Session 1: Introduction to the Musculoskeletal System
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
What is the function of bursa?
Reduce friction
What is an example of an irregular bone?
Vertebrae
Muscles which assist with the prime movers are known as...
Synergists
The muscle compartments are separated by...
Deep fascia
Flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint (bending)
Extension
Increases the angle of a joint (straightening)
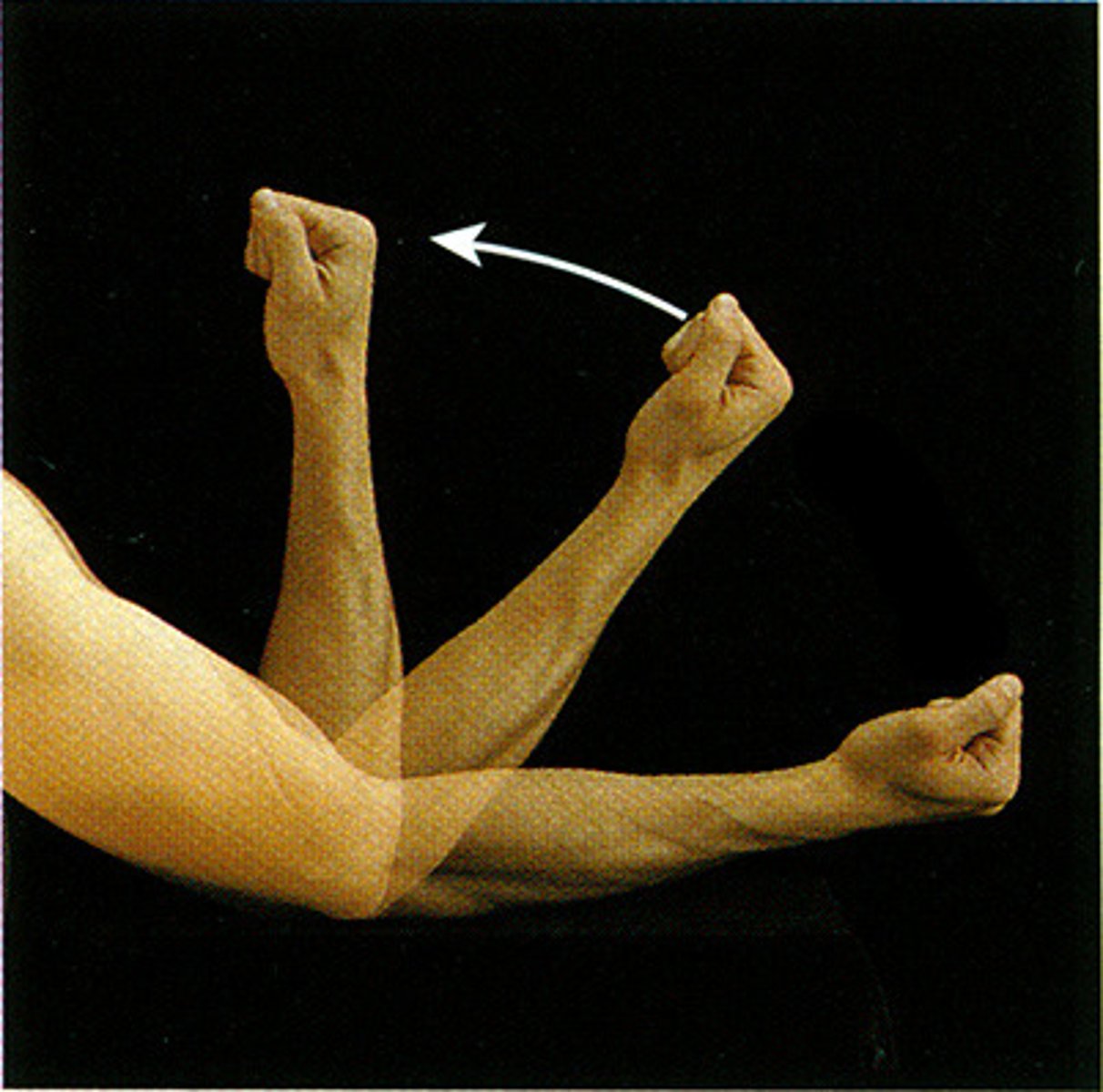
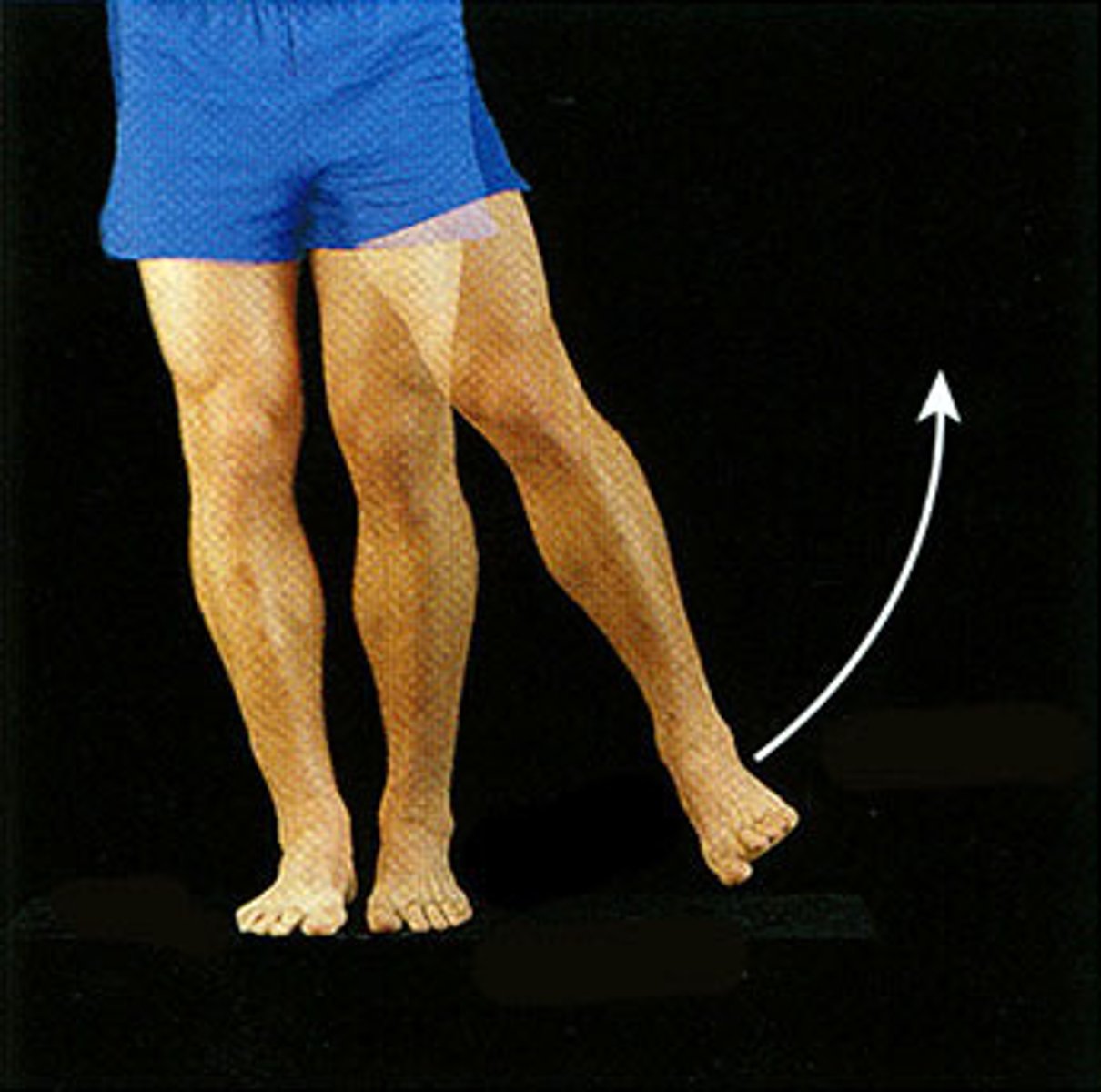
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
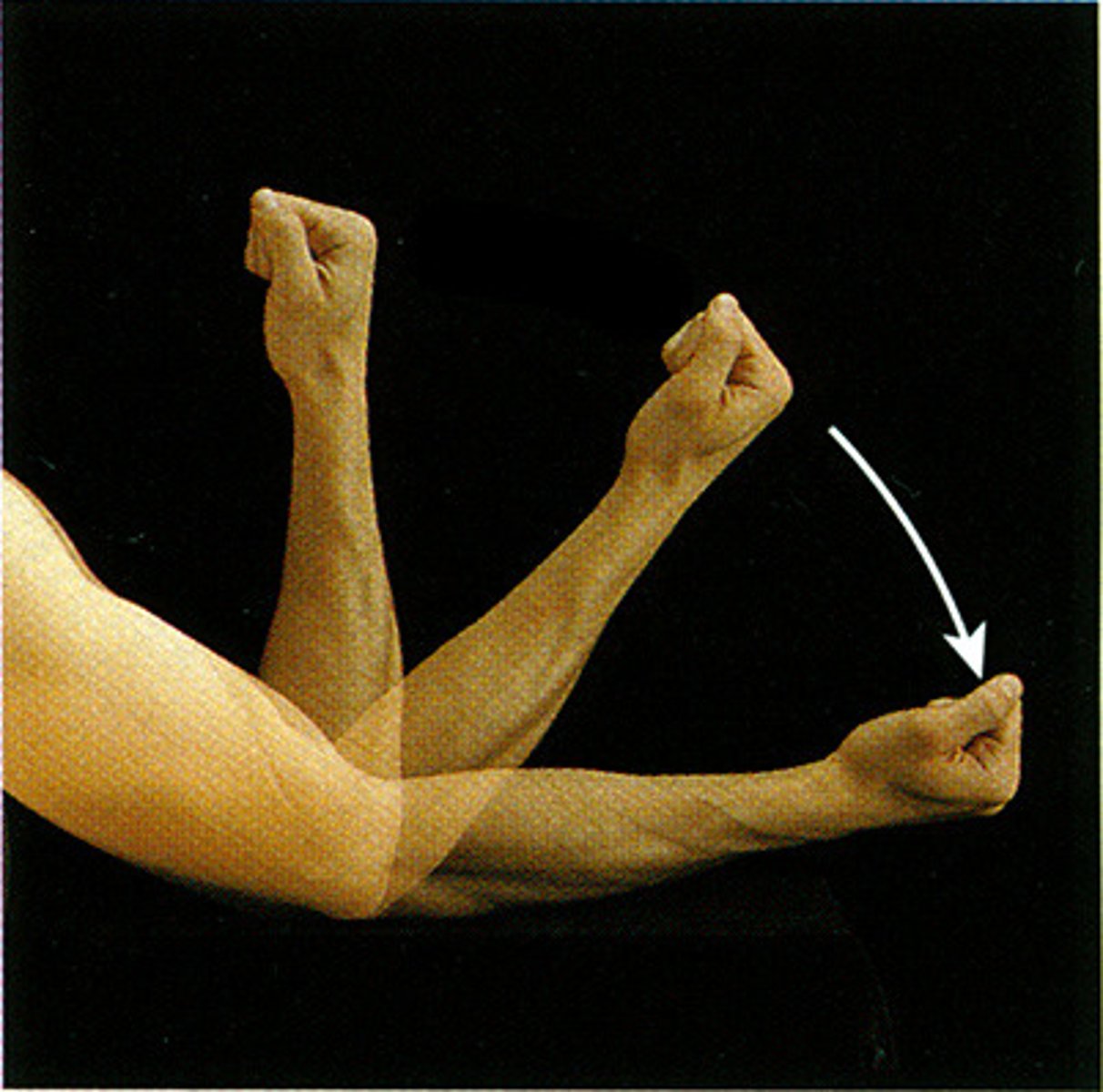
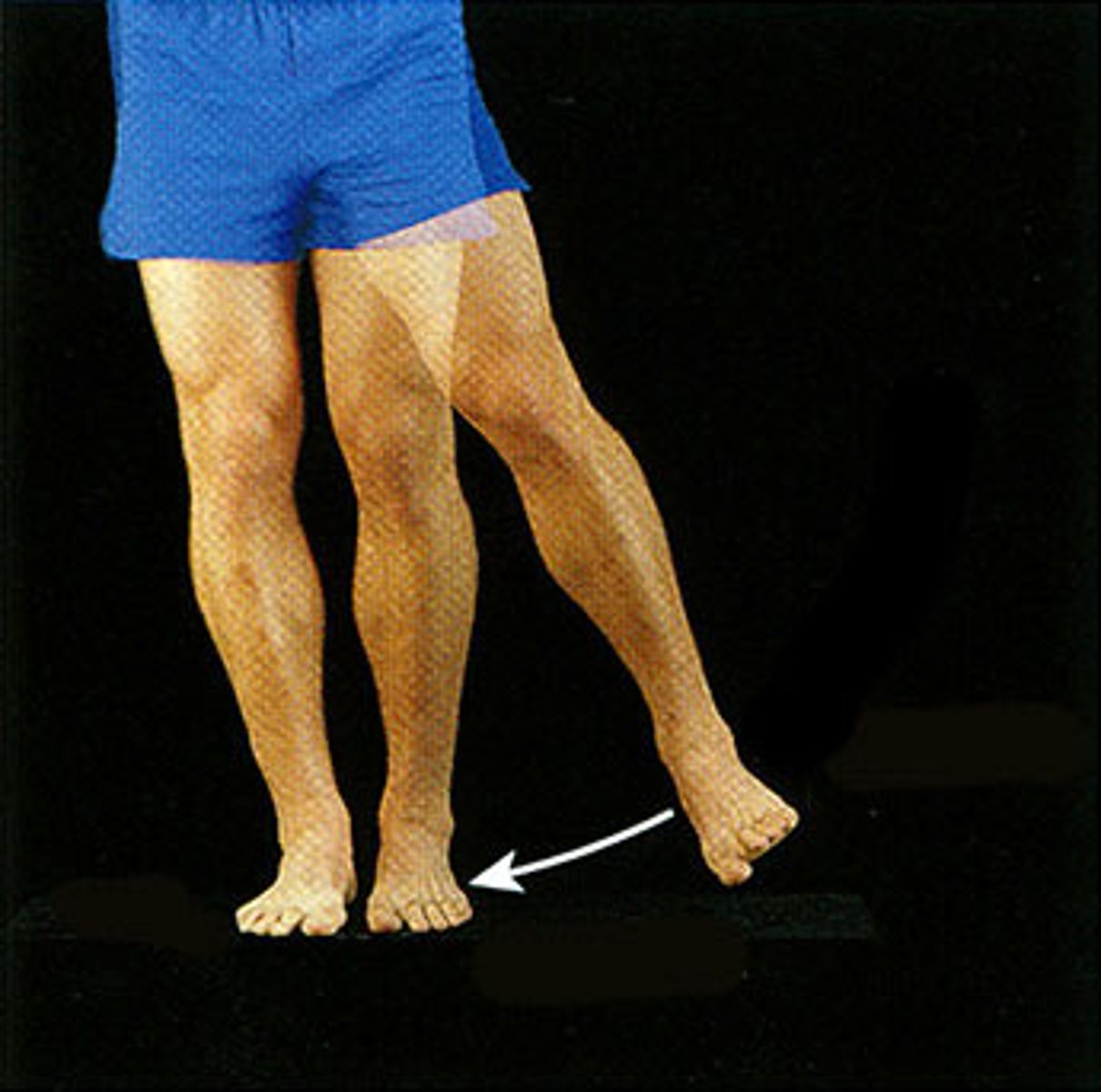
Adduction
Movement toward (add) the midline of the body
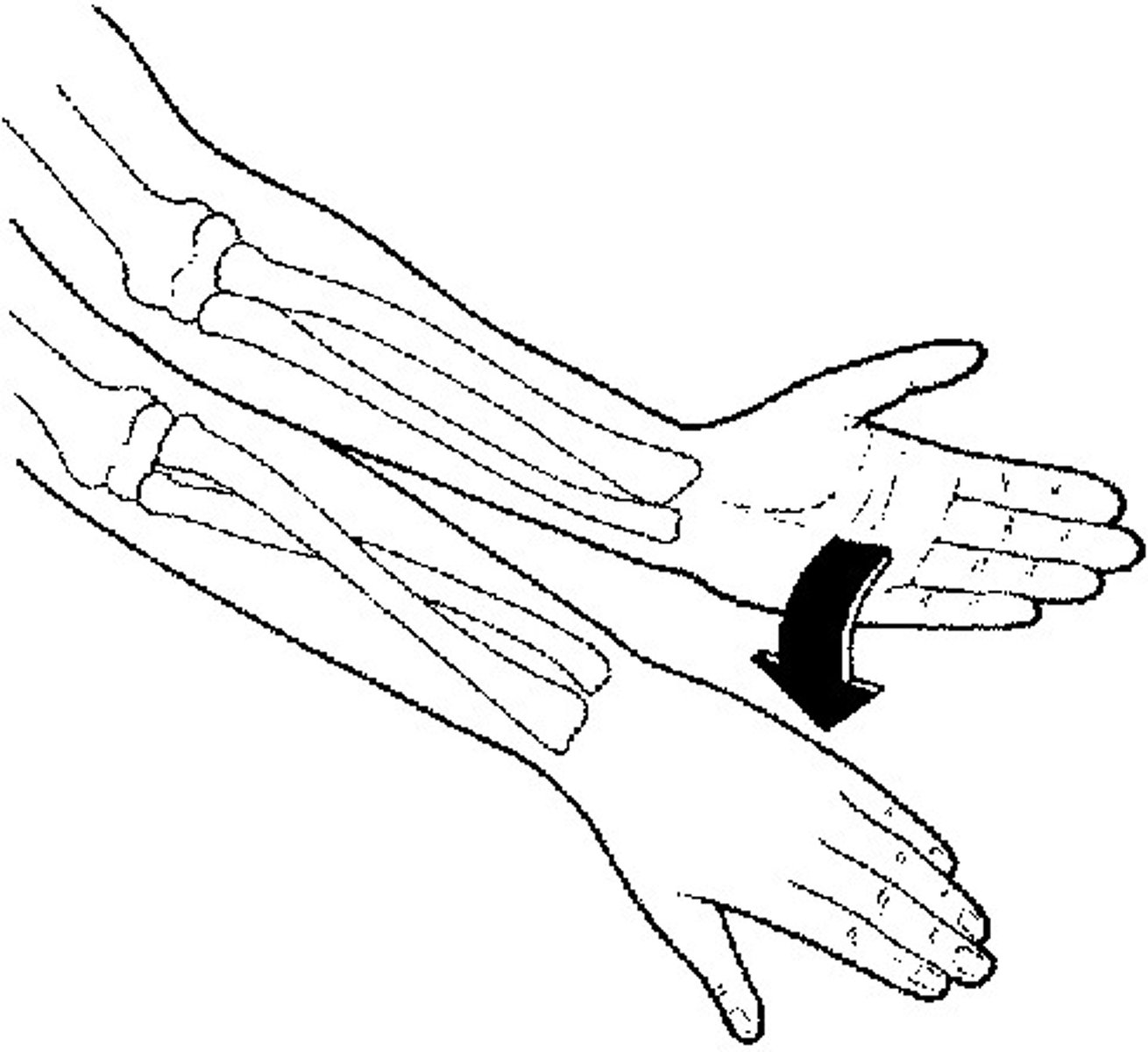
Pronation of forearm
Movement that turns the palm down (towards posterior)
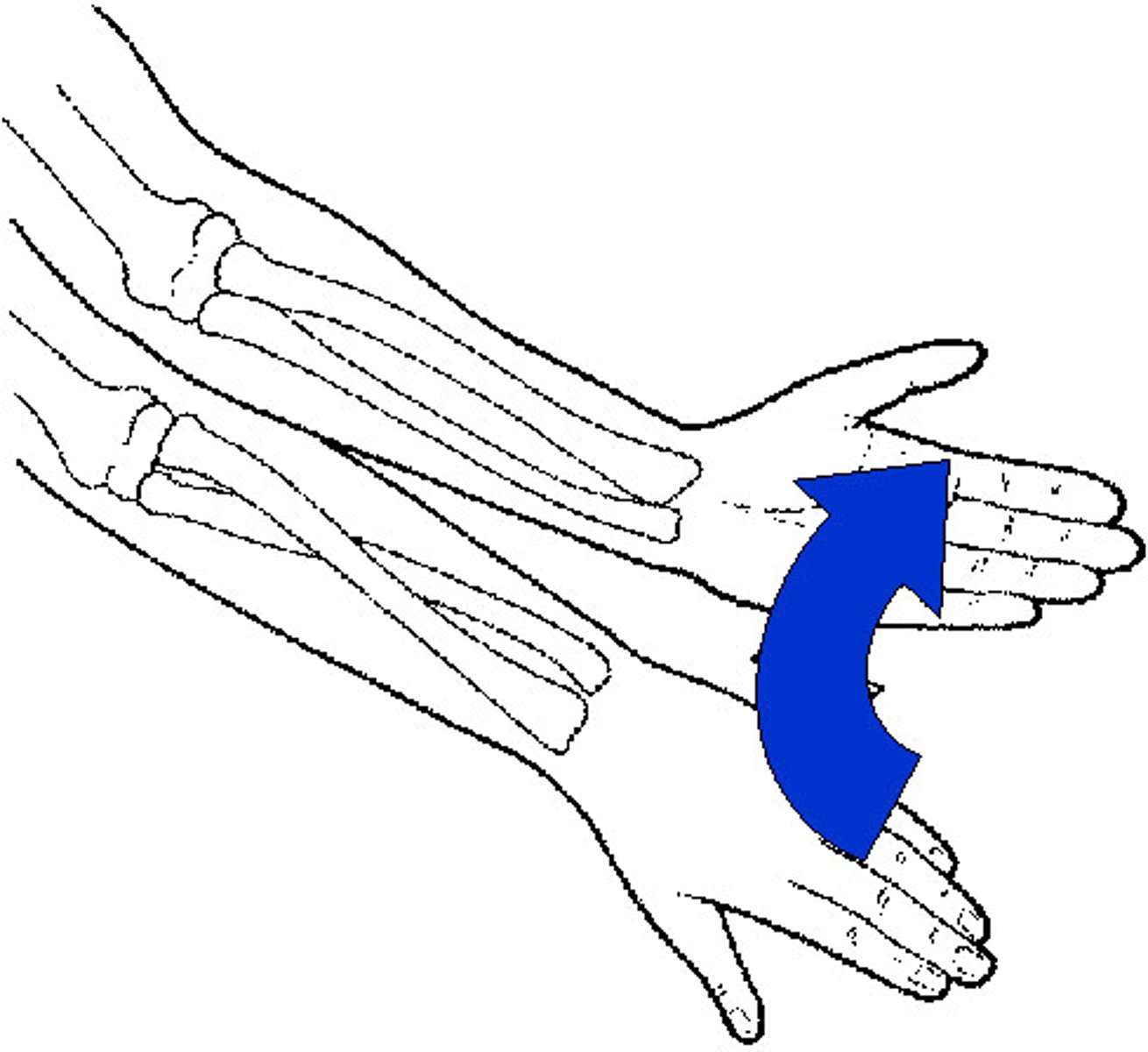
Supination of forearm
Movement that turns the palm up (towards superior)
Inversion of foot
Turning the sole of the foot inward (interior)
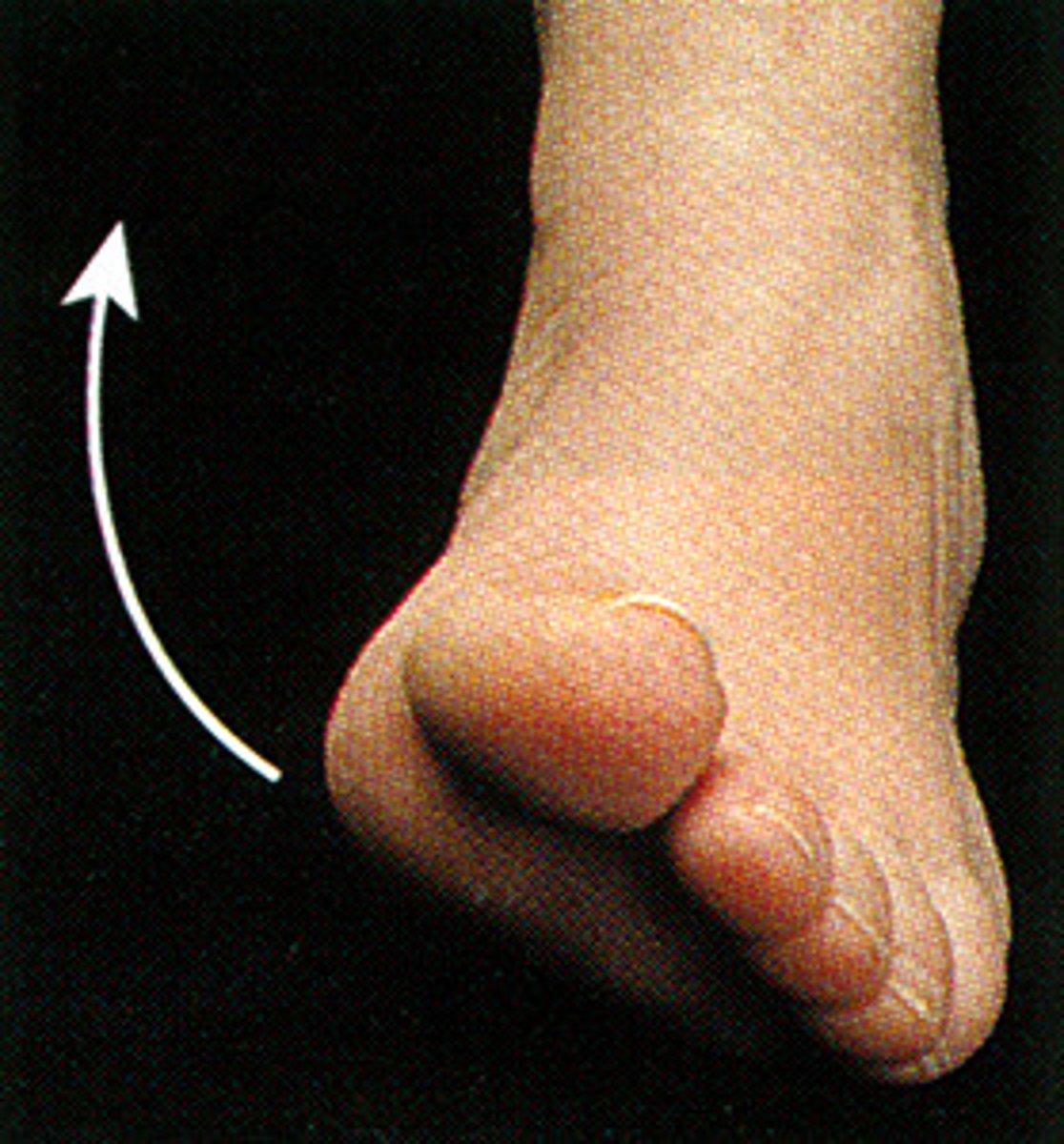
Eversion of foot
Turning the sole of the foot outward (exterior)
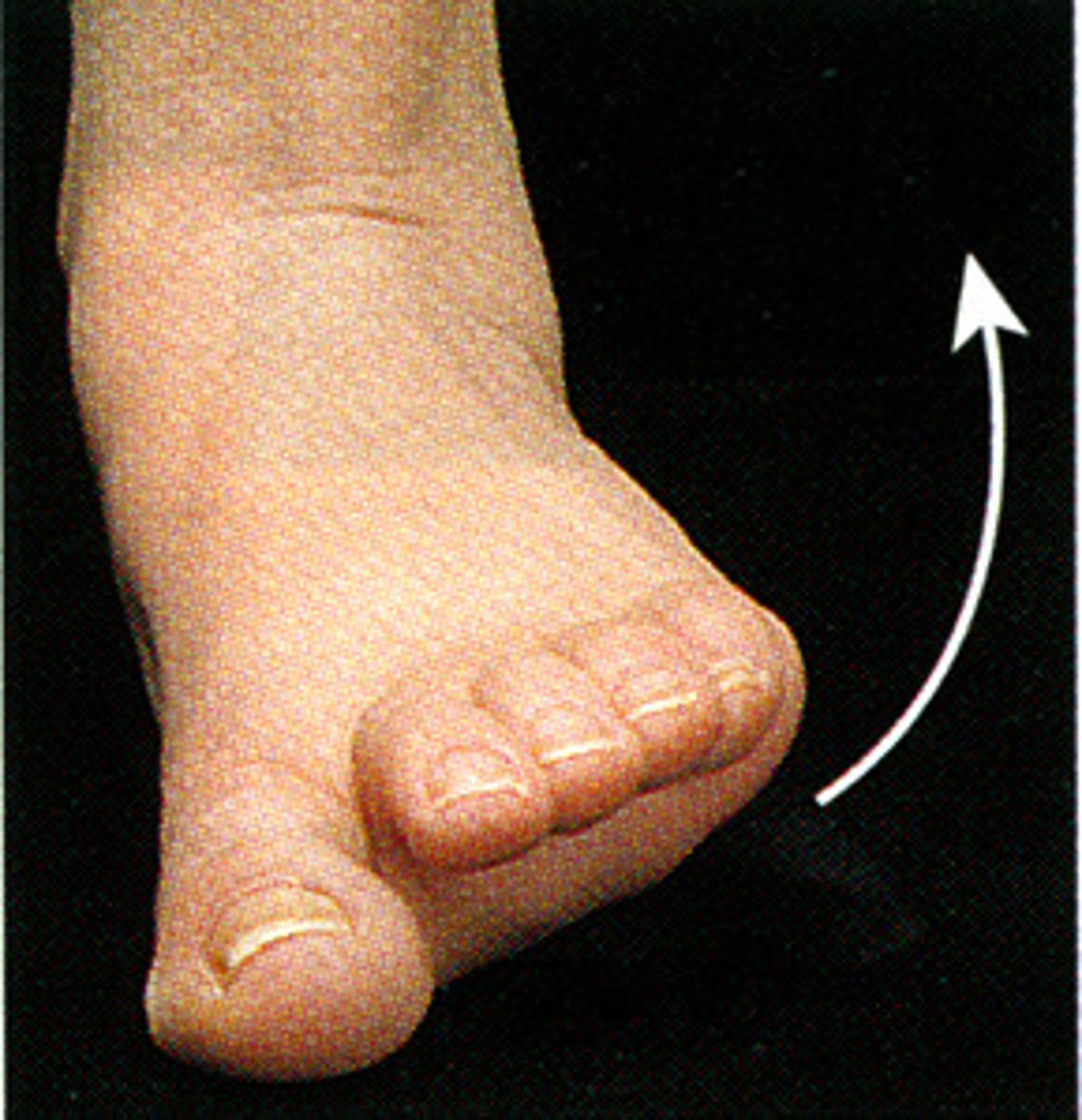
Protraction of scapula
Moving a part forward
Retraction of scapula
Moving a part backward
Adult skeleton is made up of ___ bones
206
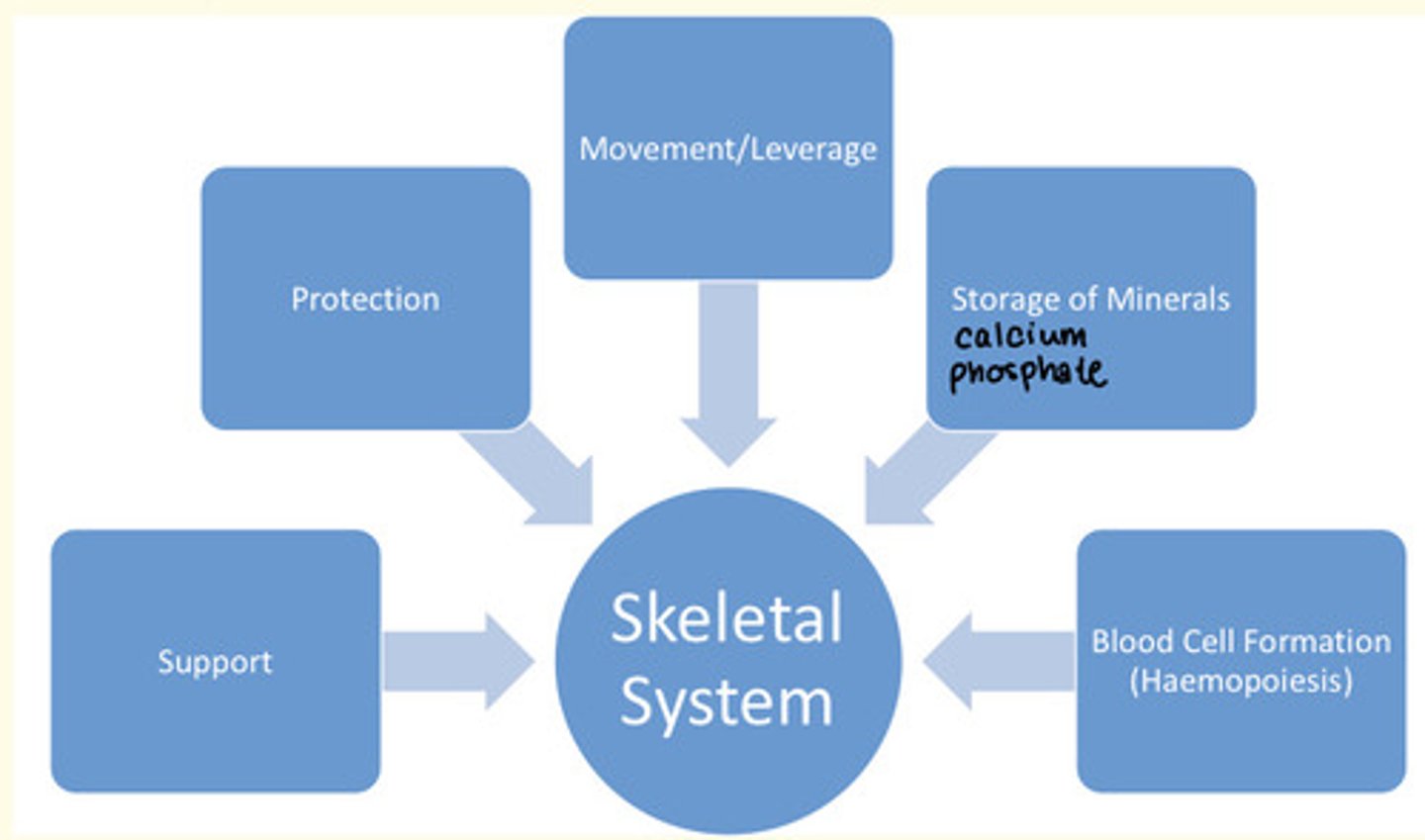
Functions of the skeletal system
1) Protection
2) Support
3) Movement/leverage
4) Storing minerals
5) Haemopoiesis
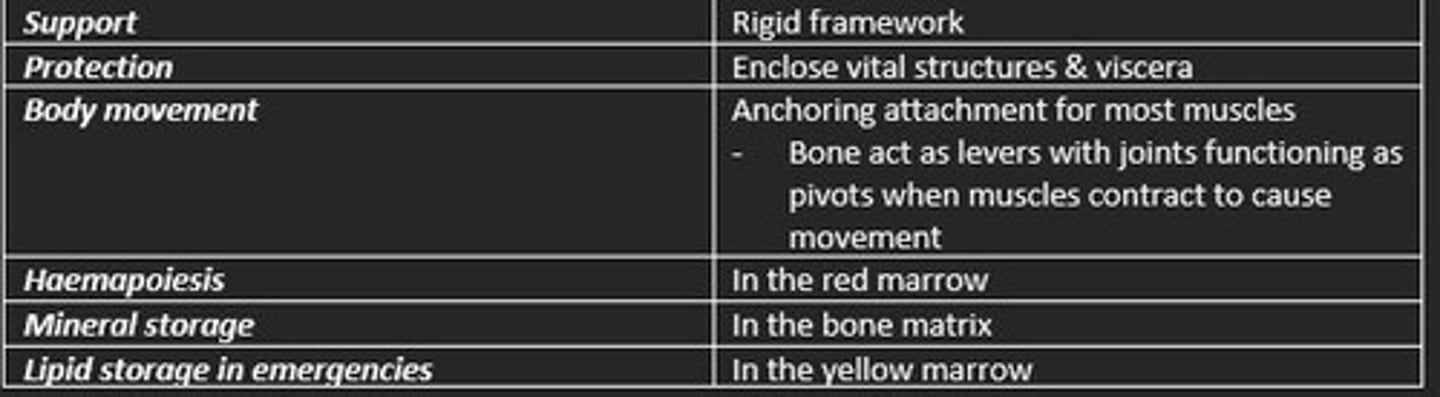
Function of bone
1) Support = rigid framework
2) Protection = encloses vital structures (viscera)
3) Body movement = anchoring attachment for muscles (levers/pivot)
4) Haemapoiesis = in red marrow
5) Mineral storage = in bone matrix
6) Lipid storage in emergencies = in yellow marrow
Inorganic matter of bone
Hydroxyapatite = calcium, phosphorus
Inorganic minerals give bones their hardness, and resistance to compression
Organic matter of bone
Collagen, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans and glycoprotein
Organic collagens give bones their flexibility, resistance to tension and pulling
Inorganic component of bone (calcium hydroxyapatite crystals) give ___
Strength

Organic component of bone (type I collagen) confers ___ and resistance to ___
Organic component of bone (type I collagen) confers flexibility and resistance to stress

The axial skeleton is mainly for ___
Protection
- Skull protects brain
- Vertebral column protect spinal cord
- Ribs protect heart and lungs

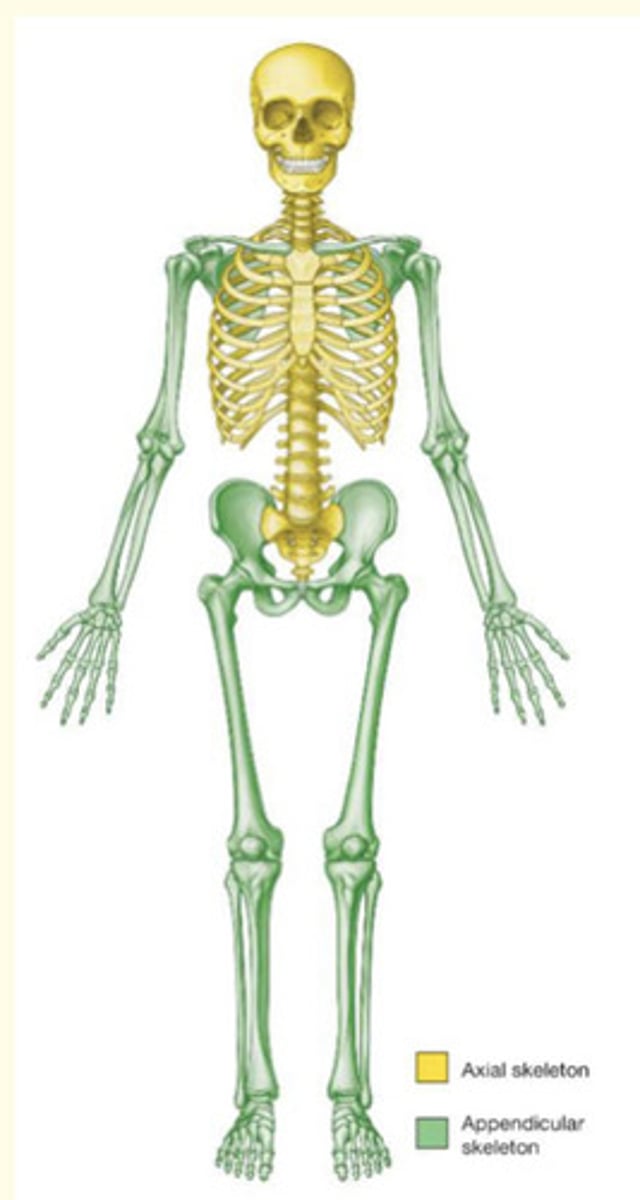
The TWO main divisions of the skeleton
Axial and appendicular skeleton
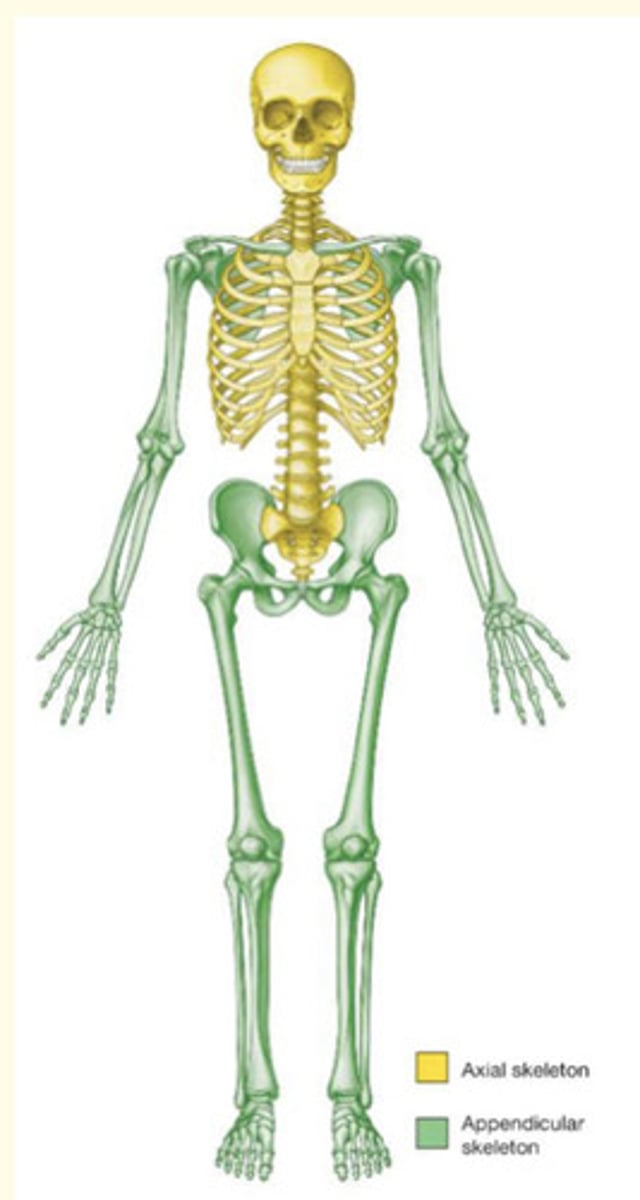
Axial skeleton
The portion of the skeleton that supports and protects the organs of the head, neck, and trunk (central)
- Skull = protects brain
- Vertebral column = protects spinal cord
- Ribs = protects heart/lungs
- Sternum = protects heart/lungs
- Hyoid
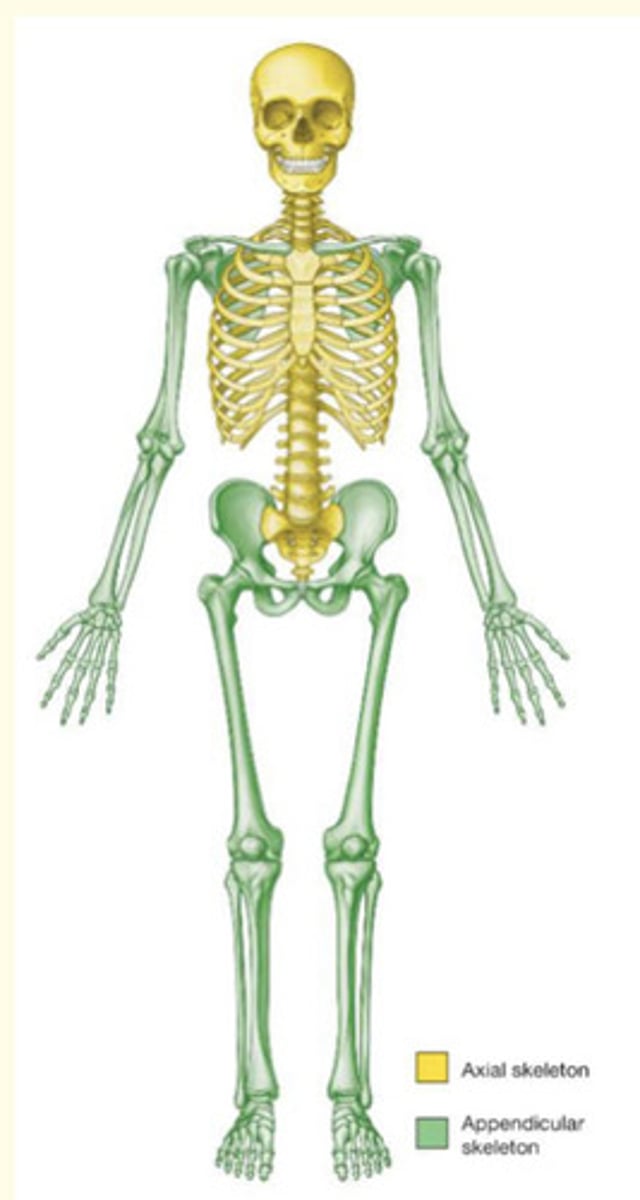
Appendicular skeleton
Everything else - provide motility
- Hip bones
- Shoulder blades
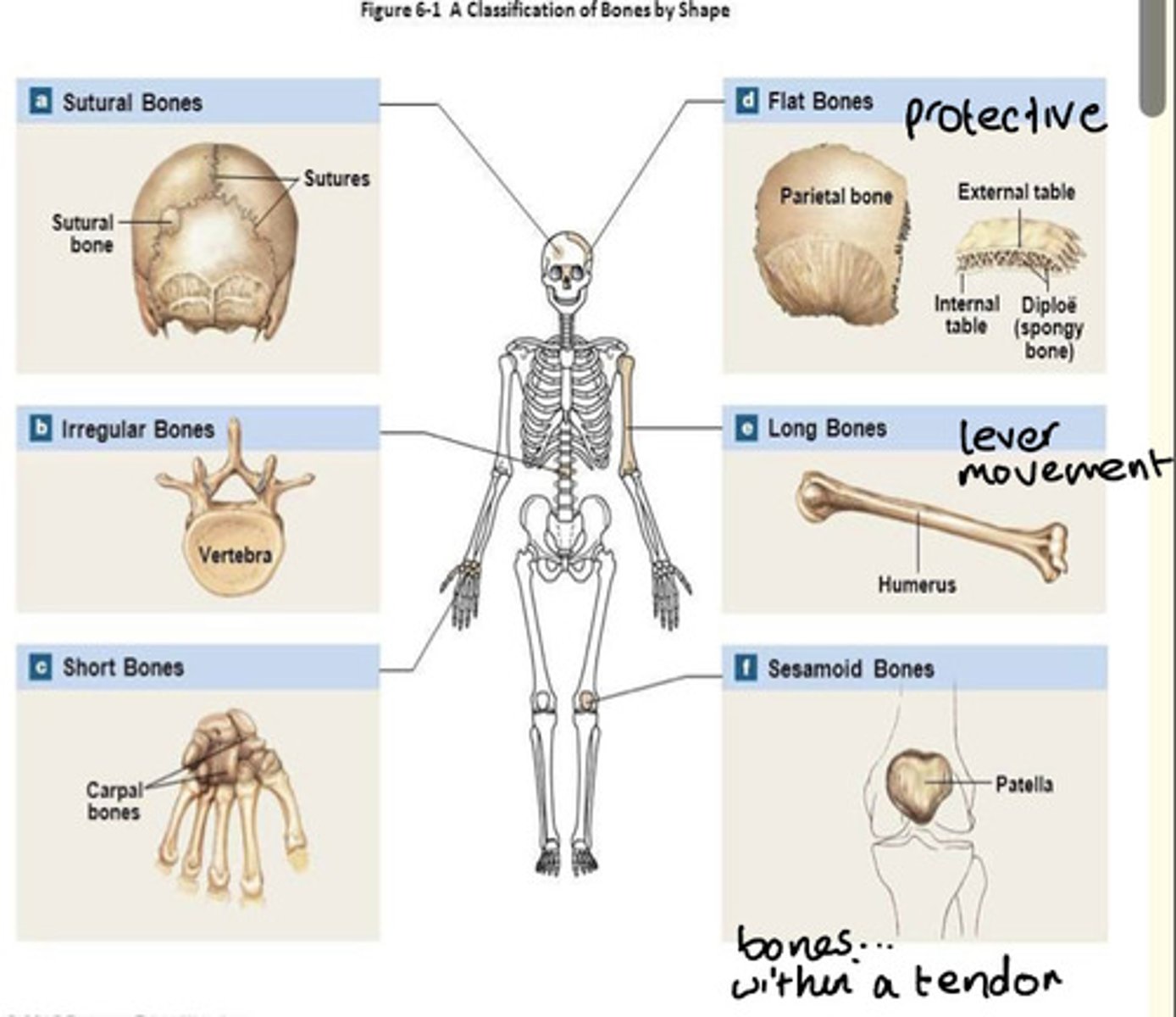
Five major shapes of bones and example of each
1) Long e.g., humerus
2) Short (cuboidal) e.g., carpal
3) Flat e.g., skull parietal
4) Irregular e.g., vertebra
5) Sesamoid e.g., patella
The appendicular skeleton is mainly for ___
Motility
- Includes upper and lower limbs & girdles attaching limbs to axial skeleton
- Includes the scapulae (shoulder blades) and pelvis structures between limbs and axial skeleton

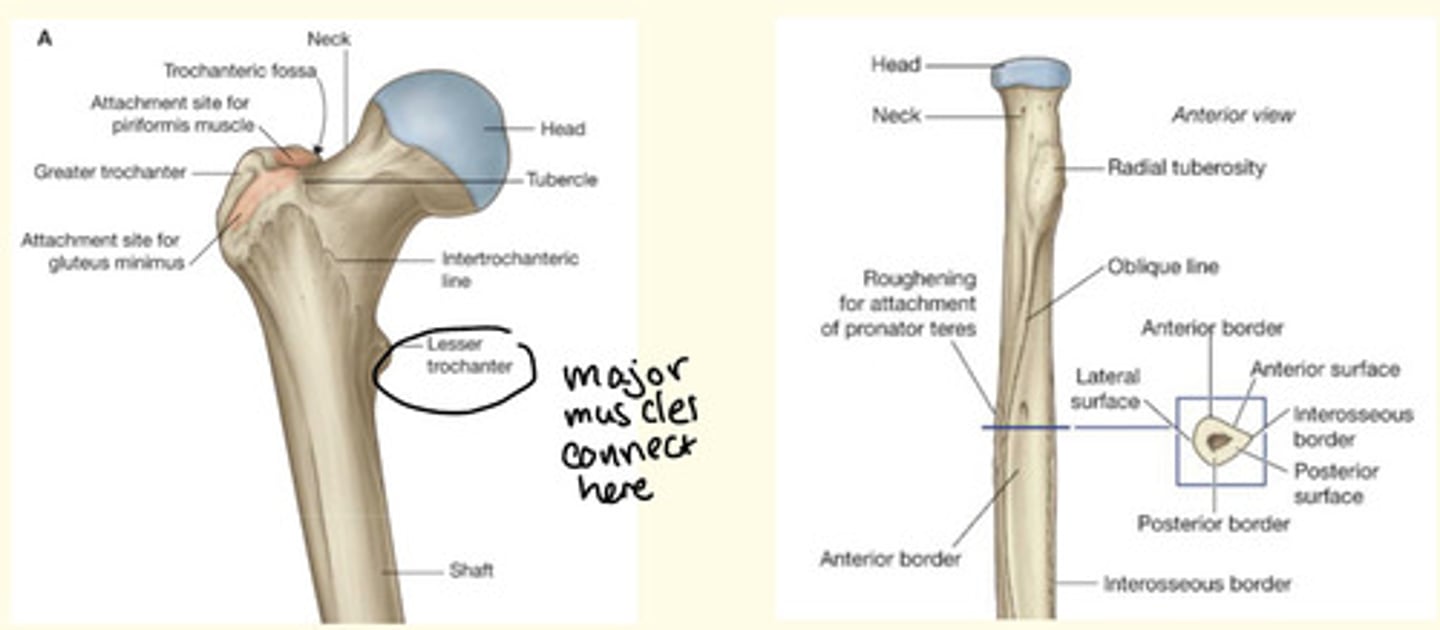
List some examples of surface markings of bones
Tuberosity = roughened, rounded elevation
Tubercle = smaller elevation
Fossa = depression
Foramen = hole/opening
The surface markings of bone are found where ___, ___, ___ or ___ are attached to bone
The surface markings of bone are found where fascia, ligaments, tendons or aponeuroses are attached to bone
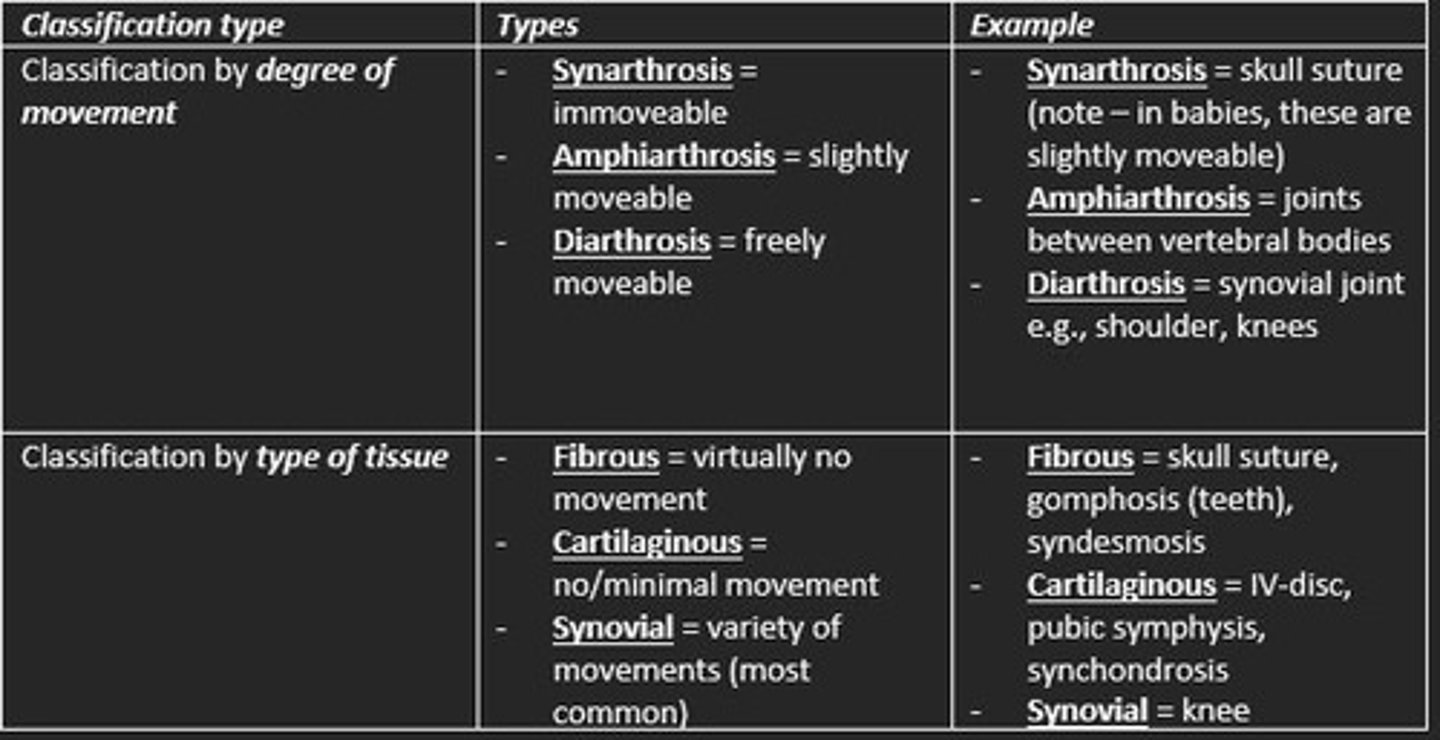
Joints classification is via two measures...
1) Classification by degree of movement
2) Classification by type of tissue
What is a joint?
Place where two bones meet
Classification of joint by degree of movement
Synarthrosis = meaning and example
Synarthrosis = immovable e.g., skull suture (in a baby, skull sutures are slightly moveable)

Classification of joint by degree of movement
Amphiarthrosis = meaning and example
Amphiarthrosis = slightly moveable e.g., joints between vertebral bodies (spine)

Classification of joint by degree of movement
Diarthrosis = meaning and example
Diarthrosis = freely moveable e.g., synovial joint (shoulders, knees)

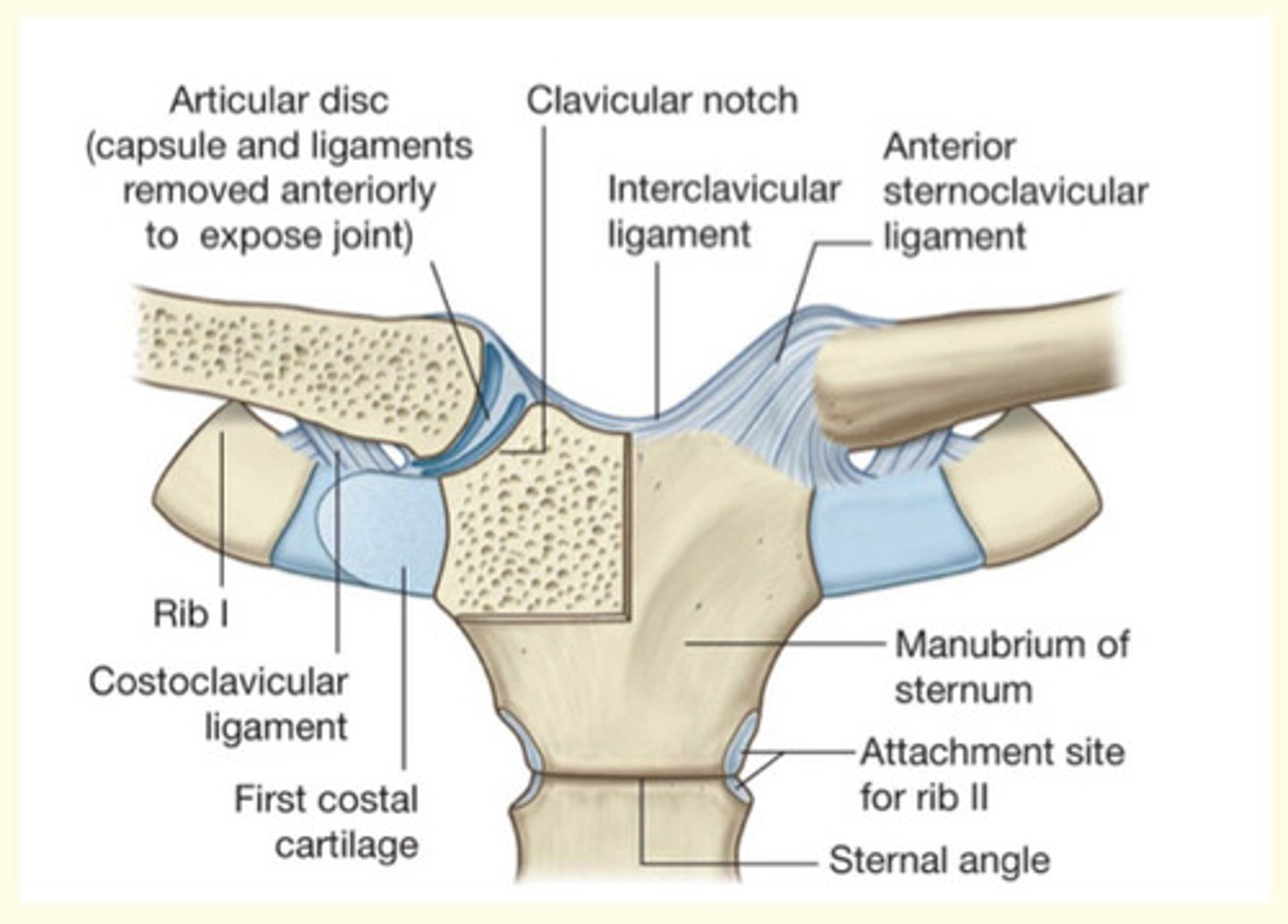
Classification of joint by type of tissue
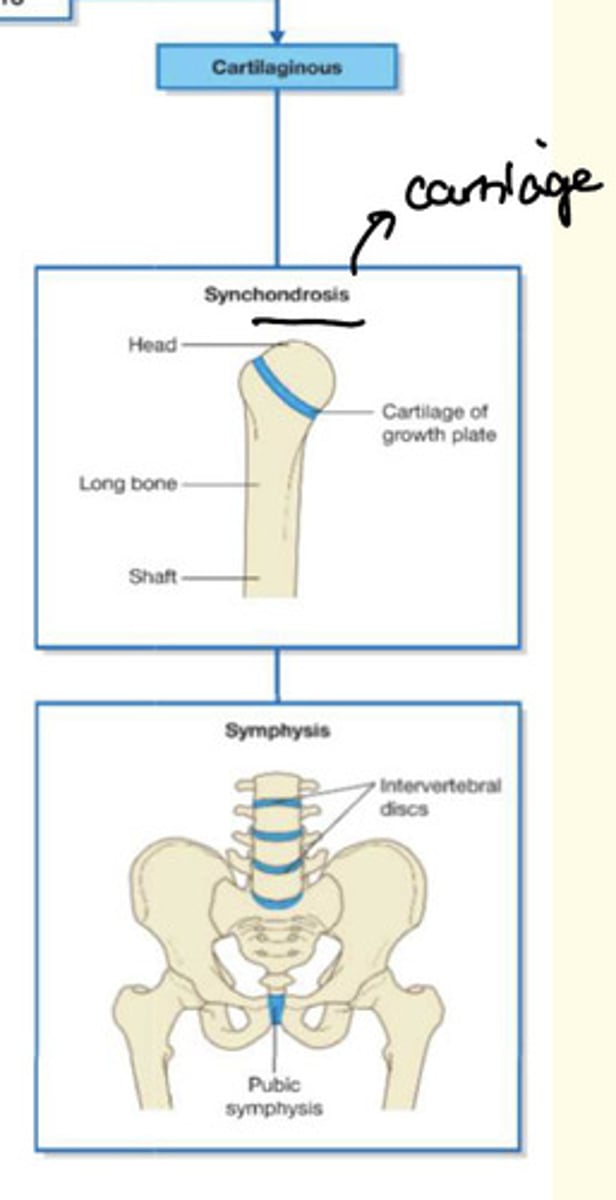
Cartilaginous = meaning and example
Cartilaginous = e.g., IV disc, pubic symphysis (no/minimal movement)
Classification of joint by type of tissue
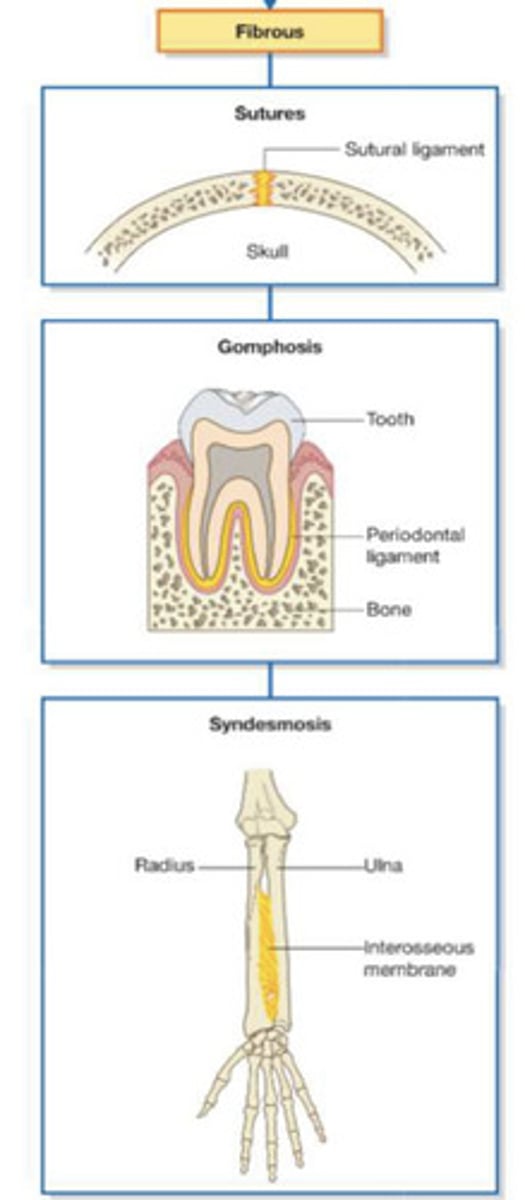
Fibrous = meaning and example
Fibrous = e.g., skull (virtually no movement)
Classification of joint by type of tissue
Synovial = meaning and example
Synovial = e.g., knee (variety of movements)
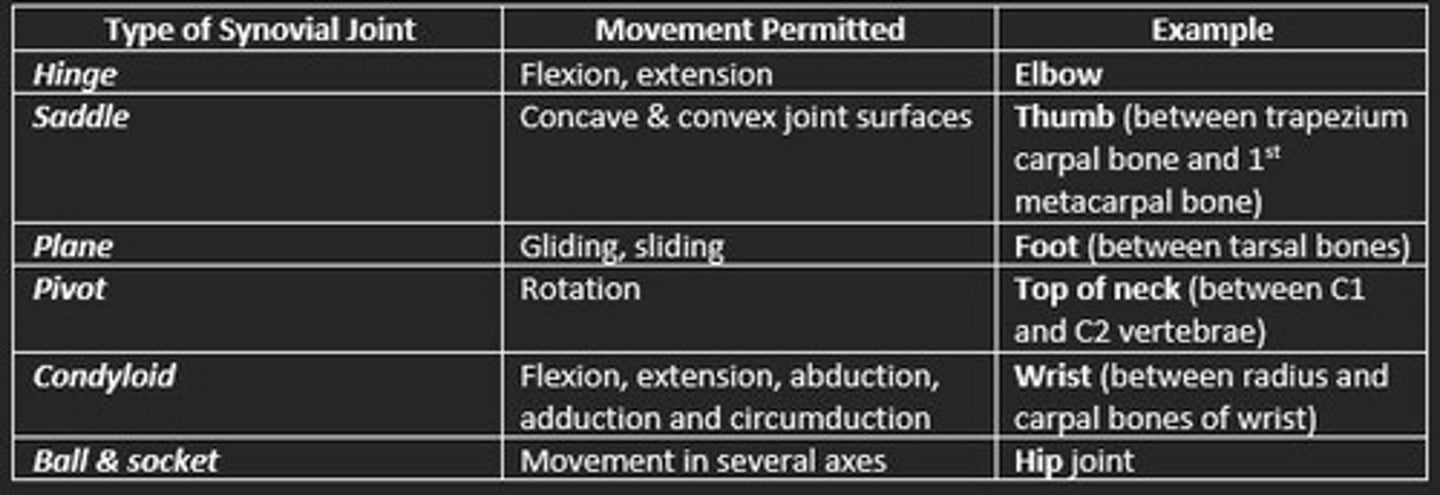
Hinge synovial joint example
Elbow and knee
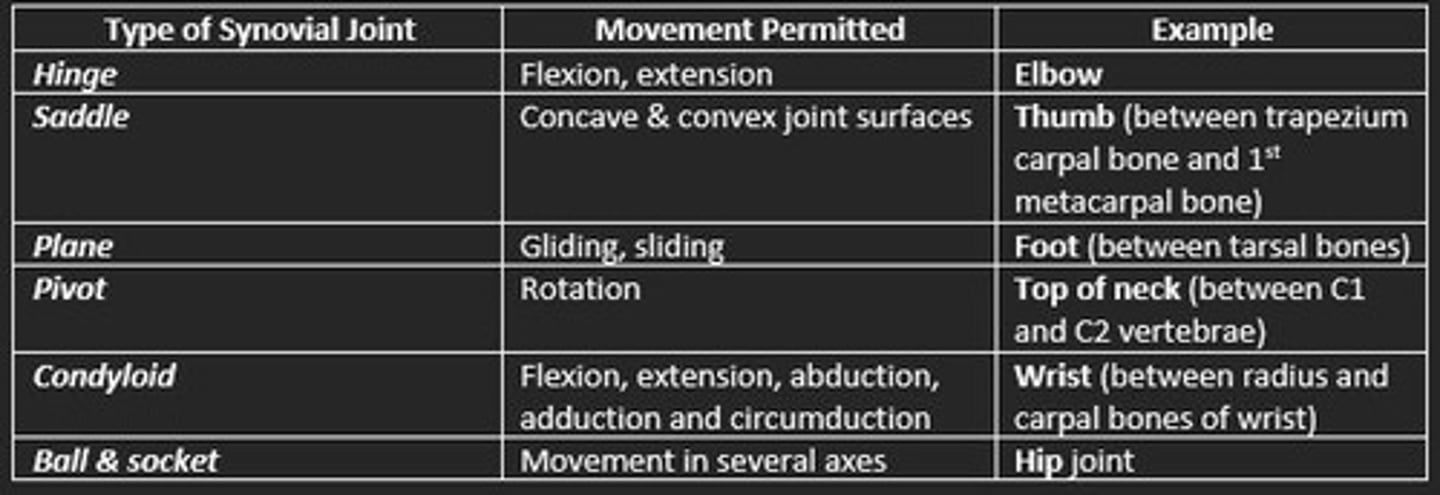
Saddle synovial joint example
Thumb
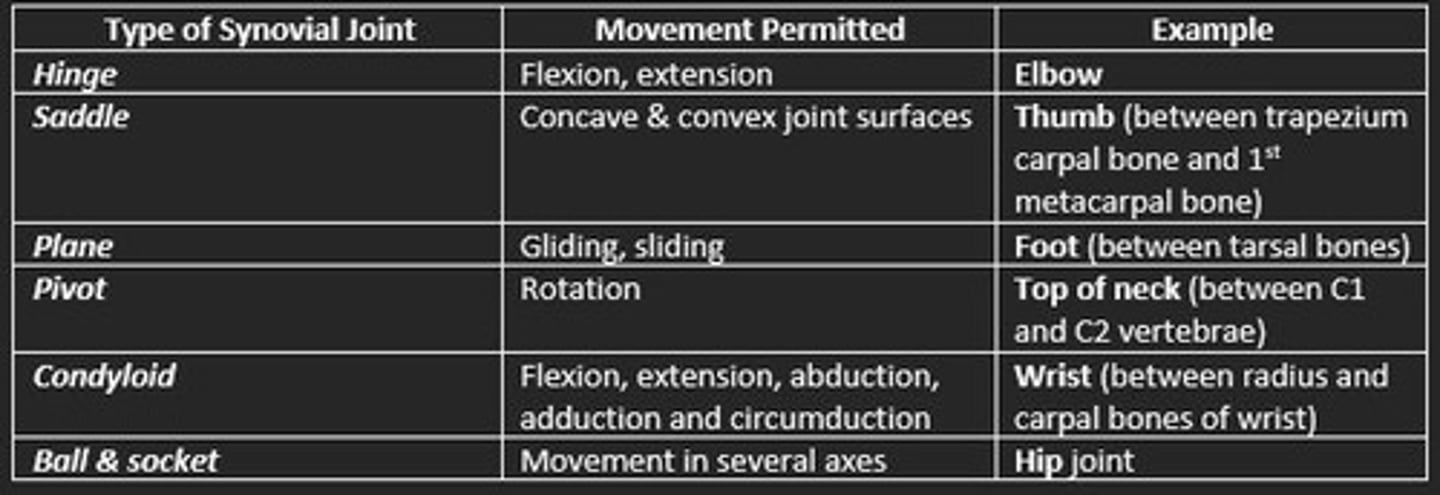
Condyloid synovial joint example
Jaw and finger joints
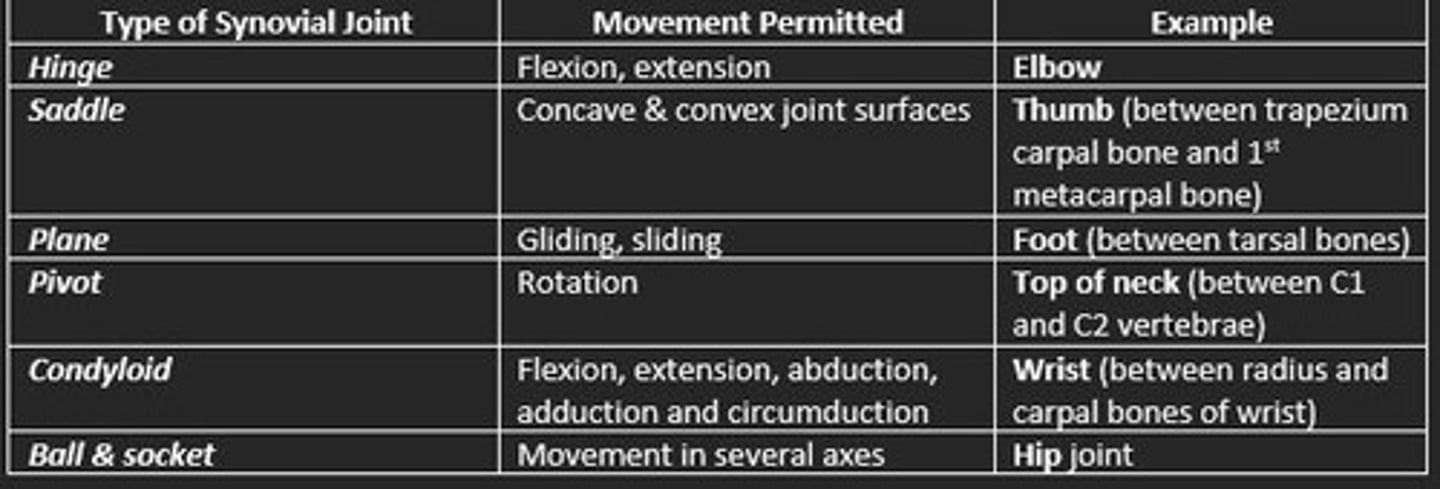
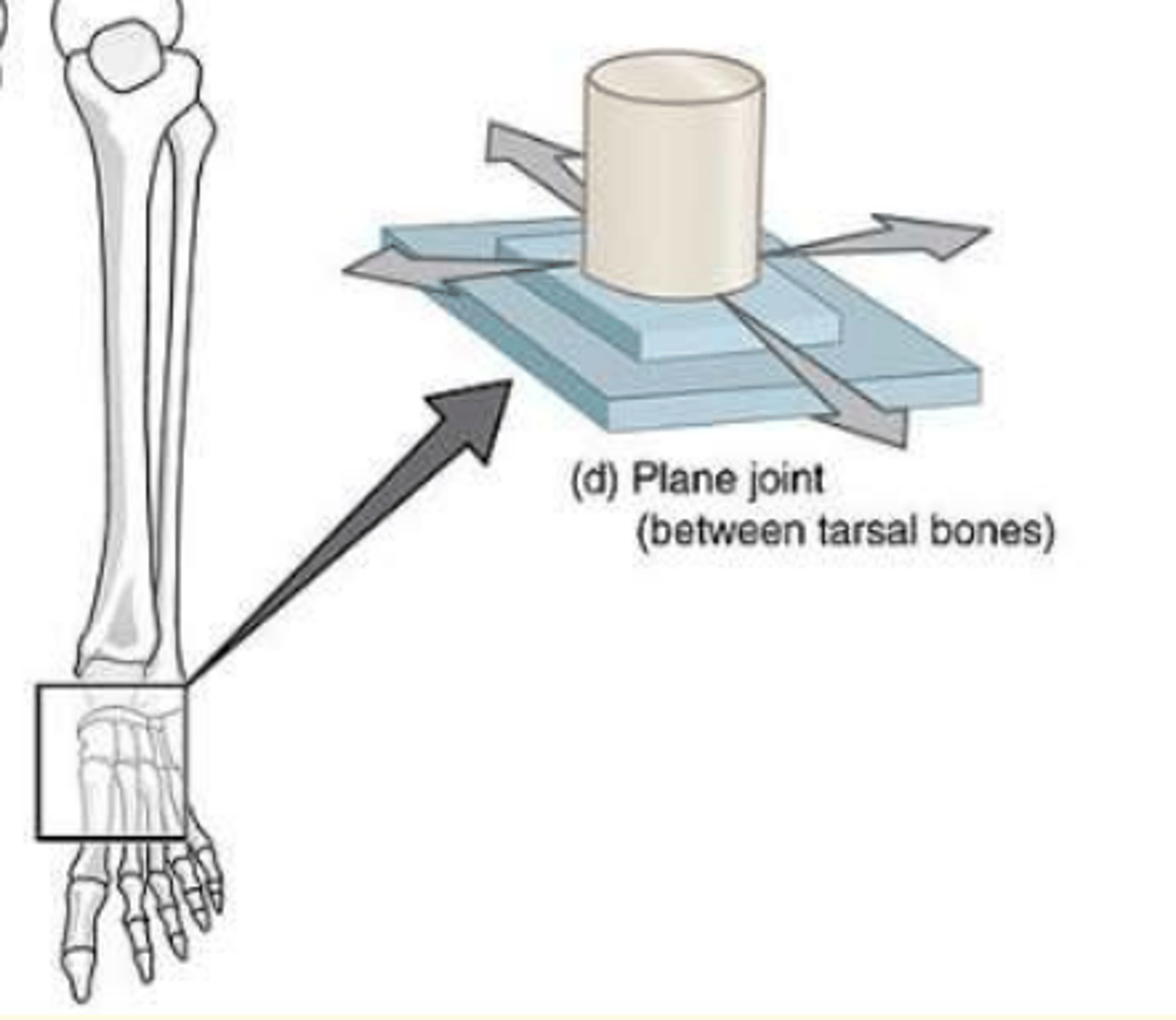
Plane synovial joint example
Bones of foot
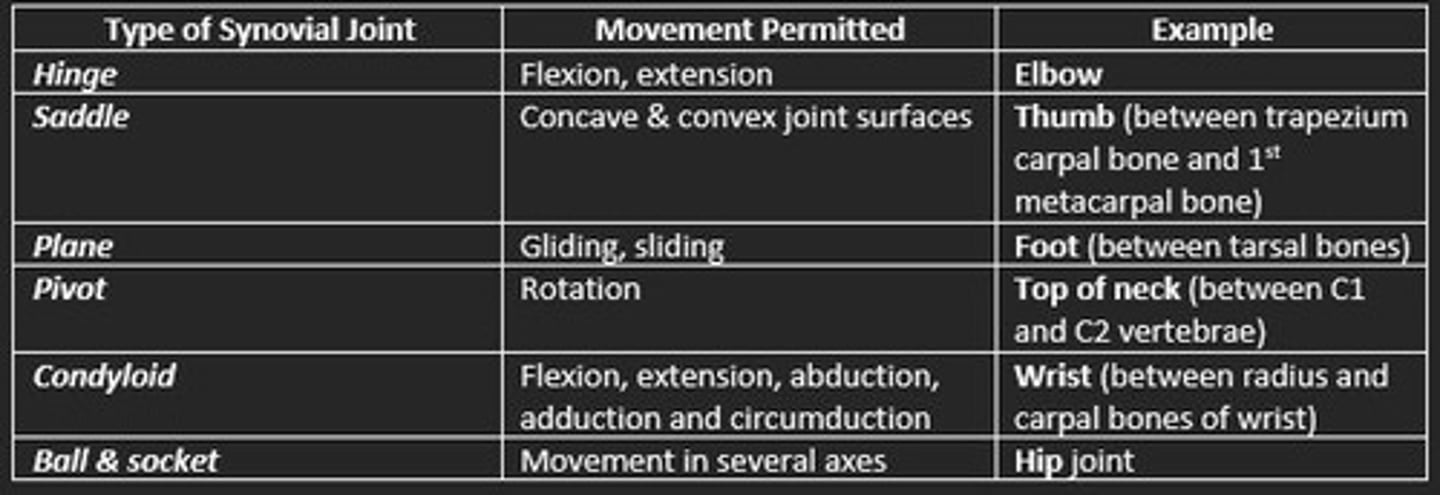
Ball & socket synovial joint example
Hip and shoulder
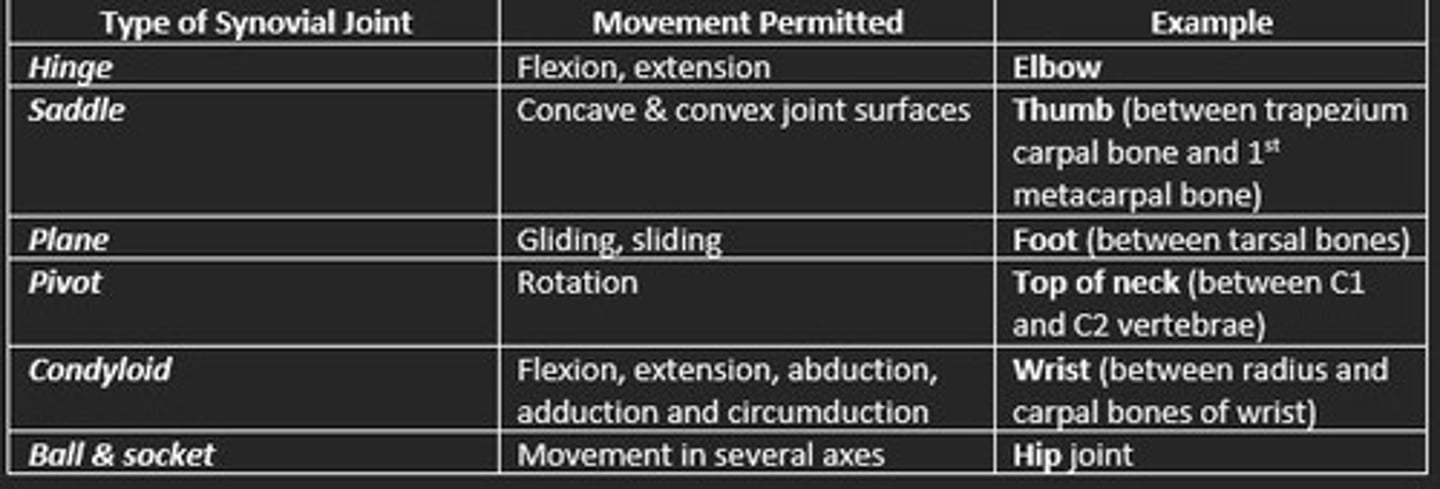
Pivot synovial joint example
Base of skull, atlas and axis
Example of fibrous joint
Skull sutures
Gomphosis
Syndesmosis
Example of cartilaginous joint
Synchondrosis
Symphysis
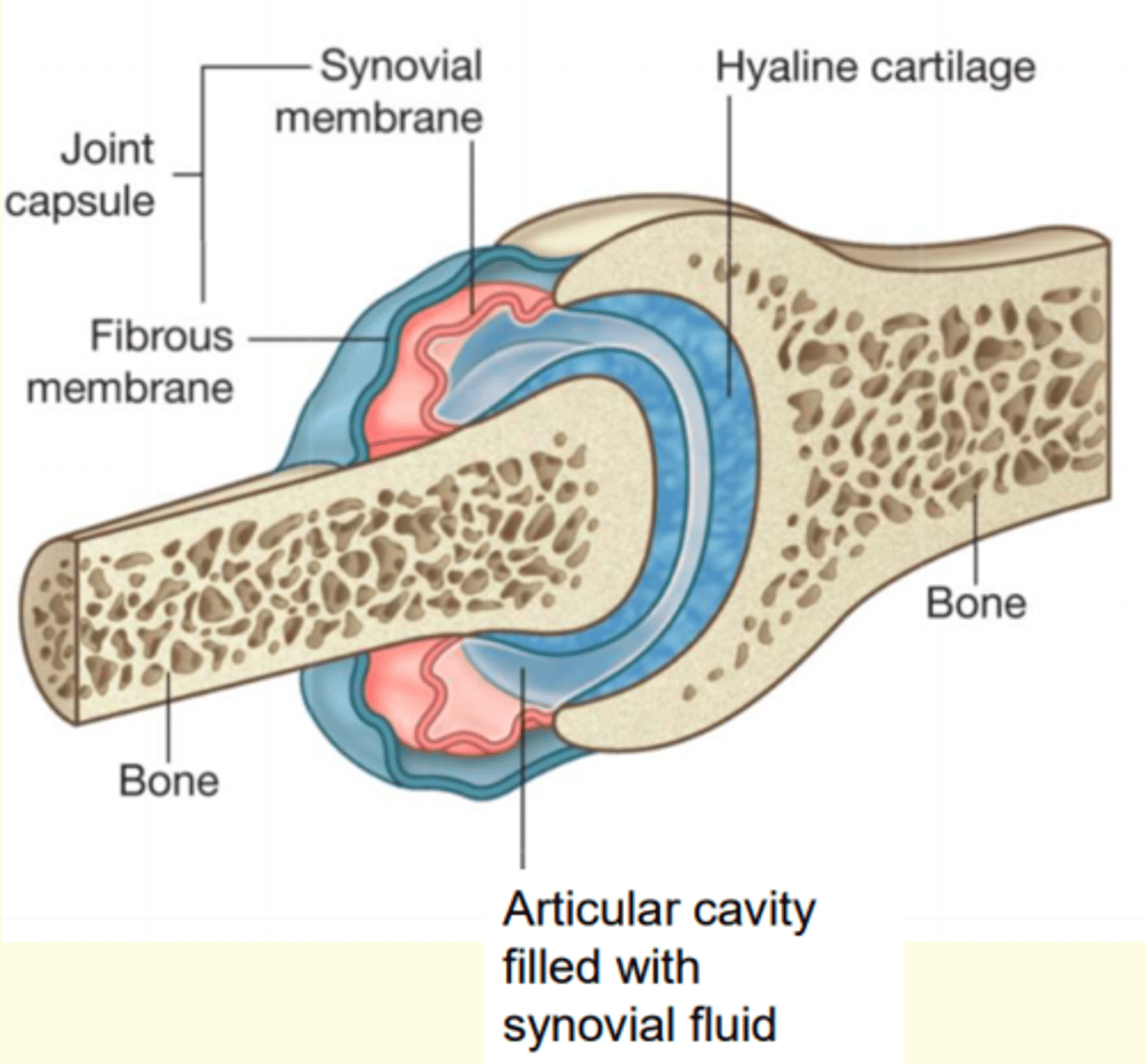
Typical features of a synovial joint
- Hyaline cartilage
- Articular cavity with synovial fluid = lubrication
- Joint capsule = made of outer (fibrous) and inner (synovial) membranes
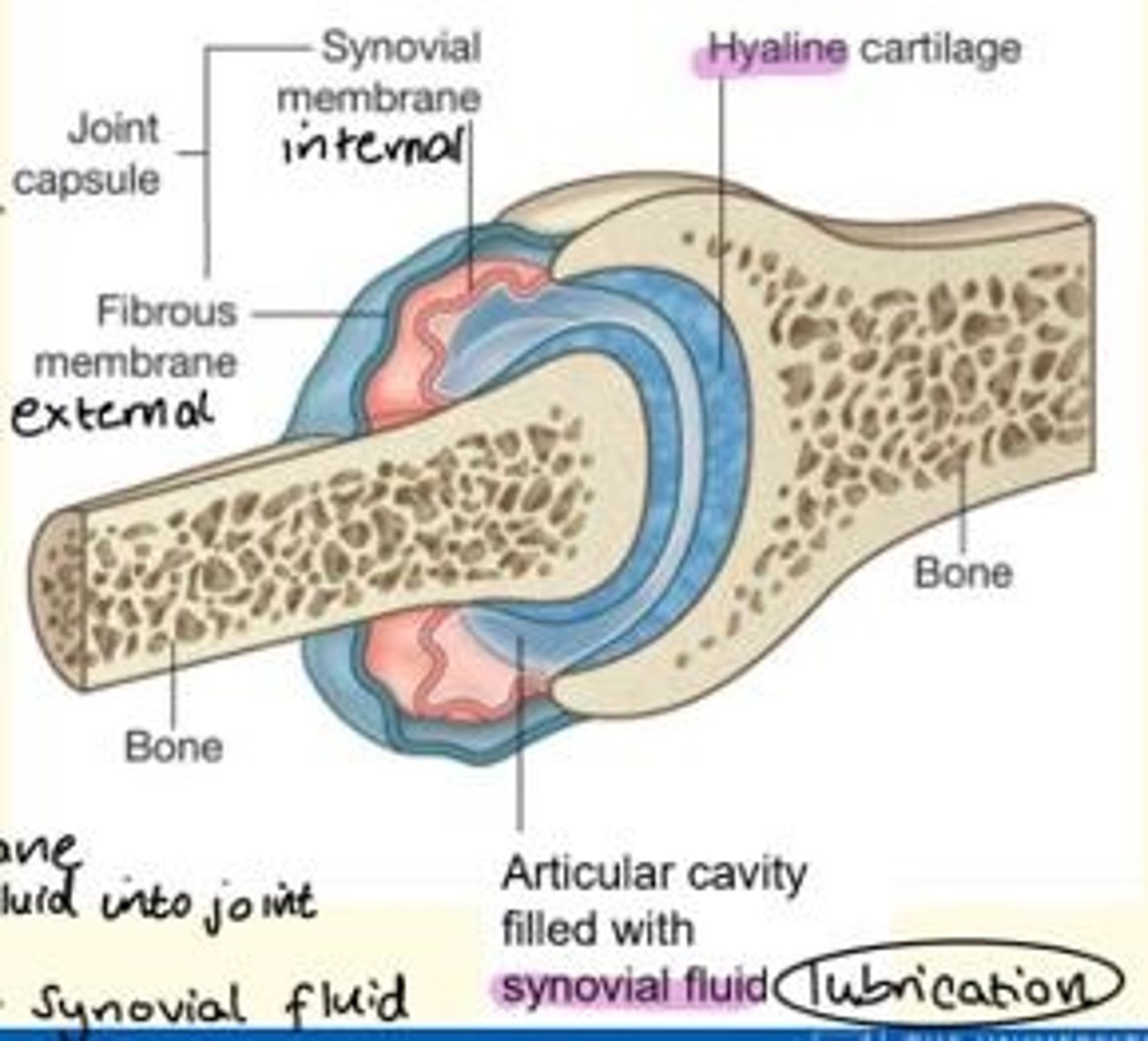
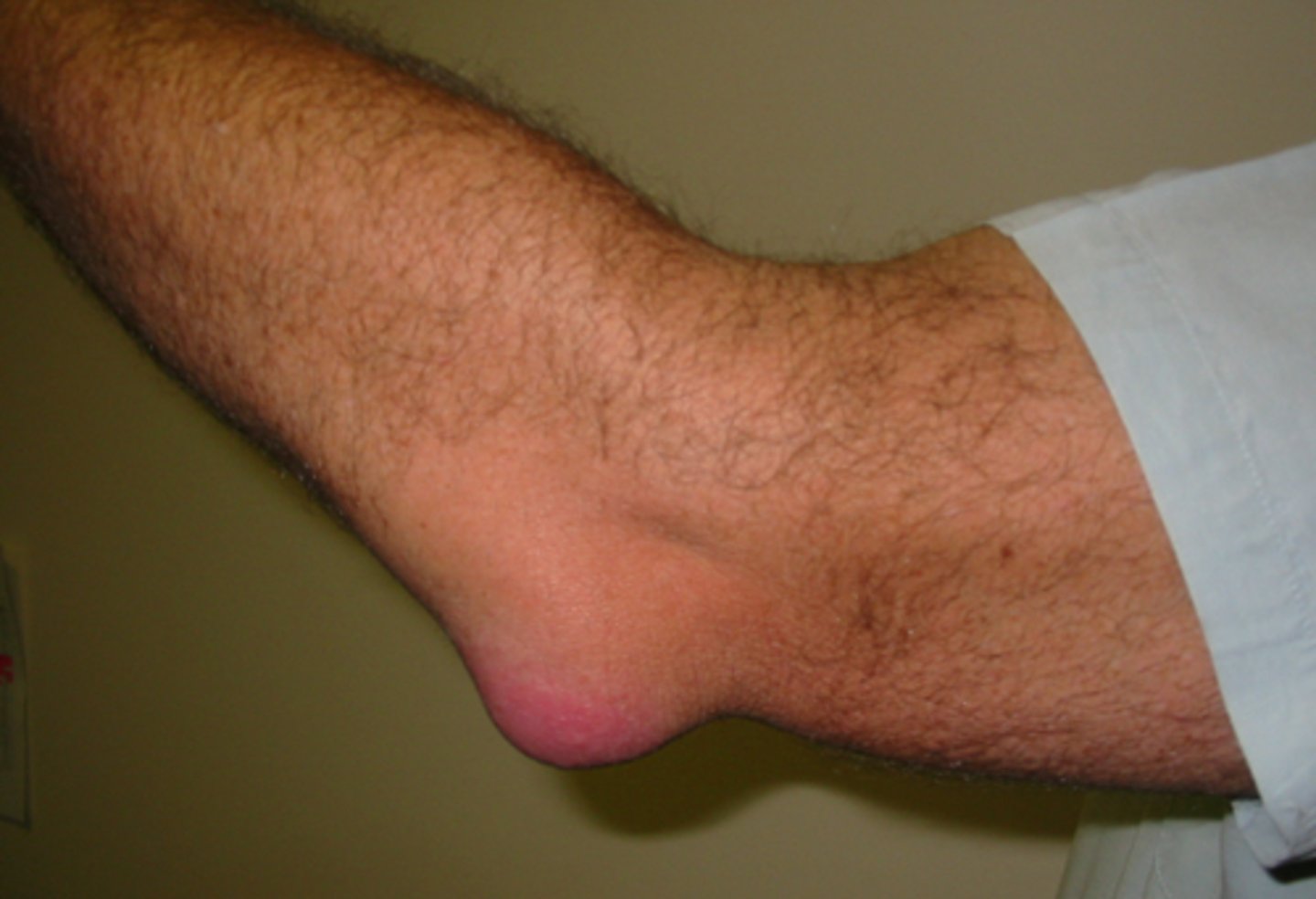
Three factors help to maintain the stability of joints (prevent dislocation of joints) - what are they?
1) Shape, size and arrangement of articular surfaces
2) Ligaments
3) Muscle tone
Types of synovial joints
Hinge
Saddle
Plane
Pivot
Condyloid
Ball & socket

Three main structures found around joints - name them
1) Ligaments
2) Tendons
3) Bursa
Ligaments join ___ to ___
Ligaments join bone to bone
Tendons join ___ to ___
Tendons join muscle to bone
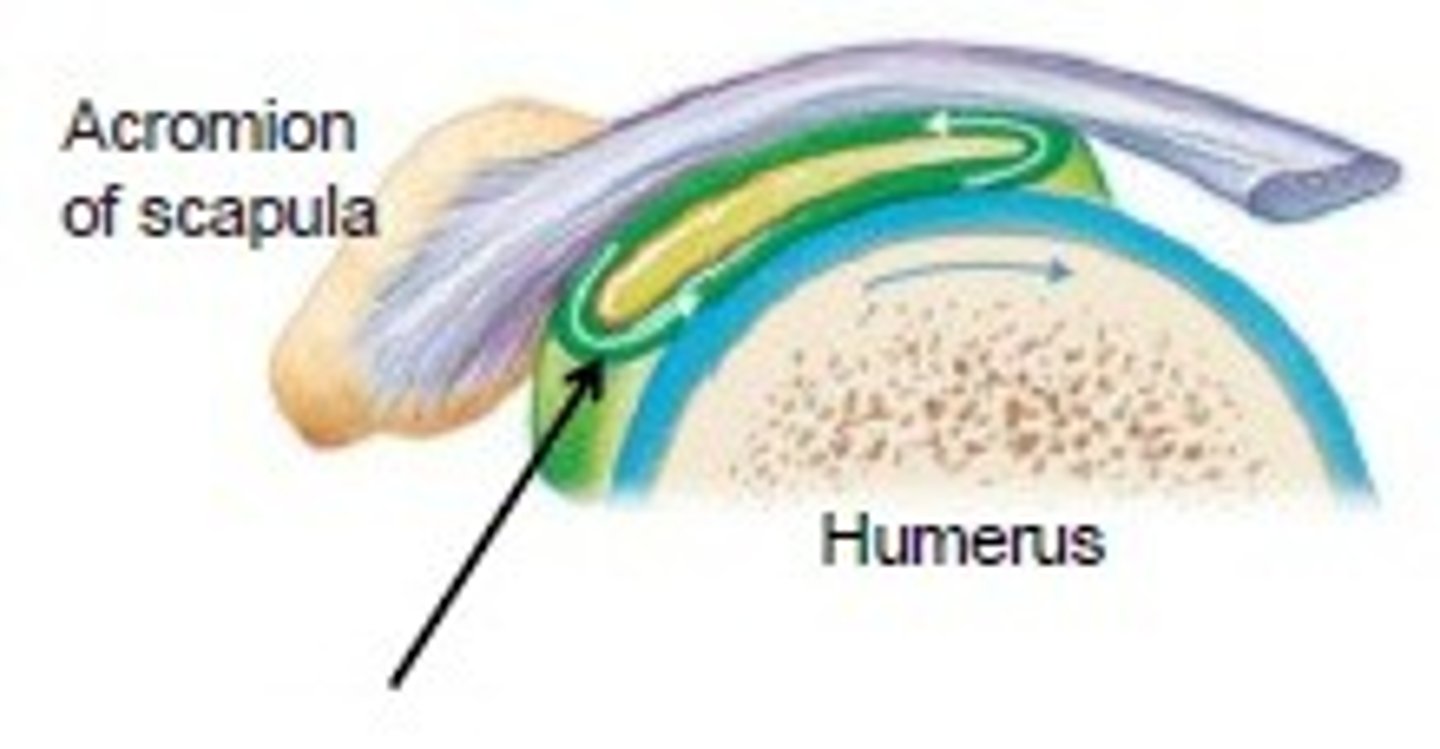
Bursa
Fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane that cushions at points of friction between bone and surrounding tissue (reduce friction)
Found in patella and elbow
Hilton's law
The sensory nerve supplying a joint also supplies the muscles moving the joint and the skin overlying the insertions of the muscle
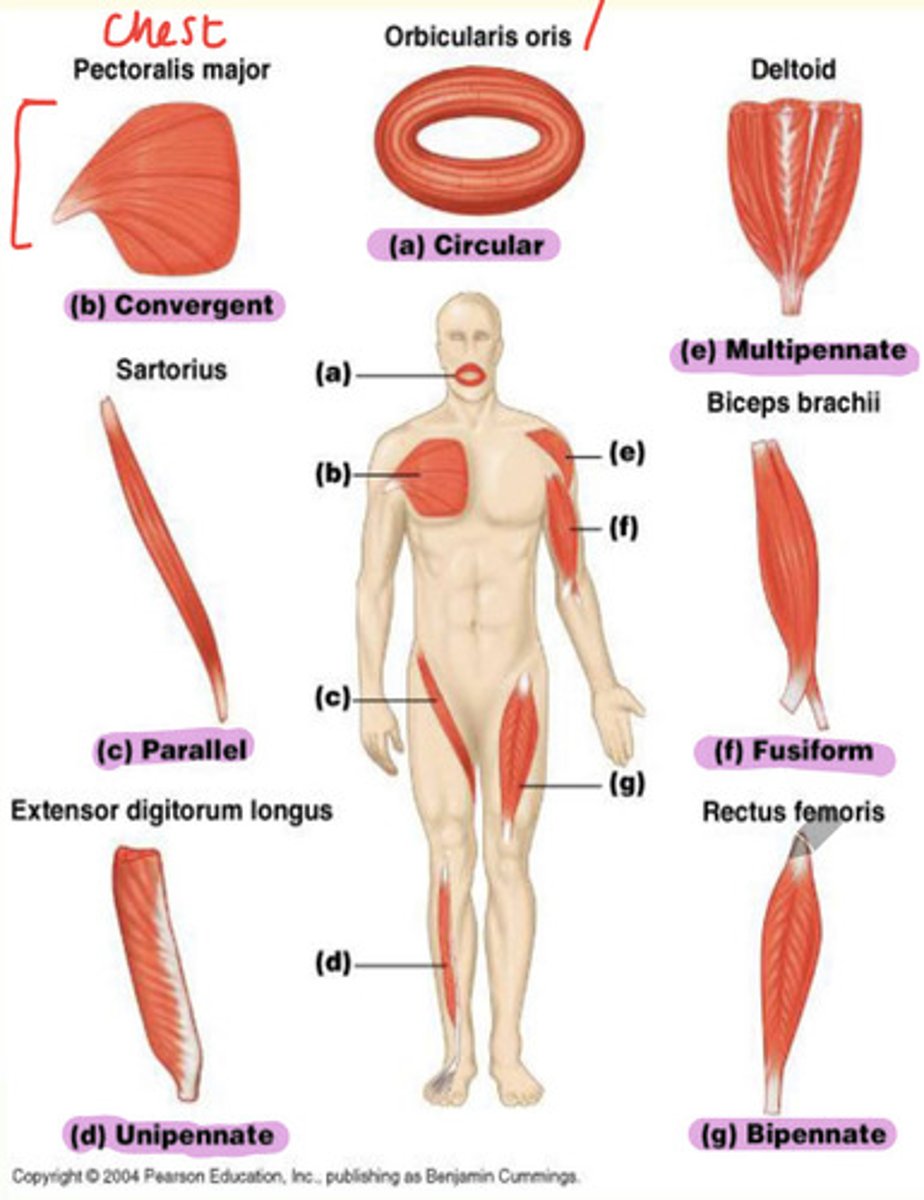
Types of skeletal muscle and examples
A) Circular
B) Convergent
C) Parallel
D) Unipennate
E) Multipennate
F) Fusiform
G) Bipennate
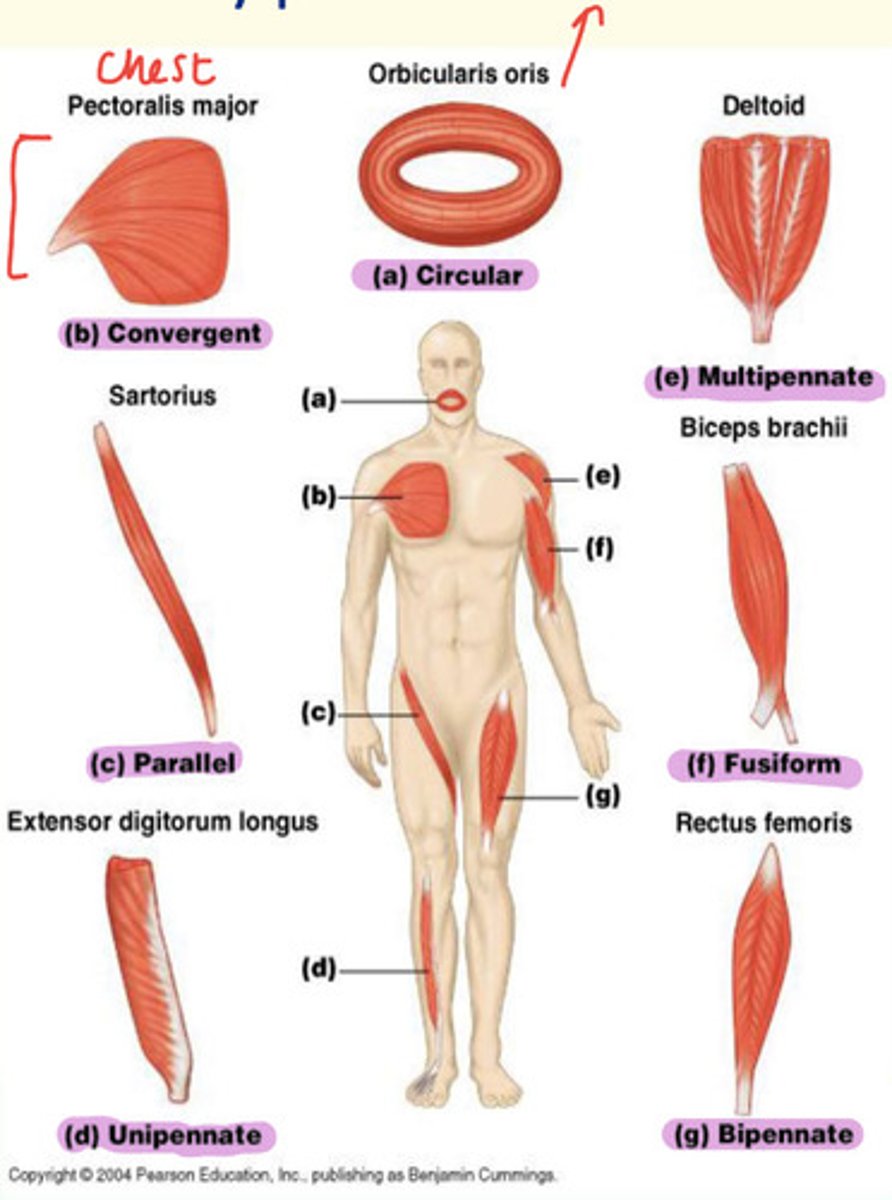
Example of a fusiform skeletal muscle
Biceps brachii found in upper arm
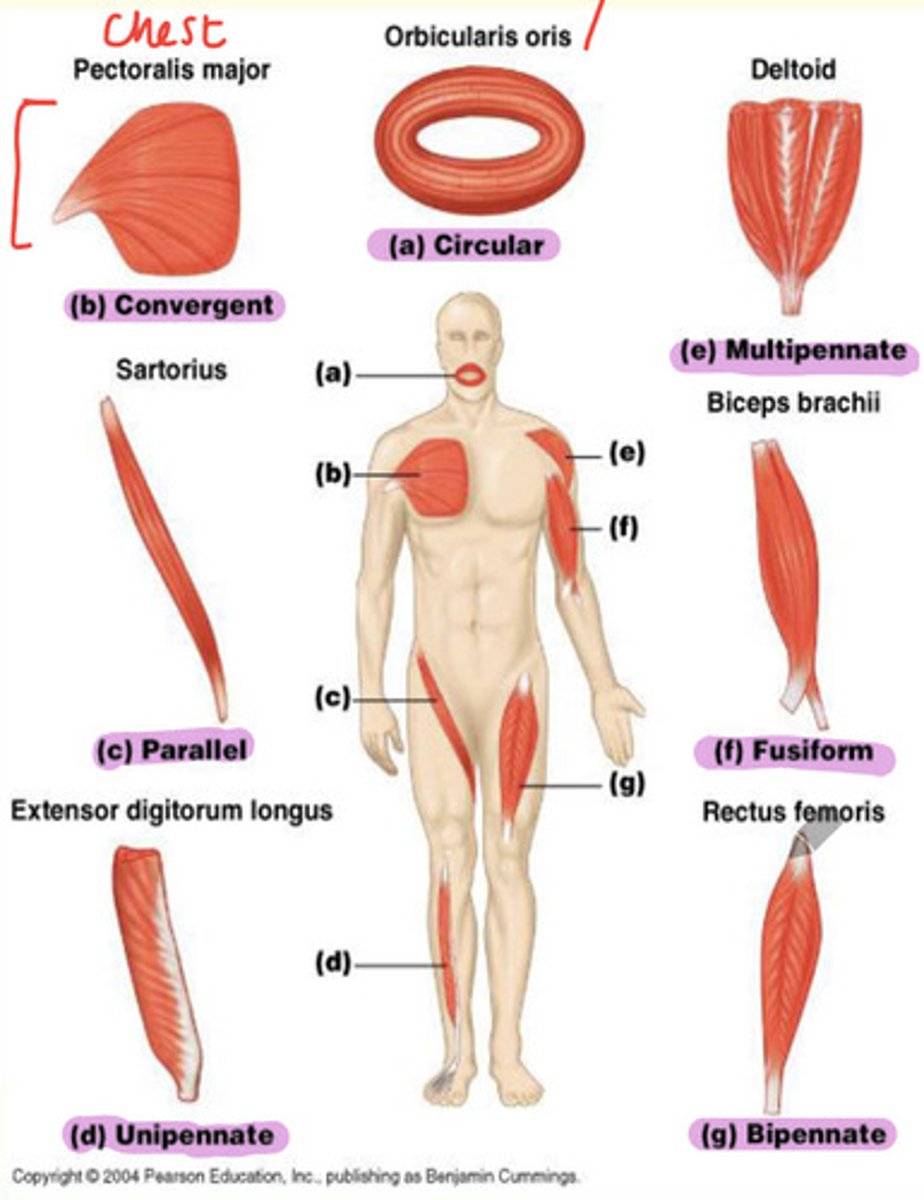
Example of bipennate skeletal muscle
Rectus femoris found in thigh
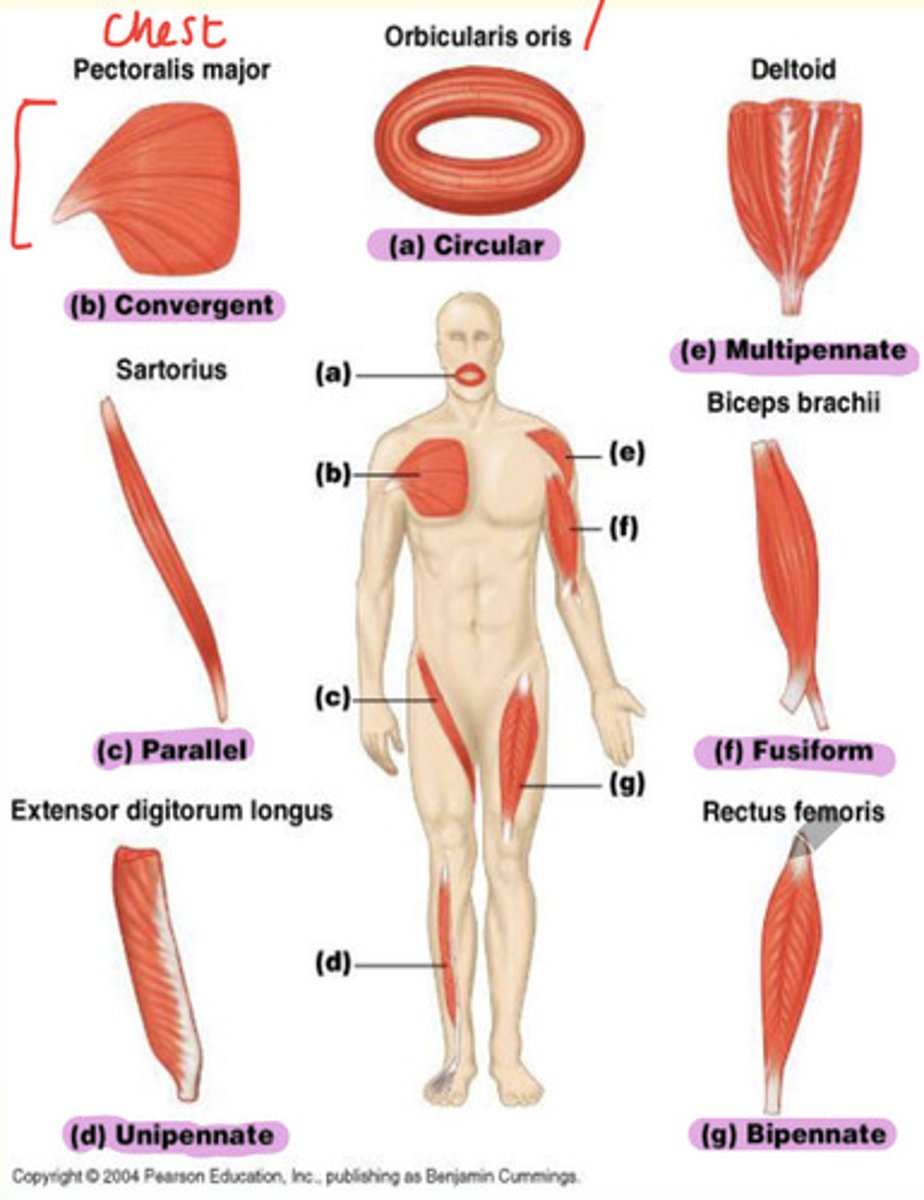
Example of unipennate skeletal muscle
Extensor digitorum longus found in lateral part of leg
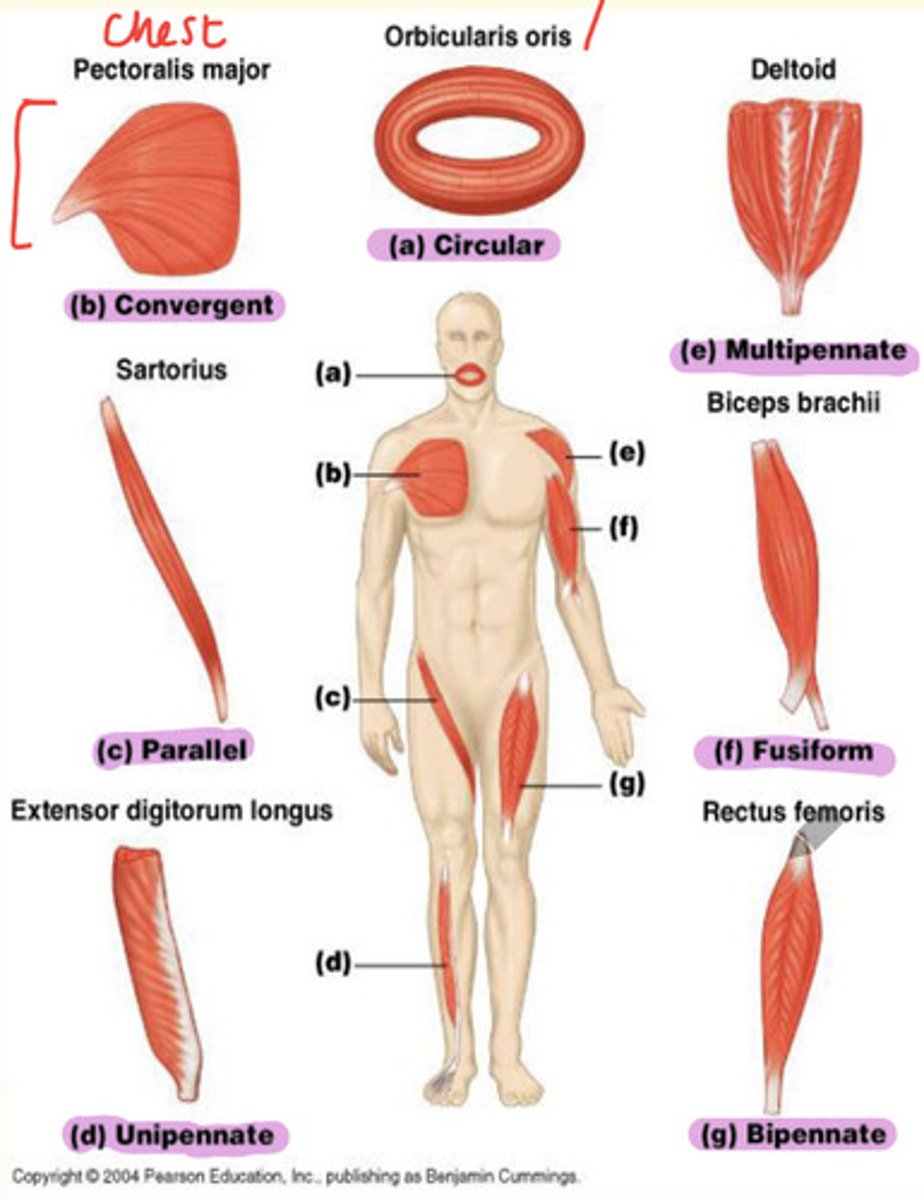
Example of parallel skeletal muscle
Sartorius found in thigh
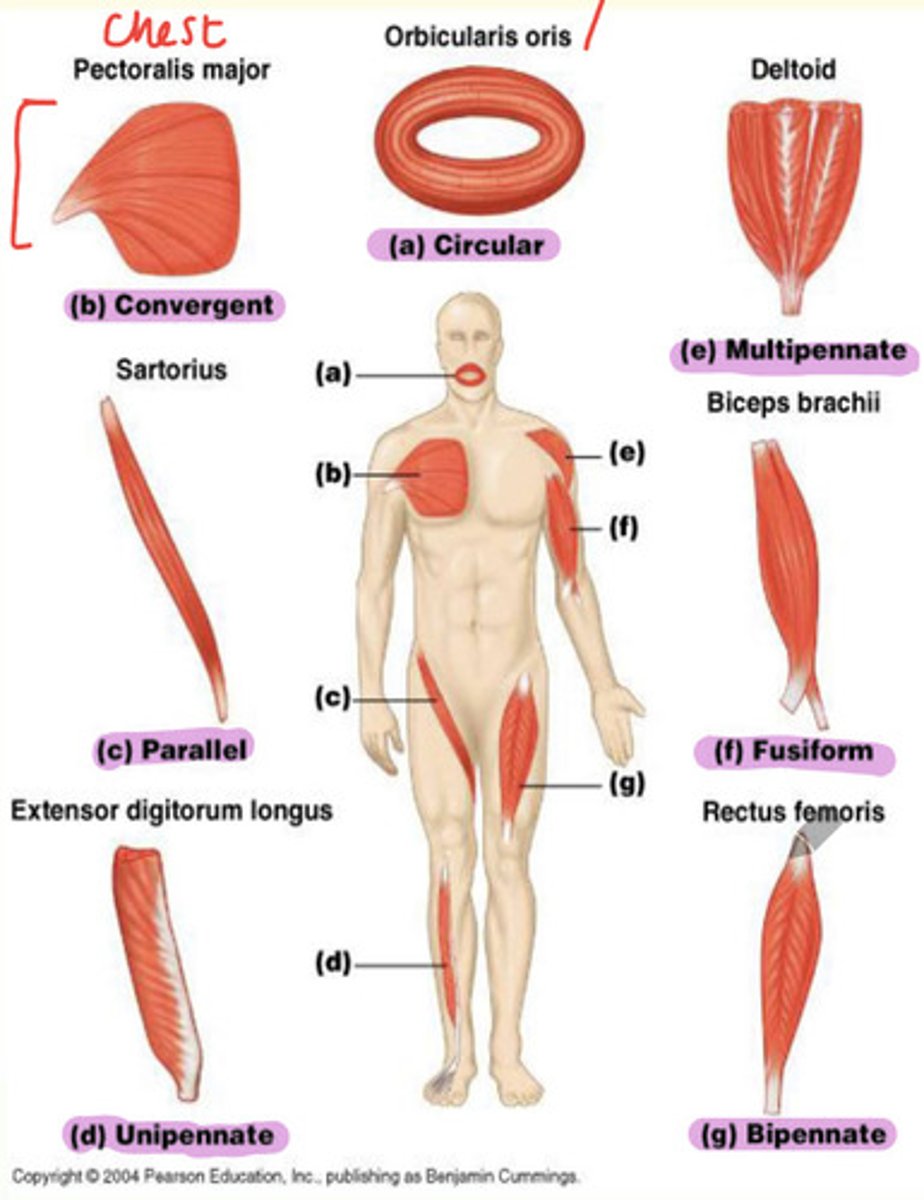
Example of convergent skeletal muscle
Pectoralis major found in chest
When bursa become inflamed, ___ occurs
Bursitis
Function of skeletal muscle
1) Movement
2) Stability of joints
3) Posture
4) Heat generation
5) Convert chemical energy to power mechanical work
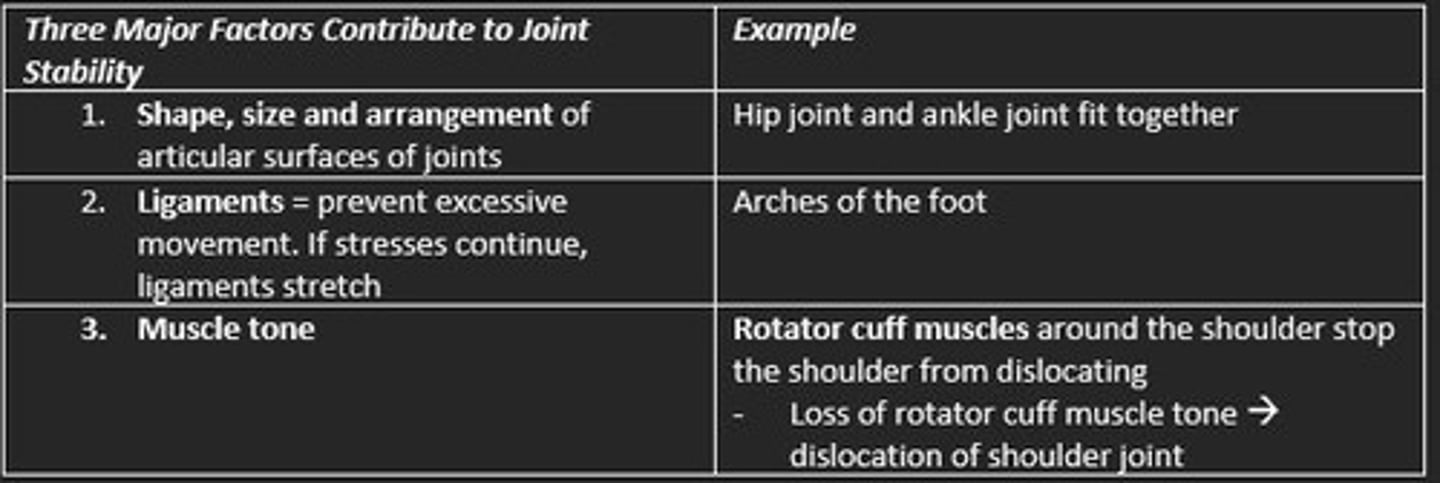
Three factors that increase stability of joints
1) Shape, size & arrangement of articular surfaces
2) Ligaments
3) Muscle tone e.g., rotator cuff muscle (shoulder)
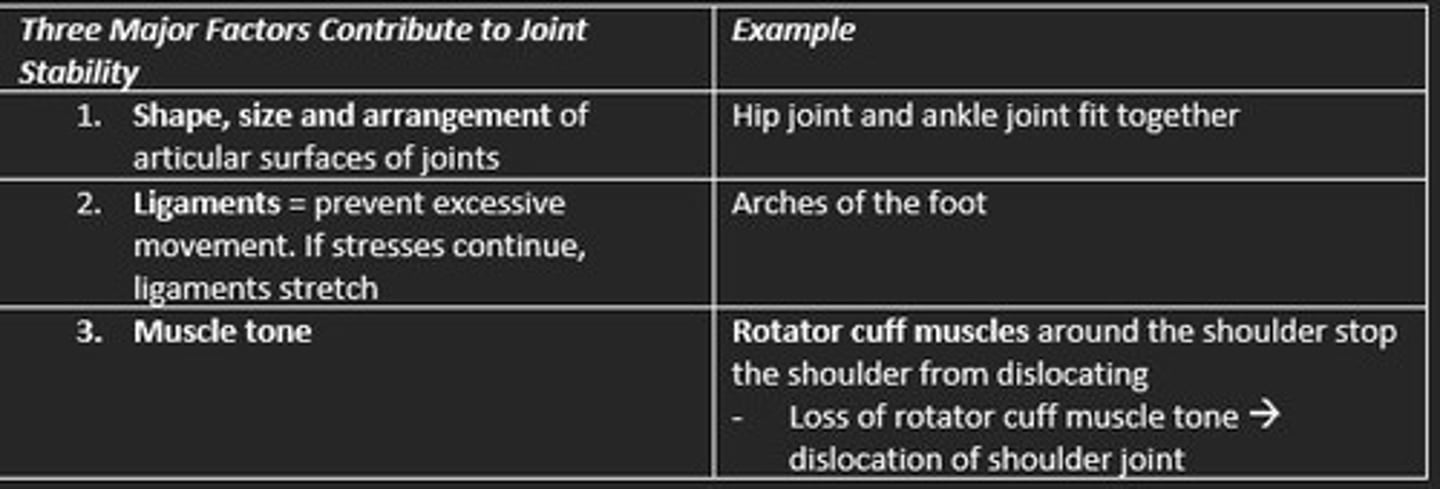
A lever consists of...
1) Rigid structure (bone)
2) Force acting upon it (muscle)
3) Fulcrum fixed point (joint)
4) Load/resistance placed on structure (weight)

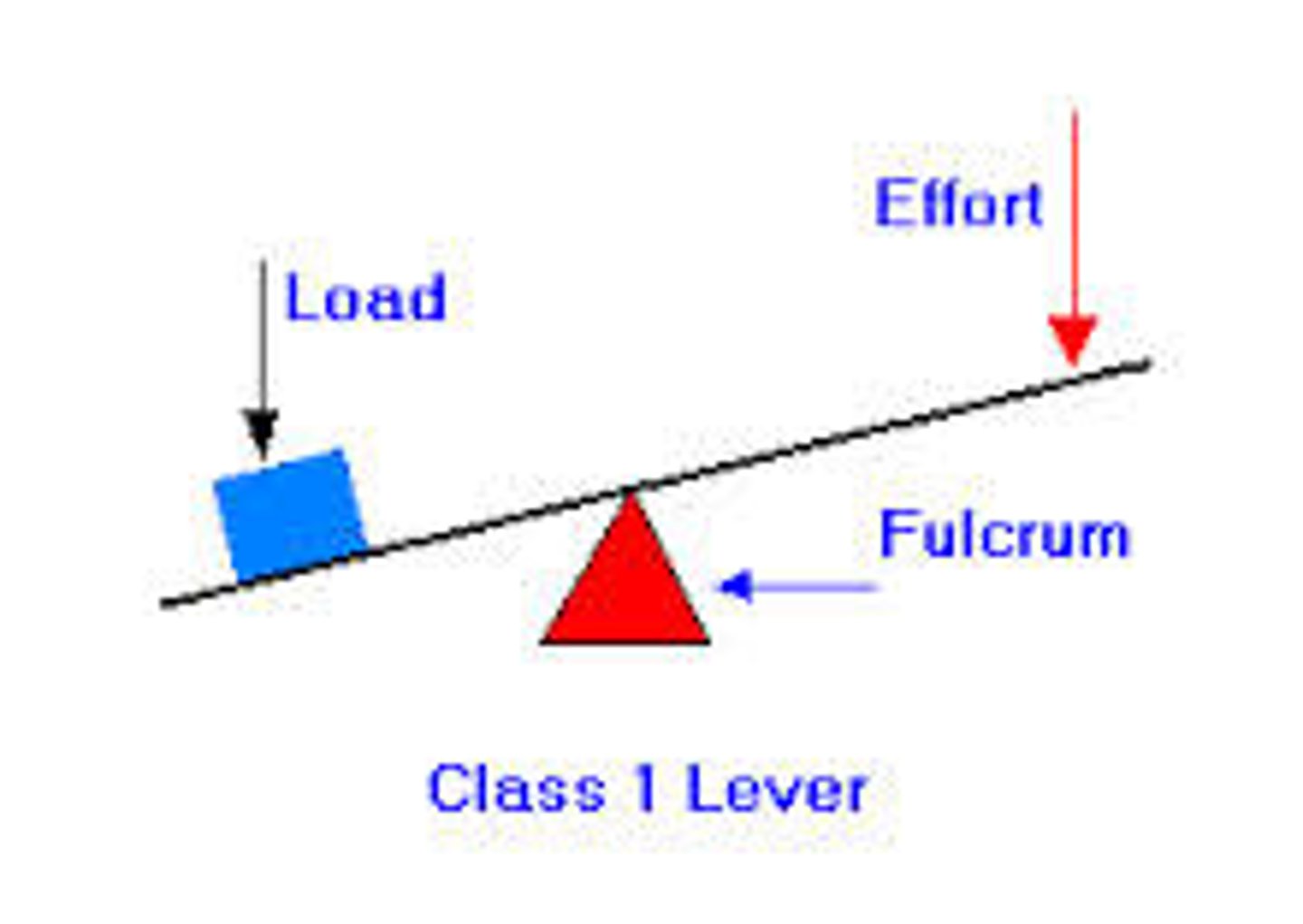
THREE TYPES OF LEVER CLASSES (FLE)
What is a first class lever?
Fulcrum is in the middle
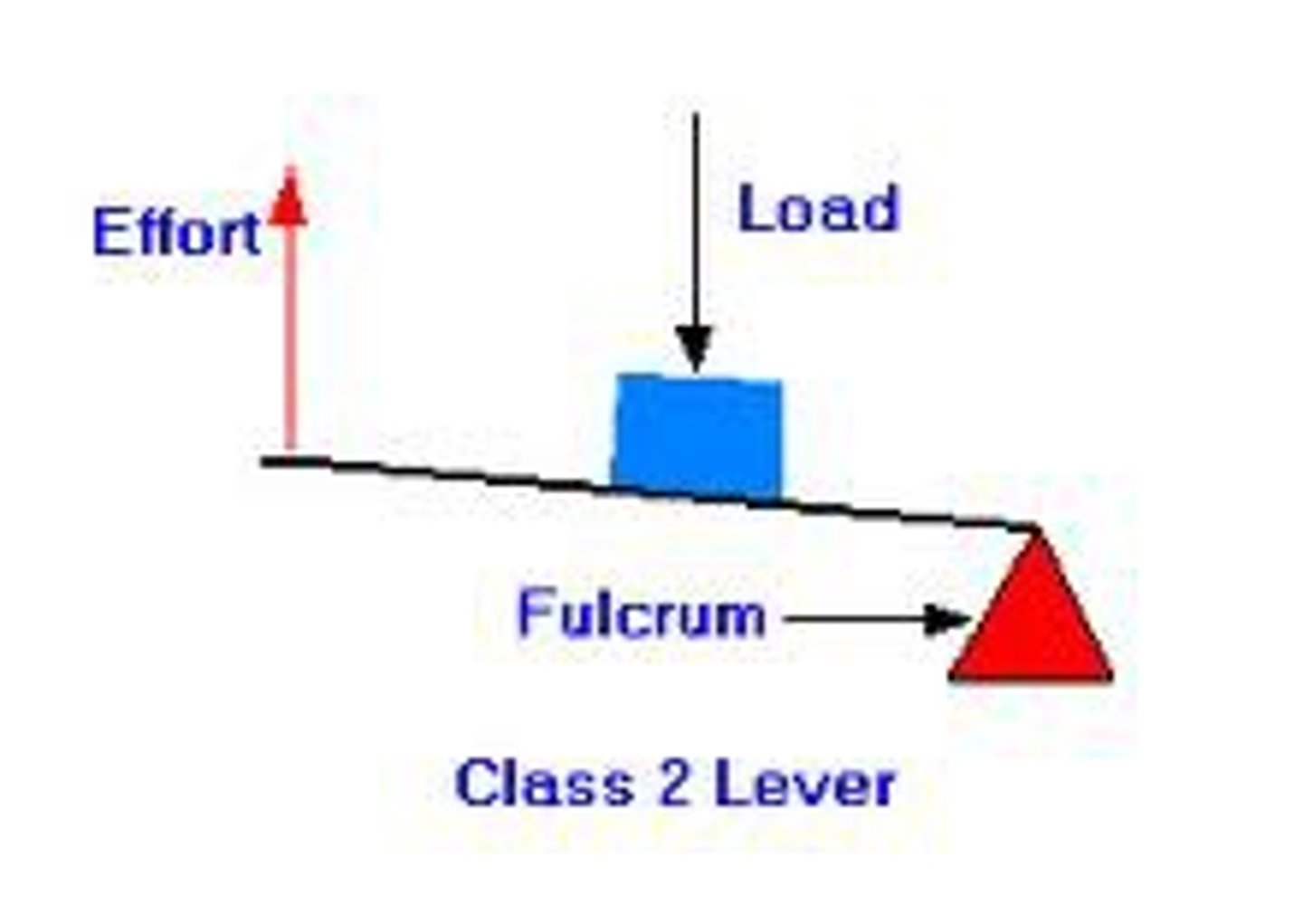
THREE TYPES OF LEVER CLASSES (FLE)
What is a second class lever?
Load is in the middle
THREE TYPES OF LEVER CLASSES (FEL)
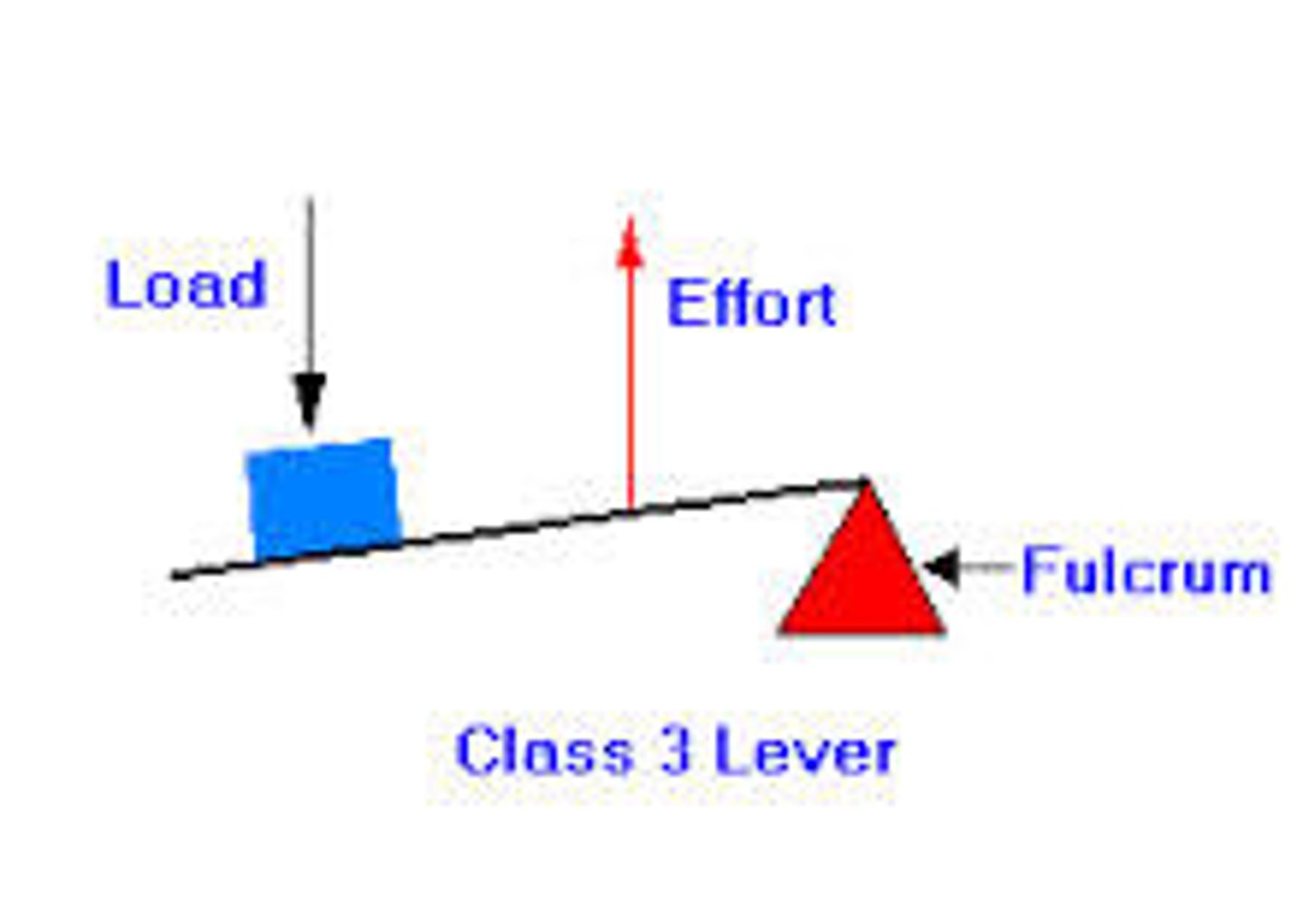
What is a third class lever?
Effort is in the middle
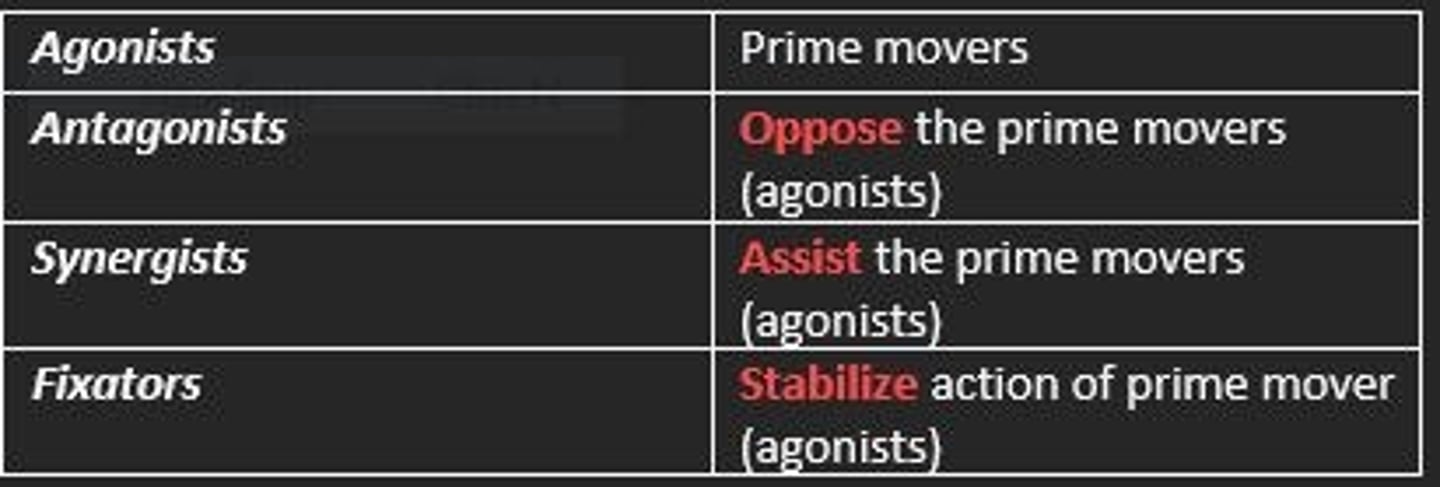
What are the four main muscle groups?
1) Agonists
2) Antagonists
3) Synergists
4) Fixators
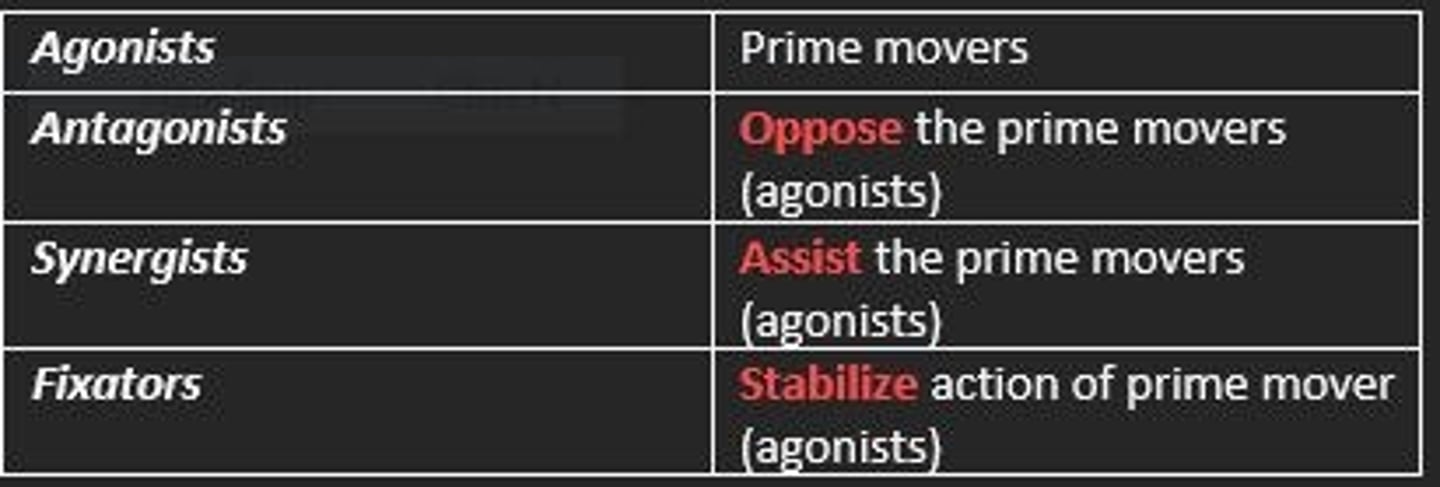
Agonist muscles
Prime movers
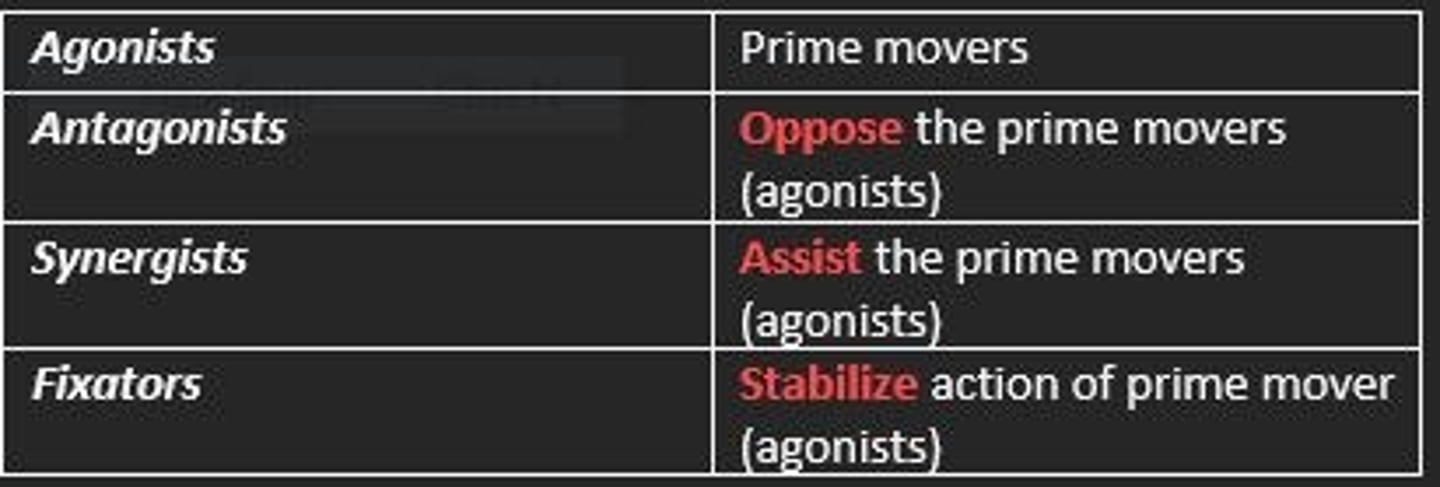
Antagonist muscles
Oppose prime movers
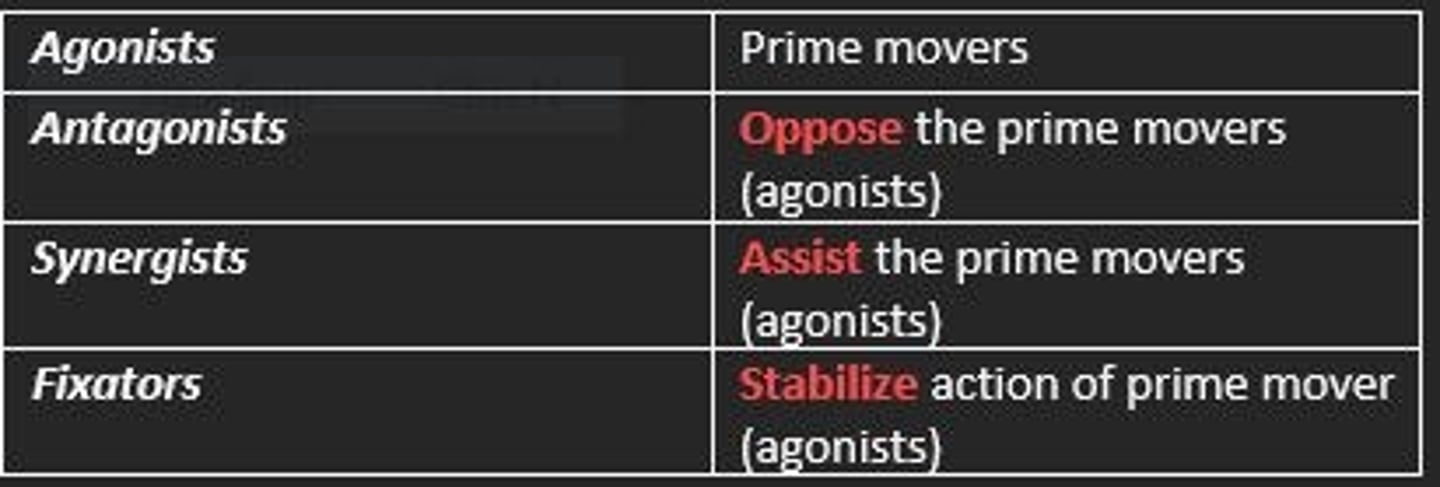
Synergist muscles
Assist the prime movers
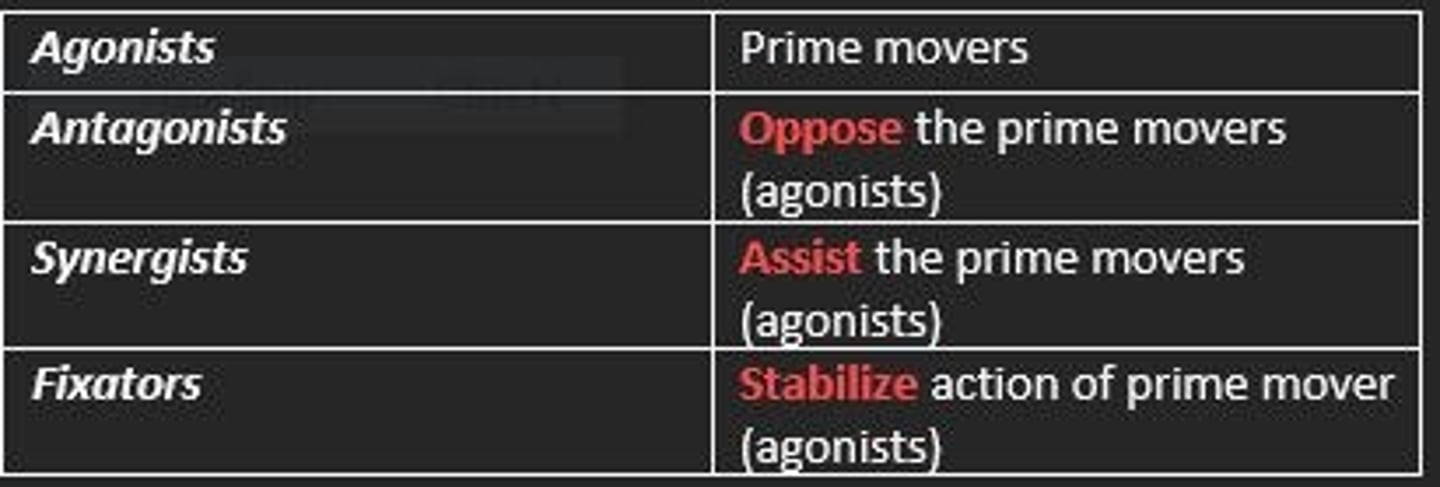
Fixator muscles
Stabilize action of prime movers
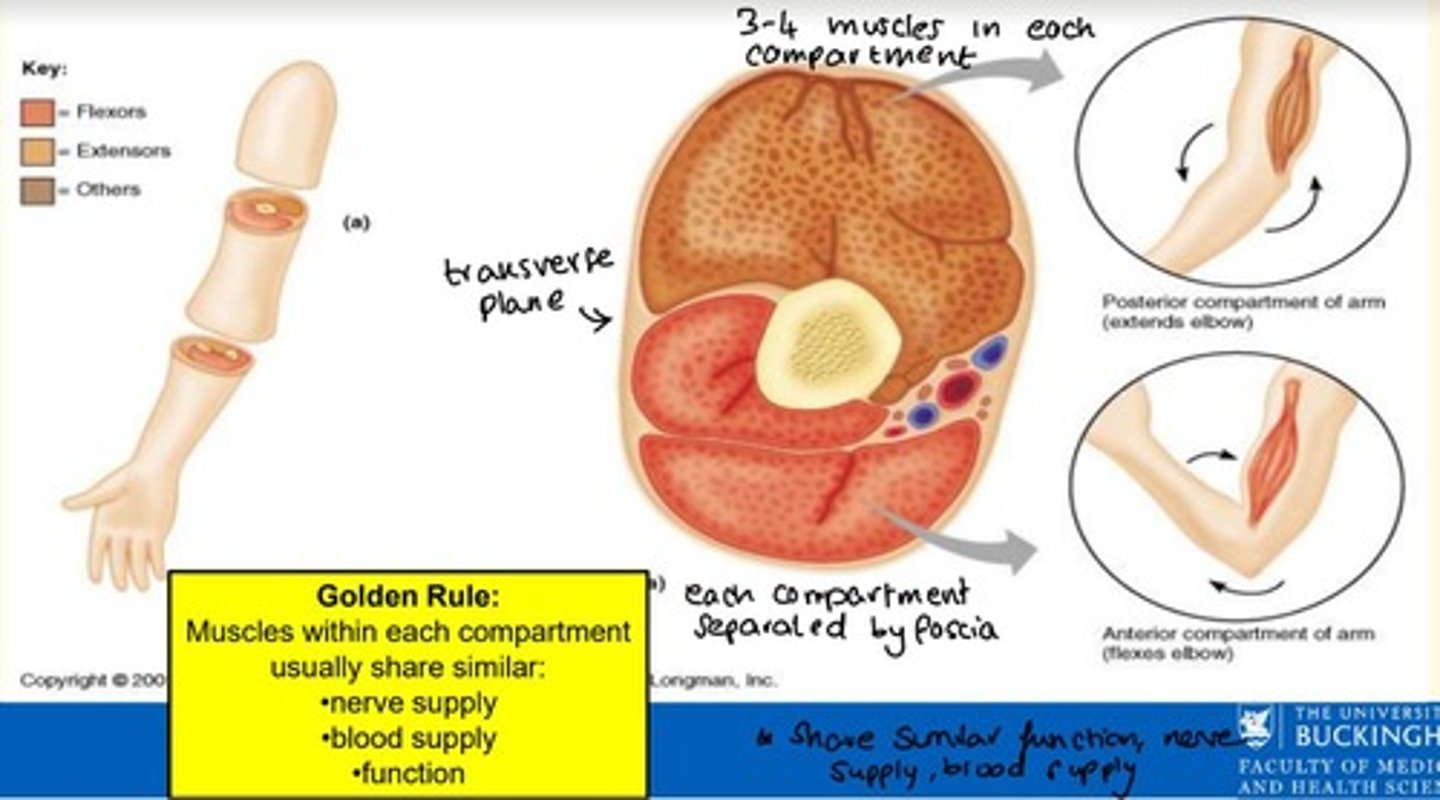
What is a muscle compartment?
A group of functionally related muscles enclosed by fascia
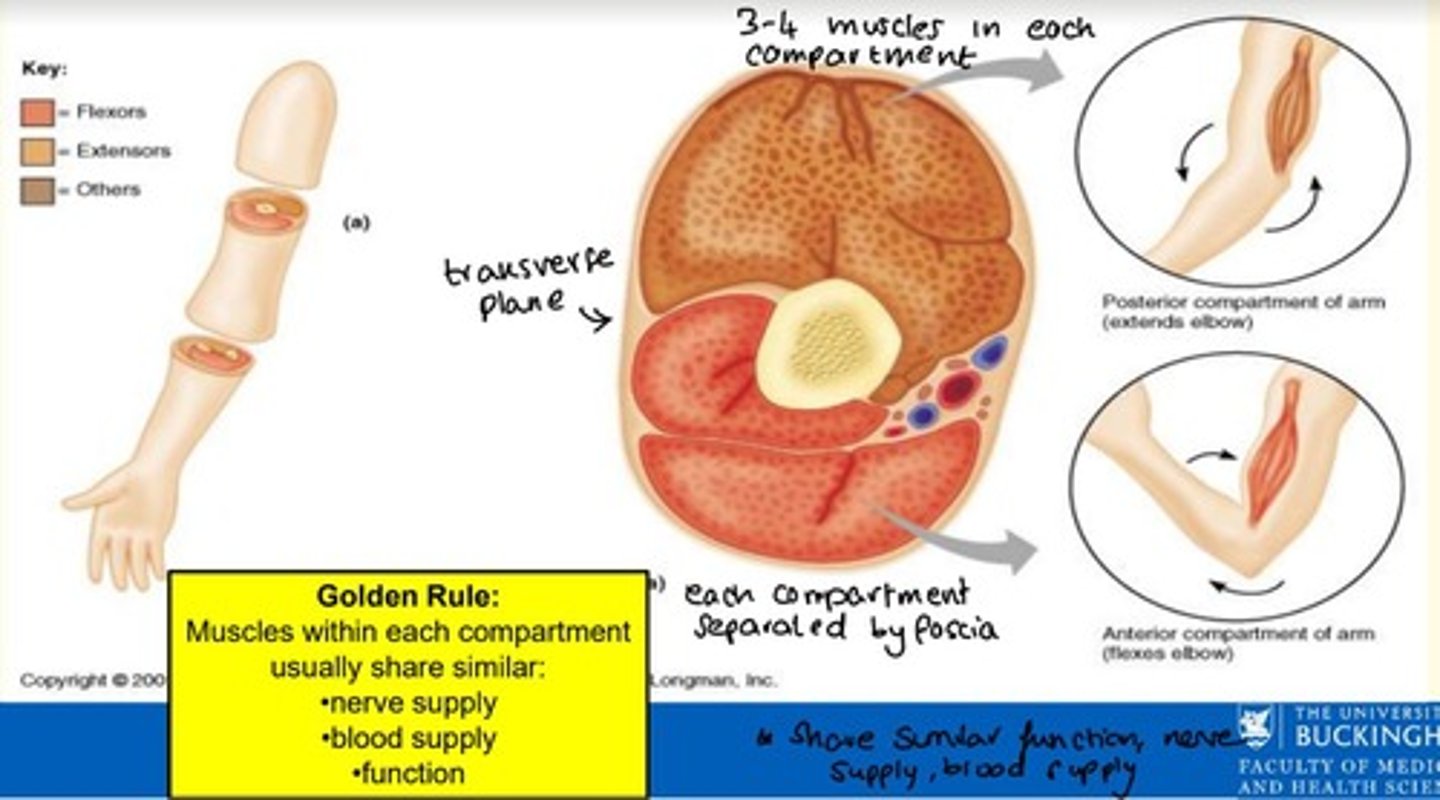
Each muscle compartment is separated by what?
Deep fascia
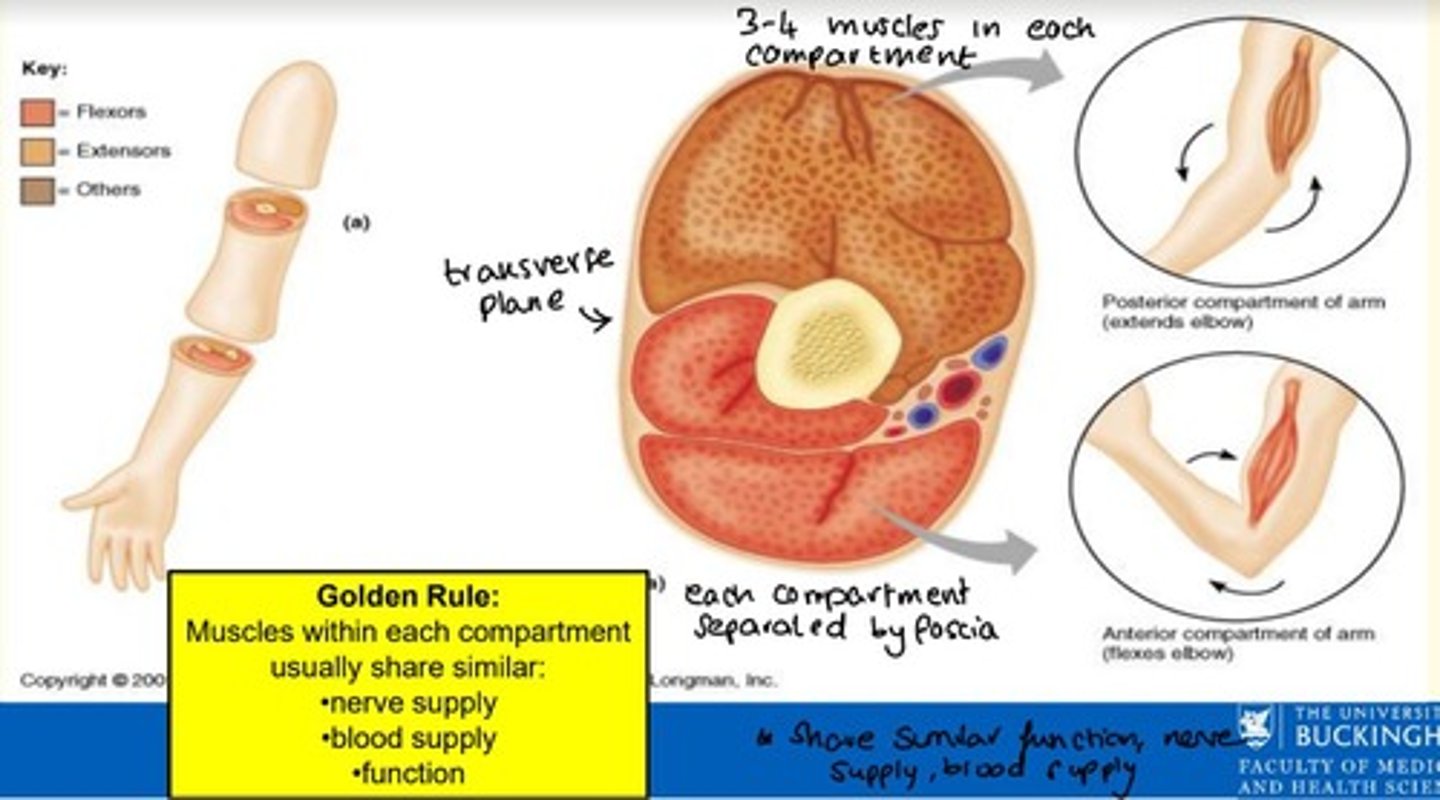
Muscles within each compartment share three similar factors - what are these?
Muscles within each compartment share similar...
1) Nerve supply
2) Blood supply
3) Function
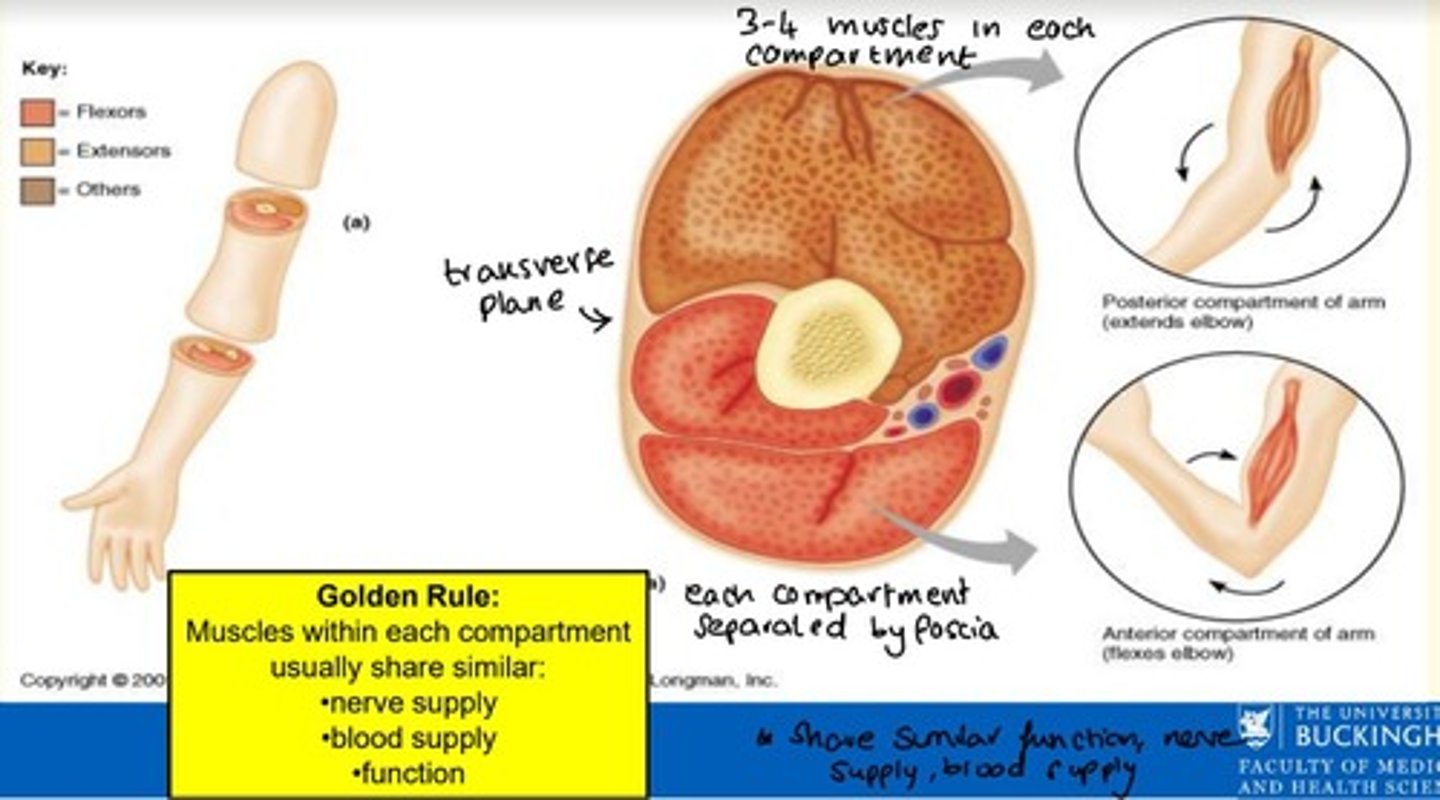
How many muscles are in each muscle compartment?
3-4 muscles per muscle compartment
Describe the 5-phase repair of a fracture of a long bone.
1) Clot formation
2) Organisation of cartilage and cartilage cells = new chondroblasts
3) Soft callus formation = made of osteoid and woven bone matrix
4) Hard callus formation = with mineralisation
5) Modelling and remodelling of new bone by osteoblasts and osteoclasts to form lamellar bone
In a striated muscle cell where is calcium stored and what stimulates it to be released?
Calcium is stored in sarcoplasmic (endoplasmic) reticulum and the release is stimulated by action potential
List and name the three types of muscle fibre and briefly describe the role of each type
Type 1 (slow oxidative) = Endurance
Type 2a (fast oxidative) = Walking and sprinting
Type 2b (fast glycolytic) = Short intense movements
Long bones enable body movement by acting as a ___
Lever
Most of the bones of the arms and hands are long bones; however, the bones in the wrist are categorised as ___ bones
Short bones
The part of a long bone where growth in diameter primarily occurs during development is known as the...
Diaphysis
The terms here are paired with their opposites.
Which is incorrect?
Caudal/Ventral
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following bones is NOT part of the axial skeleton?
Scapula
3 multiple choice options
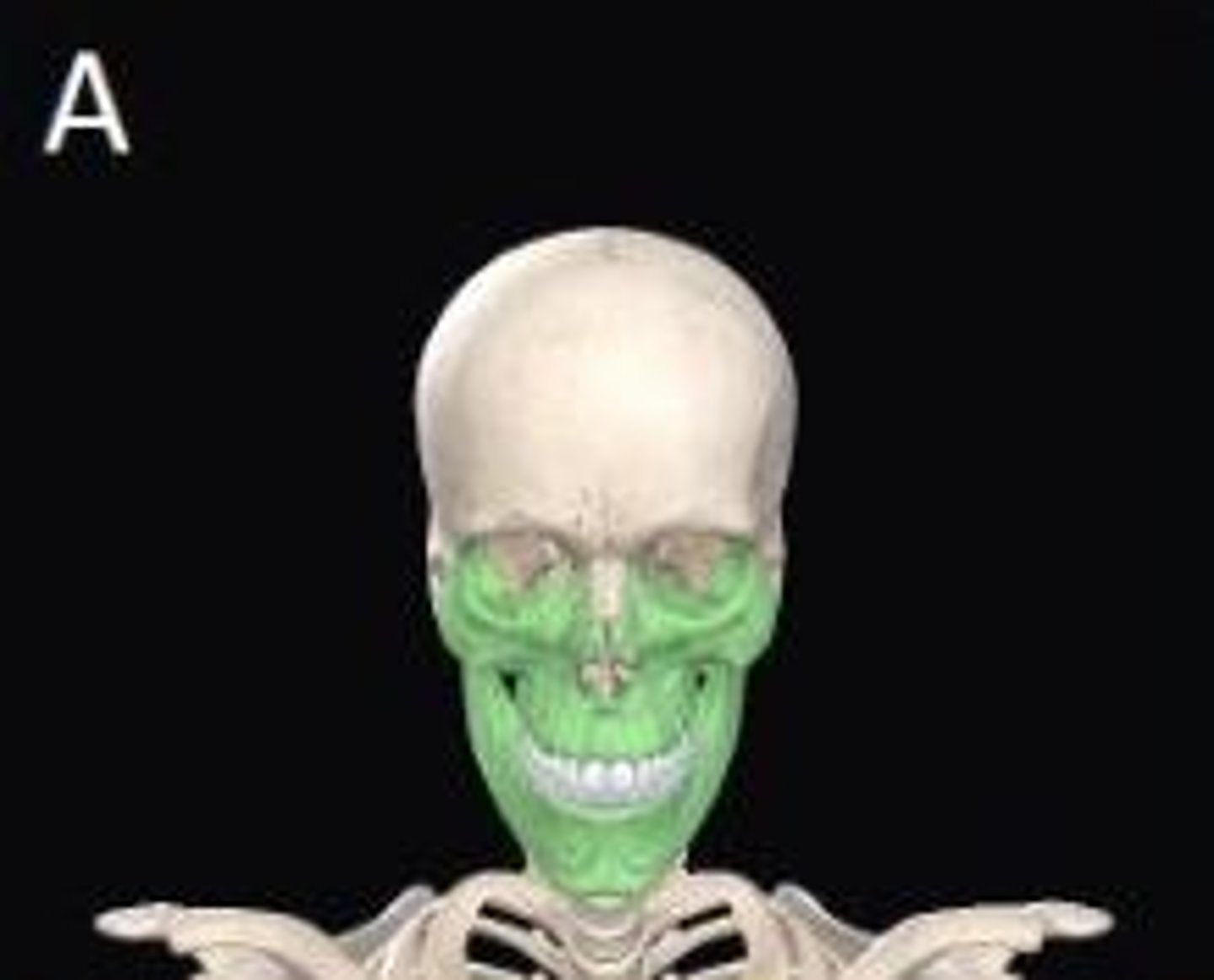
The bone shown in green is an example of what type of bone?
Irregular
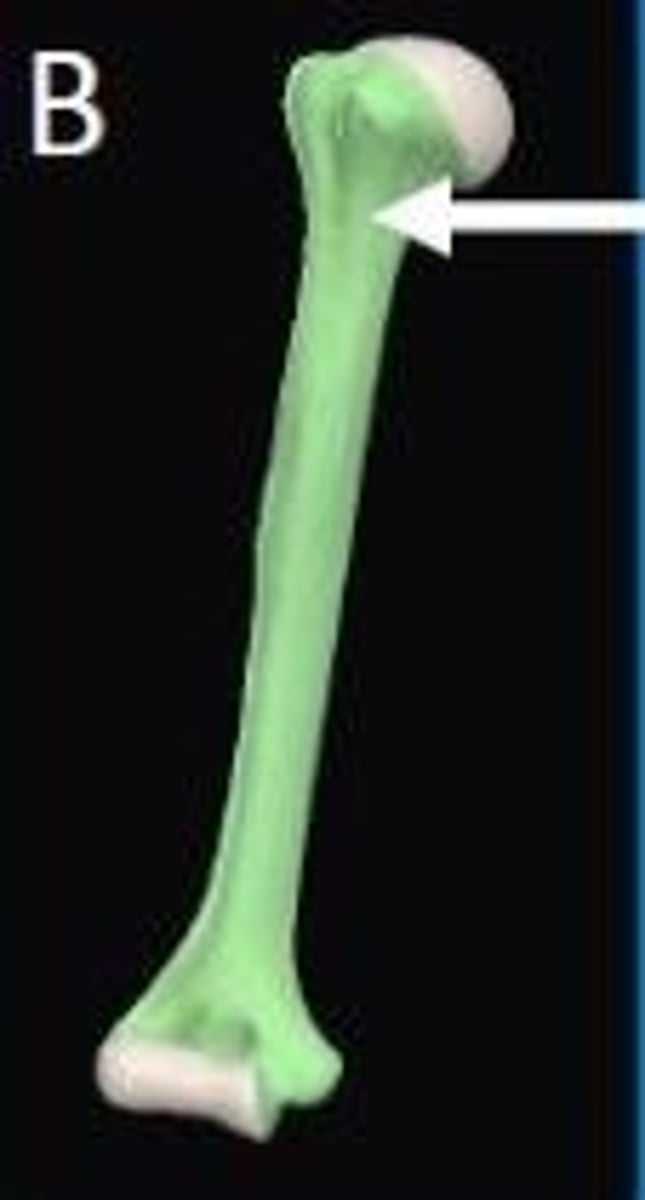
In this long bone the area marked by the arrow is a site of active bone growth in children called the...
Epiphyseal plate

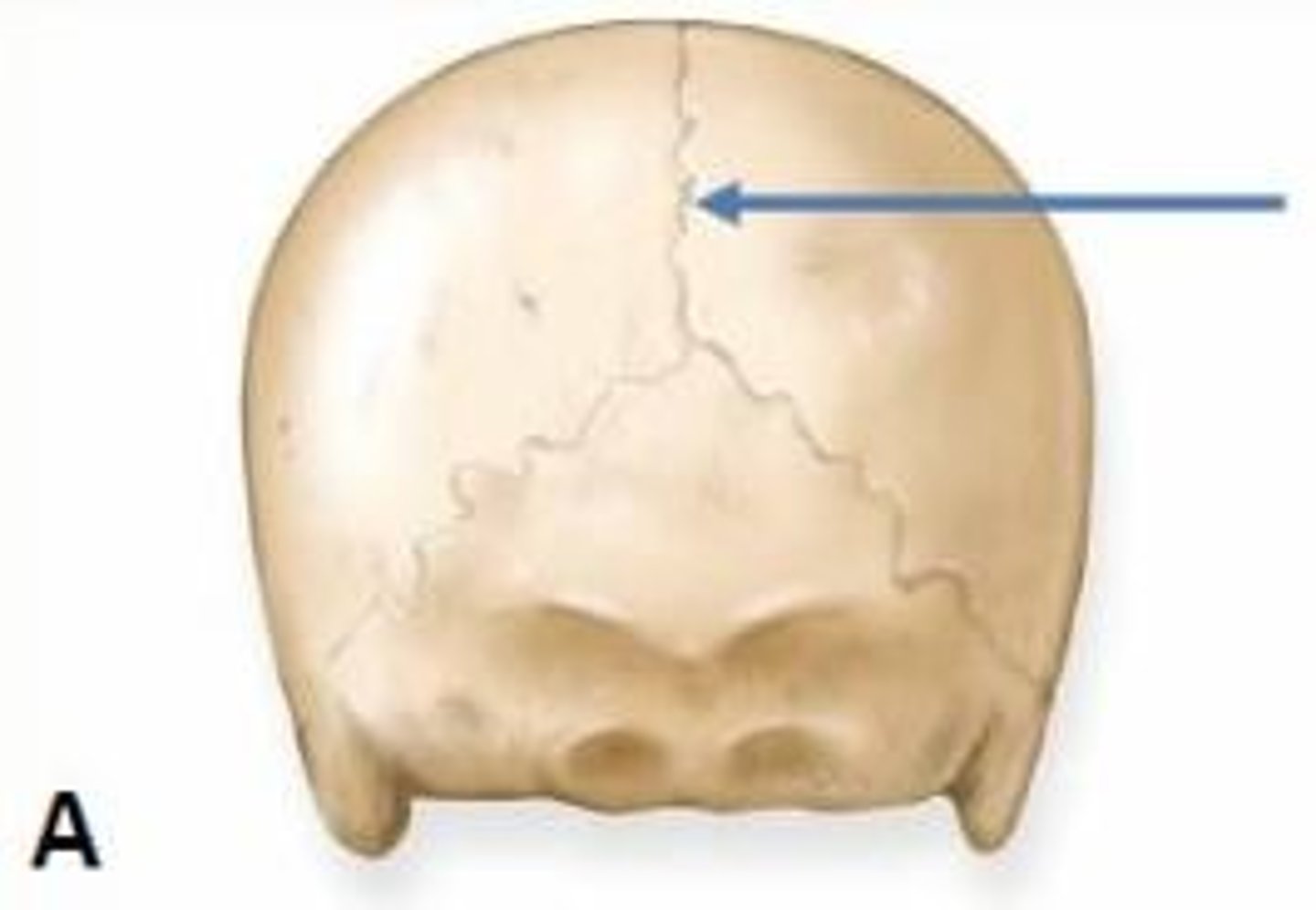
What type of joint is formed at the site indicated by the arrow?
Fibrous
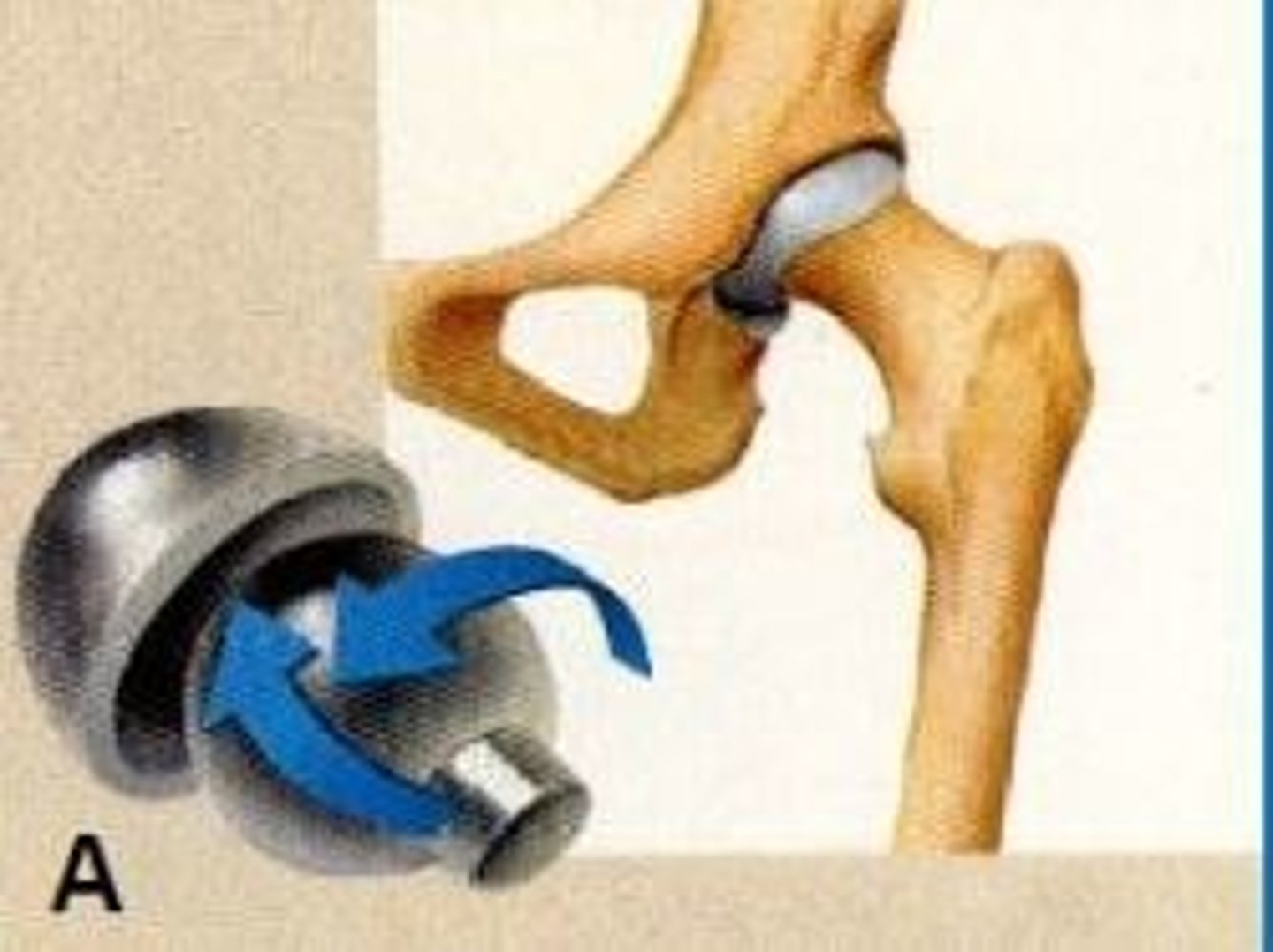
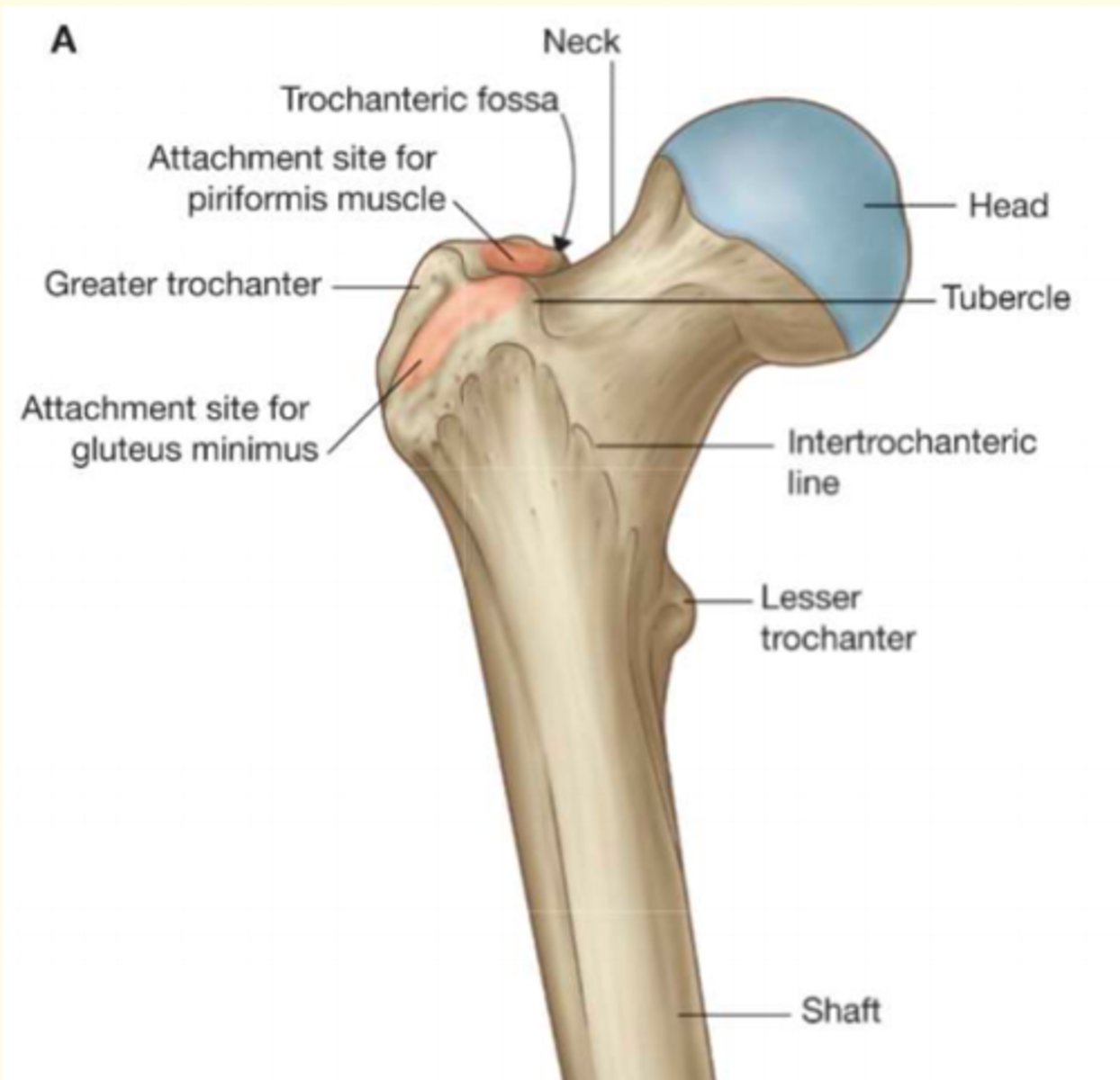
How do you classify the synovial joint shown in image A?
Ball & socket e.g., hip
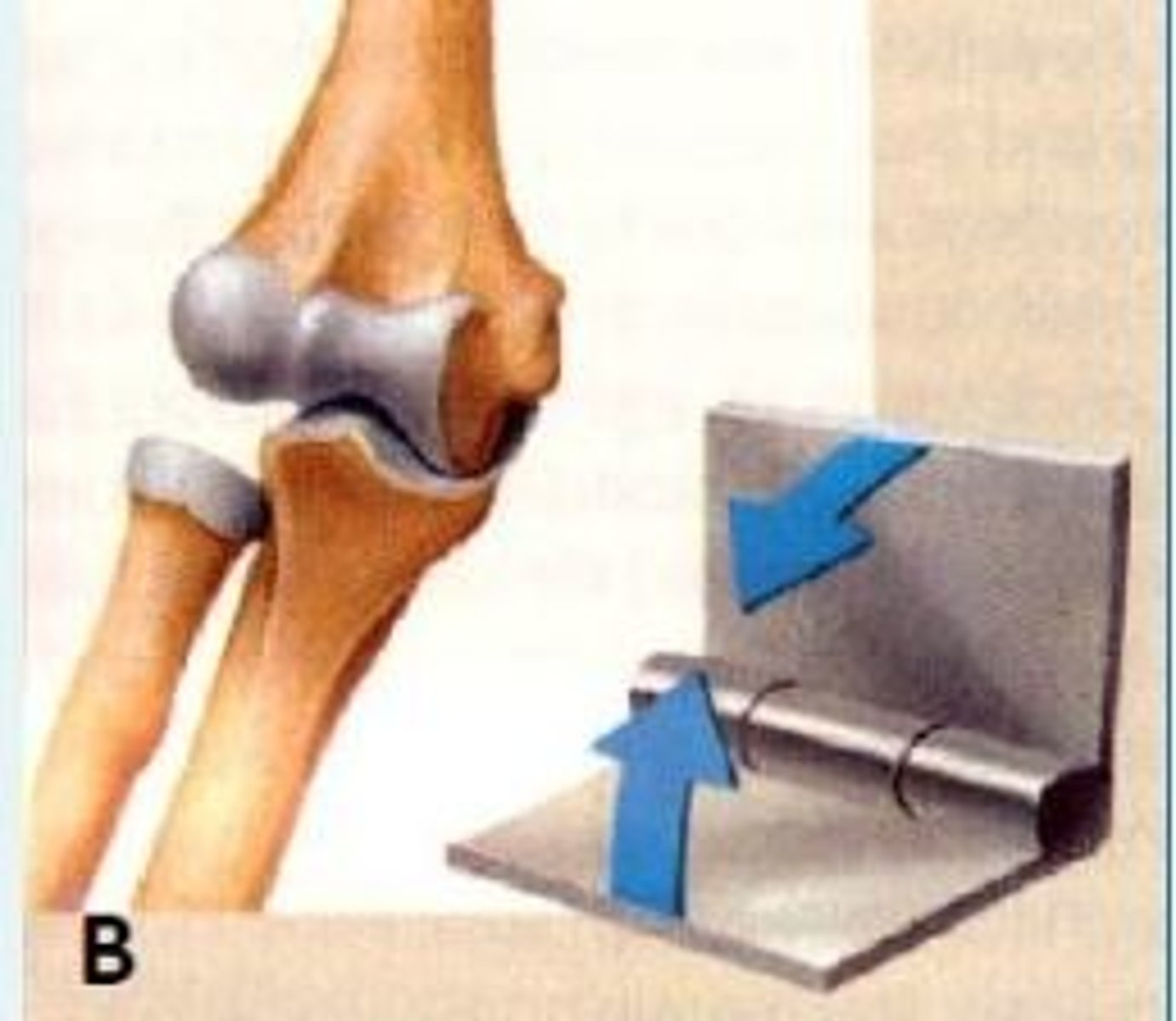
Based on axis of movements; how will you classify the synovial joint shown in image B.
Hinge joint e.g., elbow
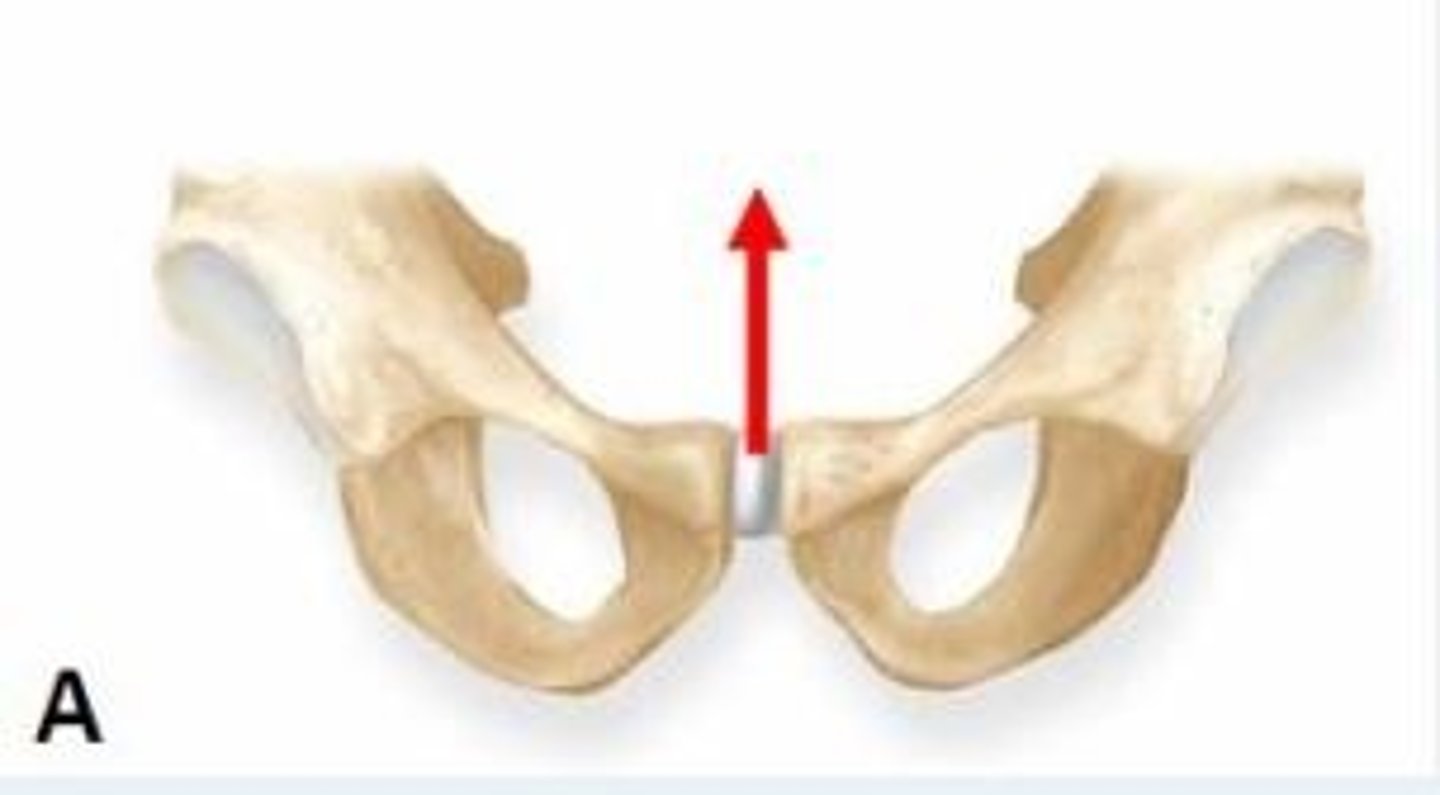
Name the type of joint formed at site indicated by the arrow in image A.
Cartilaginous joint
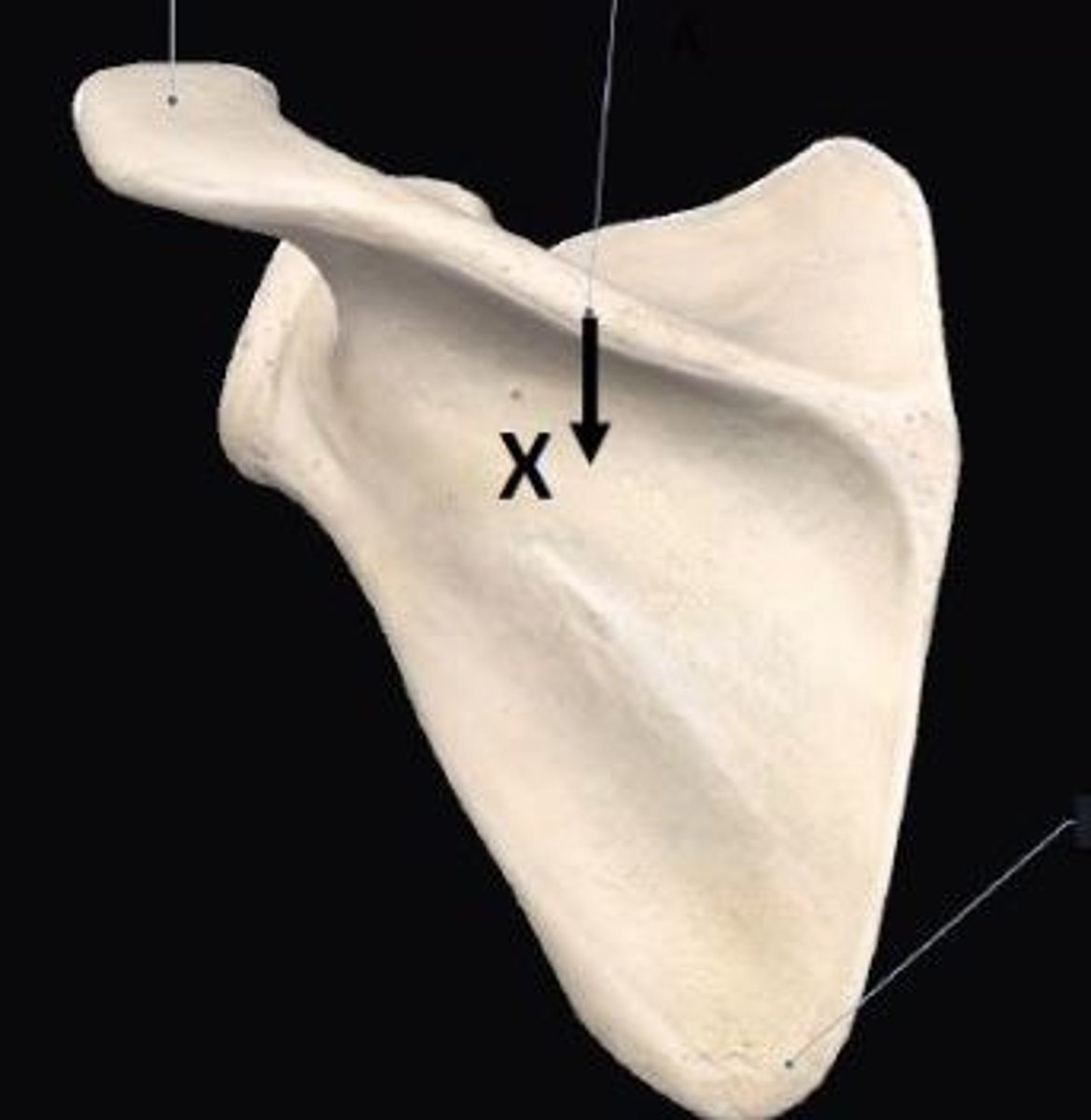
How do you classify this bone shown in this image?
Flat bone
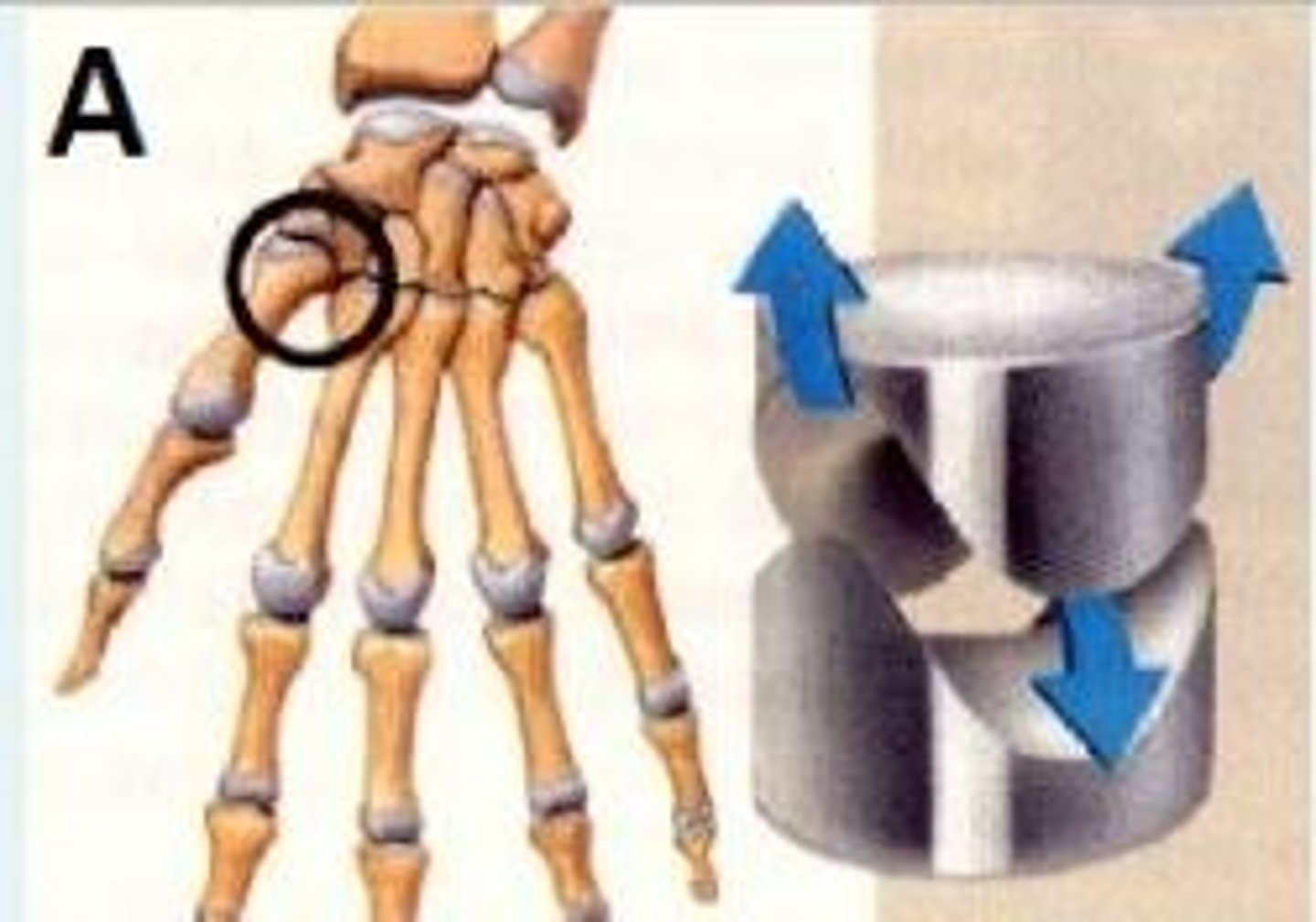
Architecturally; how do you classify the synovial joint shown in image A.
Saddle joint e.g., between trapezium carpal bone and 1st metacarpal bone
In skeletal muscle we have specialized fibres known as ___ which sense the degree of stretch and tension in the muscle.
Muscle spindles
3 multiple choice options
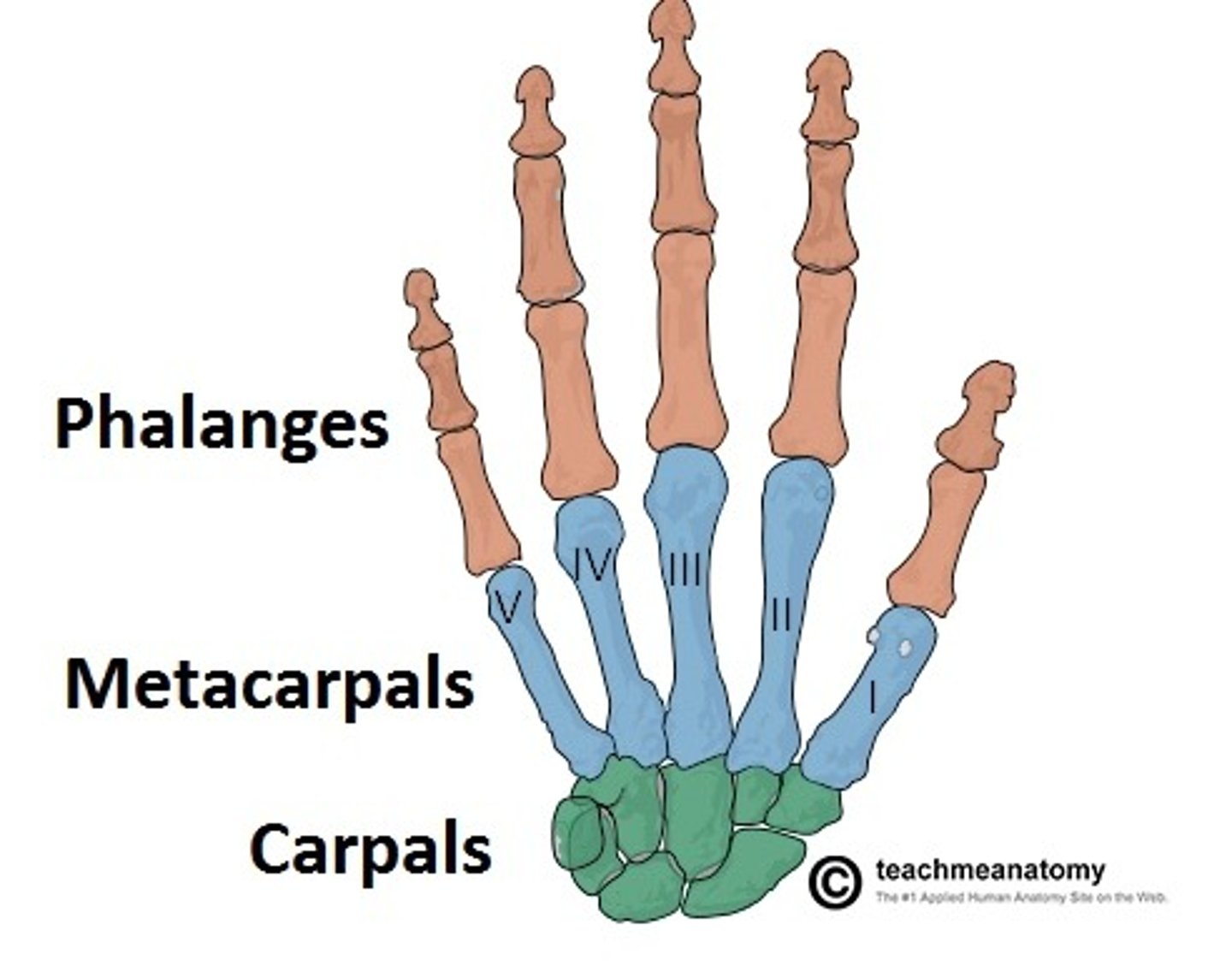
Bones of the hand
Phalanges
Metacarpals
Carpals
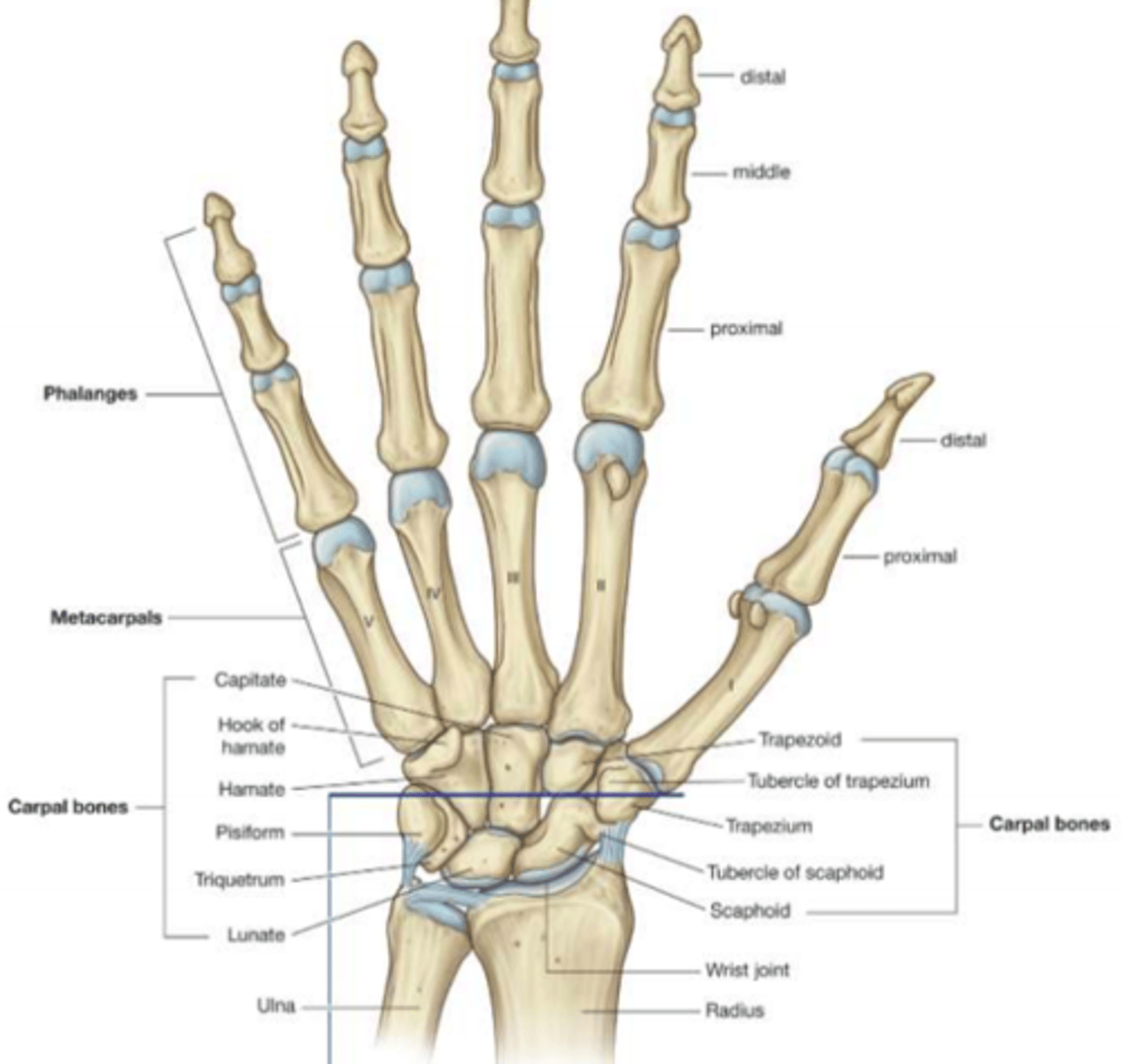
Bones of the hand (detail)
Vertebral column
Femur
Thigh bone of the leg; the longest and strongest bone in the body
Synovial joints can produce multiple movements because they are an example of a diarthrosis
List some of the movements they can produce
o Flexion
o Extension
o Abduction
o Adduction
o Internal rotation
o External rotation
o Circumduction
o Gliding
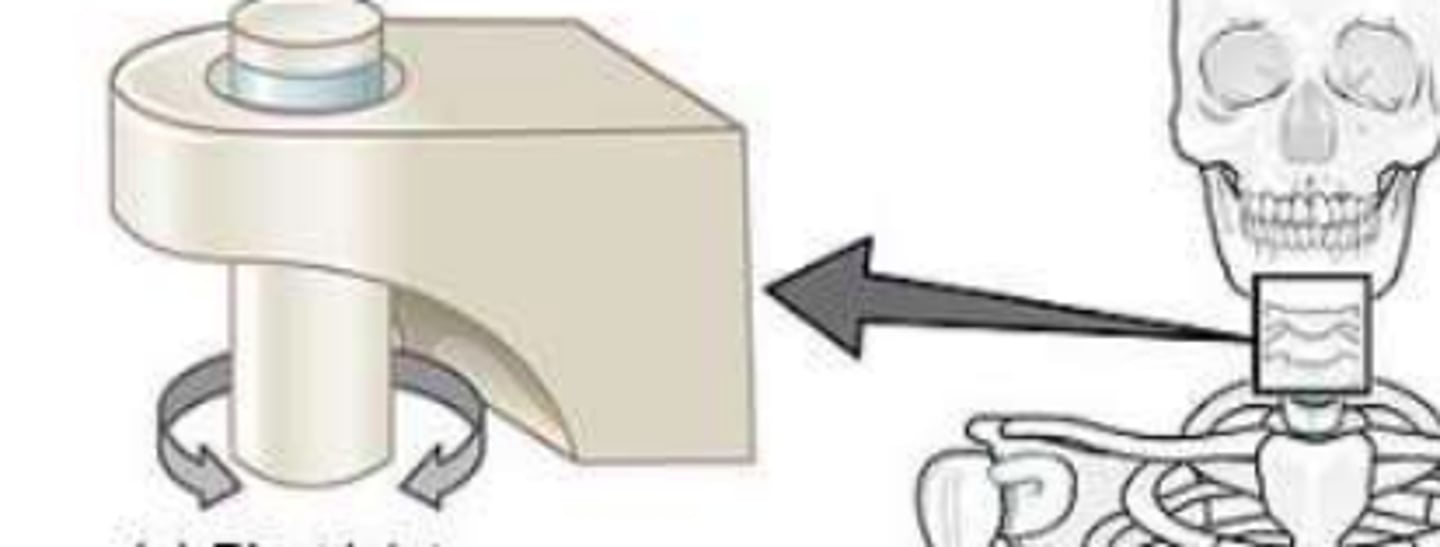
Architecturally; how do you classify the synovial joint shown in this image
Pivot joint e.g., between C1 and C2 vertebrae
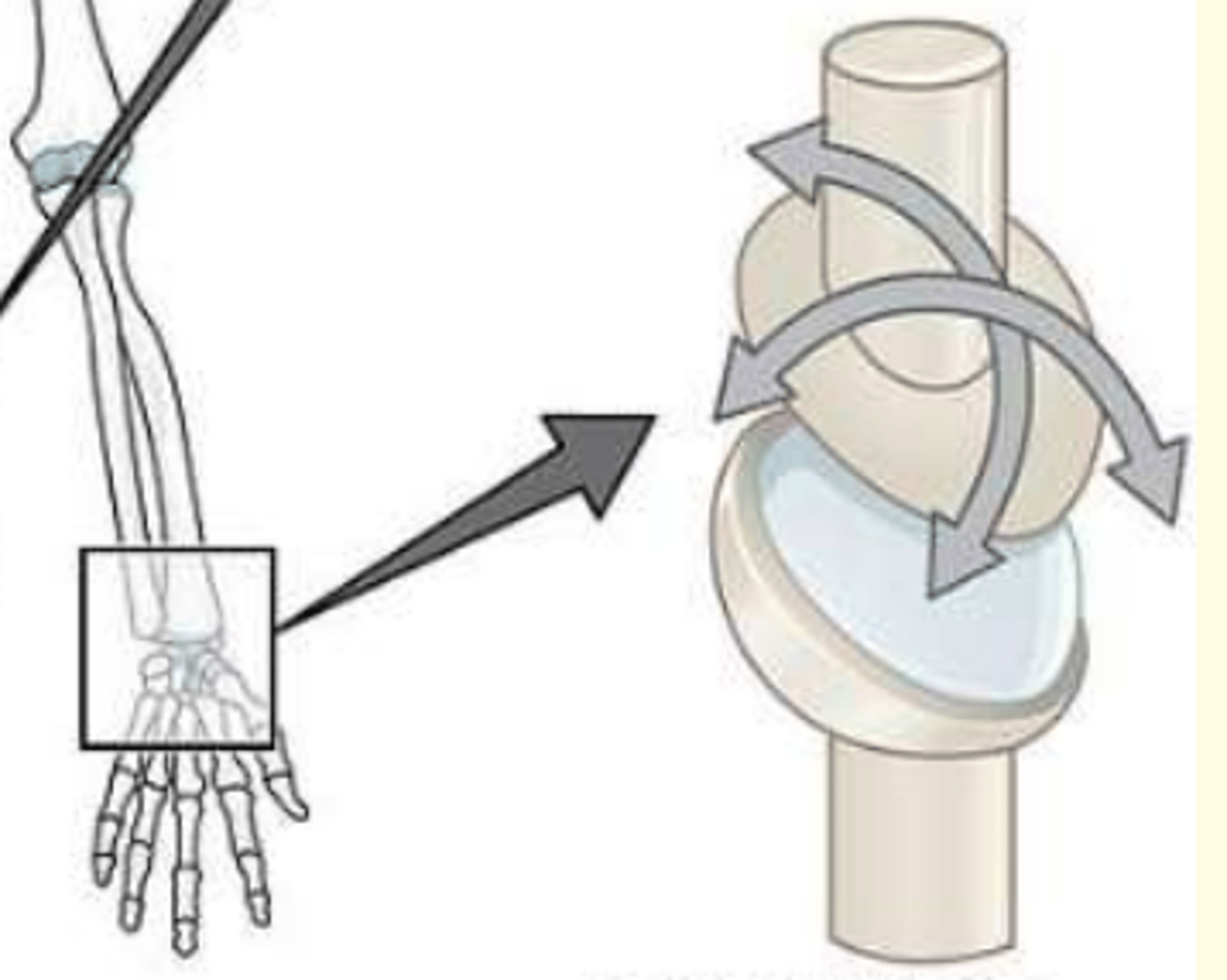
Architecturally; how do you classify the synvoial joint shown in this image
Condyloid joint e.g., between radius and carpal bones of wrist
Architecturally; how do you classify the synvoial joint shown in this image
Plane joint e.g., between tarsal bones