Edexcel IGCSE Physics : 8 Astrophysics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the universe?
a large collection of billions of galaxies
What is the galaxy?
a large collection of billions of stars
Where is our solar system located?
our solar system is located in the Milky Way Galaxy
Why does gravitational field strength different on each planet and moon ?
gravitational field strength varies based on mass of an object
Since each planet and moon have different masses the gravitational field strength varies
What are the effects of gravitational forces?
causes moons to orbit planets
causes the planets to orbit the sun
causes artificial satellites to orbit the Earth
causes comets to orbit the sun
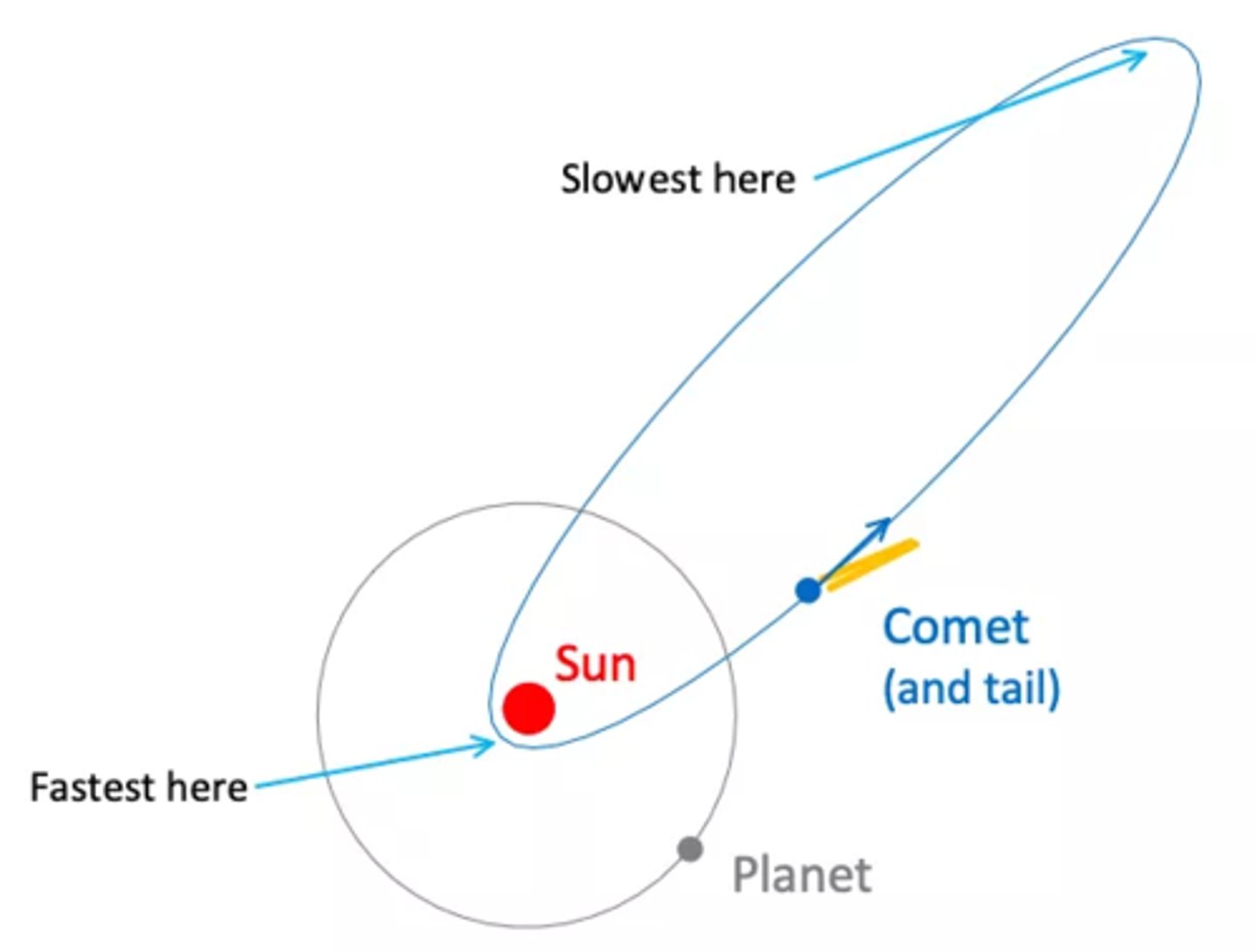
Describe the orbit of a comet
elliptical orbit of the sun , with the sun at one of its foci
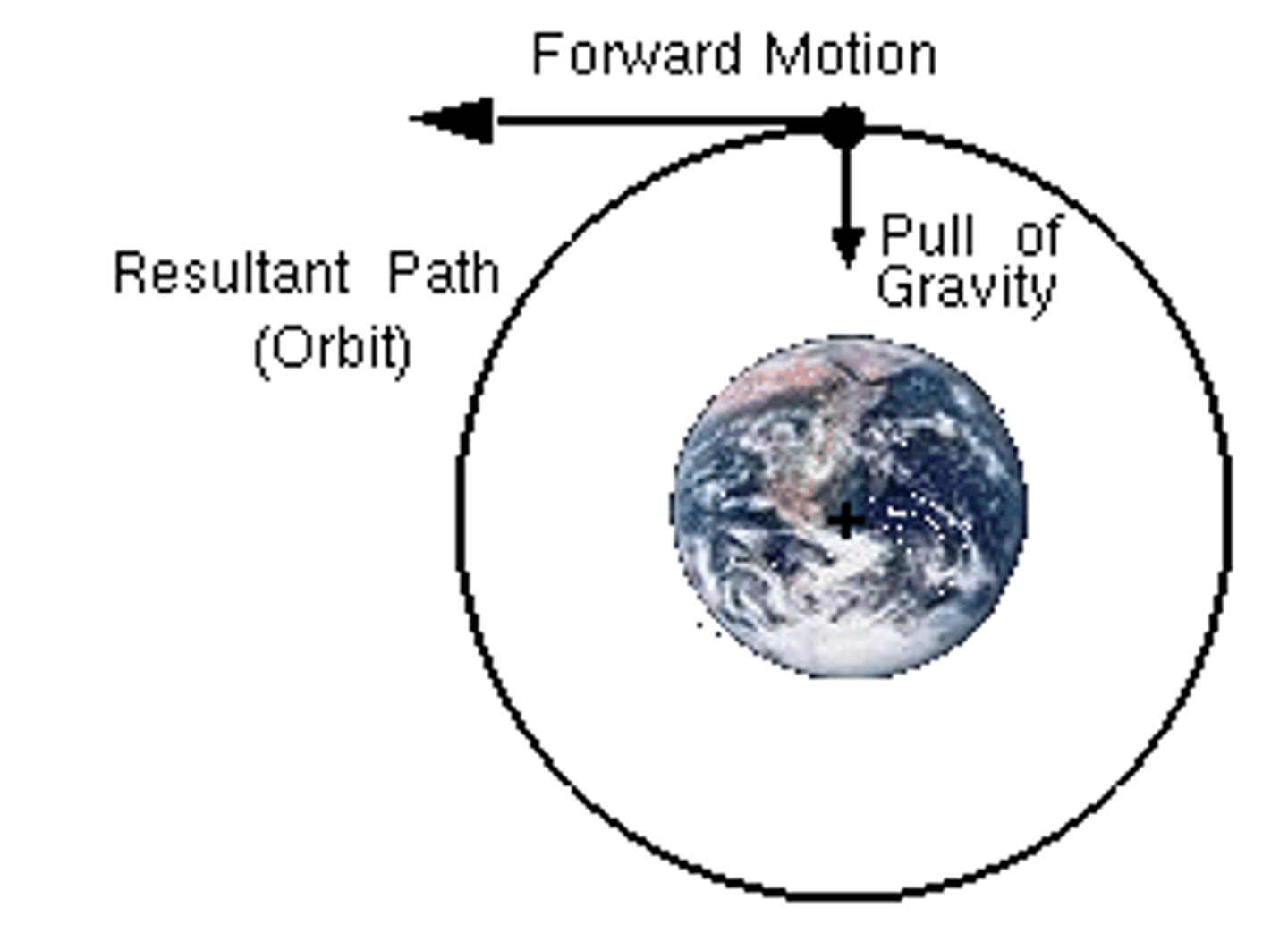
Describe the orbit of a moon
circular orbit around planets
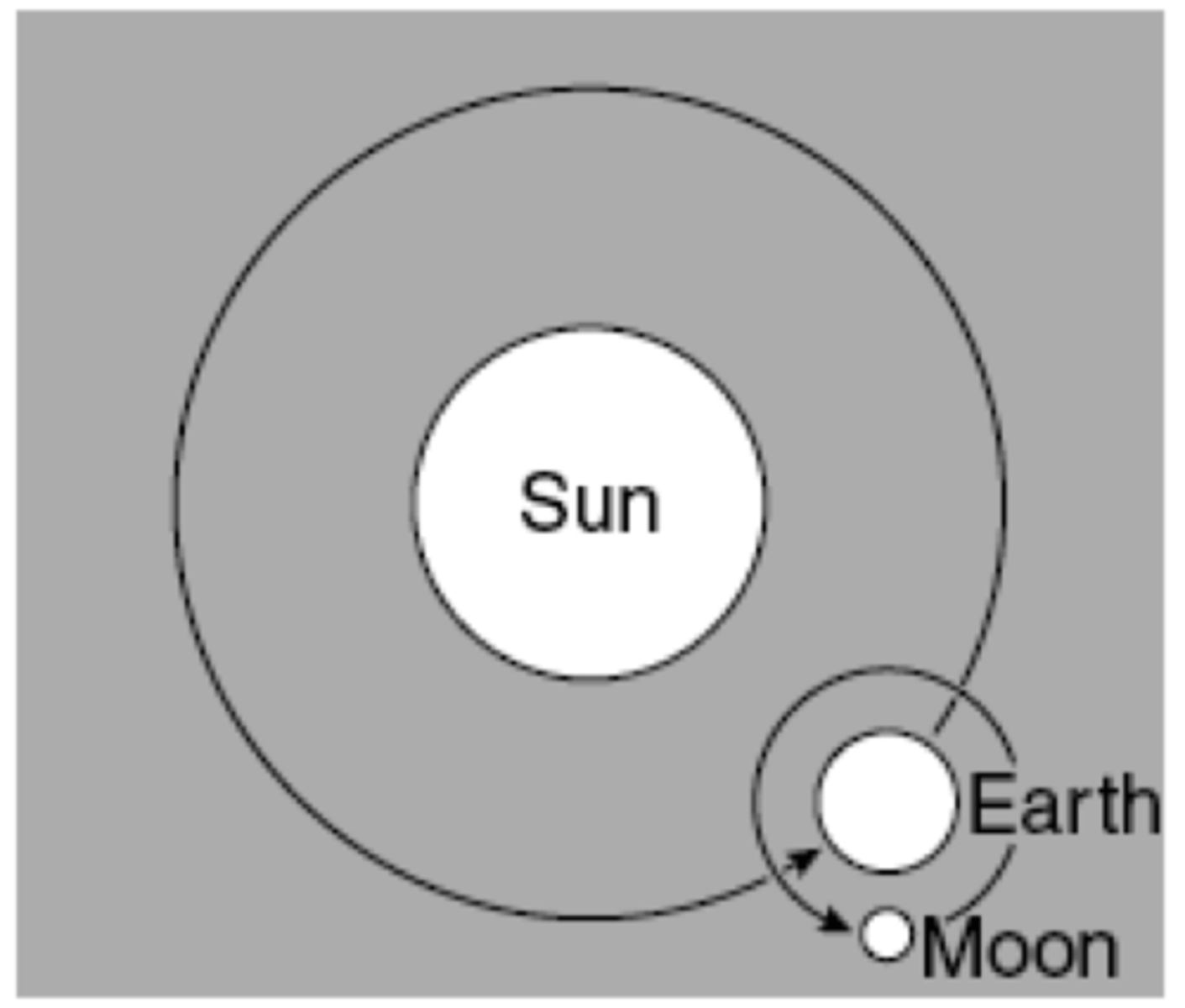
Describe the orbit of a planet
(slightly elliptical) around sun
State the relationship between orbital speed, orbital radius and time period
orbital speed = ( 2 x π x orbital radius )/ time period
v = (2 x π x r )/ T
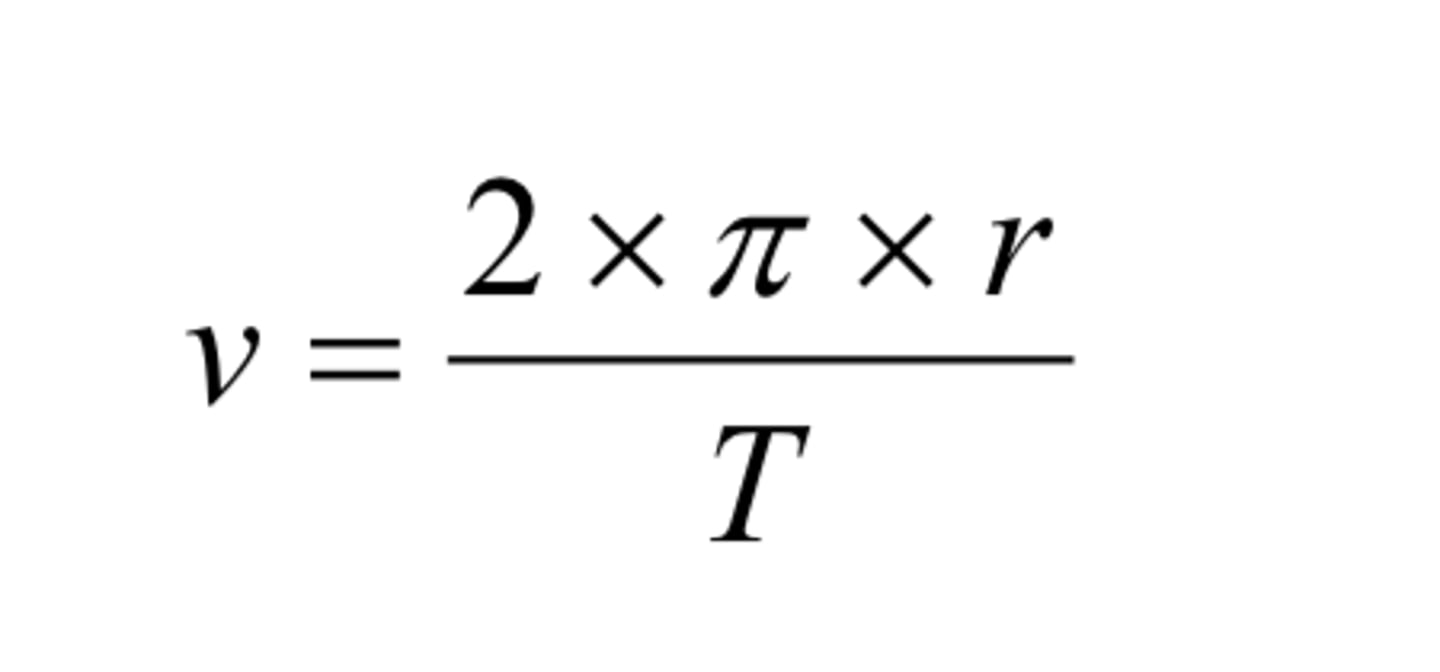
How are star's classified ?
stars can be classified according to their colour

What does a star's colour tell us about the star ?
a star's colour is related to its surface temperature
The more blue it is , the hotter the surface temperature is
Describe the stages of evolution of stars with a similar mass to the sun
1. Nebula
dust and gas particles experience weak forces of attraction and clump together forming a gas cloud (nebula)
2. Star (main sequence)
continues to clump together and pressure and temperature keep increasing, until it is great enough for nuclear fusion to occur
hydrogen nuclei fuse together to form helium nuclei which release large amount of energy and produce a large outward pressure
this large outwards pressure balances with the inwards pressure and becomes stable as a main sequence star
3. Red giant
eventually hydrogen nuclei are used up and nuclear fusion stops and the large gravitational (inward) forces compress the star
this triggers the fusion of helium nuclei, which release large amounts of energy and expands to its original size and emits (red) light energy
4. White dwarf
fusion of helium nuclei stops and so the inwards forces compress the star
The compression causes an increase in temperature and a change in colour to emit white light and becomes a white dwarf (denser)
This then cools into a black dwarf
Describe the stages of evolution of stars with a mass larger than the sun
1. Nebula
dust and gas particles experience weak forces of attraction and clump together forming a gas cloud (nebula)
2. Star (main sequence)
continues to clump together and pressure and temperature keep increasing, until it is great enough for nuclear fusion to occur
hydrogen nuclei fuse together to form helium nuclei which release large amount of energy and produce a large outward pressure
this large outwards pressure balances with the inwards pressure and becomes stable as a main sequence star
3. Red Supergiant
eventually hydrogen nuclei are used up and nuclear fusion stops and the large gravitational (inward) forces compress the star
this triggers the fusion of helium nuclei, which release large amounts of energy and expands to its original size and emits (red) light energy
4. The star then explodes and forms a supernova and then forms a neutron star or a black hole(really large)
How can the brightness of a star be represented?
The brightness of a star can be represented by using absolute magnitude
This means we measure the brightness of a star from a fixed standard distance away
(apparent magnitude is the real brightness of the star)
Draw the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram
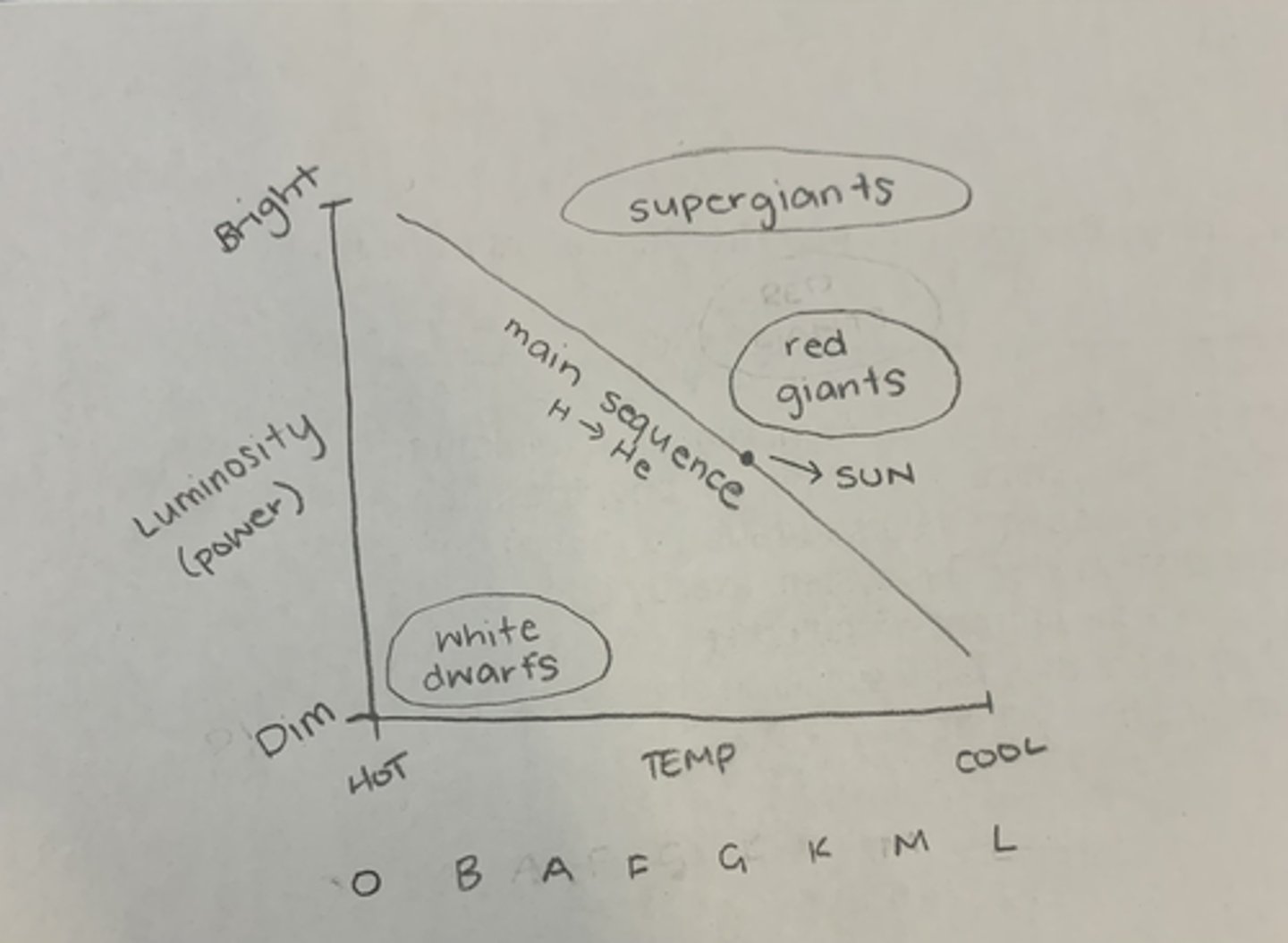
Describe the evolution of the universe ?
roughly 14 billion years ago, all matter in the universe was in one very tiny, dense place. it suddenly exploded and has been expanding ever since.
What arguments support the Big Bang Theory
1. red-shift
2. cosmic microwave background radiation
Describe evidence that supports the Big Bang theory ?
Red Shift:
the red shift of light from other galaxies
CMBR:
when the big bang occurred there was a huge release of energy (in the form of waves)
These waves/radiation should be stretched as the universe expands, this means they have a long wavelength
( The waves are microwaves )
These microwaves have been detected in all directions in the universe , proving that the big bang happened as energy was dispersed in all directions
Explain red-shift (doppler effect)
As other galaxies are moving away from us
light waves emitted by them must be stretched and the wavelength must increase
When the wavelength increases the light becomes redder, light waves move towards red end of the spectrum
as if a wave source is moving relative to an observer there will be a change in the observed frequency and wavelength
State the equation relating change in wavelength, reference wavelength, velocity of galaxy and the speed of light
change in wavelength / reference wavelength = velocity of galaxy/speed of light
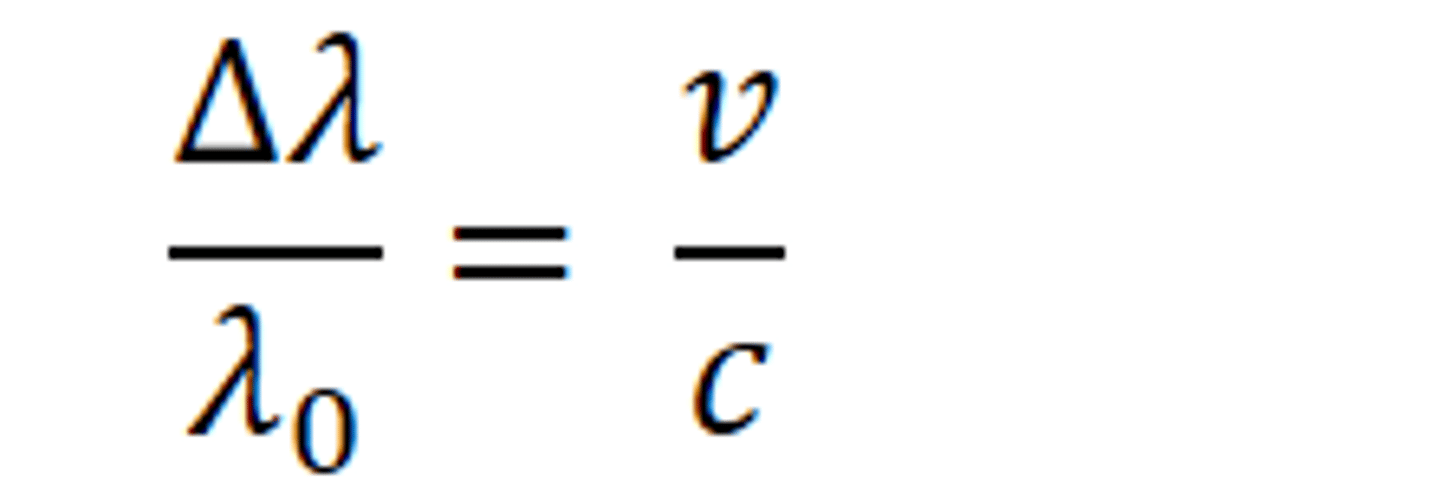
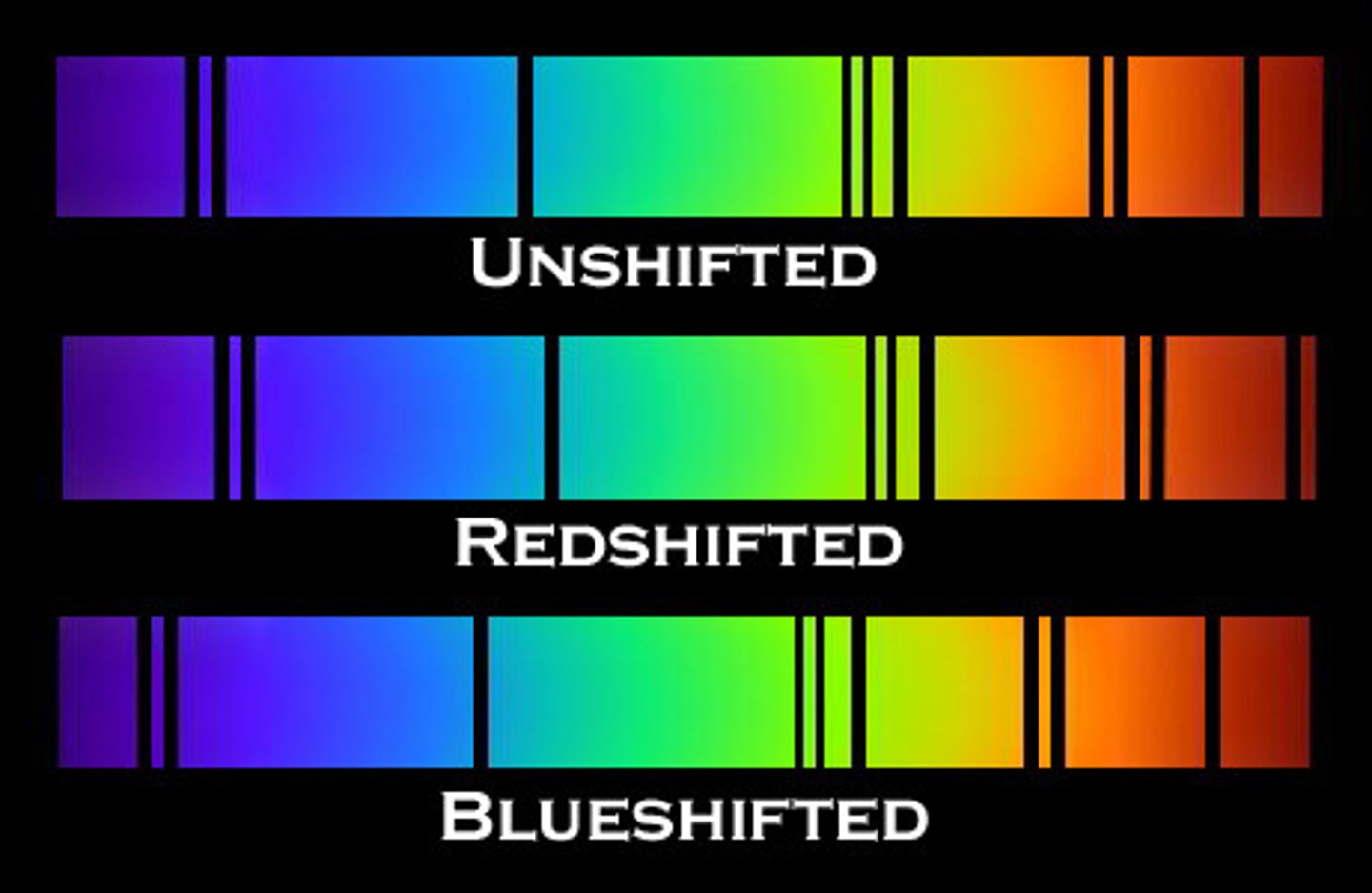
Describe the red-shift in light received from different galaxies at different distances away from the earth
if we see two spectra , the absorption lines show the frequencies of light that have been absorbed by hydrogen
(the closer you get to the source , the higher the frequency)
if the lines move towards the red part it has been red-shifted
Why does red-shift of galaxies provide evidence for the expansion of the universe
Red-shift proves that galaxies are moving away due to the change in colour of light
This means that the universe is expanding and that at one point all the galaxies will have been near each other
proving the big bang theory happened