ICF : Block 1 : Units 9-12, 4
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
NAC: What it stands for
Network Access Control
NAC
Network security solution that allows control of access based on predefined conditions that systems must meet prior to being granted onto a network.
E.g., NAC can scan a system for operating system updates before allowing it onto a network .
Types of NAC
1) Agent-Based
2) Agentless
Agent-Based NAC
Uses software installed onto clients which authenticates the client to the NAC before scanning and allowing network access.
Types of Agent-Based NAC
1) Permanent Agents
2) Dissolvable Agents
Permanent Agent-Based NAC
Software that is permanently installed, continuously monitoring the system it's installed on.
Dissolvable Agent-Based NAC
Runs the NAC check for a current status of the system but does NOT remain installed.
Agentless NAC
Does NOT require agent software to be installed on a client. (Operates on the server side).
Authentication
Verification process where secured system access requires individuals to identify themselves and for a system to verify that they are who they say they are.
This is a popular approach for hardening a network: ensure that anyone who connects supplies valid credentials before the connection is allowed.
Authentication Factors
1) Something you know
2) Something you have
3) Something you are
4) Somewhere you are
5) Something you do
Examples of something you know to authenticate
- Password
- PIN
Examples of something you have to authenticate
- Physical tokens
- Codes sent via text
Examples of something you are to authenticate
- Fingerprints
- Voice recognitions
Examples of somewhere you are to authenticate
- GPS Location
- IP Address
Examples of something you do to authenticate
- Based on habits
- Typing patterns
MFA: What it stands for
Multifactor Authentication
MFA
Combination of any two or more different authentication factors. It is much safer than any one factor.
SSO: What it stands for
Single Sign On
SSO
Method for users to authenticate once onto a network, then are granted access to multiple systems without the need to provide additional credentials.
Advantages of SSO
For the user: they don't have to remember credentials for multiple systems.
For the administrators: they don't have to manage multiple logon credentials for every user for each server.
Disadvantage of SSO
If an account is compromised, a hacker can now access multiple servers rather than just one.
Network Security Enforcement Methods
- IEEE 802.1X
- Host Health Checks
- Terms of Usage
IEEE: What it stands for
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IEEE 802.1X Authentication
A network security enforcement method that requires users to present valid credentials on a system with agent-based NAC.
Host Health Checks
A network security enforcement method that scans a system attempting to connect to the network for OS updates, antivirus software, and host-based firewalls.
Terms of Usage
A network security enforcement method that requires users to accept terms of usage before permitting them access to the network.
AAA: What it stands for
1) Authentication
2) Authorization
3) Accounting
AAA
An information security framework used to:
- control access to data and system resources
- enforce policies
- audit actions
Identification
Presenting information about yourself to a system, like a username or keycard.
Difference between identification and authentication
Identification: you claim to be someone (e.g., you type in your username)
Authentication: the validity of your claim to be that someone is determined (e.g., you type in your password and hit login)
Authorization
Determines what a user has the authority to do and access.
Accounting
Tracks and records users' access time, bandwidth usage, and use of system resources with system logs.
AAA Protocols
1) RADIUS
2) DIAMETER
*FS
RADIUS: What it stands for *NT
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service
*NT
RADIUS *NT
Allows clients to access a network remotely through UDP to a RAIDUS server.
*NT
UDP: What it stands for *NT
User Datagram Protocol
*NT
DIAMETER: What it stands for *NT
No acronym, it's just called DIAMETER.
*NT
DIAMETER *NT
Newer AAA protocol that gives a more reliable and secure communication service through TCP.
*NT
TCP: What it stands for *NT
Transmission Control Protocol
*NT
Application Security
Ensuring the integrity of software.
Application Vulnerabilities
1) P2P File Sharing
2) XSS
P2P: What it stands for
Peer to Peer
P2P File Sharing
An application vulnerability where users can share files online through P2P file sharing applications. Common method of transmitting malicious code.

Scripting
A computer script has a list of commands to be performed by a program or scripting engine, automating processes on a computer or generating web pages. Makes modifications to a system without user input.
Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
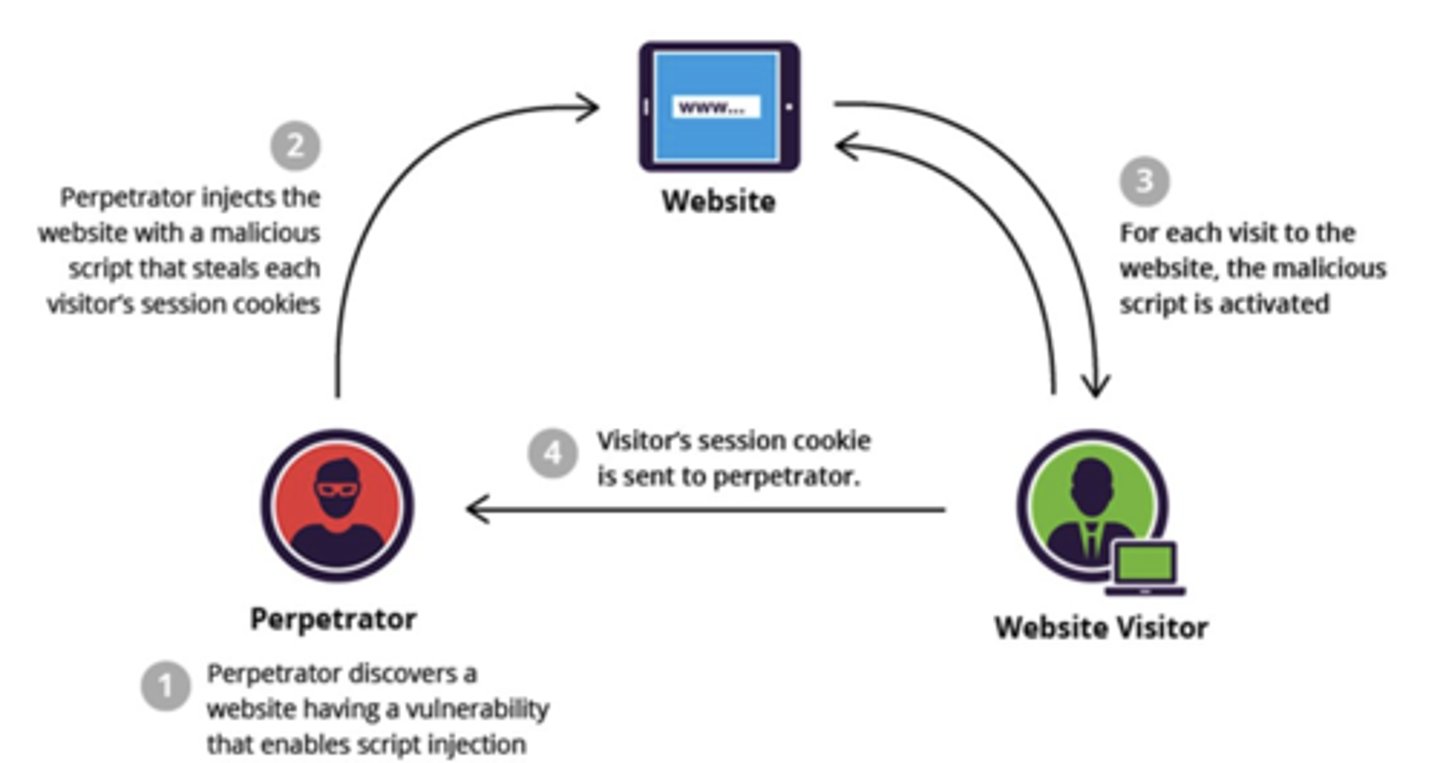
An application vulnerability where malicious code is injected into a website.
E.g., this can trigger compromising user accounts, activating Trojan horses, misleading users into revealing private data, and stealing session cookies to impersonate users.
Application Vulnerability Prevention Methods
1) Apply Software Patches.
2) Application Configuration Baseline.
3) Application Hardening.
4) Cross-Site Request Forgery Prevention.
Apply Software Patches
An application vulnerability prevention method where any software being used is kept up to date to patch out vulnerabilities (applications and OS's).
Application Configuration Baseline
An application vulnerability prevention method where the software that your network uses should be configured with security in mind.
Any options that can be modified to make the application more secure should be done, as long as necessary functionality is not impeded.
Application Hardening
An application vulnerability prevention method where you disable unnecessary application features.
Cross-Site Request Forgery Prevention
An application vulnerability prevention method to prevent websites that reference another web page that take the user’s unexpired cookies for authentication; “Remember Me” should be disabled in the browser.
Hardware Security Threats
1) Boot Sequence Threats
2) Removable Storage Threats
3) Theft
Host Intrusion Control Types
1) IDS
2) IPS
*FS: these can be either host-based (HIDS/HIPS) or network-based (NIDS/NIPS)
IDS: What it stands for
Intrusion Detection System
IDS
Detects suspicious activity on a host or a network, logs it, and alerts system or network administrators.
IPS: What it stands for
Intrusion Prevention System
IPS
Monitors hosts or networks for suspicious activity and takes corrective actions.
Hardware Security
Vulnerability protection that comes in the form of a physical device.
Boot Sequence Threats
Hardware security threat that interferes with the boot sequence.
How to prevent Boot Sequence Threats
Enable the "Secure Boot" and "Trusted Boot" settings from within the BIOS to prevent malware and corrupted components from loading as Windows is starting up.
Removable Storage Threats
Hardware security threat that comes in the form of USB drives and external hard drives; they are an easy way to store and carry information.
How to prevent Removable Storage Threats
1) Alerts
(e.g., on many bases, plugging a USB drive in will trigger a Host Based Security System (HBSS) alert & offender will lose network access rights)
2) Physically disable ports or restrict physical access to data systems.
*USB data ports are disabled on DoD computers to prevent data theft and to prevent worms from spreading.
Theft
Hardware security threat: devices are investments and must be protected (e.g., laptops, switches, routers, monitors, removable storage drives).
How to prevent Theft
Facilities should be protected through limited physical access.
- Access to server rooms should be controlled to protect routers, switches and servers.
- Portable devices can be secured with lockdown cables and secured to desks.
- Removable media and removable drives should be stored in a locked safe, cabinet or drawer.
Hardware Encryption
Uses chips physically installed in the system and applies very complex encryption more quickly than software encryption.
Types of Hardware Encryption
1) Storage Drive Encryption
2) FDE
Storage Drive Encryption
Permanent & removable storage devices, such as hard drives & USB drives, can and should be encrypted.
FDE: What it stands for
Full Disk Encryption
FDE
Encrypts an entire hard disk drive in case of theft or loss.
FDE Types
1) TMP
2) HSM
*FS
TPM: What it stands for
Trusted Platform Module
TPM *NT
*NT: Stores cryptographic keys used to encrypt data, located on the motherboard.
(e.g., BitLocker encrypts your files and saves the keys in the TPM; without the BitLocker key, an encrypted Windows 7 machine cannot boot up).
HSM: What it stands for
Hardware Security Module
HSM *NT
*NT: Stores crypto processors on a separate card installed on a system.
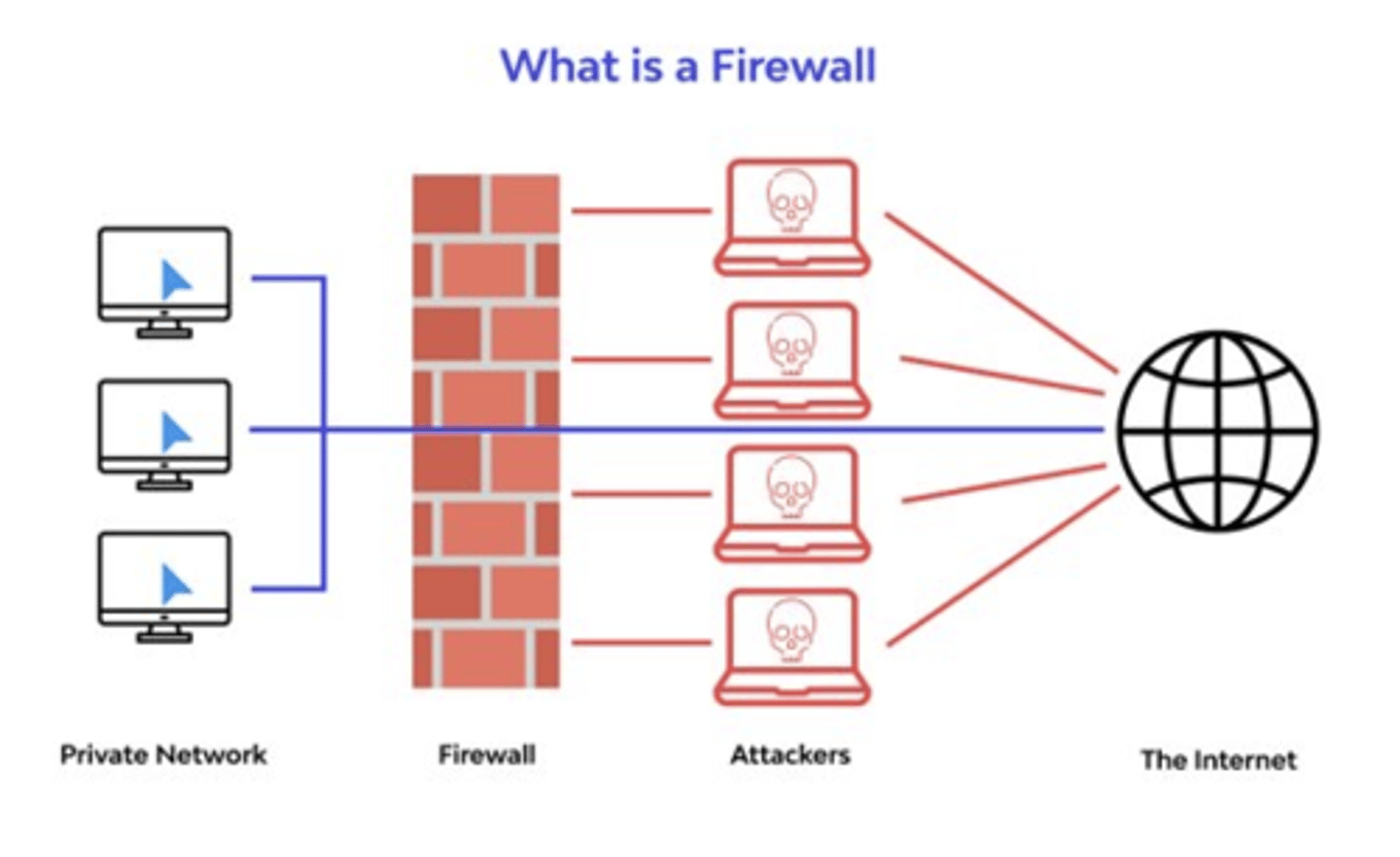
Firewalls
Hardware or software that protects computers and networks from outside systems on the other side.
Allowlisting
Denying everything by default and only allowing trusted traffic into the network.
Denylisting
Allowing everything by default and only blocking known bad traffic from entering the network.
Allowlisting vs Denylisting
Allowlisting is more secure than denylisting but requires the user to sacrifice accessibility and ease of use.
Software-Based Firewall
Piece of software that is installed on a single system to protect it.
Software-Based Firewall Features
1) Blocks incoming and outgoing traffic; packets sent to/from the system from a host on the network or internet can be blocked.
2) Notifications; shows message if someone tries to connect to your system or if an application tries to send data out.
3) Default rule; denies all traffic except the packets you specify.
4) Create rules; allows you to add rules on top of the default rule to customize what traffic is permitted/denied to enter/leave the system.
What Software-Based Firewalls are also known as
1) Application-based firewalls
2) Host-based firewalls
3) Personal firewalls
Windows Firewall
The software firewall that comes with Windows OS. Its features include:
- Allow a Program or Feature through
- Change Notification Settings
- Turn Windows Firewall on/off
- Restore Defaults
- Advanced Settings
Hardware-Based Firewall
Stand-alone appliance that acts as a secure gateway between devices inside the network perimeter and those outside.
Hardware-Based Firewall Features
1) More Efficient
- Funnel protection through single point
- Don't consume processing power of a host device
- Ideal for medium-large networks
2) More Complex: require more knowledge to configure and manage.
Types of Firewalls
1) Packet filtering
2) Stateful inspection
3) Application Layer
Packet-Filtering Firewall
Filters based on source/destination IP/Port.
AKA: Stateless Firewall
*FS: least advanced
Stateful Inspection Firewall
Checks if the packet is part of a new or ongoing communication.
E.g., allow all outbound packets, but only allow inbound packets in response to outbound requests.
*FS: mid advanced

Deep Packet Inspection
Understands how protocols operate and can view packet contents to provide filtering.

Application Layer Firewall
Combines Packet, Stateful, Application, and Deep Packet Inspection. Can also include IDS/IPS and anti-malware.
AKA: Next Generation
*FS: most advanced
Firewall Security Zones
Segmenting a network into zones to control communication between them for protection.
Main Security Zones
1) Private Zone
2) Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
3) Public Zone
*FS
Private Zone
Security zone that can only be accessed by authorized users. This is where the LAN should be placed; no traffic from other networks is sent to the private LAN.
AKA: private zone, private LAN, or intranet zone
LAN: What it stands for
Local Area Network
DMZ: What it stands for
Demilitarized Zone
DMZ
Security zone that occupies the space between two firewalls. Allows selected traffic from Internet to pass through its external firewall. This is where you place any servers that need to be reached by the public (web, SMTP, FTP, or DNS).
Internal firewall (private side) does not allow any traffic originating from the public to pass through it.
Public Zone
Security zone that has any network not controlled by the admin (i.e., the Internet).
ESD: What it stands for
Electrostatic Discharge
ESD
Sudden flow of electricity between two charged objects.
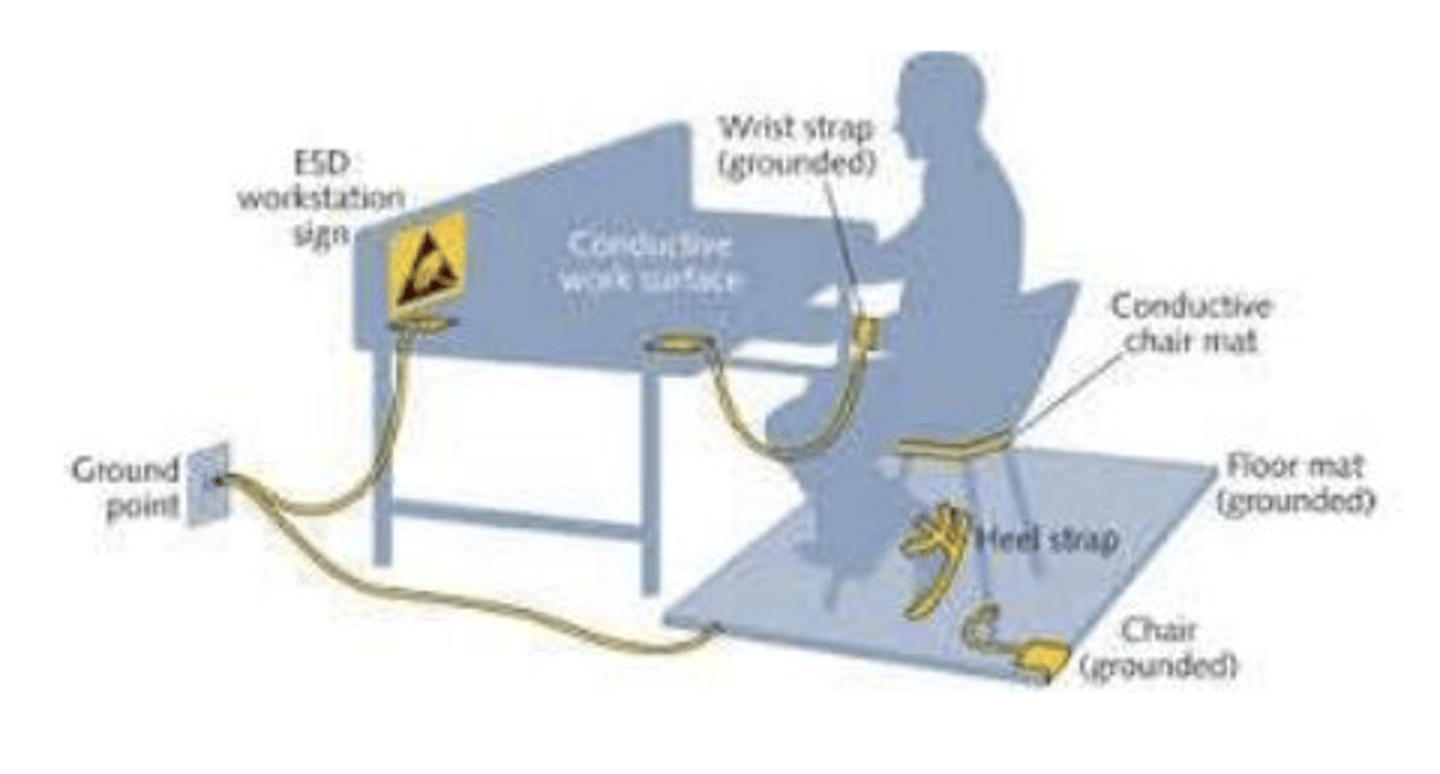
Ways to avoid ESD
1) Grounding
2) Bonding
Grounding
Provides a path for electric charges to flow safely into the ground, avoiding ESD.
Bonding
Minimizes potential differences between conductive objects, avoiding ESD.