Biochem Exam 1 (Homework + Quiz)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Which of the following is not a weak force that contributes to the structure of biological macromolecules?
Ionic interactions
Hydrogen bonding
Disulfide bonding
Van der Waals forces
Disulfide bonding
Peptide bonds have partial double-bond character and are planar (True or False)
True
At physiological PH (7.4), the amino group of an amino acid is typically
Neutral
Positively charged
Negatively Charged
Zwitterionic
positively charged
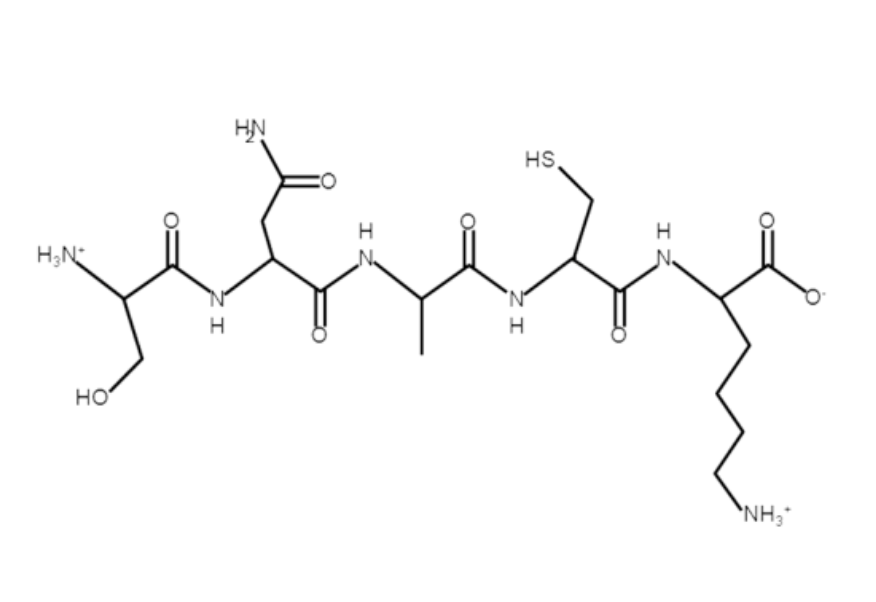
What is single letter amino acid sequence?
SNACK
Ionic interactions are stronger in water than in non-polar environments (True or False)
False
Tertiary structures refer to the interactions between multiple polypeptide chains (True or False)
False
Which of the following is not considered one of the four major classes of biochemicals?
Protein
Lipid
Nucleic Acids
Vitamin
Vitamin
Which of the following contributes to a proteins tertiary structure?
The order of amino acids
Interactions between R-groups
A-helices and B-sheets
Peptide bonds
Interactions between R-groups
Primary protein structure description
Linear sequence of amino acids
Secondary protein structure description
Localized structures such as alpha-helices and beta-sheets
Tertiary structures structure description
Overall 3-D folding of a single polypeptide
Quaternary protein structure description
3-D arrangement of polypeptide chains in a multi-subunit complex
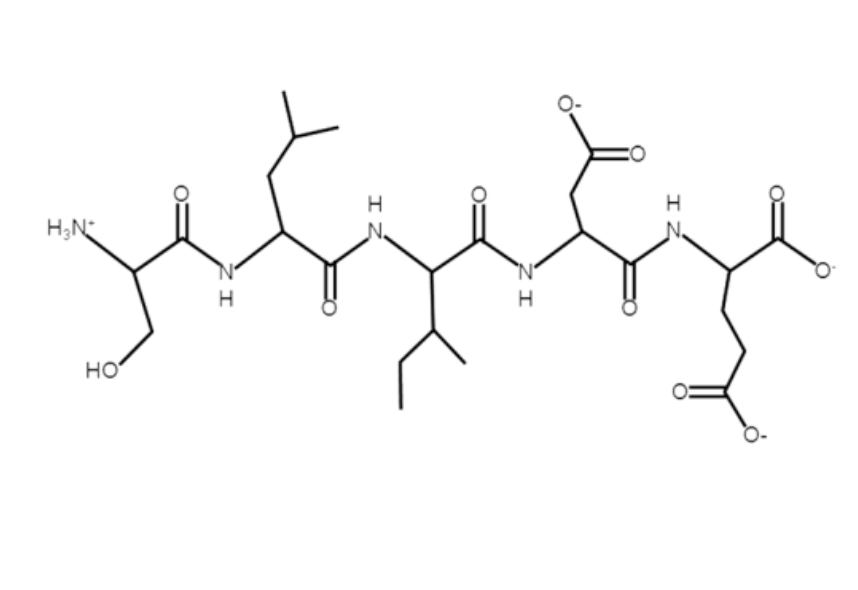
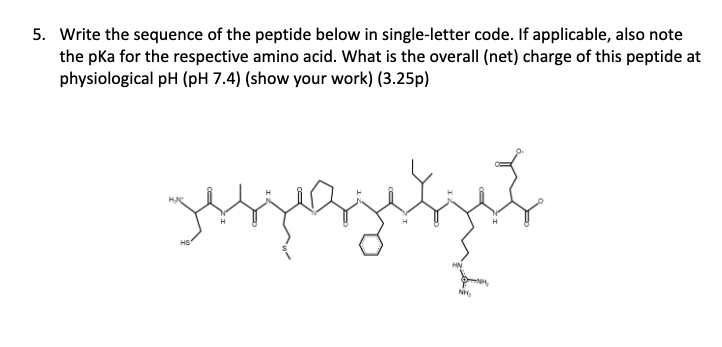
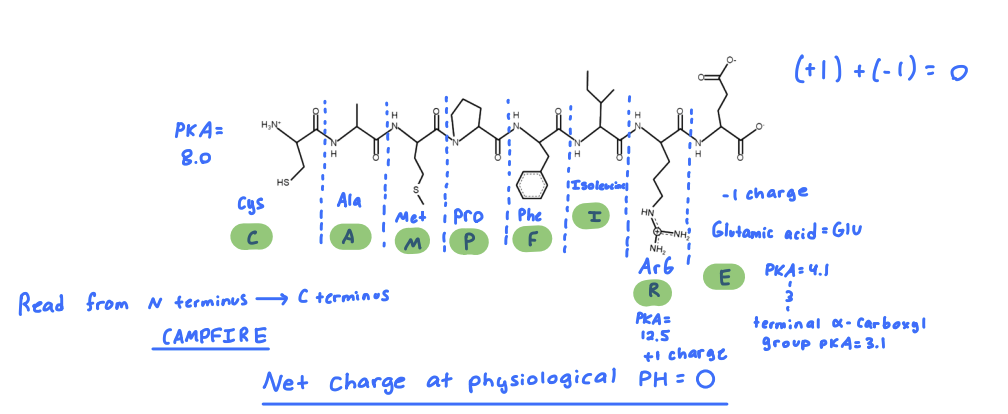
What is the single-letter amino-acid code for the peptide below.
SLIDE
Lipids are polymers made of repeating monomer units. (True or False)
True, assembled from monomers like glycerol and fatty acids
Briefly write out and describe the central dogma of molecular biology. What are the relevant molecular machines and molecular building blocks in each step of the central dogma.




Describe Anfinsen’s experiment
-Ran experiments using denaturing agents urea and BME that focused on an enzyme called RNase to study tertiary structure and study proper conditions it was formed
-Experiment #1- Excess Urea and BME added together where it denatured enzyme. When re-added enzyme tertiary structure was re-formed
-Experiment #2- Excess Urea and BME added together where first B. Merca was removed and then Urea where then a scrambled enzyme was seen with improper disulfide bonds
Experiment #3-Trace amounts of BME. and Urea were added to the scrambled enzyme where the correct tertiary structure was re-formed.
Three experiments combined showcased that the structure and function of a protein are encoded in the primary sequence.
(answer key asks for explanation about ureas role in unfolding and BME



-Ramachandran plot organizes possible steric combinations and tells us about secondary structure of an amino acid
-Shows allowed angles of rotation for the backbone of a protein

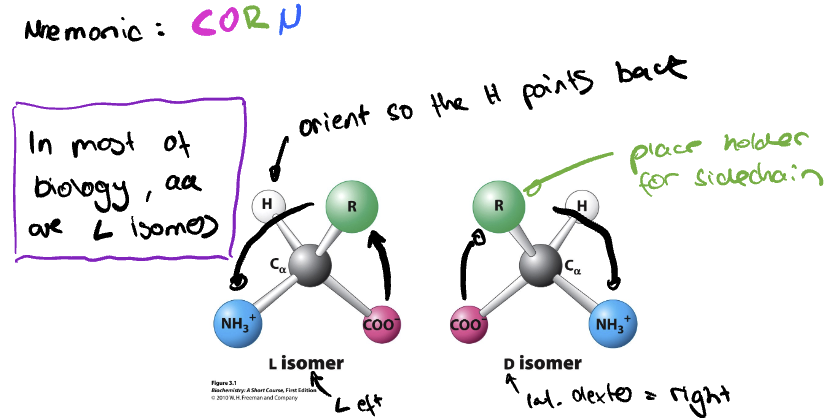
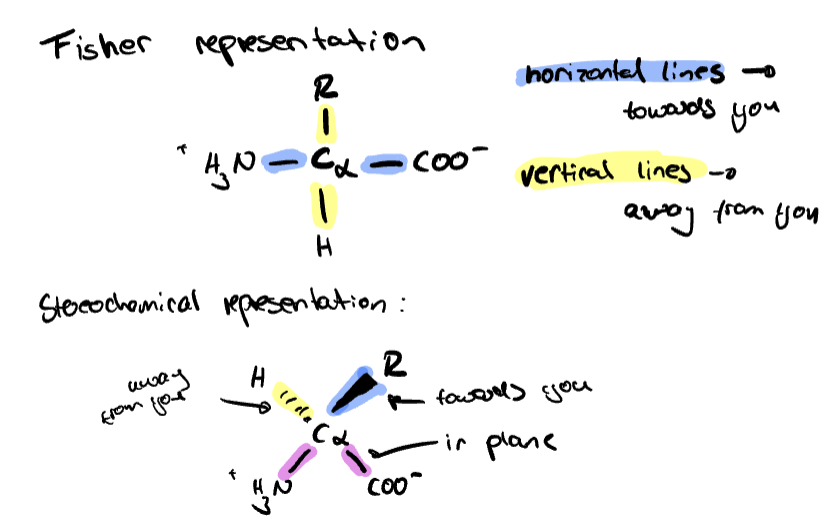
All amino acids are found in the L-form (true or false)
True

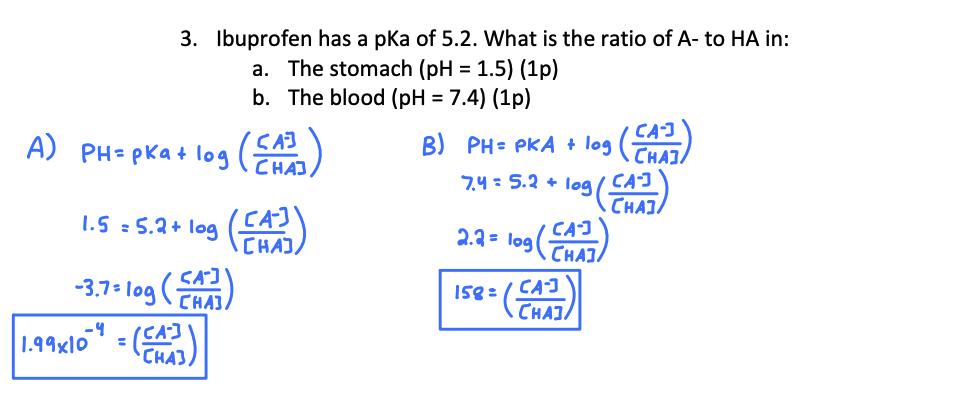
The henderson Hasselbach equation explains the relationship between?
pH and pKA
Buffer solution contains 0.36 M sodium acetate (CH3COONa) and 0.45 M acetic acid (CH3COOH), pKa=4.8, What is the pH of this buffer solution?
4.7 pH
If the pH=pKa, the log of the ratio of dissociating acid and associated acid will be?
Zero
Calculate the pH of a buffer that contains 0.7 M ammonia and 0.9 M ammonium chloride (pKa=9.248)
pH=9.1
In your own words, describe the levinthal paradox. What are the logical implications for how proteins fold in cells?
The idea that if a protein tried every possible folding shape possible it would take longer than the age of the universe.
Logical implications of how proteins fold in a cell is to have preferred energetically favored routes often viewed by the folding funnel shaping comparing free energy and entropy.
Describe two types of protein secondary structures and the non-covalent bonding pattern that stabilizes them
Alpha-Helices: Hydrogen bonds form between the backbone of C=O one first amino acid and N-H of 4 amino acid. Bonds spiraling into a helical shape.
Beta-Sheet: Hydrogen bonds form between backbones of different strands, either parallel, anti parallel, or mixed that form a sheet like structure.
Explain the protein folding (or tunnel) model. What is the significance of local vs. global minima, entropy, and free energy in this model?
Protein folding funnel model visualizes the folding process as an energy landscape. Top of funnel unfolded protein has high entropy and energy. As folding progresses, entropy decreases and lowers energy eventually reaching lowest energy shape known as native state.
Global minima represents the overall lowest energy and entropy state known as the native state; while local minima (local valley) represents partially folded states that are kinetically trapped.
Entropy overall represents the number of possible conformations a protein can adopt for example at top of tunnel model entropy is high because the unfolded protein can exist in many shapes.
Free-energy drives folding process, starts from high free energy to native state w/ lowest free energy (most stable)
What interaction primarily stabilizes the alpha-helix?
Hydrogen bonds between backbone atoms
Which of the following statements about protein tertiary structure are TRUE?
Tertiary structure is stabilized only by hydrogen bonds
Disulfide bridges may form between cysteine residues
Hydrophobic residues tend to cluster on the surface of soluble proteins
Tertiary structure results from interactions between side chains
Disulfide bridges may form between cysteine residues
Tertiary structure results form interactions between side chains
What is an enzyme? What is its generic role in biological systems ?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst (usually protein) that reduces the activation energy required for a chemical reaction. Increasing the rate of reaction.
Define activation energy. How do enzymes affect it?
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to begin.
Enzymes lower the activation energy, increasing the rate of reaction.
Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found in the interior of a protein?
Serine
Aspartate
Valine
Glutamine
Valine
Which statement about the peptide bond is true?
The can easily hydrolyzed at room temperature
They can freely rotate
They are planar due to resonance
They carry a net charge at pH 7
They are planar due to resonance
Define Active Site
Region of enzyme where catalysis occurs
Define Standard free energy
Change in free energy under standard conditions
Define induced fit model
The enzyme adjusts shape to fit the substrate more tightly
Which of the following features is NOT typical of an enzyme active site?
Usually hydrophobic
Binds substrates with high specificity
Always located on the protein surface
Stabilizes the transitions state
is NOT Always located on the protein surface
Which model of substrate binding proposes that the enzyme changes shape upon binding?
Induced fit
Lysozyme contains many basic residues. At physiological pH, is it likely to have a net positive or negative charge?
net-positive charge because it contains basic residues like lysine and arginine that gains protons and becomes positively charged.
What ion exchange chromatography technique would best retain lysozyme at pH 7.4, cation exchange or anion exchange? please explain why?
Cation exchange because lysozyme is positively charged at physiological pH, negative bonds are ultimately used in order to target positive charge like a magnet.