PSY 355 Brain Dissection Terms
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
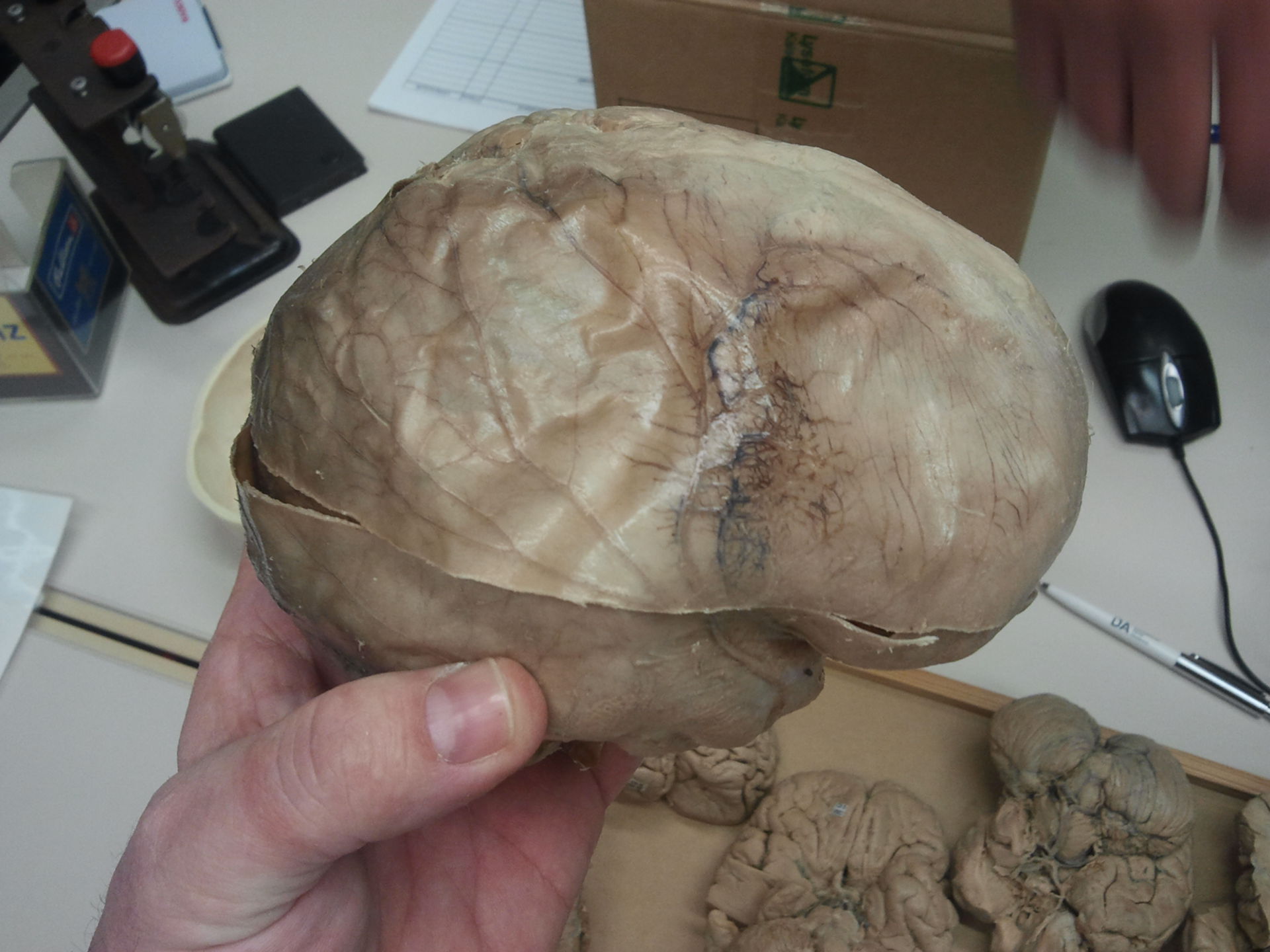
Dura Mater
Tough, outer layer of the meninges
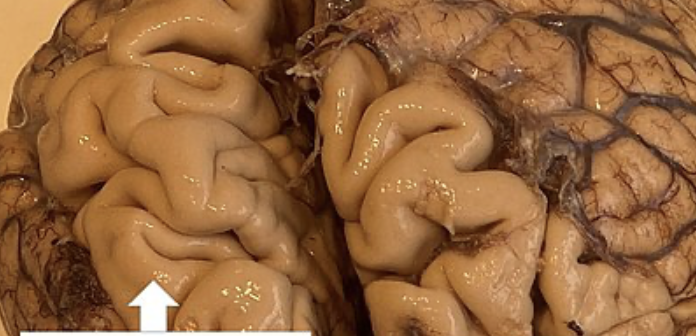
Arachnoid
Web-like layer of the meninges filled with fluid that cushions the brain
Pia Mater
Delicate, inner layer of the meninges
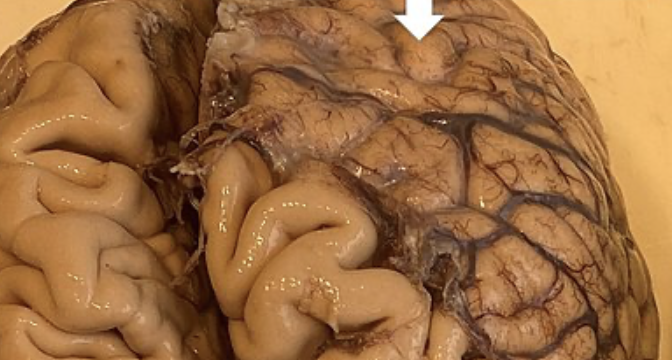
Longitudinal Fissure
Deep grove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres
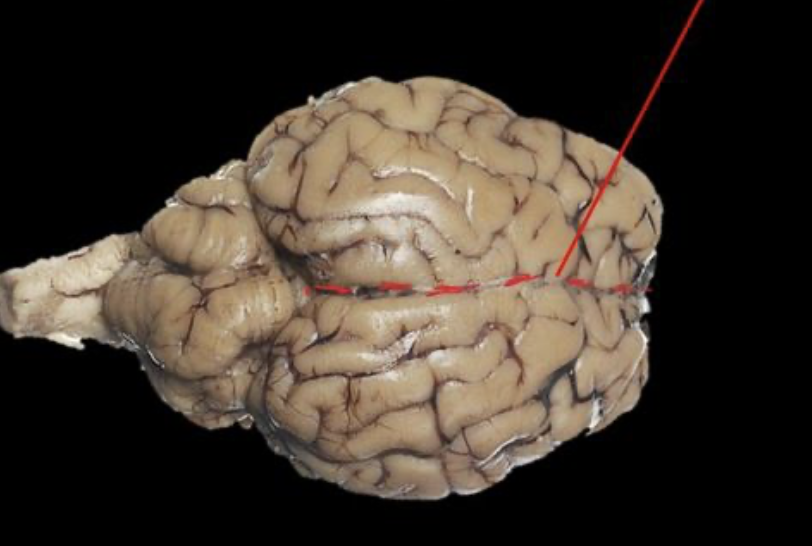
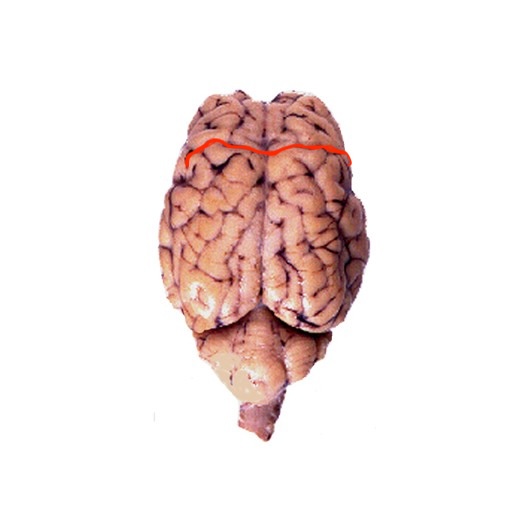
Central Sulcus
Separates the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe, and the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex
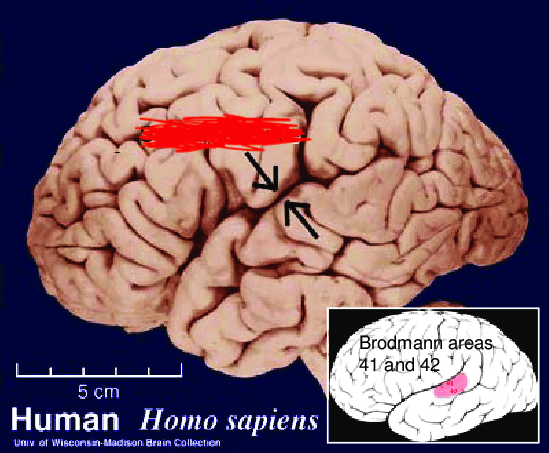
Sylvian Fissure
Separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
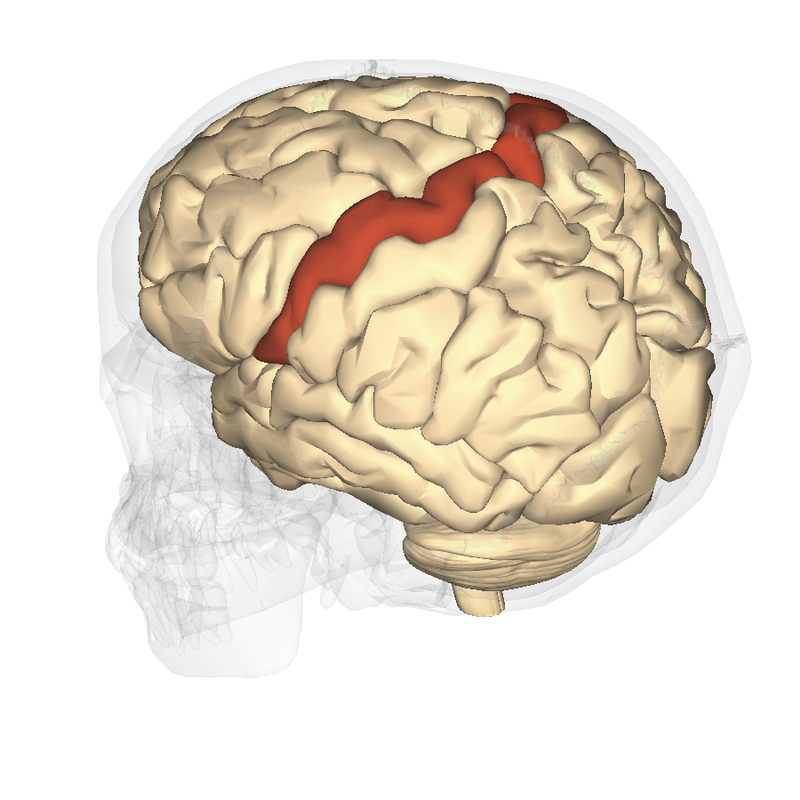
Pre-central Gyrus
Location of the primary motor cortex
Post-central Gyrus
Location of the primary somatosensory cortex
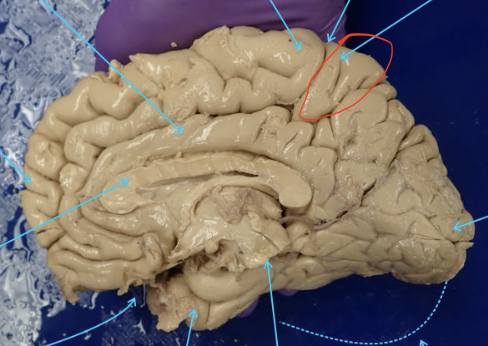
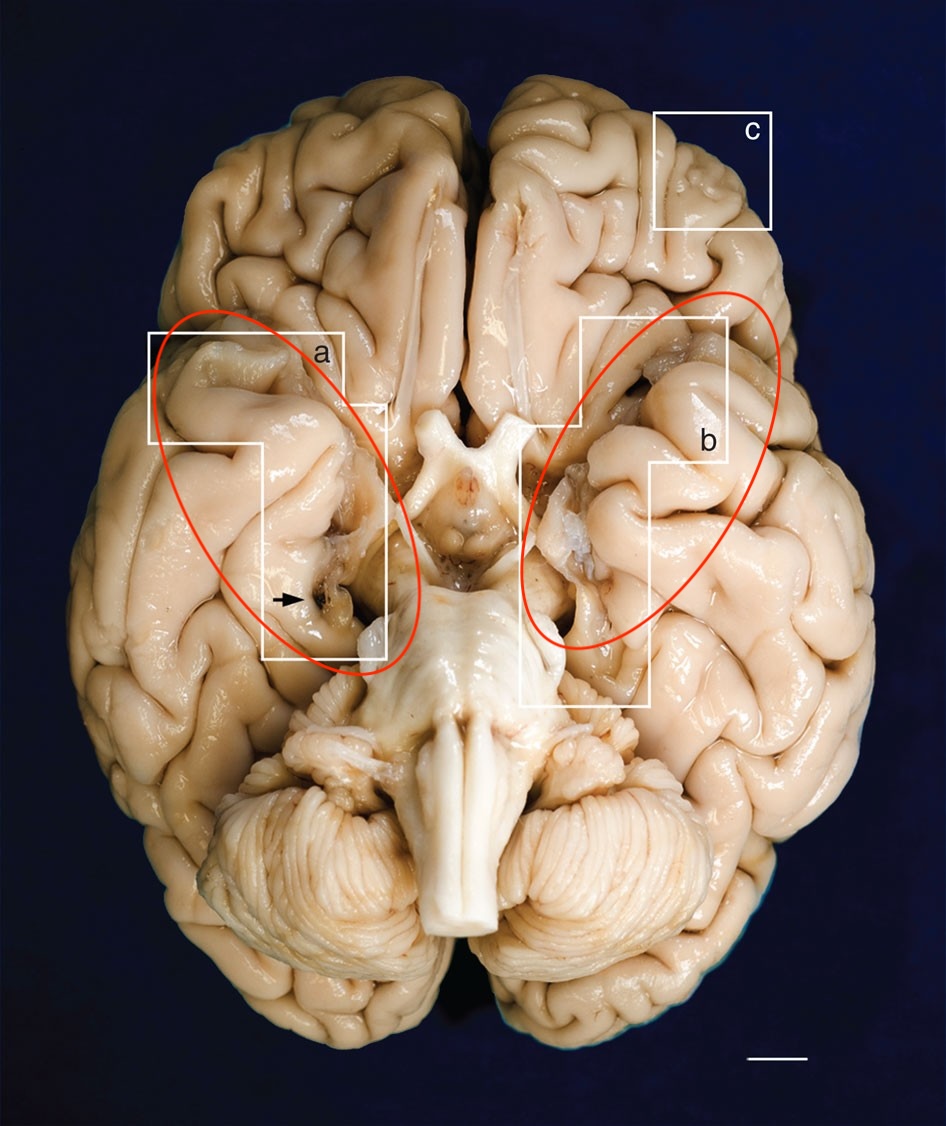
Olfactory Bulbs
Located at the forebrain, receives neural input about odors detected in cells by the nasal cavity
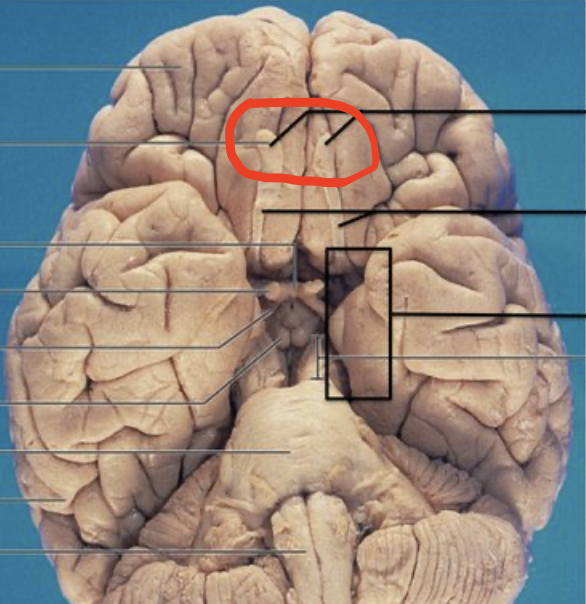
Optic Nerve
Transmits electrical impulses from the eyes to the brain
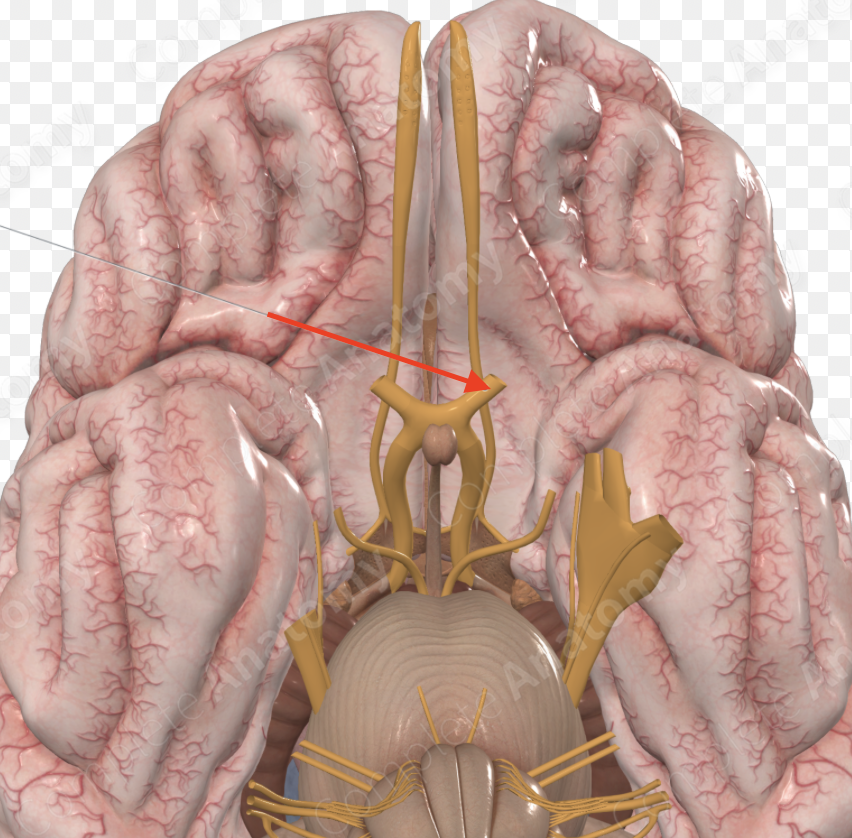
Optic Chiasm
Part of the brain where the optic nerves cross; importance for the visual pathway
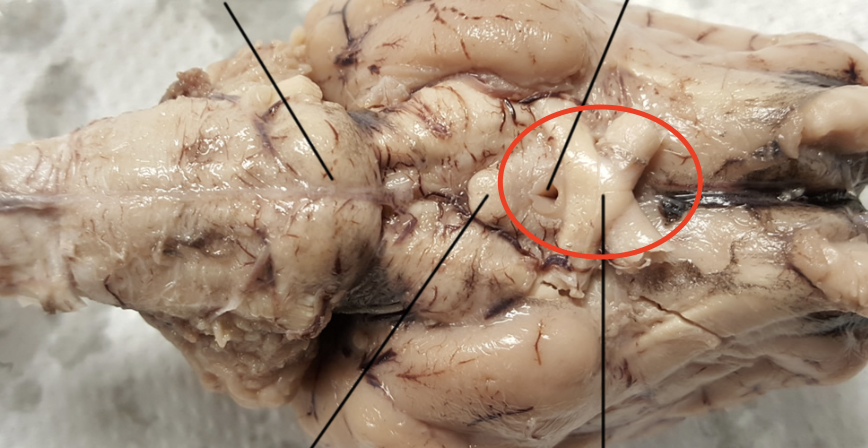
Optic Tract
Bundle of nerve fibers that carries visual in formation from the optic chiasm to the left and right geniculate bodies as a part of the visual pathway
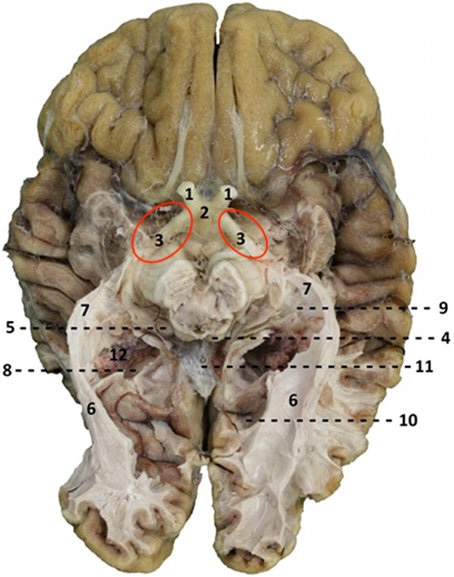
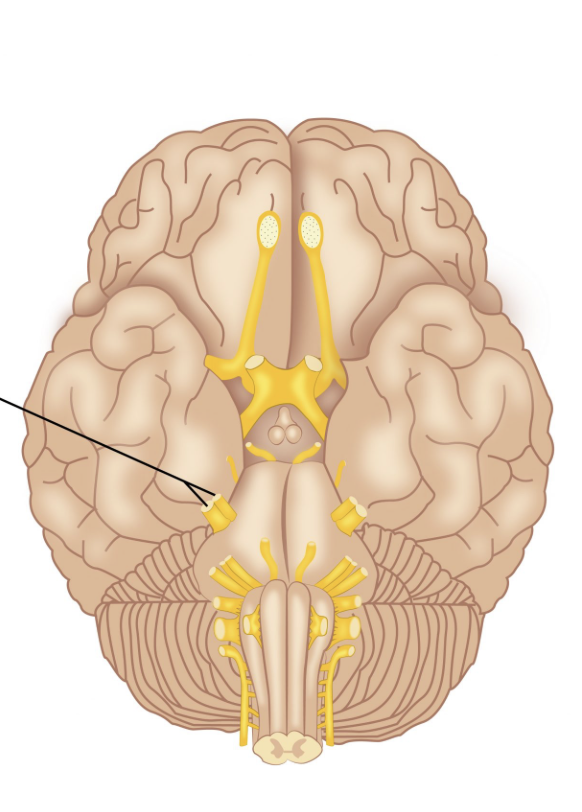
Oculomotor Nerve
The main functions: innervation to the pupil and lens, innervation to the upper eye lid, and innervation of the eye muscles that allow for visual tracking and gaze fixation
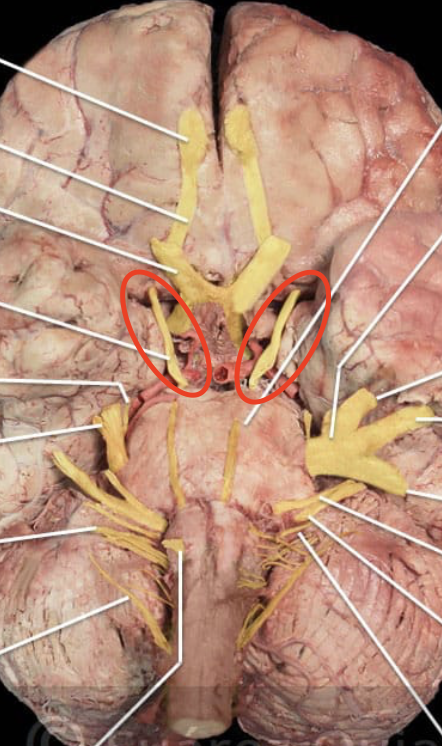
Trigeminal Nerve
Provides sensory information to the face
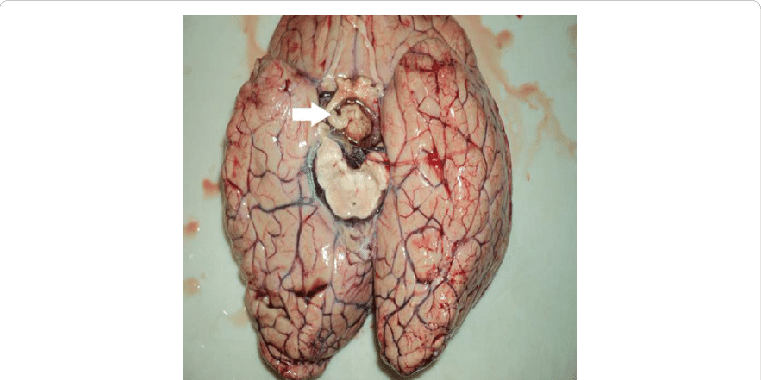
Pituitary Gland
Monitors and regulates bodily functions with the hormones it produces
Cerebellum
Vital component of motor regulation and balance control
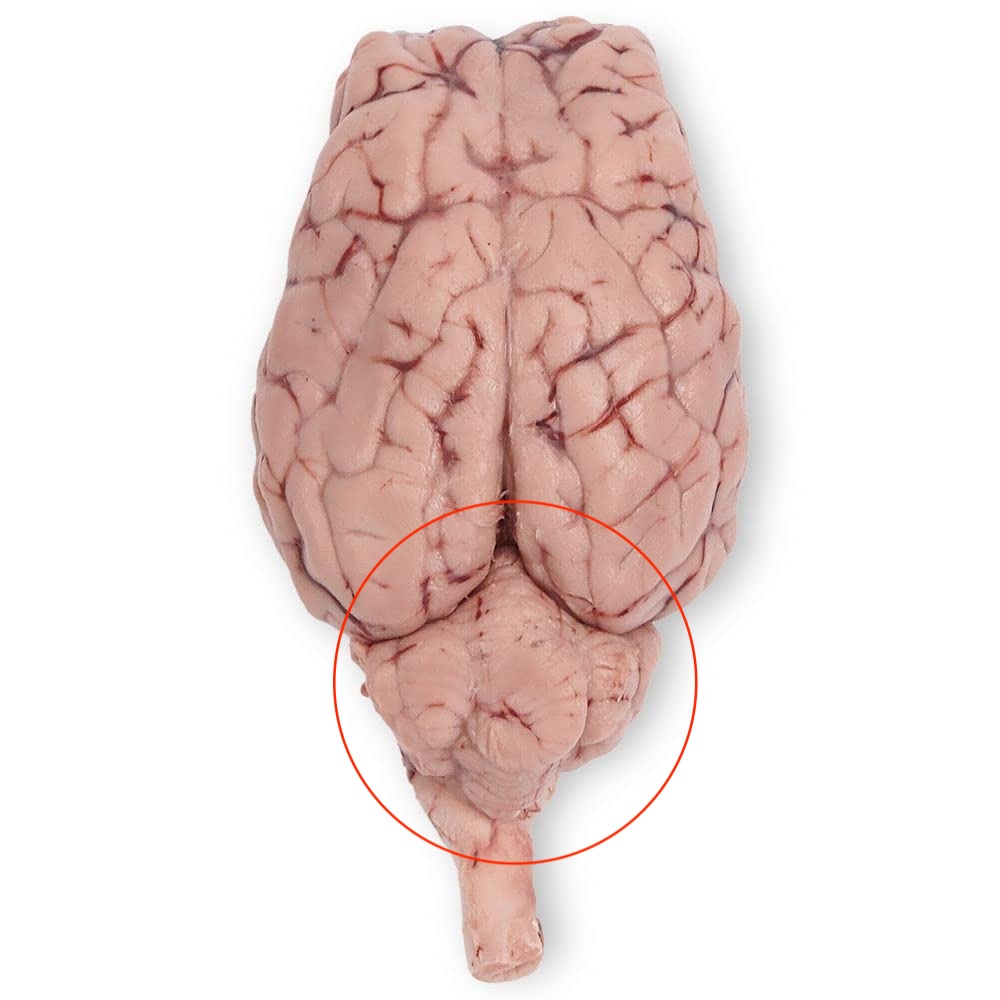
Medulla Oblongata
Carries signals from the brain to the rest of the body for essential life functions like breathing, circulation, and digestion
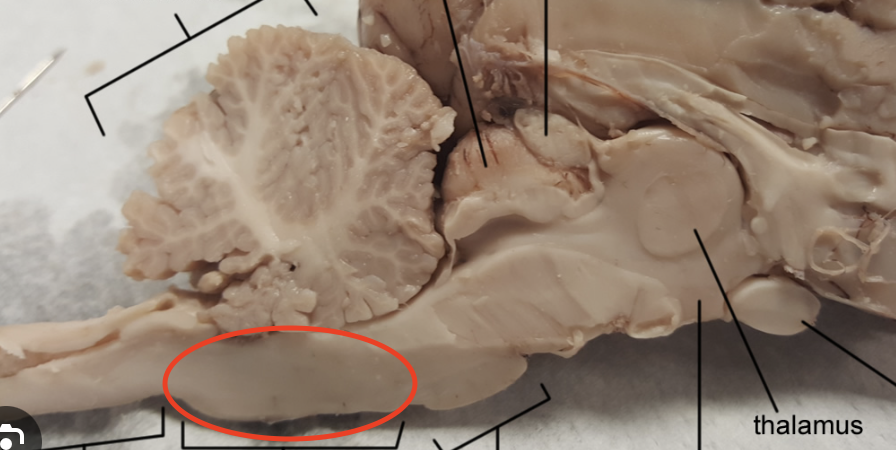
The Pons
Transmits signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum, giving sensory cues and motor information
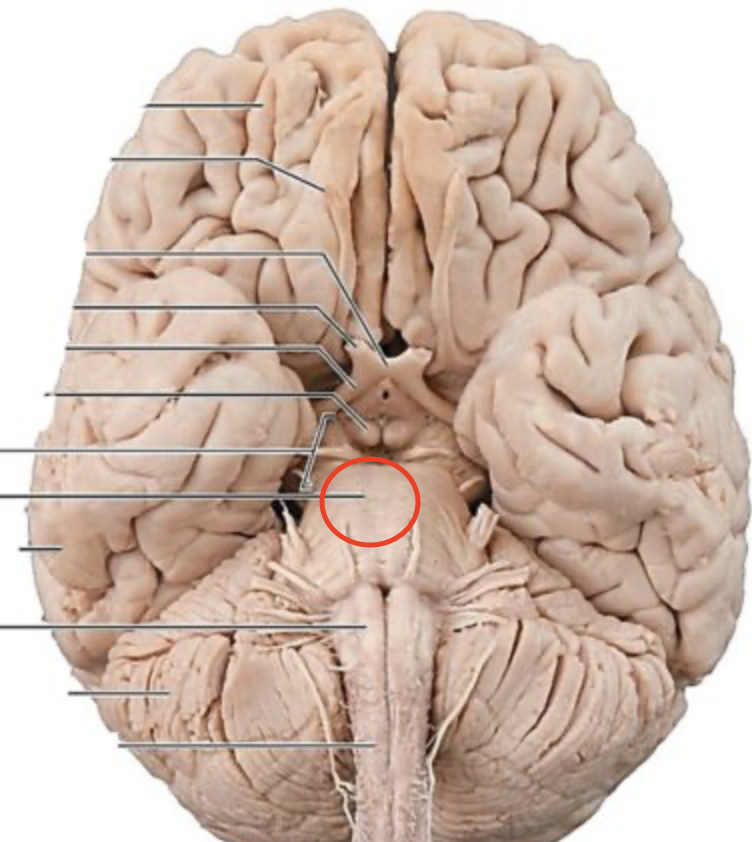
Corpus Callosum
Region that allows information from one hemisphere to travel to another hemisphere
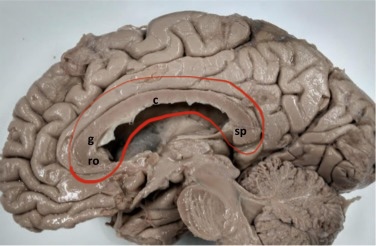
Cingulate Gyrus
Helps regulate emotions and pain
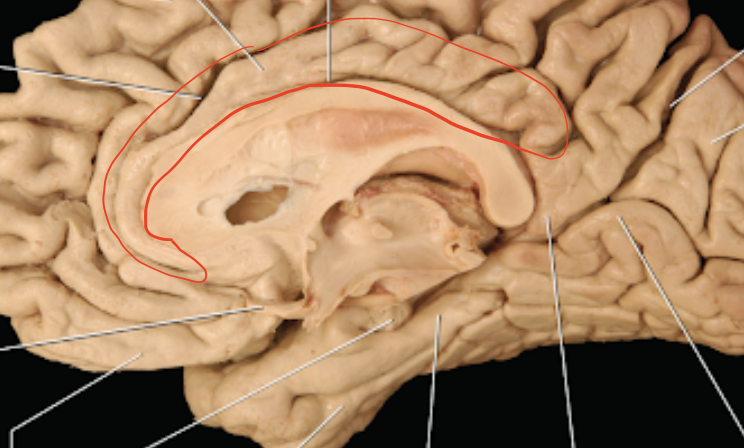
Septum Pellucidum
Positioned between the two hemispheres and separates the lateral ventricles
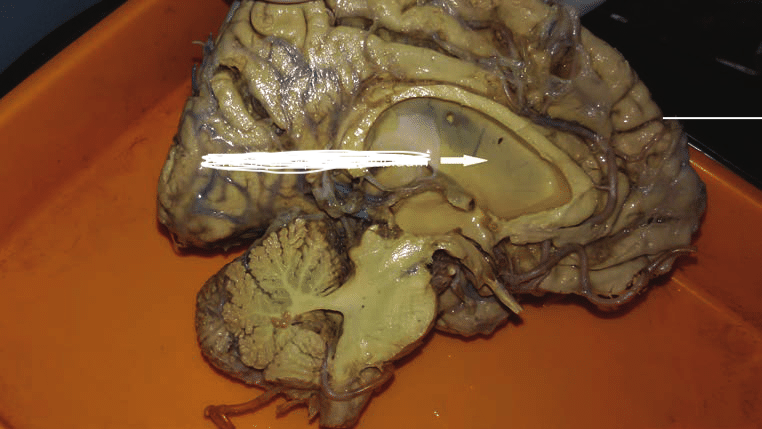
Pineal Gland
Endocrine gland important for the sleep-wake cycle
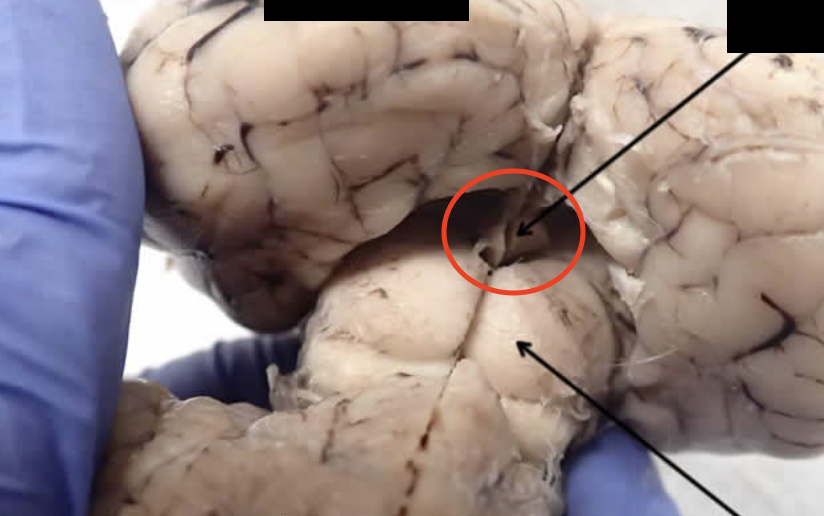
Cerebral Peduncles
Communicates information to and from the cerebellum (there’s like no good pictures of this one)
Superior Colliculi
Involved in detecting, localizing, ad orienting toward external stimuli
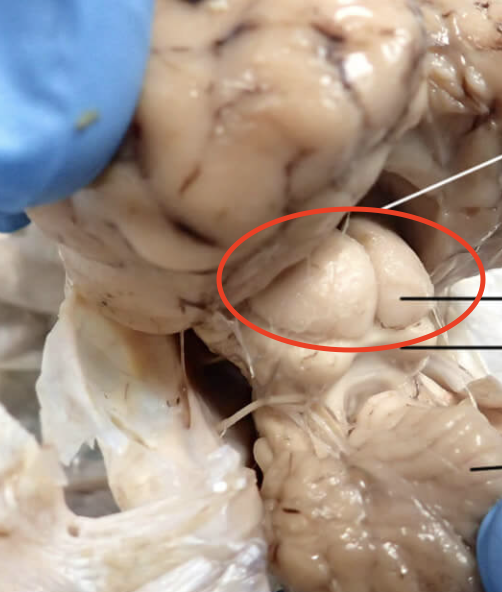
Inferior Colliculi
Acts as a channel for almost all auditory signals in the human body; involved in signal integration, frequency recognition, and pitch discrimination
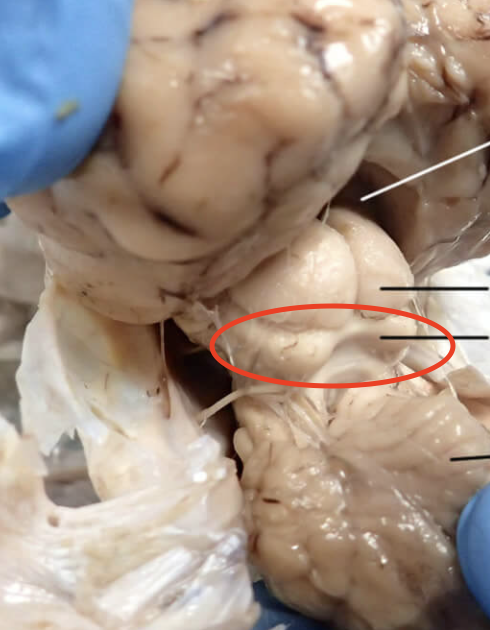
Mammillary Bodies
Involved in recollective memory
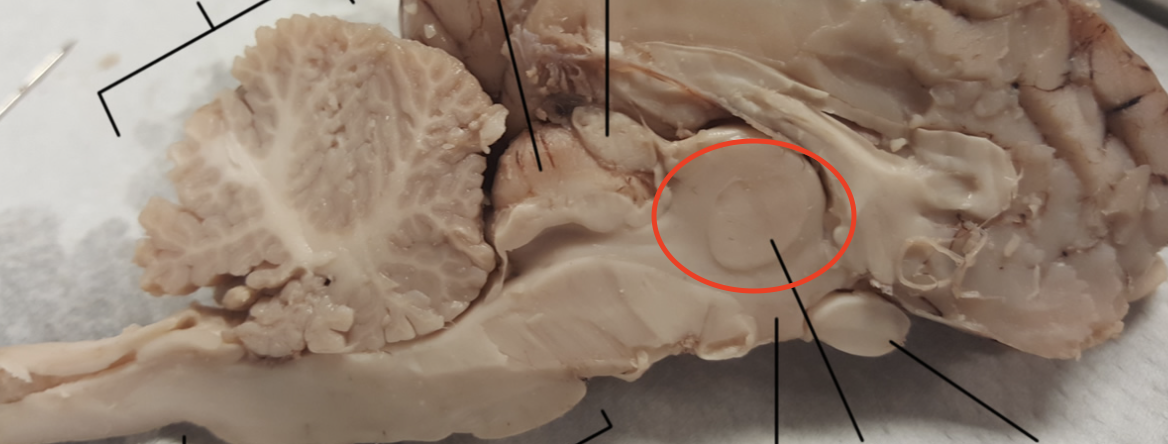
Thalamus
Relays motor and sensory information from the body to the brain
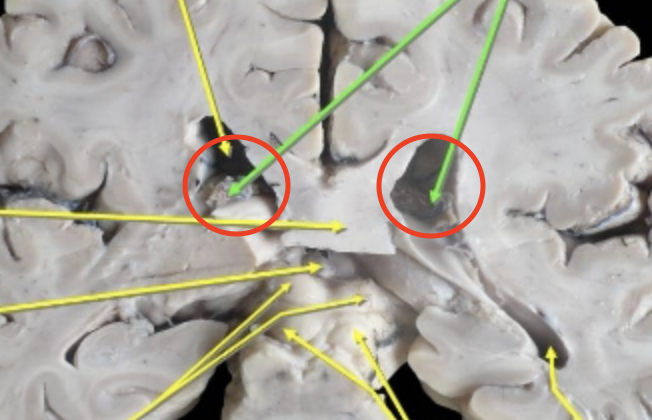
The Basal Ganglia
Subcortical nuclei that are responsible for motor control, motor learning, executive functions and behaviors, and emotions (there’s no good pictures for this one either)
Cerebral Ventricles
Filled with cerebrospinal fluid (google is failing me rn there’s no pictures of this one either)
Choroid Plexus
Responsible for producing cerebrospinal fluid
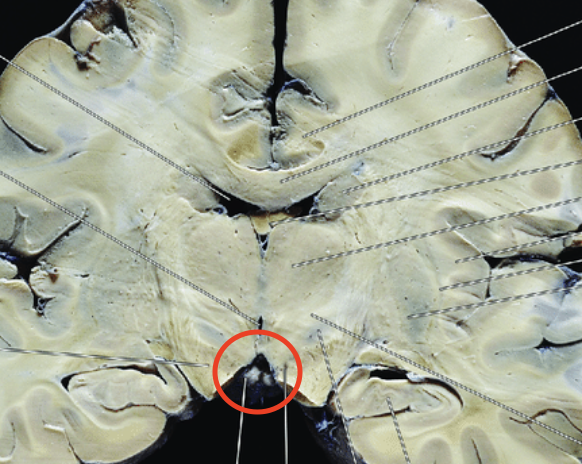
Cerebral Aqueduct
Allows cerebrospinal fluid to flow between the third an fourth ventricle
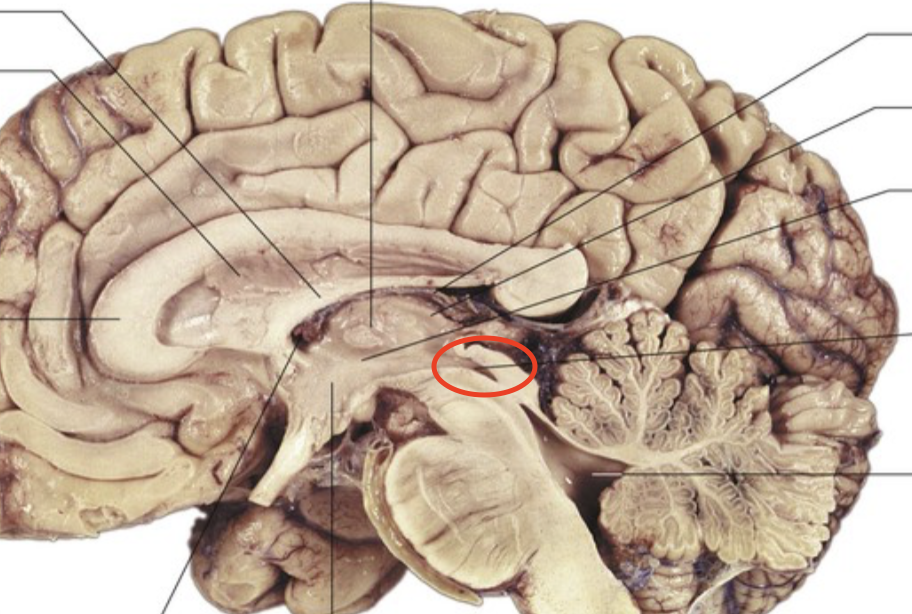
Hypothalamus
Maintains homeostasis
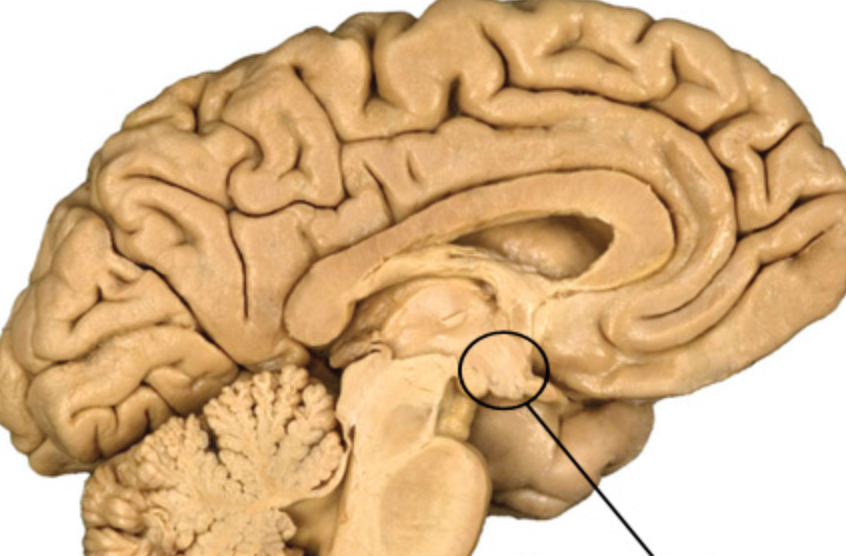
Hippocampus
Plays a role in memory, learning, and emotion
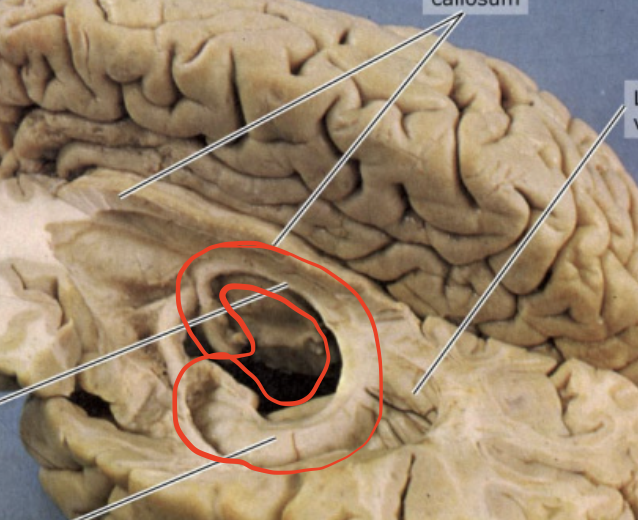
Hippocampal Gyrus
Plays important role in memory encoding and retrieval