, grapes, grapefruit, steak, hot dog
Acute inflammation
Anaphylaxis
Insects, medications, peanut butter
Those at rick include infants, elderly, mentall ill, or under influence of drugs or ethanol
Cafe coronary syndrome
Choking games
Popular in teenagers
Game of choking each other or yourself and then removing pressure from neck
Gained popularity via social media
Experiencing “high” without taking drugs
Numerous death reported, real statistics unknown
Autoerotic asphyxiation
Usually young adult males
Intentionally induced hypoxia (low oxygen) to enhance orgasm
Planned escape mechanism with elaborate knots and contraptions
Scene examination is crucial
Can observe cross dressing, pornography, bondage, webcams, no suicide notes
MOD Accidental
Fire Related deaths
Most common cause of death is inhalation of noxious gases rather than thermal injuries
Rapid oxidation of material in chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light and various reaction products
Flame is the visible portion of the fire
Flames consist of CO2, water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen
National fire protection association data
U.S. fire departments responded to an estimated average of 358,300 home structure fires per year during 2010-2014
Home fires caused an annual average of
2,560 civilian fire deaths, or 93% of all civilian structure fire deaths
12,720 civilian fire injuries, 87% of all civilian structure fire injuries
$6.7 billion in direct damage, or 69% of total direct damage in structure fires
Heat Injuries
First degree
Erythema and blistering
Second degree
Destruction of full thickness of skin
Third degree
Destruction of deeper tissue
30-50% body surface involvement is not compatible with survival
Moist thermal injury (scalds) due to hot liquid
Water, oil, steam
Dry heat
Radiant heat, sunlight, articial sunlamps, hot gas
Fire Related Deaths
CO forms from incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons during fire and is inhaled if someone is alive in fire
CO binds to hemoglobin molecule with affinity 200-250 times more than oxygen
COHb is formed which impairs release of oxygen to tissues
Normal level is less 6% in chronic smokers levels can be 10-15%
Younger or sick are affected by lower level of COHb and can cause death with minimal exposure
Hydrogen cyanide also can be released during fire
Used in production of acrylic fibers, synthetic rubber and plastics
Increased frequency of cyanide posioning in house fires
Can act independently or together with carbon monoxide
Thermal Injuries
Total body surface burned is estimated using rule of 9’s
Help guide fluid resuscitation and/or transfer to specialized ICU Burn Unit
Those who survive initial effect of burns can die later from complications
Infection due to breach of skin barrier
Multi-organ failure
Shock
Fire-related deaths always need in-depth investigation
Can be accidental or homicide
Scene investigation is performed by Fire Marshall office and police
Investigation is crucial for determination of MOD
Important factors in both the criminal investigation and physical examination
How, where and when the fire started
Use of accelerant
Equipment malfunctioning
Medical history of victim(s)
Evidence of any other injuries
Determining COD is crucial in investigation
Homicide: other significant injuries found or accelerant used
Postmortem burning
Victims set on fire to destroy evidence
Accidental
Lit cigarettes, portable heaters, cookers, kids playing with matches or lighters, candles
Postmortem burning
Ex: victim or motor vehicle accident with blunt force trauma then car catches fire
Suicide
Self-immolation as sacrifice
Mass fatalities
First responders
Wild fires
X-ray needed to look for bullets or metal objects
Clothing must be saved in sealed metal cans
Proper identification needed
Blood is collected for CO determination
Medical, social and psychiatric history needs to be obtained
Evidence that may help determine cause of death in Thermal Injuries
Soot in airways
Victim was breathing
Determination of carbonxyhemoglobin in blood
Victim was breathing noxious gases of combustion
Cherry red discoloration of tissue and blood
Need to determine what actually caused death in Thermal Injuries
Burns
Smoke and soot inhalation
Natural disease
Injury
Drugs
Combination of factors
Thermal Injuries - Artifacts
Artifacts: important not to confuse with real trauma
Puglistic posturing (resembles stance of bozer) due to heat effect on muscle
Splitting of skin with exposure of underlying tissue resembling incised wounds
Epidural hemorrhage
Thermal fractures
Early decomposition changes and thermal induced skin slippage is seen
Hyperthermia
Humans need to maintain body temp within narrow range
Hypothalamus regulates heat loss and gain
High temp can be fatal
More dangerous in young, elderly and sick
High-related death
Direct effects
Indirect effects
Worsening of underlying medical condition
Body temp above 105 F (40.5 C)
Heat stroke is severe form
Mild form
Heat cramps and heat exhaustion
Exercising/manual labor in heat
Diabetes mellitus
Obesity
Dementia
Certain medication (tricyclic antidepressants)
Coronary artery disease
Alcoholism
No specific finding on autopsy
Most important to document condition at scene
Working a/c or not
Electricity on/off
Temp inside and outside (heat advisory)
Fans on/off
Medical history
Availability of drinking water
Infants and young children left inside the cars
Reduced capacity for sweating as a means of heat loss
Higher metabolic rate
Death can be ruled as accidental or homicide
Hypothermia
Core temperature below 95F (35C)
Death due to exposure to cold
The temperature does ont have to be below 0C
Very important to know if wet clothing, drugs, alcohol or meications invovled, age, other medical conditions
If taken to the hospital, must document core body temp prior to re-warming
Physiological response:
Vasoconstriction
Increased cellular metabolism (to produce heat)
Shivering
Can occur on land or water-immersion hypothermia
Water much more rapid
Scene investigation crucial
Was there a heater or electricity?
Document temperature inside and outside
Clothing and body temperature
Paradoxical undressing due to cerebral vasoconstriction leading to confusion, causing sensation of hot flash
Terminal burrowing
Victims found in cupboards
Surrounded by furniture
Wishnevsky ulcers: small gastric mucosal hemorrhages
Electrocution
Passage of electric current through the body
Mostly accidental
Need to consider current, voltage, resistance and time
Body must be incorporated into electric circuit
Current enters at one point (usually hand) and leaves at exit point usually to the earth
Scene investigation is most important, death is often not observed
From direct contact to live parts or indirect contact
Point of contact burns or electric marks
May absent when in bath
Passage of current heats issue fluids and produces steam, blister form
Extent of injury or death depends on resistance, duration of contact, surface area of contact, and pathway of the current through the body
Most common passage of current through heart, but it will always take the path of least resistance
Dry skin - 1 million ohms
Wet skin - 1200 ohms
If hand to head, the current goes through brain
Brain steam death and immediate death
If hand to leg, the current goes through heart
Ventricular arrhythmias, death within seconds
If hand to hand, the current goes through chest wall
Diaphragmatic paralysis and traumatic asphyxia
Requires contact for minutes for death to occur
Electric Chair
Wood chair, metal electrodes strapped to scalp and leg, with moist sponge over the head
Brought to light as a more humane method of capital punishment by Albert Southwick, a dentist from Buffalo, in 1880s
First use in 1890
Last use in 2013, Richard Gleason in VA
Drowning
Hypoexmia leading to irreversible cerebral anoxia due to submersion in liquid
Natural bodies of water, they do not have to be deep
Pools, bath tub
Can occur while swimming, fishing, boat, ship, ferry malfunction, walking on ice, taking shower, etc.
Can be accidental, suicidal or homicide
Postmortem examination shows non specific findings
Frothy fluid mouth and nostrils
Lung edema
Fluid in stomach
Hemorrhages in petrous temporal bones
Body Found in Water
Need to consider the following scenarios:
Died from natural disease and fell into water
Died from natural disease while in the water
Died from injury and thrown/found in water
Homicide, GSW, stabbing, strangled
Diving into shallow pool, C1 fracture/dislocation
Died from injury while in water
Died from drowning
Mechanical Trauma
Occurs when the force applied to skin or bone exceeds the mechanical or tensile strength of the tissue
Can result from sharp or blunt forces
Blunt Force Trauma
Factors in determining the severity, extent, and appearance of blunt force injuries
Amount of force delivered to the body
Time over which the force is delivered
Area of body struck
The amount of surface area of the body struck
Nature of weapon or device used to deliver force
Categories of Injuries
Four categories:
Abrasions
Injury to the skin, in which there is removal of the superficial epithelial layer of the skin (epidermis) by friction against a rough surface or destruction of the same layer by compression
Three types:
Scrape of brush abrasion
leaves denuded surface; “road rash”; “raspberry from sliding”
Impact abrasion
Force directed perpendicular to the surface, crushing it; over bony prominences
Patterned abrasion
Version of impact; imprint of object or intervening material
Contusions
Area of hemorrhage into soft tissue due to rupture of blood vessels caused by blunt trauma (synonym: bruise)
Can be present only in the skin, but may also be seen in internal organs as well
Factors influencing the size of the contusion: age, sex, condition, and health of the individual, site, and tissue struck
Skin contusions are not good indicators of the severity of underlying organ injuries
Contusions: Aging
Rough estimate
Color changes from blue-red to dark purple to green to yellow to brown
“The change of color may be used as a guide for aging the injury.”
Current data: aging bruises are fraught with difficulty
Lacerations
A tear in the tissue caused by either a shearing or crushing force
Characteristics:
Tend to be irregular with abraded and/or contused edges
It occurs over bony prominences, where skin is fixed and can only be stretched and torn
Incomplete separation of skin components (nerve, blood vessels) leads to “bridging” within the wound and differentiates a laceration from an incised wound
Undermining of skin on one side can help determine the direction from which the force was delivered (avulsions)
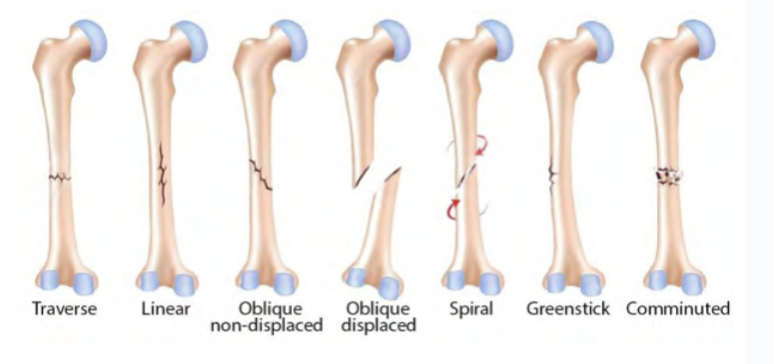
Fractures of the skeletal system
It occurs when a force acts on a long bone
It can be caused by direct or indirect application of force
Direct force fractures: penetrating, focal, or crush
Indirect force fractures: traction, angulation, rotational, vertical compression, angulation, compression and angulation, rotation, and compression
Bite Marks
Actual injury rare
Patterened abrasion with underlying hemorrhages
Often sexual in nature
Can be compared with the suspect’s dentition
Internal Organ Injuries
Ribs: pathologic, iatrogenic, direct localized violence and indirect violence
Heart: Commotio Cordis
Aorta: lacerations of the thoracic aorta occur distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery; ascending lacerations from increased pressure
Solid abdominal organs: parenchymal lacerations
Urinary bladder: rupture
Sharp Force Wounds
Wounds caused by pointed and sharp-edged devices
Categories:
Stab wounds: depth of wound exceeds length in the skin
Incised wounds: length of wound exceeds depth
Chop wounds
therapeutic/diagnostic wounds
Stab Wounds
The length of the wound in the skin can be less than, equal to, or greater than the width of the knife
The depth of the stab wound can be less than, equal to, or greater than the length of the knife
Appearance of wound depends on nature of blade and knife; direction of force; movement of blade in wound; movement of victim; and state of the skin
Incised Wounds
Wounds produced by sharp-edged devices, wherein the length is greater than the depth
Characteristics:
Clean cut, straight edges free of abrasion or contusion
No bridging of soft tissue in the wound
Usually not fatal; seen more in suicides than homicides
Chop Wounds
Wounds produced by heavy devices with a cutting edge, e.g., axes, machete
An incised wound with a long groove or a comminuted fracture of the underlying bone suggests a chop wound
Can have characteristics of incised wounds and lacerations
Defensive Wounds
Special consideration for these wounds
Usually along the palms of hands, the back of the forearms, and arms, and on the ulnar aspect of the forearm
Sustained trying to ward off the attacker
Venous Air Embolism
Penetrating wound of the neck or upper chest
Neurosurgical procedures
Central venous catheter placement
Vaginal air insufflation (especially if the woman is pregnant)
Dental procedures
Therapeutic/Diagnostic Wounds
Created in the condition of medical care, e.g., surgical incisions, surgical stabs for placement of tubes and drains