Periodicity: Periods & groups 2 and 3
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
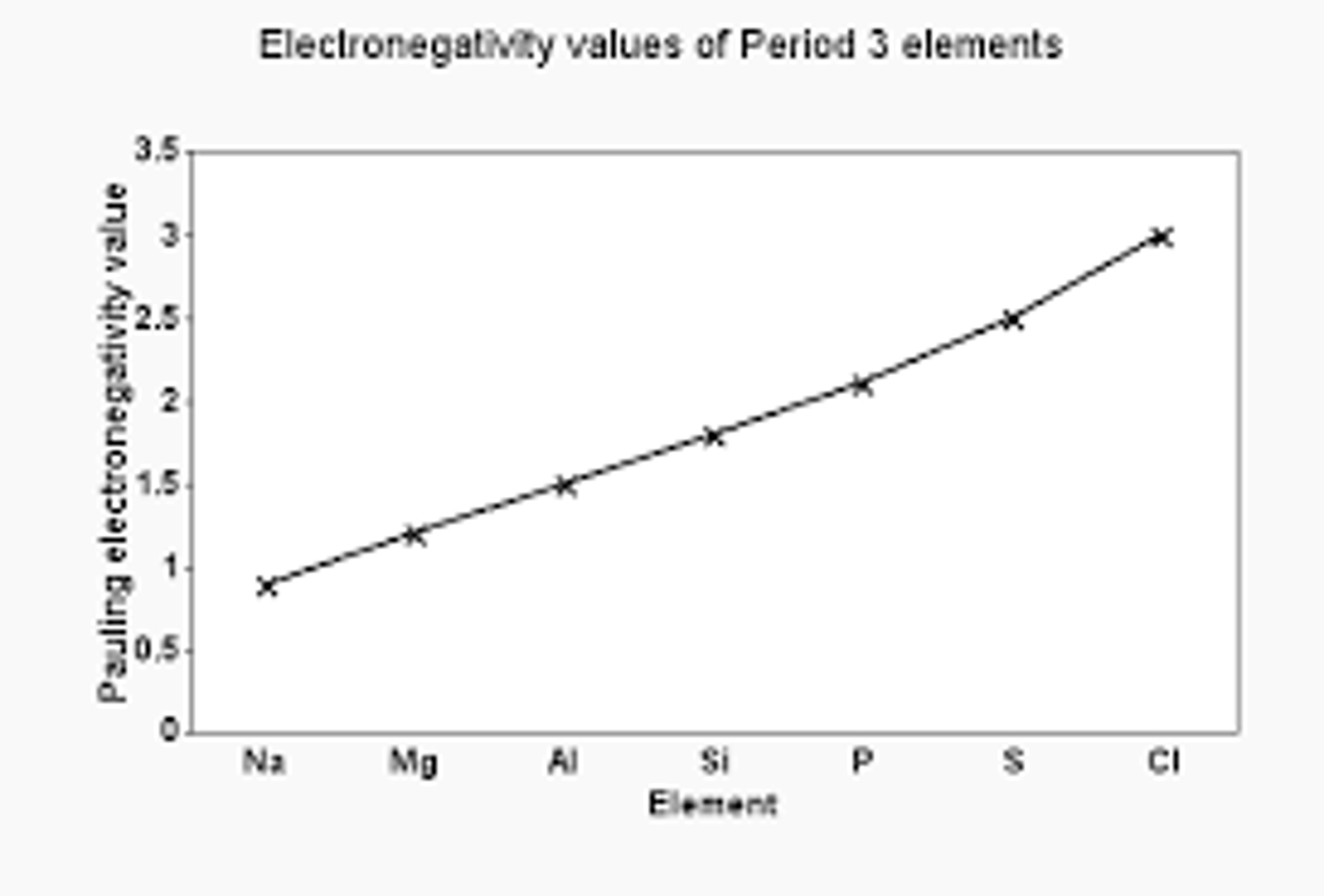
What happens to electronegativity going across a period (and why)
electeonegativity increases across a period - as the nuclear charge increases (more protons), so does the attraction for the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond
What happens to ionization energy down a group?
decreases down a group - despite the increase in nuclear charge, the increased shielding and the increased distance from the nucleus means the electrons are held less strongly and need less energy for their removal
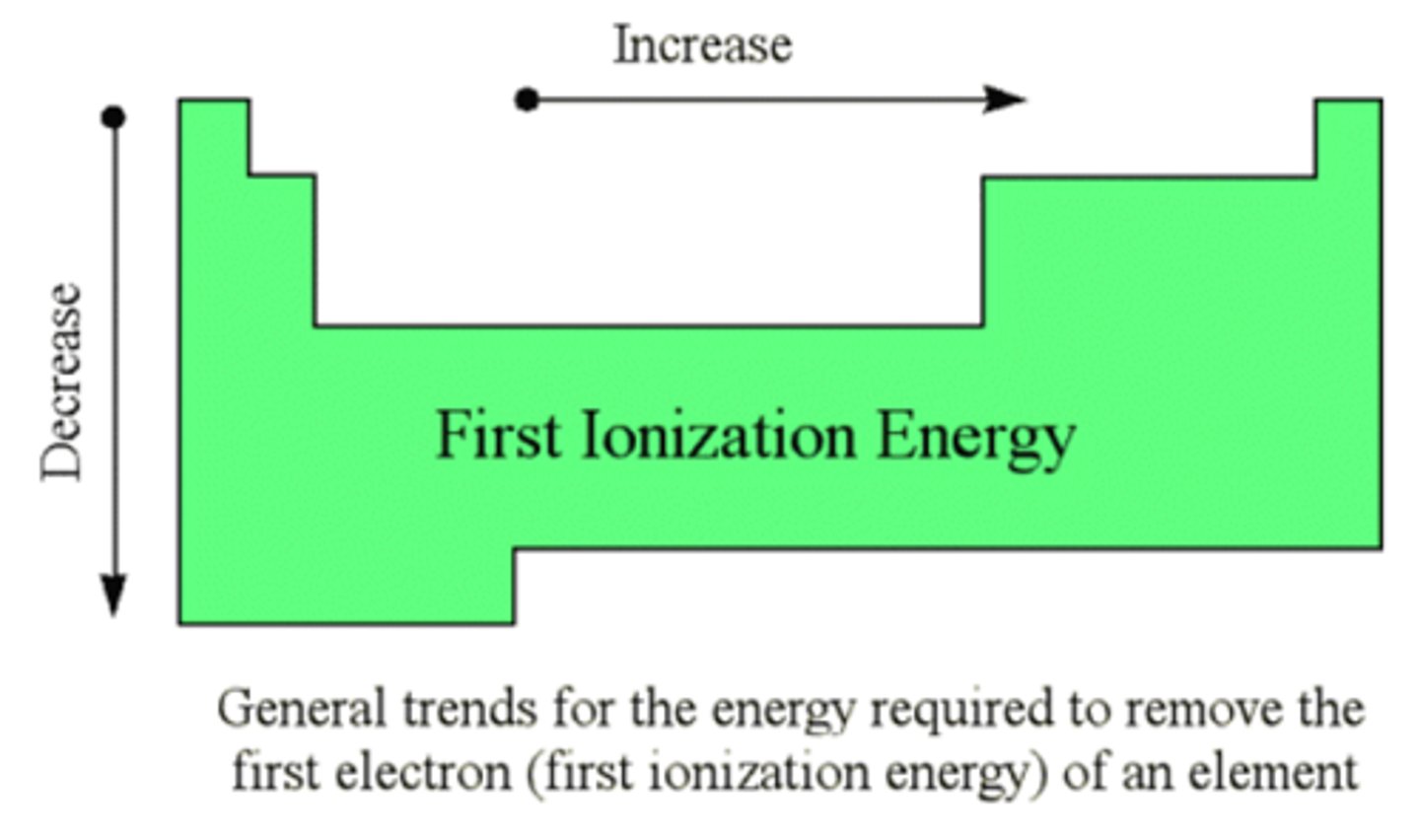
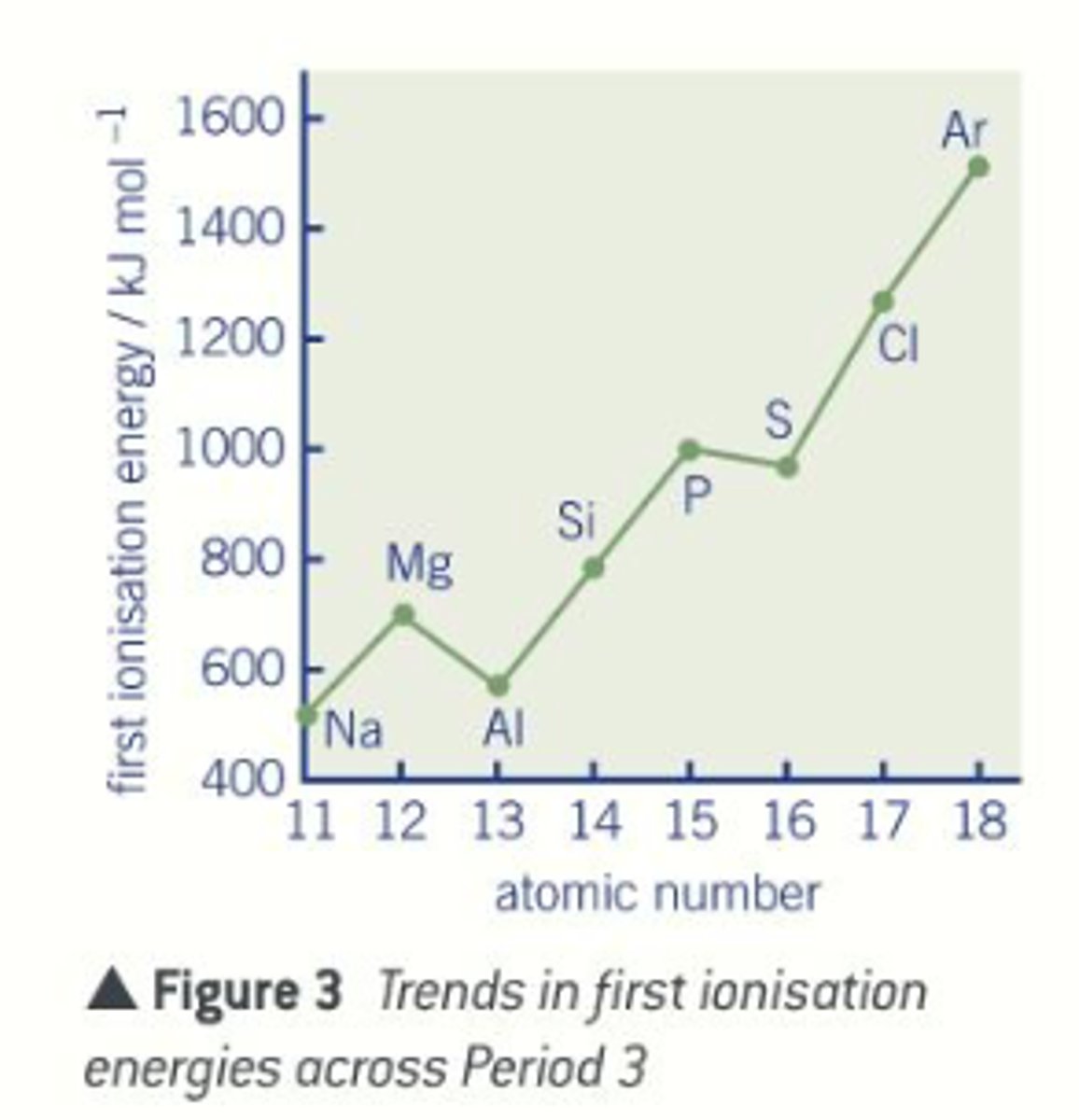
How does ionization energy increase across a period
- nuclear energy increases by one each time
- each extra electron is going into the same main energy level
- each electron is subject to similar shielding and is a similar distance away from the nucleus
- the electrons and held increasingly more strongly and are harder to remove
What is the periodic table?
An arrangement of elements by
-increasing atomic num
- in periods showing repeating trends in chemical & physical properties
- in groups having similar chemical properties
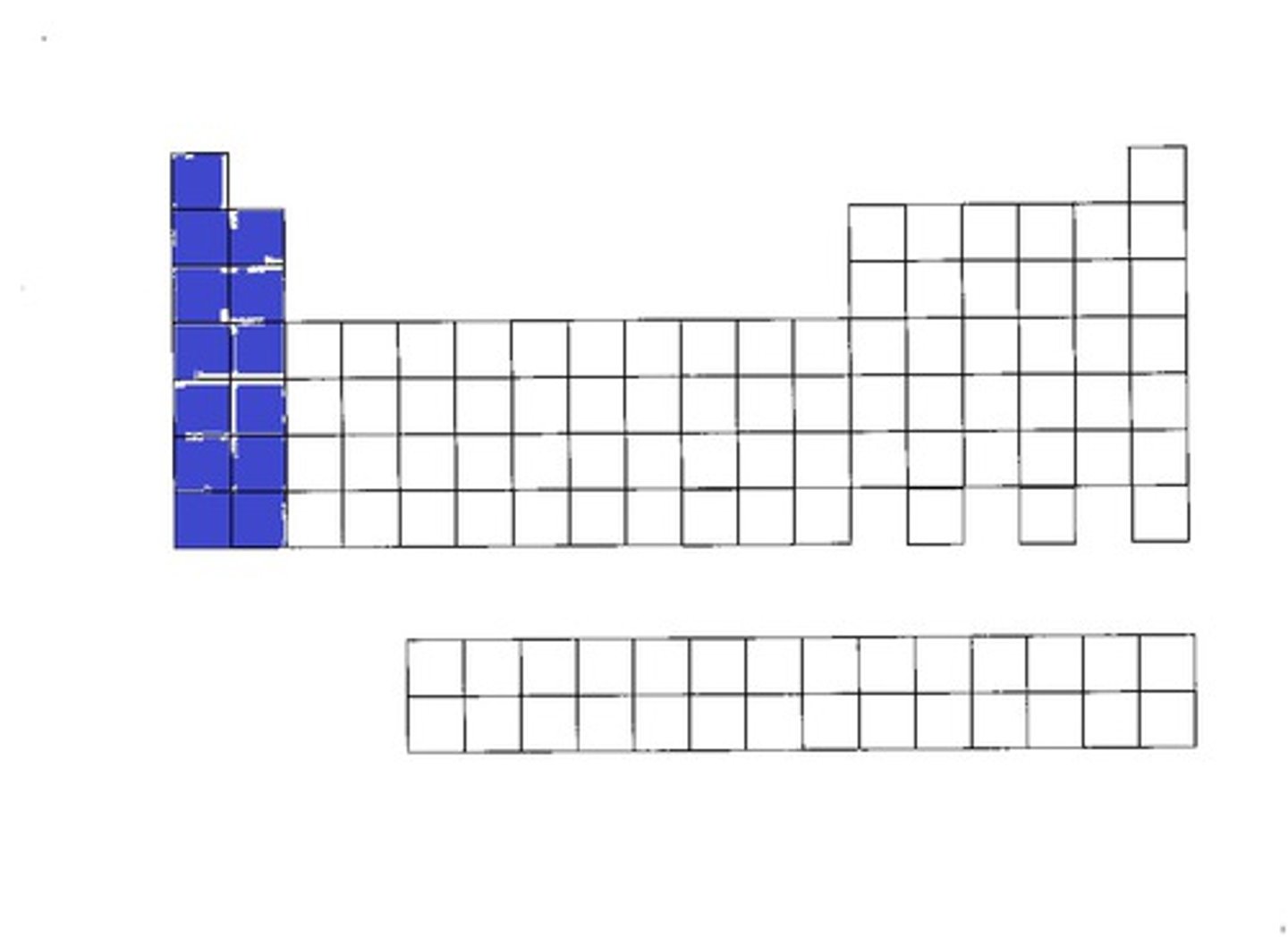
Elements in the s-block are:
metals
Elements in the P-block are
non-metals
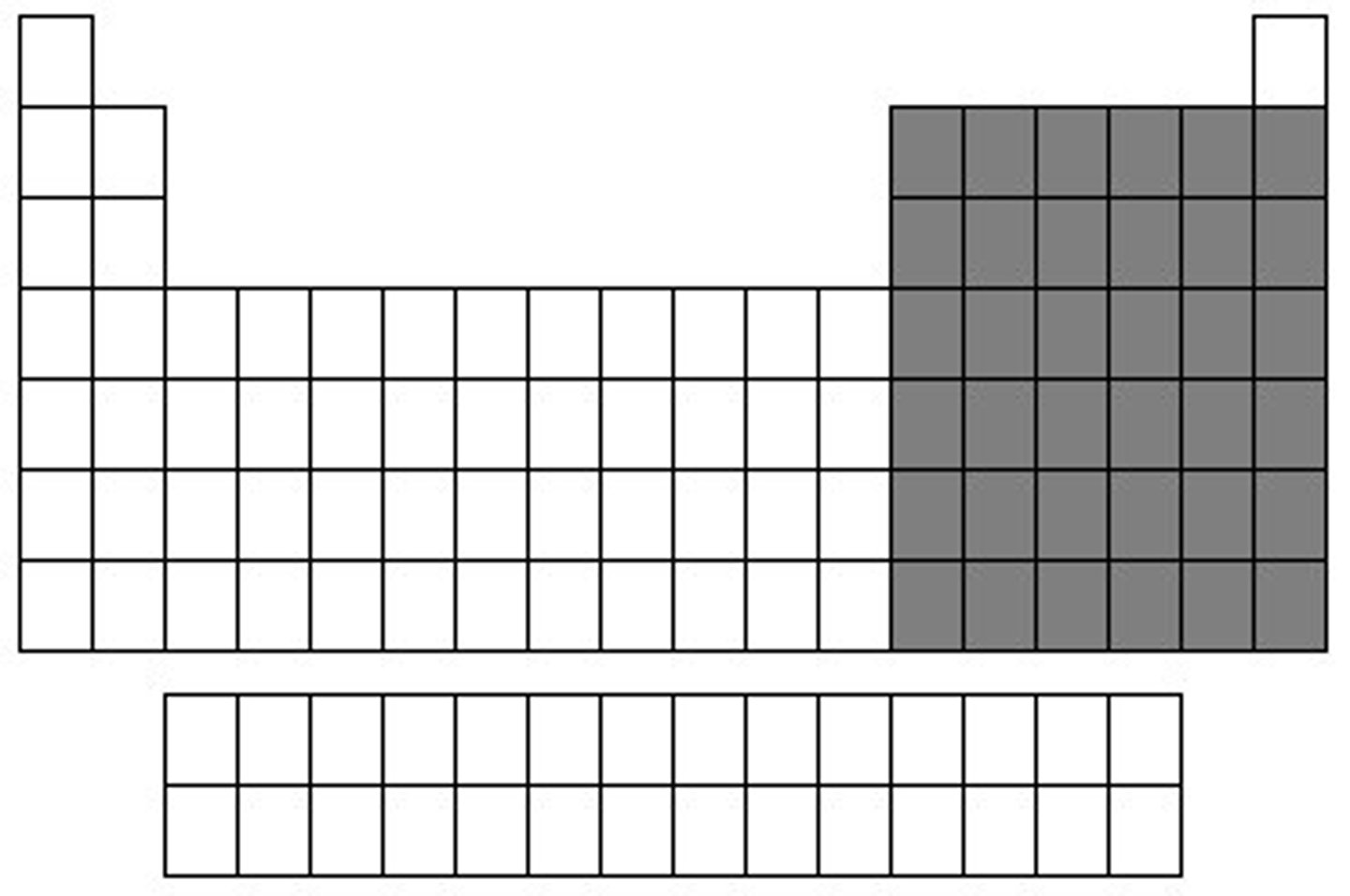
Elements in the D-block are:
metalloids
Characteristics of metals:
have metallic bonding & properties
Characteristics of metalloids:
have both metallic and non-metallic properties
Characteristics of non-metals:
have non-metallic properties
What happens when you move across periods 2 & 3?
the elements go from highly elecetropositive through metalloids to non-metals
How do electrons fill orbitals?
fills the s-orbitals first then p-orbitals
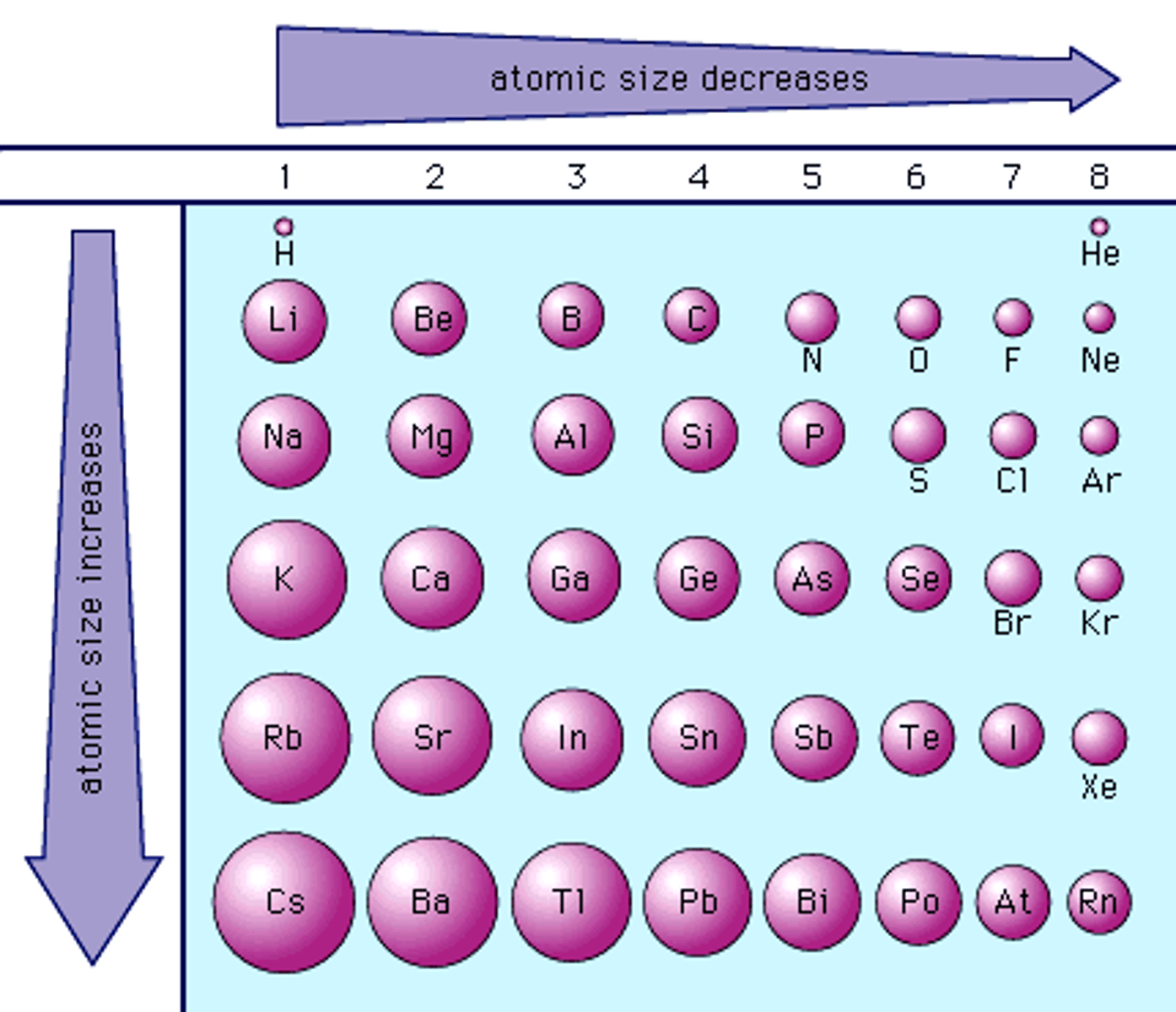
what happens to atomic radius across a period?
it decreases across a period due to increased nuclear charge attracting the electrons (which are going into the same shell) more strongly
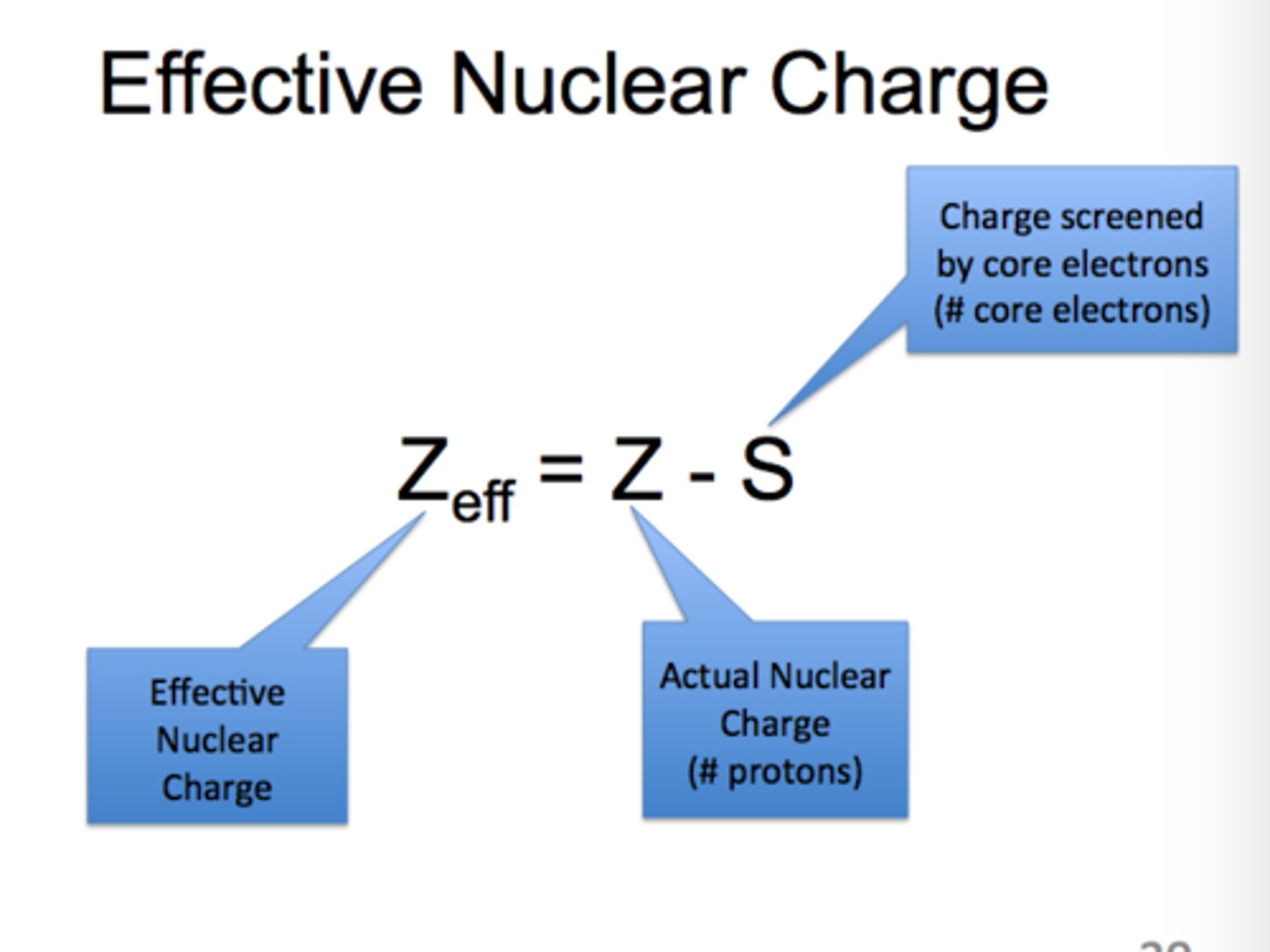
What is the effect nuclear charge?
the attraction of the nucleus for the electrons
Effective nuclear charge equation:
Z* = Z - S
What is electronegativity?
a measure of the attraction an atom has for the electron pair in a covalent bond
what happens to electronegativity going down a group
electronegativity decreases down a group
Difference between the trends for atomic radius and electeonegativity:
both have the same reasoning but opposite trend
What is ionization energy?
the energy required to remove a mole of electrons from a mole of gaseous atoms
What happens to ionization energy across a period
increase across a period
Ionization energy: Aluminium ([Ne] 3s² 3p¹)
1st ionisation energy is lower than Mg because of the shielding effect of the newly filled 3s orbital
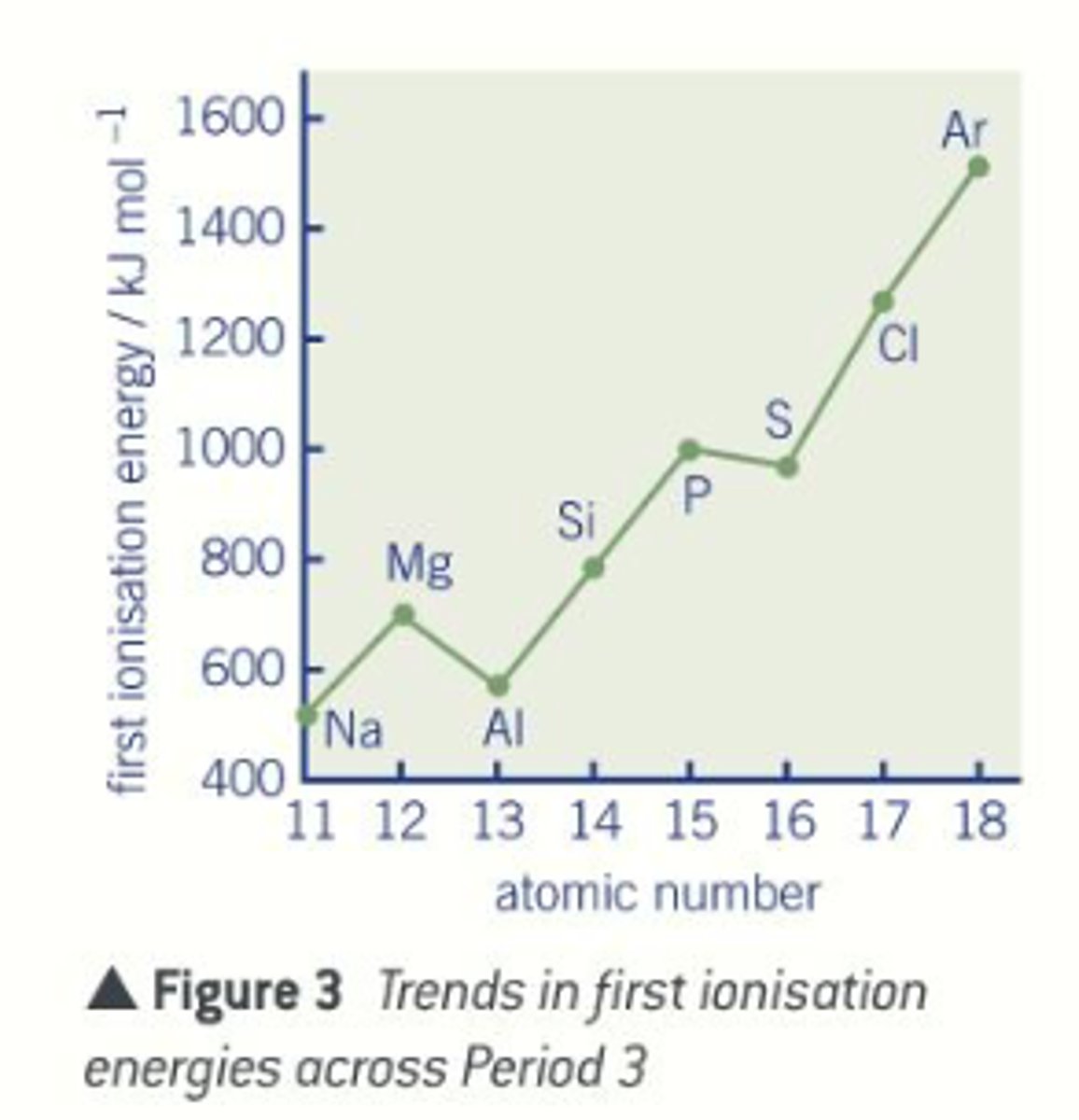
Ionization energy: Sulphur ([Ne] 3s² 3p⁴)
1st ionisation energy is less than phosphorus due to additional repulsion between the newly paired up electrons in one of the p-orbitals.
What is electrical conductivty?
the ability of a material to carry an electric current
When does electrical conductivity occur?
when ions/electrons are free to move
What happens to electrical conductivity down a group?
it decreases down a group
What happens to electrical conductivity across a period?
it decreases across a period (metals ->metalloids ->non-metals)
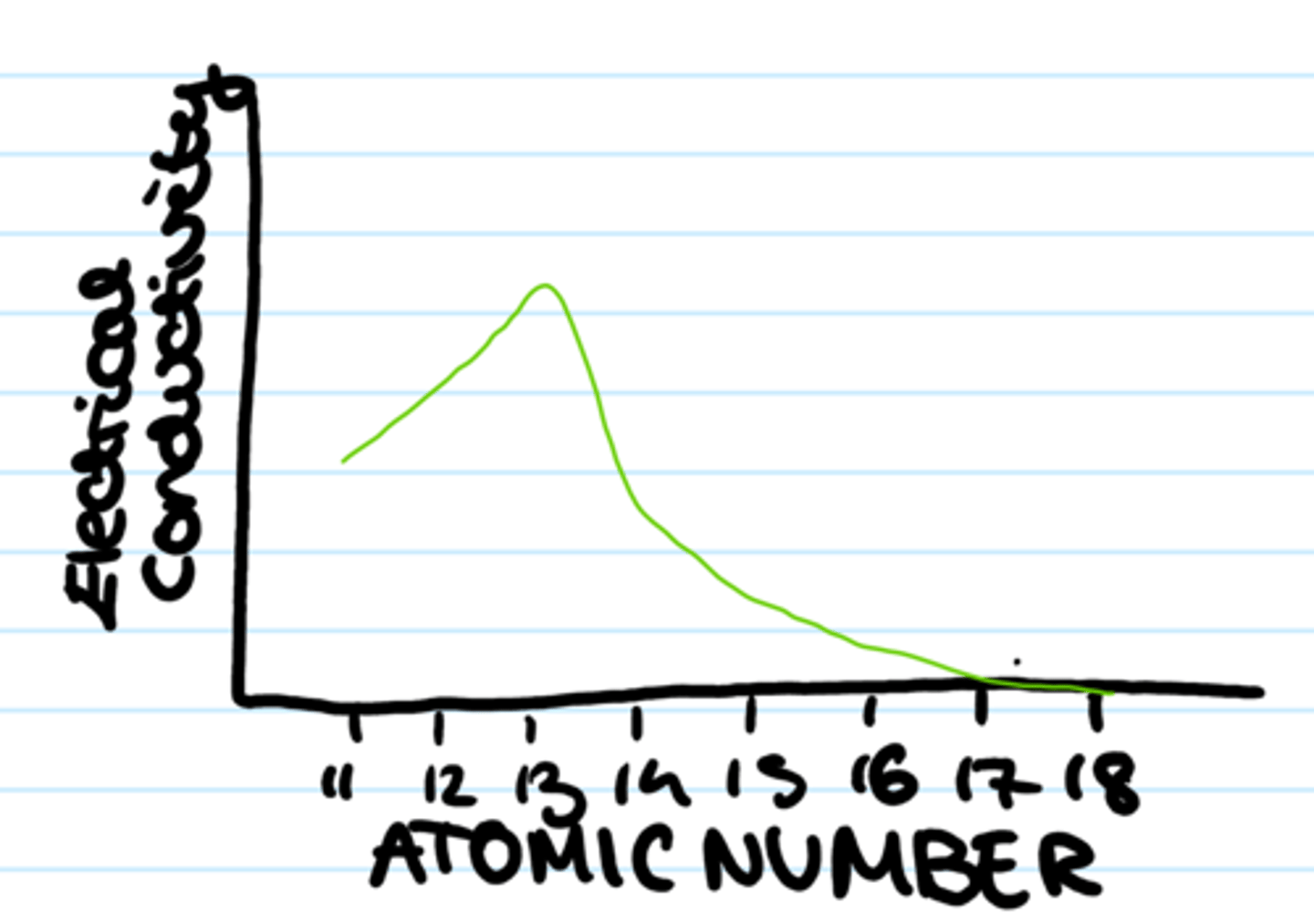
Why does electrical conductivity decrease across a period?
- Na, Mg & Al have metallic bonding with delocalised electrons: so a current can be carried
- Si, P, S & Cl are covalently bonded so no electrons move
- Ar is monatomic so electrons are held very tightly
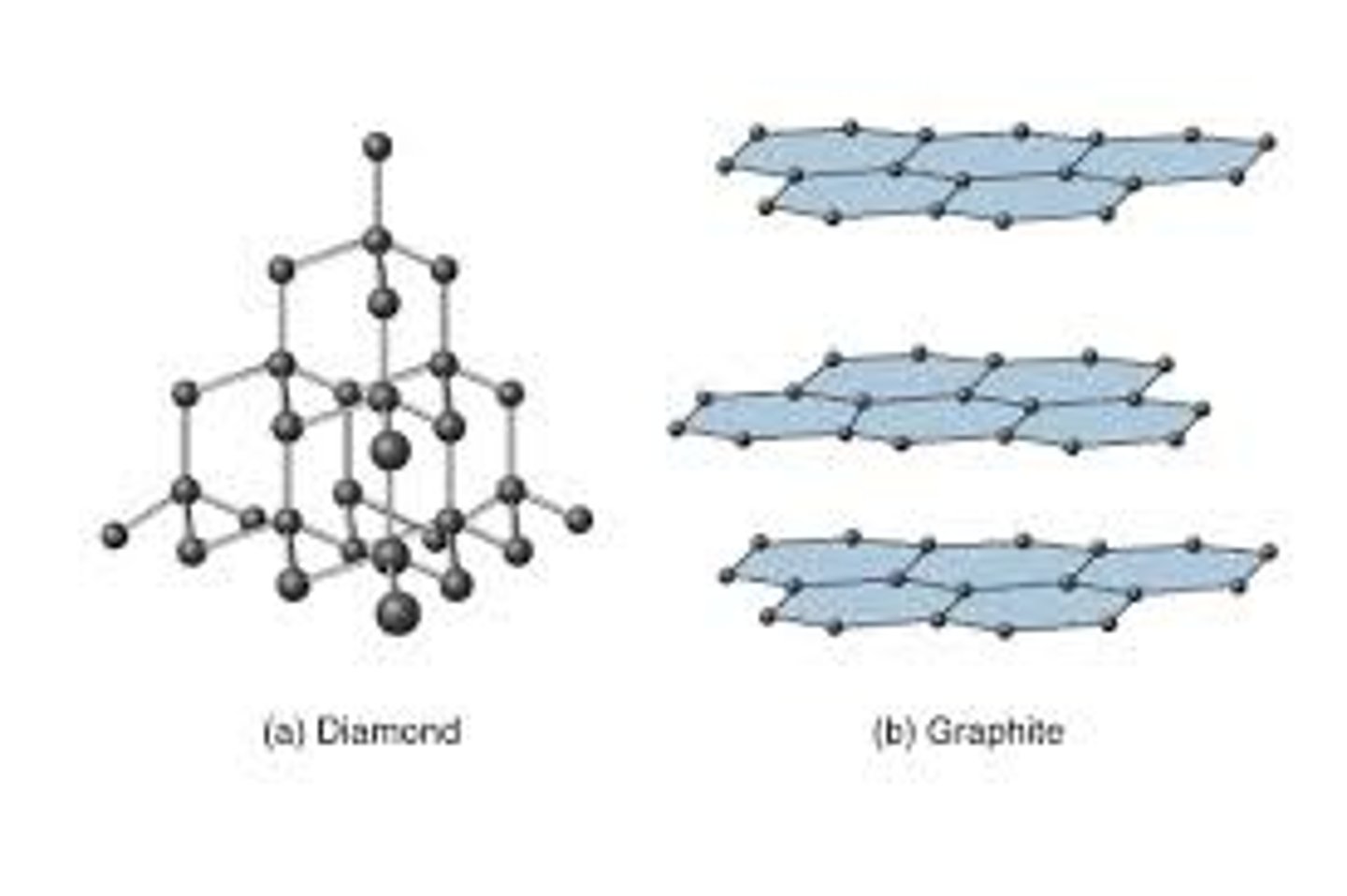
Electrical conductivity Silicon, Si:
*silicon is a semi-conductor:
- at r.t.p silicon has no charge (electrons are unable to move)
-> has the structure of diamond (but weaker bonds)
- w/ elevated heat, silicon has the structure of graphite
-> graphite-like structure w/ delocalised electrons
-> delocalised electrons carry charge
Electrical conductivity: Why is there only a slight increase from Na to Mg, but a steep increase from Mg to Al?
Al^3+ has a greater charge than Na^+ and Mg^2+; it is therefore surrounded by an increased number of delocalised electrons
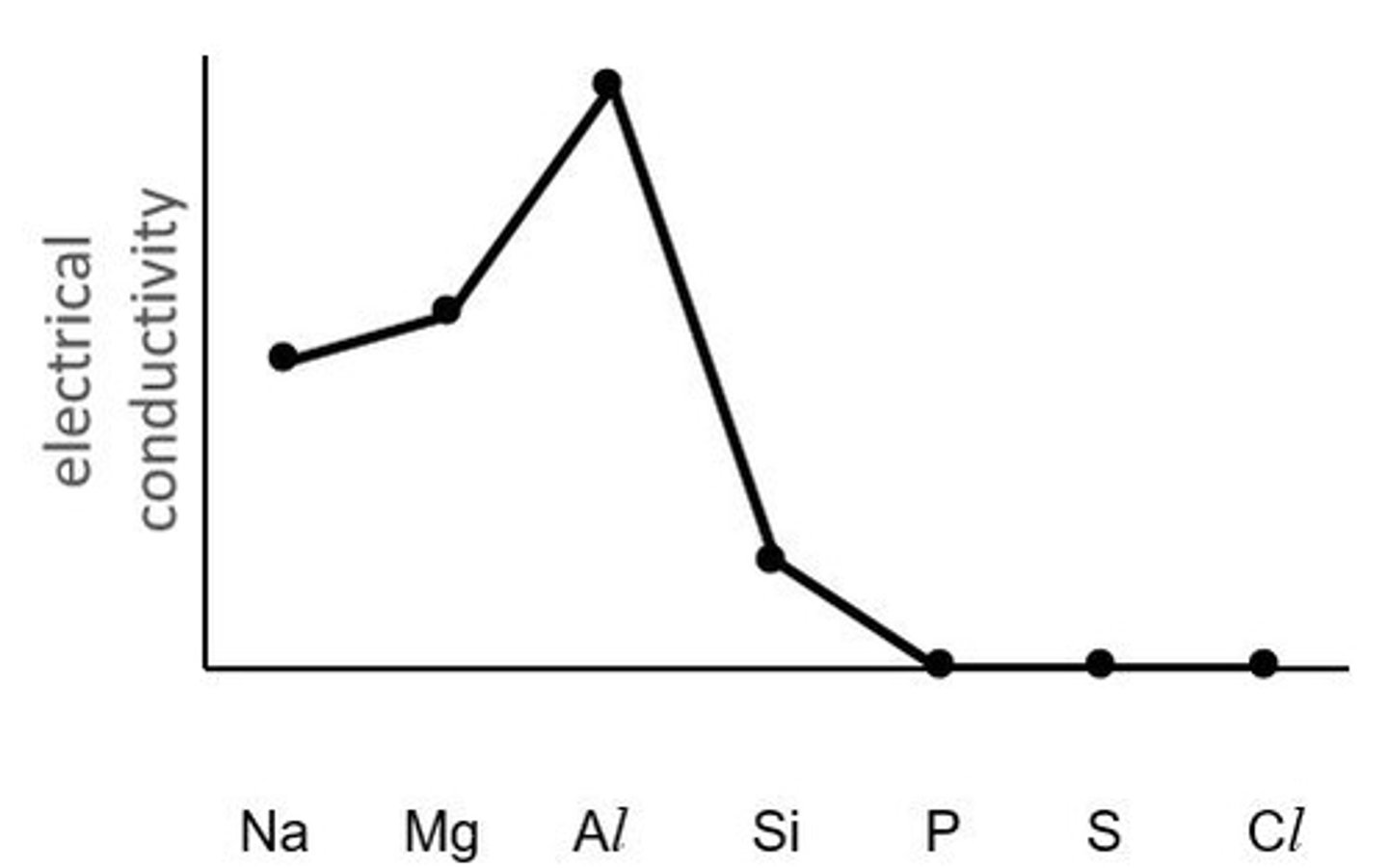
Why do Si, P, S. Cl and Ar have no electrical conductivity?
they exist as simple molecular elements
What are melting and boiling points?
a measure of the energy required to separate the particles in a substance
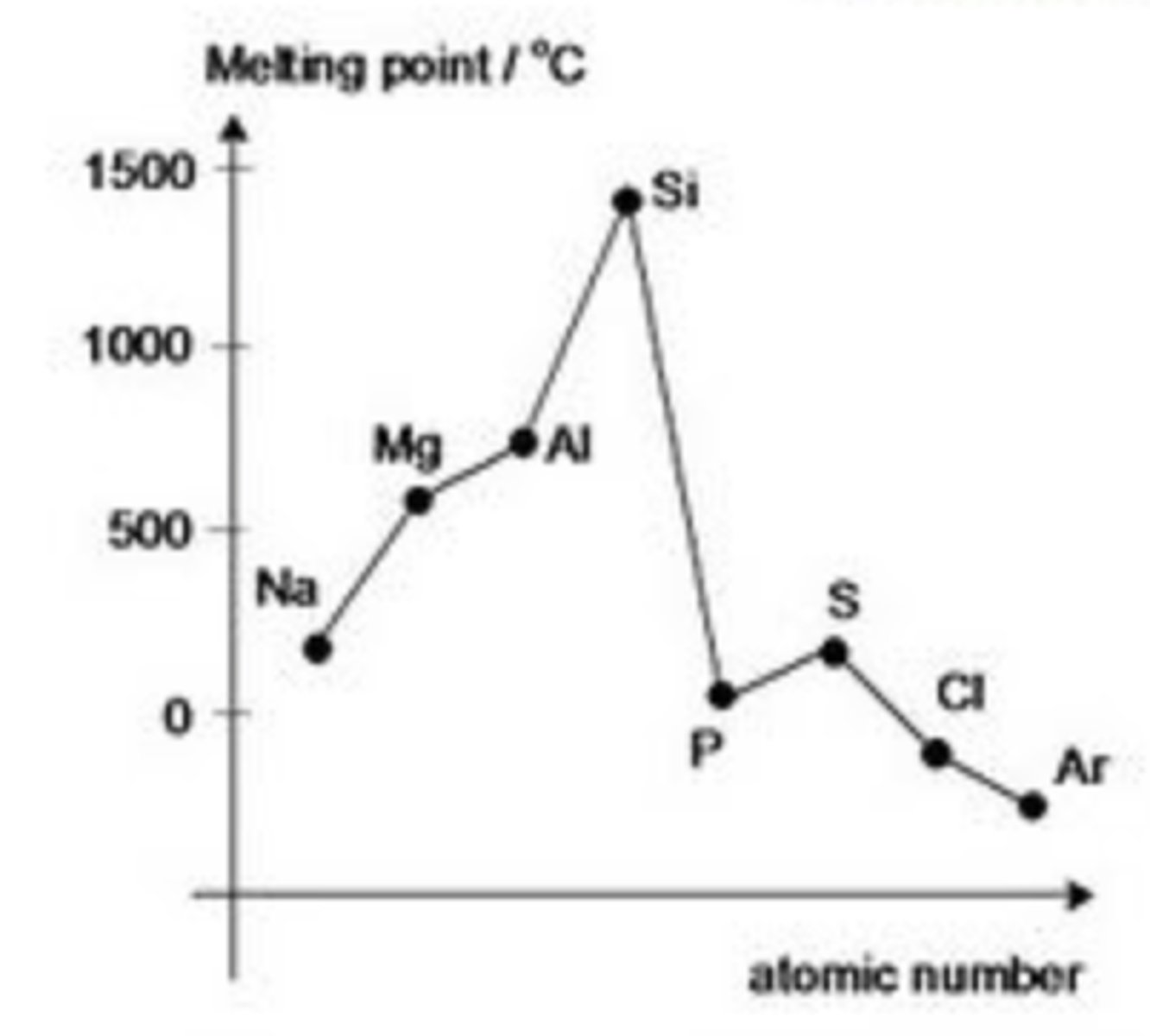
What happens to the melting point across a period?
a general increase then a decrease
Cause and effect of a high melting point:
cause: more delocalised electrons lead to more attraction between the cations and sea of electrons
effect: more energy is required to overcome the forces of attraction to break the bonds.
Why does melting point increase: metals?
due to the increasing metallic bonding caused by:
- more electrons contributed to the 'cloud"
- larger charge & smaller size of ions give rise to larger charge density
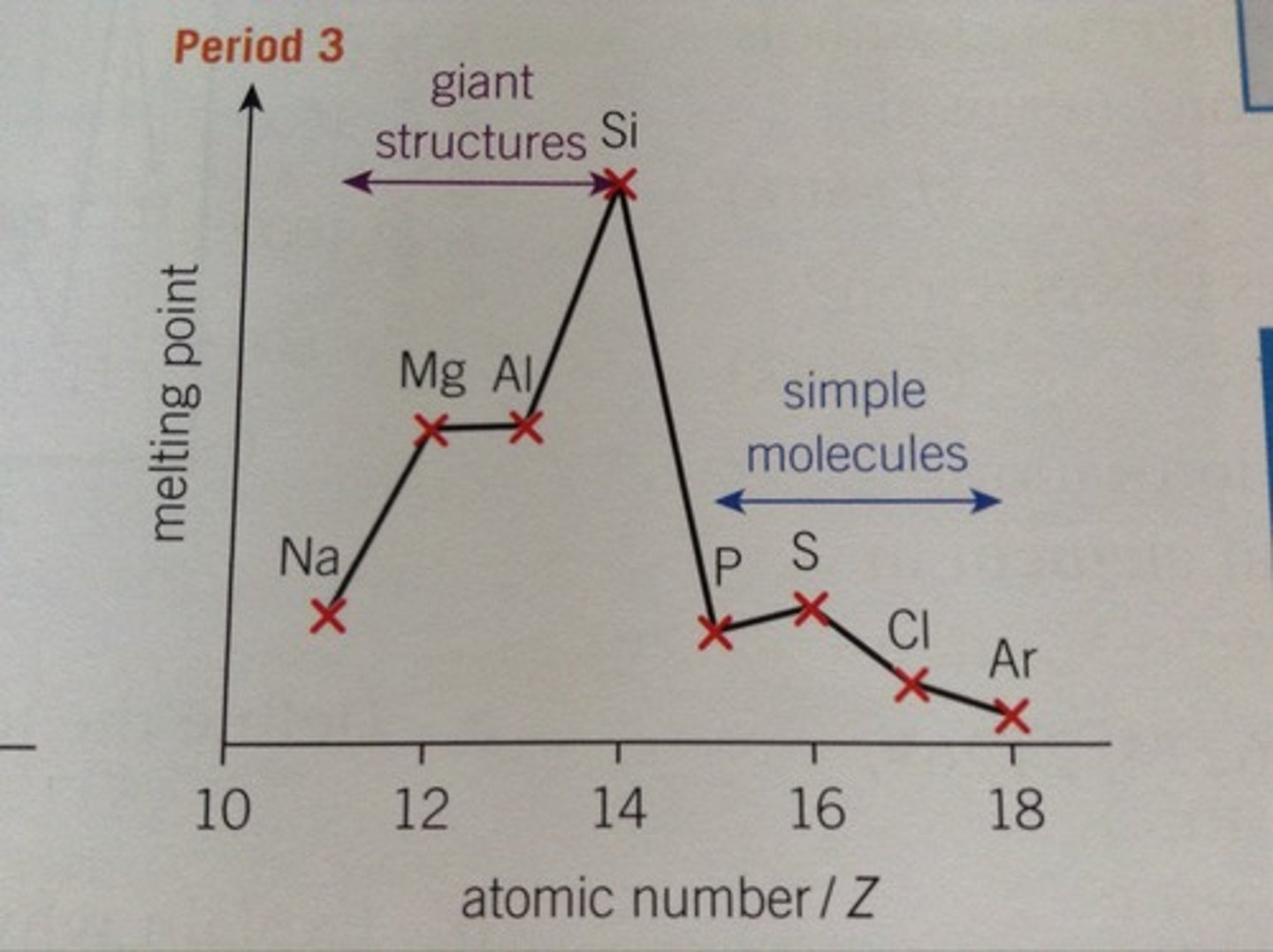
Why does melting point largely increase: Si?
it has a giant molecular structure (like diamond) ∴ a lot of energy is needed to break the strong, directed covalent bonds holding atoms together
Why does P, S & Cl have a lower melting point than Si?
- since they are simple molecular structures
*the melting point depends on the weak intermolecular Van Der Waals forces; these forces are size-dependent (i.e. the larger the molecular, the greater the forces)
Which element in the period has the lowest melting point?
Argon
What is electron affinity?
the ability of an atom to attract free electrons toward itself to form an anion
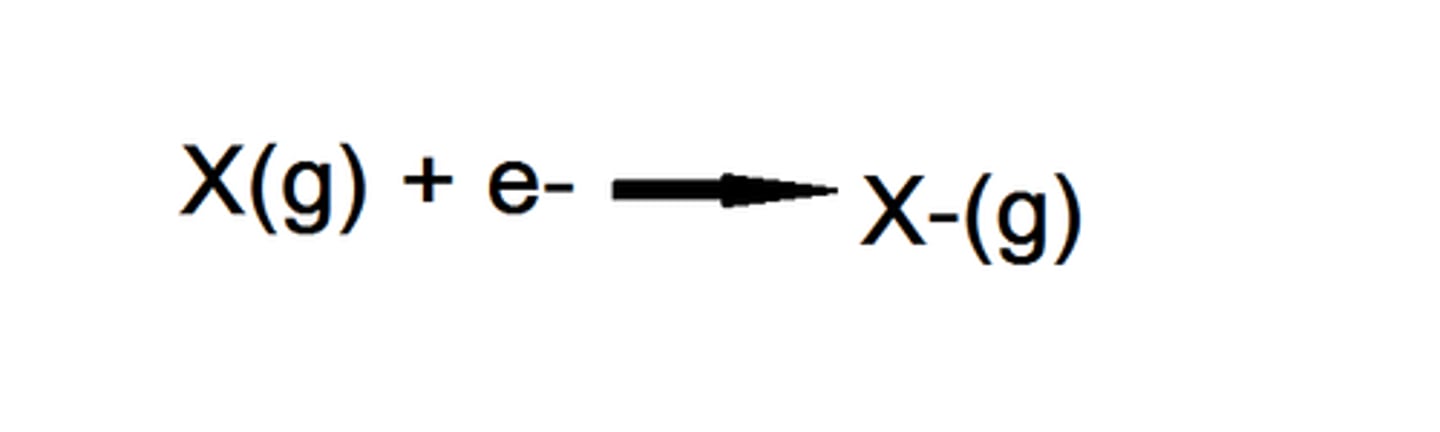
difference between electron affinity & electronegativity
electron affinity: the attraction to free electrons
electronegativity: attraction to electrons involved in a covaelnt bond
What happens to electron affinity across the period?
increases across the period - due to increased nuclear charge as the atoms increase their number of protons
What happens to electron affinity down a group?
decreaes down the group - due to shielding of the nuclear charge by the extra shells of electrons