Chapter 10: Photosynthesis
1/43
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
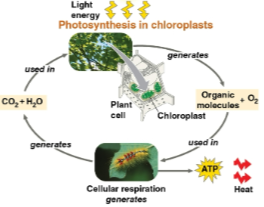
Photosynthesis
A process that uses light to change carbon dioxide and water into organic molecules and oxygen for cellular respiration
Occurs within chloroplasts
Nourishes the entire living world directly or indirectly
Chloroplasts
The organelles within cells where photosynthesis occurs
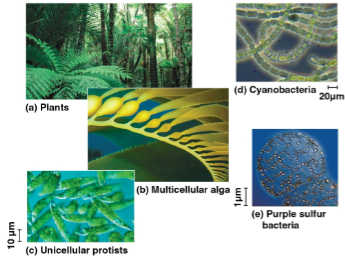
Autotrophs
Organisms that sustain themselves without eating anything derived from other organisms
Producers of the biosphere that produce organic molecules from CO2 and other inorganic molecules
Includes most plants as well as some algae, protists, and prokaryotes
Heterotrophs
Organisms that obtain organic material from other organisms
Consumers of the biosphere that eat other living things, dead organic material, or feces
Almost all of these depend on photoautotrophs (directly or indirectly) for food and O2
Decomposers
Subsection of heterotrophs that eat dead organic material or feces
Fossil fuels
Fuel stores under the earth formed from the remains of organisms that died hundreds of millions of years ago, representing ancient stores of the sun’s energy
Chloroplasts
Organelles within plants and other photosynthetic organisms that are structurally similar to and likely evolved from photosynthetic bacteria
Structure allows for chemical reactions of photosynthesis
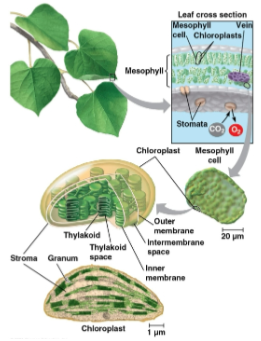
Leaves
The area of most photosynthesis in plants
Mesophyll
The interior tissue of the leaf where chloroplasts are mainly found
Stomata
Pores in a plant’s leaf where CO2 enters and O2 exits for gas exchange
Veins
Structures within a plant that transport water from the roots and export sugar to nonphotosynthetic parts of the plant
Stroma
Dense fluid within the chloroplast envleloped by two membranes
Thylakoids
Connected sacs in the chloroplast that compose a third membrane system, stacked in columns called grana
Chlorophyll
The pigment that gives leaves their green color that resides in thylakoid membranes
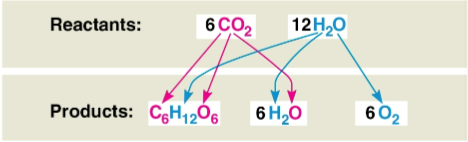
Photosynthesis
A complex series of reactions represented by the equation 6CO2 + 12H2O + Light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Represents the effective reverse of cellular respiration in electron flow to make sugar in two stages
Oxidizes H2O and reduces CO2 in an endergonic process powered by light
Water
Substance used in photosynthesis as it is split into hydrogen and oxygen
Electrons from hydrogen are used to create sugar molecules while releasing O2 as a by-product
Hydrogen may also be obtained via other sources, such as from H2S that creates S2 as a waste product
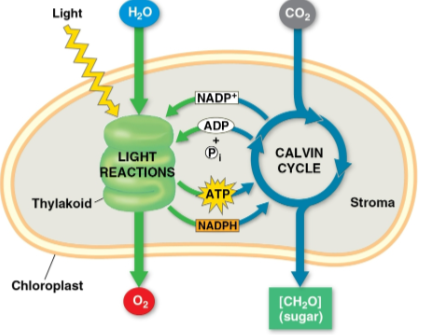
Light reactions
The first part of photosynthesis that occurs in the thylakoids
Splits H2O, recieving electrons and protons as H+
Releases O2 as a by-product
Reduces the electron acceptor NADP+ to NADPH
Generates ATP from ADP by photophosphorylation
NADP+
An electron acceptor reduced in the light reactions in the thylakoids to NADPH for transfer to oxygen
Photophosphorylation
The generation of ATP from ADP in the light reactions in the thylakoids
Calvin cycle
Second part of photosynthesis within the stroma that makes sugar from CO2, using ATP and NADPH generated from light reactions
Begins with carbon fixation, incorporating CO2 into organic molecules
Reduces fixed carbon to carbohydrate by transferring electrons from NADPH
Carbon fixation
The incorporation of carbon from CO2 into organic molecules via the Calvin cycle in the stroma
Chloroplasts
Solar-powered chemical factories
Thylakoids transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH, providing energy and reducing power needed by the Calvin cycle to make sugar
Electromagnetic energy (electromagnetic radiation)
Energy that travels in rhythmic waves via electromagnetic forces; light is one example
Wavelength
A measure of the distance between crests of electromagnetic waves
Can range from less than a nanometer (gamma rays) to more than a kilometer (radio waves)
Electromagnetic spectrum
The entire range of electromagnetic energy, or radiation
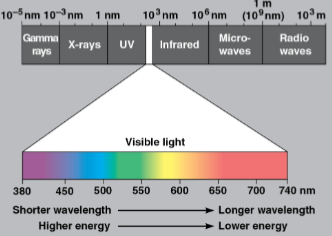
Visible light (visible spectrum)
The electromagnetic spectrum between wavelengths 380 nm to 740 nm which drive photosynthesis and produce the colors seen by the human eye
Photons
Discrete particle-like units of light
Each particle has a fixed quantity of energy inversely related to the wavelength of the light — shorter wavelengths have more energy per photon
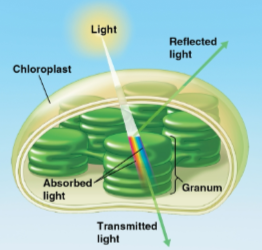
Pigments
Substances that absorb visible light; differs for every type
Wavelengths that are absorbed disappear, while wavelengths that are not absorbed are reflected or transmitted
Most leaves appear green because the pigment chlorophyll absorbs violet-blue and red light while reflecting and transmitting green light
Light causes electrons in a pigment to go to an unstable excited state, which can later fall back to a ground state releasing energy as heat or light
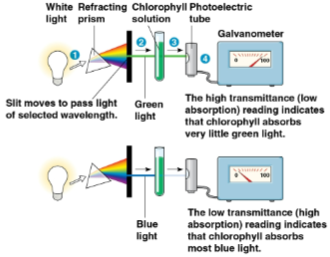
Spectrophotometer
A device that measures a pigment’s ability to absorb various wavelengths, sending light through pigments and measuring the fraction of light transmitted at each wavelength
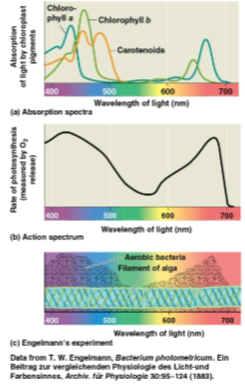
Absorption spectrum
A graph plotting a pigment’s light absorption versus wavelength
Chlorophyll a
The key light-capturing pigment that participates directly in light reactions
Absorbs violet-blue and red light for photosynthesis for most energy while reflecting green light
Chlorophyll b
An accessory pigment to chlorophyll a
Carotenoids
A separate group of accessory pigments to chlorophyll a, absorbing violet and blue-green light and thus broadening the spectrum for photosynthesis
Some can also absorb excessive light that would otherwise damage chlorophyll or react with oxygen
Action spectrum
A profile of the relative effectiveness of different wavelengths
Higher for violet-blue and red light in photosynthesis
Broader for overall photosynthetic processes in combination with chlorophyll b, due to a slight structural difference in the pigment molecules
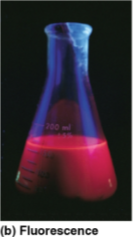
Fluorescence
The release of excess energy by electrons in the form of light
Photosystem
A reaction-center complex surrounded by light-harvesting molecules
Photosystem II (PS II)
Also known as P680, it is the first photosystem in the thylakoid membrane that functions best with absorbing light with chlorophyll a at 680 nm
Named for its secondary discovery to Photosystem I
Photosystem I (PS I)
Also known as P700, it is the second system in the thylakoid membrane that functions best with absorbing light with chlorophyll a at 700 nm
Named for it being discovered first before Photosystem II
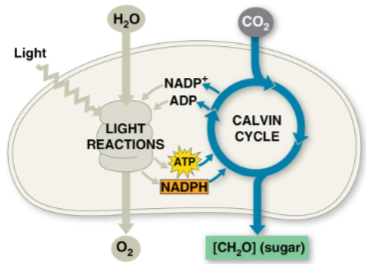
Calvin cycle
An anabolic process within the stroma of the chloroplast that builds sugar from smaller molecules using ATP with the reducing power of electrons carried by NADPH
Has the three phrases of carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of the CO2 acceptor (RuBP)
Consumes 9 ATP and 6 NADPH overall to make 1 G3P molecule for other molecular synthesis processes, which are regenerated with light reactions
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
The sugar that is produced from carbon that enters as CO2
One of these requires three complete cycles to fix three CO2 molecules
Carbon fixation
The binding of CO2 to a five-carbon sugar named ribulose biphosphate, catalyzed by RuBP carboxylase-oxygenase (rubisco)
This is then split into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate for each CO2 fixed
Rubisco
Enzyme that catalyzes the binding of CO2 to ribulose biphosphate in carbon fixation
Reduction
The phosphorylation of each molecule of 3-phosphoglycerate by six ATP and six NADPH to produce a G3P sugar
Results in a 3:6 CO2 input to G3P output ratio
Only one G3P molecule can be counted as a net gain of carbohydrate as it is passed on, the rest remain to regenerate the CO2 acceptor RuBP
Regeneration of RuBP
The rearrangement of the five molecules of G3P in a complex series of reactions to yield three molecules of RuBP
This uses three additional ATP molecules