Biology Unit 3 Section 1 + 2 Test Studyguide
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions within each cell of an organism (provide energy for life’s processes; create key molecules)
Chemical reactions
the breaking and forming of bonds between different substances during chemical changes
Breaking a bond
requires energy to be absorbed; endothermic
Creating a bond
releases energy; exothermic
Catabolic
breaks down larger molecules into simpler compounds; a release of energy
Exergonic
a release of energy
Anabolic
builds larger molecules from smaller ones; requires consuming energy to do it
Endergonic
requires consuming energy to do it
Reactants
(substrate): substances that are CHANGED during a chemical reaction
Products
Substances that are MADE by a chemical reaction
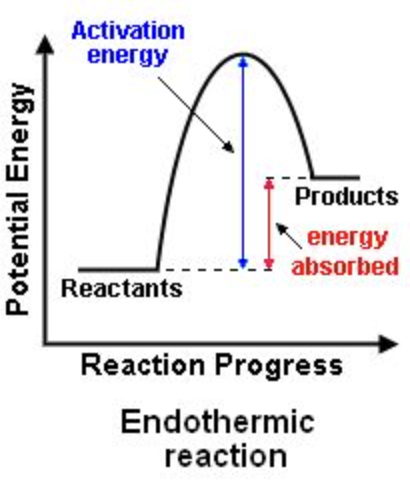
Endothermic
absorbs energy
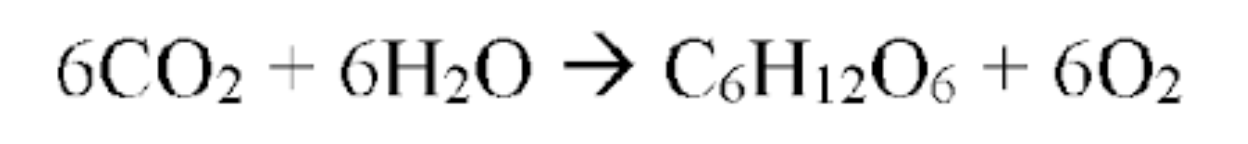
Photosynthesis
EX of endothermic reactions
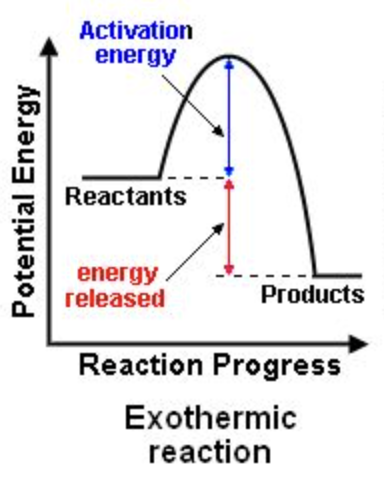
Exothermic
releases energy
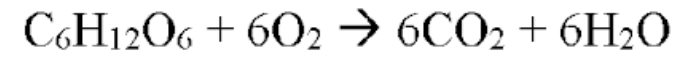
Cellular respiration
EX of exothermic reactions
Light energy is STORED as chemical energy in SUGAR
Photosynthesis
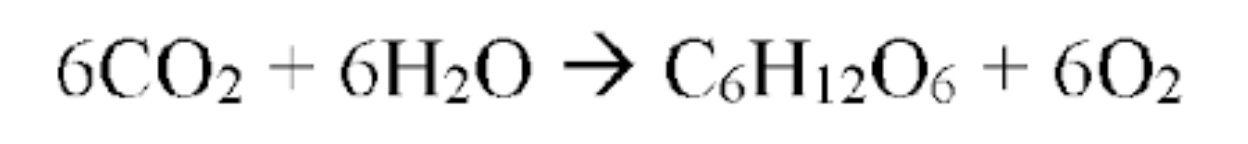
Chemical energy in sugar is converted to chemical energy RELEASED as ATP
Cellular respiration
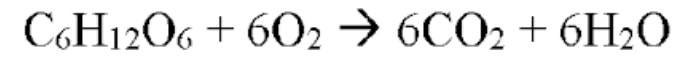
Enzymes
mostly proteins that speed up biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy
Catalysts
(enzymes) are substances that speed up reactions without being permanently altered (Lower activation energy)
very specialized molecules that bind to reactants; help to break or form bonds, releasing a newly created product; an active site that fits only one substrate (induced fit)
What are enzymes?
Can be used over and over again
What is a special quality of enzymes?
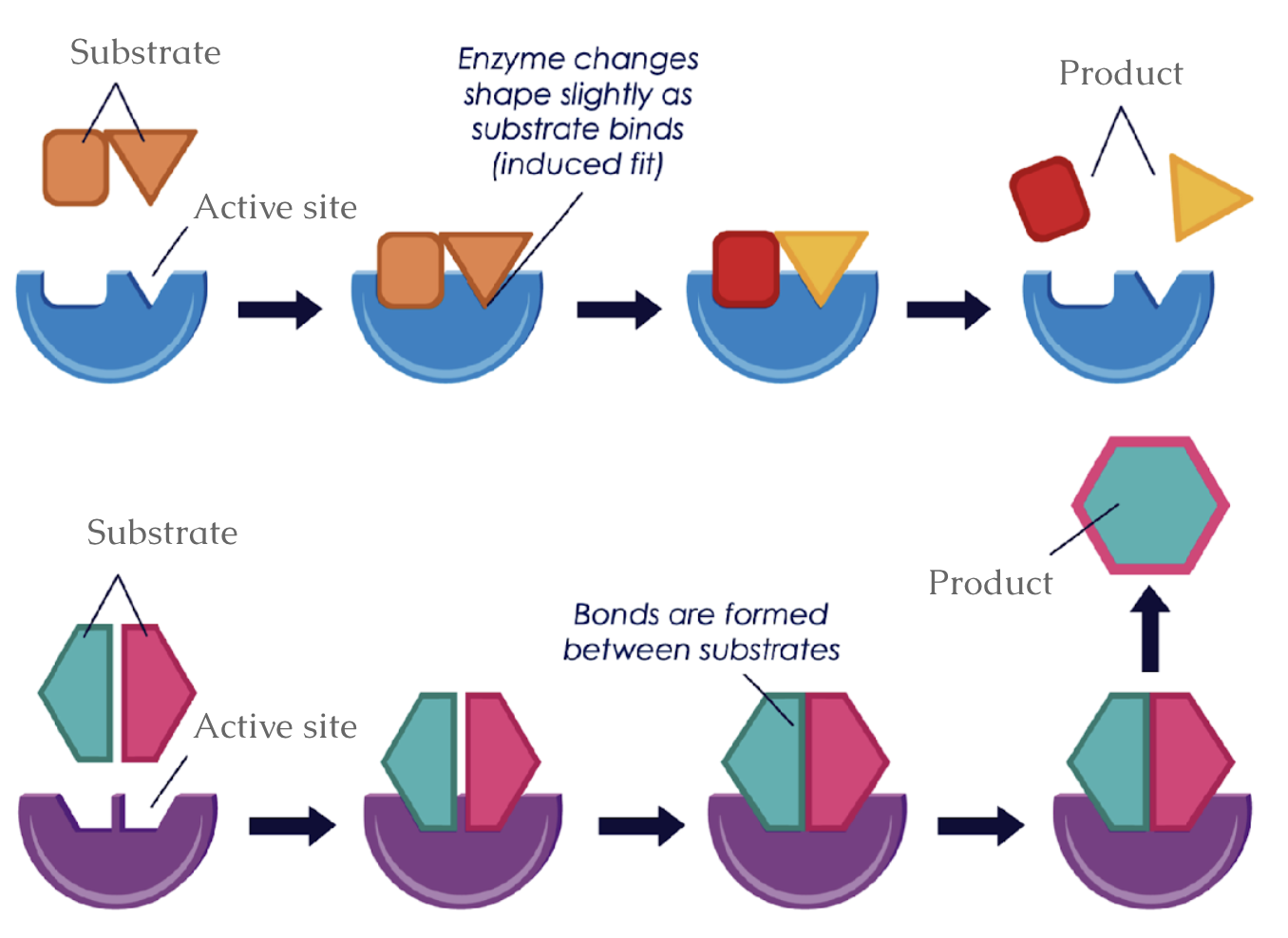
Enzymes can break bonds in a substrate to form two products or can make bonds between substrates to form one product
What can enzymes do?
Denaturation
Enzyme’s active site gets deformed and loses its specific shape —> loss of biological activity
Temperature
increasing temperature increases the rate of the reaction
pH
how acidic or basic a solution is (Most enzymes only work at a very specific pH so if the pH changes, it can affect the speed of reaction/cause denaturation)
Substrate Concentration
the higher the amount of substrate, the faster the reaction (more particle collisions)
Co-enzymes
helper enzymes that speed up reactions
Competitive Inhibitor
slows down the reaction; and competes with the substrate for the active site on the enzyme
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate: An energy-carrying molecule that carries/stores energy for cell functions
Adenine
Nitrogen base
Ribose
Sugar ring
Phosphate
an anion, salt; 3 groups in ATP, 2 groups in ADP
Adenine (green), Ribose (blue), Phosphate (red)
Label ATP structure
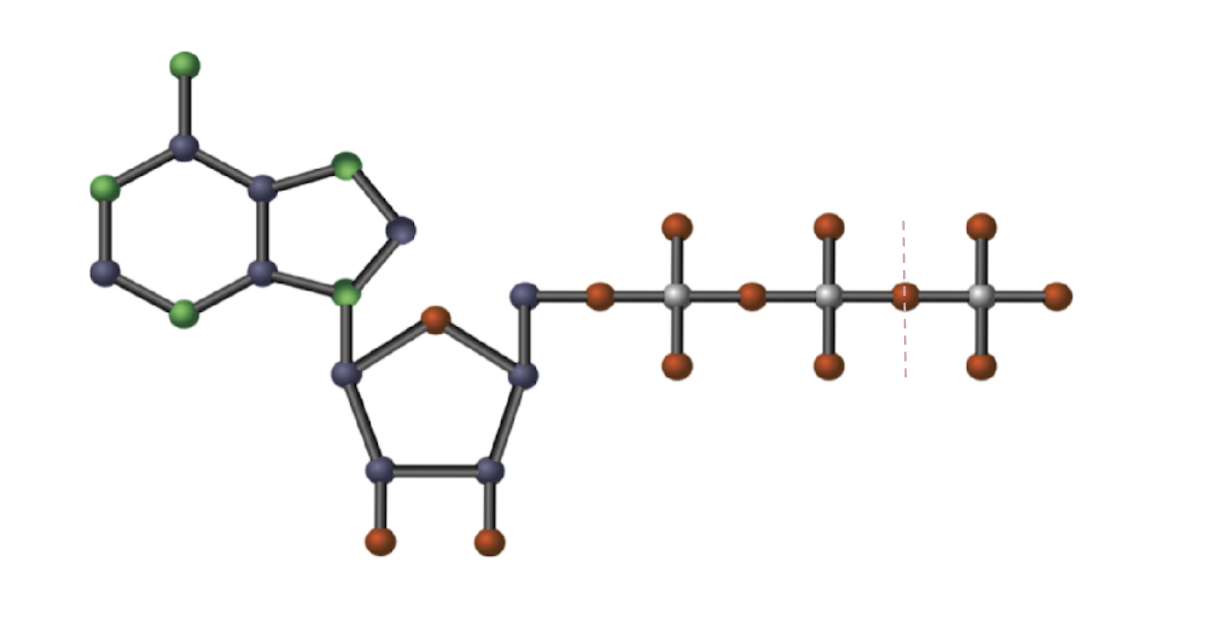
NOT a stable molecule (easy to break the bonds between the second and third phosphate groups)
Why can the third phosphate group break easily?
ADP
Adenosine di-phosphate (2 phosphates); used to create ATP (recycled)
ADP and a phosphate group combine together using energy from broken down food to create ATP. ATP breaks its bond with the third phosphate group and the energy released goes to other cell processes and becomes ADP and a phosphate group.
Process of making ADP to ATP
Exothermic reaction (breaking bonds)
ATP to ADP
Endothermic reaction (creating bonds)
ADP to ATP
Carbohydrates (commonly broken down for ATP), Lipids/fats (broken down after carbs), proteins (least likely to be broken down)
Where does energy come from?