ECON 0200 CH 13
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Last chapter we learned
businesses require capital to start up and grow
to get this they need
investors with more money that they don’t immediately need to spend
Where do they put their savings? Into an investment that promises growth
any investment must be
someone’s savings
economics is concerned with real activity i.e. GDP, employment
but the 2008 crisis taught us finance can’t be separated from real activity
macrofinance studies this connection
financial system
the group of institutions in the economy that match those who wish to save with those seeking to borrow
the financial system moves
savers’ money to productive investments
The financial system broadly consists of two components
Financial markets
• Financial intermediaries
financial markets
financial institutions where savers provide funds directly to borrowers
The two largest financial markets in the US:
the stocks and bonds markets
A bond is
a debt certificate that specifies the:
principal - the size of the initial investment
2. interest rate
3. maturity - when repayment with interest is due
debt finance
Raising money through issuing bonds
2 types of bonds
Government bonds (i.e. national debt)
• Corporate bonds
interest is compensation to investors for
not being able to use their money
• taking on some risk that the investment fails
reasons for high interest rate
The bond matures in a long time (has a long term)
• The borrower is likely to not repay (high default risk)
• The bond is subject to taxes
• The bond is not protected from inflation
stock
a claim to partial ownership of a firm
equity finance
Raising money through issuing stocks
a firm’s value/market capitalization calculation
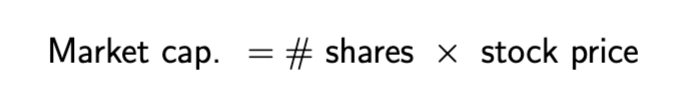
issuance
A firm chooses how many shares of their company are for sale
The price of a stock is just like anything else
driven by supply and demand
factors that affect stock demand
How profitable the firm is (paid to shareholders through dividends)
• How optimistic people feel about the firm’s future
In general, stocks are
more risky than bonds but offer greater returns
financial intermediaries
financial institutions where savers provide funds to borrowers indirectly
In a financial market, you are responsible for picking your investments
Financial intermediaries employ analysts to do the thinking for you
two common intermediaries:
banks and mutual funds
intermediary tradeoff
less risk through an intermediary, but lower potential returns
in terms of accounting GDP
Investment is what’s left of output after consuming and gov’t spending
definition of saving
the share of output we don’t spend
national saving
is the share of output left after consumption and government expenditures
saving calculation
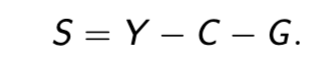
every dollar invested
is a dollar saved
S = I
GDP decomposition involving taxes
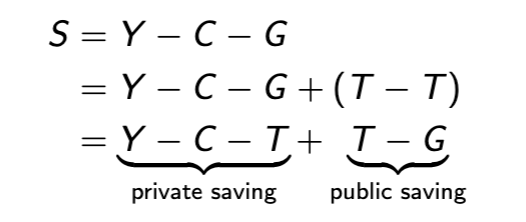
disposable income
what’s left of output after taxes are collected
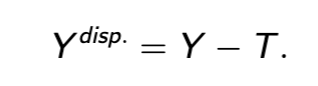
private saving
what’s left of disposable income after consumption
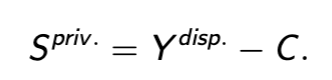
a nation’s income equals
its output
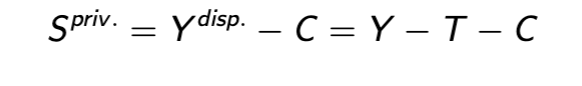
public saving
what’s left of government revenues after government expenditures
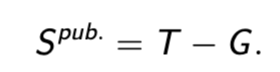
budget surplus
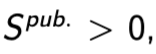
in the event of a surplus
They can pay down existing debts, issue a tax refund
budget deficit
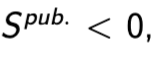
in the event of a deficit
Issue debt in the form of bonds
building a market model
Savers supply funds, borrowers demand funds
• Where do they meet and determine the terms of trade? A market
market for loanable funds
the market where savers supply funds and borrowers demand funds for investment purposes
the interest rate
the price in the market for loanable funds
supply of loanable funds
Households’ and firms’ savings
How does the supply of loanable funds react to changes in the interest rate
supply of loanable funds S(r ) is increasing in r

demand of loanable funds
Households’ and firms’ investment
Households take out mortgages for new houses
• Firms issue debt/equity to acquire capital
How does the demand of loanable funds react to changes in the interest rate
demand of loanable D(r ) funds is decreasing in r

equilibrium interest rate
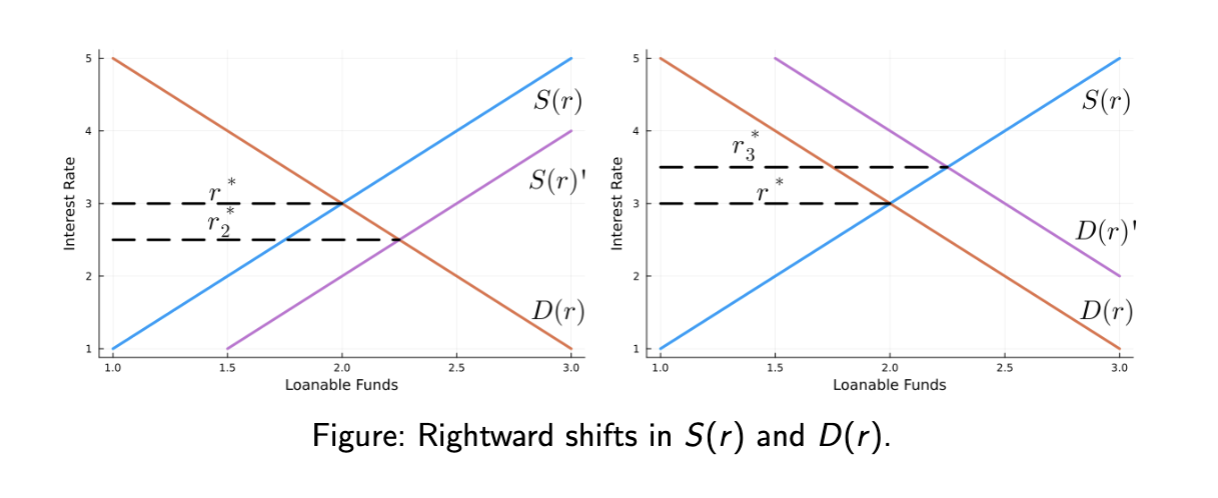
If S(r ) shifts right,
savers supply more for at given r than before
what causes a rightward shift in S(r )
Policies that incentivize saving (i.e. tax cuts/credits)
• An decrease in the government’s deficit (S = Spub. + Spriv ., Spub. ↑)
If S(r ) shifts right and D(r ) doesn’t move,
then r ∗ falls
For a leftward shift
flip all the information on the last 3 flashcards
If D(r ) shifts right
borrowers demand more for at given r than before
What can cause a rightward shift in D(r )?
• Policies that incentivize borrowing (i.e. tax cuts/credits)
If D(r ) shifts right and S(r ) doesn’t move,
then r ∗ rises
For a leftward shift
flip everything around on the last 3 flashcards
shifts graphically