Somatic Nervous System
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Which cortex is the sensory cortex?
Postcentral gyrus/Somatosensory cortex, posterior (by parietal lobe)
Which is the primary motor cortex?
Precentral Gyrus/Motor cortex
anterior (by frontal lobe)
What does the central sulcus divide?
The precentral gyrus (motor cortex) and the sensory cortex
What are "sulcas"? Are more better? What about larger?
Valleys/wrinkles/folds in the brain
More is better --> more pathways for innervation. Larger, however, is not always better
What would a brain with Alzheimers show in relation to the sulci?
Deeper sulci
(dementia patients as well)
Is the corticospinal tract descending or an ascending pathway?
Descending
Are descending pathways motor pathways or sensory?
Motor.
Moving from the motor cortex to motor neuron to activate a response
What myotome is associated with spreading the fingers (abduction)?
T1
What myotome is involved with bending at the hips (flexion)?
L1-L2
Which myotome is involved with the muscles of the chest and abdomen?
T1-T12
What does the diameter of a neuron indicate?
How fast it will be
What kind of innervation does the dorsal root ganglion provide?
Sensory
Having few muscle fibers is associated with coarse, or gross, control. (T/F)
False
Gross motor would be many muscle fibers
Slow motor units supply only __________ fatiguing ________ muscle fibers.
Slowly
red
Fast motor units supply only _____ fatiguing _____ muscle fibers.
Rapidly
white
What comprises the Ventral horn?
Motor neurons (innervating skeletal muscle)
Where is the motor end plate?
Neuromuscular junction
Axon terminal function
transmits impulse to next cell and releases neurotransmitters
The motor end plate invaginates inside the muscle fiber and forms a depression, known as ________ _________, where the _______ ________ is.
synaptic trough
axon terminal
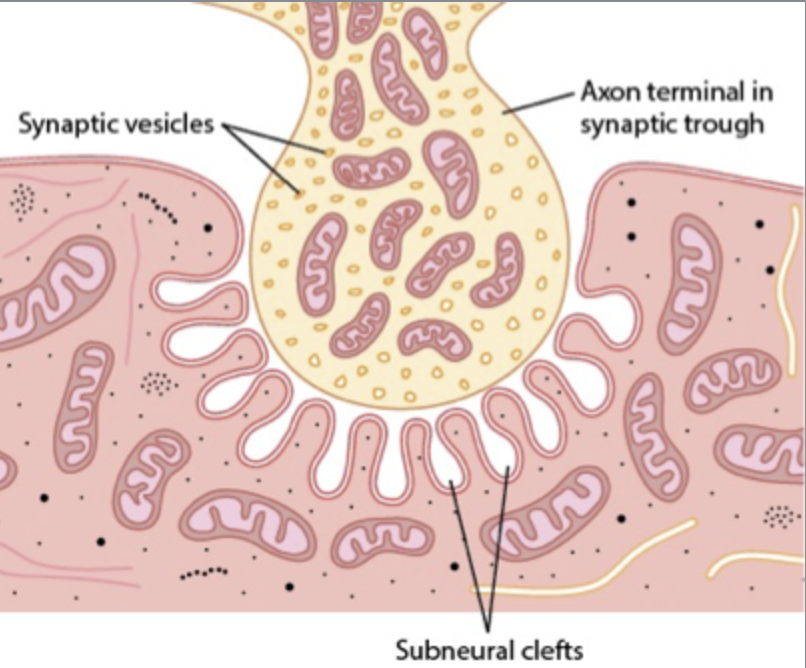
After action potential is triggered, what voltage gated ion channels open first?
Ca2+
After calcium is released, what is the neurotransmitter is released?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Once the ACh has binded to its receptors, which voltage gated channels open to allow this ion to enter the cell?
Na+ (sodium)
What is postsynaptic action potential in muscle fiber?
A twitch
What is happening with synaptic transmission in Myasthenia Gravis? Where does this occur in the motor unit?
ACh receptors are not working correctly
Antibodies against ACh receptors block the transmission
At the NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION
What is a classic diagnostic sign of Myasthenia Gravis?
Ocular fatigue
Is the sensory pathway ascending or descending?
Ascending
Sensory receptors send signals to the brain for interpretation
Who is considered the "gatekeeper" of the brain?
Thalamus
"regulator"
The pain pathway has multiple brain processing centers. (T/F)
True
What is the term for neurons that sense pain?
Nociceptor
What kind of testing is required to understand if the path of pain is following a peripheral nerve or a dermatome?
Sensation testing --> differential diagnostics
Describe the Reflex arc
stimulus → receptor → sensory neuron → central nervous system → motor neuron → effector → response
Describe the Crossed extensor reflex
Occurs with flexor reflexes in weight bearing limbs to maintain balance; ipsilateral (same side) flexor reflex and contralateral (opposite) extensor reflex; right side flex-left side extends
Which neurons during the Crossed extensor reflex activate the thigh extensors and plantarflex the contralateral foot (providing balance)?
Excitatory interneurons
What neurons turn off ipsliateral leg extensors and foot dorsiflexors and contralateral thigh flexors to prevent injury to antagonistic muscle groups in both limbs?
Inhibitory interneurons
How do the Golgi Tendon organs detect muscle tension?
1. Tension on tendon activates sensory neuron
2. Sensory neuron stimulates interneuron
3. Interneuron inhibits motoneuron
4. Tension on tendon is reduced
Feedback mechanism to control the tension of muscle before tension becomes high enough to cause damage
What are the afferent muscle fibers?
Intrafusal muscle fibers
Are the afferent or efferent fibers the sensor?
Afferent are the sensor
Describe alpha motor neuron activity during Co-activation
The alpha motor neurons innervate extrafusal muscle fibers and are the primary means of skeletal muscle contraction
Describe gamma motor activity during muscle contraction Co-activation
Gamma motor neurons innervate intrafusual muscle fibers to keep the muscle spindle taut at all times to maintain its sensitivity to changes in the muscle length, in parallel with alpha neuron contraction
mechanism of spasticity
Hyper excitability of alpha-motor neurons in the spinal cord. Increased stimulation of the stretch reflex arc.
What are the muscle fibers inside the spindle of skeletal tissue?
Intrafusal
What muscle fibers make up the bulk of the muscle?
Extrafusal
Which fibers are innervated by gamma neurons to keep the spindle taut and maintain sensitivity to muscle tension?
Intrafusal
Which fibers are innervated by alpha neurons to initiate contraction?
Extrafusal fibers
Where does the corticospinal tract originate from?
Pre-cortical region
Motor cortex
What is the term for exaggerated contraction?
Hyperrflexia/spasticity
Is the corticospinal tract ascending or descending? Motor or sensory?
Descending
Motor
Polio - what neuron in the corticospinal tract is affected?
Alpha motor neuron disease
What is spasticity dependent on?
Speed
Lower motor neuron syndromes are associated with what type of motor effects?
Flaccid paralysis
Upper motor neuron syndromes would present as what kind of motor effect?
Spastic paralysis
In upper motor neuron syndrome, would reflexes be increased or decreased?
increased
Are muscle fasciculations (twitches) associated with lower motor neuron syndrome? what about upper?
May be present in lower
Absent in upper
Is it possible to have a C5 injury but still have innervation enough to walk?
Yes; this would be an incomplete SCI (spinal cord injury)
What qualifies as a complete spinal cord injury?
Paraplegia (lumbar spine injury)
Tetraplegia (cervical spine injury)
Complete SCI, no sensory or motor function preserved in the sacral segments S4-S5.
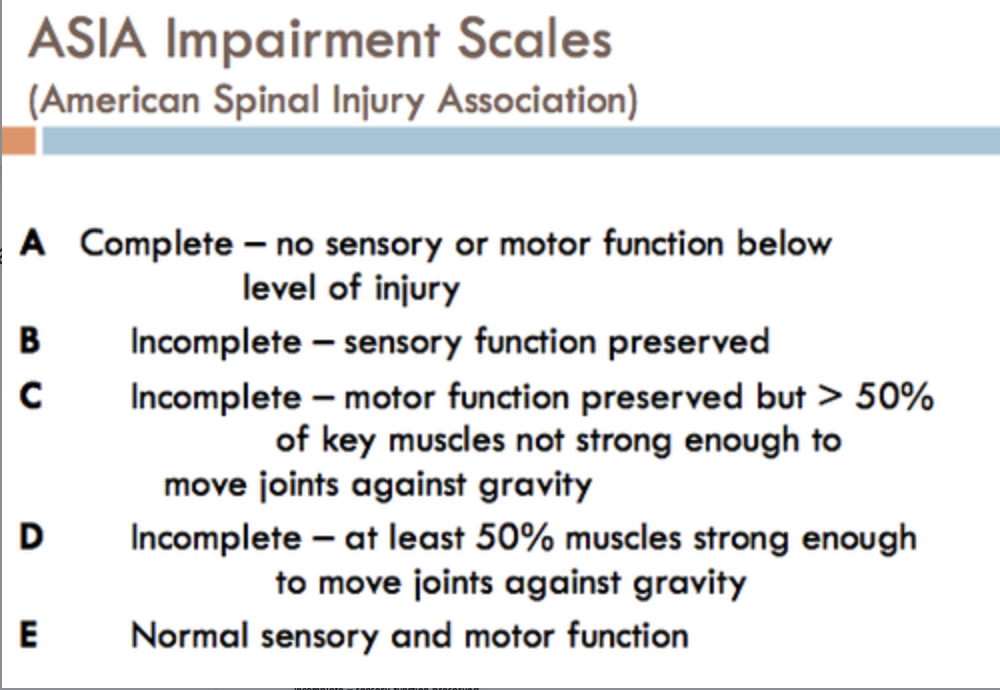
What is ASIA?
American Spinal Injury Associations Impairment Scale
(A- complete, B-D incomplete, D - normal)
What spasticity dependent on?
Speed
With nerve damage at a higher level of the spinal cord (i.e. C1), what happens to the myotomes and dermatomes?
They stop working. NO innervation underneath
Signal from motor end plates (in the knee or other part affected) in muscles goes into the spine from ___________
Dorsal root ganglia
Why does a sensory homunculus look like it does?
The hands and mouth are required for more complex, accurate movements (fine motor skills)
The homunculus utilized more fine motor skills than gross, causing the adaptation of large hands and mouth
___________ root sends a response back to effector limbs
Ventral