unit 11
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations.
\
ex. Dundunga is not very intelligent, the only solution he knows is swinging an axe really hard.
\
ex. Dundunga is not very intelligent, the only solution he knows is swinging an axe really hard.
2
New cards
intelligence test
a method for assessing an individual’s mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores.
\
ex. can be achievement or aptitude
\
ex. can be achievement or aptitude
3
New cards
general intelligence
a general intelligence factor that, according to Spearman and others, underlies specific mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test.
\
ex. explains why those who score high in one area typically score higher than average in other areas
\
ex. explains why those who score high in one area typically score higher than average in other areas
4
New cards
factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person’s total score.
\
ex. grouping literacy questions with each others and grouping arithmetic together
\
ex. grouping literacy questions with each others and grouping arithmetic together
5
New cards
Charles Spearman
Came up with general intelligence
\
ex. His idea of a single score was very controversial
\
ex. His idea of a single score was very controversial
6
New cards
L. L. Thurstone
gave 56 different tests to people and mathematically identified seven clusters of primary mental abilities
\
ex. He was an opponent of Spearman
\
ex. He was an opponent of Spearman
7
New cards
savant syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill, such as in computation or drawing.
\
Chris is a living calculator but cannot write an essay.
\
Chris is a living calculator but cannot write an essay.
8
New cards
Howard Gardner
views intelligence as multiple abilities that come in different
packages.
\
ex. brain damage may affect one package but not the other
packages.
\
ex. brain damage may affect one package but not the other
9
New cards
Robert Sternberg
Proposed a triarchic theory
\
ex. Analytical, Creative, and Practical
\
ex. Analytical, Creative, and Practical
10
New cards
grit
in psychology, grit is passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals.
\
ex. Smarts + grit = success
\
ex. Smarts + grit = success
11
New cards
emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions.
\
ex. Andy has low emotional intelligence and continues to bother his friend even though his face looks disgusted
\
ex. Andy has low emotional intelligence and continues to bother his friend even though his face looks disgusted
12
New cards
Francis Galton
wondered if it might be possible to measure “natural ability”
\
ex. …and to encourage those of high ability to mate with one another.
\
ex. …and to encourage those of high ability to mate with one another.
13
New cards
mental age
a measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet; the chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance.
\
ex. Jill is a 5 year old child prodigy with a mental age of 21
\
ex. Jill is a 5 year old child prodigy with a mental age of 21
14
New cards
Stanford-Binet
the widely used American revision (by Terman at Stanford University) of Binet’s original intelligence test.
\
ex.
Adapted some of Binet’s original items, added others, established new age norms, and extended the upper end of the test’s range from teenagers to “superior adults.”
\
ex.
Adapted some of Binet’s original items, added others, established new age norms, and extended the upper end of the test’s range from teenagers to “superior adults.”
15
New cards
intelligence quotient (IQ)
defined originally as the ratio of mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca) multiplied by 100 (thus, IQ = ma/ca × 100). On contemporary intelligence tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned a score of 100, with scores assigned to relative performance above or below average.
\
ex. I once saw a person call another person an ‘idiot with an iq lower than room temperature’
\
ex. I once saw a person call another person an ‘idiot with an iq lower than room temperature’
16
New cards
Alfred Binet
Him and Theodore Simon came up with mental age
\
ex. The French government told him to do this
\
ex. The French government told him to do this
17
New cards
Louis Terman
Came up with the Stanford-Binet revision
\
ex. he found that the french questions did not work so well with Californians
\
ex. he found that the french questions did not work so well with Californians
18
New cards
achievement test
a test designed to assess what a person has learned.
\
ex. AP exam
\
ex. AP exam
19
New cards
aptitude test
a test designed to predict a person’s future performance; aptitude is the capacity to learn.
\
ex. College entrance exam
\
ex. College entrance exam
20
New cards
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
the WAIS is the most widely used intelligence test; contains verbal and performance (nonverbal) subtests.
\
ex. also has a kiddy varient, Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children
\
ex. also has a kiddy varient, Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children
21
New cards
David Wechsler
created the WAIS
\
ex. he worked with the United States Army to develop psychological tests to screen new draftees while studying under Charles Spearman and Karl Pearson
\
ex. he worked with the United States Army to develop psychological tests to screen new draftees while studying under Charles Spearman and Karl Pearson
22
New cards
standardization
defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group.
\
ex. SAT gives the same test to all takers on the same day
\
ex. SAT gives the same test to all takers on the same day
23
New cards
normal curve
the symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes. Most scores fall near the average, and fewer and fewer scores lie near the extremes.
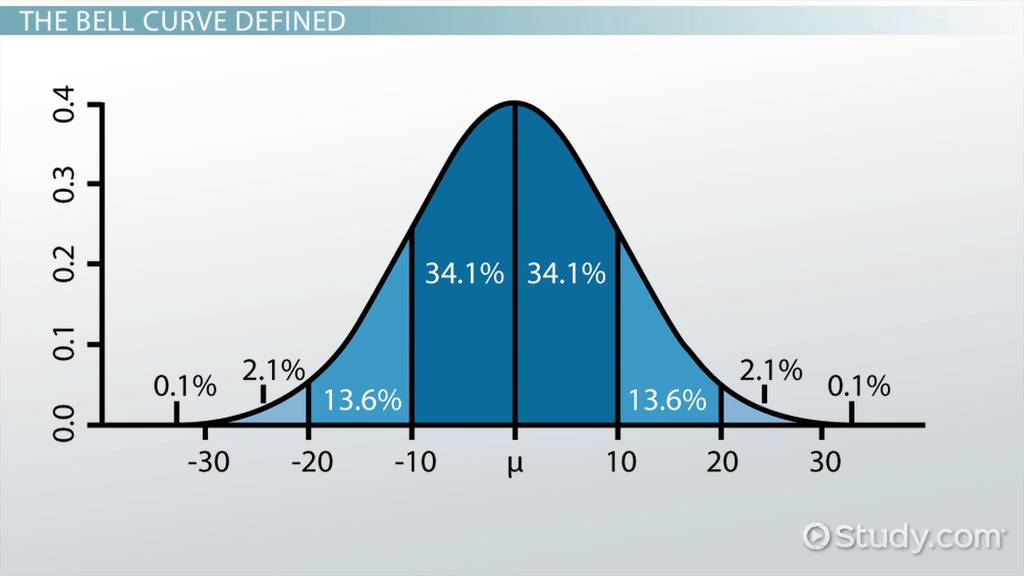
24
New cards
reliability
the extent to which a test yields consistent results, as assessed by the consistency of scores on two halves of the test, on alternate forms of the test, or on retesting.
\
ex. Half of the takers who answer even questions and the other half who answers odd questions should get around the same score
\
ex. Half of the takers who answer even questions and the other half who answers odd questions should get around the same score
25
New cards
validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to.
\
ex. a ruler with correctly measured lines has validity
\
ex. a ruler with correctly measured lines has validity
26
New cards
content validity
the extent to which a test samples the behavior that is of interest.
\
ex. a test about math ability that is full of grammar questions has low content validity
\
ex. a test about math ability that is full of grammar questions has low content validity
27
New cards
predictive validity
the success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict; it is assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior.
\
ex. SAT scores are strongly predictive of college performance
\
ex. SAT scores are strongly predictive of college performance
28
New cards
cohort
a group of people from a given time period.
\
ex. me and my friends during high school
\
ex. me and my friends during high school
29
New cards
crystallized intelligence
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age.
\
ex. my ability to recall history facts
\
ex. my ability to recall history facts
30
New cards
fluid intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood.
\
ex. my ability to solve a coded puzzle
\
ex. my ability to solve a coded puzzle
31
New cards
intellectual disability
a condition of limited mental ability, indicated by an intelligence score of 70 or below and difficulty in adapting to the demands of life.
\
ex. formerly known as mental retardation
\
ex. formerly known as mental retardation
32
New cards
Down syndrome
a condition of mild to severe intellectual disability and associated physical disorders caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21.
\
ex. Chromosome 21 traces a police investigation into a young man with down syndrome involved in a murder
\
ex. Chromosome 21 traces a police investigation into a young man with down syndrome involved in a murder

33
New cards
heritability
the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. The heritability of a trait may vary, depending on the range of populations and environments studied.
\
ex. Today’s researchers have identified chromosomal regions important to intelligence, and they have pinpointed specific genes that seemingly influence variations in intelligence and learning disorders
\
ex. Today’s researchers have identified chromosomal regions important to intelligence, and they have pinpointed specific genes that seemingly influence variations in intelligence and learning disorders
34
New cards
Carol Dweck
reported that believing intelligence is bio- logically set and unchanging can lead to a “fixed mindset,” whereas a “growth mindset” results from believing intelligence is changeable, which focuses on learning and growing
\
ex. has also developed interventions that effectively teach young teens that the brain is like a muscle that grows stronger with use as neuron connections grow.
\
ex. has also developed interventions that effectively teach young teens that the brain is like a muscle that grows stronger with use as neuron connections grow.
35
New cards
stereotype threat
a self- confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype.
\
ex. negatively stereotyped minorities and women may have unrealized academic potential
\
ex. negatively stereotyped minorities and women may have unrealized academic potential