L05 and L06 - Carbohydrates I & II (Glycolysis) Quiz
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Flip card for question.
A. D-glucose
--------------------
- aldose = has an aldehyde attached -R-CH=O
- ketose = has a ketone attached -C=O-
(fructose = ketose)
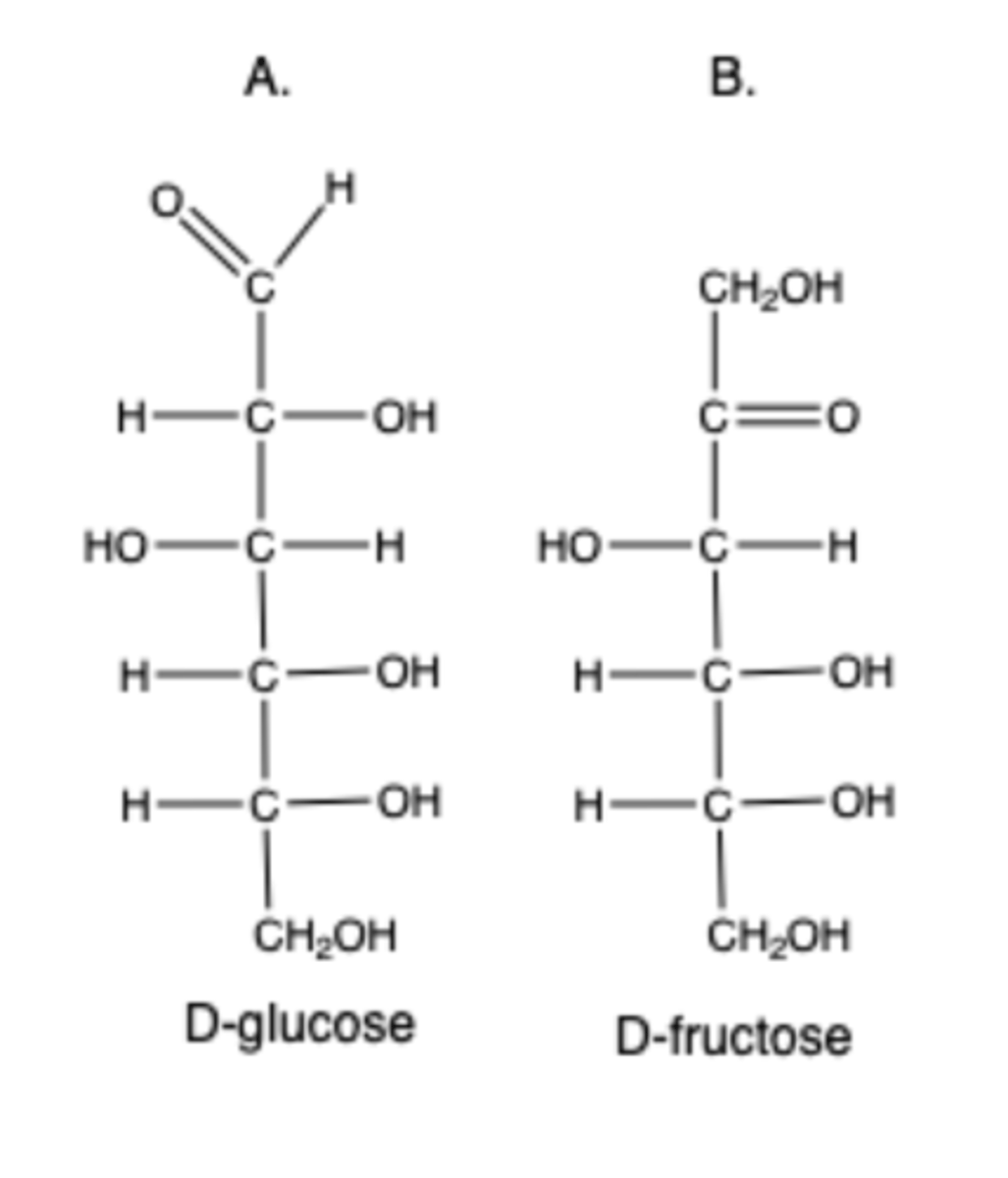
Which of the following two monosaccharides is an aldose?
B. D-fructose
A. D-glucose
Glycoproteins differ from proteoglycans in that they have ______ sugars attached to the protein moiety.
a. More
b. Less
b. Less
------------
- proteoglycans are made of 50-60% carbohydrate
- glycoproteins have short chains of 3-20 sugars
The predominant amino acids found in mucins are
a. phenylalanine and tyrosine
b. alanine and glycine
c. lysine and asparagine
d. arginine and glutamine
e. serine and threonine
e. serine and threonine
----------------------------
a. phenylalanine and tyrosine = glucogenic and ketogenic
b. alanine and glycine = glucogenic, turned into pyruvate (CT SWAG)
c. lysine and asparagine
d. arginine and glutamine = glucogenic, turned into alpha-ketoglutarate (PRE HQ)
e. serine and threonine = also can be turned into pyruvate, most abundant O-glycoproteins in mucins
Glycogen and starch are both storage polysaccharides. The feature that distinguishes these polysaccharides is
a. Glycogen contains beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds
b. Starch contains galactose epimers in addition to glucose subunits
c. Starch has more branching
d. Starch contains beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds
e. Glycogen has more branching
e. Glycogen has more branching
------------------------------------
a. Glycogen contains beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds = FALSE, they have alpha 1, 6 and alpha 1, 4 glycosidic bonds
b. Starch contains galactose epimers in addition to glucose subunits = FALSE, starch does not have galactose epimers, it's primarily made of alpha-glucose monomers
c. Starch has more branching = FALSE, glycogen has more branching
d. Starch contains beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds = FALSE, has alpha not beta bonds
e. Glycogen has more branching = TRUE, it has more branching that starch
Which monosaccharide pairs with glucose to produce lactose?
a. D-glucose
b. D-galactose
c. D-psicose
d. D-mannose
e. D-fructose
b. D-galactose
----------------------
a. D-glucose + glucose = maltose
b. D-galactose + glucose = lactose
c. D-psicose
d. D-mannose
e. D-fructose + glucose = sucrose
A protein attached to a glycosaminoglycan is known as a/an
a. collagen
b. aggrecan
c. proteoglycan
d. mucin
e. mucus
c. proteoglycan
---------------------
a. collagen = fibrous protein
b. aggrecan = a type of proteoglycan, but NOT a glycosaminoglycan (GAG)
c. proteoglycan
d. mucin = globular protein with serine and threonine
e. mucus
The formation of a glycosidic bond between two monosaccharides is known as a dehydration synthesis reaction. It is also known as a _____________ reaction.
a. Decarboxylation
b. Hydrolysis
c. Condensation
d. Deamination
e. Isomerization
c. Condensation
------------------------
a. Decarboxylation = remove carboxyl group, forms an amine
b. Hydrolysis = breaks peptide bonds
c. Condensation = makes peptide bonds
d. Deamination = removes amino group
e. Isomerization = molecule is transformed into a different isomer (cis or trans)
A glycosaminoglycan (GAG) found in connective, epithelial, and neural tissue is
a. Keratin
b. Hyaluronic acid
c. Chondroitin sulfate
d. Heparin
b. Hyaluronic acid
-------------------------
a. Keratin = cartilage, bone, cornea
b. Hyaluronic acid = CT, epithelial tissue, neural tissue (also known as hyaluronate)
c. Chondroitin sulfate = cartilage
d. Heparin = produced by basophils, mas cells, and used as an anticoagulant
Flip card for question.
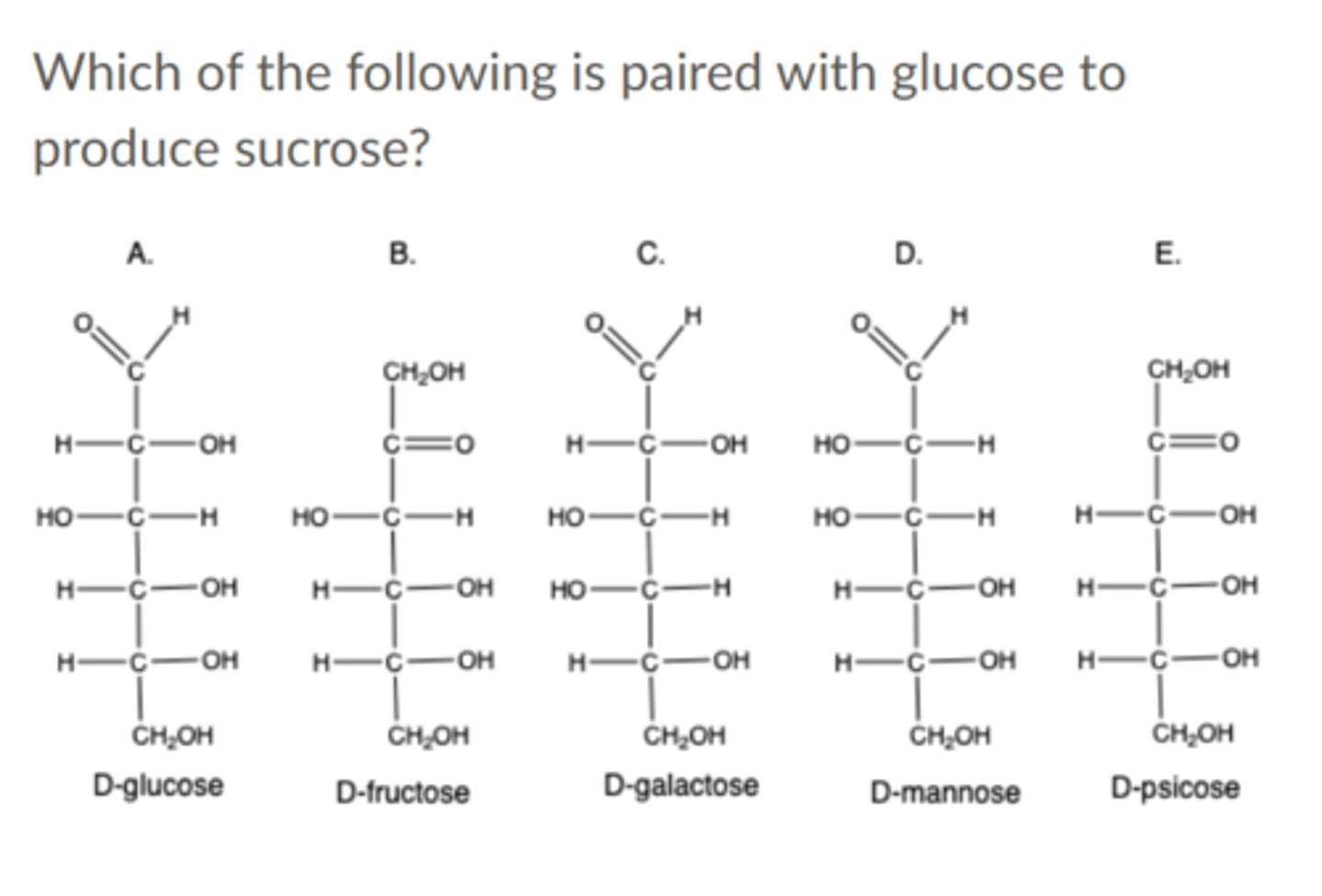
B. Fructose
---------------------
A. Glucose + glucose = maltose
B. Fructose + glucose = sucrose
C. Galactose + glucose = lactose
D. Mannose
E. Psicose
Which of the following is paired with glucose to produce sucrose?
A. Glucose
B. Fructose
C. Galactose
D. Mannose
E. Psicose
Which of these carbohydrate linkages is indigestible by humans?
a. glucose β-1,4 glucose
b. glucose α-1,6 glucose
c. glucose α-1,2 fructose
d. galactose β-1,4 glucose
a. glucose β-1,4 glucose
------------------------------
a. glucose β-1,4 glucose = peptidoglycan, cellulose, and chitin
b. glucose α-1,6 glucose = alpha bonds can be broken down
c. glucose α-1,2 fructose = alpha bonds can be broken down
d. galactose β-1,4 glucose = bond found in lactose = can be digested
Which of the following is a non-reducing sugar?
a. Glucose
b. Sucrose
c. Lactose
d. Maltose
b. Sucrose
---------------
Note: non-reducing sugar = a sugar without a hemiacetal
a. Glucose = reducing sugar
b. Sucrose = non-reducing sugar
c. Lactose = reducing sugar
d. Maltose = reducing sugar
To which amino acid residue are N-linked glycans are carbohydrates usually bound?
a. Serine
b. Aspartate
c. Asparagine
d. Glutamate
e. Tyrosine
c. Asparagine
----------------------
a. Serine (and threonine) = O-glycans, found in mucous fluids
b. Aspartate
c. Asparagine = N-glycans, found in membrane and secretory proteins
d. Glutamate
e. Tyrosine
GLUT5 transports both glucose and fructose from enterocytes into the blood.
a. True
b. False
b. False - GLUT5 is a FRUCTOSE ONLY transporter from enterocytes in the small intestine.
--------------
- GLUT2 = in the lining of intestine and beta cells of pancreas
Which of the following is an example of a monosaccharide?
a. pectin
b. fructose
c. glycogen
d. starch
e. cellulose
b. fructose
---------------------
a. pectin = polysaccharide
b. fructose = monosaccharide
c. glycogen = polysaccharide
d. starch = polysaccharide
e. cellulose = polysaccharide
GLUT proteins are examples of which kind of transport mechanism?
a. Simple diffusion
b. Facilitated diffusion
c. Active transport
b. Facilitated diffusion
Flip card for question.
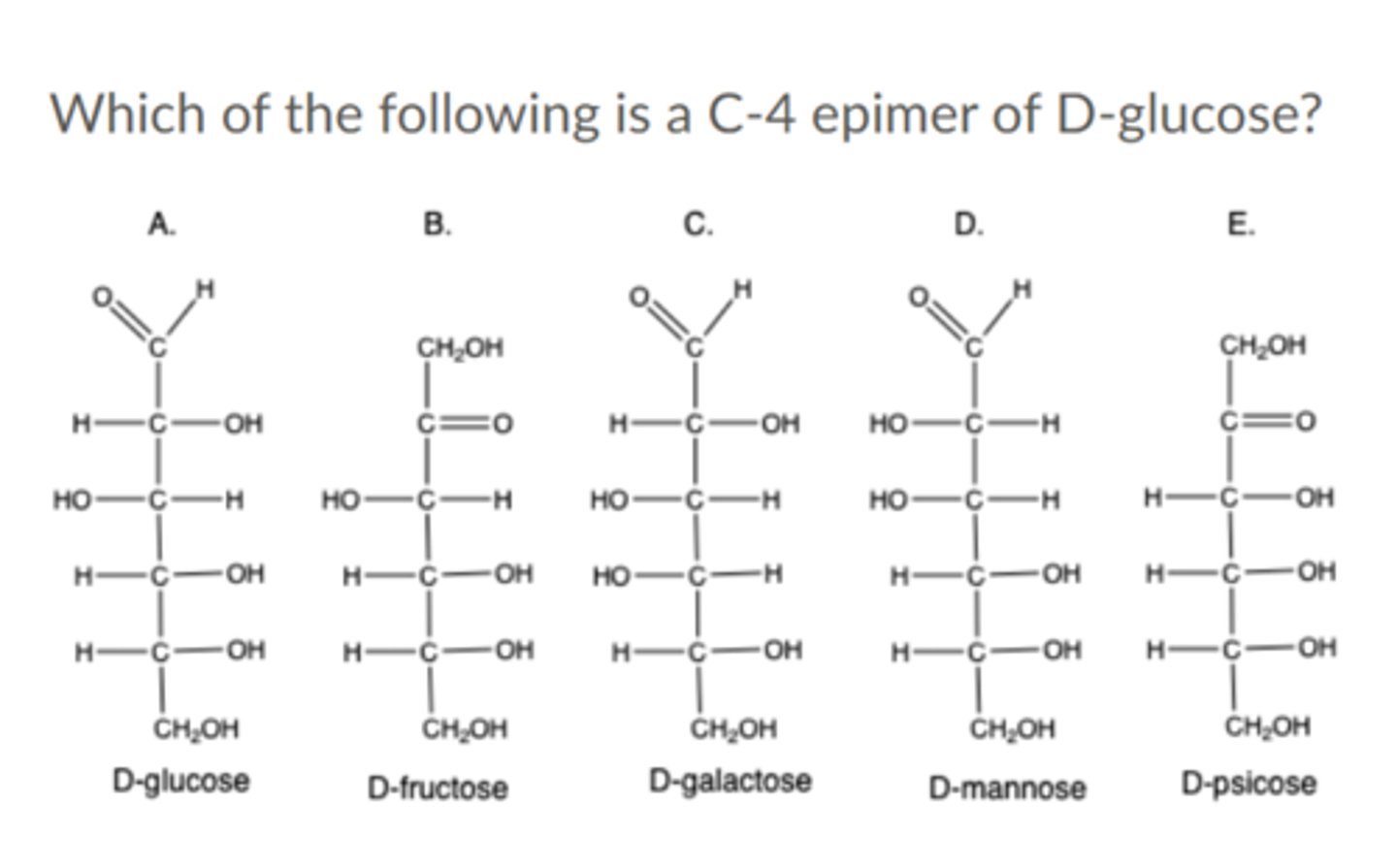
b. D-galactose
---------------------
Note: A C-4 epimer is where the difference between two stereoisomers occurs at the fourth carbon atom.
Which of the following is a C-4 epimer of D-glucose?
a. D-psicose
b. D-galactose
c. D-fructose
d. None of the above
e. D-mannose
The recommended daily allowance for carbohydrates is about how many grams (per day)?
a. 200 g/day
b. 100 g/day
c. 70 g/day
d. 50 g/day
e. 130 g/day
e. 130 g/day
The enzyme that converts fructose to fructose-1-phosphate in the liver is
a. protein kinase A
b. phosphofructokinase
c. fructokinase
d. hexokinase
e. triose kinase
c. fructokinase
-------------------
a. protein kinase A = ?
b. phosphofructokinase = converts fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate = KEY enzyme in glycolysis
c. fructokinase = converts fructose to fructose-1-phosphate
d. hexokinase = converts fructose to fructose-6-phosphate everywhere BUT the liver
e. triose kinase = ?
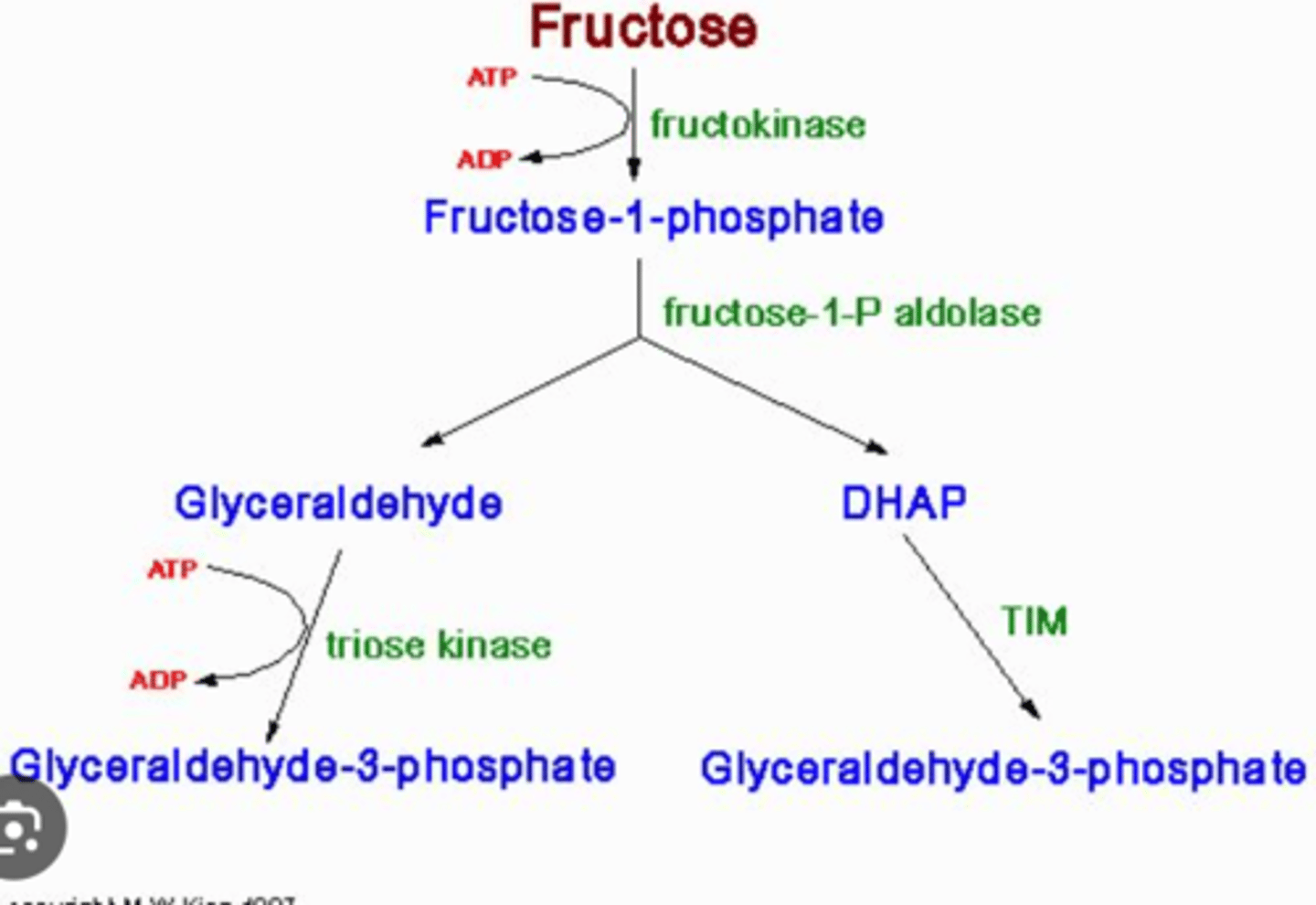
Glycoproteins are usually oriented towards the _____ of the cell.
a. outside
b. both inside and outside
c. inside
a. outside
Where in the cell does anaerobic glycolysis occur?
a. In the mitochondrial matrix
b. In the cytoplasm
c. In the Golgi apparatus
d. In the plasma membrane
e. In the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion
b. In the cytoplasm
-----------------------
1. Glycolysis = cytoplasm
2. TCA (Kreb's cycle) = mitochondrial matrix
3. Oxidative phosphorylation = mitochondrial membrane
4. electron transport chain = inner mitochondrial membrane
Which of the following glycolytic enzymes produces ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation?
a. Phosphoglucose isomerase
b. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
c. Hexokinase
d. Phosphoglycerate kinase
e. Phosphofructokinase
d. Phosphoglycerate kinase
-------------------------------
a. Phosphoglucose isomerase = converts 1,3-bisphospohglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate
b. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase = ?
c. Hexokinase = converts glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
d. Phosphoglycerate kinase = ?
e. Phosphofructokinase = converts fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
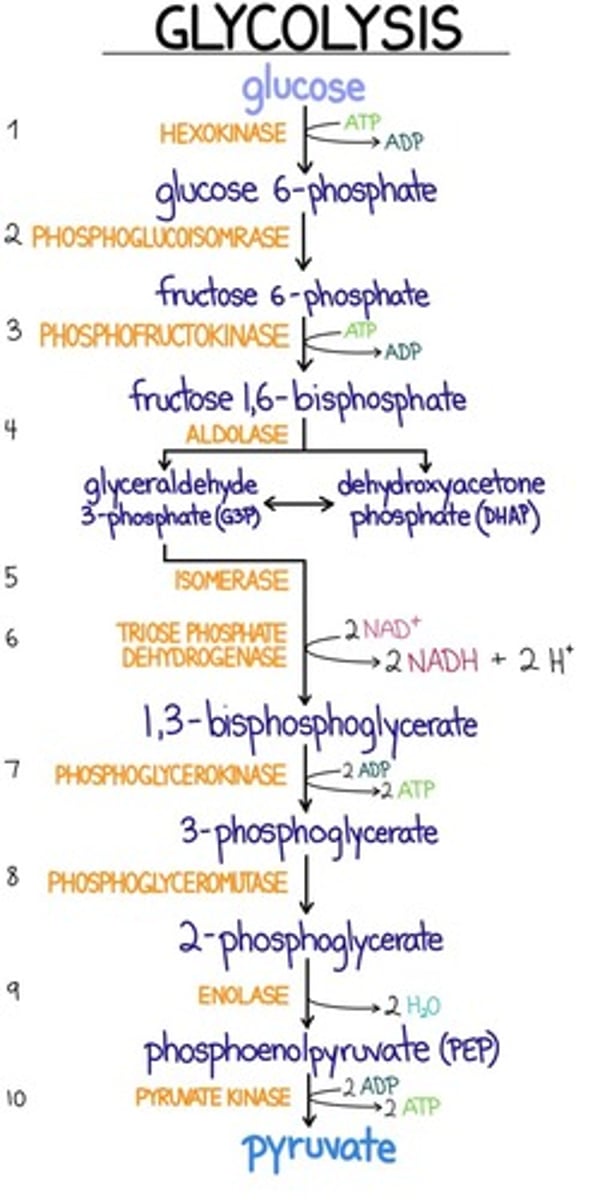
Which of the following statement is true about Cori's Cycle?
a. It is active during resting stages and in well-fed condition
b. The Cori cycle involves three tissues muscle, liver, and brain
c. It involves the transport of lactate from the liver to skeletal tissue for gluconeogenesis
d. It involves the transport of lactate from skeletal muscle to the liver for gluconeogenesis
d. It involves the transport of lactate from skeletal muscle to the liver for gluconeogenesis
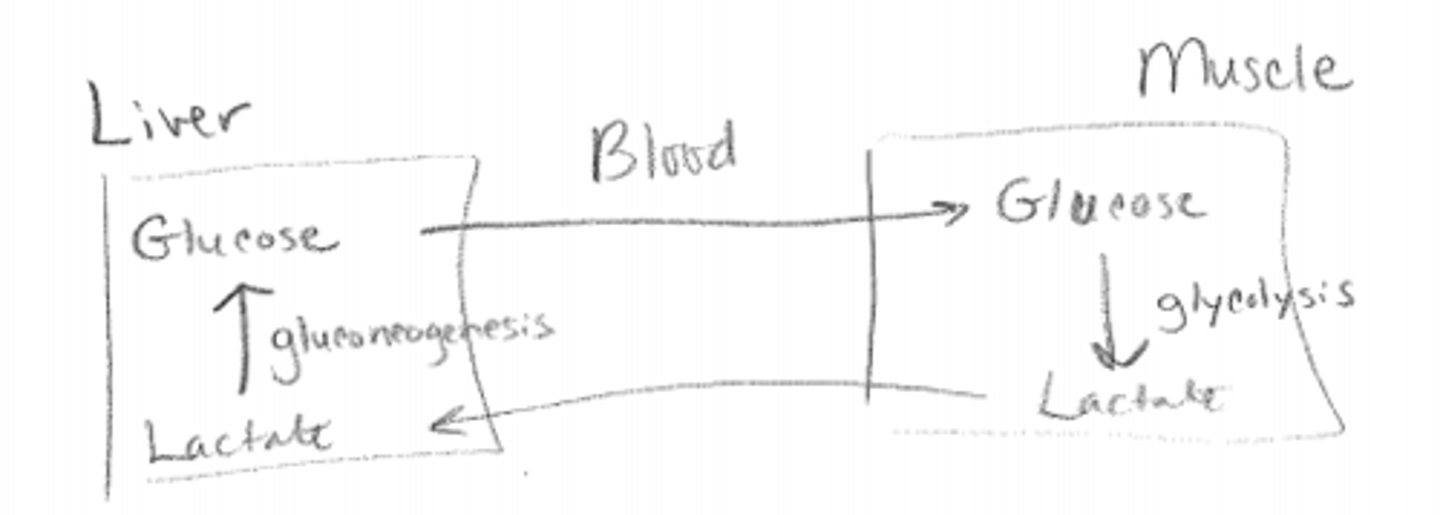
Which of the following steps generates NADH?
a. Conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate
b. Conversion of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate to 1-3-bisphosphoglycerate
c. Conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate
d. Conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1-6-bisphosphate
b. Conversion of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate to 1-3-bisphosphoglycerate
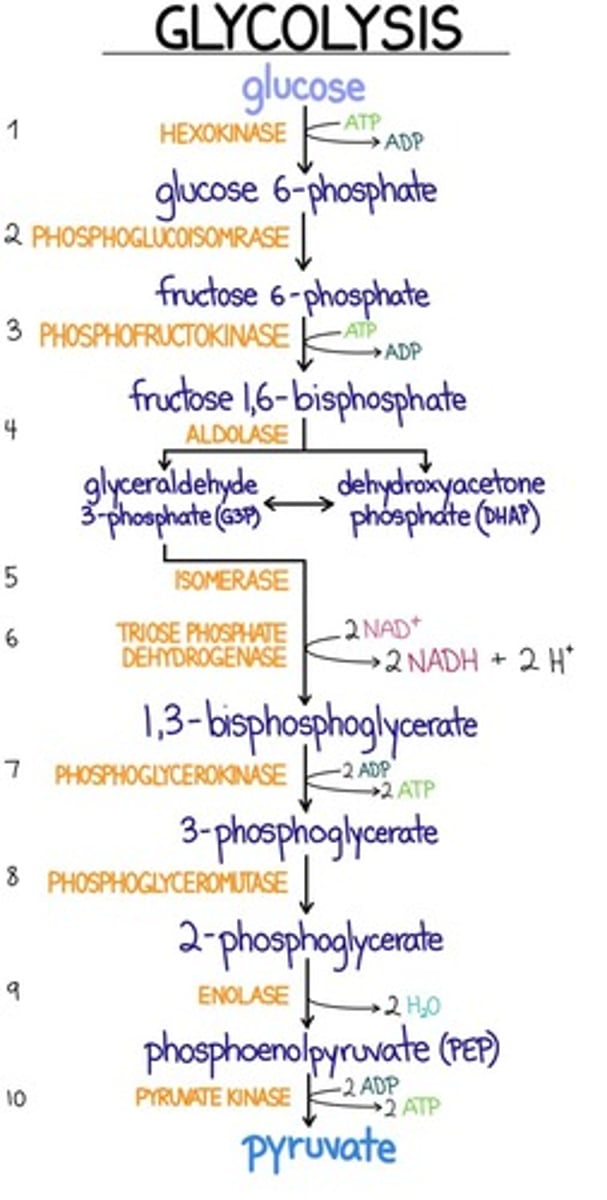
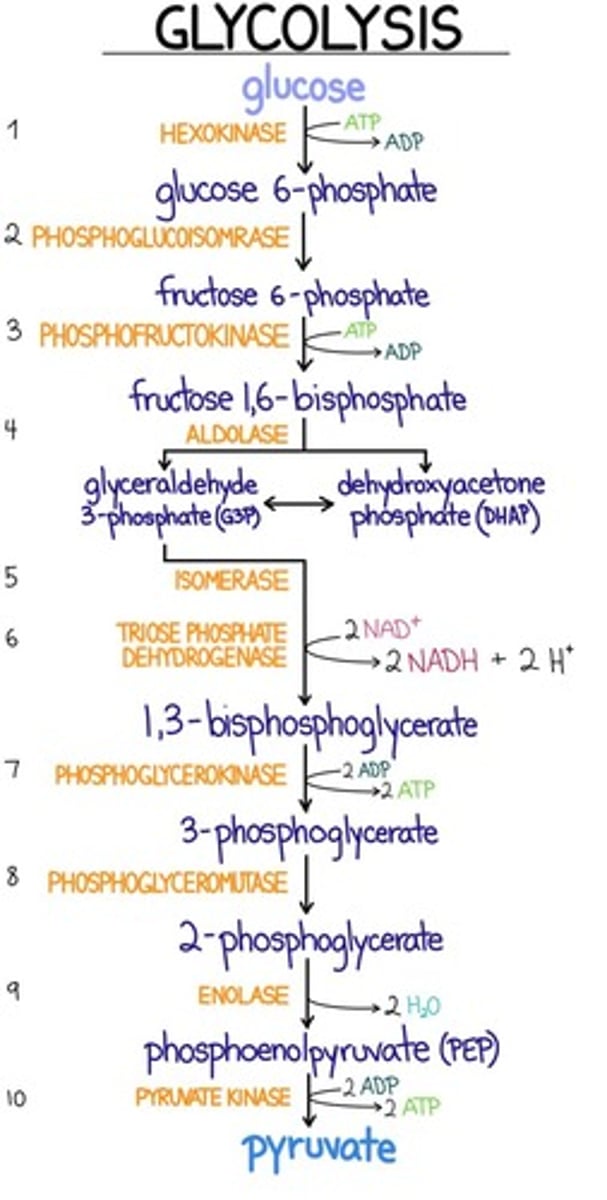
Glycolysis consists of three irreversible steps. Which of the following enzyme-catalyzed reactions is a reversible step in glycolysis?
a. Phosphoglycerate kinase
b. Phosphofructokinase
c. Hexokinase
d. Pyruvate kinase
a. Phosphoglycerate kinase
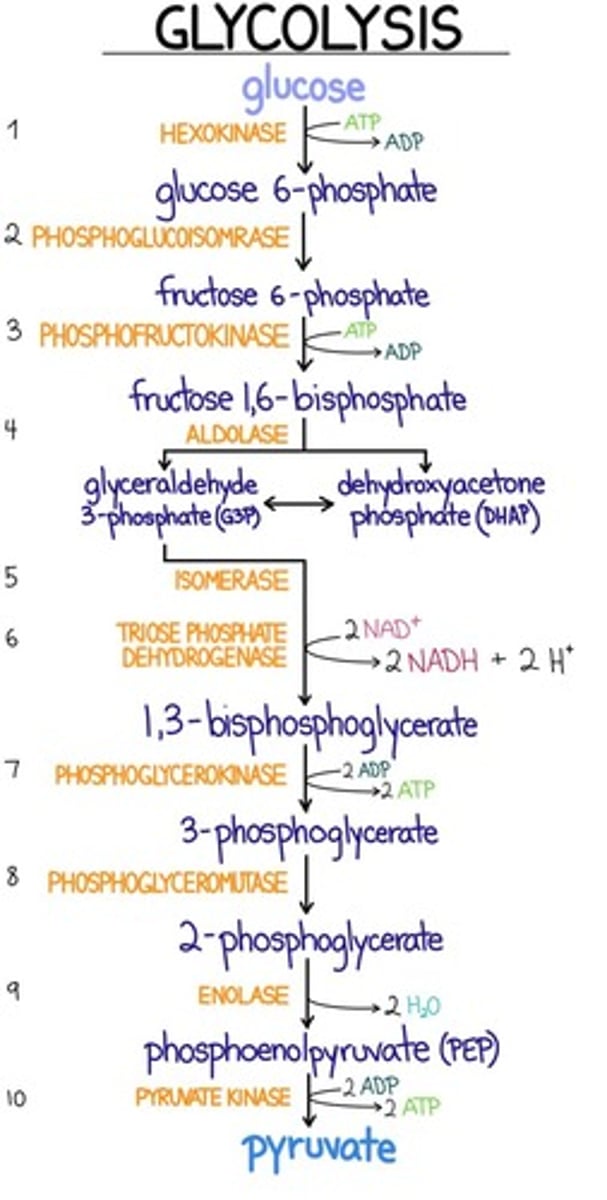
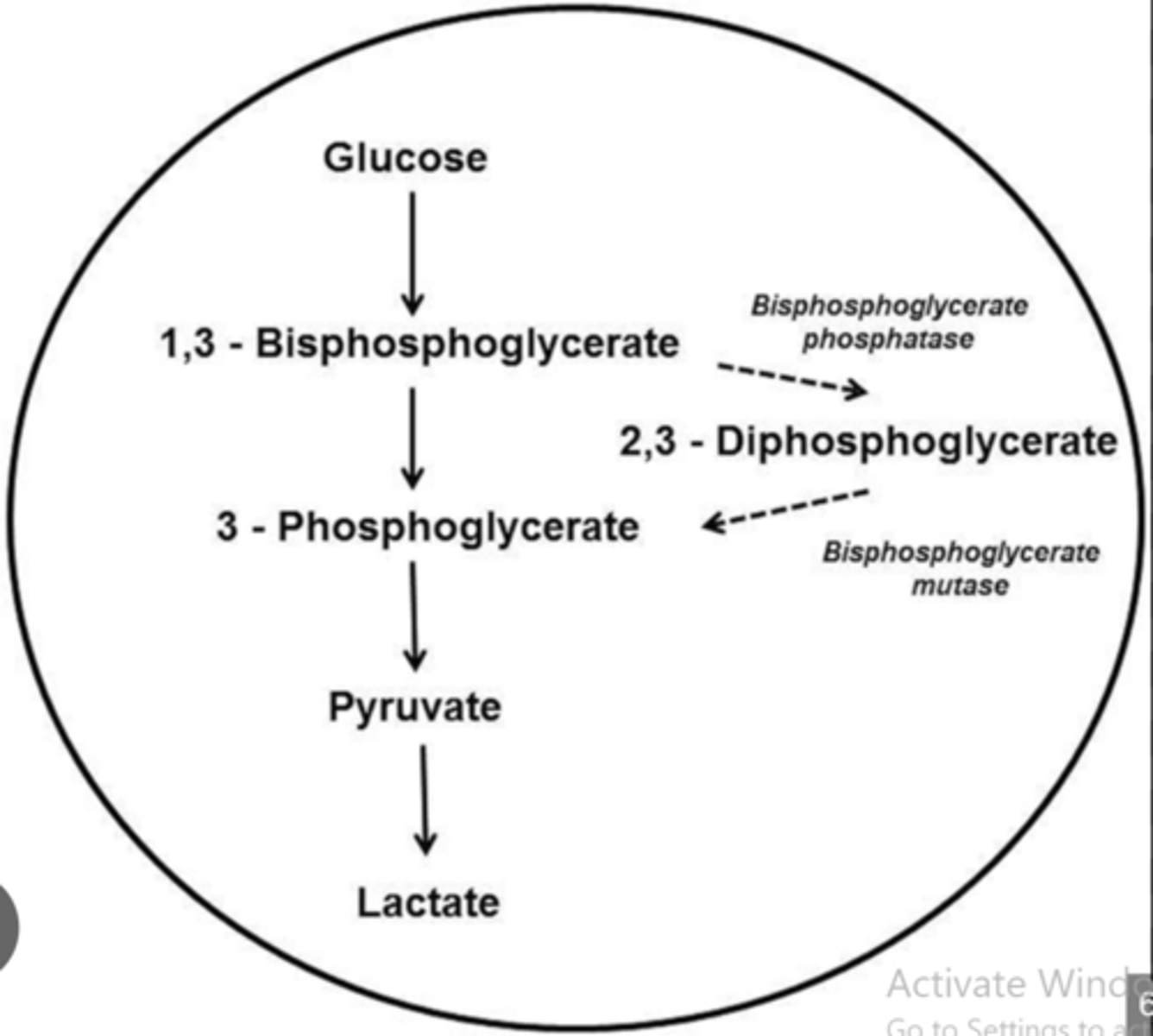
For what reason is the biosynthesis and degradation of 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate energetically unfavorable?
a. 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase requires 2 ATPs to make 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate
b. Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) is bypassed and the cell loses the ability to make 2 ATP
c. Pyruvate dehydrogenase produces 2ATP but no 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate is produced.
d. 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate phosphatase requires 2 ATPs to make 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate
e. Producing 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate requires 2ATPs to move it into the cytoplasm.
b. Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) is bypassed and the cell loses the ability to make 2 ATP
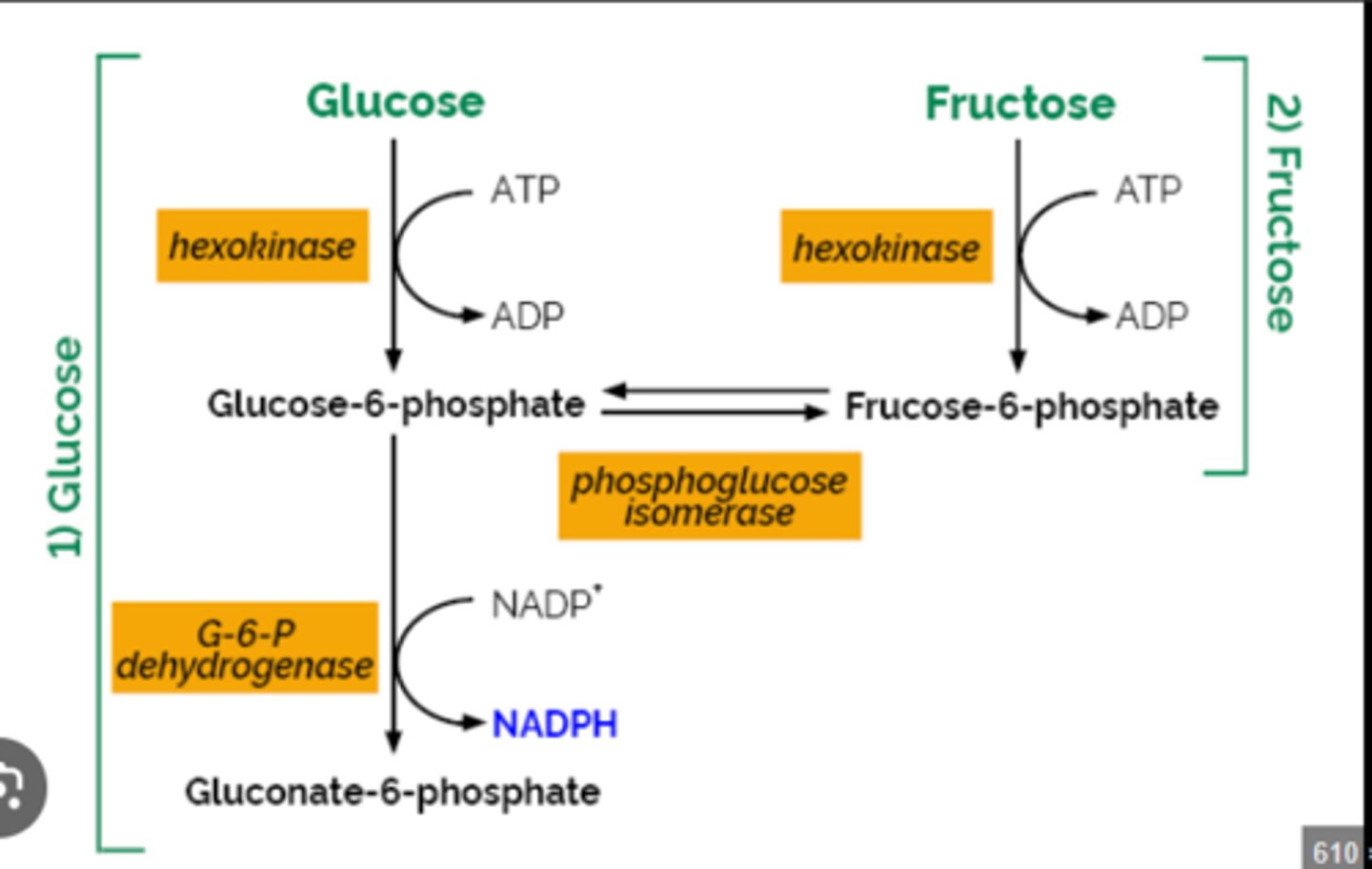
Gluconeogenesis is the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate molecules.
Which of the following is not substrate for gluconeogenesis?
a. Leucine
b. Lactate
c. Glucose
d. Acetyl-CoA
e. Glycerol
a. Leucine
In body tissues other than the liver, fructose is phosphorylated by hexokinase to
a. glucose-1-phosphate
b. triose phosphate
c. fructose-6-phosphate
d. fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
e. fructose-1-phosphate
c. fructose-6-phosphate
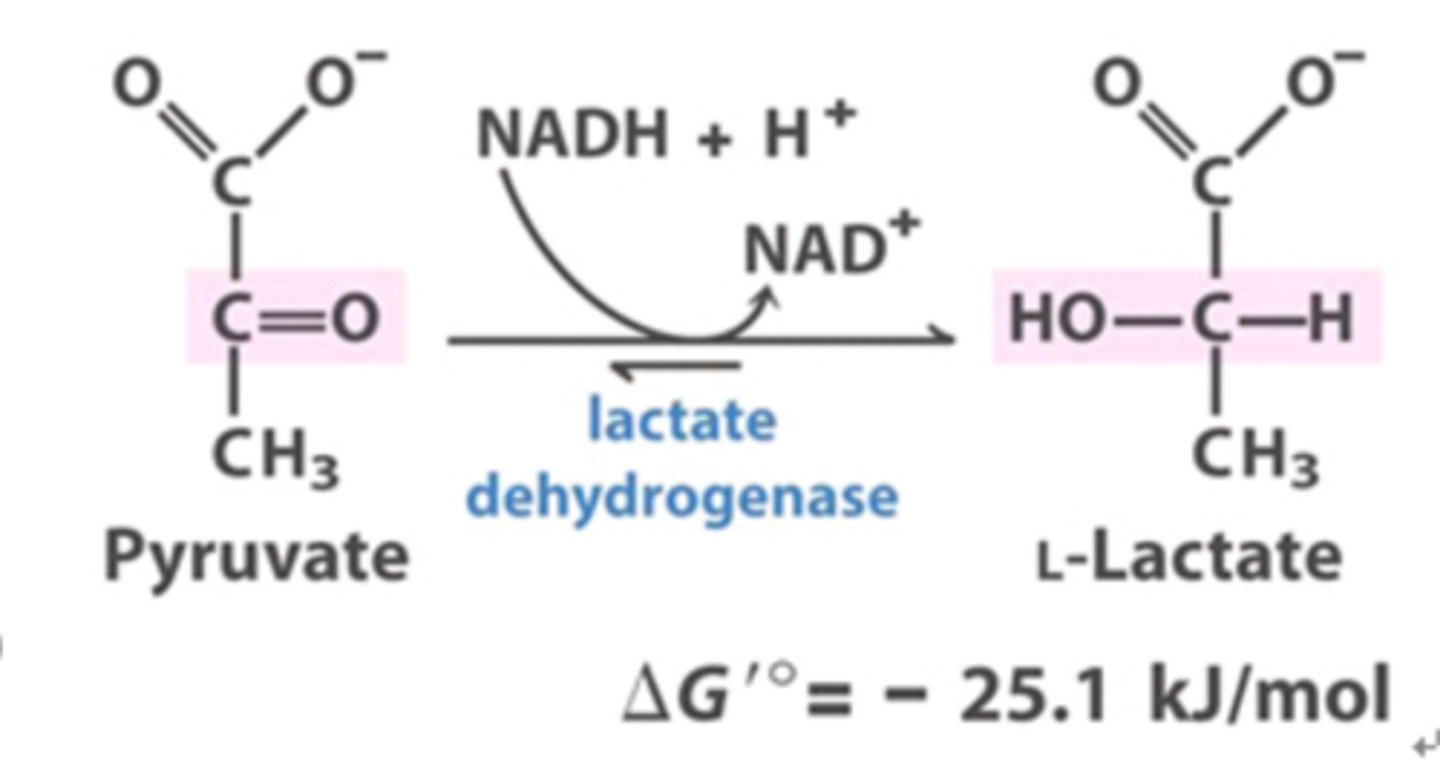
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate?
a. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
b. Pyruvate dehydrogenase
c. Pyruvate carboxylase
d. Lactate reductase
a. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Production of ATP in anaerobic glycolysis is primarily by means of
a. oxidative phosphorylation
b. substrate-level phosphorylation
c. photophosphorylation
d. glucokinase
e. dehydrogenation
b. substrate-level phosphorylation
----------------------------------------
a. oxidative phosphorylation = generates most of the ATP made during cellular respiration
Which of the following glycolytic enzymes is irreversible?
a. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
b. Pyruvate kinase
c. Triose phosphate isomerase
d. Phosphoglucose isomerase
e. Phosphoglycerate mutase
b. Pyruvate kinase
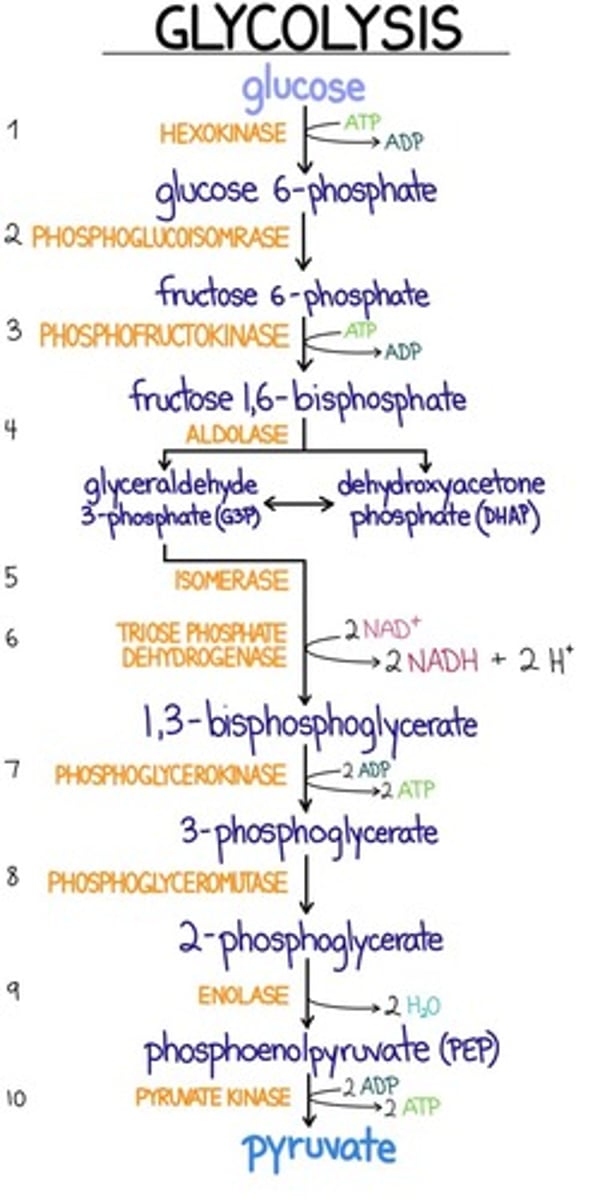
In glycolysis, fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated by phosphofructokinase to make fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. What is the consequence of adding a second electronegative functional group to fructose-6-phosphate in this reaction?
a. NAD+ is reduced to produce NADH.
b. ADP is hydrolyzed to form ATP, the first of the ATP molecules made in glycolysis.
c. The bond between the third and fourth carbon atoms in fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is weakened.
d. Aldolase splits it to produce dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
c. The bond between the third and fourth carbon atoms in fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is weakened.
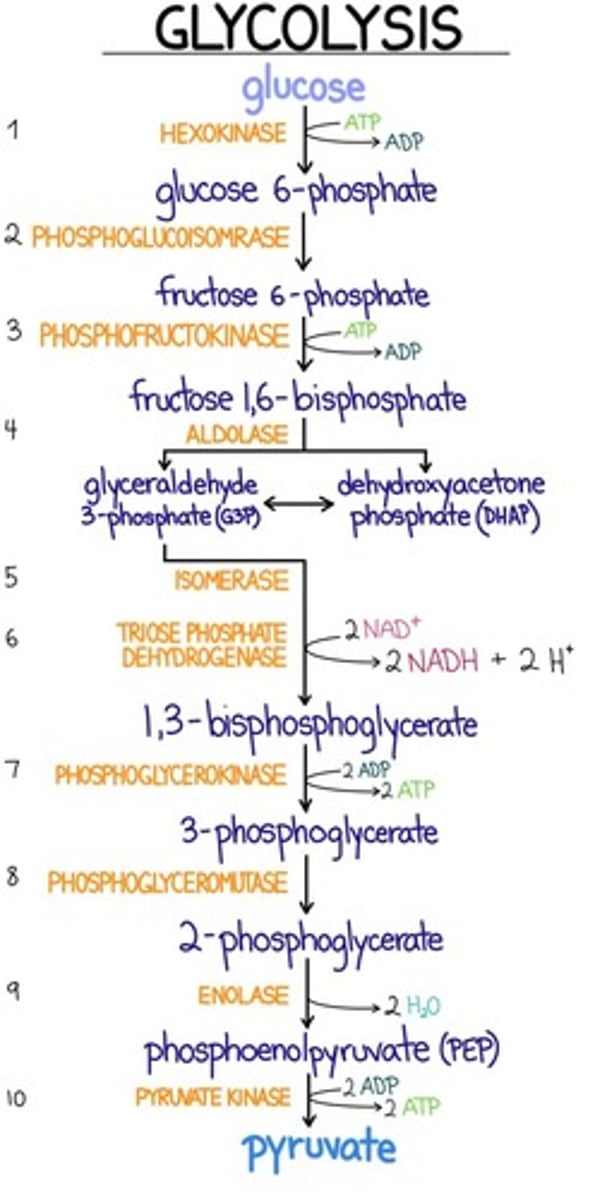
Anaerobic glycolysis oxidizes glucose to pyruvate, which is then reduced to lactate. What is the principal reason for which the cell reduces pyruvate to lactate?
a. To facilitate oxidative phosphorylation
b. To synthesize citrate
c. To reduce NADH
d. To regenerate NAD+
e. To phosphorylate glucose
d. To regenerate NAD+
Production of which negative allosteric inhibitor of oxygen-binding in hemoglobin results in the loss of 2 ATPs produced in anaerobic glycolysis?
a. Fructose-6-phosphate
b. 2-phosphoglycerate
c. Phosphoenolpyruvate
d. 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
e. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
d. 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
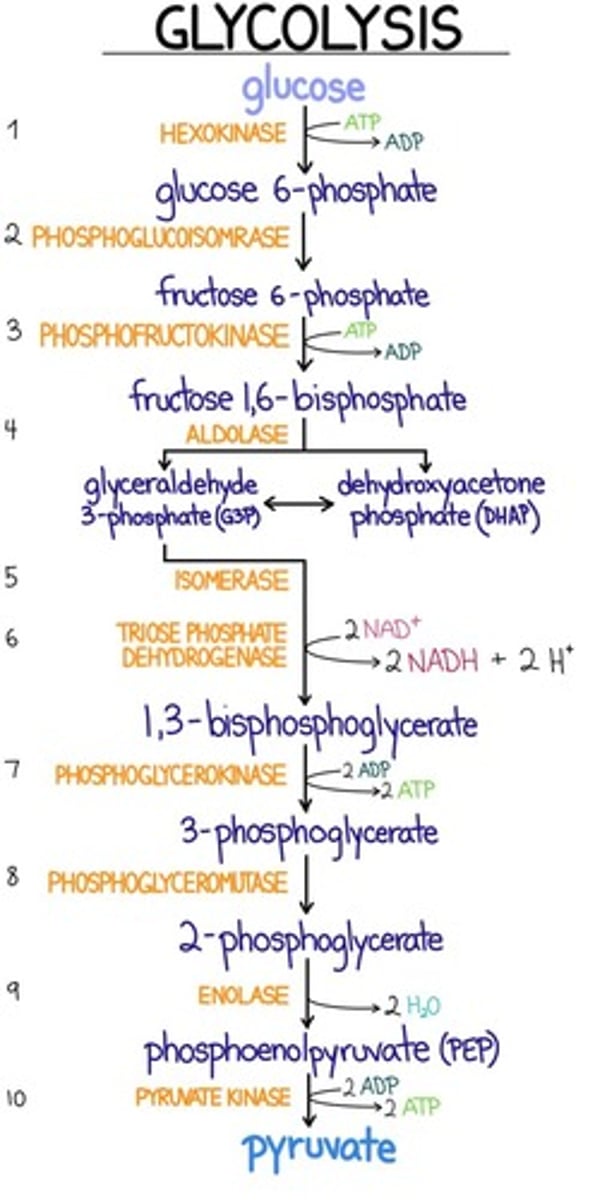
A significant (biological and biochemical) reason for anaerobic glycolysis reactions is
a. Production of biosynthetic intermediates
b. Production of alcohol
c. Production of lactic acid
d. Use of NADPH
e. Regeneration of NAD+
e. Regeneration of NAD+
The following are the negative regulators of phosphofructokinase except:
a. citrate
b. ATP
c. AMP
c. AMP
The regulatory enzyme in anaerobic glycolysis is
a. aldolase
b. pyruvate dehydrogenase
c. phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
d. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
e. glucokinase
c. phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
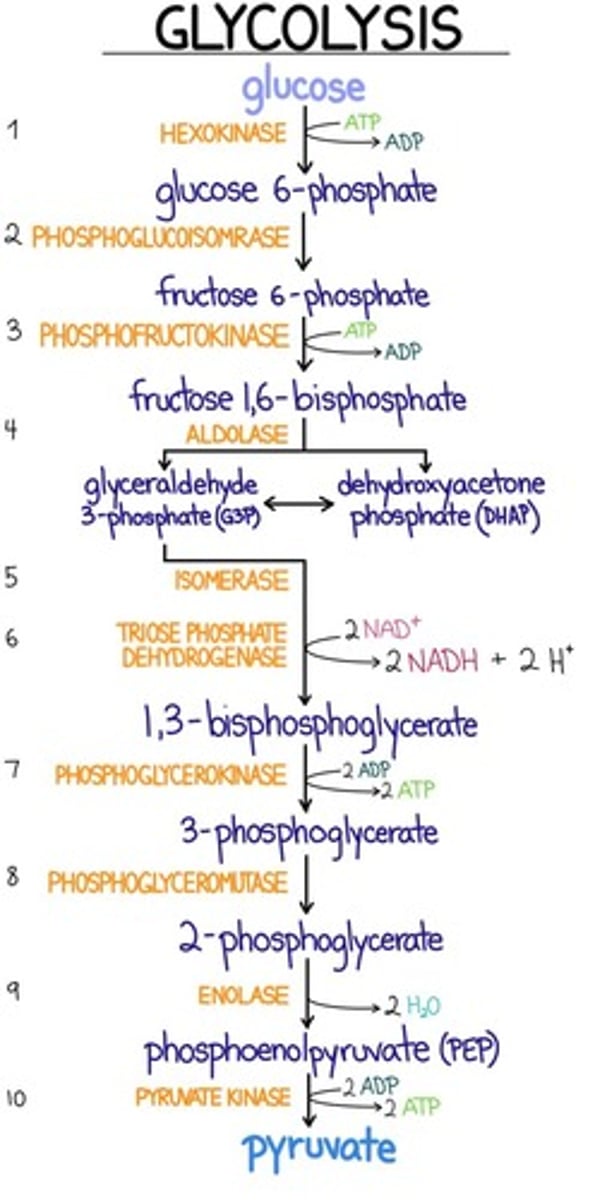
Which of the following factors lead to an increase of glucose in blood?
a. Hypoglycemic hormone (insulin)
b. Glycogen synthesis
c. Lipogenesis
d. Glycogenolysis
e. Use of glucose by tissues for energy
d. Glycogenolysis
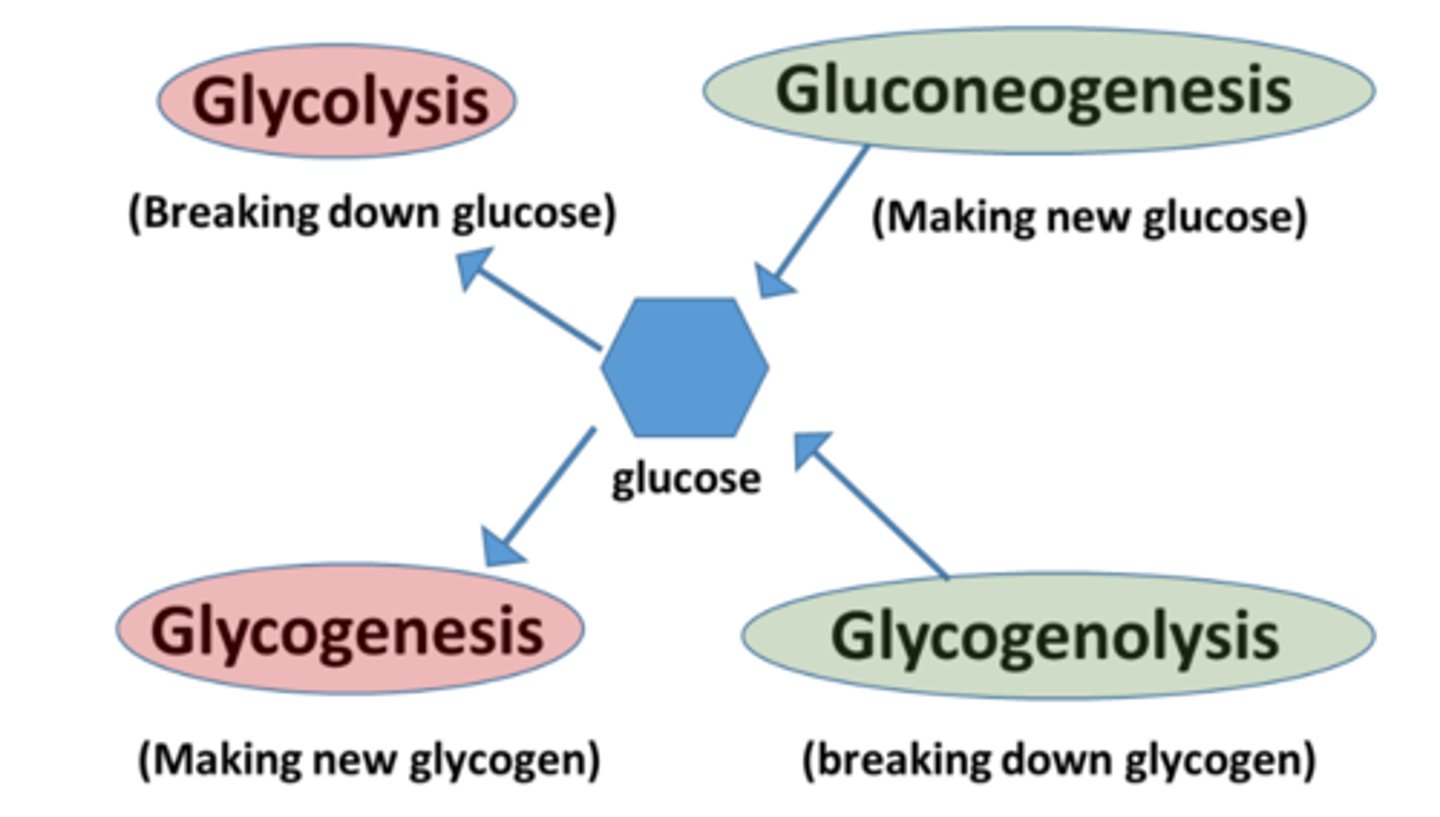
Synthesis of 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate requires which enzyme?
a. Pyruvate dehydrogenase
b. Bisphosphoglycerate mutase
c. 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate phosphatase
d. Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK)
e. Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
b. Bisphosphoglycerate mutase