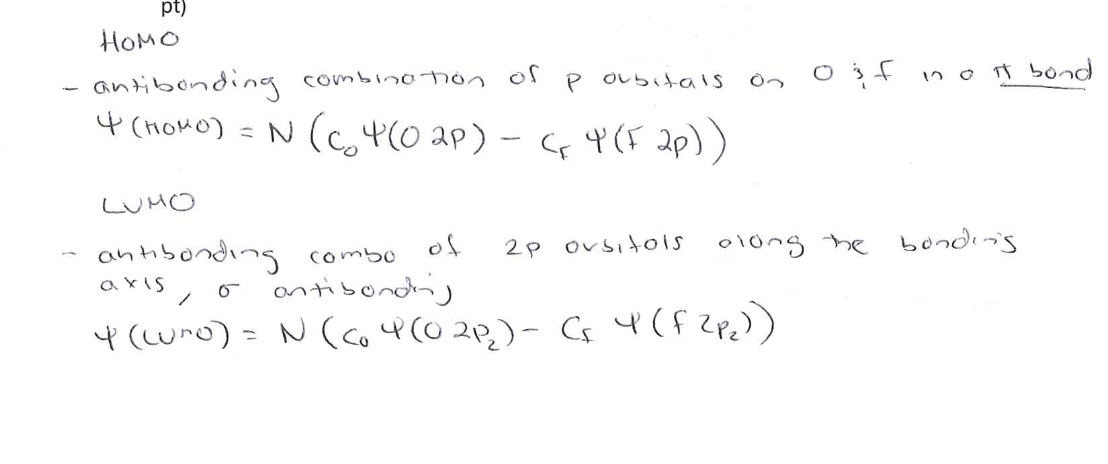Foundational Inorganic Units 1-4
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Allowed energy states are described by the principal quantum number ___
n
To promote an electron from lower to higher n, energy must be what?
energy must be input as light or heat
When an electron relaxes from higher (excited state) to lower n, energy is what?
energy is released as emitted light
What does a higher n mean?
higher n = less negative energy so less negative is less stable
What was Bohr’s model of the atom?
Electrons are held in orbit around the nucleus by a balance of electrostatic attraction and centripetal force
What happens to the electron when it is in an excited state (energy level diagram)?
The electron is further from the positive nucleus, so its less stabilized and it has higher energy
What happens to the electron when it is in the ground state (energy level diagram)?
The electron is closest to the positive nucleus, it is most stabilized by the attraction to the nucleus and it is lowest in energy
What was the problem with Bohr’s model?
Accelerating electrons would lose energy by giving off radiation. As electrons lose energy, they would move more slowly and collapse into the electrostatic pull of the nucleus. So all atoms with orbiting electrons would collapse within picoseconds.
Each wave function can be broken into a __ and a __ component
radial and angular
Each wave function contains three quantum numbers what are they?
n, l, ml
What does the quantum number n mean?
energy level
How do you find the total node amount?
n-1
How do you find the amount of radial nodes?
n-l-1
What does the quantum number l mean?
gives orbital shape in space
what are the angular momentum values (l) for the s, p, and d orbitals?
l=0 for s
l=1 for p
l=2 for d
How do you find the amount of angular nodes?
angular nodes = l
Sketch the Pz orbital
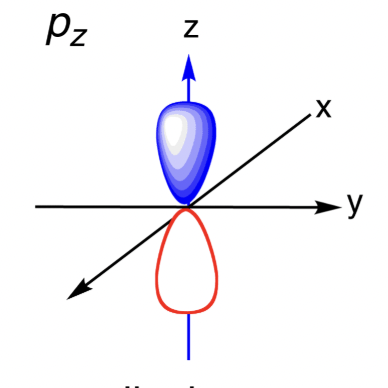
Sketch the Px orbital
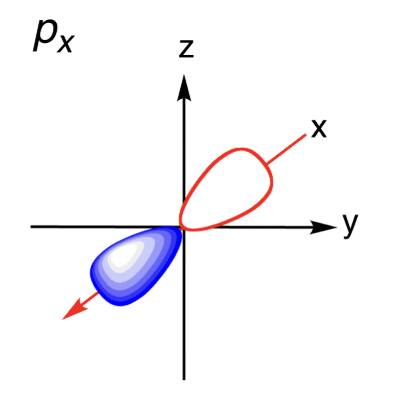
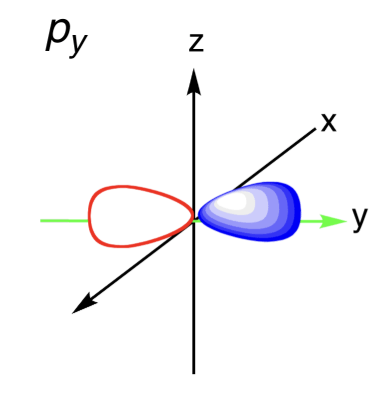
Sketch the Py orbital
sketch the dz²
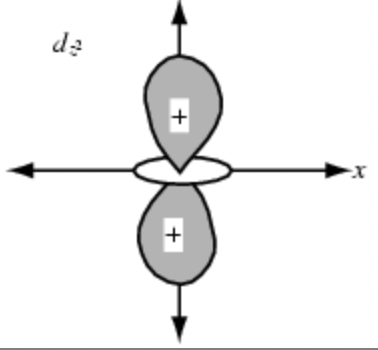
sketch the dxz orbital
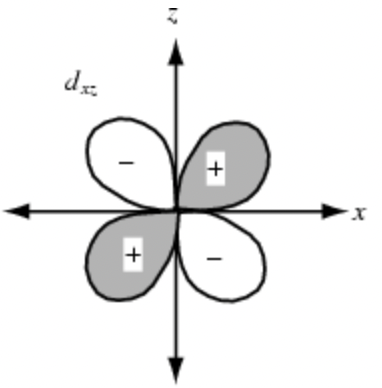
Sketch the dxy orbital
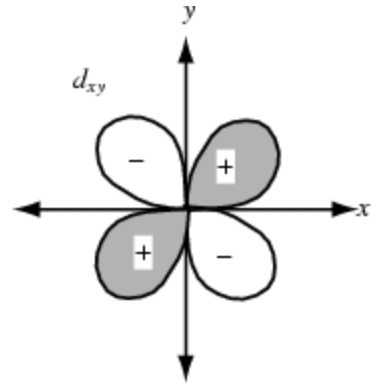
Sketch the dx²-y² orbital
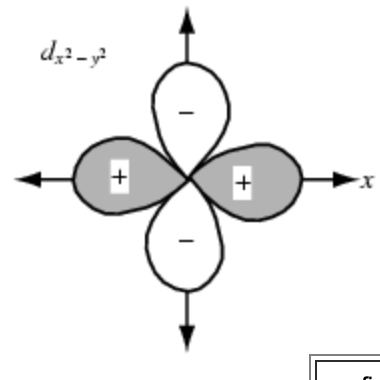
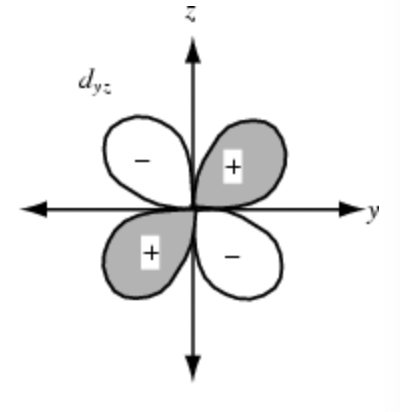
Sketch the dyz orbital
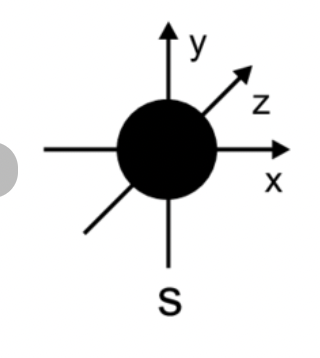
sketch the s orbital
What does Aufbau Principle state?
electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first
What does the Pauli exclusion principle state?
Electrons in the same orbital have opposite spin quantum numbers (+1/2 vs -1/2) so that no 2 electrons have identical sets of quantum #’s
What does Hund’s Rule state?
When filling degenerate orbitals (i.e. same energy), electrons fill any empty orbital before pairing and this limits repulsion. Electrons in degenerate half-filled orbitals have the same (“unpaired”) spin and this maximizes exchange energy
In cations what is the rule when filling the d orbital?
In cations the d orbitals sink below the higher shell’s s orbital and fill first
What is the exception for the d electrons filling the orbital? What does the electron configuration of Cr look like?
In neutral atoms, one “s” electron can move to the higher “d” orbitals if a half filled or completely filled d shell would result so for Cr [Ar]4s13d5
What is the trend of Effective Nuclear Charge (Zeff) on the periodic table?
Zeff increases from left to right
What is the trend of Neutral Atomic Radii (main block) on the periodic table?
The size increases moving down the periodic table and from right to left
What is the trend for Neutral Atomic Radii (transition metals (d-block)), period 6,5,4, on the periodic table?
The size starts big and then gets smaller after the first one until it gets to the 4th to last one where starts to increase again but that last one will not be anywhere as nearly as big as the first element that started that period
What is the trend for ionic radii on the periodic table?
Cations are smaller than their neutral atoms because electrons have been lost for Ti²+ (100 pm) > Ti³+ (81 ppm). So for the same element, more positive charge = lower radius
Anions are larger than their neutral atoms because electrons have been added. For the same element, more negative charge = larger radius
What is ionization energy?
Energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion
What do positive values mean for ionization energy? What does a higher value mean for ionization energy?
Positive value: putting energy in to remove the electron. The electron is more stable in the atom
Higher value: Harder to become a cation. The electrons are tightly held within the atom/highly stabalized
What is the trend for ionization energy (main group (no d-block)) on the periodic table?
Increasing IE goes from left to right and from bottom to top. But the exception is it drops in groups 13 and 16
What is electron affinity?
energy required to remove an electron from the gaseous anion (-1 charge) of an element
What is the trend of the electron affinity on the periodic table?
EA increases from left to right and from bottom to top. The exceptions here are group 15 have small values and period 3 has higher EA values
What is electronegativity?
Ability of an atom to attract electron density
What is the trend of electronegativity on the periodic table?
Electronegativity increases from left to right and from bottom to top. D-block is the exception, electronegativity starts to decline as d orbitals fill
Ionic bonding forms bonds to achieve ___ full shell electron configurations
FAVORED
What are the three unit cells covered in class?
primitive cubic
body centered cubic
face-centered cubic
Covalent bonding occurs between what?
Occurs between non-metals or between non-metals and metalloids
What is the difference between covalent bonding and ionic bonding?
In covalent bonding electrons are shared to allow each atom to obtain a full electron configuration. In ionic bonding electrons are fully transferred from one atom to the other
What are the “rules” for the best lewis structure?
minimize or eliminate formal charges
place negative formal charge on the MOST electronegative atom
place positive formal charge on the LEAST electronegative atom
What is formal charge?
Difference between a neutral atoms valence electron count and the number of electron assigned to the atom in a structure
What is the equation to find bond order?
bond order = # of bonds/ # of bonding pairs in resonance
If the electron pair equals 2 what is the electron pair geometry assignment? What is its angle?
linear, 180°
If the electron pair equals 3 what is the electron pair geometry assignment? What is its angle?
trigonal planar, 120°
If the electron pair equals 4 what is the electron pair geometry assignment? What is its angle?
tetrahedral, 109.5°
If the electron pair equals 5 what is the electron pair geometry assignment? What is its angle?
trigonal bipyramidal, 120° (equitorial), and 90°
If the electron pair equals 6 what is the electron pair geometry assignment? What is its angle?
octahedral, 90°
If the electron pair geometry is trigonal planar and it has a lone pair what is the molecular geometry?
Bent
If the electron pair geometry is tetrahedral and it has a lone pair what is the molecular geometry?
Trigonal pyramidal
If the electron pair geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and it has a lone pair what is the molecular geometry?
Seesaw
If the electron pair geometry is octahedral and it has a lone pair what is the molecular geometry?
Square Pyramidal
If the electron pair geometry is tetrahedral and it has two lone pairs what is the molecular geometry?
Bent
If the electron pair geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and it has two lone pairs what is the molecular geometry?
T-shaped
If the electron pair geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and it has three lone pairs what is the molecular geometry?
linear
If the electron pair geometry is octahedral and it has two lone pairs what is the molecular geometry?
square planar
Lone pairs are less confined and need more space than bonding pairs in electron geometry, so how does that affect bond angles?
Adding lone pairs squeezes boning pairs together which lower bond angles. As the number of lone pairs increases, bond angles decreases.
True or False? Pi bonds take up more space than single bonds but less space than lone pairs
True
Trigonal bipyramidal shape has two distinct positions. Axial which is separated from 3 atoms by 90° and 1 atoms by 180°. Equatorial which is separated from 2 atoms by 90° and 2 atoms by 120°. Lone pairs must be added to which position?
Equatorial
All octahedral positions are equivalent separated from 4 atoms by 90° and 1 atom by 180°. If two lone pairs are added, they must be what?
Opposite of each other
Polarity determines solubility how does that affect polar molecules?
Like dissolves like
Polar compounds show high solubility in polar solvents like water and low solubility in nonpolar solvents
Polar substances experience stronger intermolecular forces, how does that affect distinct features of that molecule?
Stronger intermolecular forces mean higher boiling point, melting point, and viscosity
Simplest repeating structure within a lattice is called what?
unit cell
How are radial probability functions for atomic orbitals derived? Select the best answer.
a. The radial and angular wave functions of the atomic orbital are multiplied and the product is integrated over all radius values
b. Radial wavefunctions are added with areas of constructive interference giving a larger probability and areas of destructive interference having lower probability
c. The radial wavefunction is squared and integrated over all theta and phi coordinates
d. The radial wavefunction is plotted after being normalized such that integration over all space equals one
c. The radial wavefunction is squared and integrated over all theta and phi coordinates
Which series below correctly arranges the atoms in order of DECREASING radius?
a. Mg > Ca > Ga > Se > Cl > Br
b. Ca > Mg > Ga > Se > Cl > Br
c. Ca > Mg > Ga > Se > Br > Cl
d. Ga > Ca > Mg > Se > Cl > Br
e. none of the above
c. Ca > Mg > Ga > Se > Br > Cl
Which series below correctly arranges the atoms in order of DECREASING radius?
a. Zr > Mo > Au > Ag
b. Au > Zr > Mo > Ag
c. Au > Ag > Zr > Mo
d. Au > Ag > Mo > Zr
e. none of the above
e. none of the above
Which species has the LARGEST radius?
Ca²+, Se, Se²-
Se²-
Which species has the LOWEST electron affinity?
Br, Se, As, Ge
Which atom has the LOWEST electronegativity?
Br, Se, As, Ge
Ge
Which series below correctly arranges the atoms in order of DECREASING ionization energy?
a. Ca > Ga > As > Se > Br
b. Br > Se > As > Ga > Ca
c. Br > Se > As > Ca > Ga
d. Br > As > Se > Ca > Ga
d. Br > As > Se > Ca > Ga
True or False: KrBr+ is a stable ion?
Yes, the bond order is greater than 1/2
Give the short hand notation for the electron configuration of Fe2+
[Ar]3d6
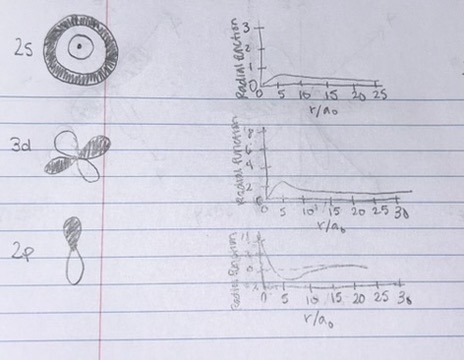
Match each orbital on the left to the correct radial wavefunction graph on the right
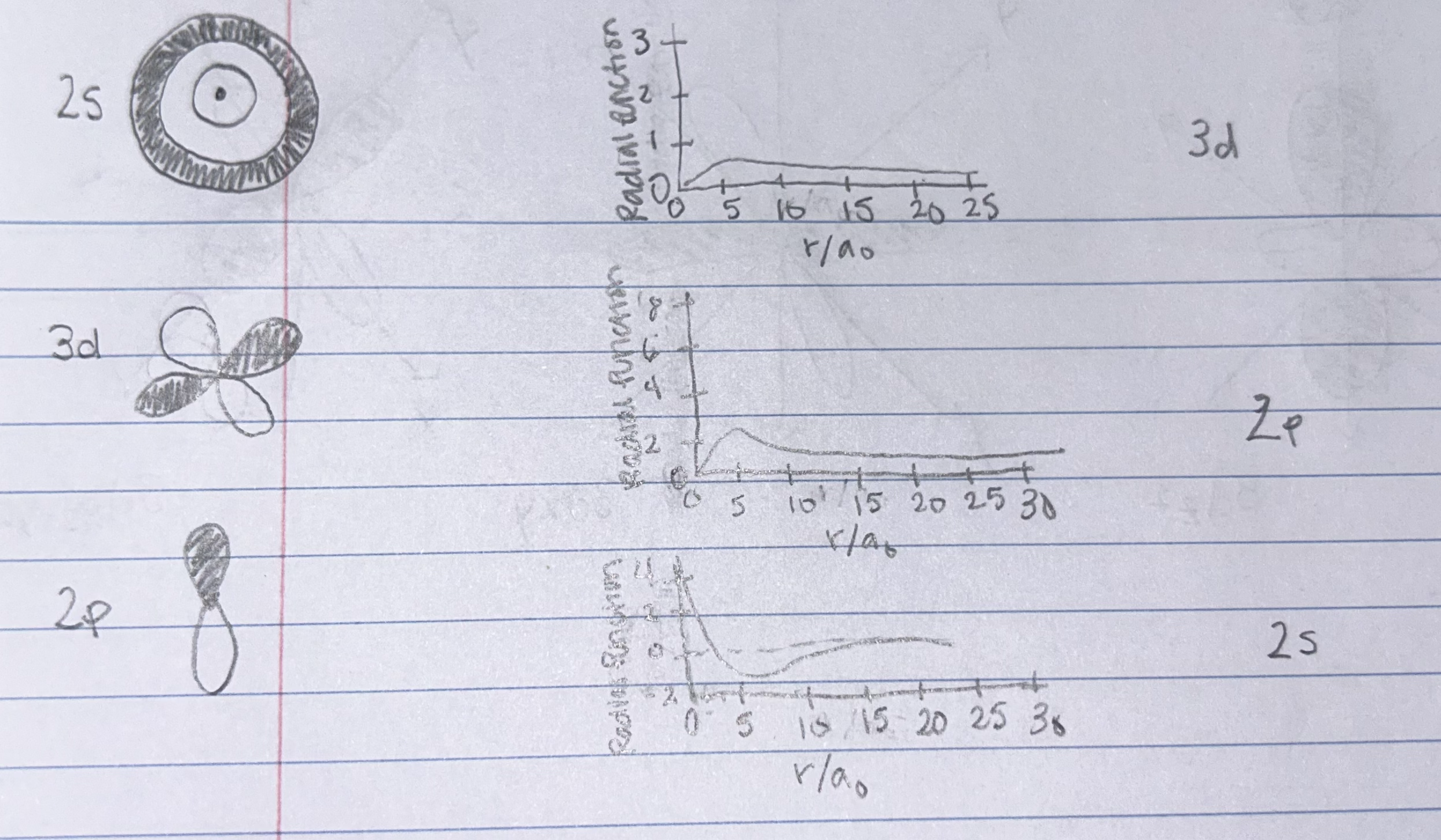
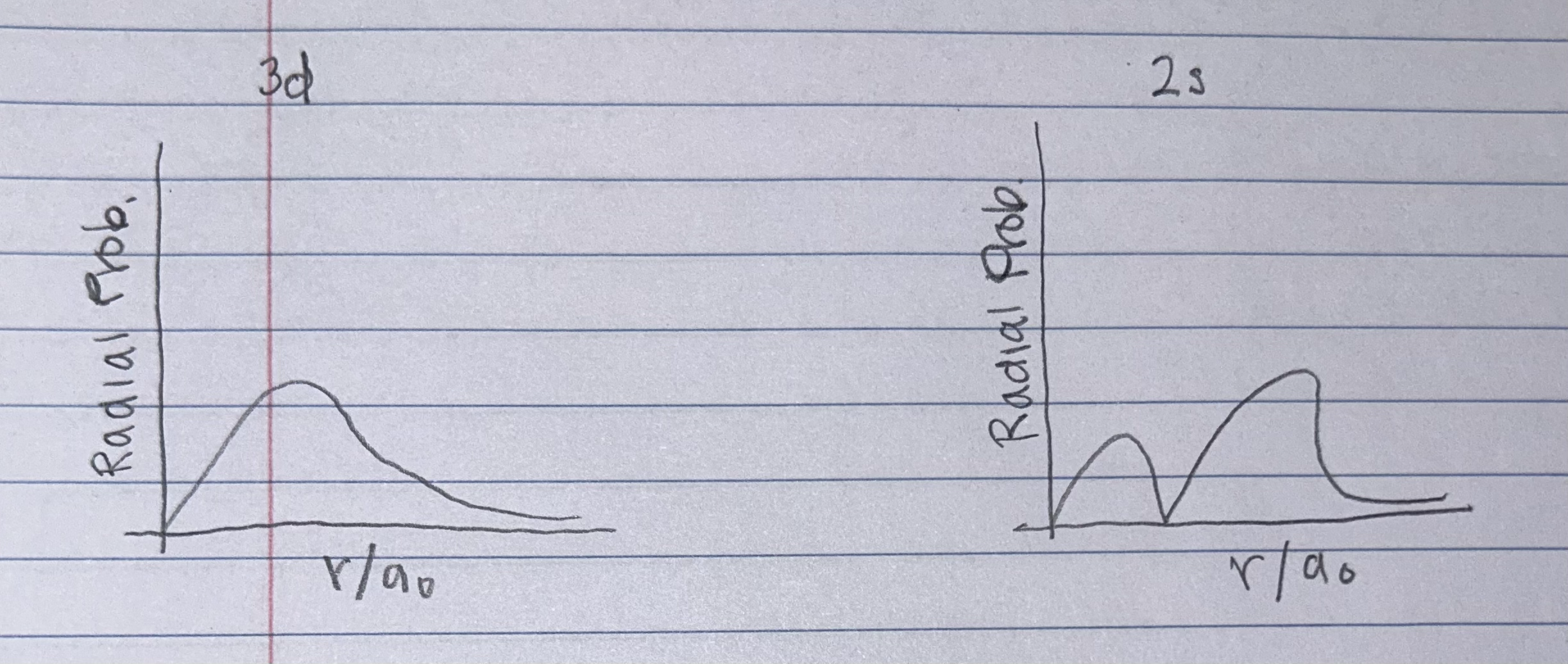
For the 3d AND 2s orbitals shown above, draw graphs of the Radial Probability Functions. Be sure that the differences in the graphs are clear and axes are labeled
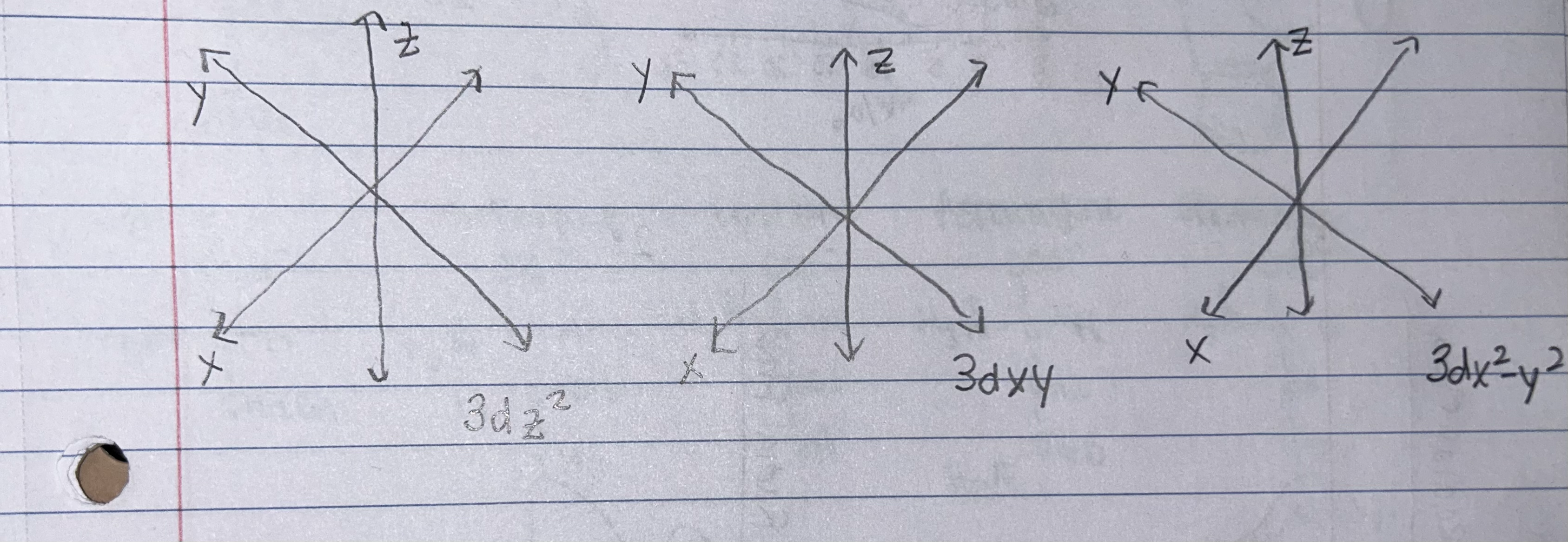
Use the cartesian axes below to draw the specified orbitals. INCLUDE shading.
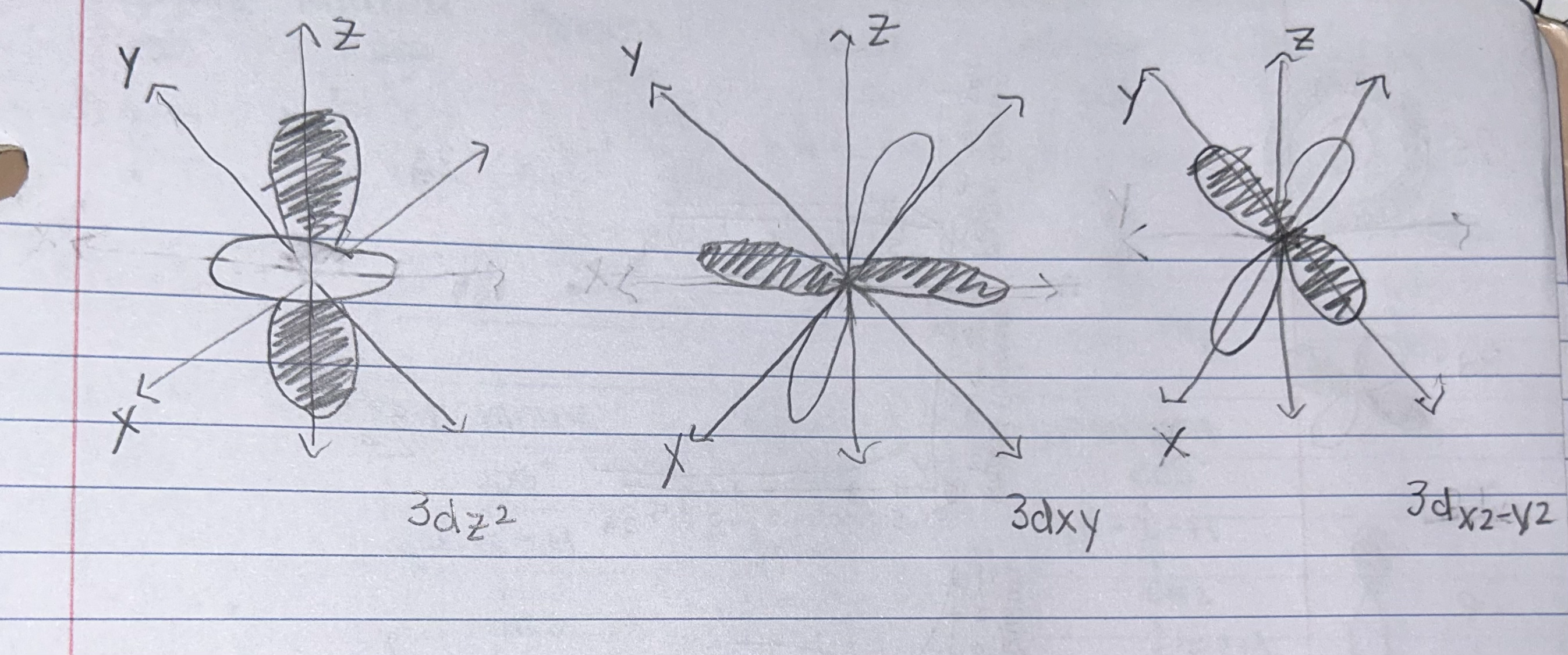
Which quantum number distinguishes the different orbitals of 3dz2, 3dxy, and 3dx2-y2
a. n
b. l
c. ml
d. ms
c. ml
For the set of quantum numbers below, indicate whether the set is valid. If the set is valid, then name the corresponding orbital. If not, then indicate which part of the set is invalid and why?
a. n=2, l=2, ml=1, ms=+1/2
b. n=3, l=2, ml=-2, ms=-1/2
c. n=4, l=0, ml=4, ms=+1/2

For the 5dx2-y2 orbital fill in the blanks below:
a. number of total nodes =
b. number of radial nodes =
c. number of angular nodes =

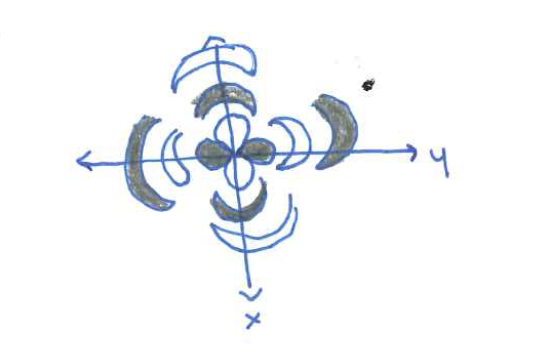
For the 5dxy-y2 orbital draw the orbital and its orbital boundary surfaces
Draw the energy diagram and give the shorthand notation describing the electron configuration for:
a. Ge
b. Tc3+

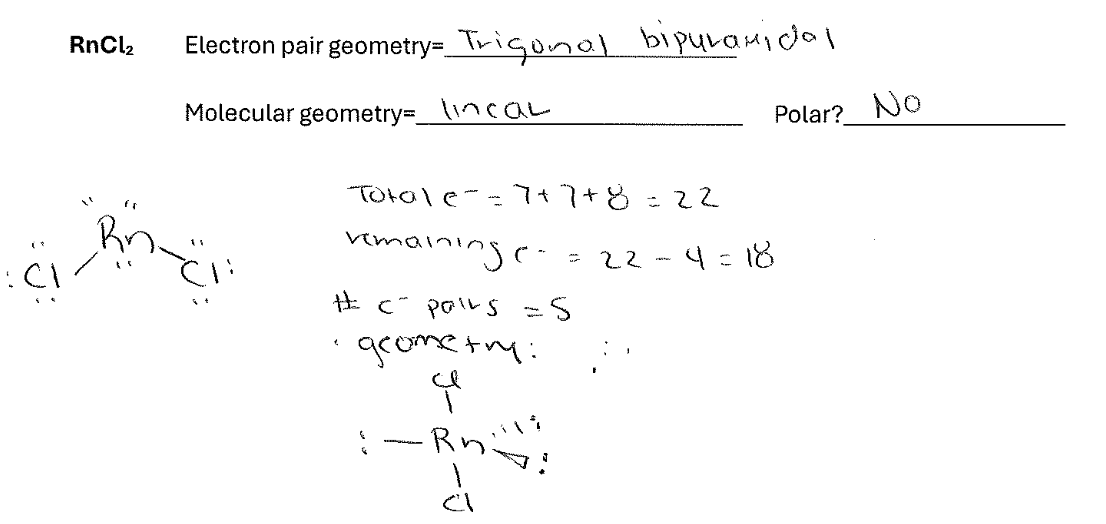
For the molecule RnCl2 draw the best Lewis Dot structure and indicate both the electron pair and molecular geometry. Also indicate whether the molecule will be polar.
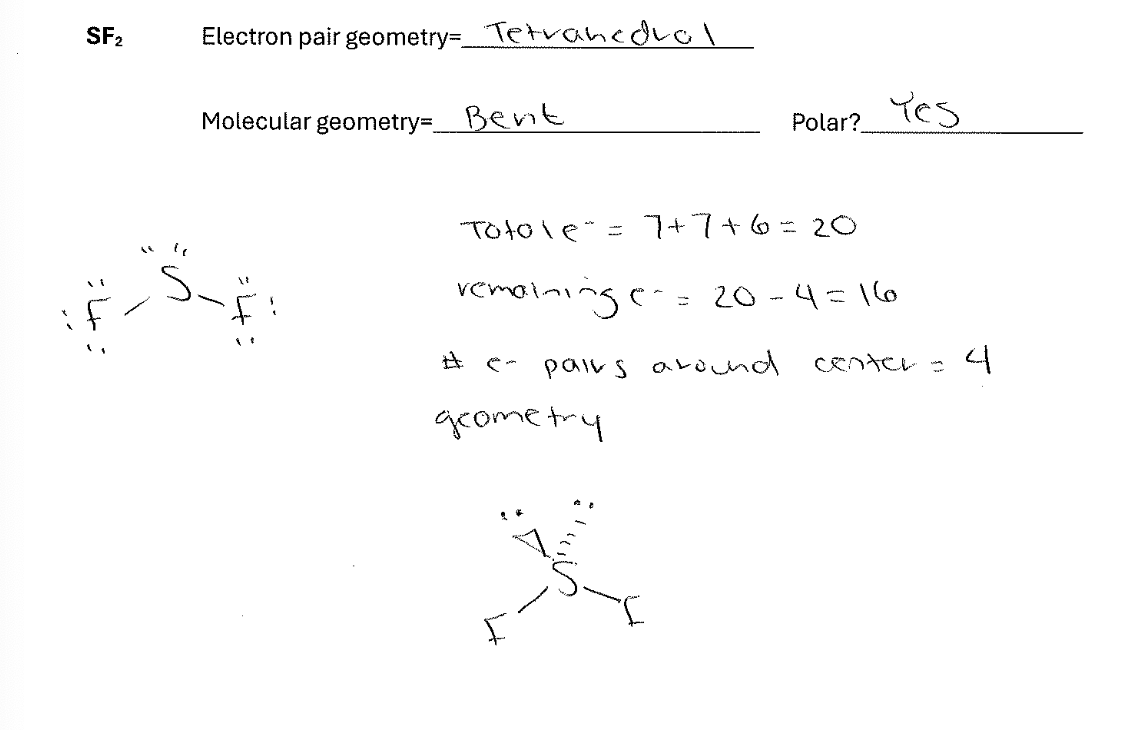
For the molecule SF2 draw the best Lewis Dot structure and indicate both the electron pair and molecular geometry. Also indicate whether the molecule will be polar.
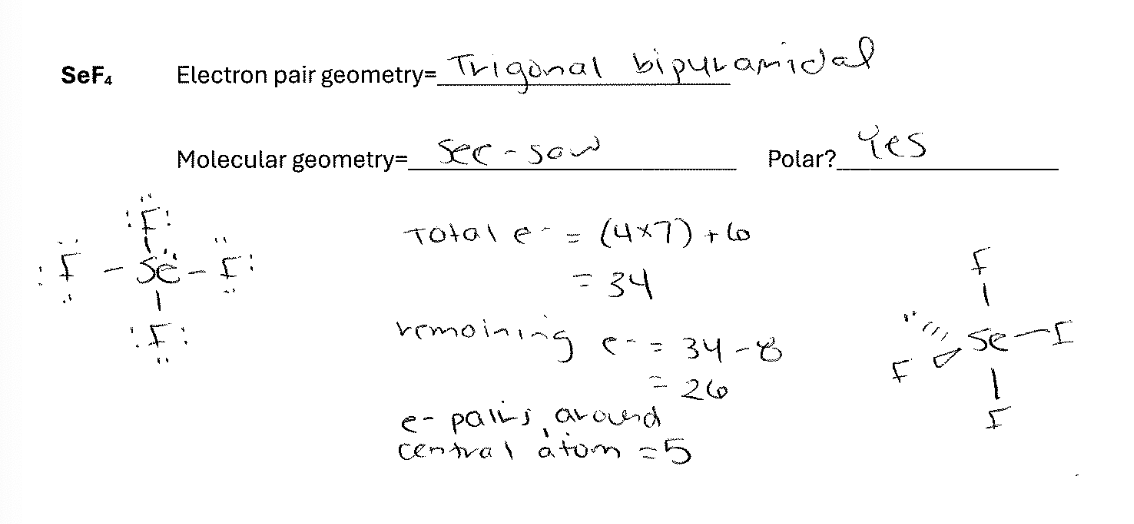
For the molecule SeF4 draw the best Lewis Dot structure and indicate both the electron pair and molecular geometry. Also indicate whether the molecule will be polar.
Draw the resonance structure of chlorate (ClO3-). What is the bond order and the oxygen formal charge for chlorate?
Bond order = 5/3 = 1/66
Formal charge = total charge/ # O atoms = -1/3
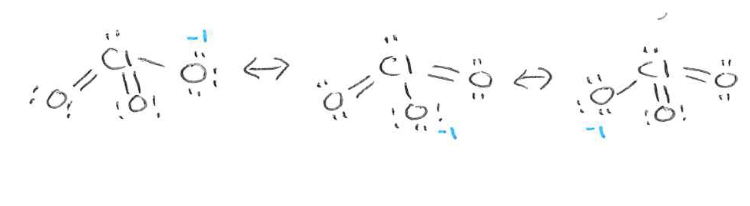
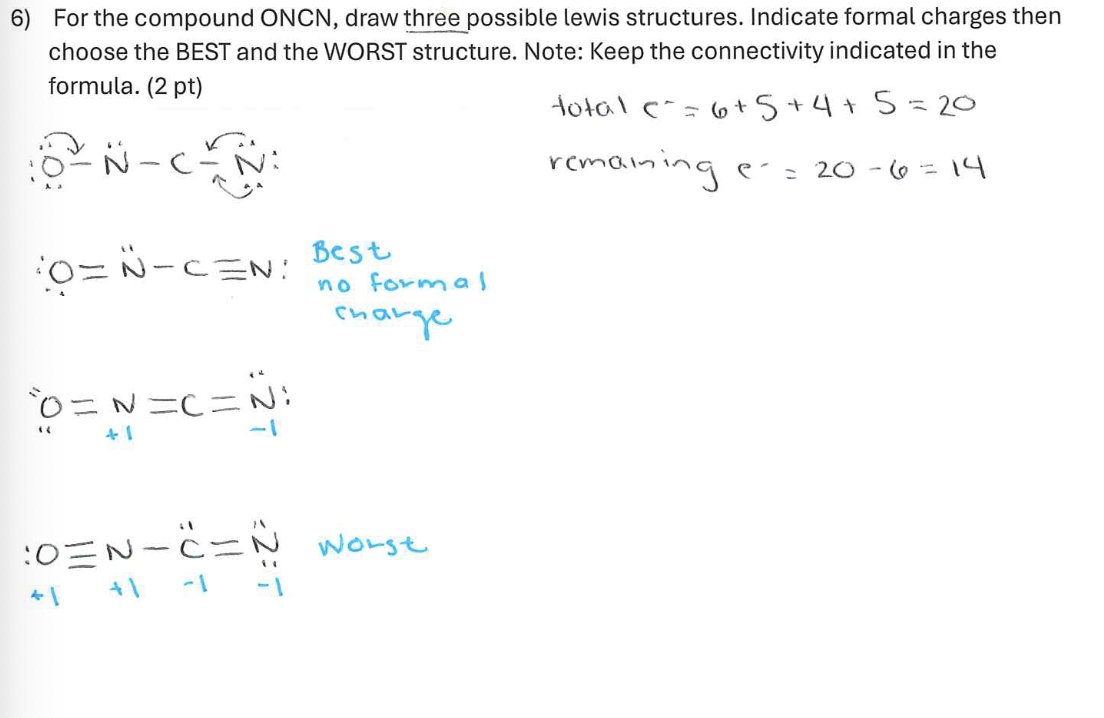
For the compound ONCN, draw three possible lewis structures. Indicate formal charges then choose the BEST and the WORST structure. Note: Keep the connectivity indicated in the formula
Draw the MO diagram for the ion OF-. Be careful to accurately depict the energies of relative orbitals and INCLUDE sketches as well as labels for each MO. Fill in electrons
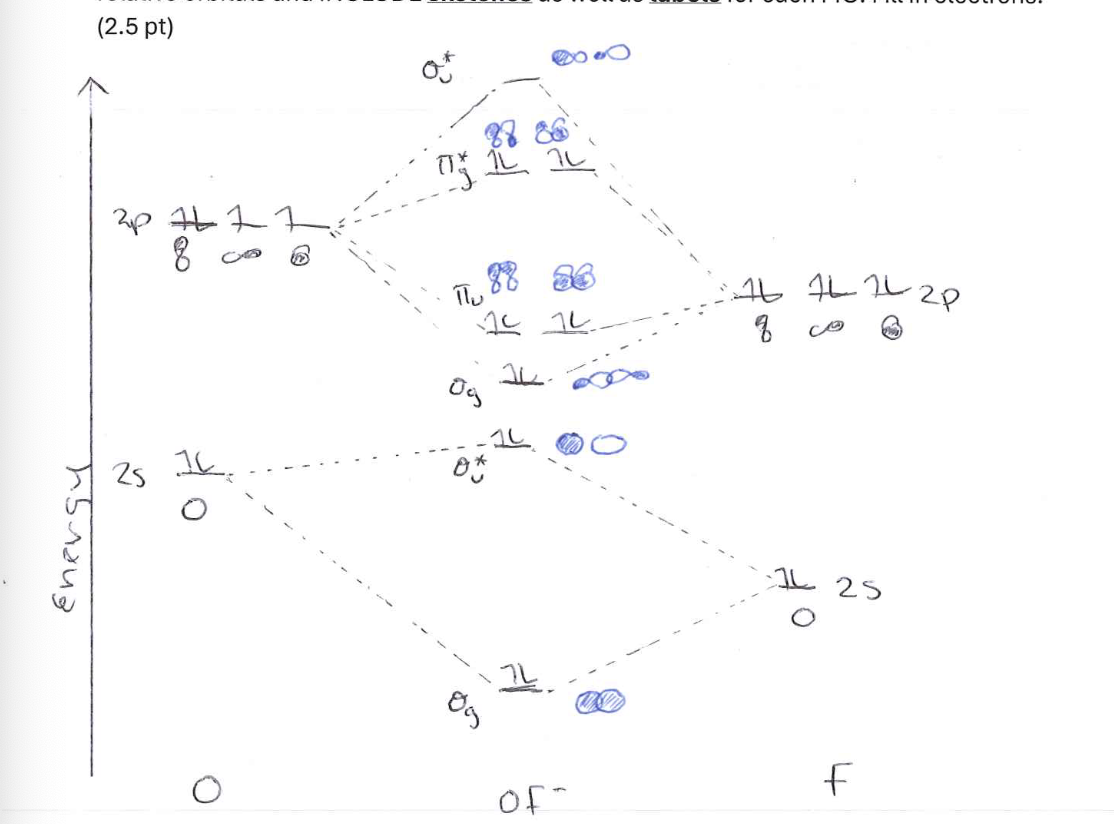
Based on the MO diagram for OF- describe the anions HOMO and LUMO. Give descriptions in words and as a mathematical expression for Ѱ(HOMO) and Ѱ(LUMO)