AP Psychology: Topic 1.3 - The Neuron and Neural Firing
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
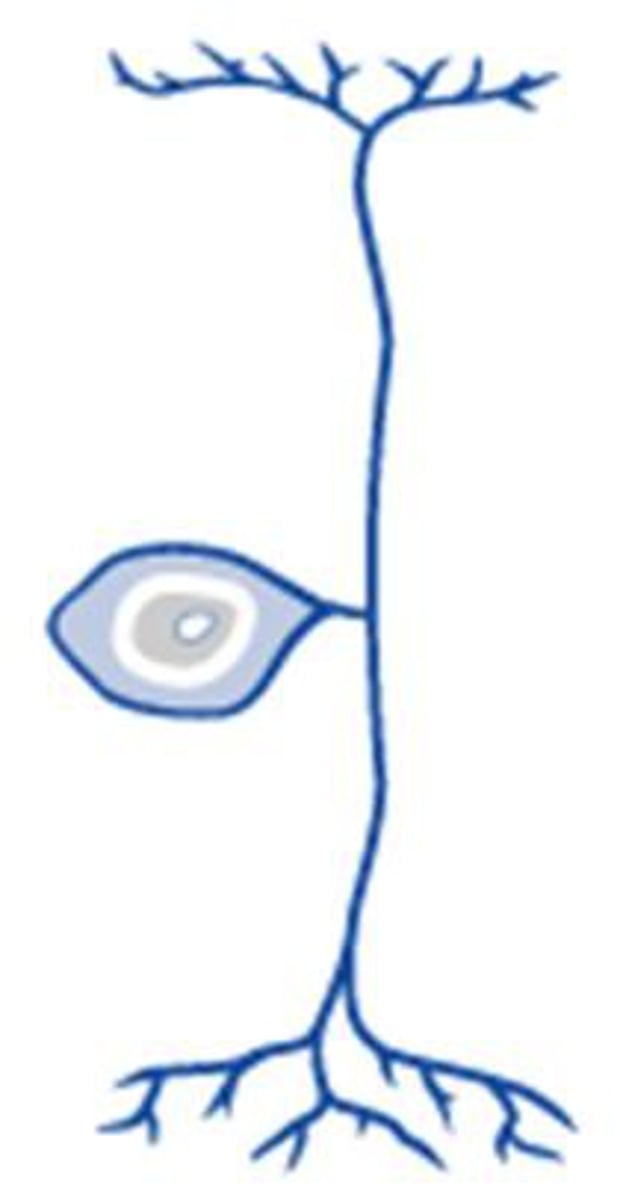
Neuron
specialized nerve cell for sending messages all over the body
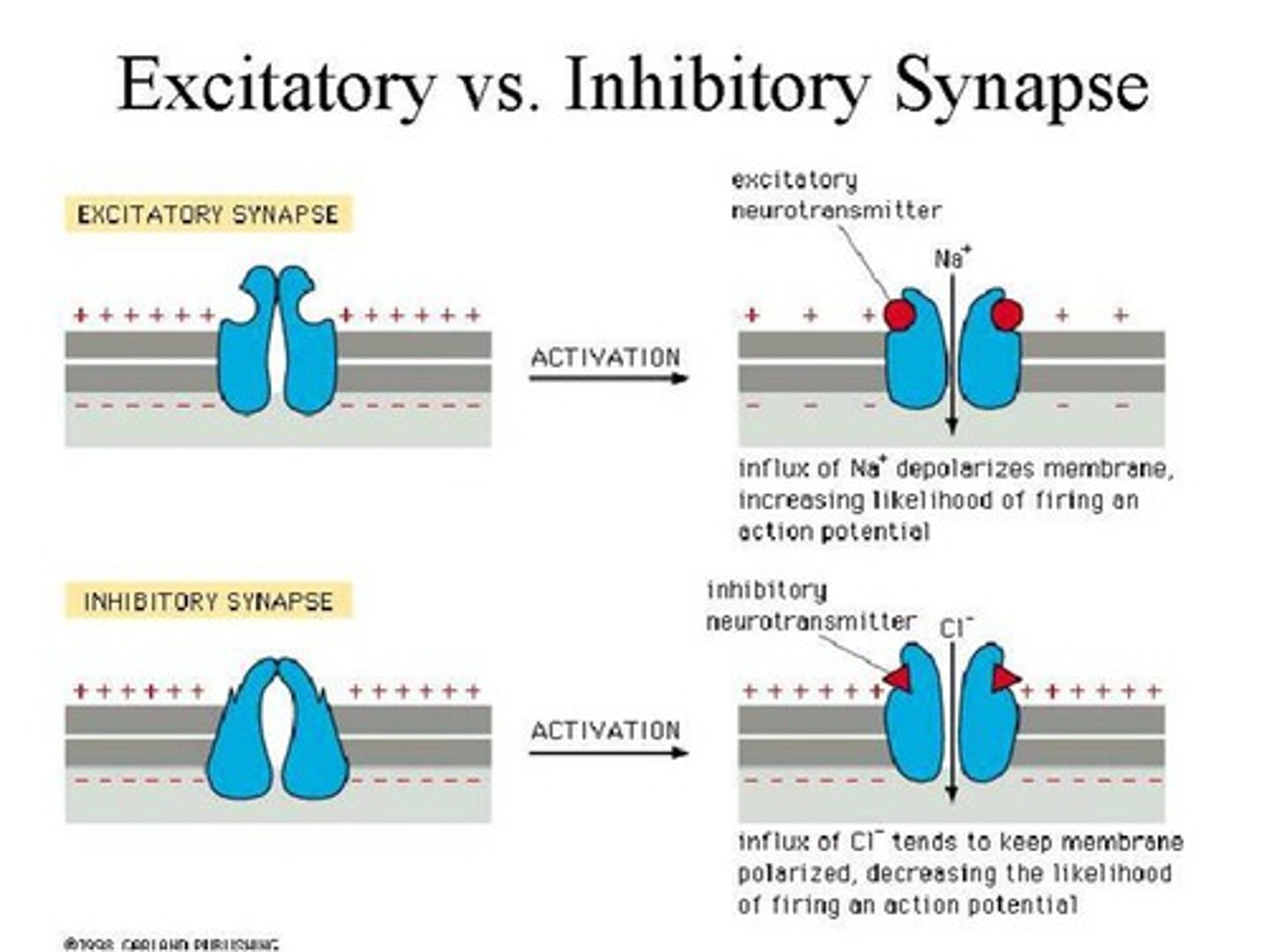
Excitatory neurotransmitter
"excites" the neuron to "fire off the message" to the next cell (includes glutamate, epinephrine and norepinephrine)
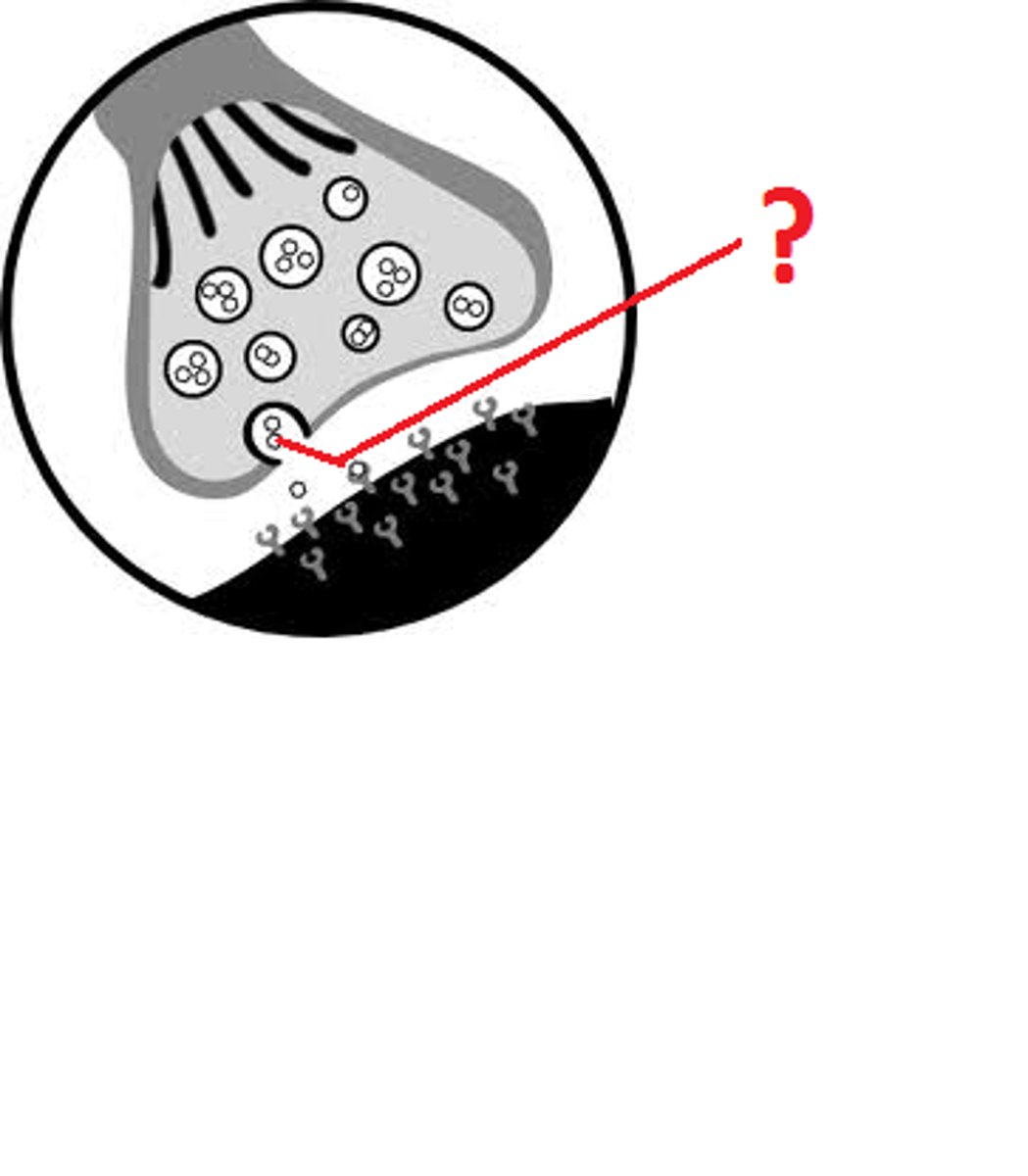
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
blocks/prevents the chemical message from being passed along (includes Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine, and serotonin)
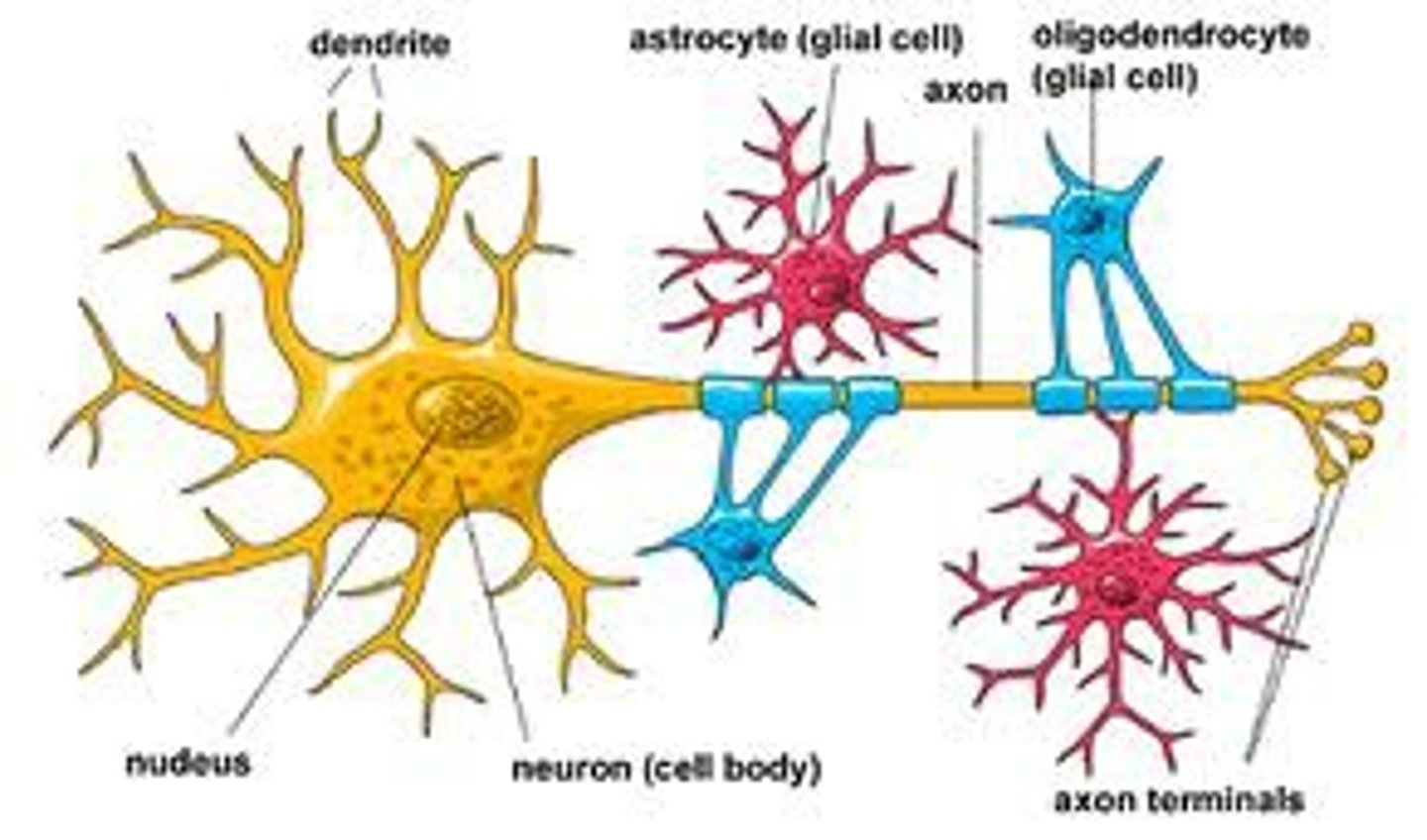
Glial cells
play a role in the formation of myelin and the blood-brain barrier, response to injury, removal of debris, and enhancing learning and memory
Threshold
the membrane voltage that must be reached in an excitable cell (e.g., neuron or muscle cell) in order to generate an action potential
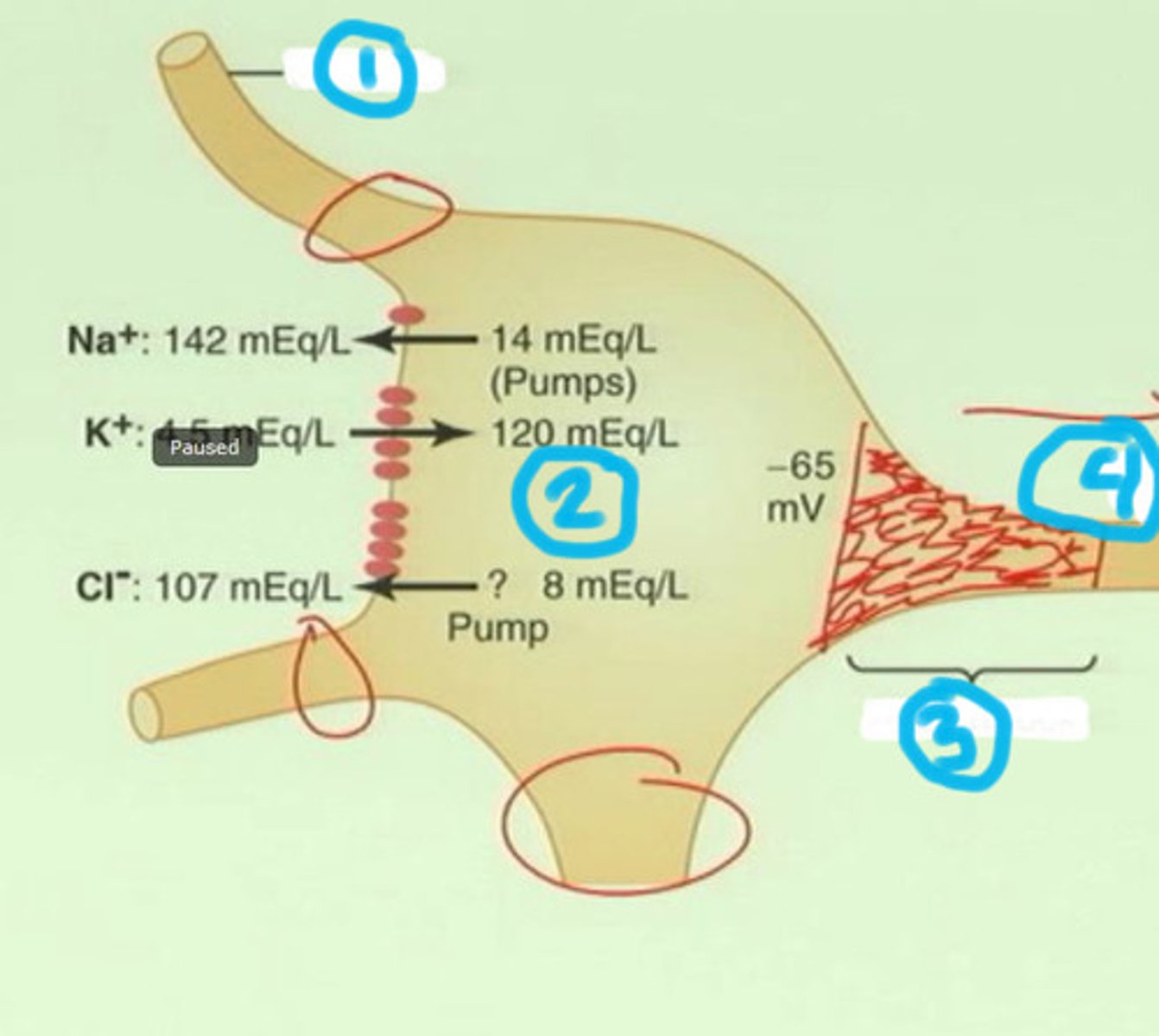
Action potential
a neural impulse (brief electrical charge) when a neuron sends information down an axon
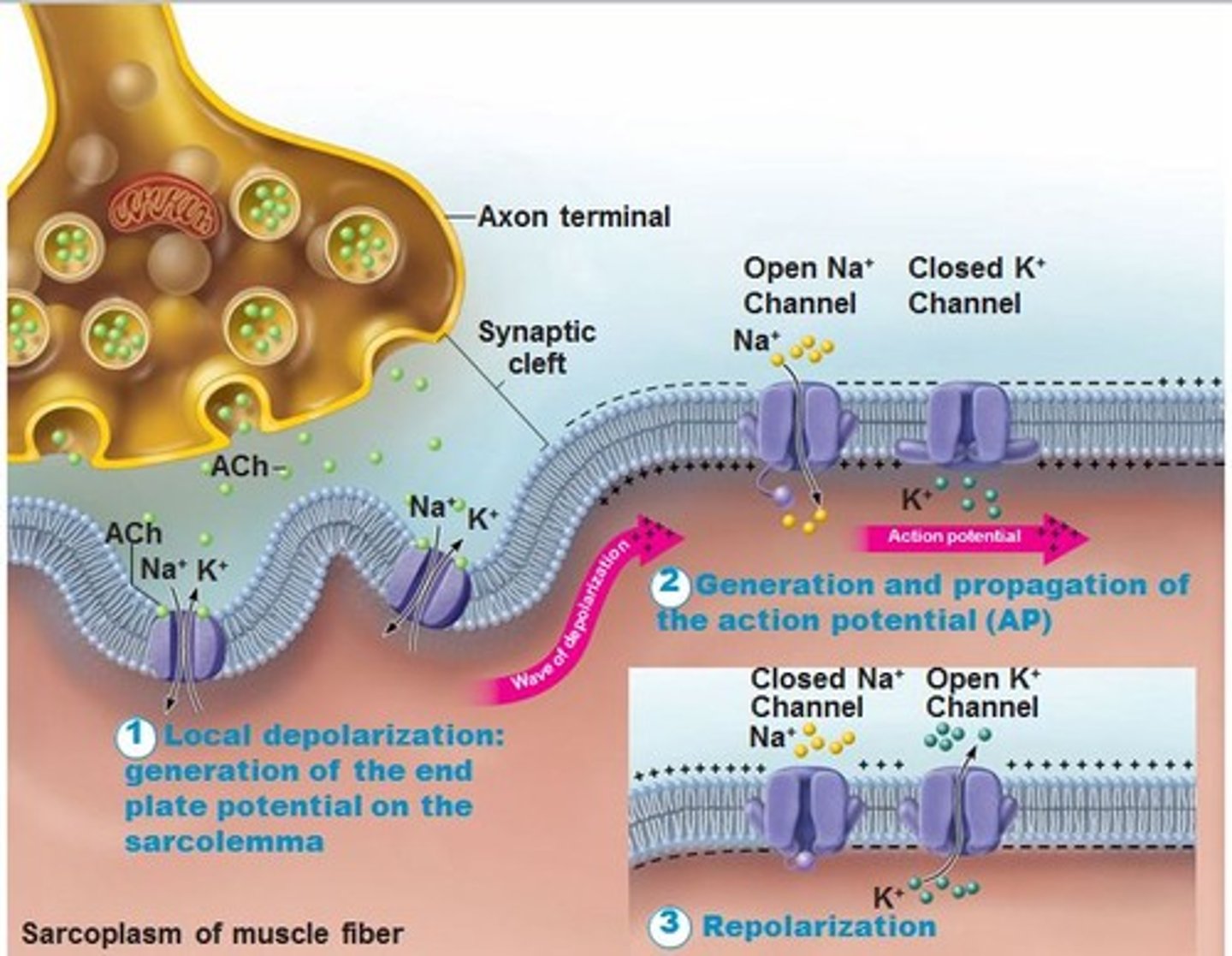
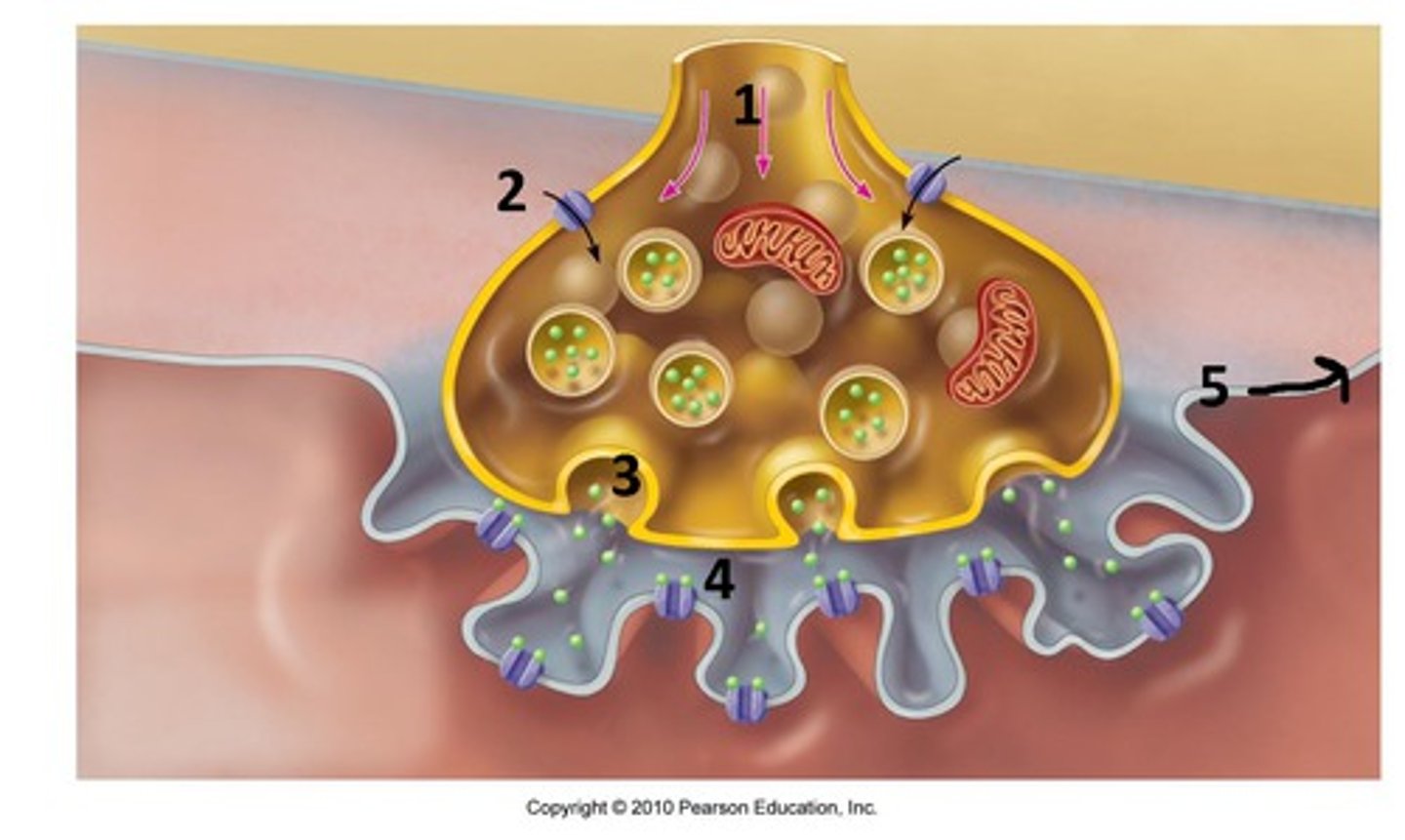
Reuptake
reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by the sending neuron after it completes its work
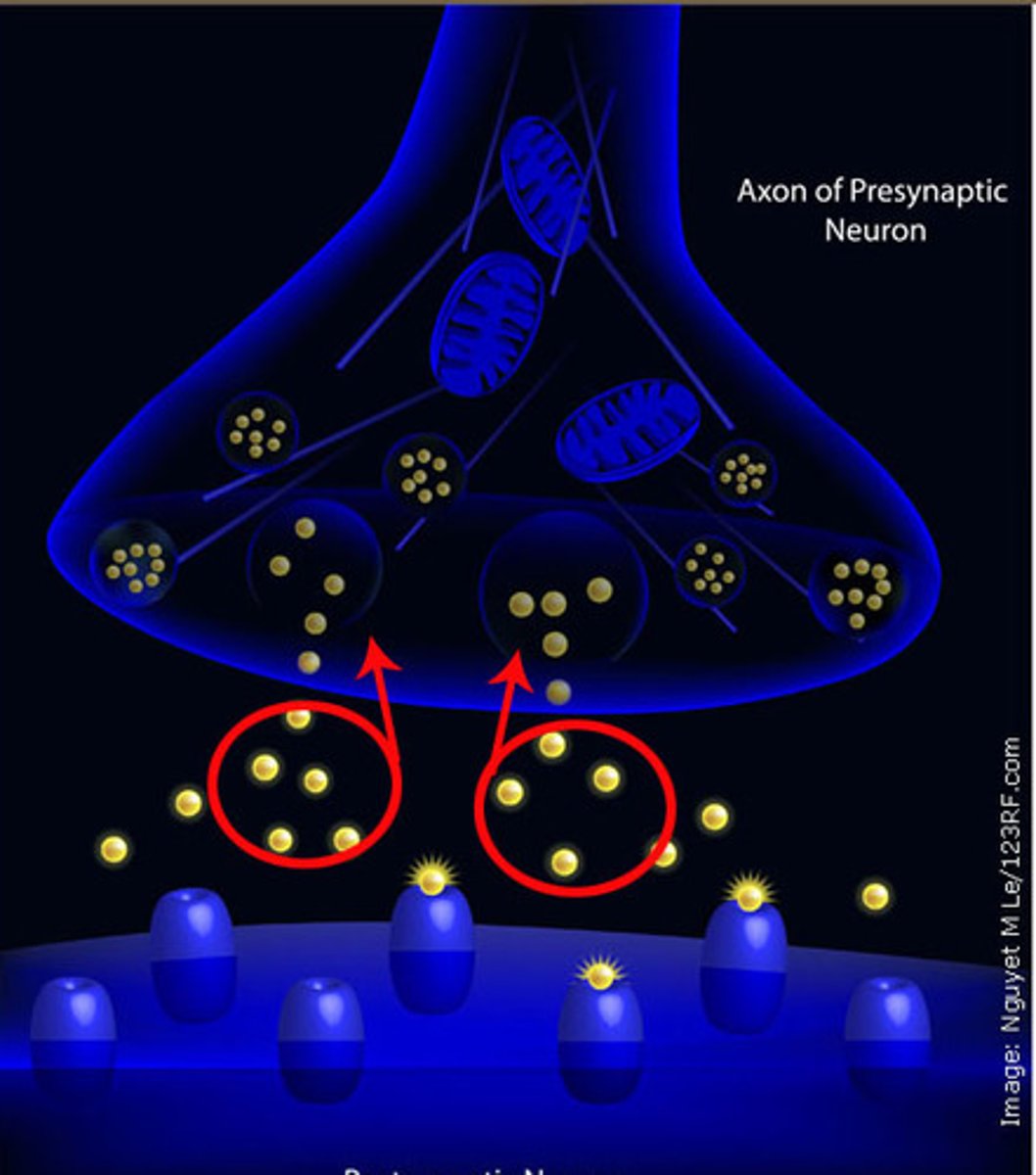
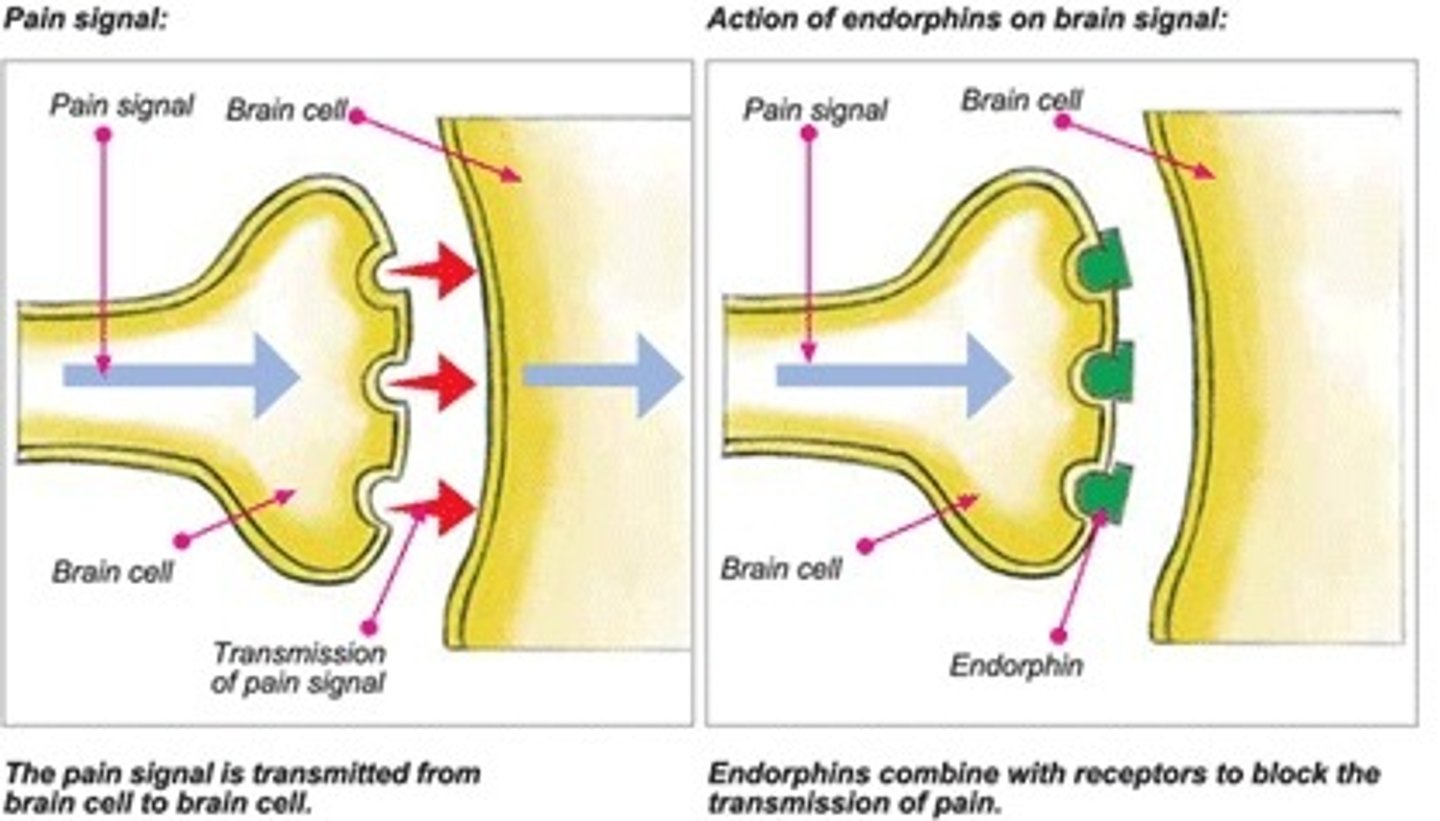
Endorphins
natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters that help manage pain, pleasure, stress, mood
Glutamate
main excitatory neurotransmitter in the nervous system; participates in relay of sensory information and learning
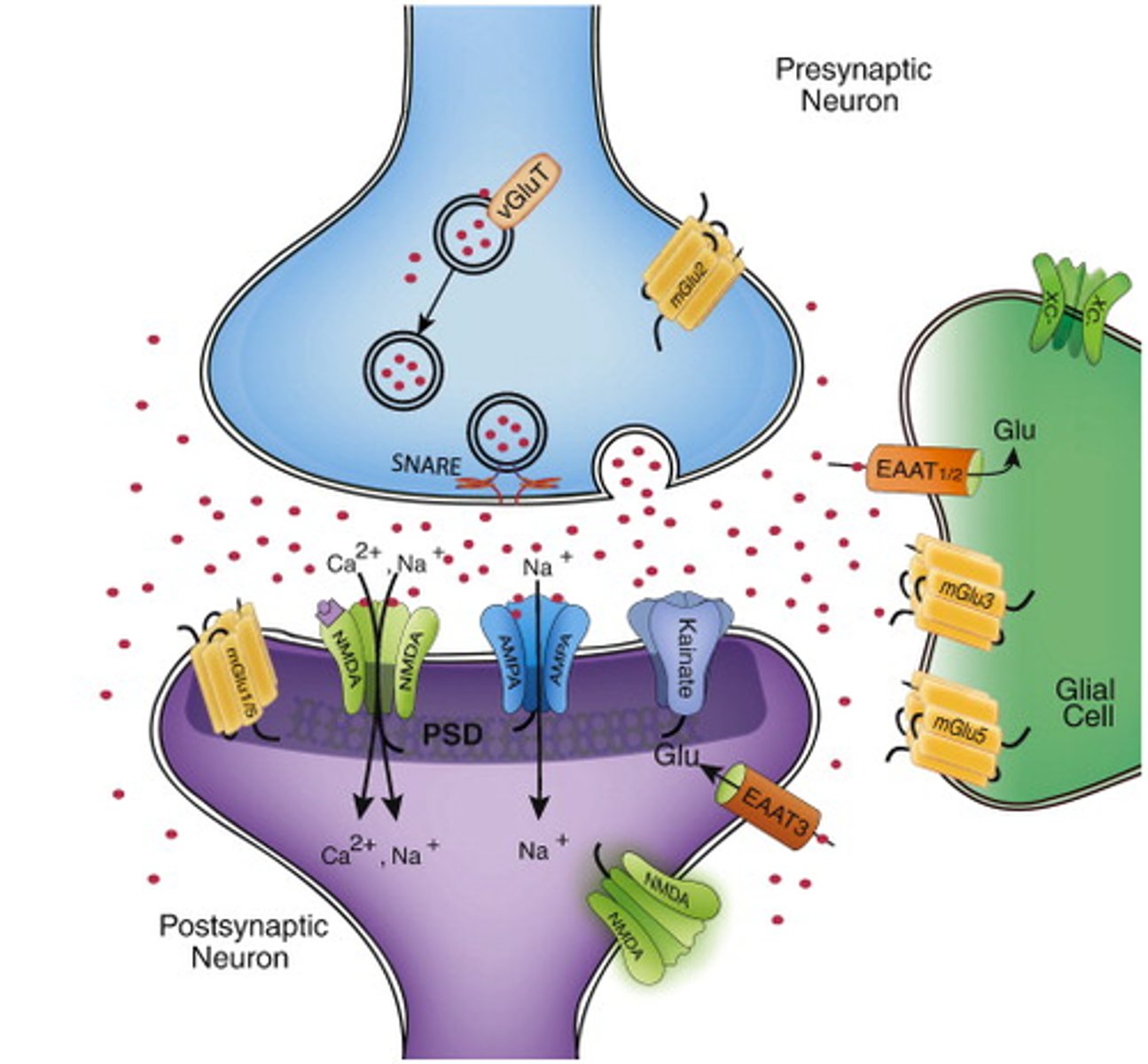
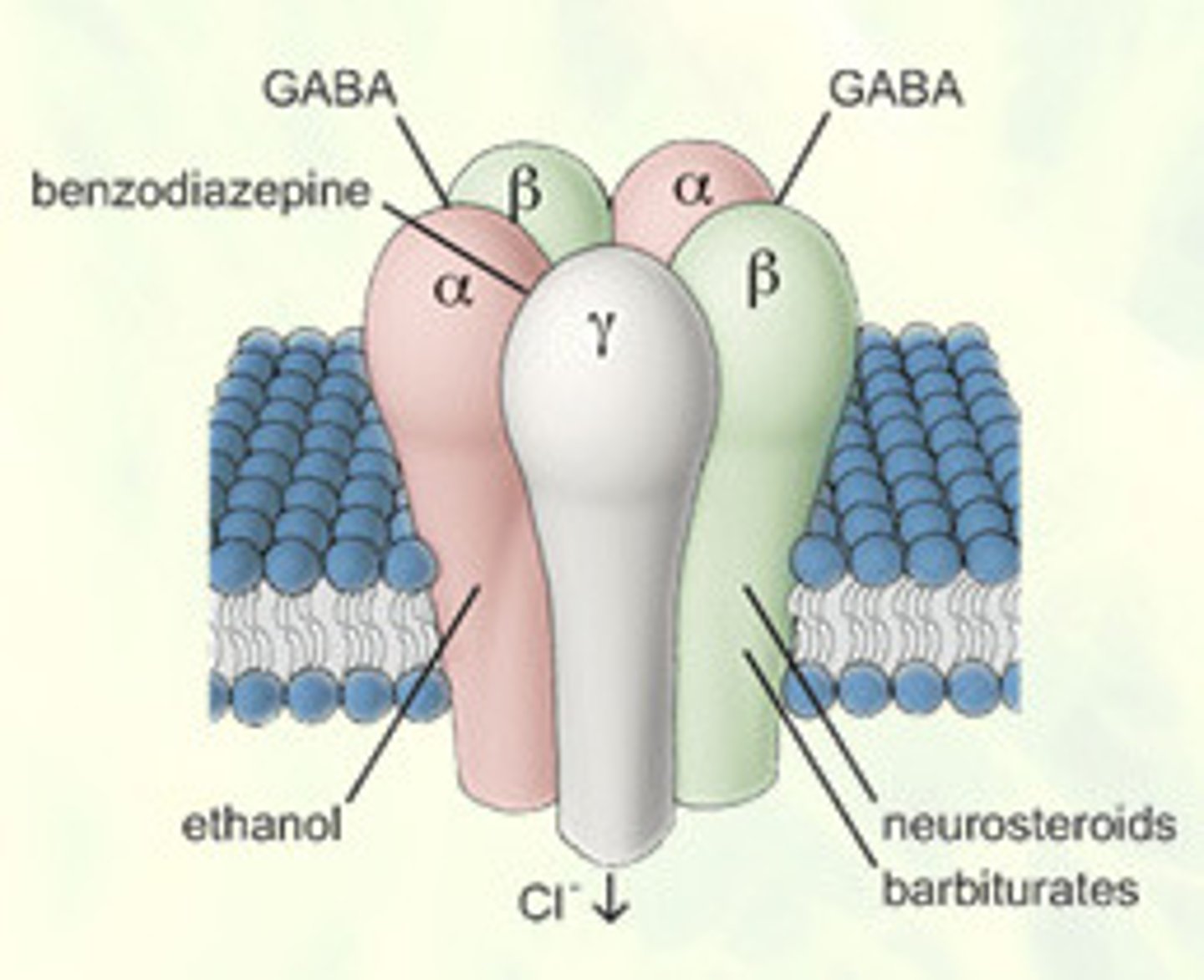
Gamma-aminobutyricvcacidc (GABA)
main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the nervous system
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter released by motor neurons to activate muscles; plays a role in arousal, attention, memory, and motivation
Norepinephrine (NE)
neurotransmitter that regulates brain arousal and other functions like mood, memory, hunger, and sleep
Dopamine
neurotransmitter involved in motor function, pleasure, satisfaction, and motivation

Serotonin
a neurotransmitter related to things such as mood, sleep, temperature regulation, memory, pain, and sexual activity
Interneurons
neurons that transfer messages to other neurons nearby
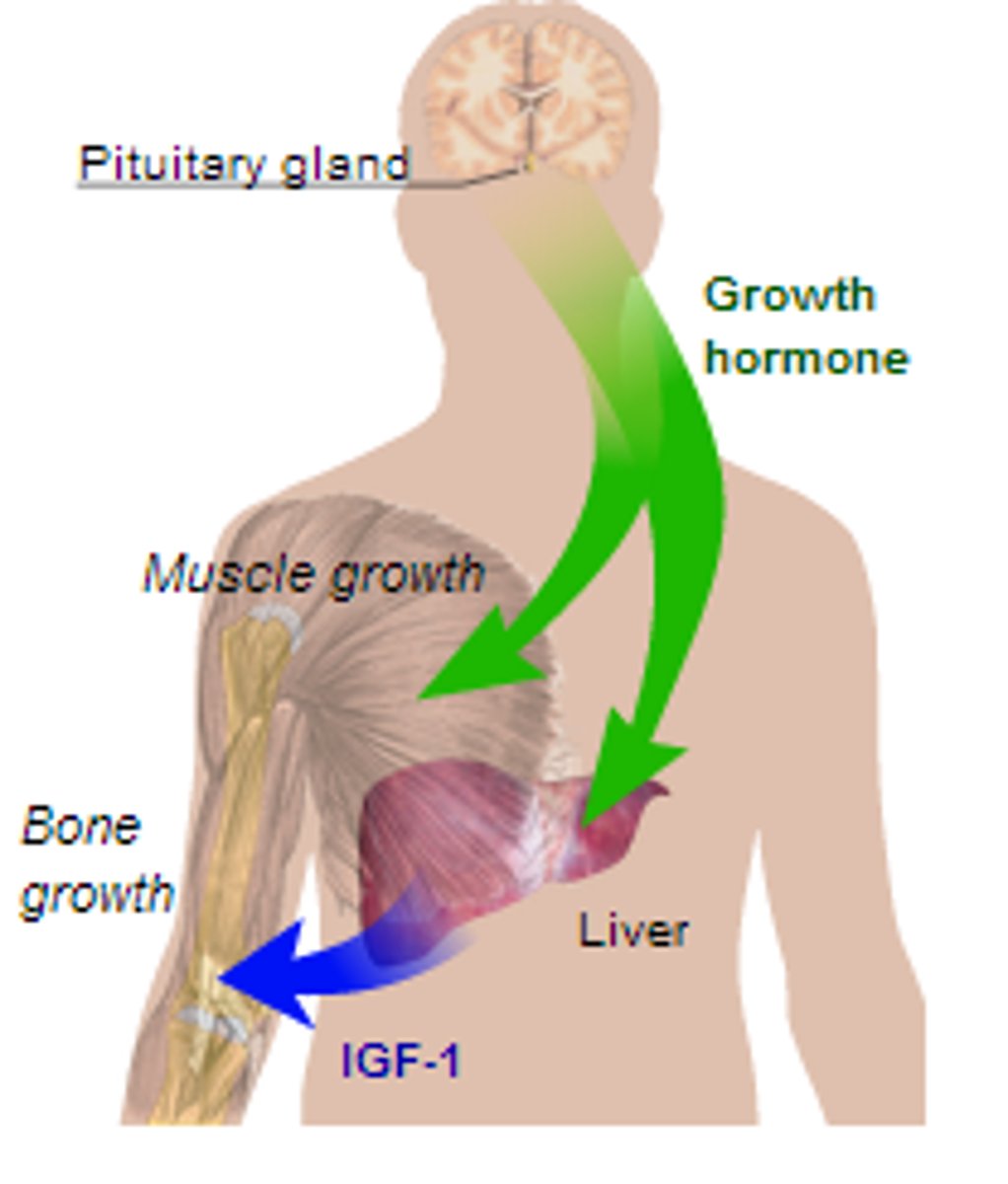
Hormones
chemicals released into the bloodstream that
control many body functions, such as growth, repair and reproduction
All-or-nothing principle
a neuron can release all of its neurotransmitters or none

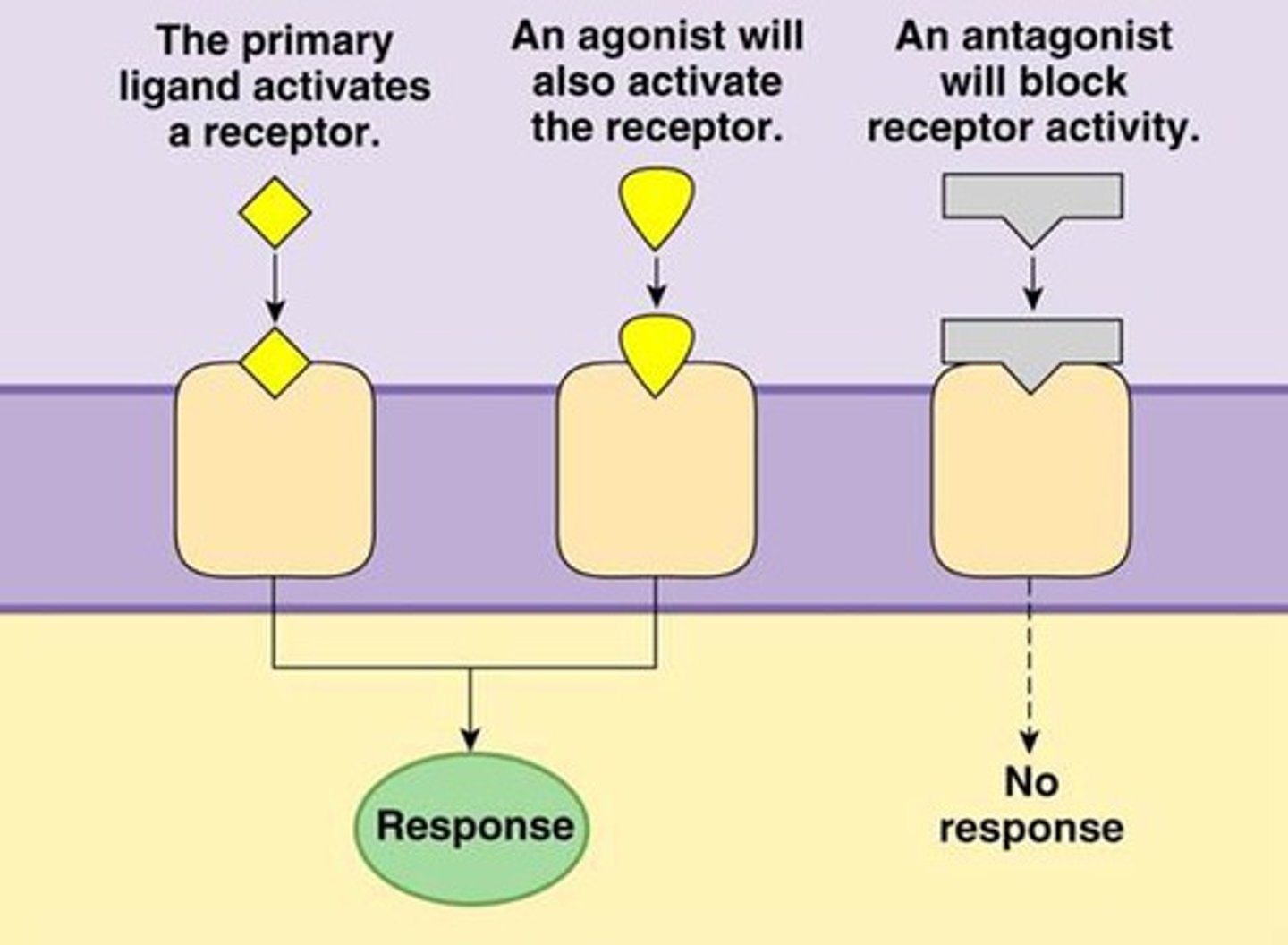
Antagonists
bind to receptors and block a neurotransmitter's functioning

Agonists
these mimic a neurotransmitter and stimulate an action (e.g., morphine mimics endorphins)
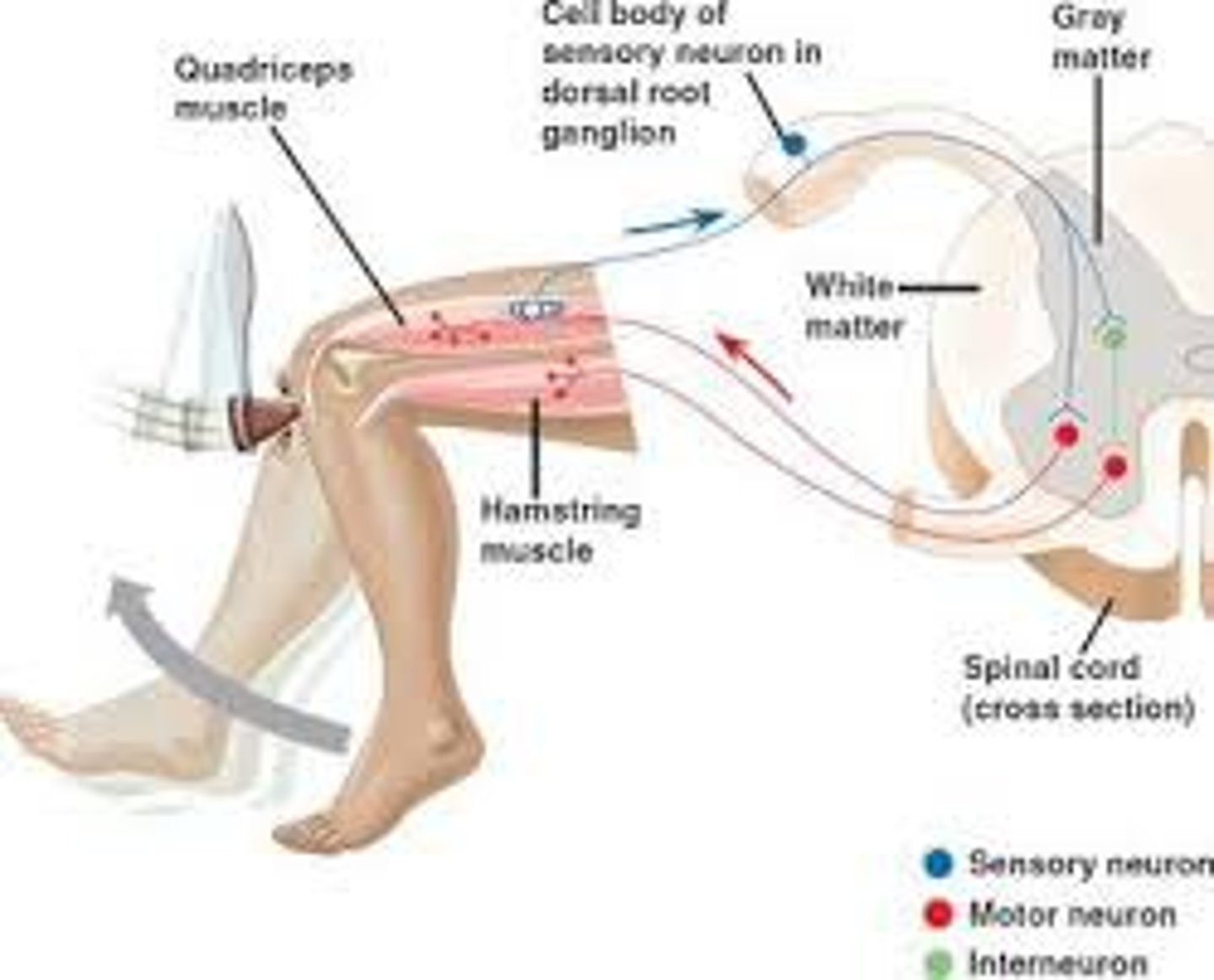
Reflex arc
a relatively direct connection between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron that allows an extremely rapid response to a stimulus, often without conscious brain involvement
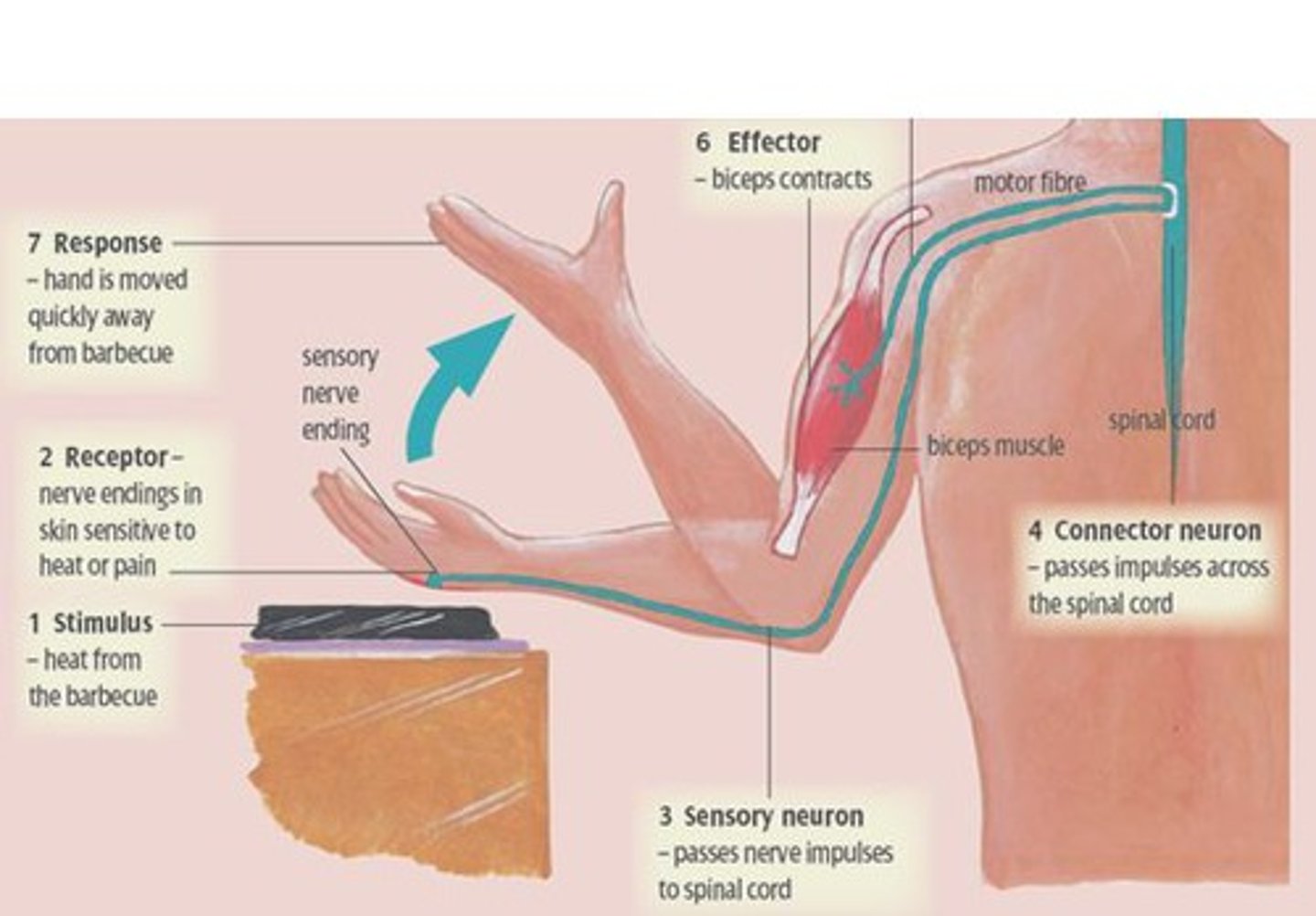
Sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
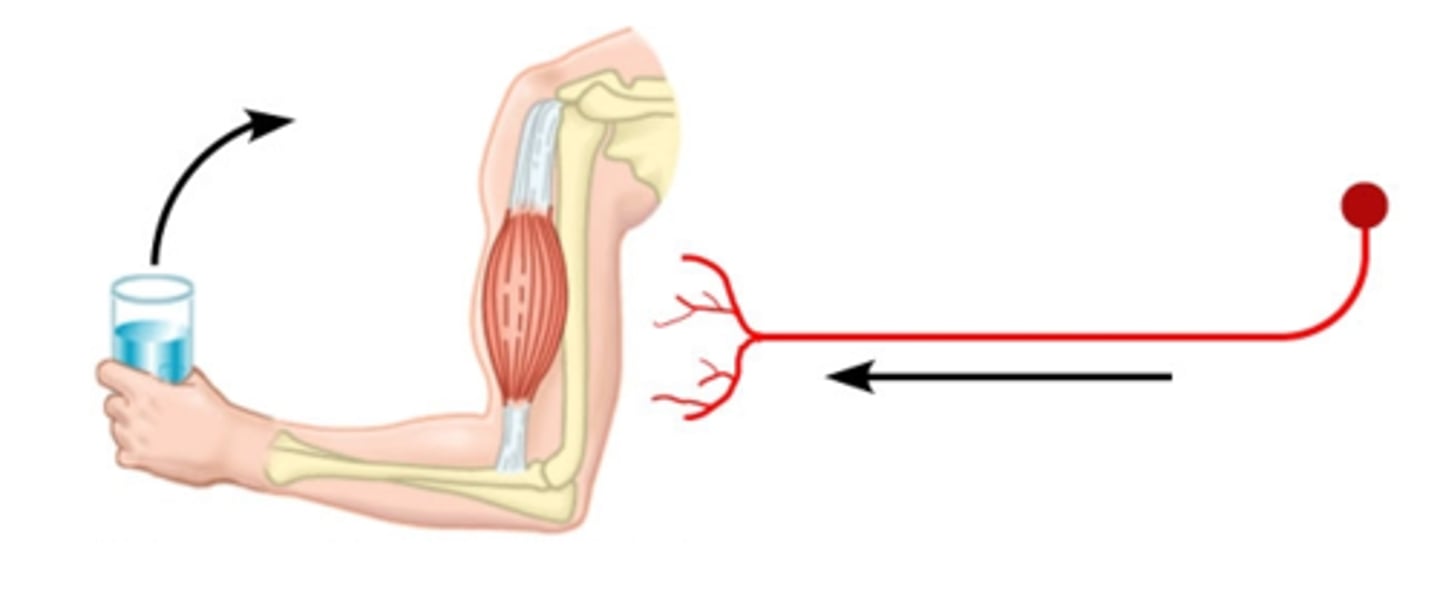
Motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
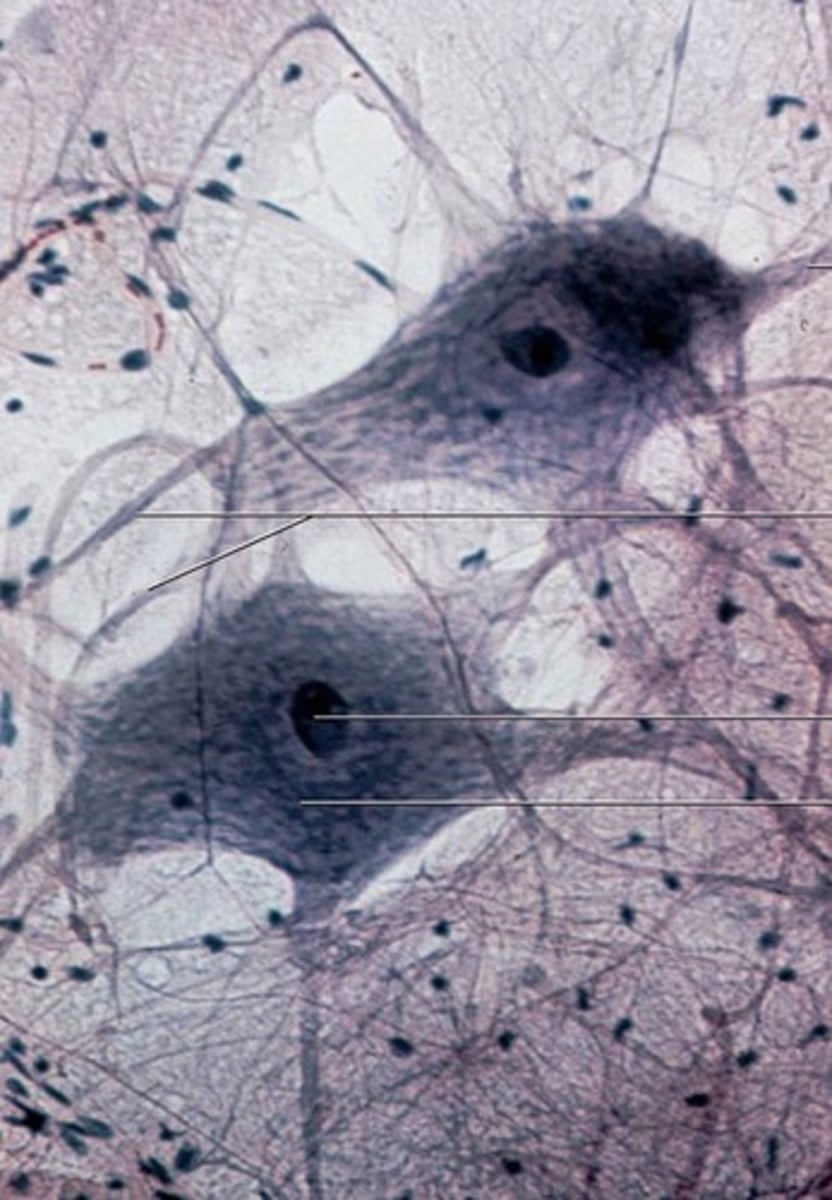
Neural transmission
electrochemical communication within and between neurons and the final destination
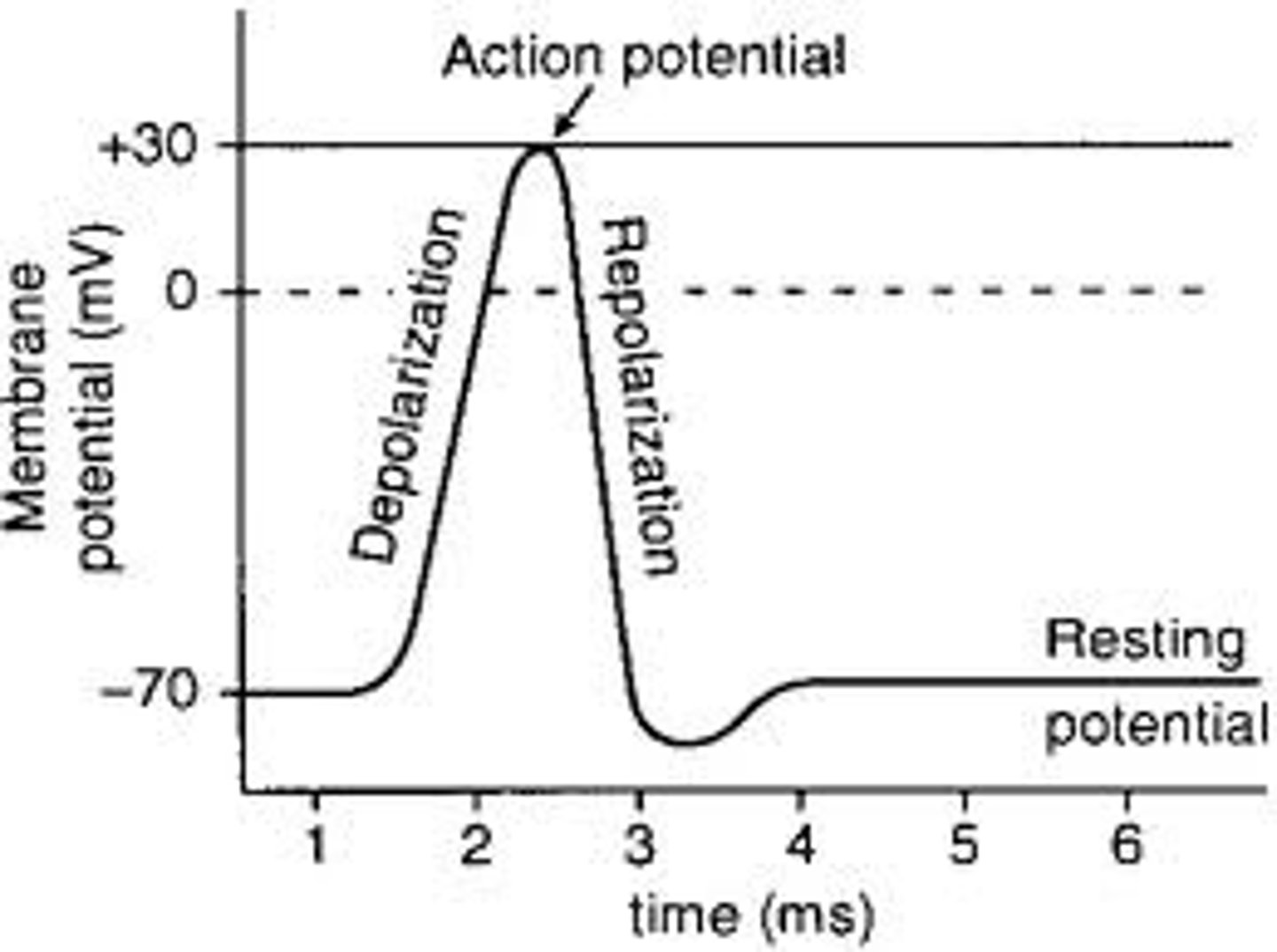
Depolarization
a rapid rise in potential in a neuron triggered by the opening of sodium ion channels within the plasma membrane (a positive value)
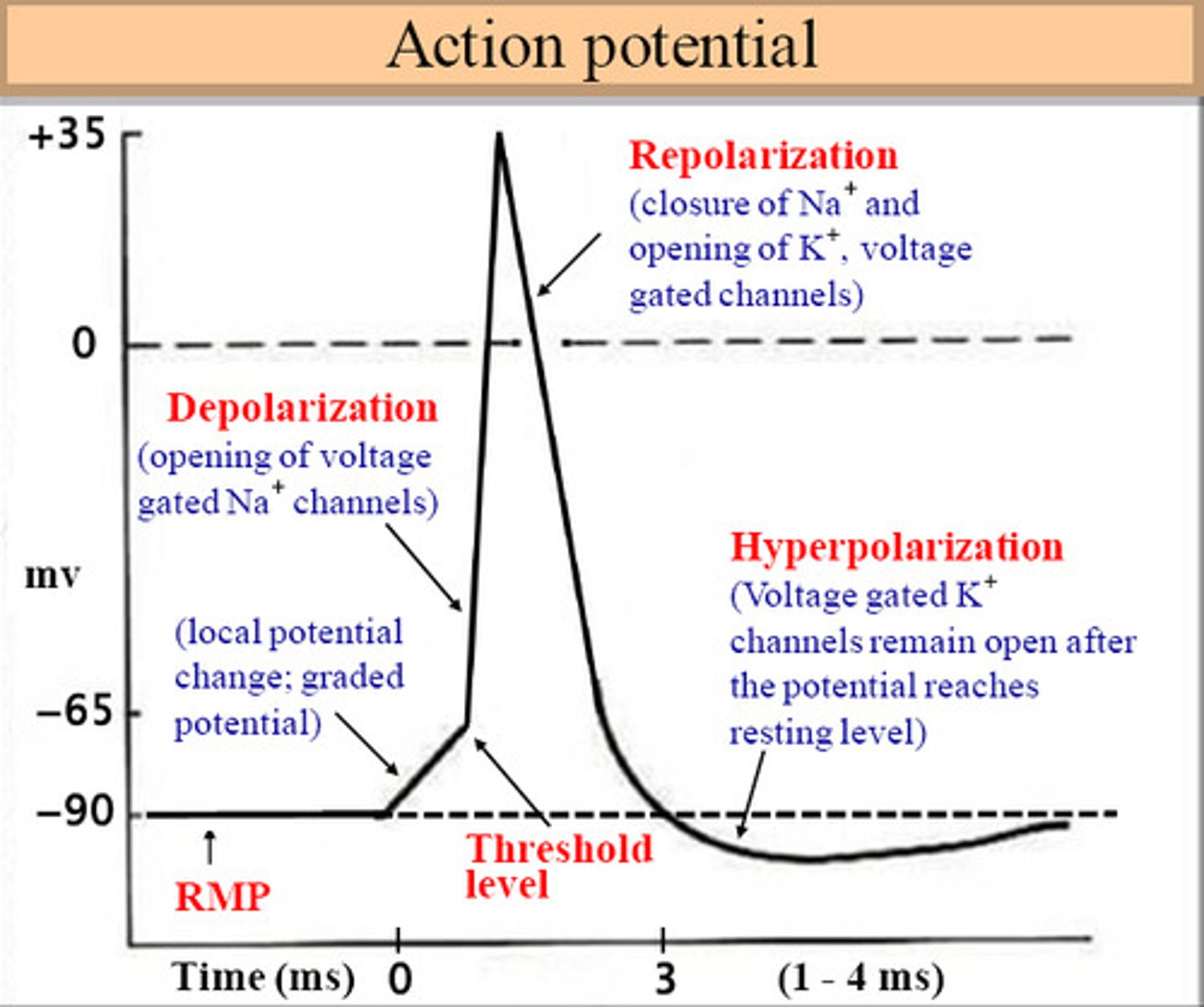
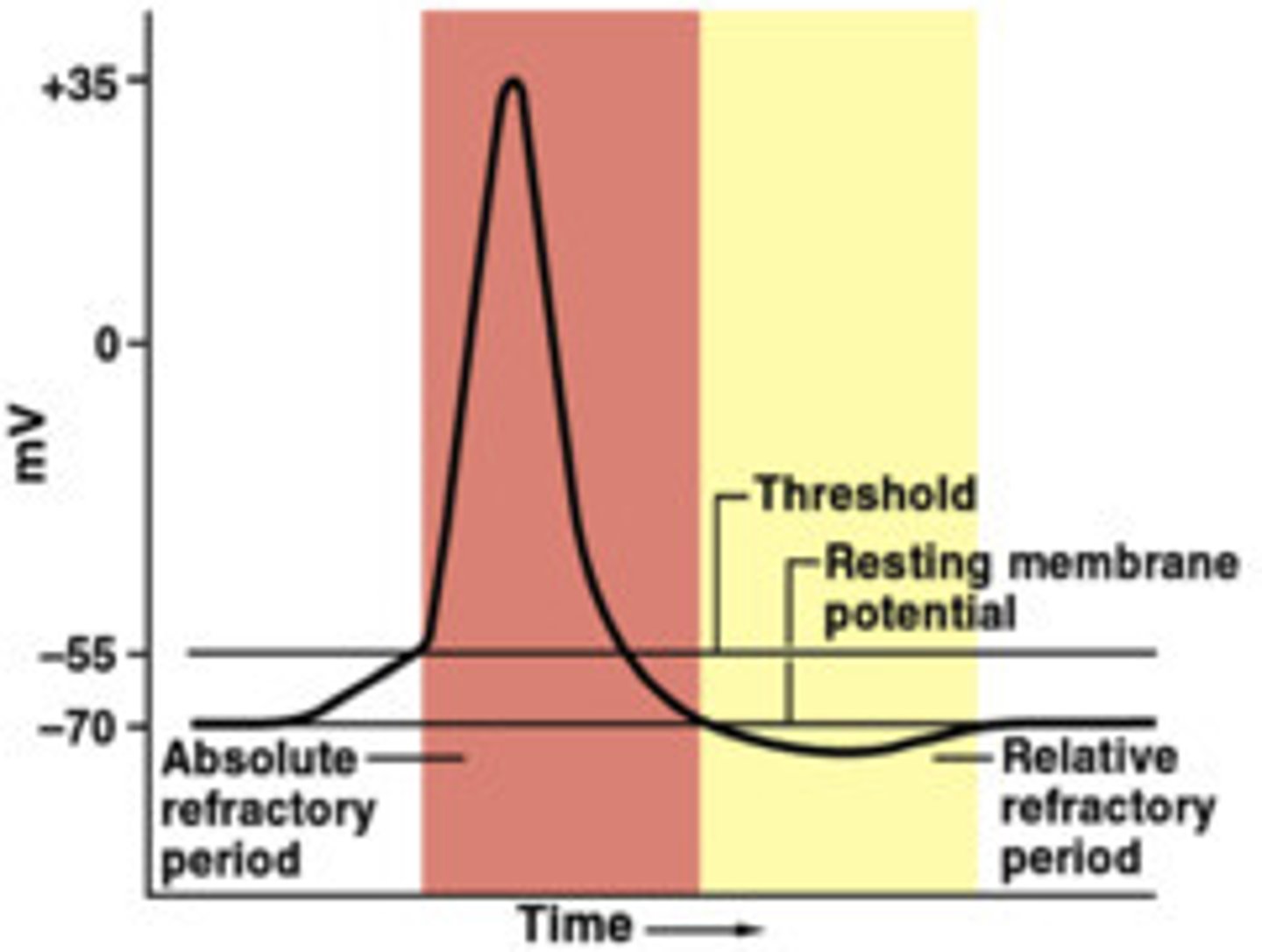
Refractory period
after a neuron has fired; the time following an action potential during which a new action potential cannot be initiated
Resting potential
the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse
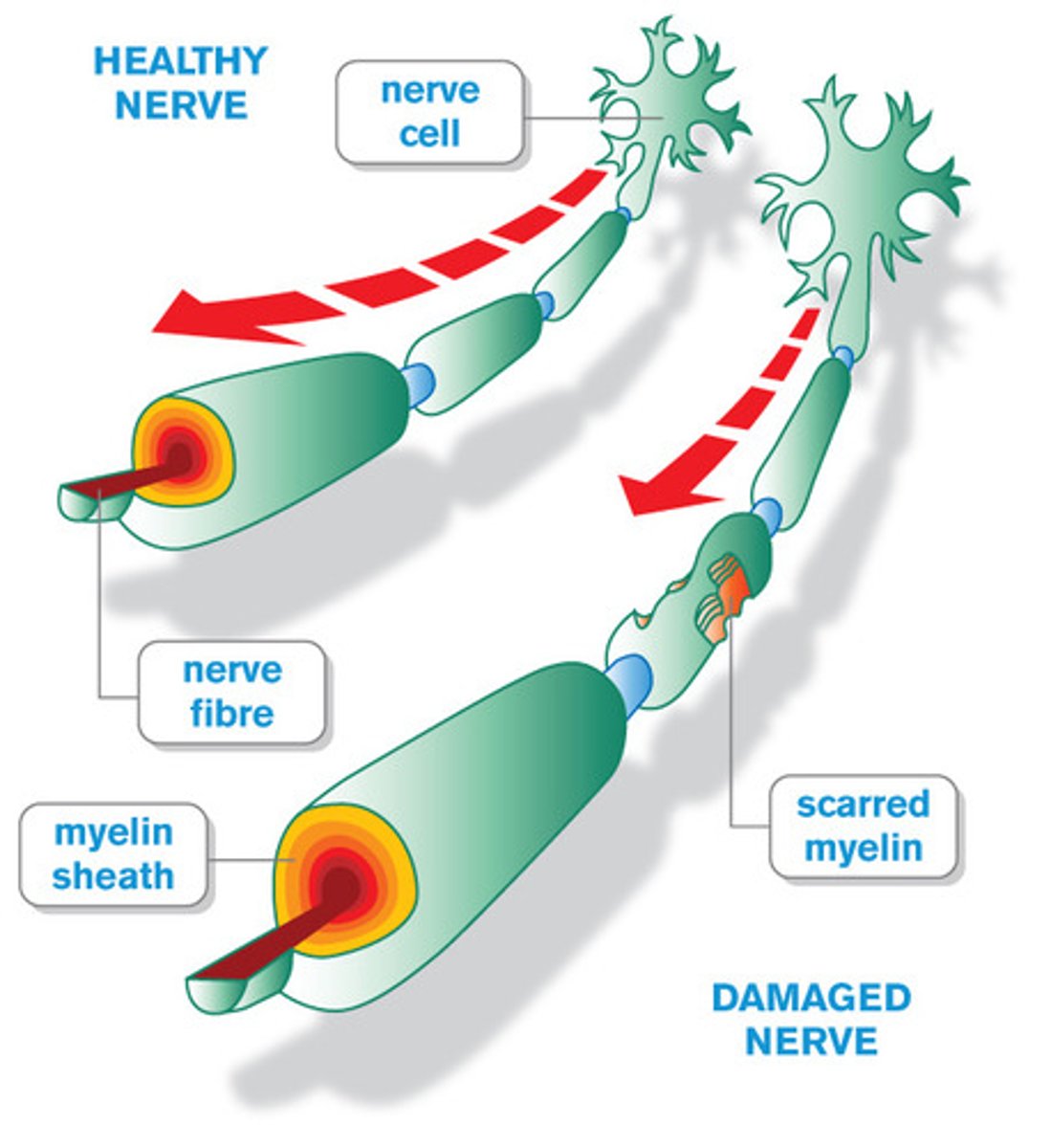
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
a degenerative disease caused by destruction of the myelin sheath on neurons in the CNS characterized by sclerotic patches along the brain and spinal cord
Myasthenia gravis
a chronic autoimmune disorder in which antibodies destroy the communication between nerves and muscle, resulting in weakness of the skeletal muscles
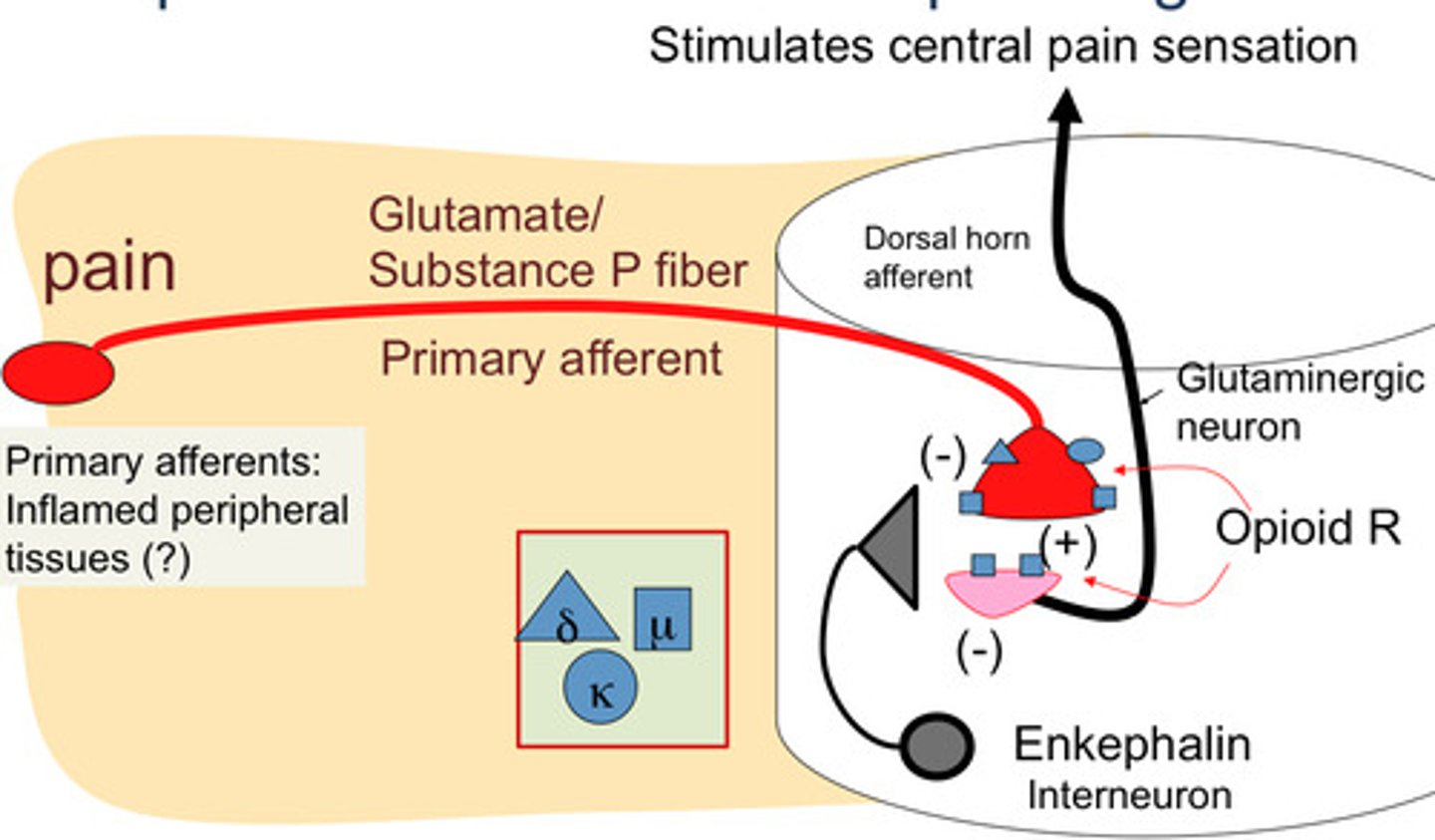
Substance p
a neurotransmitter that is involved in the transmission of pain messages to the brain
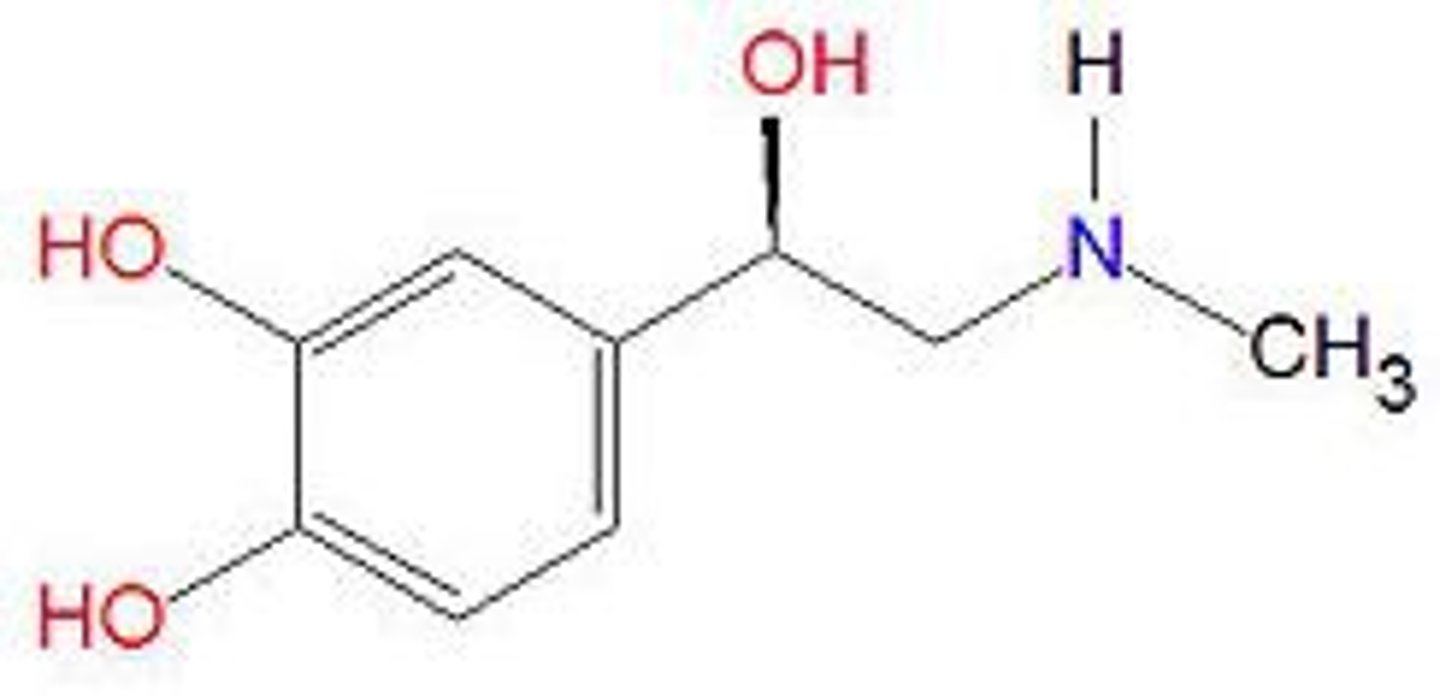
Adrenaline
a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands, especially in conditions of stress, increasing rates of blood circulation, breathing, and carbohydrate metabolism and preparing muscles for exertion
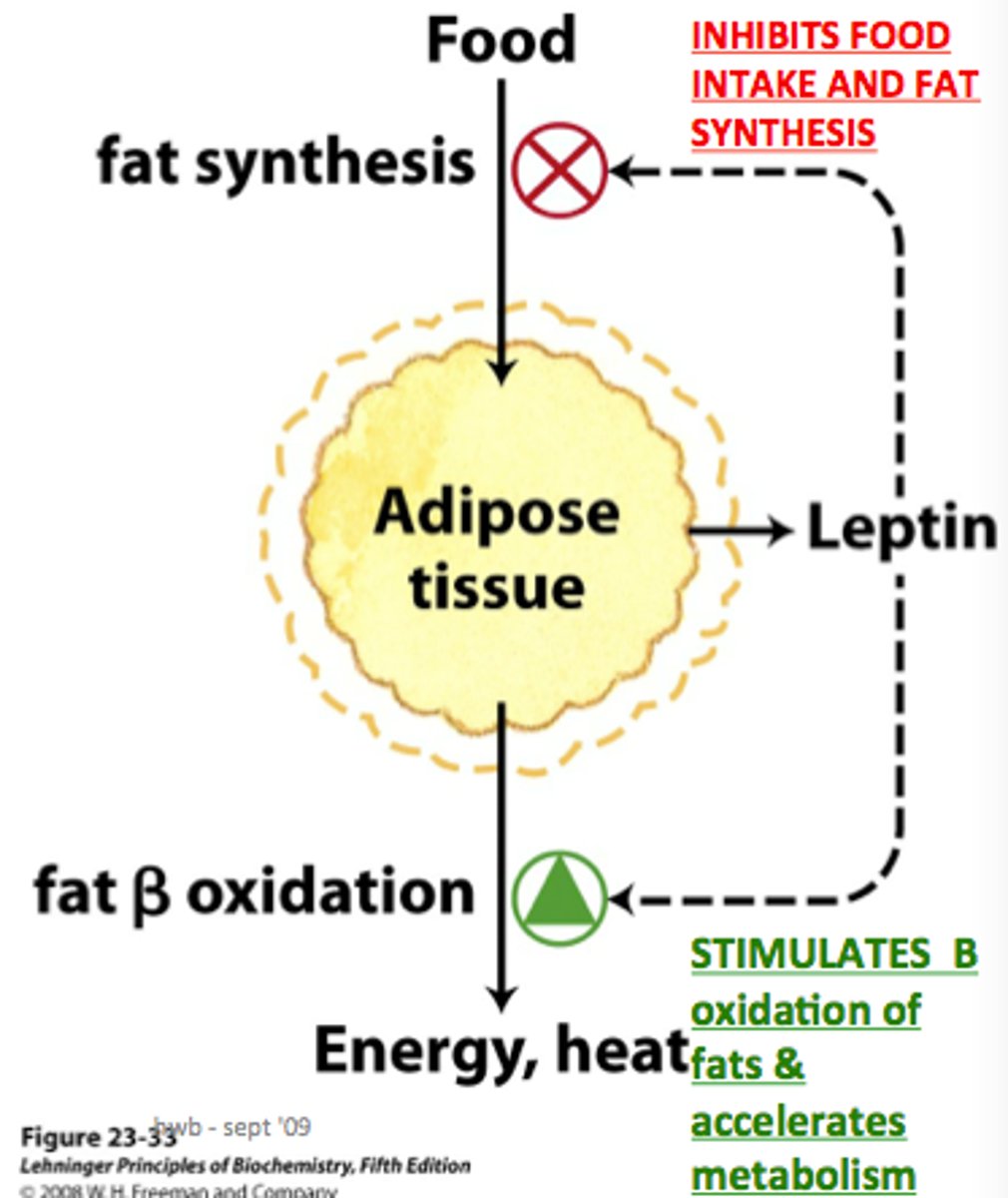
Leptin
hormone that signals the hypothalamus and brain stem to reduce appetite and increase the amount of energy used
Ghrelin
a hunger-arousing hormone secreted by an empty stomach

Melatonin
a hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.
Oxytocin
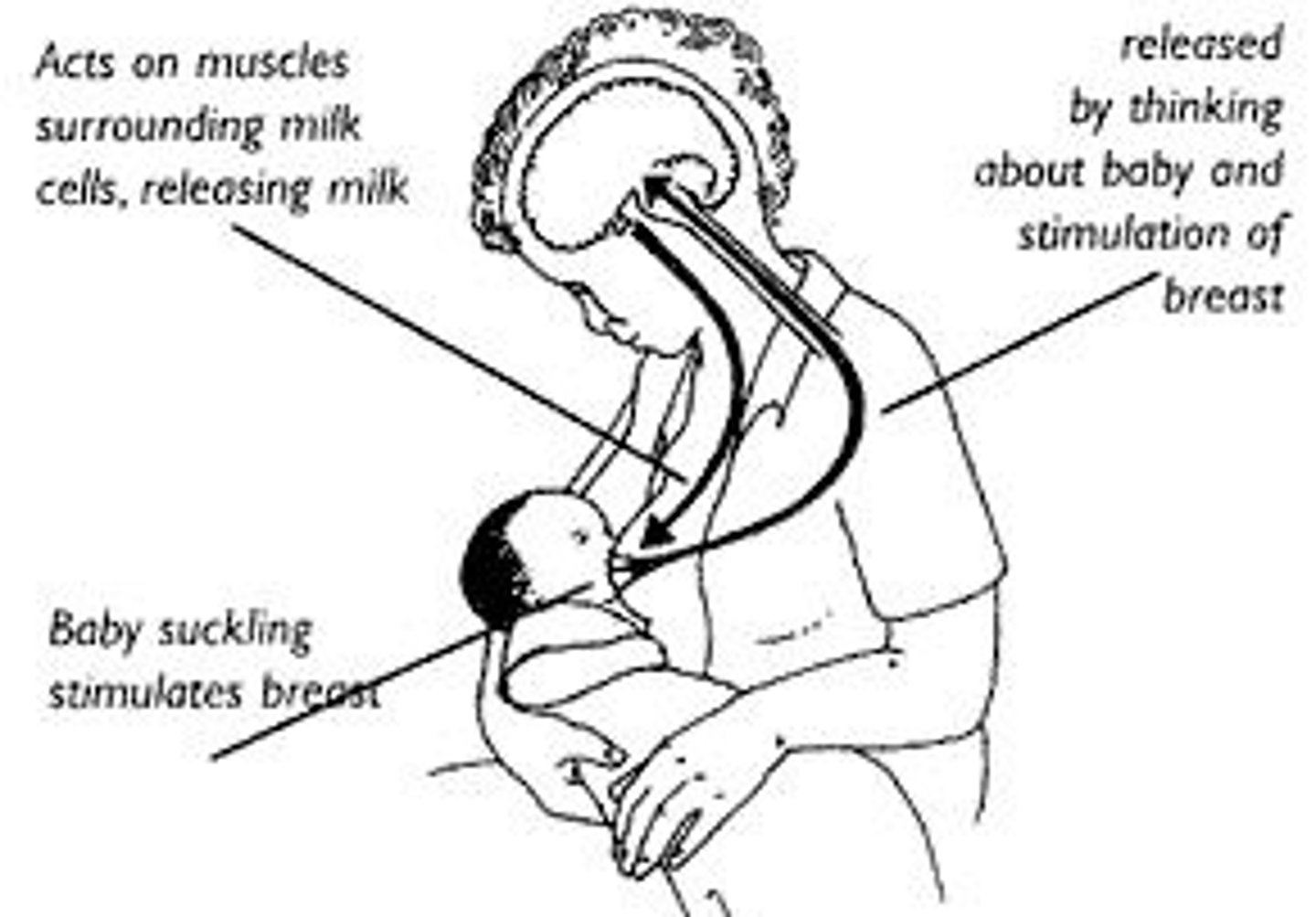
a hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates contraction of the uterus during labor and stimulates lactation after child birth
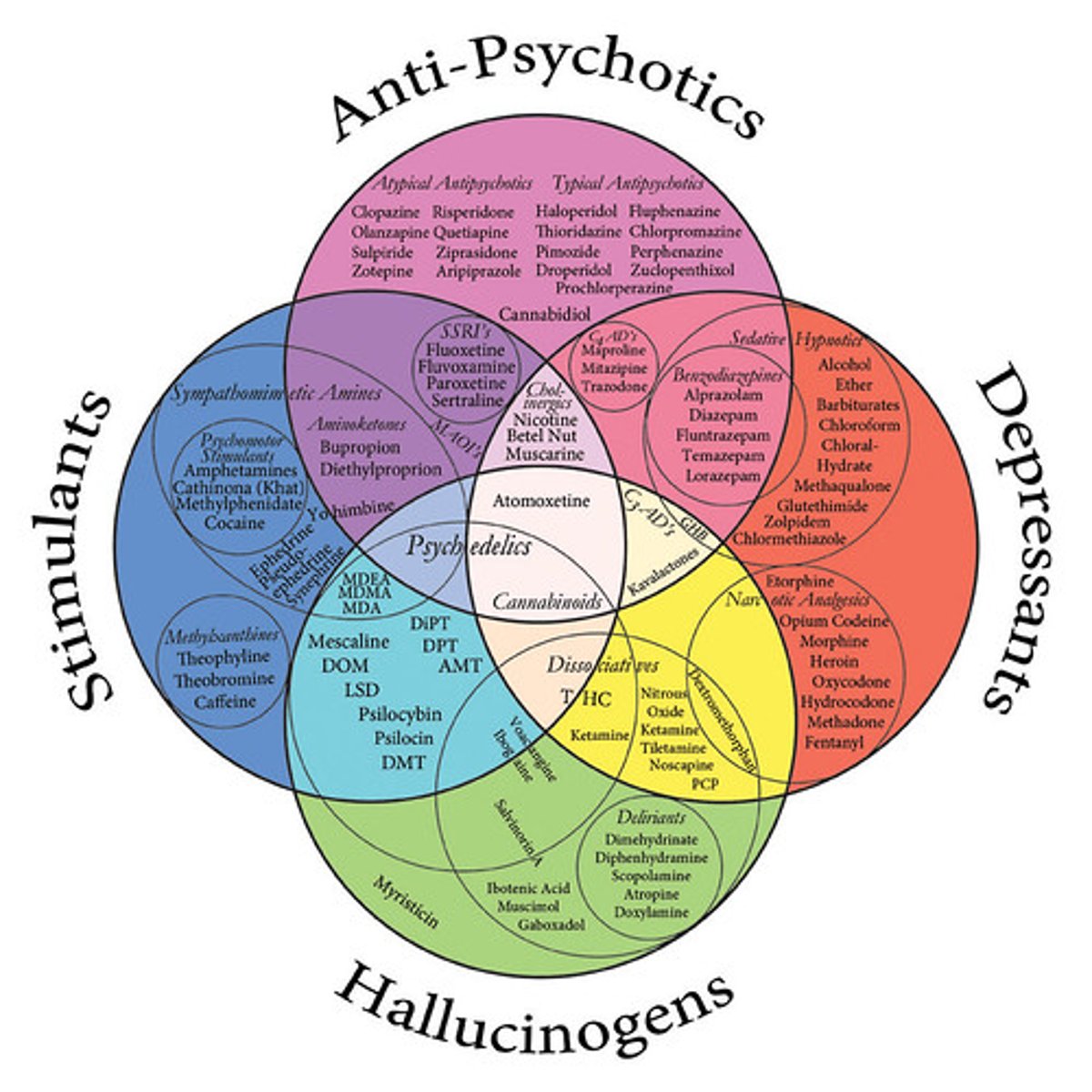
Psychoactive drugs
chemical substances that alter perception, mood, consciousness, perception, etc.
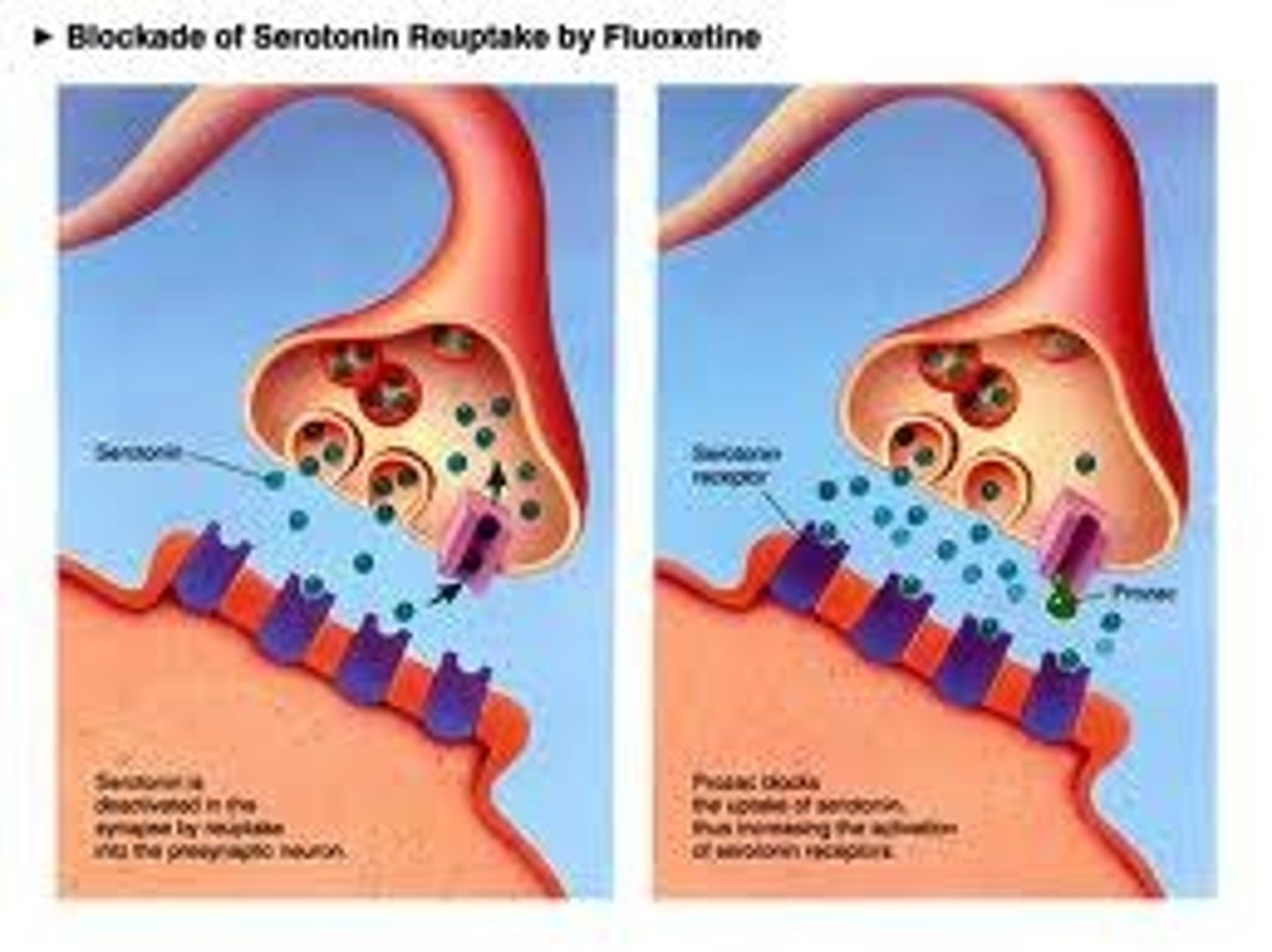
Reuptake inhibitors
drugs that interfere with the reabsorption of neurotransmitters in the synapse so that a greater amount remains in the synapse
Stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions

Caffeine
a stimulant drug found in coffee, tea, cola drinks, chocolate, and many over-the-counter medications

Cocaine
a powerful and addictive stimulant, derived from the coca plant, producing temporarily increased alertness and euphoria
Depressants
drugs (such as alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates) that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
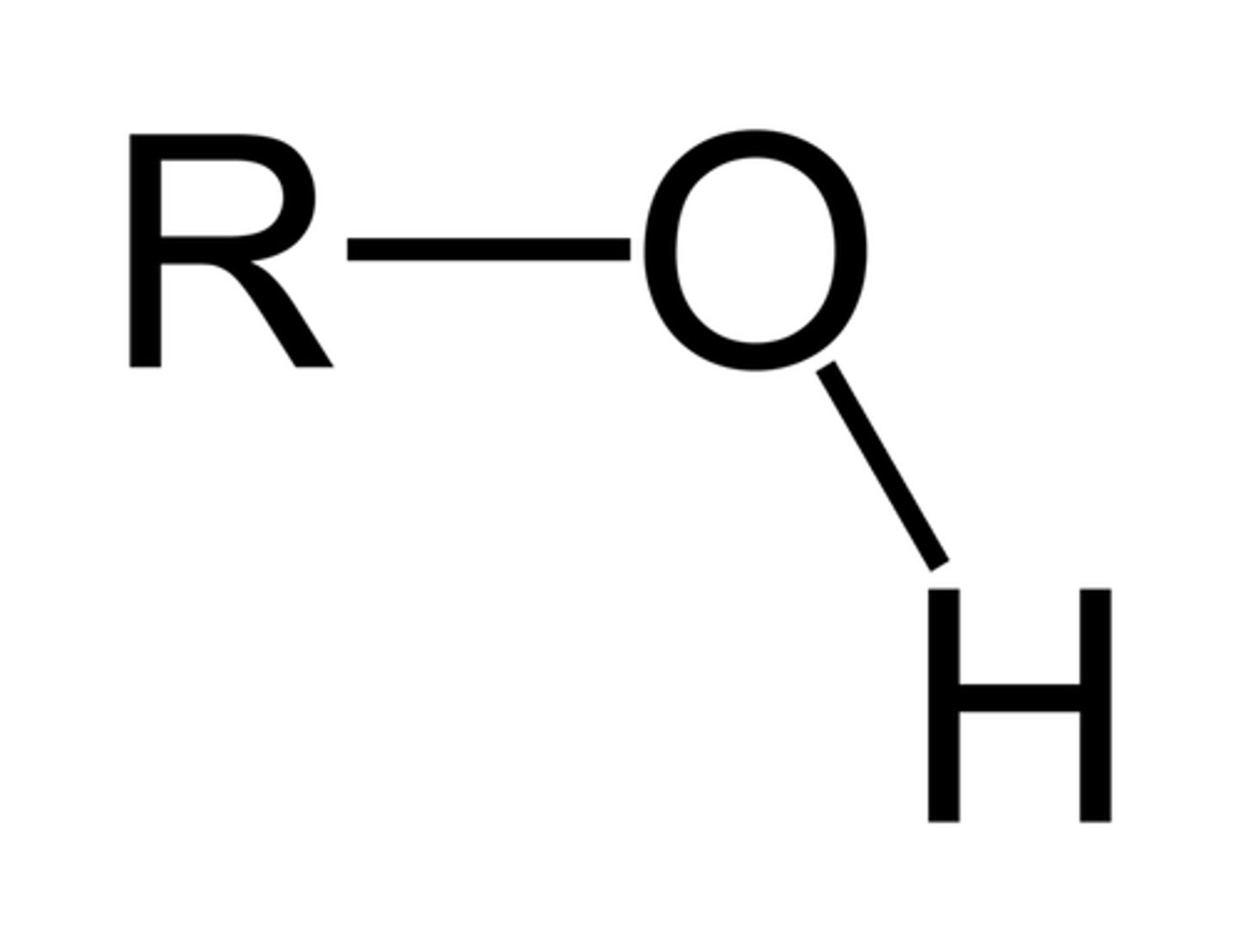
Alcohol
a psychotropic drug (ethanol), usually consumed in a beverage, that slows brain activity, impacting cognition, emotions, and perception
Hallucinogens
psychedelic drugs, such as LSD, that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
Marijuana
a drug, often smoked, causing euphoria, impairment of judgment and concentration and occasionally hallucinations

Opioids
synthetic opiates that are prescribed for pain relief
Heroin
narcotic drug derived from opium (an opioid) that is extremely addictive
Tolerance
the diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose of a drug, requiring the user to take larger and larger doses before experiencing the drug's effect
Addiction
A physiological or psychological dependence on a drug
Withdrawal
the discomfort and distress that follow discontinuing the use of an addictive drug
