Life Science_ Term 1 (2023)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/82
Last updated 4:34 PM on 6/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
Functions of the cytoplasm
Give cell its shape
Transport medium for dissolved substances
Storage area for water insoluble substances
Storage and circulation of substances within cell
Transport medium for dissolved substances
Storage area for water insoluble substances
Storage and circulation of substances within cell
2
New cards
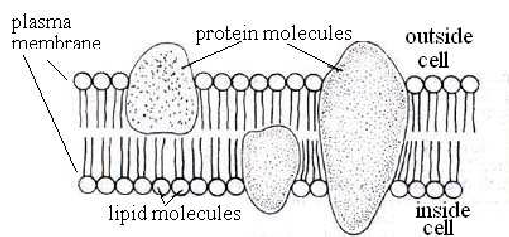
Cell membrane (plasmalemma)
Fluid mosaic model
Phospholipid bilayer
Protein molecules embedded into the two phospholipid layers
Provide support and flexibility
Phospholipid bilayer
Protein molecules embedded into the two phospholipid layers
Provide support and flexibility
3
New cards
Functions of the cell membrane
Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
Respiration (dissolved gases enter) and nutrients enter the cell
Excretion
Secretion
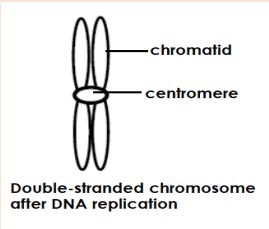
Respiration (dissolved gases enter) and nutrients enter the cell
Excretion
Secretion
4
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until the concentration in both regions are the same
- passive transport
- passive transport
5
New cards
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules from an area of high concentration to a low concentration across a selectively permeable membrane
6
New cards
Flaccid
Condition between turgid and plasmolyzed when a cell is placed in an isotonic solution
7
New cards
Turgid
Cell has reached maximum tension
8
New cards
Active transport
Molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration, they move against the concentration gradient
9
New cards
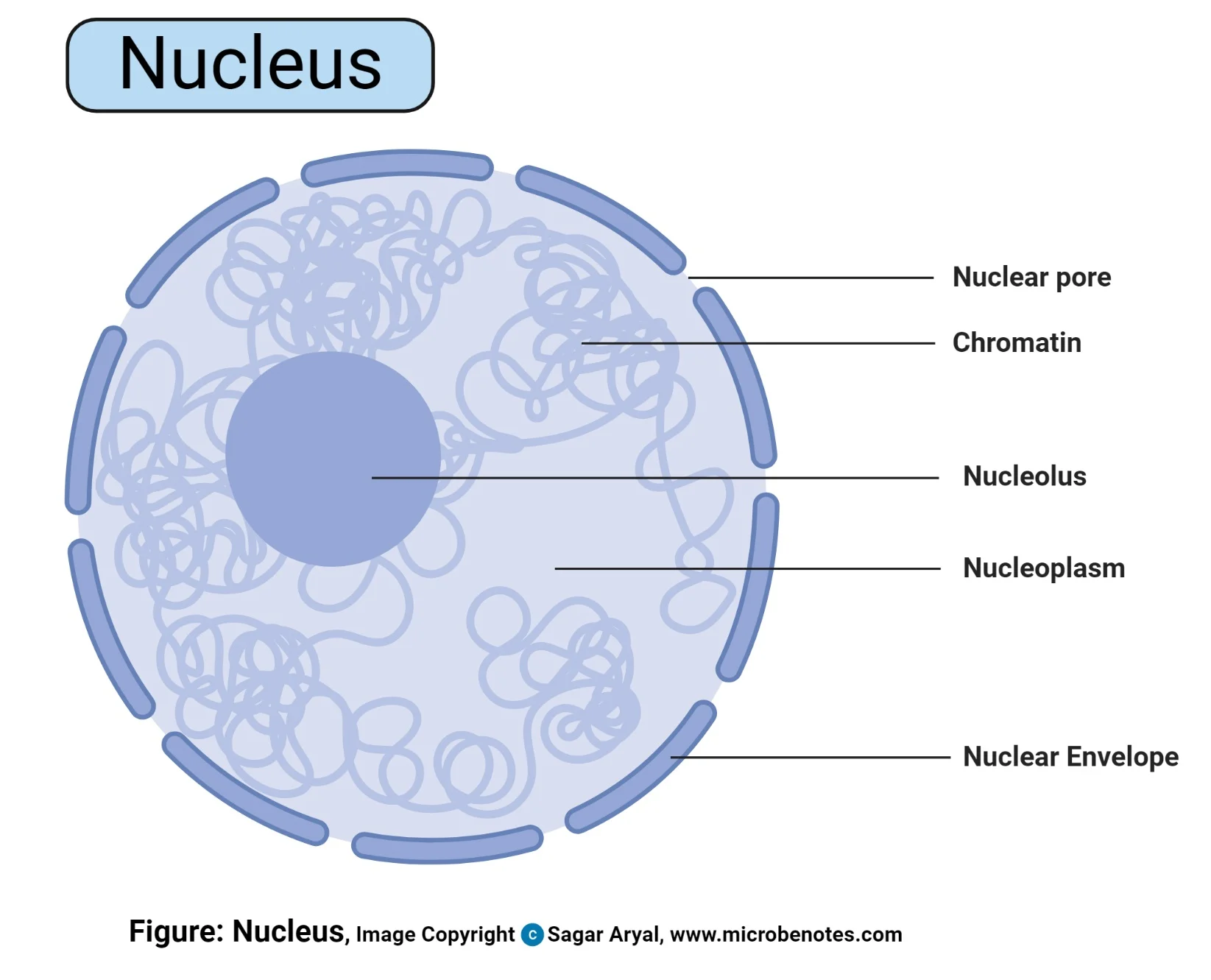
Function of Nucleus
Contains chromatin network which contains hereditary information in DNA
Contains information that controls all metabolic processes
Nuclear pores allow certain substances in and out
Makes ribosomes
Contains information that controls all metabolic processes
Nuclear pores allow certain substances in and out
Makes ribosomes
10
New cards
Chromatin Network
Long threads of chromosomes folded and packed loosely
11
New cards
DNA
Two long strands of genetic information made of sugars, phosphates and nitrogenous bases. Formed in a double helix
12
New cards
Replicated chromosome
Contain the genetic information of the cell
13
New cards
Chromosome
Strand of DNA twisted around a backbone of proteins
Thread like structures found in the nucleus
Thread like structures found in the nucleus
14
New cards
DNA replication
The process during which a DNA molecule makes an identical replica of itself
15
New cards
Haploid
One full set of chromosomes that includes a single copy of each gene.
16
New cards
Diploid
Two sets of chromosomes that include a double copy of each gene.
17
New cards
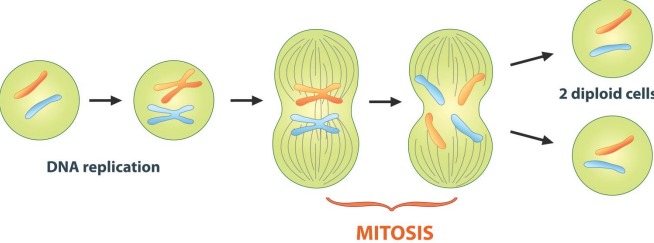
Mitosis
The process of cell division where two new identical diploid "daughter" cells are formed from diploid "mother" cell.
18
New cards
Role of mitosis
Development and growth
Asexual reproduction
Cell replacement
Replacement of damaged tissues
Asexual reproduction
Cell replacement
Replacement of damaged tissues
19
New cards
Location of mitosis
Any living diploid cell
Stem cells
At growing points at the tip of roots and stems
Specialized tissue called Cambium
Stem cells
At growing points at the tip of roots and stems
Specialized tissue called Cambium
20
New cards
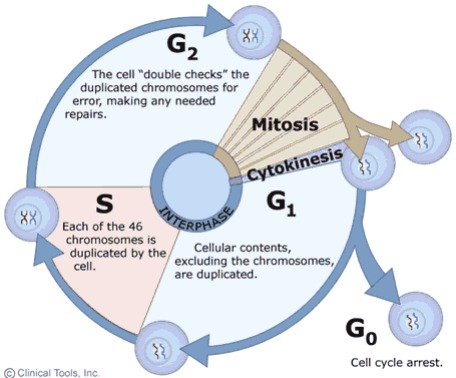
Stages in the cell cycle
Interphase - cell grows and replicates its DNA
Mitotic phase - cell divides and transfers one copy of its DNA to two identical cells
Mitotic phase - cell divides and transfers one copy of its DNA to two identical cells
21
New cards
Interphase
Period between two consecutive cell divisions
Cell growth and DNA replication takes place
Extra organelles formed
Cell growth and DNA replication takes place
Extra organelles formed
22
New cards
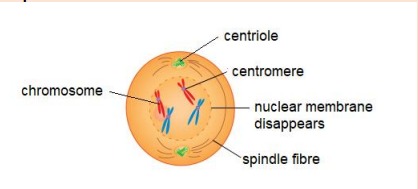
Events in prophase
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear
Chromatin network shortens and thickens to form individual chromosomes
Centrioles separate and move to opposite poles of cell, spindle fibre forms between them
Chromatin network shortens and thickens to form individual chromosomes
Centrioles separate and move to opposite poles of cell, spindle fibre forms between them
23
New cards
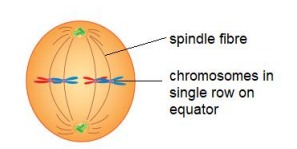
Events in Metaphase
Spindle enlarges
Cytoplasmic threads pull double-threaded chromosomes to the 'equator' of the cell
Cytoplasmic threads pull double-threaded chromosomes to the 'equator' of the cell
24
New cards
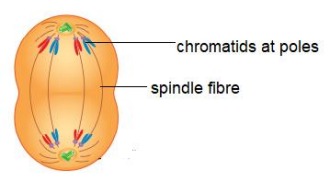
Events in Anaphase
Centromere of each chromosome divides into two
The two chromatids separate (kyrokinesis)
Spindle fibre contracts and pulls chromatids to opposite poles
The two chromatids separate (kyrokinesis)
Spindle fibre contracts and pulls chromatids to opposite poles
25
New cards
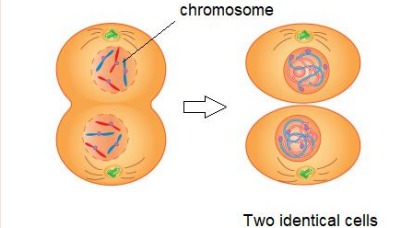
Events in Telophase
Chromosomes arrange themselves at the poles
Spindle fibre disappears
Cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis) into two daughter cells
Nuclear membrane forms around each group of chromosomes at each pole and a nucleolus forms
Spindle fibre disappears
Cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis) into two daughter cells
Nuclear membrane forms around each group of chromosomes at each pole and a nucleolus forms
26
New cards
Cancer
Result of uncontrolled cell division in the body
27
New cards
Malignant cancer cells
Able to invade tissues and spread to other parts of the body
28
New cards
Metastasis
The spread of cancer cells to locations distant from their original site.
29
New cards
Carcinoma
Cancer that begins in the skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs
30
New cards
Sarcoma
Cancer that begins in bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels or other connective or supportive tissue
31
New cards
Leukemia
Cancer that starts in blood-forming tissue such as the bone marrow and causes large numbers of abnormal blood cells to be produced and enter the blood
32
New cards
Lymphoma and Myeloma
Cancers that begin in the cells of the immune system
33
New cards
Central nervous system cancers
Cancers that begin in the tissues of the brain and spinal cord
34
New cards
Ways to treat cancer
Surgery
Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
35
New cards
Radiotherapy
The destruction of cancer cells using radiation. Treatment is carefully directed at the site of the tumor.
36
New cards
Chemotherapy
Using chemicals to kill dividing cells. Treatment may be administered by drip or orally.
37
New cards
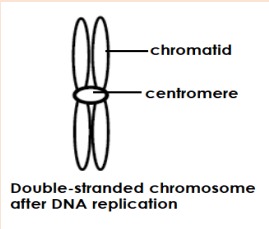
Centromere
Structure which joins to chromatids when the chromosomes are replicated
38
New cards
Chromatid
One of the two DNA threads which form part of a replicated chromosome
39
New cards
Genes
Sections of DNA located at specific regions on chromosomes
Contain the necessary information responsible for the unique characteristics present in living organisms
Contain the necessary information responsible for the unique characteristics present in living organisms
40
New cards
Centrioles
Arranged at right angles to each other
Control the formation of spindle involved in the movement of replicated chromosomes away from one another during cell division
Control the formation of spindle involved in the movement of replicated chromosomes away from one another during cell division
41
New cards
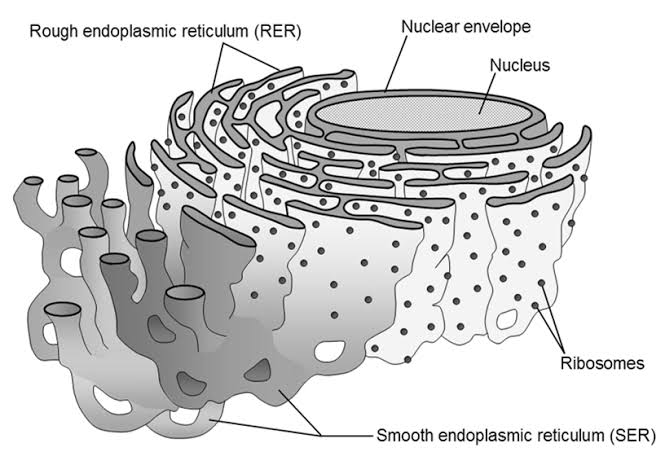
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Increases internal surface area of cell
Makes, stores and transports carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
Makes, stores and transports carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
42
New cards
Ribosomes
Small granules found in the cytoplasm of all cells Make new proteins
Those in cytoplasm produce proteins needed by cytoplasm
Those in ER produce proteins that form part of the membranes or are secreted
Those in cytoplasm produce proteins needed by cytoplasm
Those in ER produce proteins that form part of the membranes or are secreted
43
New cards
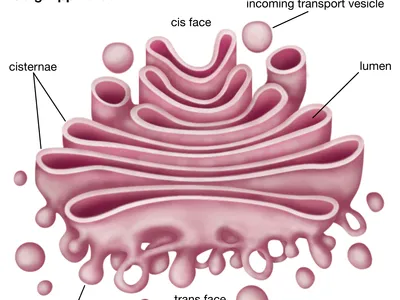
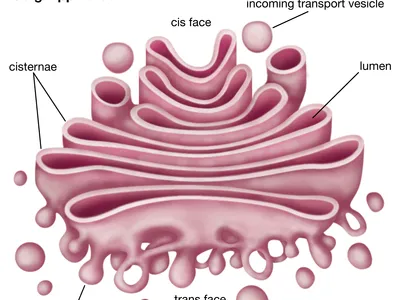
Golgi Bodies
Consist out of a stack of membranes called cisternae
Membranes pinch off to form vesicles that contain proteins and lipids
Membranes pinch off to form vesicles that contain proteins and lipids
44
New cards
Function of Golgi Bodies
Collect molecules from the ER, pack them into vesicles and distribute them to different parts of the cell where they are needed or secreted
Proteins secreted from the cell can be hormones or enzymes needed in the body
Form lysosomes
Proteins secreted from the cell can be hormones or enzymes needed in the body
Form lysosomes
45
New cards
Vesicles and Vacuoles
Structures filled with fluid and surrounded by a membrane
Control amount of water in the cytoplasm
Vesicles from Golgi Bodies contain proteins and lipids
Control amount of water in the cytoplasm
Vesicles from Golgi Bodies contain proteins and lipids
46
New cards
Lysosomes
Tiny sacs formed from vesicles produced by the Golgi Body
Contain enzymes that can breakdown lipids, proteins and carbohydrates
Contain enzymes that can breakdown lipids, proteins and carbohydrates
47
New cards
Function of Lysosomes
Destroy foreign material inside or outside cell
Digest and breakdown food particles
Breakdown dead cells and organelles
Digest and breakdown food particles
Breakdown dead cells and organelles
48
New cards
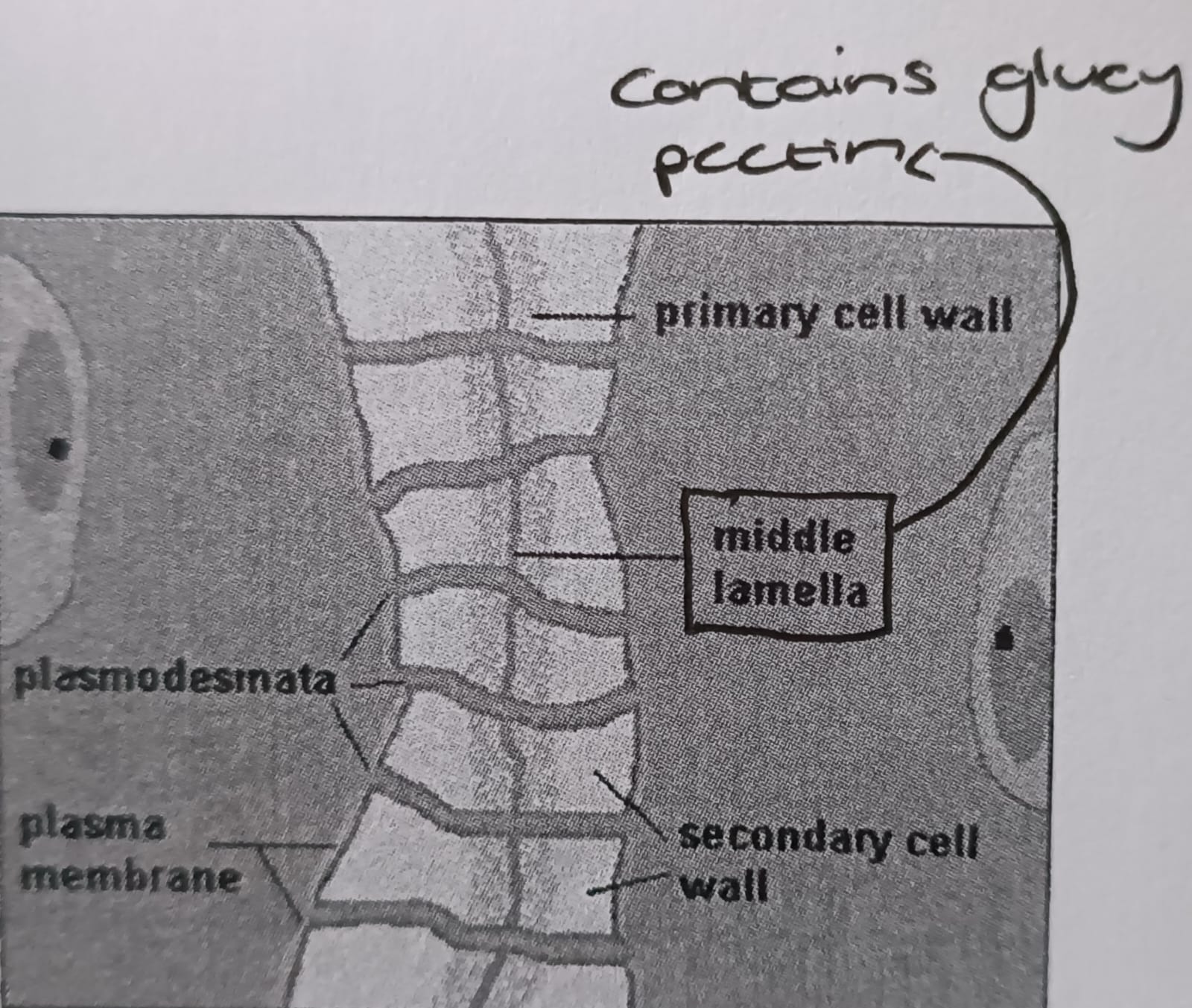
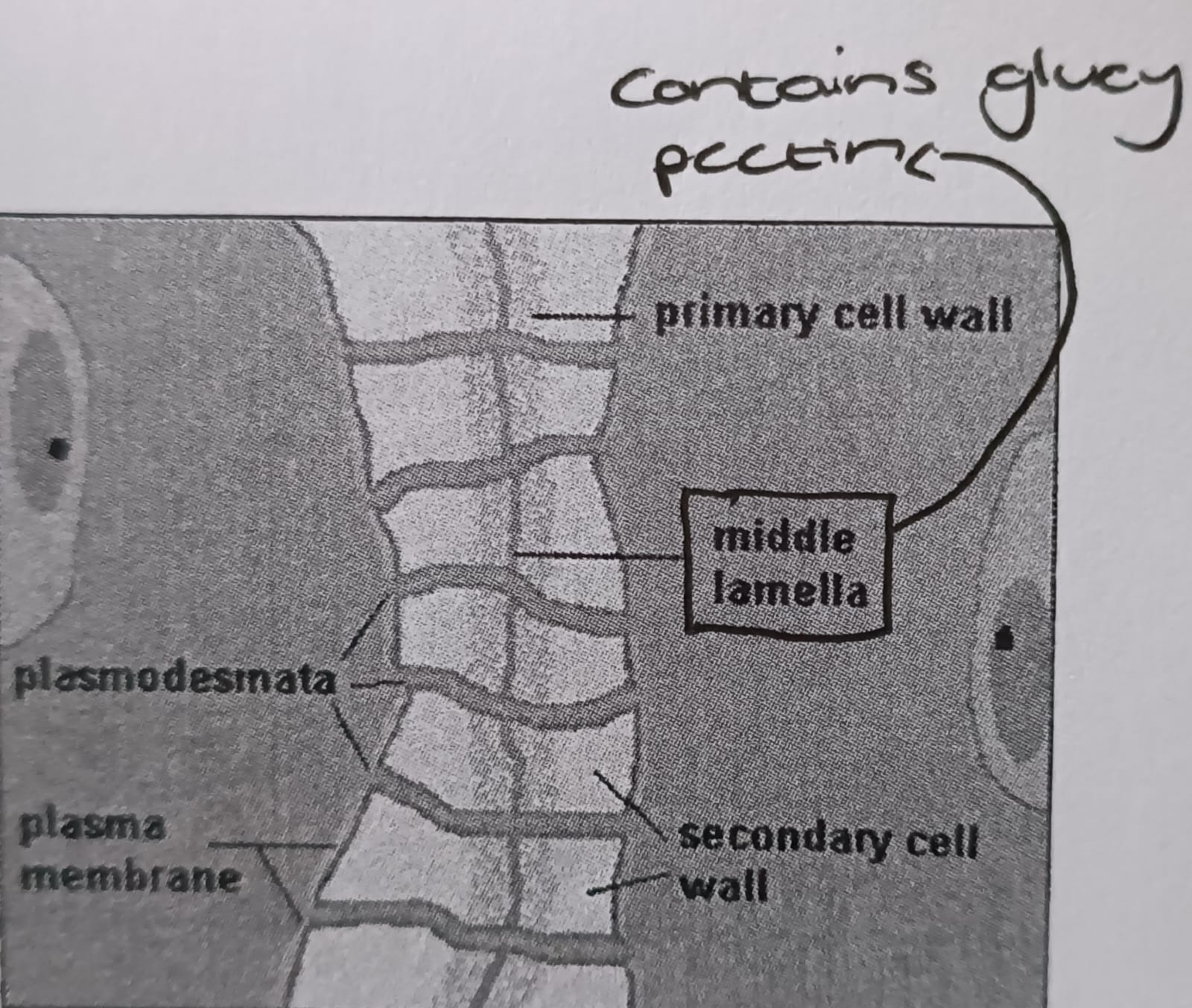
Cell wall
Made out of cellulose
Some cells have lignin in the cell walls (extra strength)
Permeable to water and mineral salts
Cell walls of adjacent cells joined by thin layer of lamella
Some cells have lignin in the cell walls (extra strength)
Permeable to water and mineral salts
Cell walls of adjacent cells joined by thin layer of lamella
49
New cards
Function of Cell wall
Gives cell its shape
Supports and protects the cell
Supports and protects the cell
50
New cards
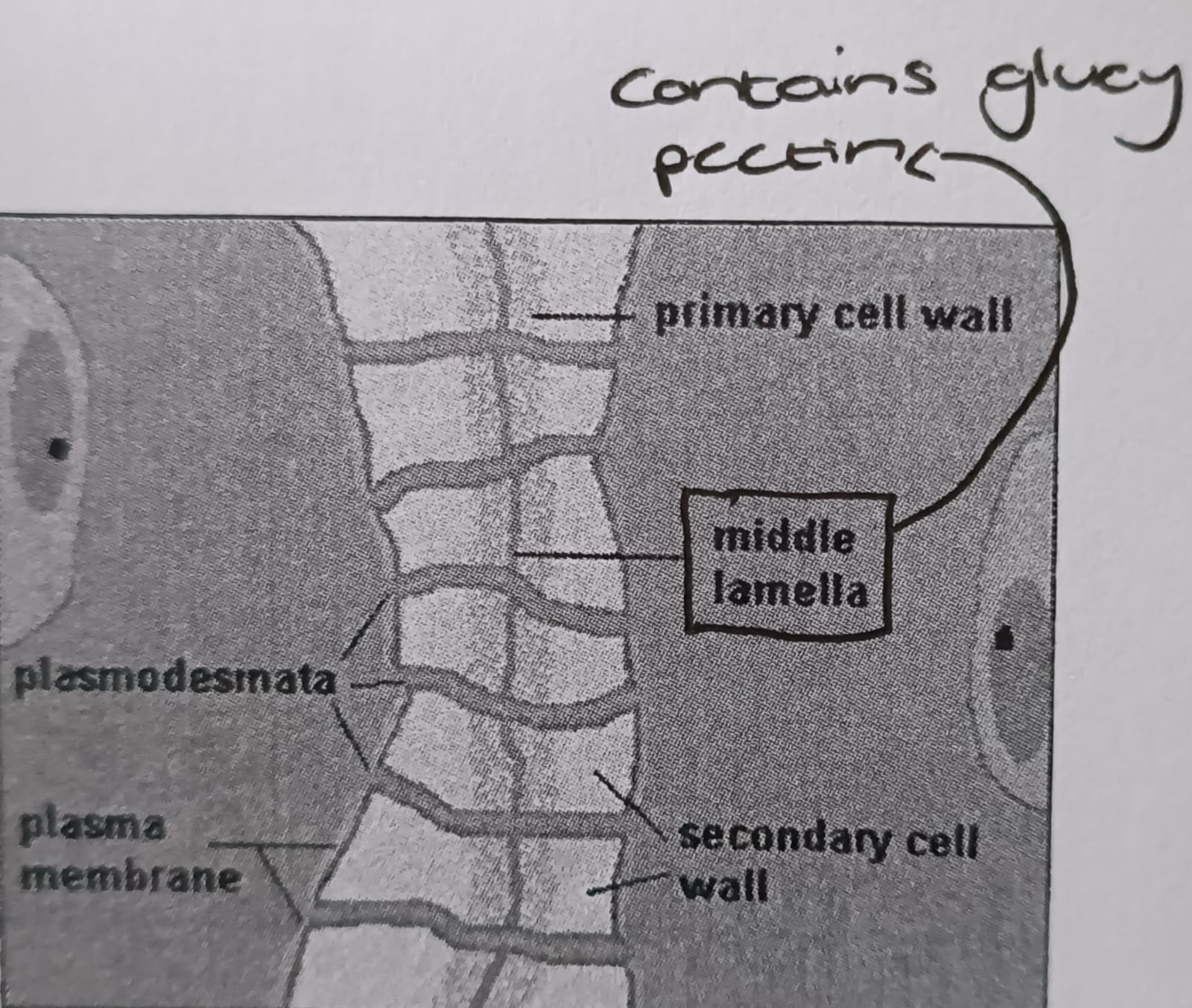
Plasmodesmata
Cytoplasmic channels that connect adjacent plant cells
51
New cards
Plant vacuoles
Surrounded by tonoplast
Contains cell sap
Contains cell sap
52
New cards
Function of plant vacuoles
Store sugars, minerals and pigments
Cell sap helps give cell its shape
Plays a role in the digestion and secretion of cellular waste
Osmoregulation
Cell sap helps give cell its shape
Plays a role in the digestion and secretion of cellular waste
Osmoregulation
53
New cards
Turgor pressure
The pressure exerted by the swollen vacuole outwards on the cell wall
54
New cards
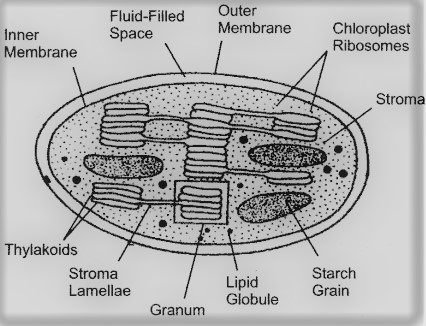
Chloroplasts
Contain chlorophyll
Made up of stroma
Contains the NB enzymes for photosynthesis
Has a double membrane
Made up of stroma
Contains the NB enzymes for photosynthesis
Has a double membrane
55
New cards
Leucoplasts
Colorless
Store starch
Store starch
56
New cards
Thylakoids
Suspended in stroma
Stacks of membrane like structures
The site of photosynthesis
Stacks of membrane like structures
The site of photosynthesis
57
New cards
Chemical Equation for photosynthesis
CO2 + H2O → C6H12O6 + O2
58
New cards
Validity
Refers to the experimental procedures (the method used)
Repeat investigation
Record data over longer period
Increase sample size
Repeat investigation
Record data over longer period
Increase sample size
59
New cards
Reliability
Refers to the results (amount of data obtained)
Control and Experimental setup
Fixed variables
Control and Experimental setup
Fixed variables
60
New cards
4 Types of animal tissue
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
61
New cards
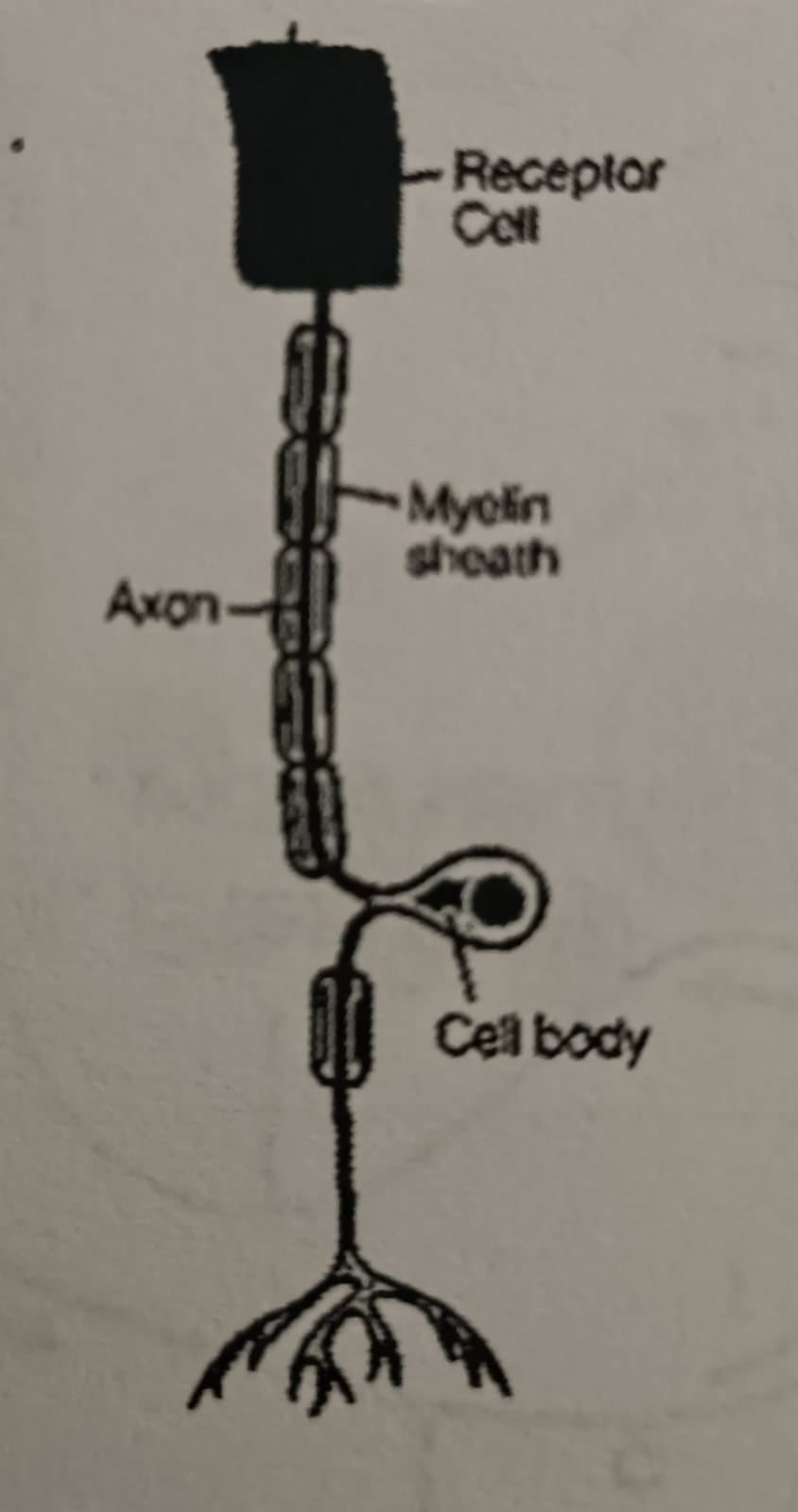
Sensory neurons
Send information gathered by receptors from internal and external stimuli to the brain.
- located in the skin, eyes and ears
- located in the skin, eyes and ears
62
New cards
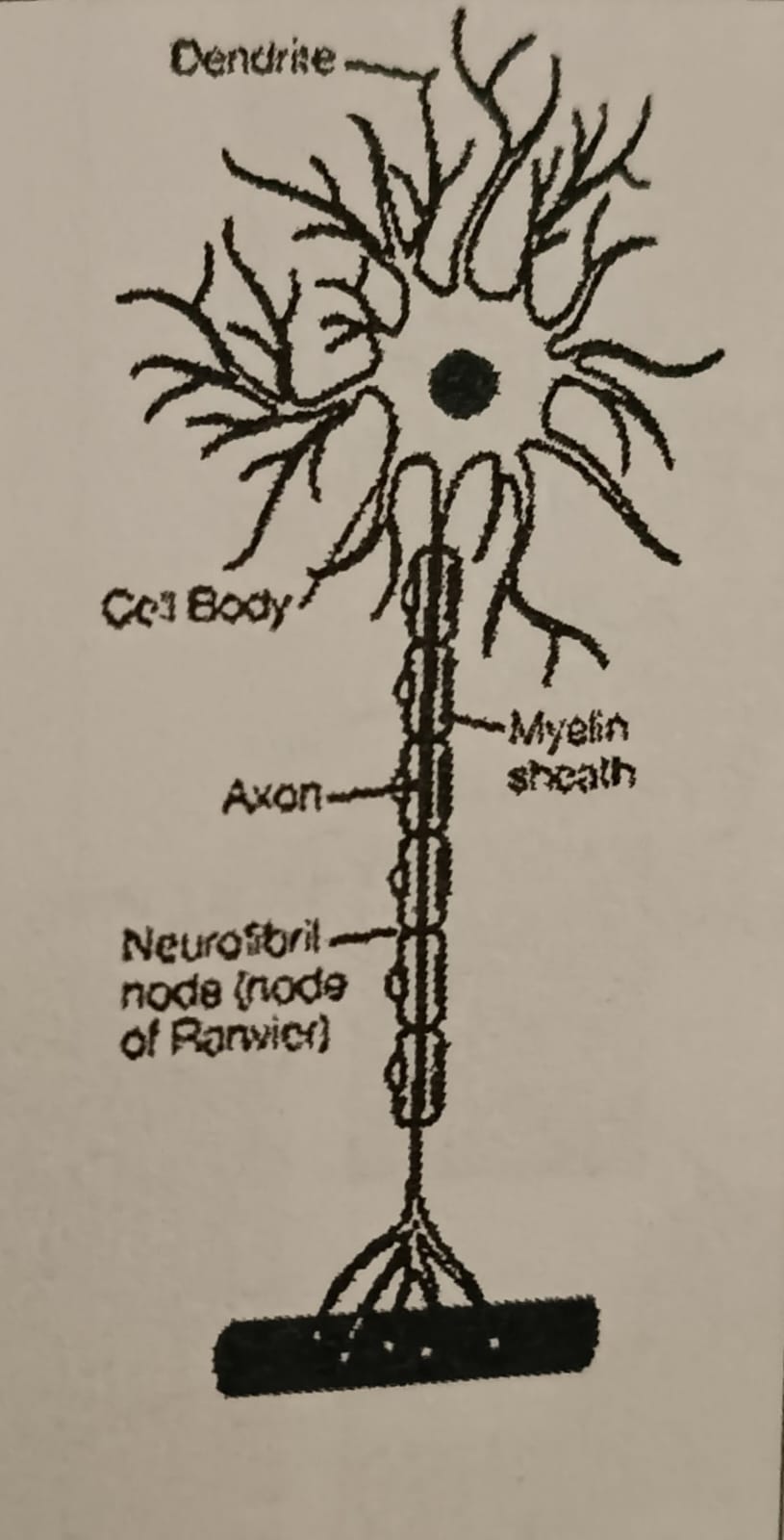
Motor neurons
Send information from the brain to the effectors (muscles and glands).
* located in the spinal cord, brain and body
* located in the spinal cord, brain and body
63
New cards
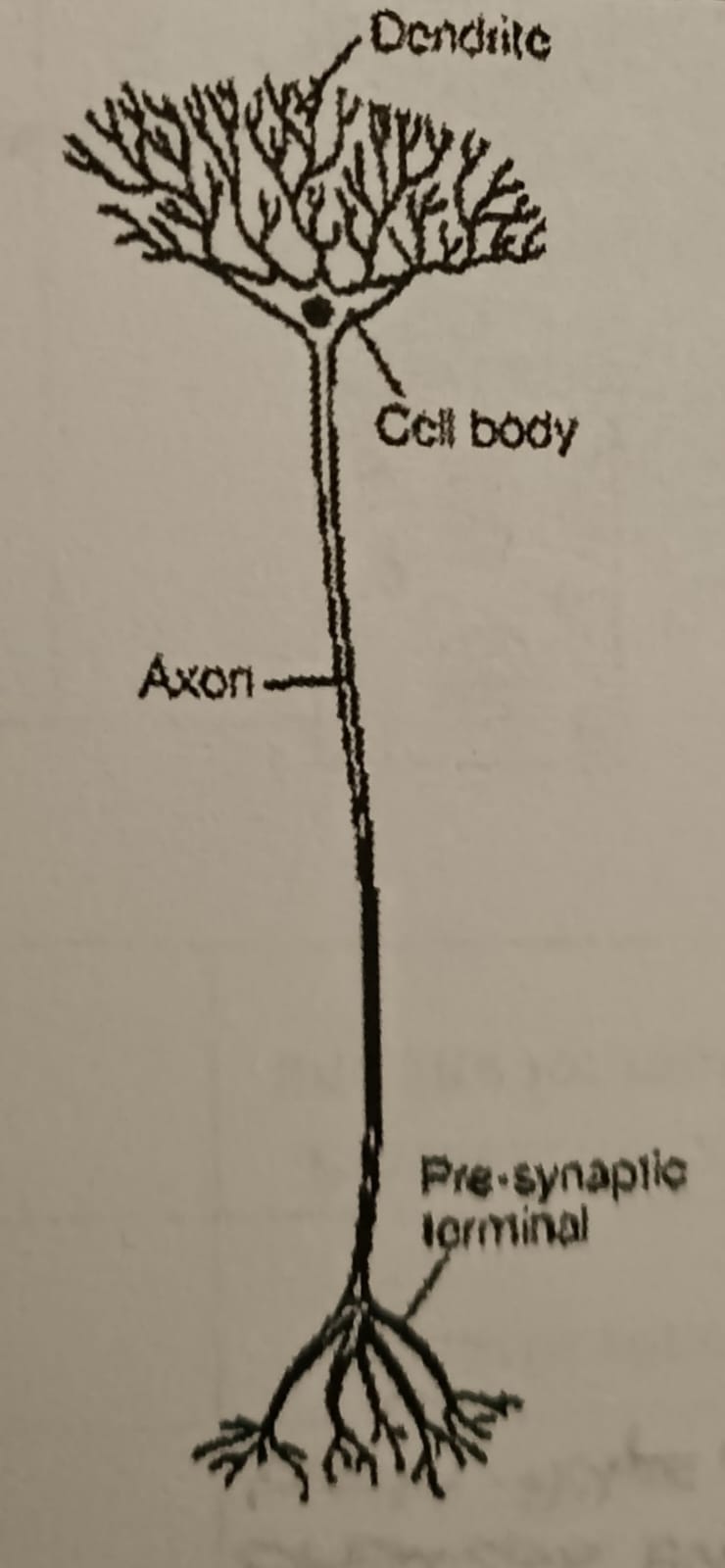
Interneurons
Connect sensory neurons to motor neurons
- located in the brain and spinal cord
- located in the brain and spinal cord
64
New cards
Nervous tissue
Produces and conducts electrochemical signals between organs of the body and the brain.
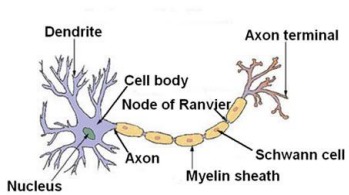
65
New cards
Connective tissue
Supports, stablizes and protects the body's many organs. Consists of cells surrounded by fluid or materials.
66
New cards
Dense connective tissue
Connect muscle to bones and bones to bones.
- located in the tendons, around muscles and under the skin
- located in the tendons, around muscles and under the skin

67
New cards
Loose connective tissue
Supports, insulates and nourishes organs.
- located between organs and under the skin
- located between organs and under the skin

68
New cards
Blood
Transports oxygen, nutrients, water and other chemicals throughout the body. Helps develop immunity.
- located in the circulatory system
- located in the circulatory system
69
New cards
Cartilage
Absorbs shock and friction.
- located near the joints and in the ear, nose and trachea
- located near the joints and in the ear, nose and trachea
70
New cards
Bone
Provides framework for body and site for muscle attachment
71
New cards
Skeletal muscle tissue
Striated, Multinucleated
Voluntary movement
Attached to bones in the skeleton
Voluntary movement
Attached to bones in the skeleton
72
New cards
Smooth muscle tissue
Non-striated, Spindle shaped, One nucleus per fibre
Involuntary movement
Found in the digestive system and walls of veins and arteries
Involuntary movement
Found in the digestive system and walls of veins and arteries
73
New cards
Cardiac muscle tissue
Striated, One nucleus per fibre
Involuntary movement
Responsible for heartbeat
Involuntary movement
Responsible for heartbeat
74
New cards
Squamous epithelium tissue
Thin, irregular cells with large flattened nucleus
Protect underlying tissue from friction and allow for movement of substances
Found in the lining of the mouth, oesophagus, blood vessels and alveoli of the lungs
Protect underlying tissue from friction and allow for movement of substances
Found in the lining of the mouth, oesophagus, blood vessels and alveoli of the lungs
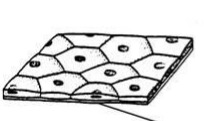
75
New cards
Columnar epithelium tissue
Elongated cells with oval nucleus, some have microvilli
Support other types of cells, involved in secretion of mucus during digestion
Lines the intestine
Support other types of cells, involved in secretion of mucus during digestion
Lines the intestine

76
New cards
Ciliated columnar epithelium tissue
Ciliated columnar epithelium cells
Cilia in lungs help trap dust particles
Lines nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi, female reproductive system
Cilia in lungs help trap dust particles
Lines nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi, female reproductive system
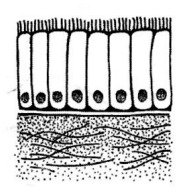
77
New cards
Cuboidal epithelium
Square shaped cells with oval nucleus
Secretory functions
Lines glands
Secretory functions
Lines glands
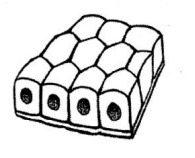
78
New cards
Stratified epithelium
Several layers of cells , cells in outer layers are dead
Reduces friction in areas exposed to heavy friction
Found on the surface of skin and inside lining of mouth
Reduces friction in areas exposed to heavy friction
Found on the surface of skin and inside lining of mouth
79
New cards
Stratified squemous epithelium
Squamous cells atop of multiple layers of cells varying from cuboidal to columnar
Functions in protection
Functions in protection
80
New cards
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Two layers of cuboidal cells
Functions in absorption and secretion
Functions in absorption and secretion
81
New cards
Stratified columnar epithelium
Single layer of columnar cells on several layers of cuboidal cells.
Functions in protection and secretion
Functions in protection and secretion
82
New cards
Transitional epithelium
Cells vary depending on stretch, surface cells often large, round and bi-nucleated.
Occurs only in bladder, ureter and urethra
Occurs only in bladder, ureter and urethra
83
New cards
Formation of organisms
Cells → Tissues → Organs → Organ systems → Organisms