Chapter 2: Brain Structures
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
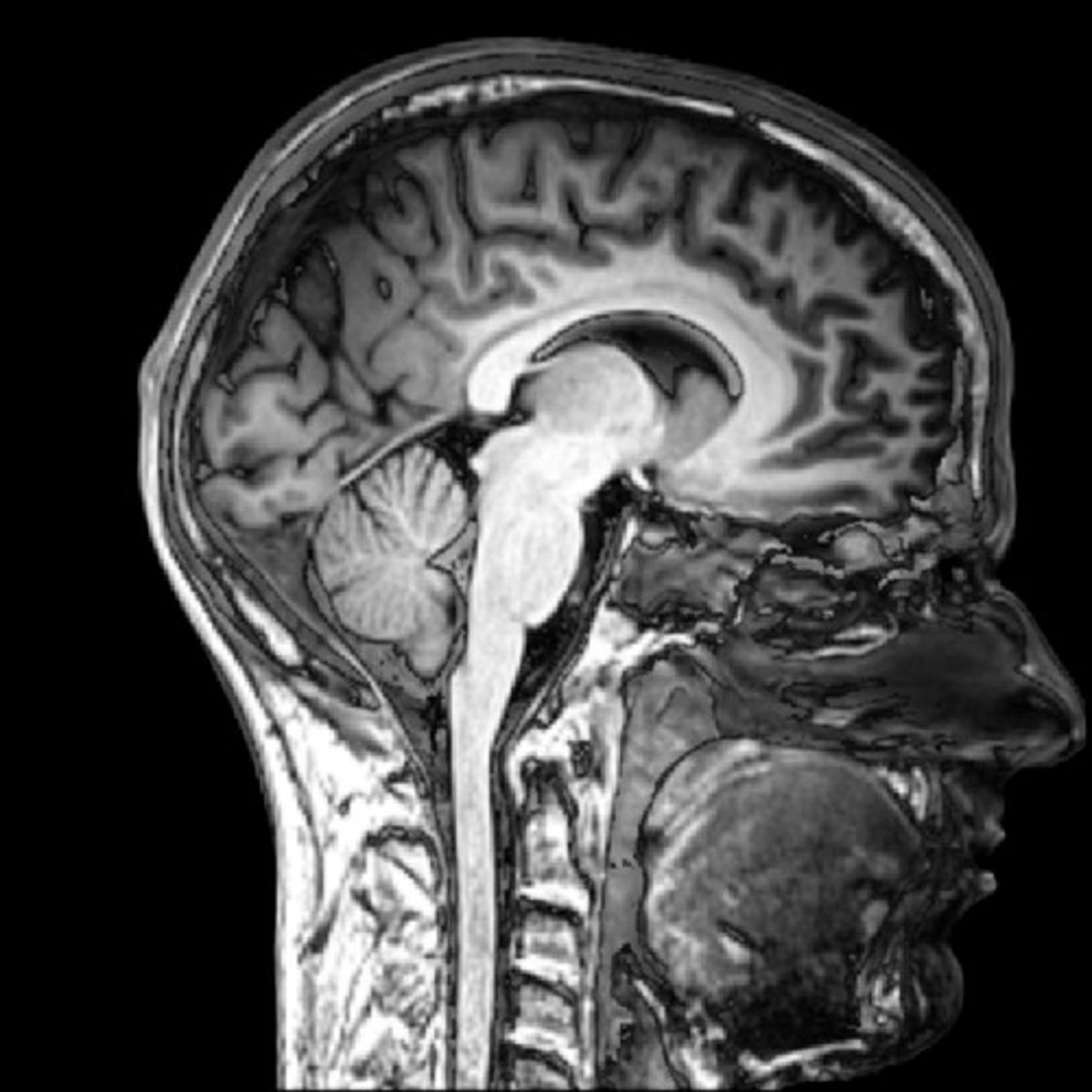
MRI
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain
PET scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
fMRI
A technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans.
CAT scan
a method of creating static images of the brain through computerized axial tomography
EEG
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
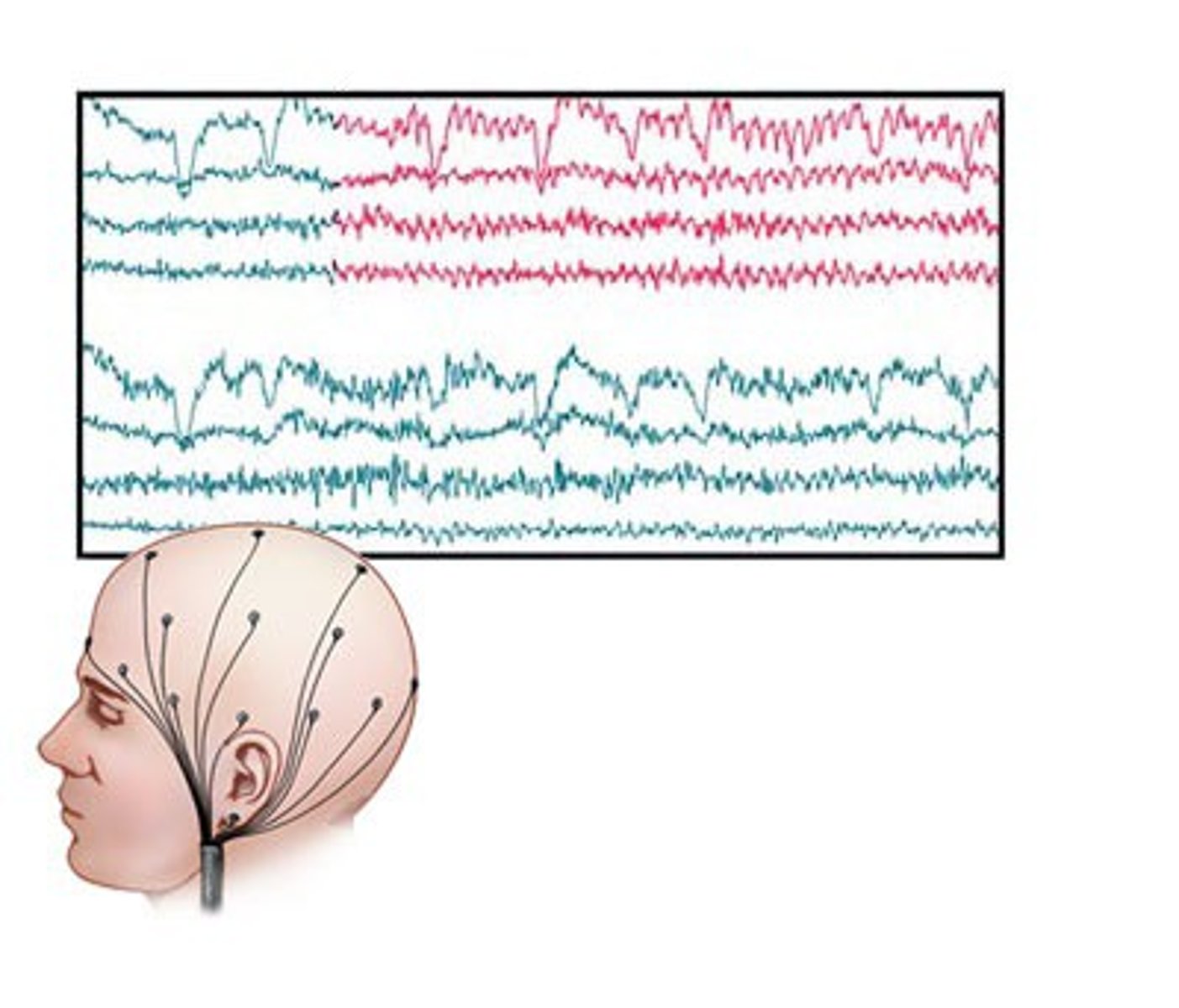
Phineas Gage
railroad worker who survived a severe brain injury that dramatically changed his personality and behavior; case played a role in the development of the understanding of the localization of brain function
Phrenology
the detailed study of the shape and size of the cranium as a supposed indication of character and mental abilities.

Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
a semipermeable network of cells in the lining of the capillaries of the brain that prevent harmful substances from entering. Researchers working to treat brain diseases such as Parkinson's must develop drugs that are capable of crossing the BBB. If a drug can't cross the BBB, it will not be able to effect the problem inside the brain.
cortical localization
The notion that different functions are located or localized in different areas of the brain; also called localization of function.
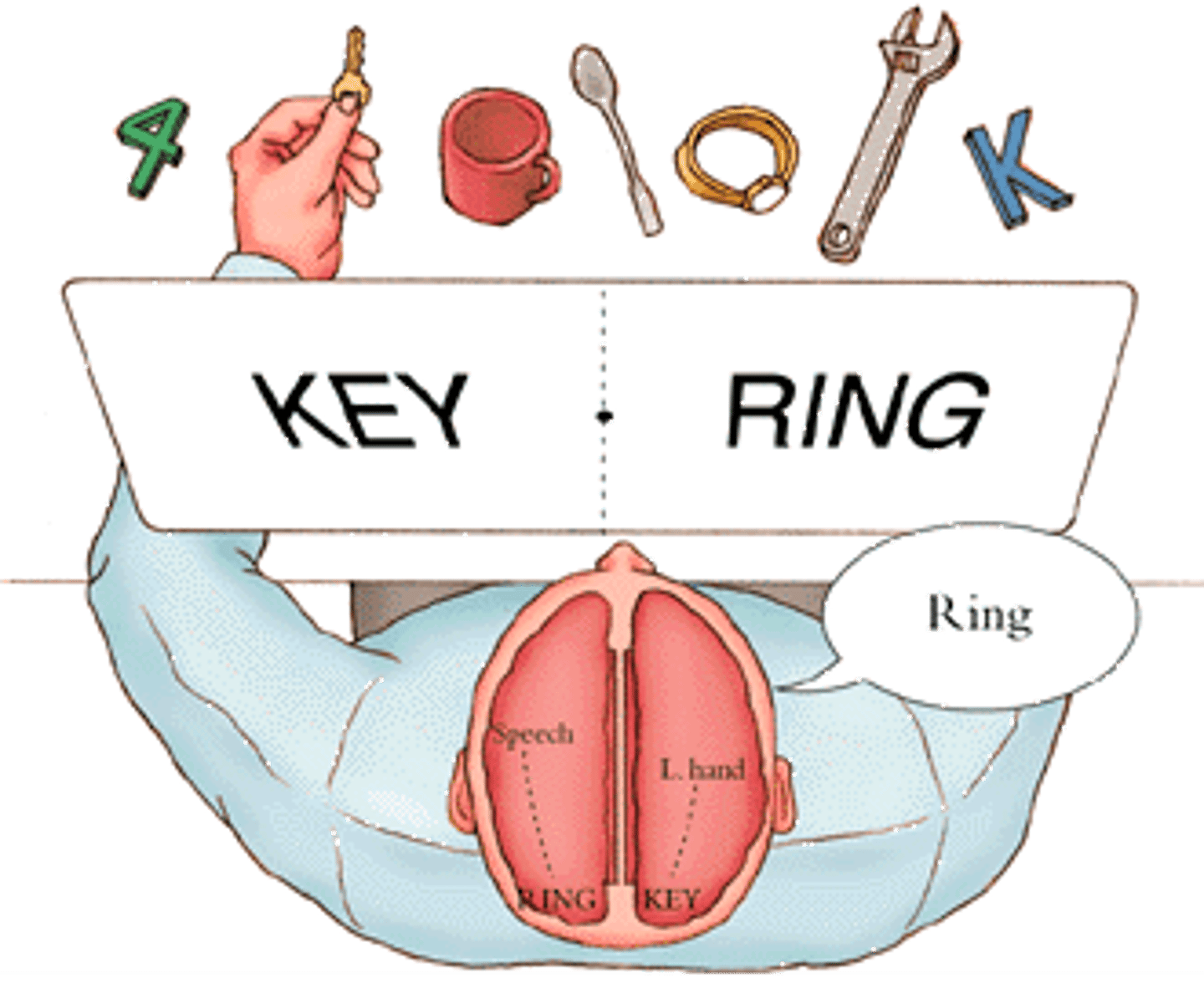
left hemisphere
Controls the right side of the body. Associated with language and logical thinking abilities
lateralization of function
the notion that specific psychological or cognitive functions are processed primarily on one side of the brain
spatial ability
capabilities associated with visual and mental representation and manipulation of objects in space. This is a right hemisphere brain function
right hemisphere
controls the left side of the body; creative, intuitive, spacial
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
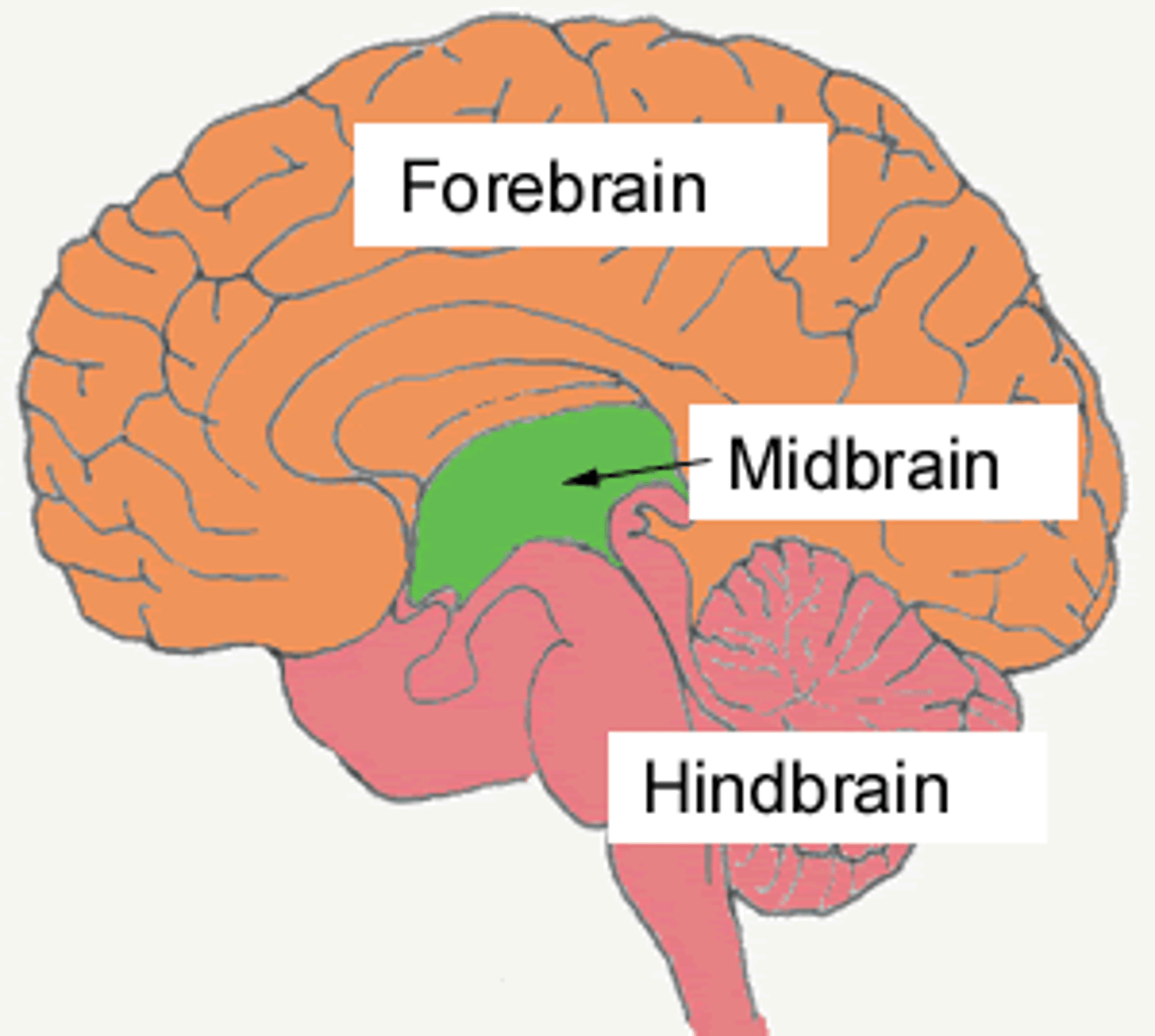
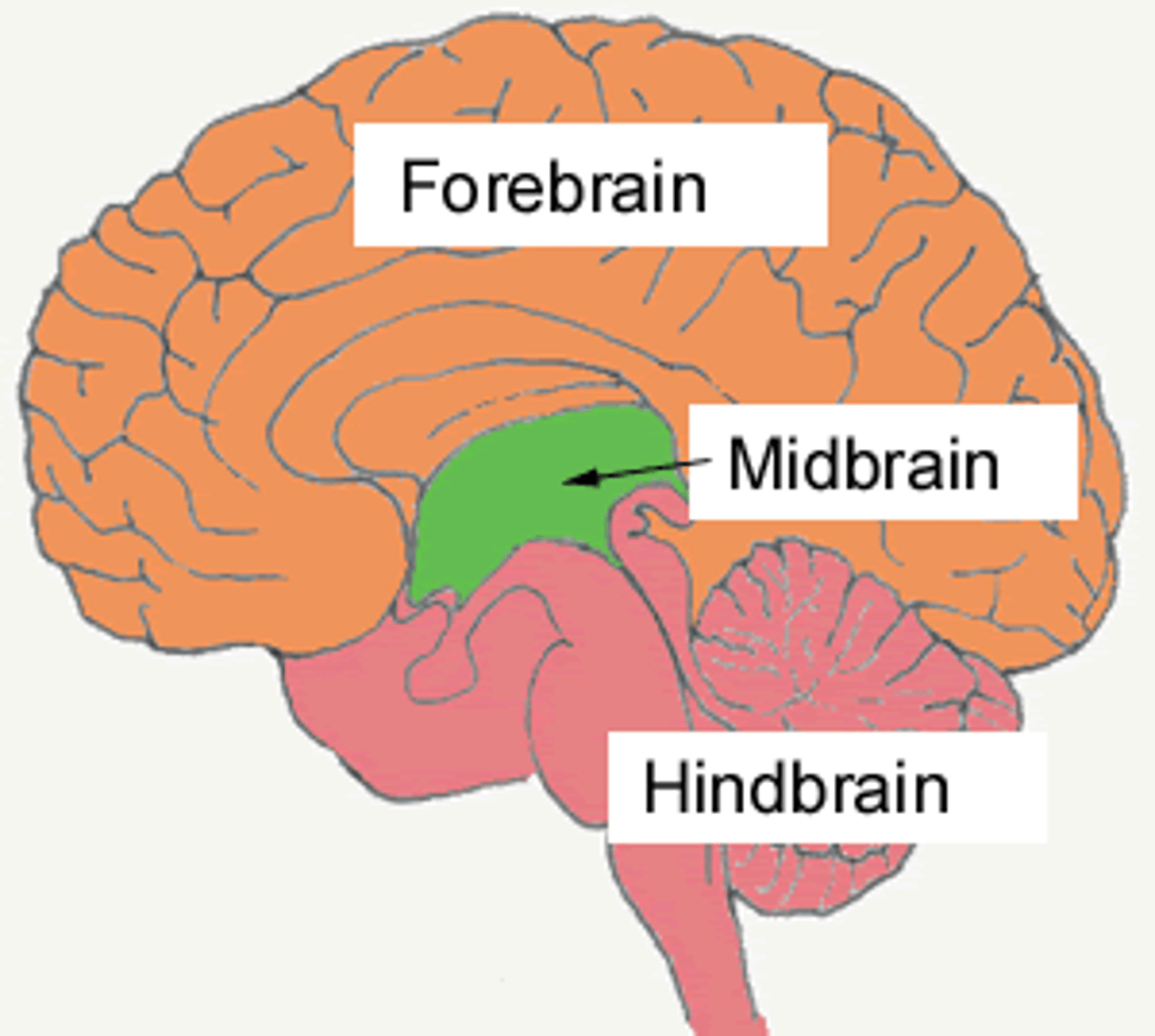
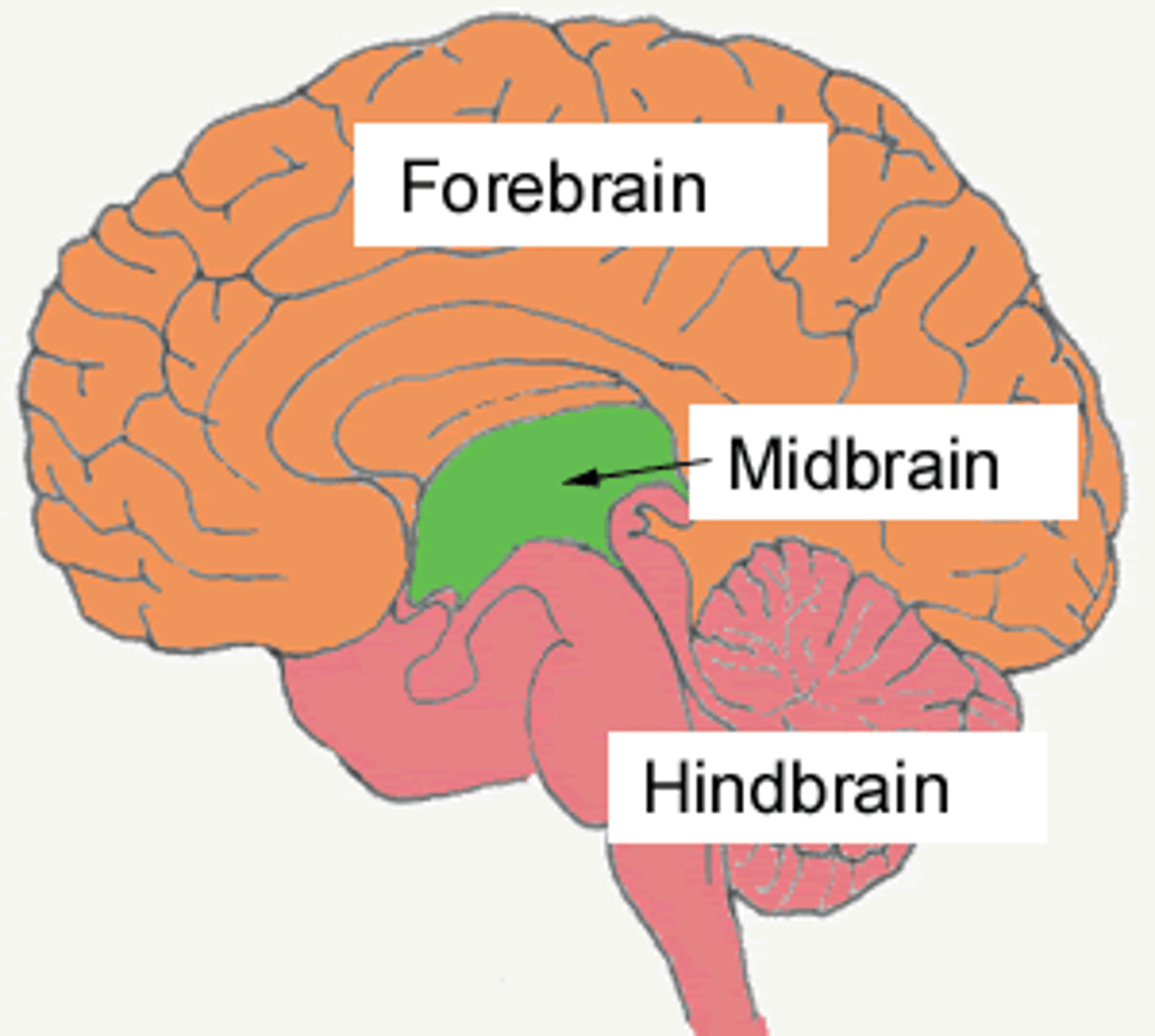
forebrain
The largest and most complex brain region, which contains centers for complex behaviors and mental processes also called the cerebrum
cerebral cortex
the wrinkled outer portion of the forebrain, which contains the most sophisticated brain centers
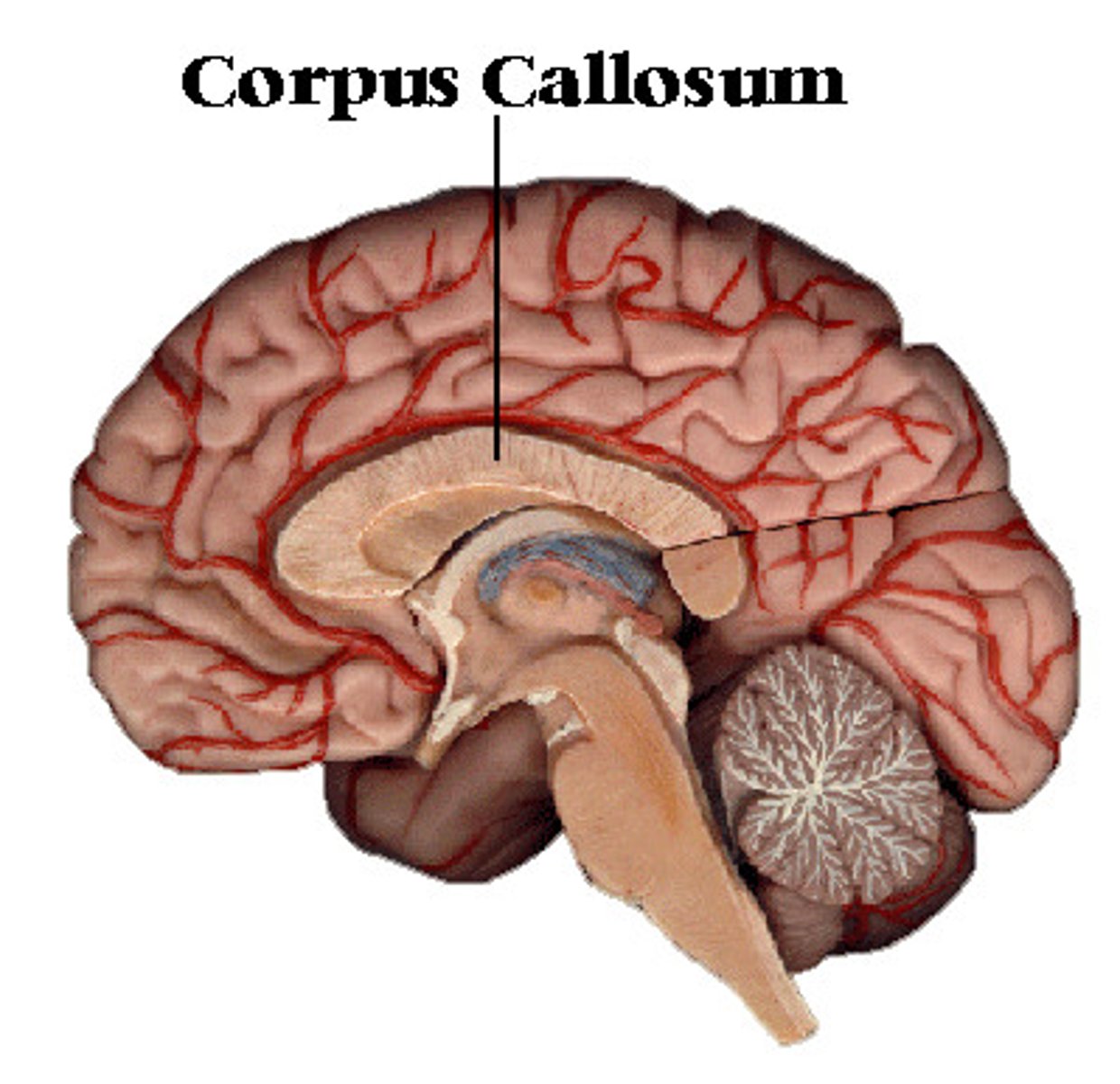
corpus callosum
A thick band of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres and acts as a communication link between them.
mnemonic: the corpus callosum allows the left hemisphere to "call" the right and communicate
split brain surgery
procedure that involves severing the corpus callosum to reduce the spread of epileptic seizures
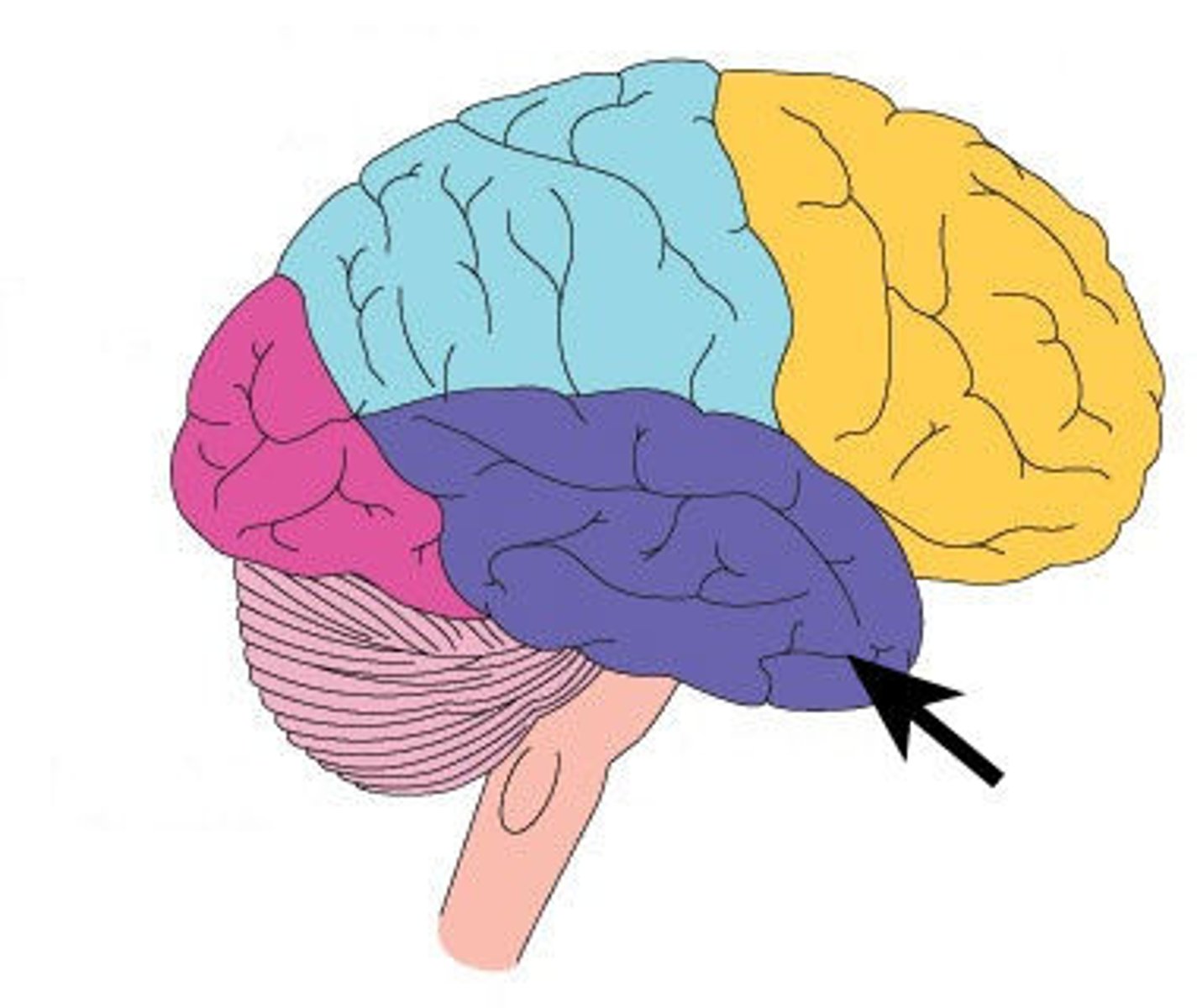
Temporal Lobe
process auditory information
mnemonic: Tempo in music is the speed of the song. Think tempo, sound, and auditory info when you see temporal lobe.
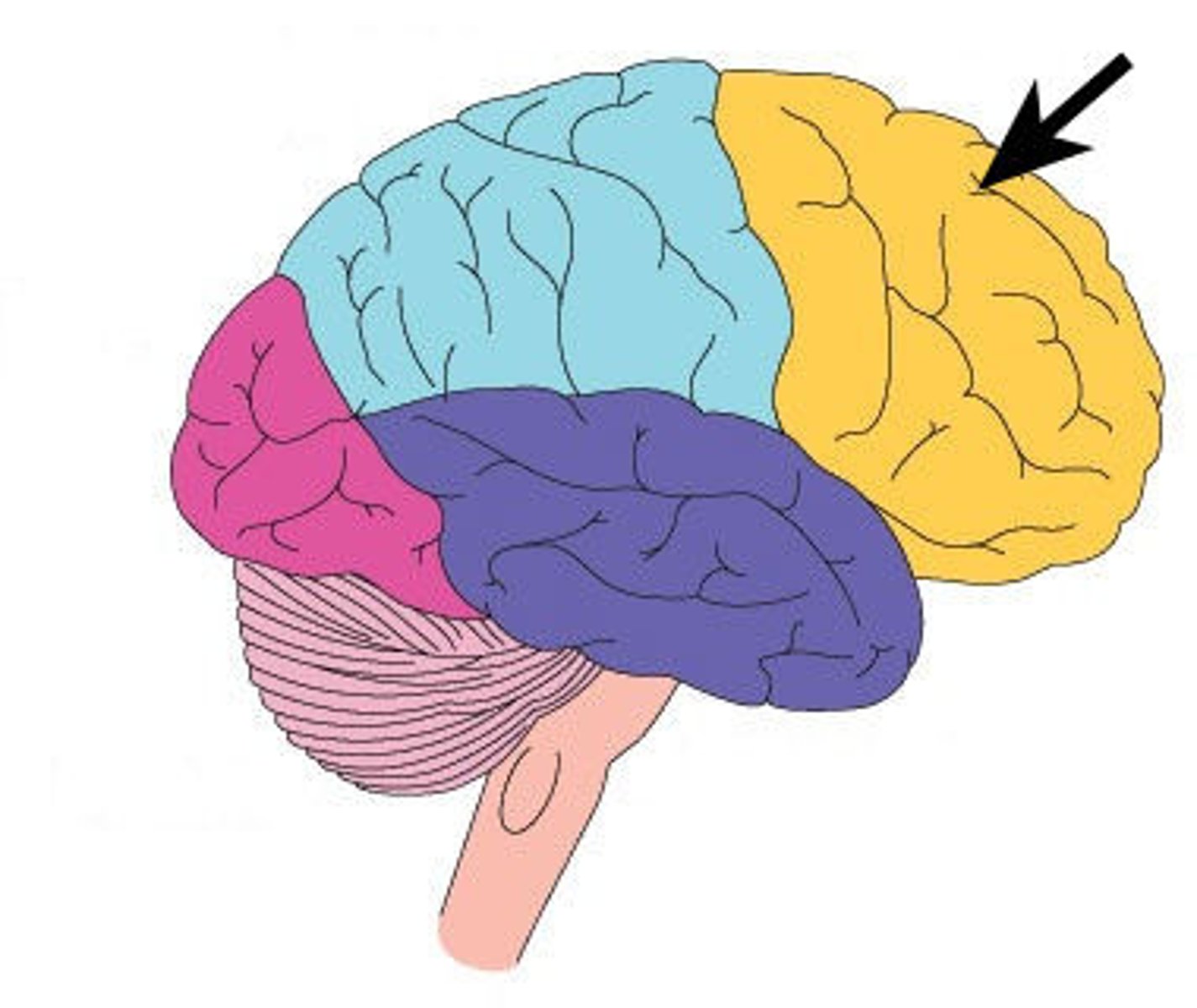
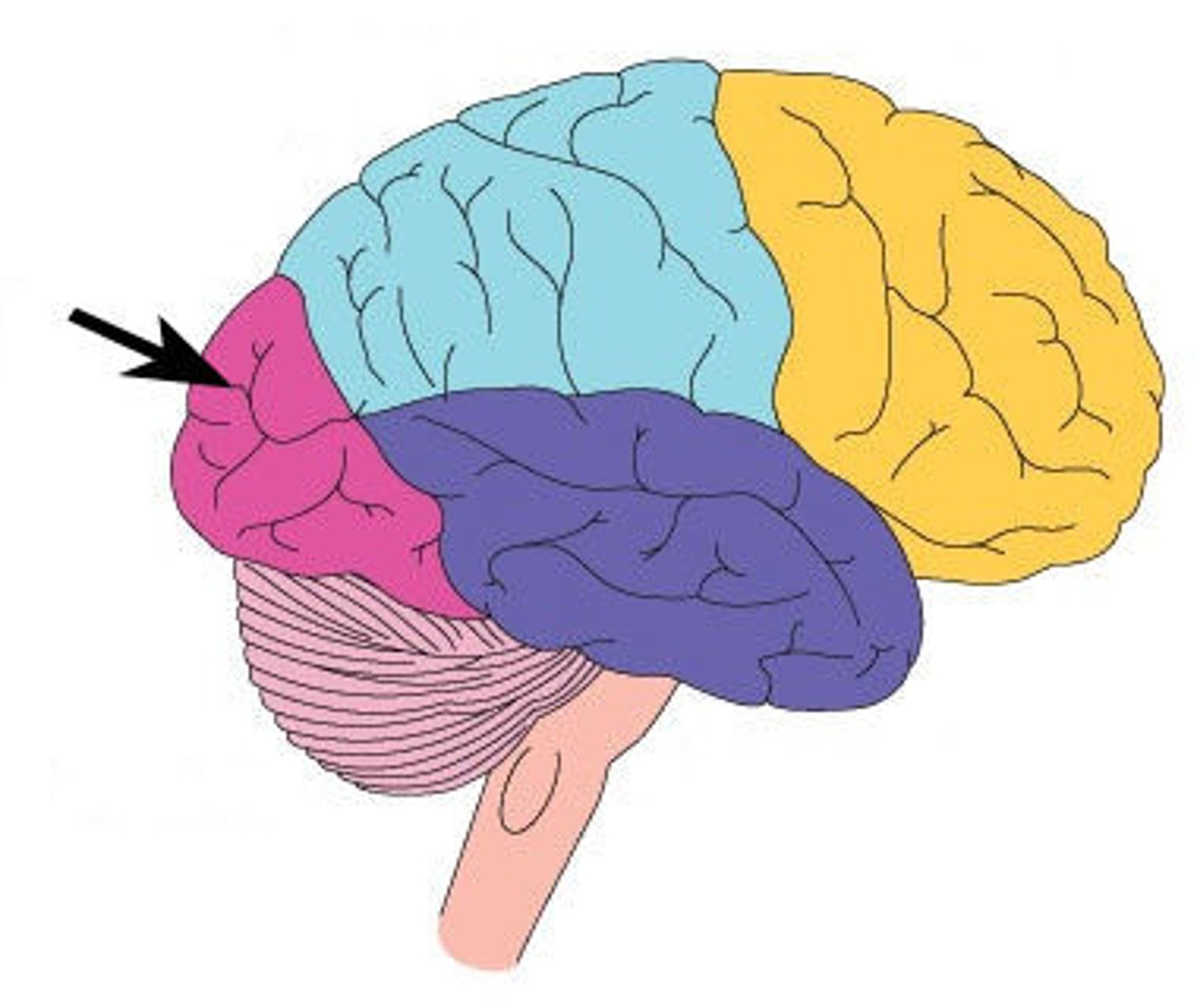
Frontal lobe
largest lobe; processes voluntary muscle movements, involved in thinking, planning, and emotional control. The left prefrontal cortex is the most sophisticated planning and thinking area.
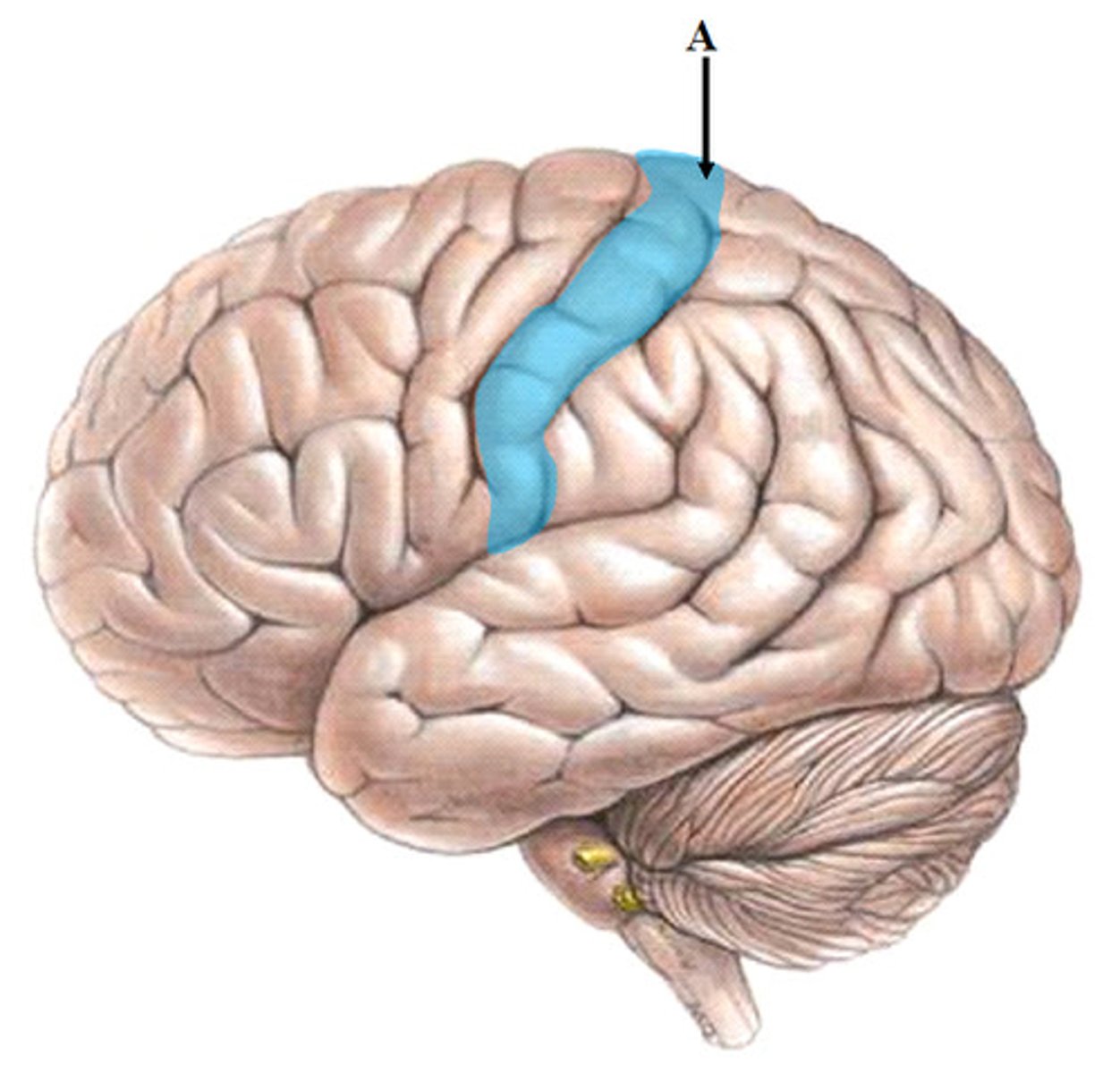
motor cortex (primary motor cortex)
Controls voluntary movement. Located on the frontal lobe.
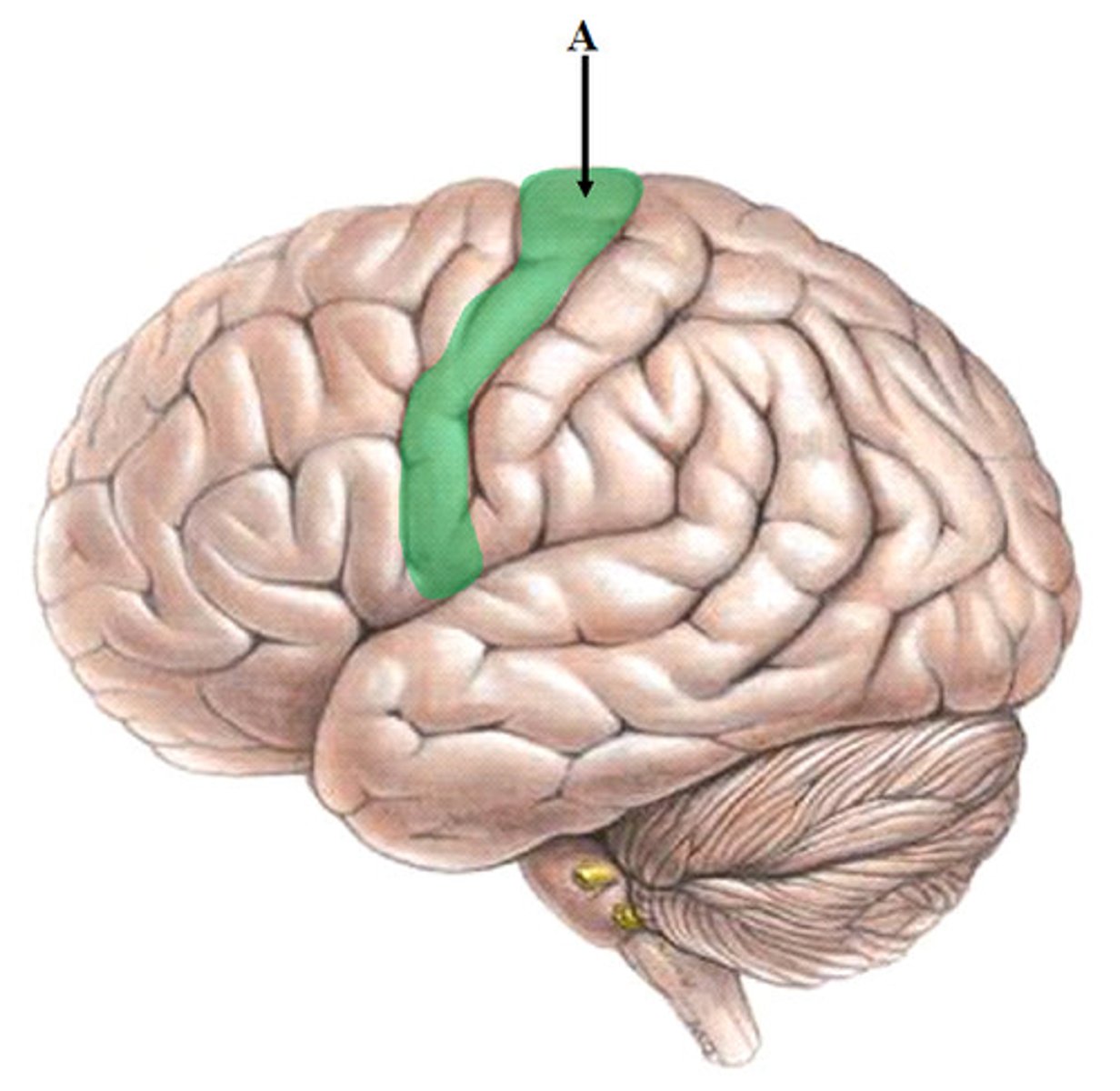
somatosensory cortex (sensory cortex)
Receives information about body sensations. Located on the parietal lobe.
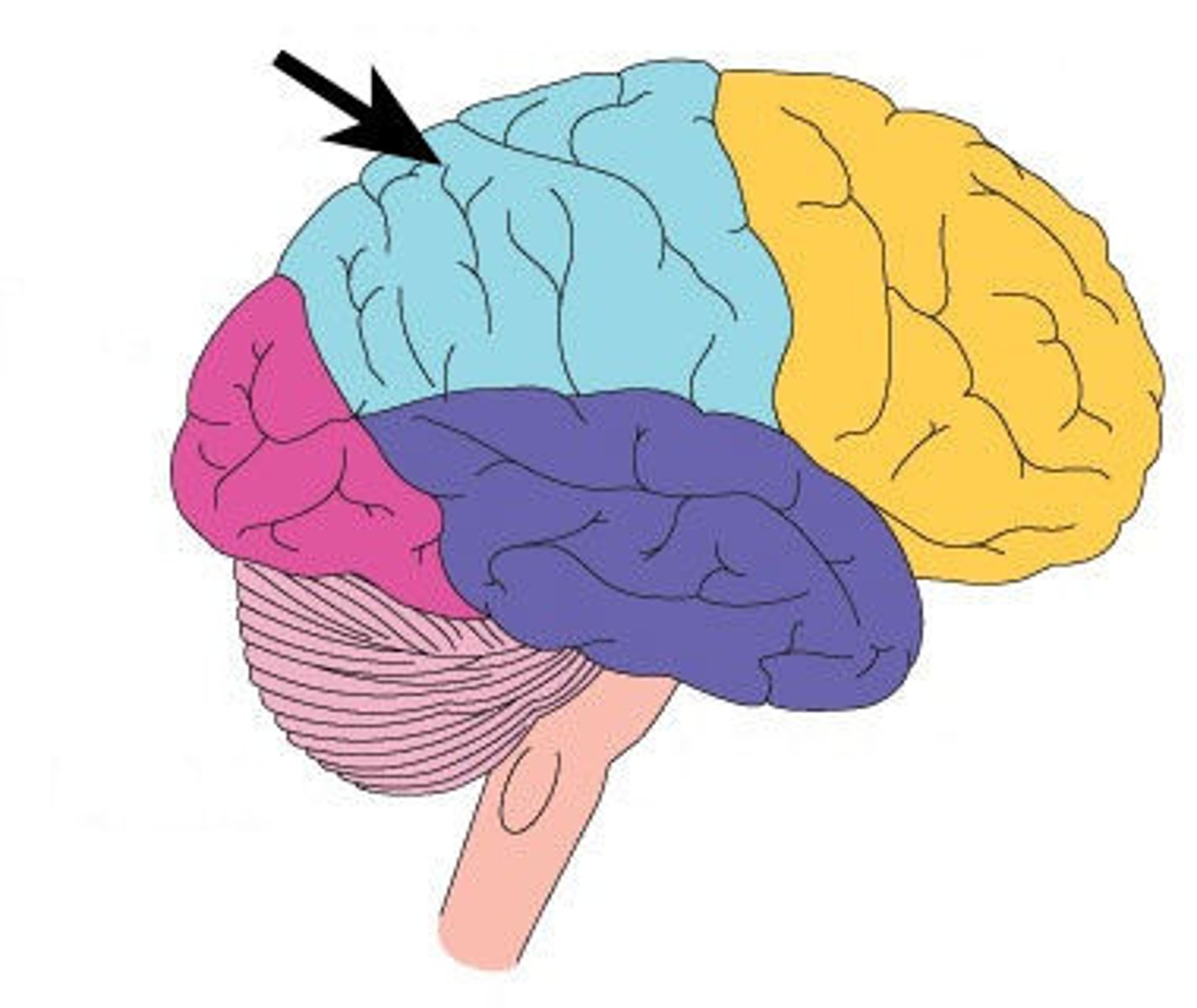
Parietal lobe
Processes sensations such as temperature, pressure, and information from muscles and joints
mnemonics: Parietal lobe processes sensations such as pressure. Use alteration to think of "P"arietal and "P"ressure.
Think of parietal as the "parental" lobe. Parents put pressure on you to do well and the parietal lobe processes things such as pressure.
occipital lobe
Processes visual information
mnemonic: Think of occipital and the word "optic"
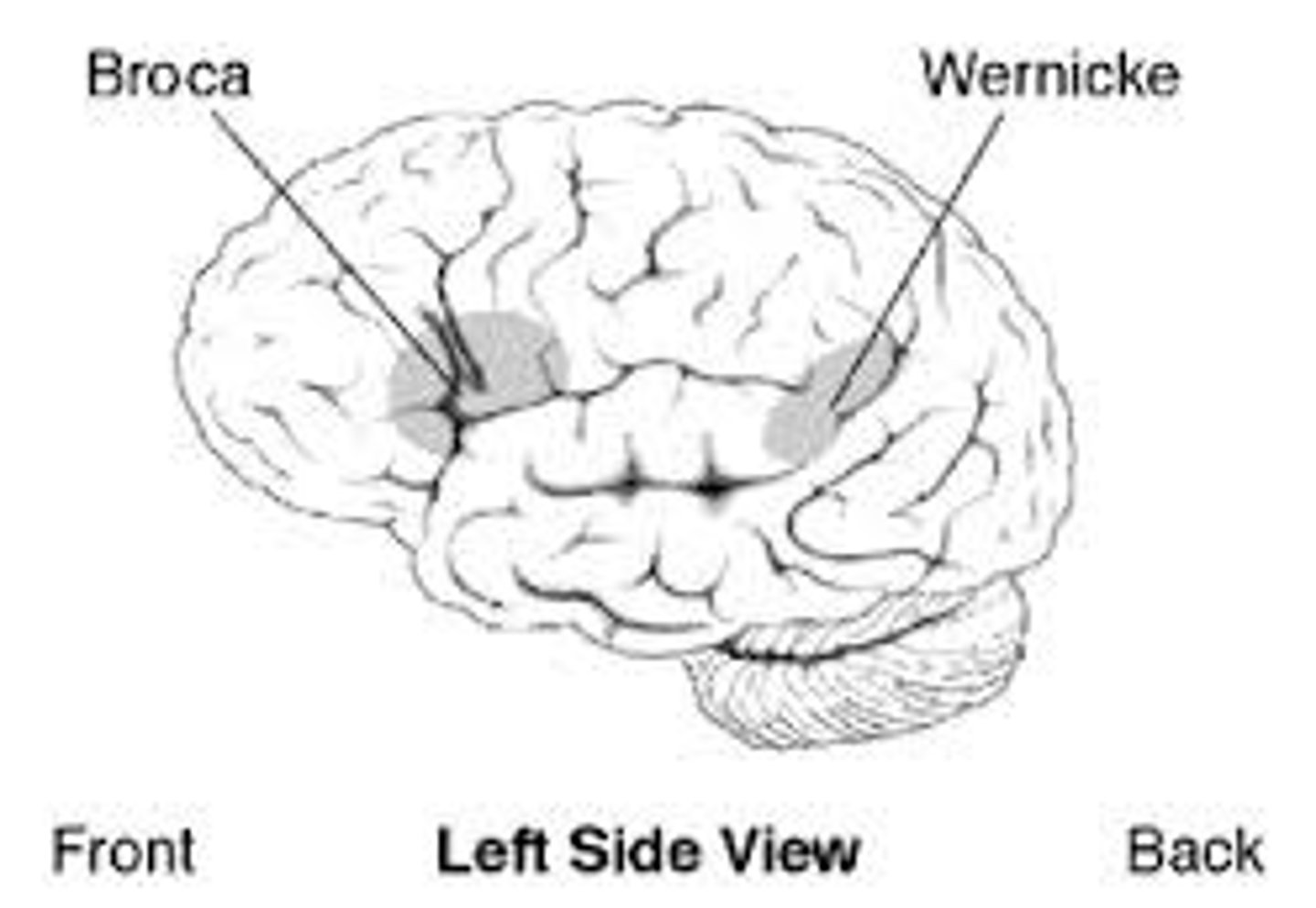
Broca's area
speech production
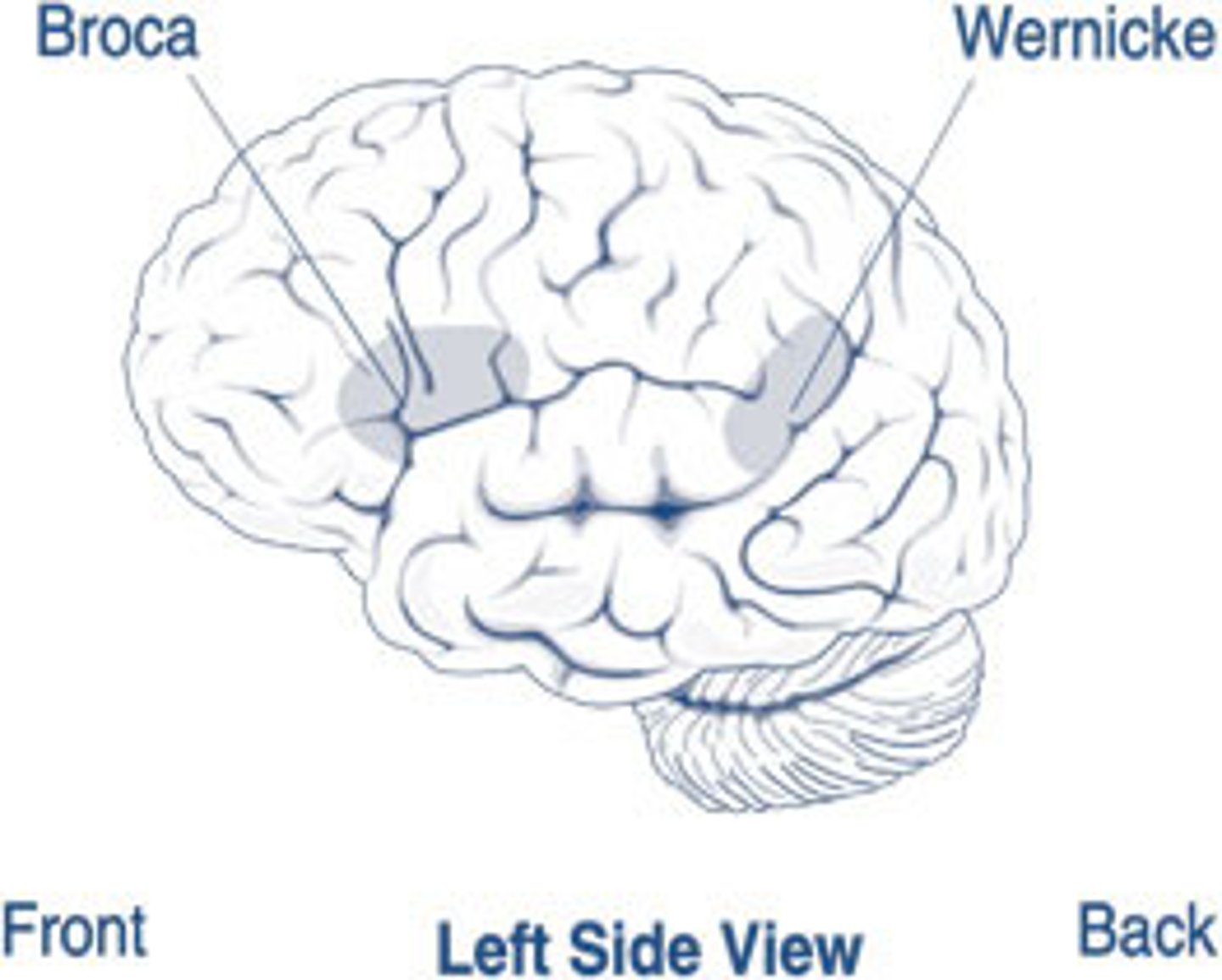
Wernicke's area
language comprehension
midbrain
Relay station for auditory and visual information
Helps localize sound
Substantia Nigra is a midbrain area for movement and has a large concentration of Dopamine receptors
aphasia
Impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca's area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke's area (impairing understanding).
Broca's aphasia aka productive aphasia limits speaking ability, where Wernicke's aphasia aka comprehensive aphasia limits language comprehension.
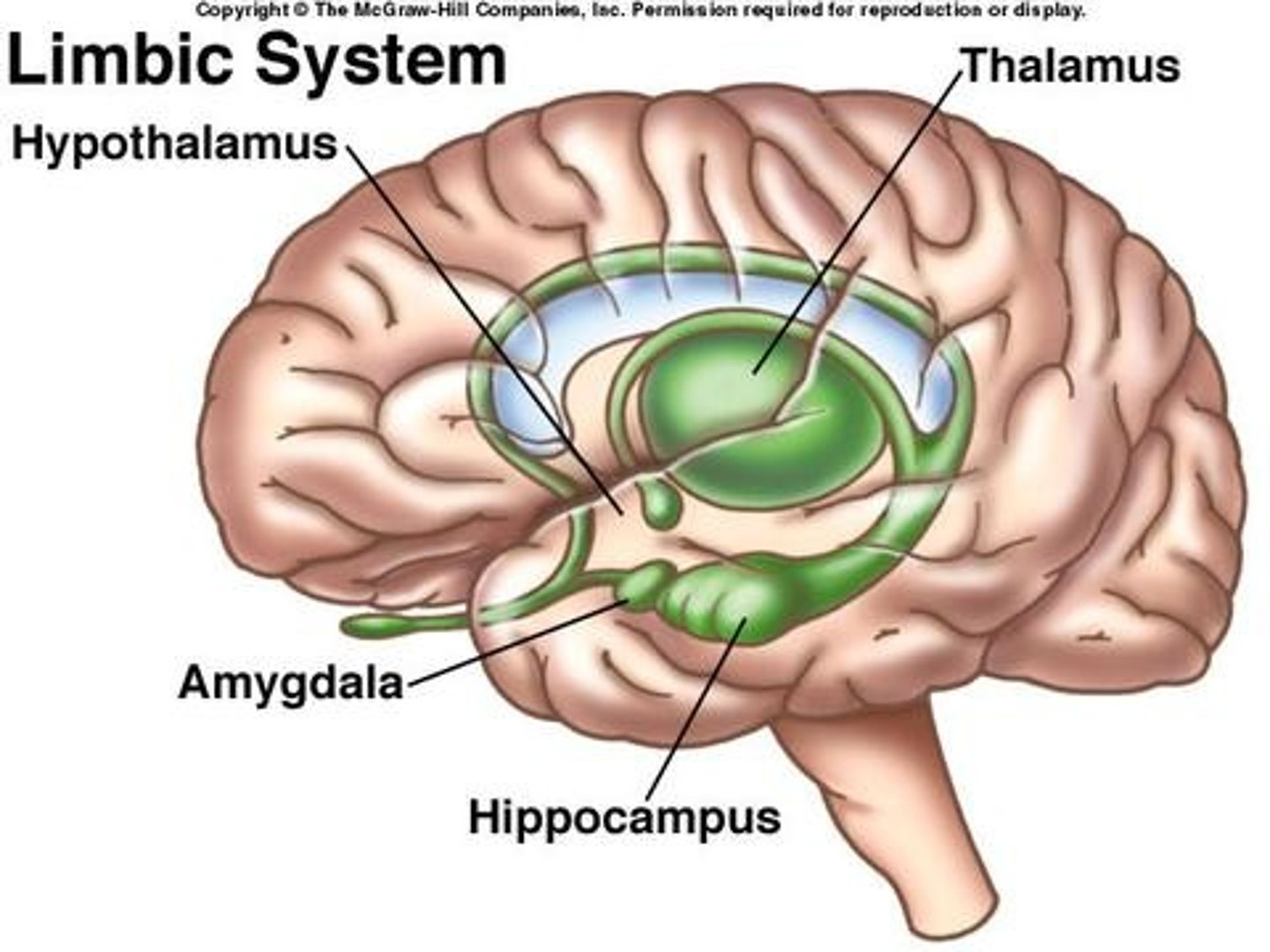
Limbic system
A group of forebrain structures that form a border around the brainstem and are involved in emotion, motivation, learning, and memory. The hippocampus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and thalamus are all a part of the limbic system.
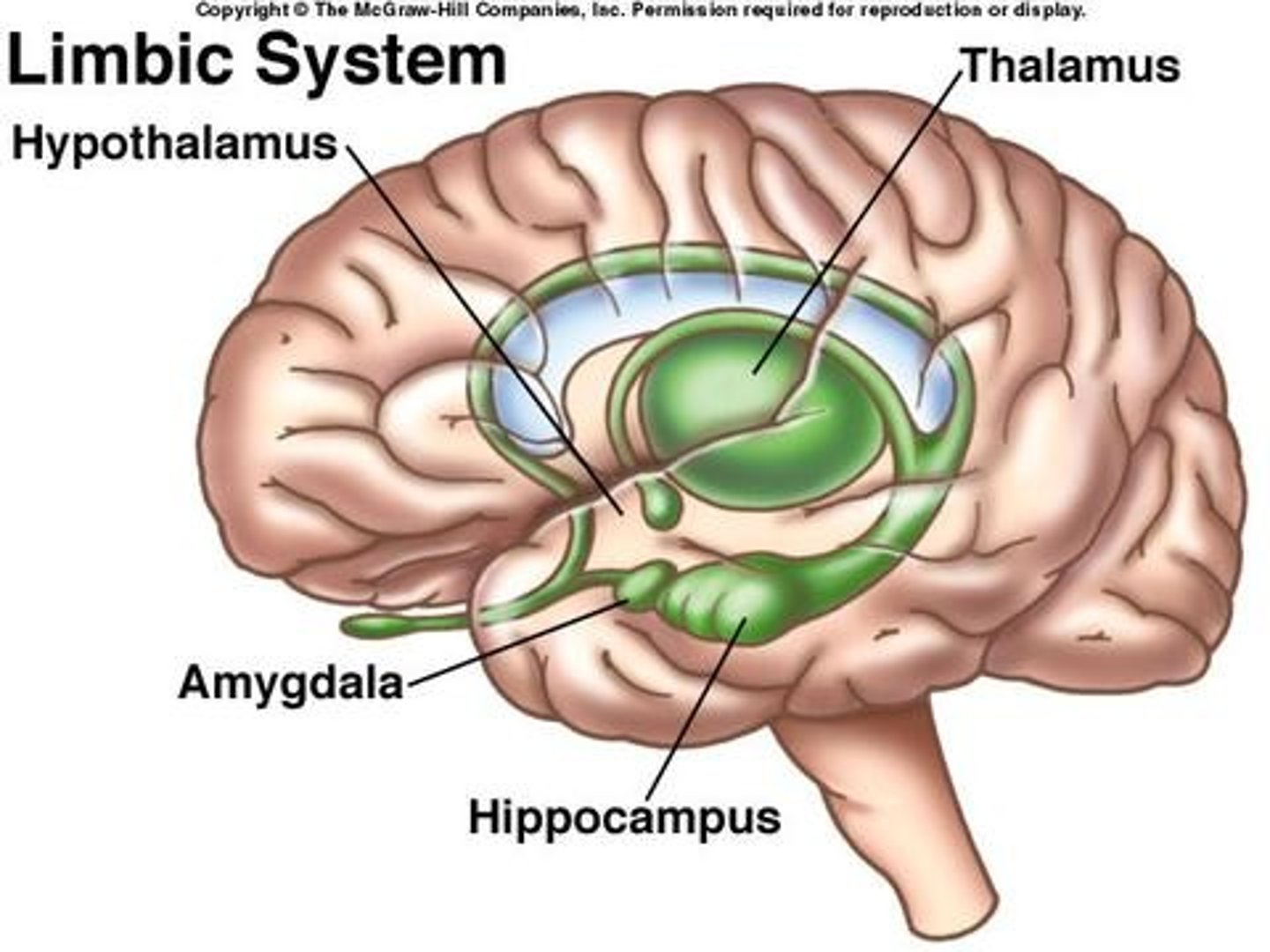
Amygdala
involved in emotion and memory, "fight or flight"
Mnemonics: "A"mygdala and "A"ngry
"Amy is angry"
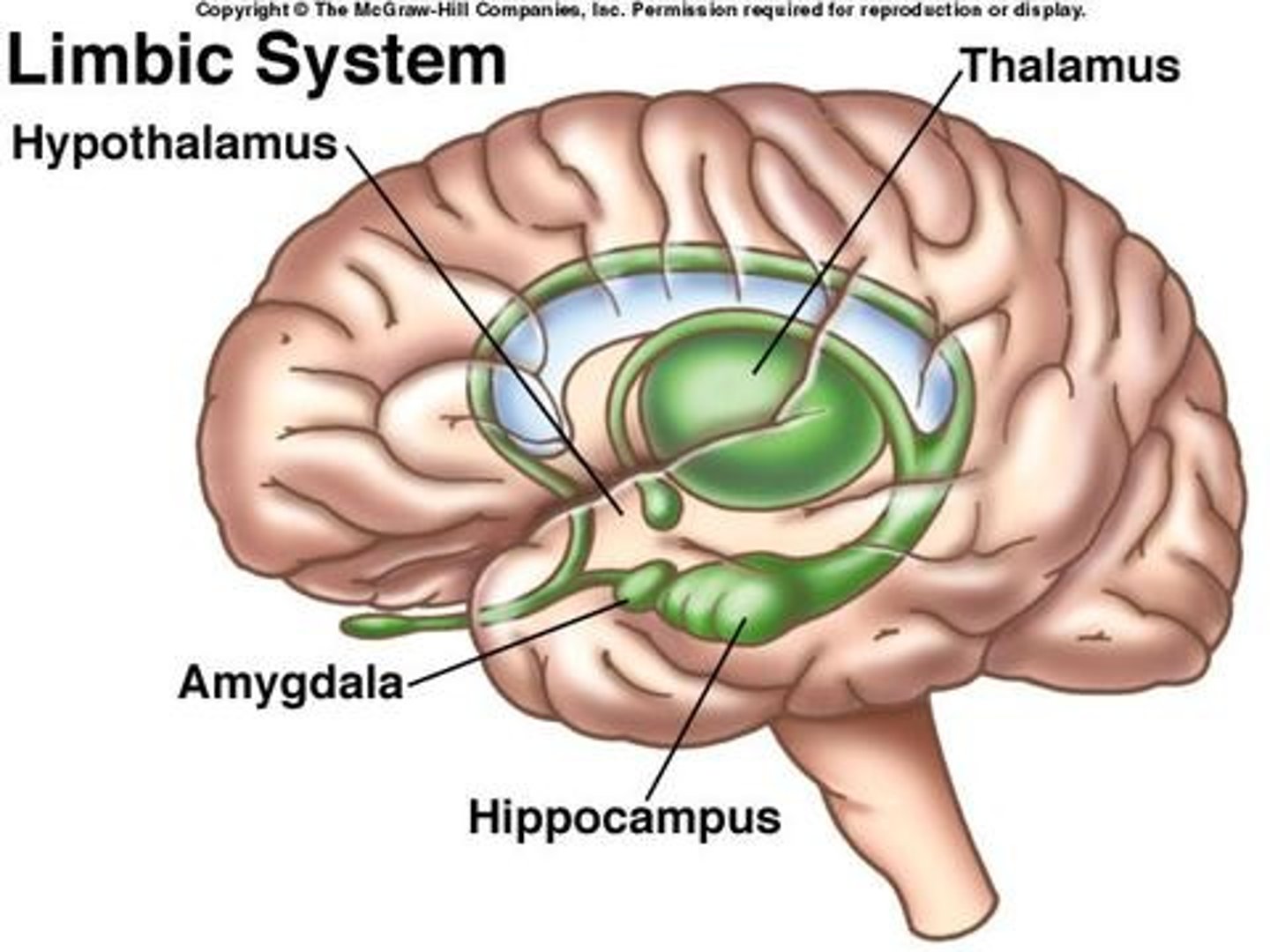
hippocampus
involved in forming new memories
Mnemonic: You might form new memories on your college campus using your hippo"campus"
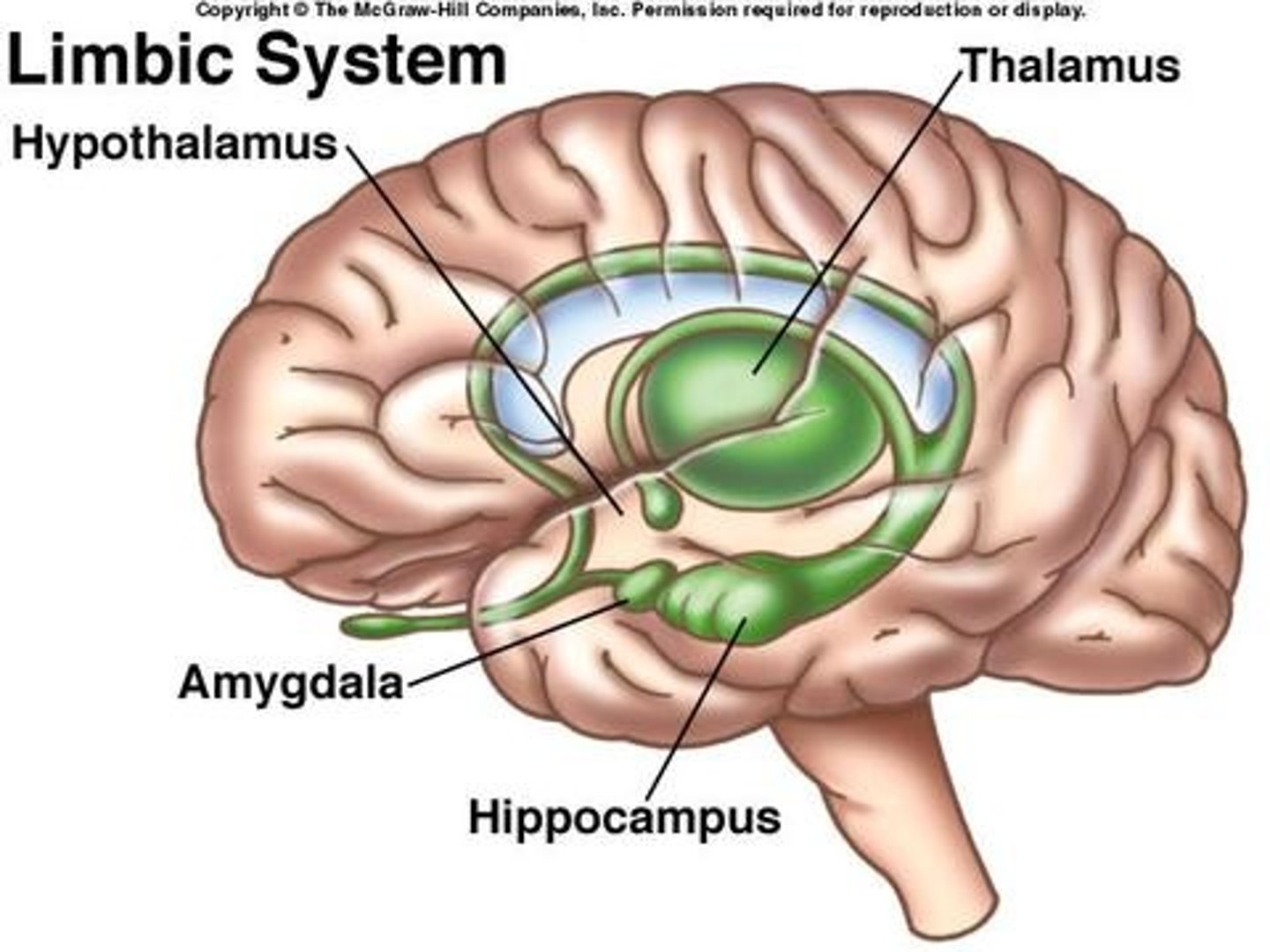
hypothalamus
maintains homeostasis, links endocrine system to the brain by influencing the pituitary gland.
mnemonic: "h"ypothalamus and "h"omeostasis
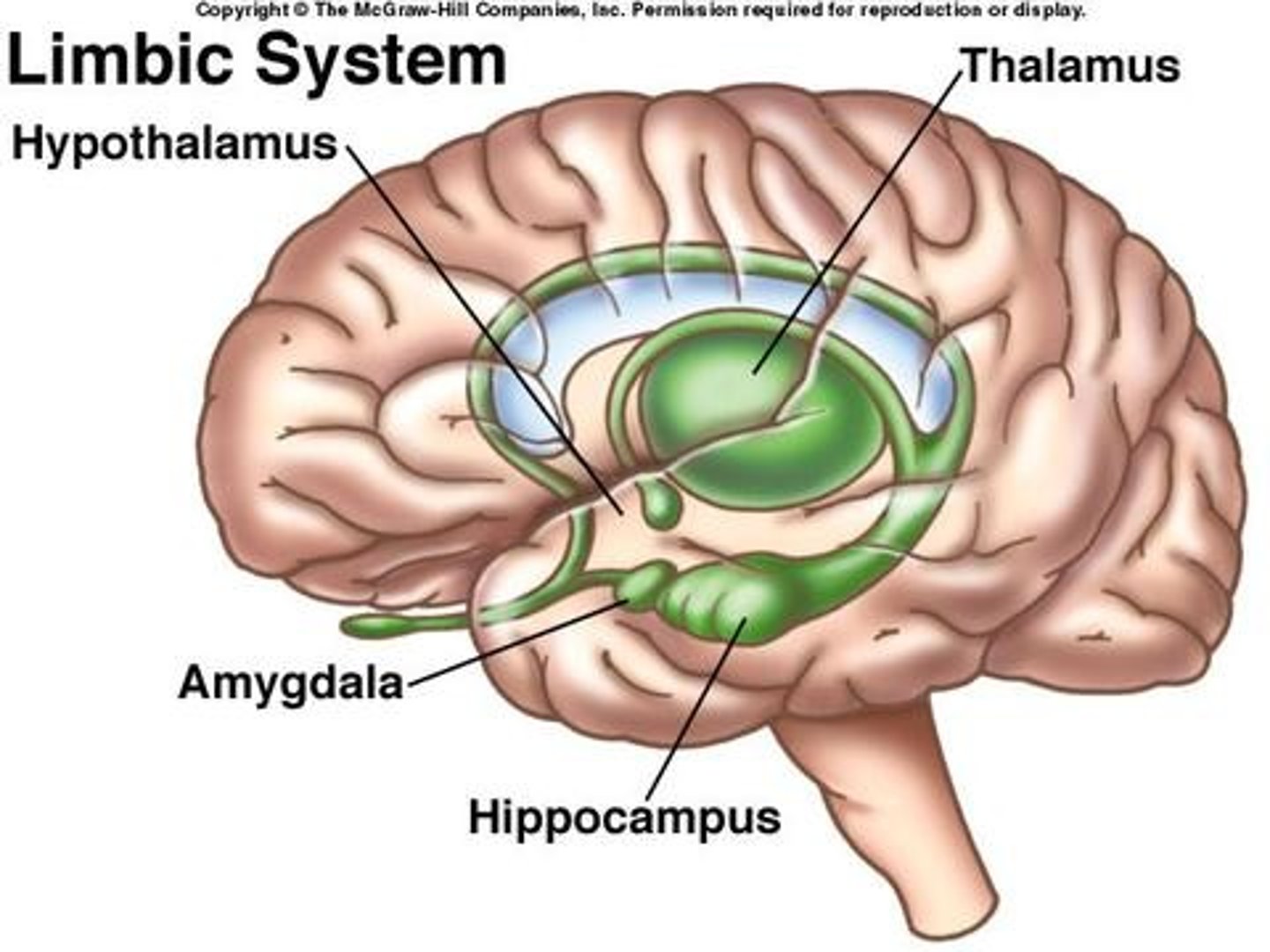
thalamus
processes information from all senses except the sense of smell. Acts as a relay center to other areas.
mnemonic: thala"mustache" reminds you that it processes all sensory info except for smell (mustache:nose:smell)
hindbrain
A region at the base of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life functions.
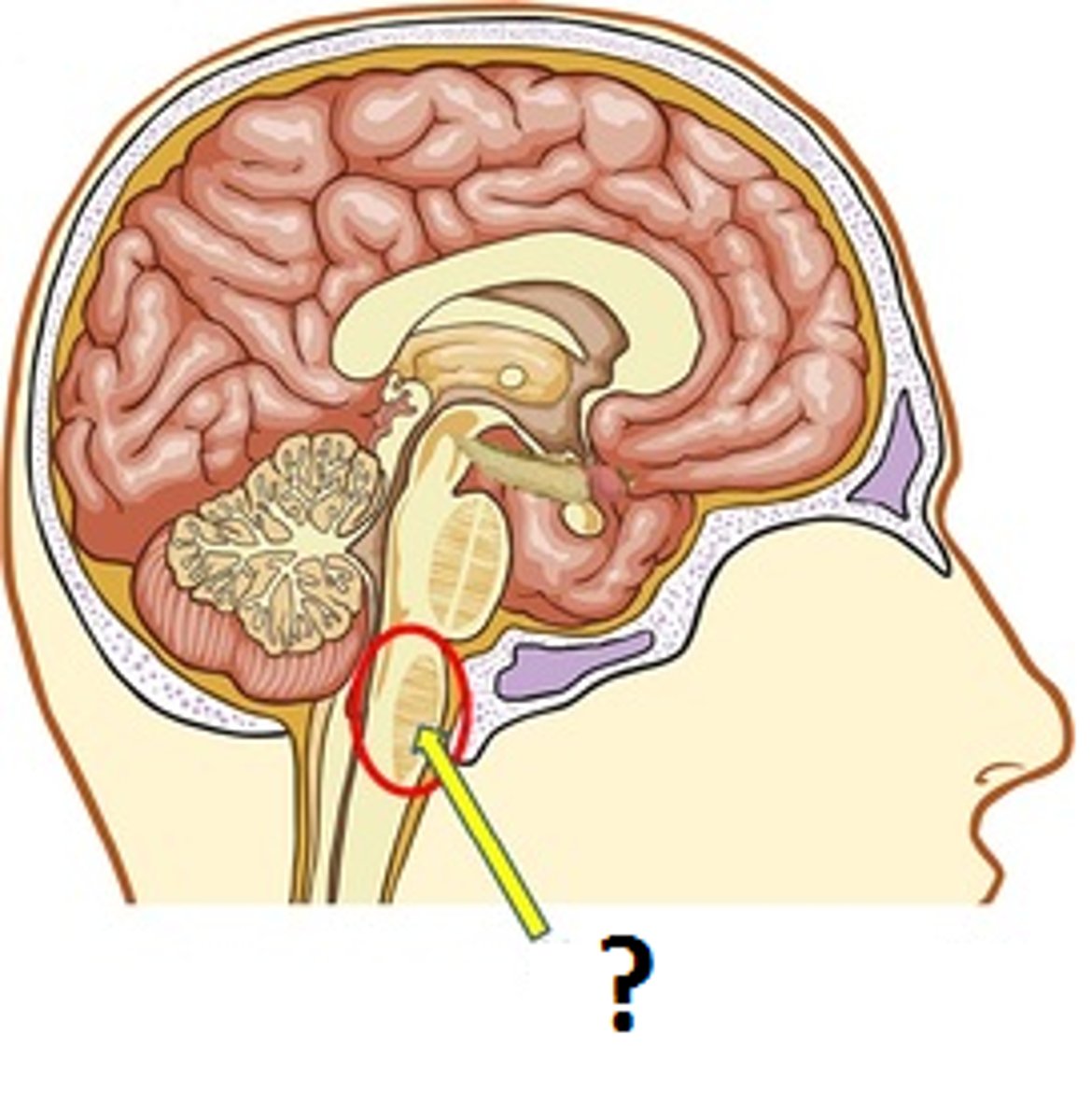
medulla
controls vital life functions such as heart rate and breathing
Mnemonic: "med"ulla and "med"ic
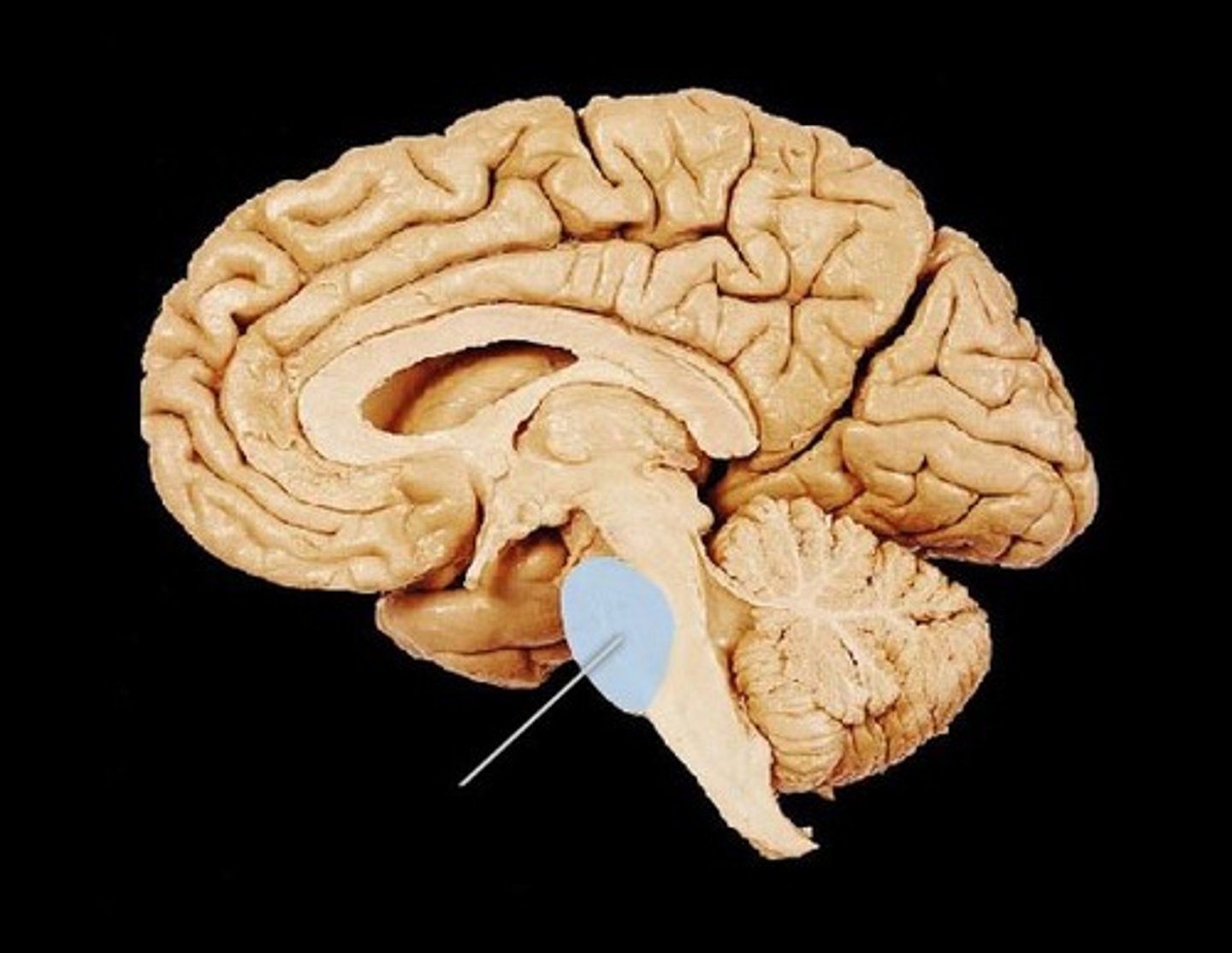
pons
helps coordinate movement on each side of the body
mnemonic: "Pons" and coordinating the movement of pons on a chessboard.
Reticular Formation AKA Reticular Activating System
located in the center of the medulla, helps to regulate attention and sleep
mnemonics: R.A.S.= Reticular activating system and "regulates attention (and) sleep.
Being in "formation" would mean you have to stand at "atttention"
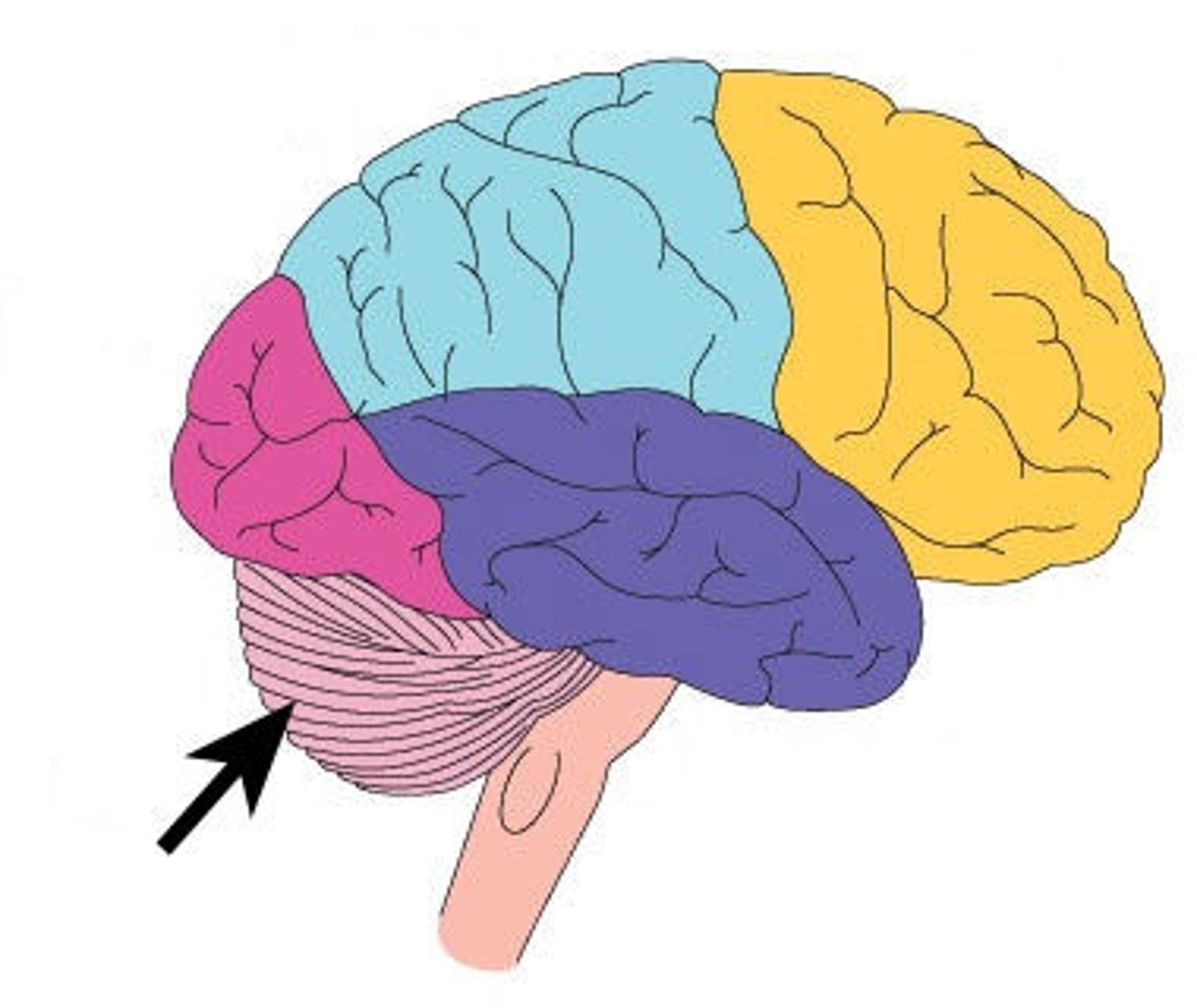
cerebellum
muscle coordination, maintaining balance and equilibrium. Coordinates rapid voluntary movement.
mnemonic: ""cerebalance"