CompTIA Security+
1/280
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
281 Terms
CompTIA
Computing Technology Industry Association
Security controls vid 2
Securirty controls
Security risks are out there
-many categoris/types
assets are also varied
-data, physical property, computer systems
prevent security events, minimize the impact, and limit damage
-security controls
Control categories
technical controls
-controls implemented using systems
-OS system controls
-firewalls, anti-virus
managerial controls
-administrative controls associated with security design and implementation
-security policies, standard operating procedure
operational controls
-controls implemented by people instead of systems
-security guards, awareness programs
physical controls
-limit physical access
-gaurd shack
-fences locks
-badges
preventive control types
preventive
-block access to a resource
-you shall not pass
prevent access
-firewall rules
-follow security policy
-gaurd shack checks all identification
-enable door locks
deterrent control type
deterrent
-discourage an intrusion attempt
-deos not directly prevent access
make an attack think twice
-application splash screens
-threat of demotion
-front reception desk
-post warning signs
detective control types
detective
- identify and log an intrusion attempt
- may not prevent access
find the issue
-Collect and review system logs
-review login reports
-regularly patrol the property
-enable motion detectors
corrective control types
Corrective
-Apply a control after an event has been detected
-Reverse the impact of an event
-Continue operating with minimal downtime
Correct the problem
-Restoring from backups can mitigate a ransomware infection
-Create policies for reporting security issues
-Contact law enforcement to manage criminal activity
-Use a fire extinguisher
compensating control type
compensating
-control using other means
-existing controls aren't sufficient
-may be temporary
prevent the exploitation of a weakness
-firewall blocks a specific application instead of patching the app
-implement a separation of duties
-require simultaneous guard duties
-generator used after power outage
directive control type
directive
-direct a subject towards security compliance
-a relatively weak security control
do this, please
-store all sensitive files in a protected folder
-create compliance policies and procedures
-train users on proper security policy
-post a sign for "authorized personnel only"
managing security controls
these are not inclusive lists
-there are many categories of control
-some organizations will combine types
There are multiple security controls for each category and type
- Some security controls may exist in multiple types or categories
-new security controls are created as systems and processes evolve
-your organization may use very different controls
CIA triad vid 3
The CIA Triad
Combination of principles
- the fundamentals of security
-aka AIC triad
confidentiality
-prevent disclosure of information to unauthorized individuals or systems
integrity
-messages can't be modified without detection
availability
-systems and networks must be up and running
confidentiality
certain information should only be known to certain people
-prevent unauthorized information disclosure
encryption
-encode messages so only certain people can read it
access controls
-seletively restrict access to a resource
two-factor authentication
-additional confirmation before information is disclosed
integrity
data is stored and transferred as intended
-any modification to the data would be identified
hashing
-map data of an arbirtrary length to data of a fixed length
digital signatures
-mathematical scheme to verify the integrity of data
certificates
-combine with a digital signature to verify an individual
non-repudiation
-provides proof of integrity, can be asserted to be genuine
availability
information is accessible to authorized users
-always at your fingertips
redundancy
-build services that will always be available
fault tolerance
-system will continue to run, even when a failure occurs
patching
-stability
-close security holes
Non-repudiation VID 4
non-repudiation
you can't deny what you've said
-there's no taking it back
sign a contract
-your signature adds non-repudiation
-you really did sign the contract
-others can see your signature
adds a different perspective for cryptography
-proof of integrity
-proof of origin, with high assurance of authenticity
proof of integrity
Verify data does not change
-The data remains accurate and consistent
In cryptography, we use a hash
-Represent data as a short string of text
-A message digest, a fingerprint
If the data changes, the hash changes
-If the person changes, you get a different fingerprint
Doesn't necessarily associate data with an individual
-Only tells you if the data has changed
Hashing
if the hash is different from an original, something has changed
-the data integrity has been compromised
proof of origin
• Prove the message was not changed
- Integrity
• Prove the source of the message
- Authentication
• Make sure the signature isn't fake
- Non-repudiation
• Sign with the private key
- The message doesn't need to be encrypted
- Nobody else can sign this (obviously)
• Verify with the public key
- Any change in the message will invalidate the signature
creating a digital signature
- hashing algorithm creates hash
- encrypt the hash with private key
- send encrypted hash along side the plain text
- attach the digital signature to the message
verifying a digital signature
-send message with digital signature
-use public key to examine and decrypt signature
-now we have original hash of text message
-now we see if the hash that just got decrypted is the same as the one that comes from running a hash function on the message
Vid 5 - Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
AAA Framework
Identification
-this is who you claim to be
-usually your username
authentication
-prove that you are who you say you are
-password and other auithentication factors
authorization
-based on your identication and authentication, what access do you have?
accounting
-resoruces used: login time, data sent and received, logout time
Authenticating people
-client on internet loging into VPN concentrator
- concentrator gives request to AAA server, asking if the username and password provided matches info in the data base
-concetrator knows that we are who we claim to be, and allows acces to file server
authenticating systems
You have to manage many devices
-often devices that you'll never see
A system can't type a password
-and you may not want to store one
How can you truly authenticate a device?
-Put a digitally signed ceriticate on the device
Other businesses process rely on the certificate
-access to the VPN from authorized devices
-Management software can validate the end device
certificate authentication
an organization has a trusted Certificate Authority (CA)
-most organizations maintain their own CAs
The organization creates a certificate for a devices
-and digitally signs the certificate with the organizations CA
The certificate can now be included on a device as an authentication factor
-The CA's digital signature is used to validate the certificate
authorization models
the user or device has now authenticated
-to what do they now have access
time to apply an authorization model
Users and services -> data and applications
-associating individual users to access rights does not scale
put an authorization model in the middle
-define by roles, organizations, attributes, etc
no authorization model
a simple relationship
-user -> resource
some issues with this method
-difficult to understand why an authorization may exist
-does not scale
using an authorization model
Add an abstracton
-reduce complexity
-create a clear relationship between the user and the resource
administration is streamlined
-easy to understand the autbhorizations
-support any number of users or resources
Vid 6 - Gap analyisis
Gap analysis
Where you are compared with where you want to be
-the "gap" between the two
This may require extensive research
-there's lots to consider
This can take weeks or months
-an extensive study with numerous participants
-get ready for emails, data gathering, and technical research
choosing the framework
Work towards a known baseline
-this may be an internal set of goals
-some orgainizations should use formal standards
determine the end goal
-NIST special publication 800-171 revision 2, Protecting controlled unclassified information in nonfederal systems and organizations
-ISO/IEC 27001, information security management systems
Evaluate people and processes
Get a baseline of employees
-formal exp[erience
-current training
-knowledge of security policies and procedures
examine the current processes
-research exisiting IT systems
-evaluate existing security policies
Compare and contrast
the comparison
-evaluate existing systems
identify weaknesses
-alng witht the most effective proccesses
a detailed analysis
-examine broad security categories
-break those into smaller segments
the analysis and report
the final comparison
-detailed baseline objectives
-a clear view of the current state
need a path to get from the current security to the goal
-this will almost certainly include money, and lots of change control
time to create the gap analysis report
- a formal description of the current state
-reccomendations for meeting the baseline
Vid 7 Zero Trust
Zero Trust
Many networks are relatively open on the inside
-once you're in the firewall, there are few security controls
zero trust is a holistic approach to network secutiy
-covers every device, every process, every person
everything must be verified
-nothing is inherently trusted
-multi-factor authentication, encryption, system permissions, additional firewalls, monitoring and analyisis, etc.
Planes of operation
split the network into functional planes
-applies to physical, virtual, and cloud components
data plane
-process the frames, packets, and network data
-processing, forwarding, trunking, encrypting, NAT
control plane
-manages all the actions in the data plane
-define policies and rules
-determines how packets should be forwarded
-routing tables, session tables, NAT tables
Controlling trust
Adaptive identity
-consider the source and requested resources
-multiple risk indicators - relationship to the organization, physical location, type of connection, IP address, etc
-make the authrentication stronger, if needed
threat scope reduction
-decrease the number of possible entry points
policy-driven access control
-combine the adaptive identity with a pre-defined set of rules
security zones
security is more than a one=to-one relationship
-broad categorizations provide a securiyt-related foundation
where are you coming from and where are you going?
-trusted, untrusted
-internal/external network
-VPN 1, VPN 5, VPN 11
-marketing, IT, accounting, HR
Using the zones may be enough by itself to deny access
-for example, untrusted to trusted zone traffic
some zones are implicitly tursted
-for example, trusted to internal zone traffic
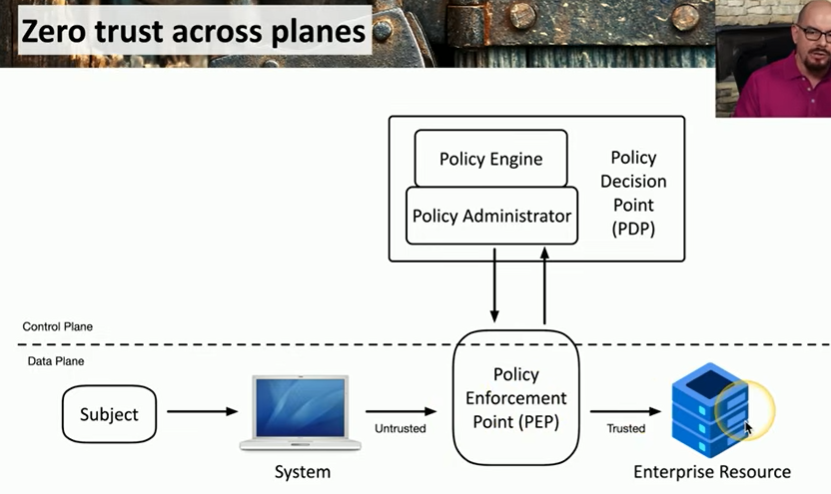
Policy enforcement point

Applying trust in planes

zero trust across planes
Vid 8 - physical security
Barricades/bollards

Access control vestibule

Fencing

Video Survailance
CCTV (closed circuit television)
-can replace physical gaurds
camera features are important
-motion recognition can alarm and alert when something moves
-object detection can identify a license plate or person’s face
often many different cameras
-networked together and recorded over time
guards and access badges

Lighting

Sensors

Vid 9 - Deception and disrutpion
Honeypots

HoneyNet

Honeyfiles

Honeytoken

Vid 10 - Change management
Change management

Change approval process

Ownership

Stakeholders

Impact analysis

Test results

backout plan

Maintenance window

Standard operating procedure

Vid 11 - Technical change management
Technical change management

Allow/deny list

Restricted activities

downtime

restarts

Legacy applications

dependencies

Documentation

Version Control

Vid 12 - public key infrastructure
Public Key infrastructure (PKI)

Symmetric encryption
-encrypting/decrypting with the same key

Asymmetric encryption
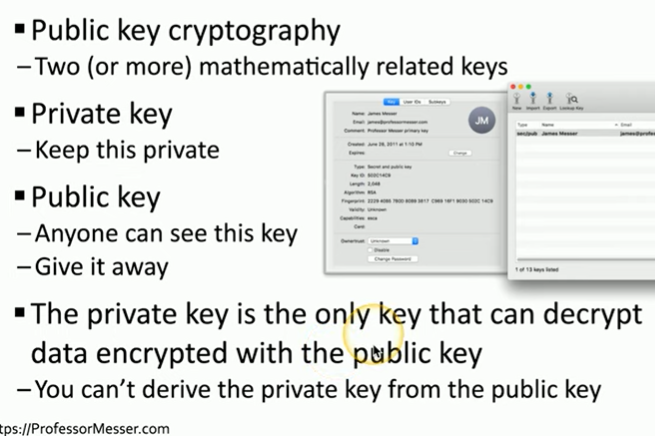
The key pair

Key escrow

Vid 13 - Encrypting data
Encrypting stored data

Database encryption

Transport encryption
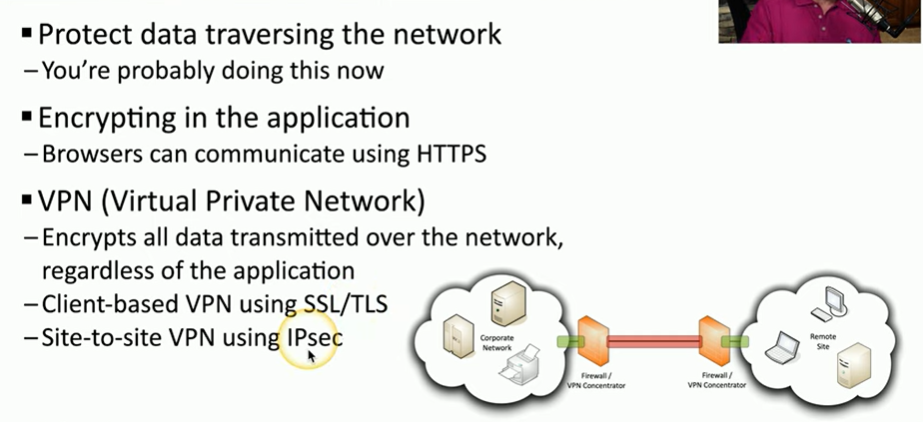
Encryption algorithms

Cryptographic keys

Key lengths

key stretching

Vid 14- key exchange
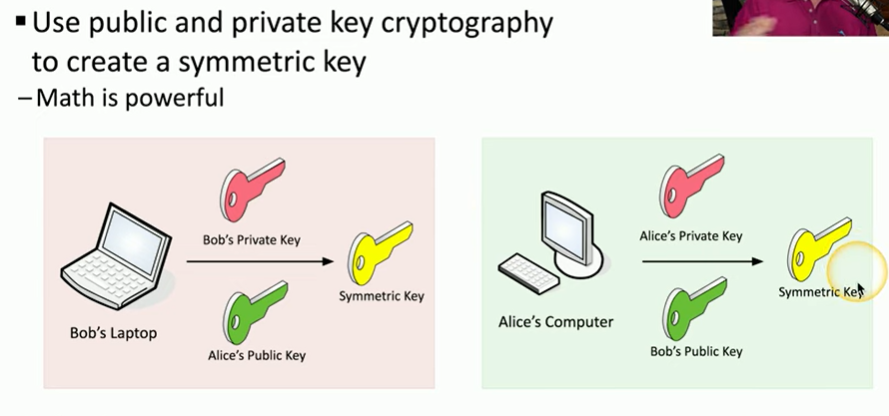
Key exchange

Real-time encryption/decryption

symmetric key from asymmetric keys
Encryption Technologies - vid 15
Trusted platform Module (TPM)

Hardware Security Module (HSM)
