Ketones and Aldehydes
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
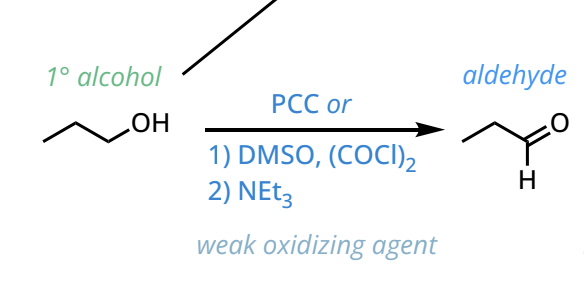
Primary alcohols to aldehydes
PCC, DMO, CH2Cl2
Swern Oxidation: 1. DMSO, (COCl) 2. Net3
ketones and aldehydes to alcohol
NaBH4 and H30
LiAlH4 and H30
Esters and carboxylic acids to alcohols
Only LiAlH4 is strong enough to reduce esters and carboxylic acids to primary alcohols
Carbonyl groups to Alkanes
Clemmensen reduction Zn (Hg) / HCl
Wolf- Kishner reduction: H2NNH2/ KOH/Heat
Acetal/ Ketal Formation
ROH, Cat H+
Acetal/Ketal Reduction
H3O
Acetal as a protecting group
acteal is part of the reagent list if there are two groups, in order to make sire only ester is reduces
Diol as a protecting group
Diol can act like for aldehydes and ketones, will create a cyclic acetal/ketal
Imine Formation
primary amine and cat. H+
Enamine Formation
secondary amine and cat H+
Hydrolysis of an imine and enamine
Cat H and H20 creates a ketone and amine
how to form a grignard Reagents
Halogen and alkyl halide
grignard reagents function as carbanions
Grignard Reagent and aldehyde or ketone plus H+
forms and alcohol and adds its carbon chain along with it
Grignard reagent with H20
will simply produce an alkane
Organolithium reagent
interchangeable with girgnard reagent
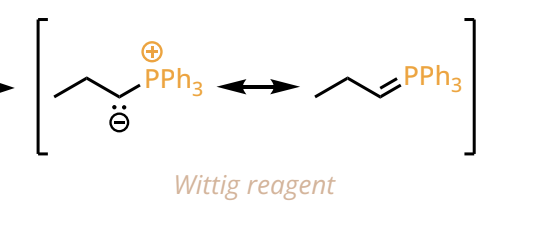
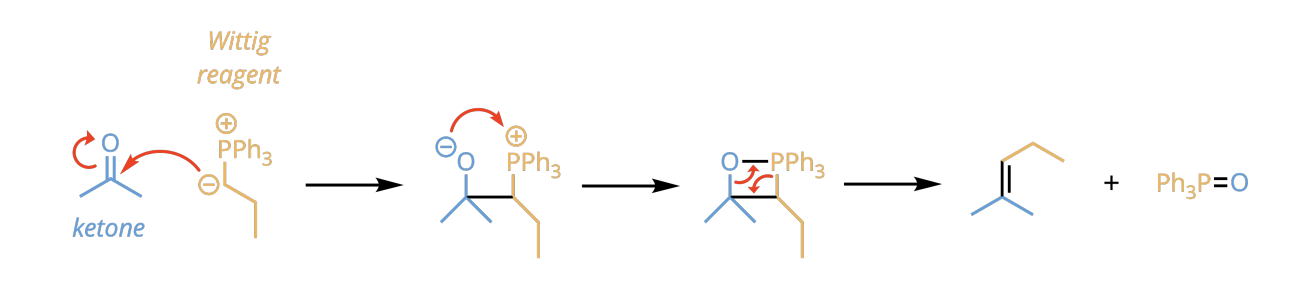
Witting Reagent formation
PPh3, CH3I
n-BuLi
Witting reagent and aldehyde and Ketone
creates almost a ring formation