2.1 Forces and Mechanics of Rigid Bodies
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is a force ?
Every action on a body that changes its state of motion (acceleration, deceleration, changing direction…)
How can a force be described ?
Direction, absolute value (strength, size, intensity), point of application
What is a concurrent force system ?
Several forces (acting on a body) that intersect at a single point
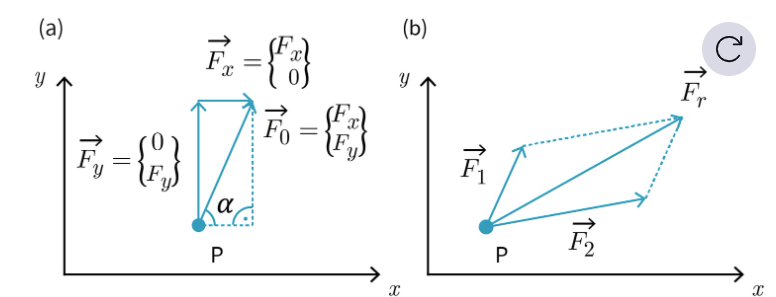
What is the parallelogram theorem ?
Sum of 2 forces acting at the same point of application corresponds to the diagonal of the parallelogram spanned by them
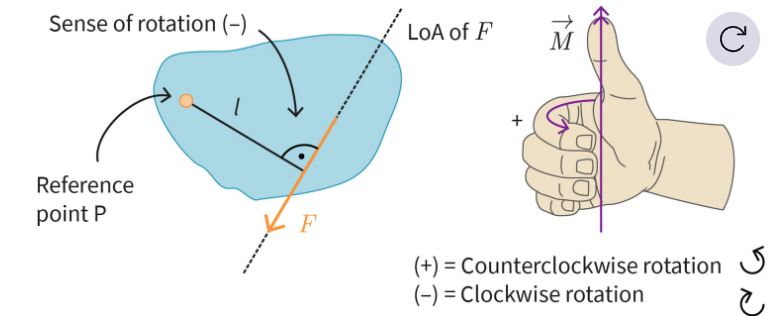
What is the Moment of a force/ Torque ?
Product of a single force F and its effectove distance l from any reference point P
What is the amount of Moment ?
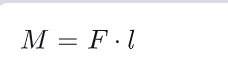
What does the effective distance l corresponds to ?
It is the distance between the reference point P and the line of actiob (LoA) of the force (perpendicular)
In technical Mechanics (Statics) what are external forces ?
They are loads that act on the system from the larger environment, the resulting forces (reaction) are also external forces.
In case of statics equilibrium, all external forces acting on a system must be in equiibrium.
What are Internal Forces ?
forces that arise inside a system as a result of the effect of external forces
How can you determine internal forces ?
Using the method of Sections :
mentally separate the components along a cut through the cross-section, resulting in 2 segments
consider equilibrium must apply between both segments and the internal and external forces and moments : there must be INTERNAL FORCES and MOMENTS on the respective cross-section that COUNTERACT the external forces and moment of the component, and on both cross-sections of the segments
the resulting internal forces & moments are called NORMAL FORCE N or Fn, SHEAR FORCE Q or Fq, and BENDING MOMENT M.
What is a rigid body ?
A body that does not deform under the influence of forces
BTW : theoretical concept that technically never applies, as all materials are deformable and every body deforms to a greater or lesser extent when subjected to force
What is the principle of transmissibility ?
The principle of transmissibility states that the point of application of a force on a rigid body can be moved anywhere along its line of action without changing the external effect of that force on the body (equilibrium or motion).
What os the degree of freedom ? (DOF)
It is the minimum number of independent parameters (coordinated) required to clearly describe the position and orientation of a mechanical system.