4.1.2 Alkanes
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Are alkanes saturated or unsaturated?
saturated
What bonds are present in alkanes?
C-C
C-H
What type of bond is a C-C bond?
sigma bond
What type of bond is a C-H bond?
sigma bond
How is a sigma bond formed?
direct single overlap of orbitals directly between the nuclei of bonding atoms
As a sigma bond is a single overlap, what does this allow?
rotation of the bond
Describe sigma bonds
saturated
single
strong
Draw a diagram of sigma bonding
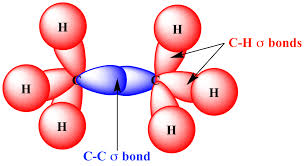
What is the shape and bond angle around each carbon atoms in alkanes and why?
109.5
tetrahedral
4 bonding pairs of electrons repel equally
What is needed to boil an alkane?
break the induced dipole-dipole attraction forces between molecules
What do you break when boiling an alkane?
induced dipole-dipole attraction forces between
Give 2 factors that determine boiling point of an alkane
carbon chain length
branching
As carbon chain length increases what happens to boiling point of the alkane?
boiling point increases
Why does increasing carbon chain length increase boiling point of alkane?
more surface contact between molecules
more induced dipole-dipole interactions between the molecules
which require more energy to overcome
What does more surface contact mean?
more induced dipole-dipole forces between the molecules
Describe the boiling point of a branched isomer and a nonbranched isomer
a branched isomer has a lower boiling point that an unbranched isomer
Why does a branched isomer have a lower boiling point than a non-branched isomer?
carbon chain length decreases
less surface contact between molecules
less induced dipole-dipole forces between molecules
requires less energy to overcome
What intermolecular forces exist between alkane molecules?
induced dipole-dipole forces
Are C-H sigma bonds polar?
no
What type of bond breaking occurs between C-C bonds and C-H bonds?
homolytic fission
Describe the bond enpalthy of alkanes
they have high bond enpalthy
Give 2 important chemical reactions that alkanes are involved in
combustion
halogenation
Is combustion endo or exothermic?
exothermic because heat is being released to the surroundings
What are alkanes useful as?
fuels
How does complete combustion occur?
with a plentiful supply of oxygen
How does incomplete combustion occur?
a limited supply of oxygen
Why is incomplete combustion dangerous?
it releases carbon monoxide as a product
Why is CO toxic?
it binds to haemoglobin in the blood, preventing RBC from binding with oxygen which can be fatal
Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of butane gas
C4H10 + 6.5O2 → 4CO2 + 5H2O
Write a balanced equation for the uncomplete combustion of octane gas
C8H18 + 8.5O2 → 8CO + 9H2O
What are the reagents for radical substitution?
X2 (halogen) and excess alkane
What are the conditions for radical substitution?
uv radiation
What is radical substitution?
a substitution type reaction because H atom in the alkane molecule is replaced by a halogen atom
Which bonds break first in radical substitution?
covalent X-X bonds within the halogen
How do the X-X halogen bonds break?
by homolytic fission
What does the breaking of X-X halogen molecule form?
two X radicals
What is a radical?
a species with an unpaired electron
How do you show radicals?
a dot is used to represent the unpaired electron
What are the limitations of radical substitution?
structural isomers created
mixture of haloalkanes produced
unwanted alkane is produced from the reaction of 2 alkyl radicals
Why does radical substitution create structural isomers?
there may be substitution reactions at different positions along the carbon chain
Why does radical substitution create a mixture of haloalkanes?
further substitution could take place until all of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced
Give an example of 3 different haloalkanes that could be produced in the radical substitution of chlorine and butane
chloromathane
dichloromethane
trichloromethane
Why is an unwanted alkane sometimes formed in the termination stage?
two alkyl radicals bond
How is further substitution in radical substitution avoided?
use of excess alkane
What are the 3 steps of radical substitution?
initiation
propogation
termination
What is initiation of radical substitution?
the breaking of the X-X bond by homolytic fission to make two X radicals
What is the equation for initiation of radical substitution?
X2 → 2X.
what provides the energy to break the X-X halogen bond in initiation?
uv radiation
What does the X radical do in propogation (i)?
attacks the alkane molecule
What happens in propogation?
a very reactive X. radical attacks an alkane molecule in a chain reaction
What is the equation for propogation i
X. + alkane → alkyl radical + HX
what is the equation for propogation ii?
alkyl radical + X2 → X. + haloalkane
Why is propogation a chain reaction?
the radical is used up in the first propogation step but it is regenerated in the second, so is able to attack a new alkane molecule - continues
What is termination in radical substitution?
when two radicals combine forming a new molecule
What are the 3 possible termination steps?
2X. → X2
X. + alkyl radical → haloalkane
2 alkyl radicals → alkane with 2x as many carbons as beginning alkane