HUMAN AP CHPT 13
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
City
an urban settlement that has been legally incorporated into an autonomous (self governing) unit known as municipality; fixed boundaries, raises taxes, & provides services
Urban area
central city plus its contiguous built-up suburbs with density of 1000 people per sq. mile or more
Metropolitan area
a city of at least 50,000, the county in which it is located, and any surrounding counties with at least 25 persons per square mile and a high degree of regular commuting to the central city; large space
photo of metropolitan area
Megalopolis (urban conurbation)
collection of adjacent, overlapping metropolitan areas that merge into a continuous urban region (clustering of cities) Ex; NE U.S from Boston, MA south to Washington DC
southern Great Lakes
Milwaukee- Chicago- gary
Southern California
los angeles- san Diego- Tijuana
German Ruhr
dortmund- Dusseldorf- essen
randstad (ring city)
Amsterdam- Rotterdam- Utrecht
tokaido in Japan
Tokyo- Yokohama
keihanshin in Japan
Osaka- Kobe- Kyoto
SE China
Guangzhou- Shenzhen- Hong Kong- macau
where would you notice a difference when moving from city to city?
overlap not noticeable in core cities as each maintains its identity but noticable in periphery where boundaries if the metropolitan regions overlap
Urban land use; commercial
retail & office
urban land use; industrial
heavy vs. light industry manufacturing and factories
urban land use; residential
houses
The central business district (CBD)
the commercial and business center of a city, characterized by a high density of retail shops, office buildings, and cultural institutions.
high density urban land use
closer; multi-story, multi family/ occupant; intensive
low density urban land use
further apart, 1-2 story, single family ; extensive
1950s CBD retail location
concentrated in CBD
1970s CBD retail location
corwth of suburban shopping malls
1990s CBD retail location
increasing presence of big box stores (super target) and outlet malls
Bid Rent Theory (William Alonso)
1960; accessibility creates high demand & competition for limited sites ; High demand= high cost
bid rent theory photo
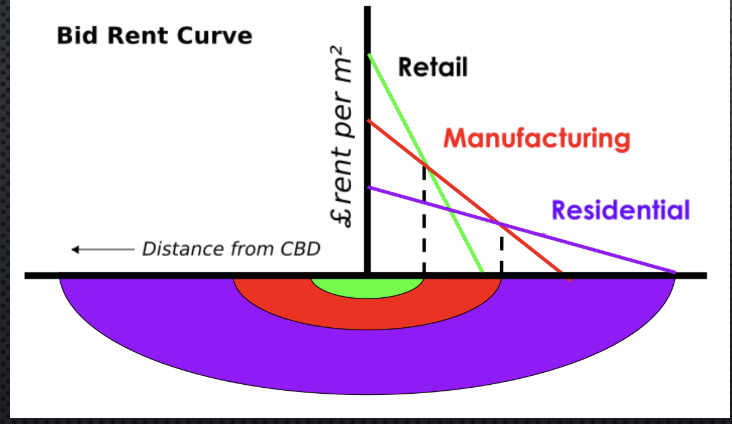
relationship between the bid rent, von thunen, & concentric theories?
The relationship explains how land value decreases as distance from the city center increases, similar to von Thünen's agricultural land use model and concentric zone model, where urban land use and rent are influenced by proximity to the CBD.
1st floor on skyscraper
retail & restaurants for more access to consumers
higher floors on skyscraper
offices, residential, hotels
limitations on skyscrapers
include zoning laws, building codes, and structural constraints that can restrict height and design swell as wind tunnels (ex; DC no buildings higher than the capital dome 13 floors)
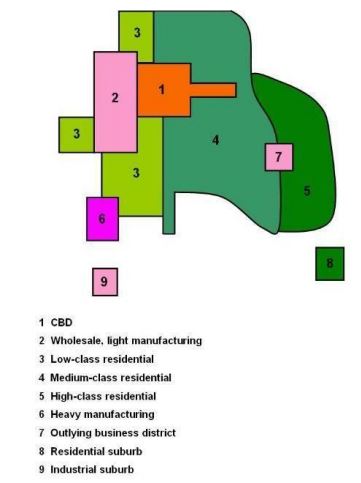
concentric zone model (burgess model)
A model that represents urban land use by dividing the city into concentric circles, each with different functions; city growing outward from CBD (rings)
concentric zone model picture
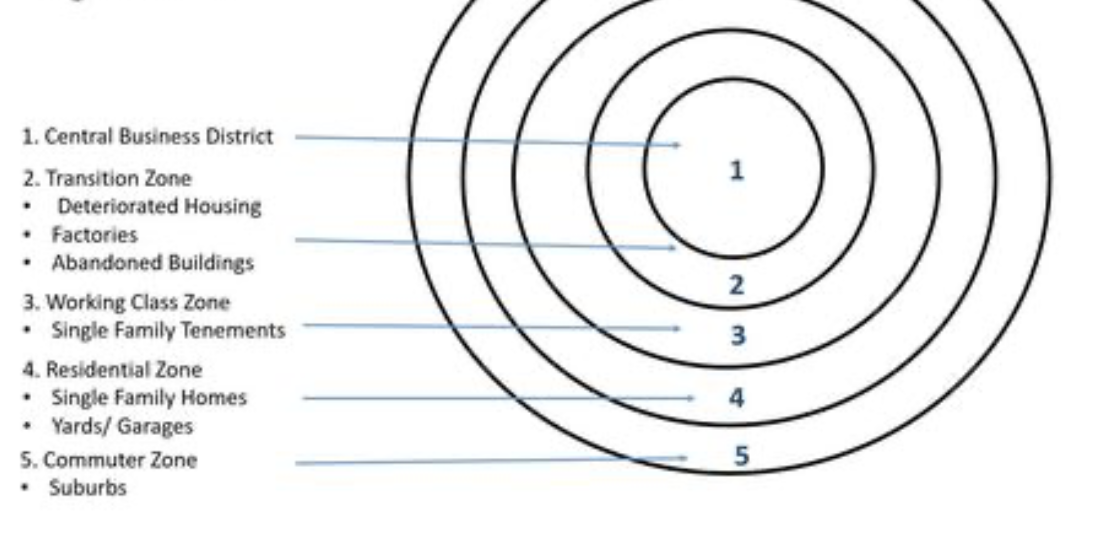
CBD (level on CZM)
inner most ring
zone of transition (lvl on CZM)
manufacturing, warehouses,and low-income housing area
zone of independent workers homes (lvl on CZM)
working class; small modest homes, more home ownership
zone of better residencies (lvl on CZM)
middle-to-high income; small, modest homes, mostly owner occupied
commuters zone (lvl on CZM)
larger homes with larger yards, lower density, suburbs discontinuous from the urbanized area serving as a bedroom communities; home ownership
When considering the concentric zones what is important to know about the CBD lvl?
more intensive=closer to CBD & less intensive=further away, then higher transportation cost= wealthier live further away & lower income close to CBD
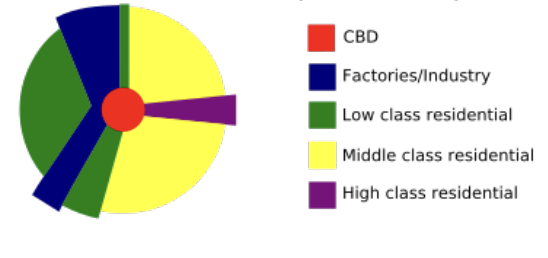
sector model
1939; by Hoyt; urban land use developed in sectors radiating from the city center, emphasizing the influence of transportation routes.
sector model picture
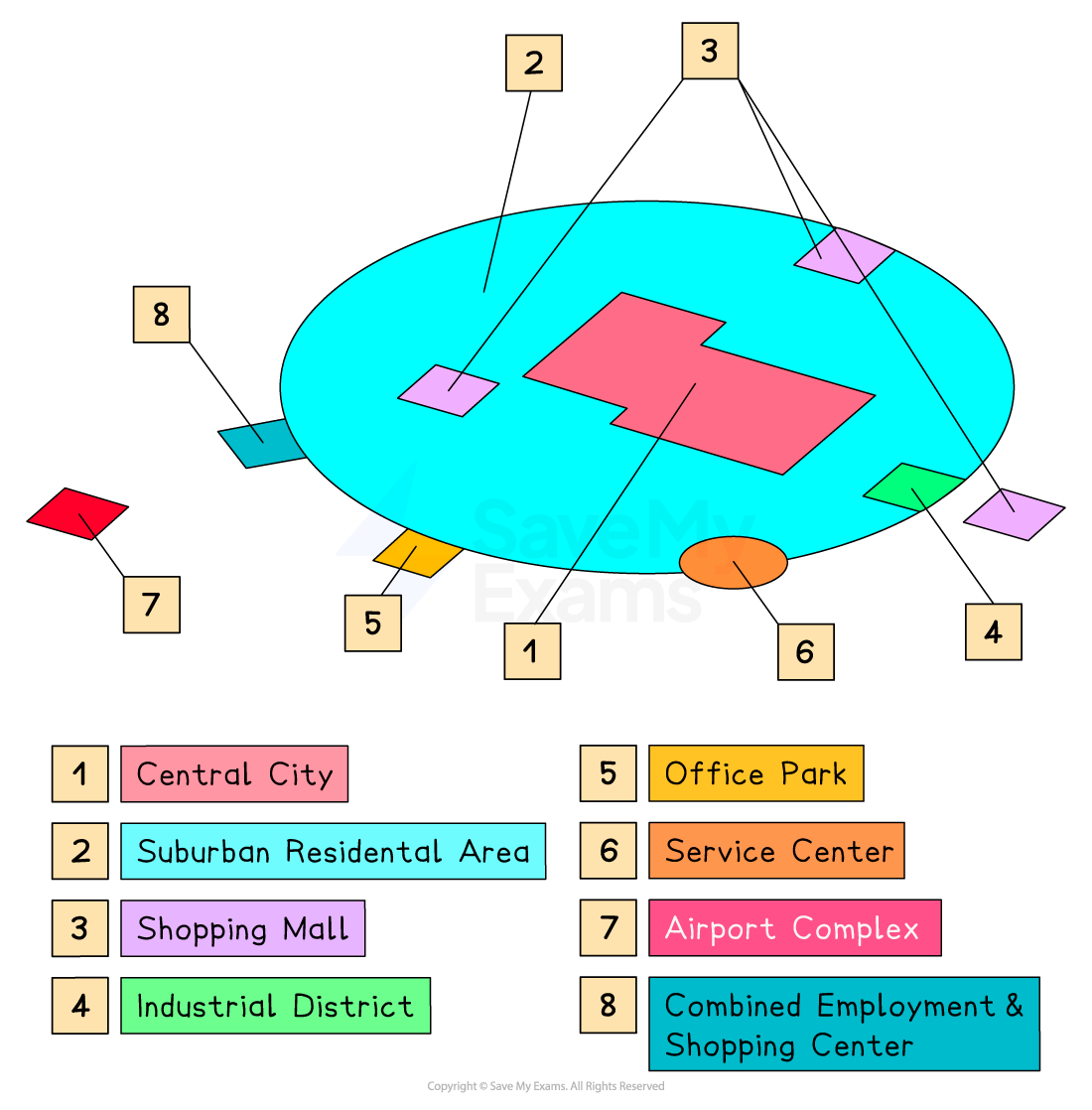
multiple nuclei model
1945 by Harris & Ullman; views city as more complex structure; CBD is not the only. node around which activity concentrates; incompatible actives do not concentrate near each other; multi nodes
multiple nuclei model picture
galactic city model (peripheral )
Harris 1960; depicts a decentralized urban landscape with multiple centers of activity, connected by highways, where residential and commercial areas are separated; retain other transportation being outside of CBD
galactic city model picture
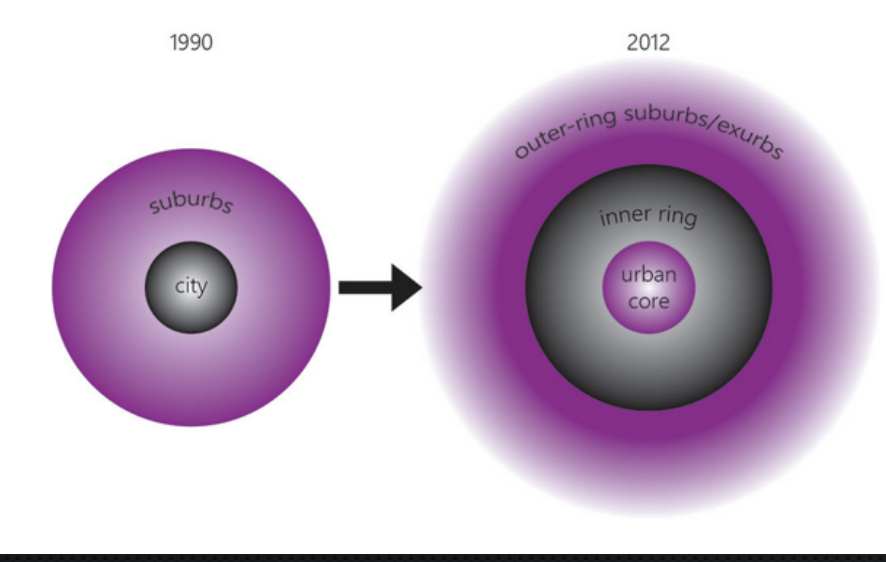
“donut effect” model of urban structure
renovation and regrowth of urban core; inner ring=older declining & outer rings= newer growing
photo of donut effect
urban realms model
James e vance 1964; growth of relatively self sustaining edge cities that occupy their won realms in the outer of the CBD
photo of urban realms model
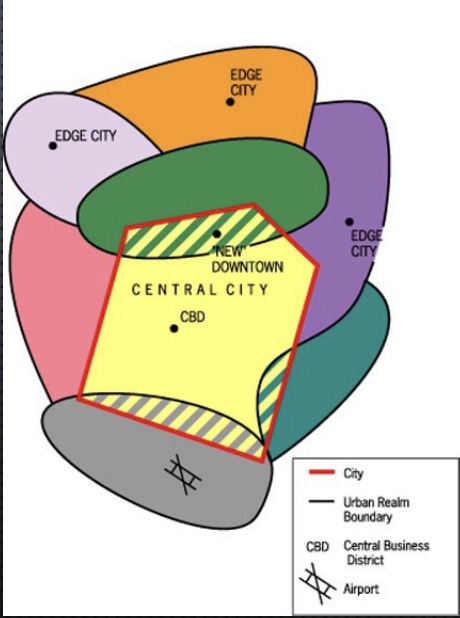
edge cities
surburb with increasing population and density that contains housing, businesses, retail, and often specialized functions outside (become less dependent on the central city)
technoburb
edge city/ suburb focused on research & tech production
boomburb
suburb grwoing rapidly and reaching a high population
census tract
correspond roughly to a neighborhood; smallest area for which US census bureau complies data; approx 5k people; important for local scale quantitative data;
Applying the concentric zone model on residences
older homes=inner lvl; more low income=inner city; more high income=suburbs; more multi family dwellings in inner city; more single family dwellings in suburbs
applying the sector model to residencies
higher income sector vs. low income sectors
applying the multi nuclei model to residencies
people of similar ethnic or racial backgrounds more likely to live near one another; ethnic enclaves and ethnoburbs
European cities
low buildings, narrow streets, older cities, more open space in CBD, few skyscrapers to none, preserve historic character, high rent
North American cities
growth of relatively self sustaining edge cities that occupy their own realms in the periphery of the central city; suburbs function within sphere of influence of central city but relatively independent of the central city
census bureau data
(QUANTITATIVE) data collected by the U.S. Census Bureau on population characteristics, including demographics, housing, and economic statistics that helps inform urban planning and policy decisions
pre colonial era in LDC
sometimes cities
colonial era in LDCs
if no city europeans built according to their culture and economic needs; coastal; preexisting city— added/changed, built new next to old, destroyed old
sector model in LDCs
wealthy sectors and low-income sectors
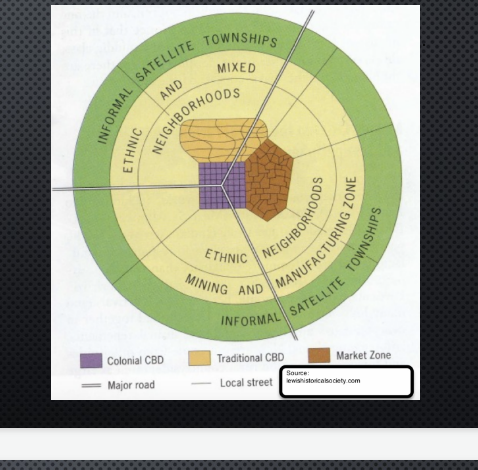
multi nuclei model in LDCs
mix of ethnicities and people cluster near those with same background
sub-saharan africa city model
harm de bli
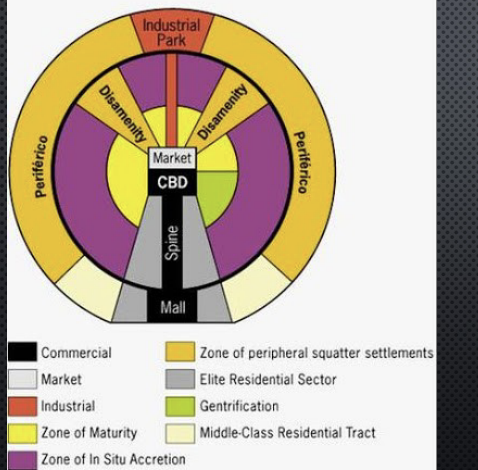
latin American city model
griffin and ford
SE asian city model
T.G McGee
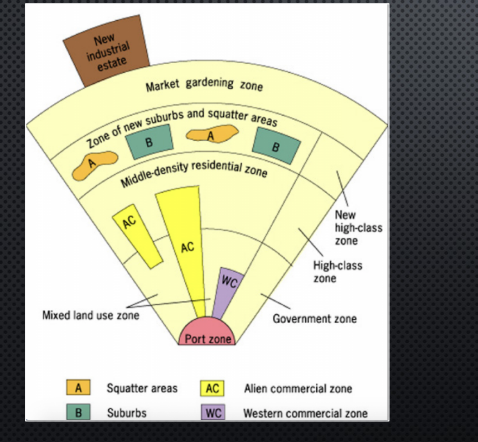
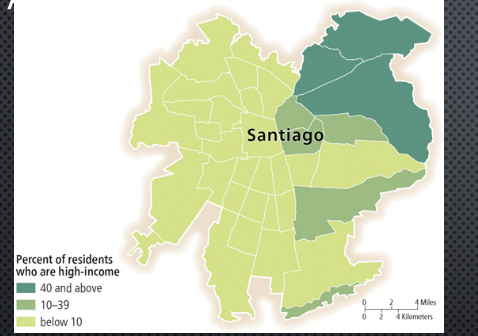
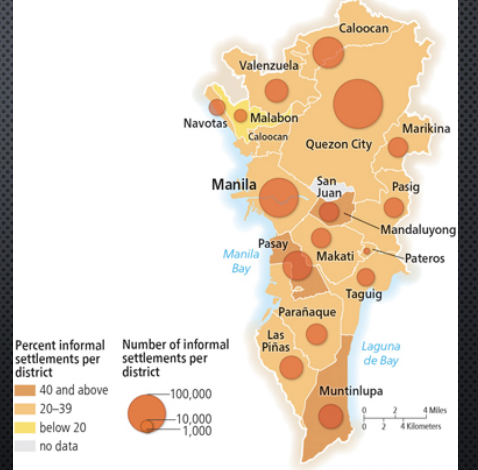
informal settlement in LDC
squatter/slum; typically characterized by a lack of formal legal ownership; periphery/outskirts
borcherts transportation model
5 epochs (eras) of changes to the growth and function of urban areas based upon domaint forms of trasnsportation
borcherts transportation model picture
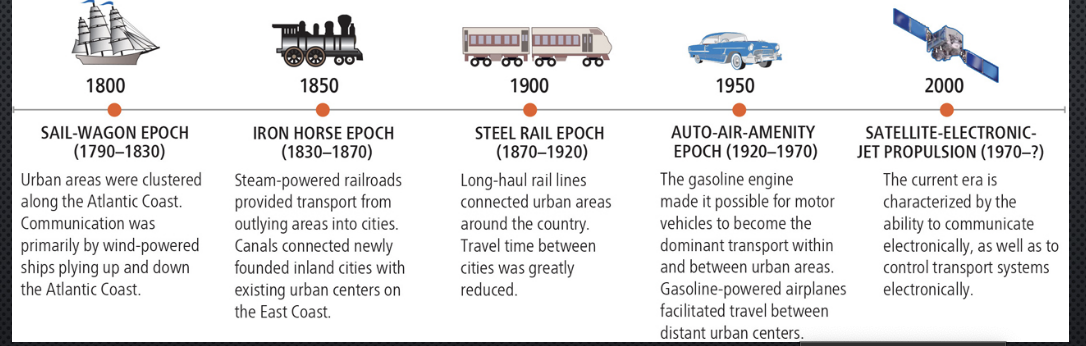
sail wagon epoch (era)
1790-1830; clustered E coast harbors or rivers; goods and communication exchanged mostly by water for long distance and wagon/cart for short distance; COMPACT cities
Iron horse epoch (era)
1830-1870; steam powered railroads & canals provided transportation from interior regions and the Great Lakes to existing urban centers on the east coast
steel rail epoch (era)
1870-1920; improved railroad tech and intercontinental rail lines connected urban areas throughout country more quickly; greater W expansion; cities clustered near trains stops (Chicago)
auto-air-amenity epoch (era)
1920-1970; gasoline engine for more flexible transportation between cities; air transportation for long distances rapidly; interstate highway= suburbs & sprawl low density (Los Angeles)
satellite electronic jet propulsions epoch
1970-present; the rise of satellite communication and jet propulsion technologies, leading to global connectivity and rapid transit; urban areas expanded with increased mobility and the growth of technology-driven amenities.
public transportation; heavy rail
subways, elevated trains and large ground level trains that transport people locally and regionally
public transportation; light rail
trams, streetcars, and smaller trains with smaller-gauge tracks for local use
new urbanism & sustainable city planning (smart growth)
legislation and regulations to limit suburban growth/sprawl and goal to create a pattern of compact continuous development while protecting rural land & reverse inner city decline
criticism of smart growth and new urbanism
potential to price out lower income in favor of middle and higher income residents; high cost to renovate or develop; uniform landscape due to same planning
residential density gradient
change of density over urban space from CBD outward; often characterized by higher density near the city center and gradually decreasing density as one moves to the suburbs
residential density gradient
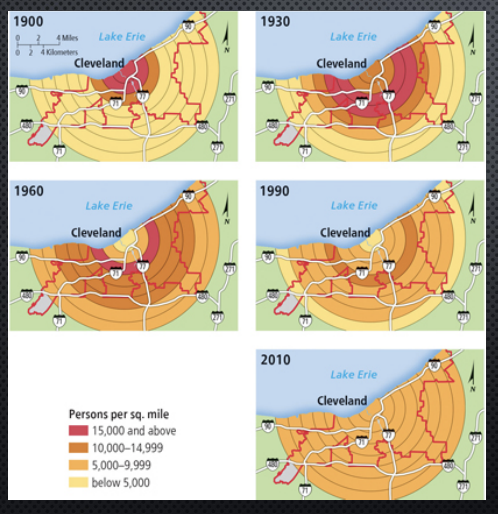
sprawl
the development of lower density suburbs that are not contiguous to existing built up areas; created by developers seeking cheaper land that can be easily prepared for construction
sprawl photo

local zoning ordinances
regulations that govern land use and development within a municipality, aiming to control how land can be used and what types of buildings can be built.
Europe transportation
high density cities more compact; more use of public transportation and biking/ predestrian; better funded public transportation; high fuel taxes
gentrification
converting a low income renter occupied urban neighborhood to a middle class owner occupied neighborhood often resulting in rising property values and displacement of original residents of building new (INFILL)