amines and amides
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
"What is the functional group of amines?"
Amines only contain the functional group NH2
"How can we prepare an amine?"
We can prepare an amine by heating excess ammonia with a halogenoalkane.
"How can we form an amide from an amine?"
We can react an amine with either an acyl chloride or acid anhydride to produce a amide
classifying amines
We classify amines according to the number of carbons bonded to nitrogen.
1 carbon bonded to nitrogen - primary amine
2 carbons bonded to nitrogen - secondary amine
3 carbons bonded to nitrogen - tertiary amine
To name amines where NH2 is at the end of the chain, we
Write the root (longest carbon chain)
add ‘yl’ to the root.
write the suffix ‘amine’.
When an amine group is attached to a benzene ring
Amine has higher priority than benzene so:
We write the suffix amine
Add the prefix phenyl
"How do we name secondary and tertiary amines in the exam?"
In the exam if you are asked to name secondary and tertiary amines they will normally have identical groups. Therefore we name secondary and tertiary amines in the same way we name primary amines but we add the multiple ‘di’ or ‘tri’ at the every front of the name depending on whether its primary or secondary
"How do we name secondary and tertiary amines with identical groups?"
To name secondary amines with identical groups, we add the multiplier ‘di’ .
To name tertiary amines with identical groups, we add the multiplier ‘tri’ .
Another example
To name primary amines where the amine group isn’t at the end of the chain, we
add ‘an’ to the root.
include a position number before the suffix.
write the suffix ‘amine’.
Naming more complicated primary alkenes
When our molecule contains lower priority functional groups we can just add them to our prefix as usual
For example:
This amine contains a methyl group on the 3rd carbon so it is called 3-methylbutan-2-amine
Positon number of functional group - functional group name - longest carbon chain - an (since NH2 isn't at the end of the chain) - position number of amine group - amine
"How do we name amines when they are the highest priority functional group?"
When the amine is the highest priority functional group, we write the suffix ‘amine'
In this example amines are higher priority than halogenoalkanes
"How do we name amines when they are not the highest priority functional group?"
When the amine isn’t the highest priority functional group, we write the prefix 'amino'
In this example alcohol is higehr prioirty.
So we write the positon number of the amine group- amino- longest carbon chain- positon of alcohol - ol suffix
"How do we classify amines as aliphatic or aromatic?"
We classify an amine as either aliphatic or aromatic according to whether a benzene ring is directly bonded to nitrogen.
"What makes an amine aromatic?"
Aromatic - if a benzene ring is directly bonded to nitrogen
"What makes an amine aliphatic?"
Allaphatic - if a benzene ring is not directly bonded to nitrogen
aromatic compounds
aliphatic compounds
We classify amides according to the number of carbons bonded to nitrogen .
In primary amides - 1 carbon bonded to nitrogen
Secondary amides - 2 carbons bonded to nitrogen
Tertiary amides - 3 carbons bonded to nitrogen
To name primary amides, we…
Use the longest carbon chain to write the root
add ‘an’ to the root.
write the suffix ‘amide’.
"How do you name amides with substituents?"
If our amide has substituents we add them to the prefix the same as always.
Amides are the 2nd highest priority functional groups.
Position numver of substitutent - name of subsituent - name of longest cabron chain (in this case its 3 carbons) - ‘an’ ( add an to root) ---- add suffix amide
To name secondary amides, we...
treat the group without the carbonyl group as a substituent. The group with the cabronyl group as the main chain.
Therefore the substituent group (group without the carbonyl group) is in the prefix
We then write N- before the prefix.
To name tertiary amides with identical substituents, we
write ‘N,N-’ at the beginning of the name.
add the multiplier ‘di’.
To name tertiary amides with identical substituents, we
write ‘N,N-’ at the beginning of the name.
add the multiplier ‘di’.
To name tertiary amides with non-identical substituents, we
write ‘N-’ before each substituent.
write the substituents in alphabetical order.
primary, secondary and tertiary amines and amides
What type of bonds can amines and amides form with water?
All amines and amides can form hydrogen bonds with water.
How does the solubility of amines and amides in water change with increasing molecular size, and why?
The solubility of amines and amides in water decreases as the size of the molecule increases. Small amides and amides are highly soluble in water but larger molecules are less soluble. This is because a greater religion of the substance is nonpolar and non polar substances are insoluble in water
Why can amines act as both nucleophiles and bases?
Amines have a lone pair of electrons so they can act as a nucleophile and a base
Why do primary and secondary amines and amides have higher boiling points than tertiary amines?
Primary and secondary amines and amides have higher boiling points than tertiary amines because they experience hydrogen bonding between molecules
How can we measure the strength of bases?
We can measure the strength of bases by measuring their pH . The higher the pH , the stronger the base.
Which type of amines are the strongest bases, and which are the weakest?
In general the strongest bases are Aliphatic amines
The weakest bases are Aromatic amine
Arrange the following from strongest to weakest base: aliphatic amines, ammonia, aromatic amines.
Strongest to weakest: alphatic amines, ammonia, aromatic amines
How is the strength of a base determined in relation to the nitrogen atom?
Base strength is determined by how available the lone pair on nitrogen is.
What makes a nitrogen lone pair more available for proton acceptance?
The better the lone pair is at accepting a proton , the more available it is. And so the stronger the base.
Why are aliphatic amines stronger bases than ammonia?
In aliphatic amines, the alkyl groups donate electron density/electrons to nitrogen.
This means that the lone pair is better at accepting a proton . And so, we say that the lone pair is more available .
This also means that aliphatic amines are stronger bases than ammonia.
"How do we show electron movement in aliphatic amides?"
We can draw the direction the electrons move with an arrow on the carbon-nitrogen (C-N) bond.
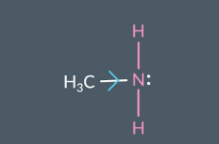
How does delocalisation of the nitrogen lone pair in aromatic compounds affect its availability
Why is phenylamine a weaker base than ammonia?
Phenylamine (aromatic compound) is a weaker base than ammonia because, in phenylamine, nitrogen's lone pair is delocalised (as it participates in the pi system). This means it is less likely to accept a proton. Therefore nitrogens lone pair is less available in aromatic compounds than amonias so it is a weaker base
"How do we show electron movement in aromatic amides?"
We can represent the direction the electron move in aromatic compounds like this. (arrow pointing away form nitrogen)
How does the number of alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen affect the strength of a base?
As the number of alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen increases, the strength of the base increases
Why do more alkyl groups increase base strength?
This is because more alkyl groups increase the amount of electron density donated to nitrogen. This makes the lone pair more available
How does the number of benzene rings directly bonded to nitrogen affect the strength of a base?
A
s the number of benzene rings directly bonded to nitrogen increases, the strength of the base decreases.
Why does an increase in benzene rings decrease base strength?
This is because nitrogens amine is delocalized across more pi systems (depending on number of rings). This makes the lone pair less available.
Exam How To: Strength of Amines
To answer these questions you get 5 marks for stating and explaining the effects of alkyl groups and benzene rings on amines base strength. To do this remember these five points
Finally you get 1 mark for writing a short sentence identifying the strongest and weakest base.
To answer these questions you get 5 marks for stating and explaining the effects of alkyl groups and benzene rings on amines base strength. To do this remember these five points
Acyl chloride + amonia = primary amide
Amonia acts as a nucelphile
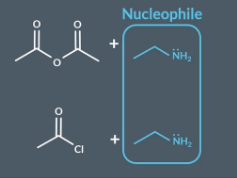
"What happens when primary amines react with acid anhydrides/acyl chlorides (recap) ?"
Primary amines react with acid anhydrides/ acyl chlorides they acts a nucleophile. This is an addition elimination reaction
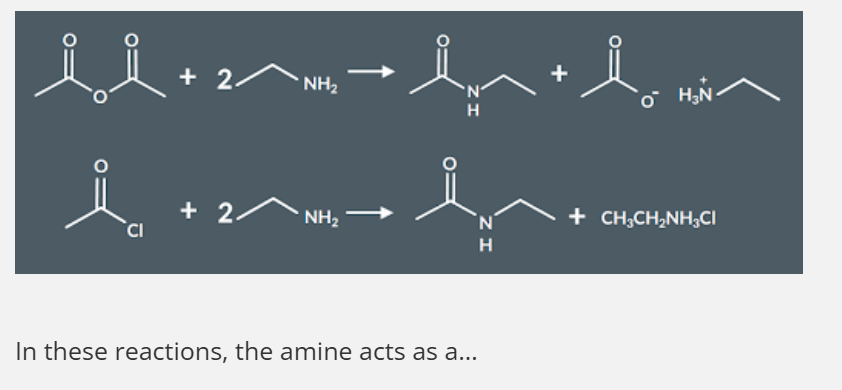
nucleophile
When we produce amines from halogenoalkanes, we use excess ammonia to…
decrease the chances of the amine reacting with the halogenoalkane.
What happens when we react amonia with eccess halogenoalkane
Amine instead of amonia reacts
Mechanism for nucleophilic substitutions for primary amine with halogenoalkane (in order for this reaction to happen halognealkane must be in excess) so technincally amonia wiht excess halogneoalkane
Mechanism for nucleophilic substitutions for secondary amine with halogenoalkane (in order for this reaction to happen halognealkane must be in excess)
Mechanism for nucleophilic substitutions for tertiary amine with halogenoalkane (in order for this reaction to happen halognealkane must be in excess)
what substances can undergo nucleophilic subsititions with halogenoalkanes
Why can ammonia, amines, and tertiary amines undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with halogenoalkanes?
Ammonia, primary amines, secondary amines and eritary amines all have lone pairs of electrons which means they can undergo nuclepphilic substitution reaction with halogenoalkanes. The chance of these reactions occurring increase when we use excess halogenoakane.
"Quaternary Ammonium Ion Structure and Properties"
This is a quaternary ammonium ion. 4 carbon directly bonded to a N with a positive charge
"Quaternary Ammonium Salt Formation"
When quaternary ammonium ions form a complex with anions, we call the compound a quaternary ammonium salt
What are quaternary ammonium salts, and how are they used in everyday items?
In A level you need to know that Quaternary ammonium salts can be used as cationic surfactant. Surfactants are found in many everyday items like soap and shampoo. The above shows a structure of a cationic surfactant
Cationic Surfactants: Cationic Surfactants:
These have a positively charged hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and a hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail. The positive charge comes from a quaternary ammonium group
How do surfactant clean
Step 1: The hydrophobic tail dissolves in the oil or grease, while the hydrophilic head remains in the water.
Step 2: The surfactant molecules arrange into micelles with the hydrophobic tails inward, trapping oil or grease inside.
Step 3: The hydrophilic heads face outward, allowing the micelles to be washed away with water, carrying the dirt or grease with them.
To prepare a primary amine from a halogenic alkane: (RECAP)
We react the halogenoalkane with
High pressure
Heat
Ecesss ammonia dissolved in ethanol
HOw can we prepare primary (aliphatic) amines from nitriles
Nitrile (CN) + H2 gas and caltalyst = amine
Nitrile in solution and add a metal catalyst (typically nickel) and bubble in hydrogen gas
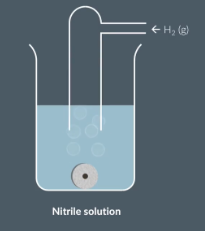
what type of reaction is it when we react nitirles withs H2 and Metal catalyst to form Primary amines
Reduciton

preparing alihpatic amines form nitiriles . You dont need to know the mechanism but you do need to know
products
Equation
Reageant
If you are asked to list the reagents you must say hydrogen and a names metal catalyst (nickel )
2 methods for preparing primary amines
It’s more efficient to prepare primary amines from nitriles than halogenoalkanes because…
.With nitriles the atom economy is 100% and there is no further reaction
With halogenoalkanes the atom economy is less than 100% and further reaction are possible (even if we do use excess ammonia)
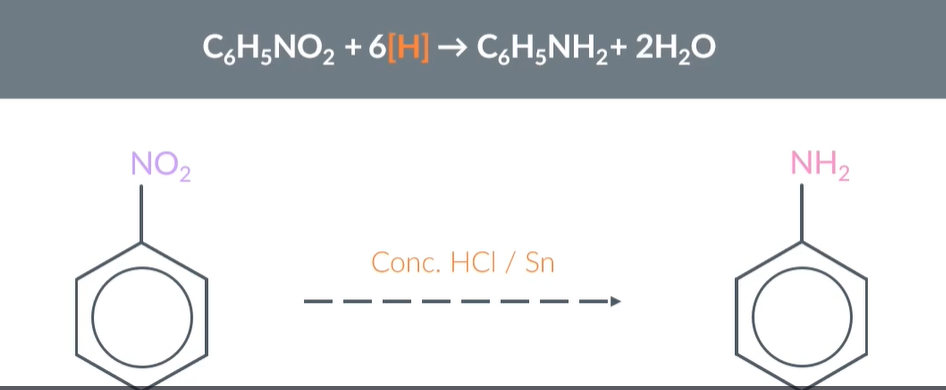
How to prepare aromatic amines
reduce aromatic nitro compounds using CONCENTRATED Hydrochloric acid and tin
"Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds to Aromatic Amines"
When we reduce aromatic nitro compounds with CONC HCl and tin, we produce an aromatic amine and H2O/water
"Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds to Aromatic Amines"
When we write equations for the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds, we represent the reducing agent with H (in square brackets)
So aromatic nitro compound + nH (sqaure brackets) -------------- aromatic amine + water
Balance the water and H out
What can aromatic amines be used for?
Aromatic amines can be used to manufacture dyes.